Stats Lecture 21 & 22: Understanding and Calculating ANOVA, Post Hoc, and Chi Square
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
ANOVA
technique used to examine differences between two or more groups
calculated F-value
value that indicates the extent to which group means differ taking into account the variability within the groups
one-way ANOVA
used to analyze data in studies with one independent variable and one dependent variable
repeated-measures ANOVA
used to analyze data from studies where the same variable(s) is(are) repeatedly measured over time on a group or group of subjects
if the p-value is greater than the level of significance, than the results are nonsignificant
what is the relationship between ANOVA, significance, and p-value?
1. normally distributed
2. groups are mutually exclusive
3. groups have equal variance (homogeneity)
4. independent observations
5. dependent variable is interval or ratio level
what are the assumptions of ANOVA?
post hoc analyses
developed to determine where the differences lie, because some of the groups might be different and others might be similar
-Newman-Keuls
-Tukey
-Scheffe
-Dunnett
what are some of the frequently used methods of post hoc analyses?
1. experimental group
2. placebo group
3. comparison group
what 3 groups might be included in a study?
it is reduced in proportion to the # of additional tests required to find significant differences
what is true of the alpha level regarding post hoc analyses?
Newman-Keuls
post hoc analyses method that compares all possible pairs of means and is the most liberal (α is not as severely decreased)
Tukey HSD
post hoc analyses method that computes one value with which all means within the data set are compared; less stringent than Newman-Keuls
equal sample sizes in each group
what is a requirement of groups in the Tukey HSD post hoc analyses method?
Scheffe
post hoc analyses method that is the most conservative test; decrease in the type I error --> there is an increase in the type II error
Dunnett
post hoc analyses method that requires a control group; the experimental groups are compared with the control group without a decrease in α
difference statistics
what type of statistics are calculated using an ANOVA?
1. randomized experimental
2. quasi-experimental
3. comparative designs
what are some research designs that might utilize ANOVA?
active
type of variable that refers to an intervention, treatment or program
attributional
type of variable that is a characteristic of the participant (gender, diagnosis, ethnicity)
may be active or attributional
what is characteristic of the independent variable in ANOVA?
mean square between groups / mean square within groups
what is the equation to calculate the F value?
variance
what is another word for "mean square"?
mean square between groups
represents differences between the groups or conditions being compared
mean square within groups
describes the variability of scores within the conditions of an experiment
(grand sum)^2 / N
what is the equation to calculate the correction term when calculating for ANOVA?
# groups - 1
how do you calculate the degrees of freedom for the mean square between groups?
# of groups
how do you calculate the degrees of freedom for the mean square within groups?
pearson chi-square
inferential statistical test that is calculated to examine differences among groups with variables measured at the nominal level
1. compute correction term (C)
2. compute the total sum of squares and subtract C
3. compute between groups sum of squares
4. compute within groups sum of squares
5. create ANOVA summary table
what are the steps to calculating ANOVA?
1st: sum of squares (SS)
2nd: degrees of freedom (dF)
3rd: mean square between groups and mean square within groups (MS)
what goes in the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd column of an ANOVA summary table?
1. data are nominal level/frequency level
2. sample size is adequate
3. measures are independent of each other or that a subject's data only fit into one category
what are the assumptions of a chi square?
based upon the number of categories examined in the analysis
what does the degrees of freedom for a pearson chi square depend on?
df = (R - 1)(C - 1)
R- rows
C- columns
what is the formula to calculate degrees of freedom for a pearson chi square?
pearson chi square:
1. randomized experimental
2. quasi-experimental
3. comparative design
what are some possible research designs for a pearson chi square?
one-way chi square
a statistic that compares different levels of one variable only
two-way chi square
a statistic that tests whether proportions in levels of one nominal variable are significantly different from proportions of the second nominal variable
researcher may collect information on gender and compare the proportions of males to females
what is an example of a one-way chi square?
presence of advanced colon polyps was studied in 3 groups of patients (normal BMI; overweight; obese)
what is an example of a two-way chi square?
will not determine where the differences lie, only determines that a statistically significant difference exists
what if more than 2 groups are being examined in a pearson chi square?
1. square the sum of each column, then divide by N
2. add each of the sums, then subtract C
how do you calculate the between groups sum of squares?
subtract the between groups sum of squares from total sum of squares
how do you calculate the within groups sum of squares?
calculating a two-way chi square
what is this equation used for?
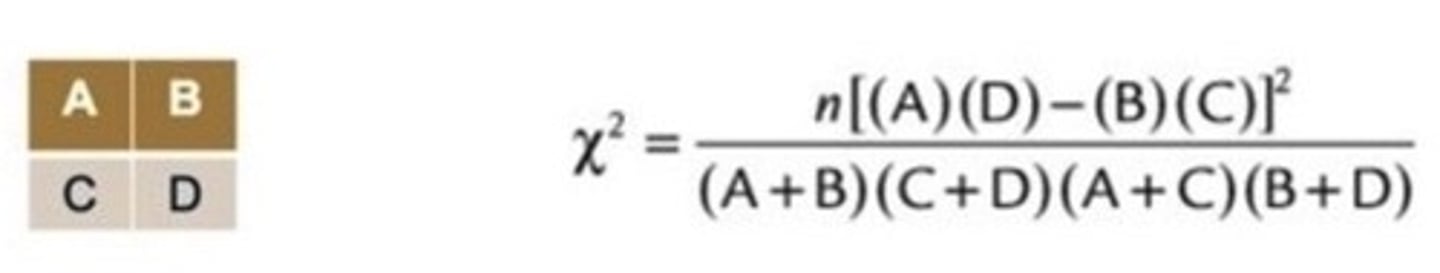
when the obtained value is larger than the critical value
when is a value considered statistically significant in a pearson chi square?
type I error
error that results form rejecting a true null hypothesis; false positive
type II error
error that results from failing to reject a false null hypothesis; false negative