UWEC GEOG 104 Exam 2
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
155 Terms
Natural Region
An area homogenous with a defined criteria
Science
Solving problems and answering questions with evidence
What do geographers do?
Work to ensure our home is livable for all
Dipolar properties of water
Adhesive
Cohesive
Capillarity
Some properties of water
Latent Heat Exchange with Phase Changes (Hurricane)
High Specific Heat
Universal solvent
Chemical Catalyst
Common in all three phases of matter
What's the number one geomorphic agent on earth?
Water
What is water a major controller of?
Earth-Sun Energy Balance
Weather and Climate
Huge roll in all Natural Regions
What are the four storage facilities of water?
Surface Water
Groundwater
Organic Tissue
Soils
Global Fresh Water Supply Stats
3% is fresh water
.003% is readily available
Why is water where it is? (2)
Water is always moving through the hydrologic cycle
Soils tell precipitation on and where to go
What is infiltration?
When water can seep in
What is runoff?
When water doesn't soak in
What are the controls on water movement? (2)
1. Capillary Forces (Adhesion and cohesion)
2. Gravitational force
What is porosity?
How much you can put in, the total volume of available pore space in soil or sediment.
Which has more porosity?
Clay is more, sand is less
What is Permeability
How fast water can move in and out - the ability of a soil or sediment to allow water to pass through it
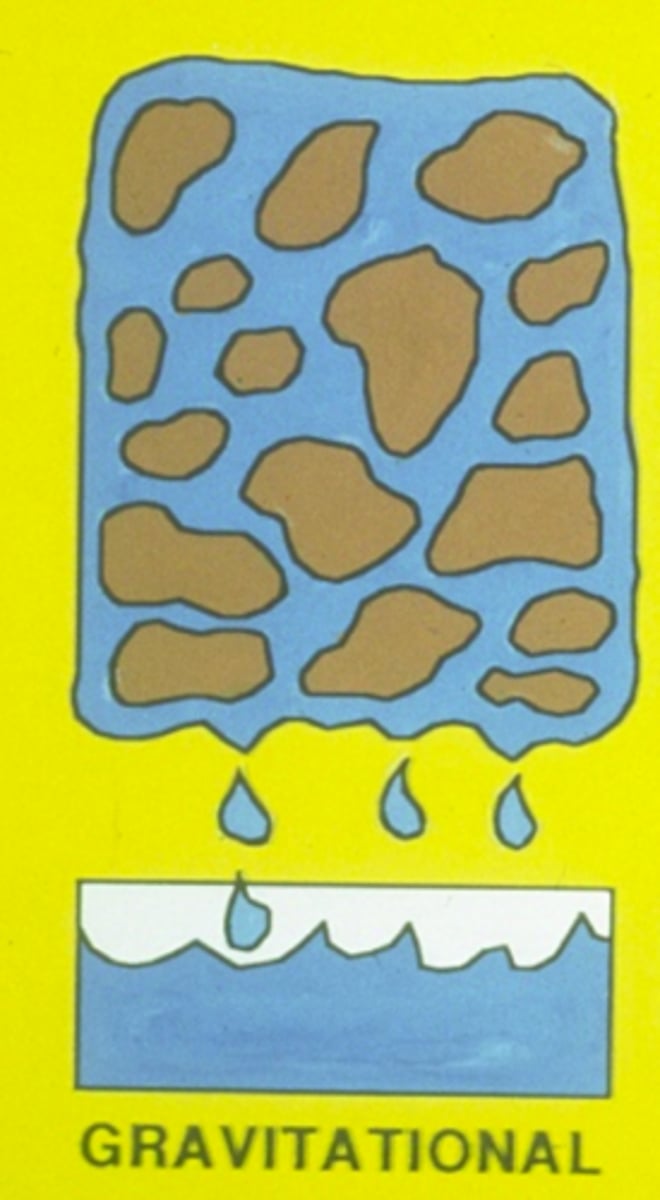
What is the saturated soil moisture state?

What is the Field capacity moisture state?
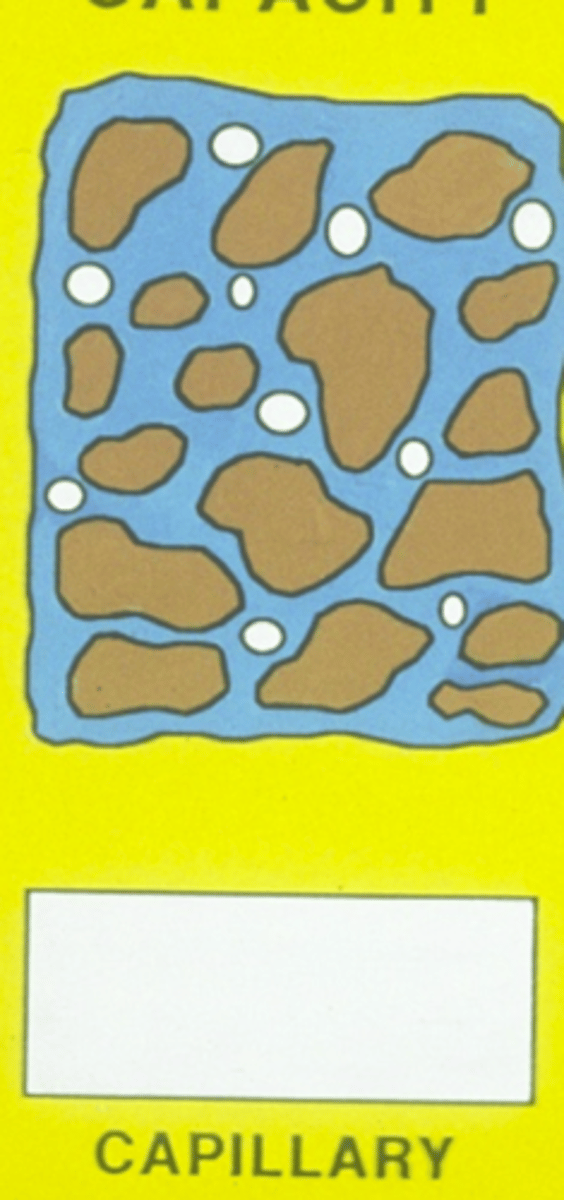
What is the Wilting point moisture state?

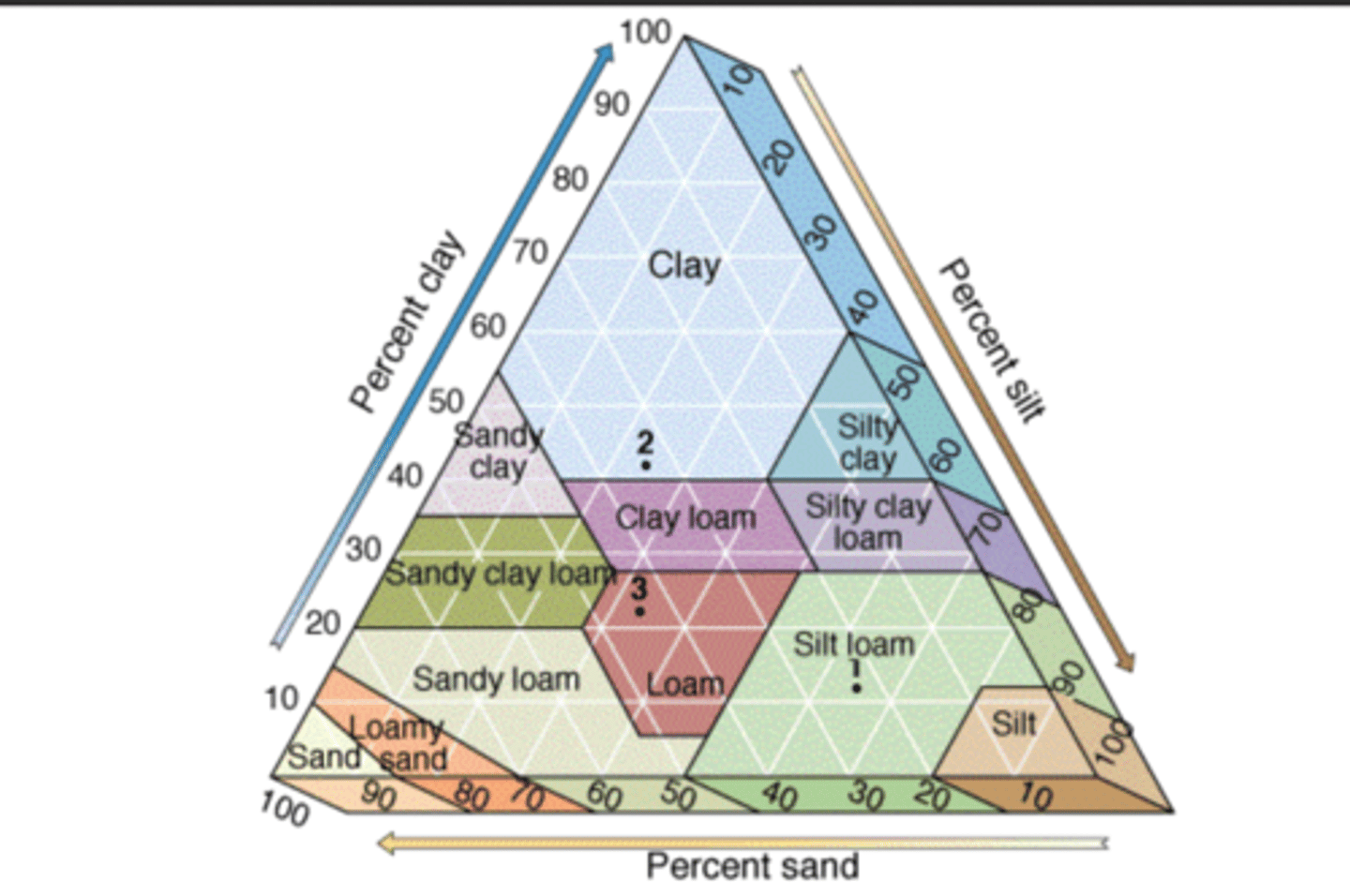
What is the percent clay, silt and sand in the triangle?
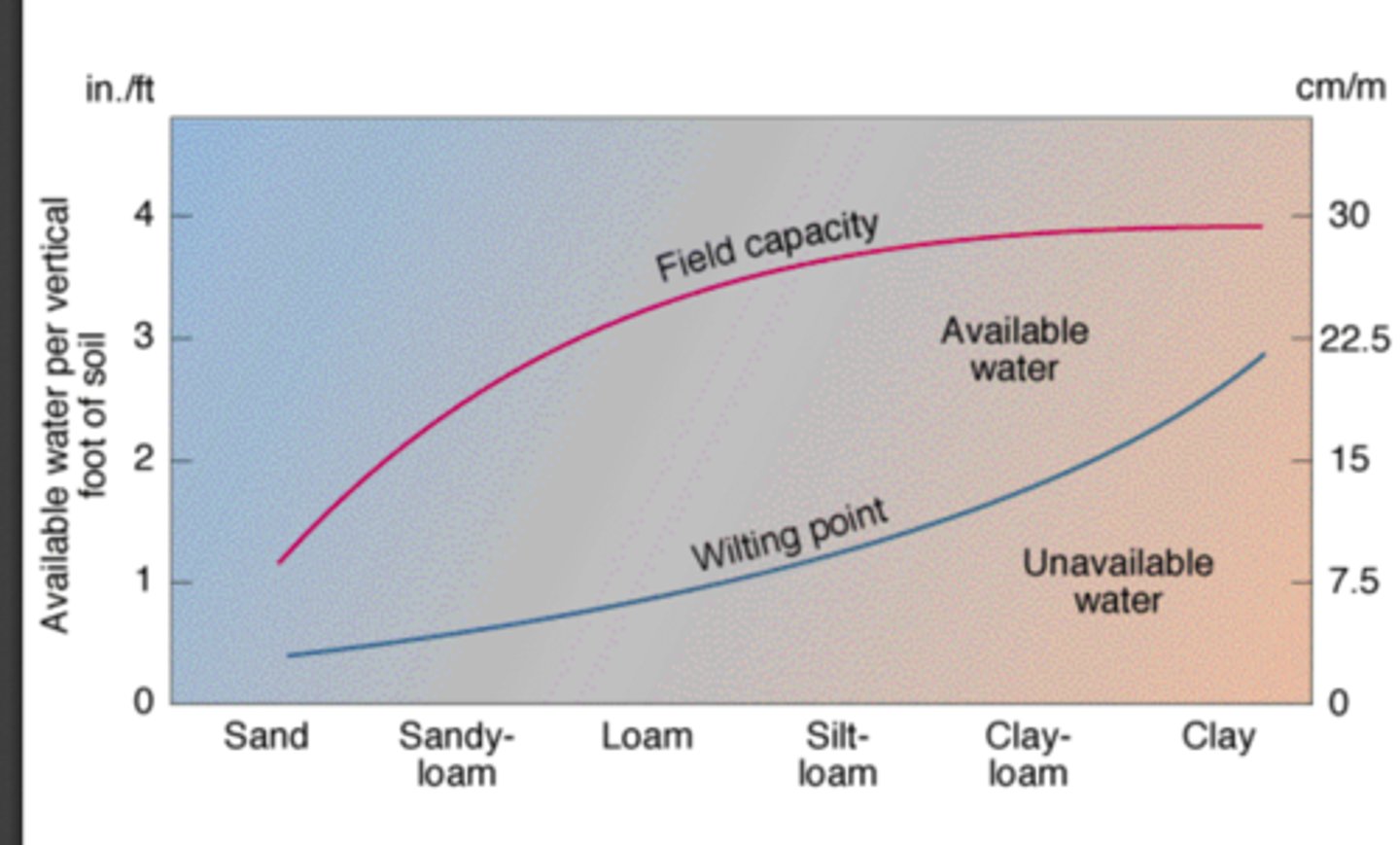
What is the field capacity, available water, wilting point and unavailable water of the soils?
In order - Sand, Sandy-loam, Loam, Silt-loam, Clay-loam, Clay
What are the three reasons for water being the soil and water gate keeper?
1. Control how much soaks in (Infiltration) versus how much runs off (Runoff, causes erosion and flash floods)
2. Control how much water is held by capillary forces (Available soil water - extractable by plants)
3. Control how much free or gravitational water can recharge (percolate to) groundwater - soil pores must be saturated
What is percolation?
Soil recharging from ground water
Field capacity and wilting point are capillary forces - what is the water plants can use equation?
Field capacity - permanent wilting point = available water
Where does free of gravitational water go?
Into the groundwater
What is a major storage facility in the hydrologic cycle?
Groundwater
What is the groundwater system?
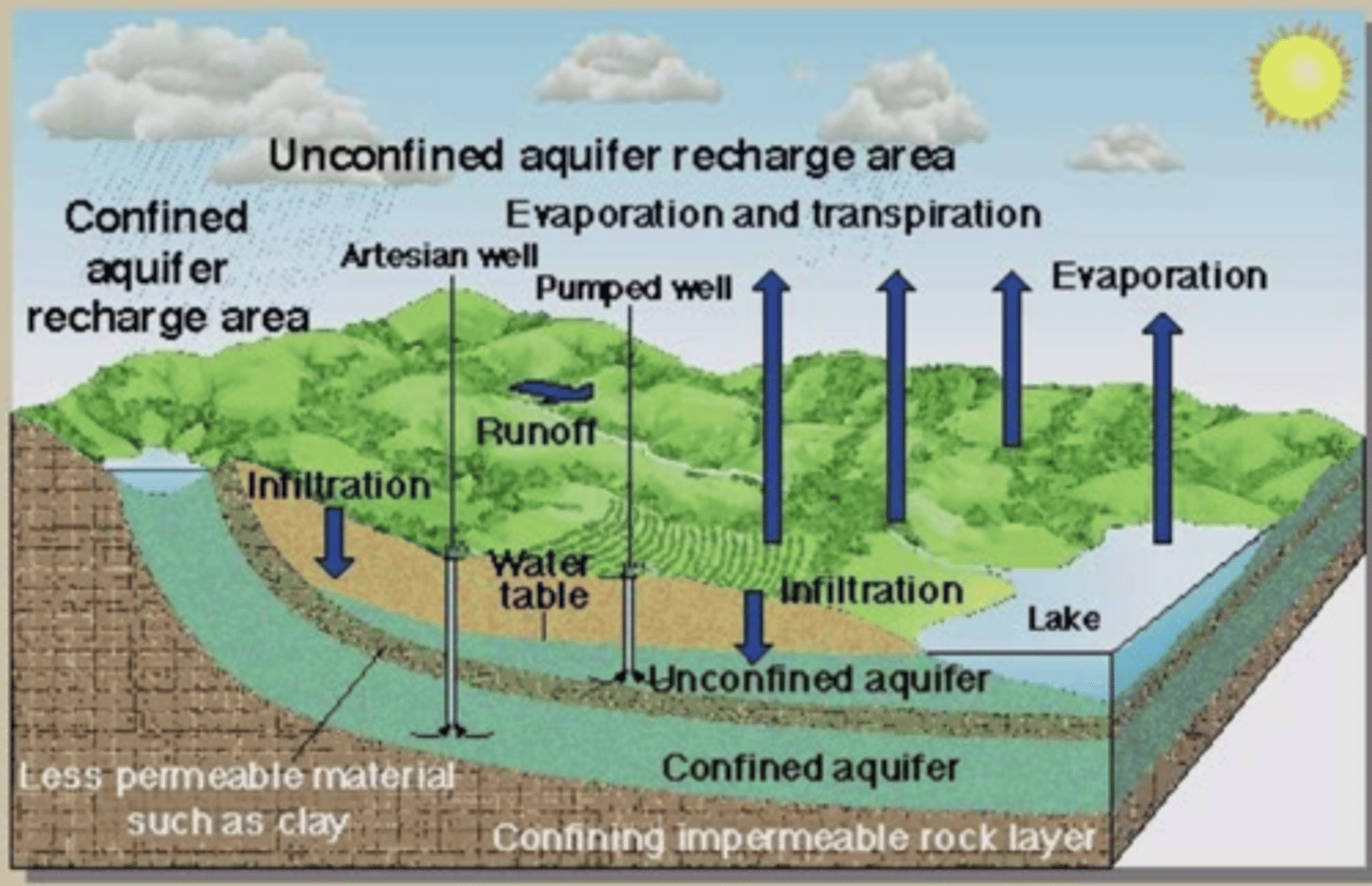
Stream diagram
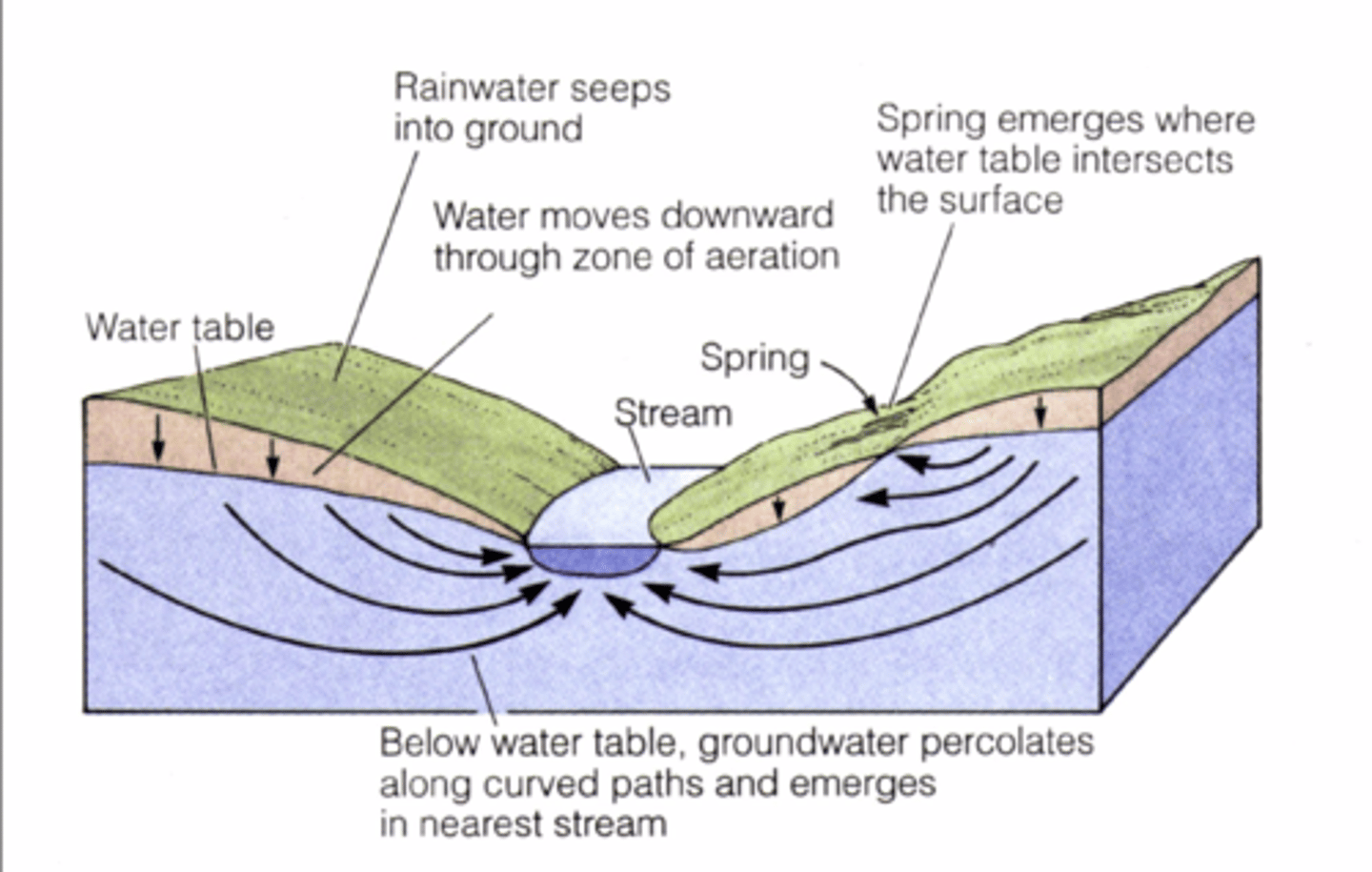
Where does 40% of stream flow come from?
Baseflow - Groundwater discharge-derived
What is cool, clean, steady and oxygenated?
Baseflow groundwater
What do most streams receive?
Runoff + baseflow input
What is "flashy"?
Runoff dominated waterflow
What causes more frequent and more severe flooding?
More runoff
What are four properties of runoff?
Warm
Sediment-laden
Nutrient enriched
poorly oxygenated
What are the inputs and outputs in the Saturated Zone?
Inputs (percolation)
-Aquifer recharge
Outputs
-Aquifer discharge (baseflow, springs)
-Some plants under some conditions
What are some streams that loose water to groundwater?
Exotic stream - nile and CO
What's the BIG groundwater problem?
Unsustainable withdrawal
What is the other big groundwater problem?
Groundwater contamination
What is the definition of climate?
The average long term weather of an area, a region's general pattern of atmospheric conditions including seasonal variations, weather types, and extremes
What is a climate region?
An area with homogeneous atmospheric conditions
Water Table Diagram 1
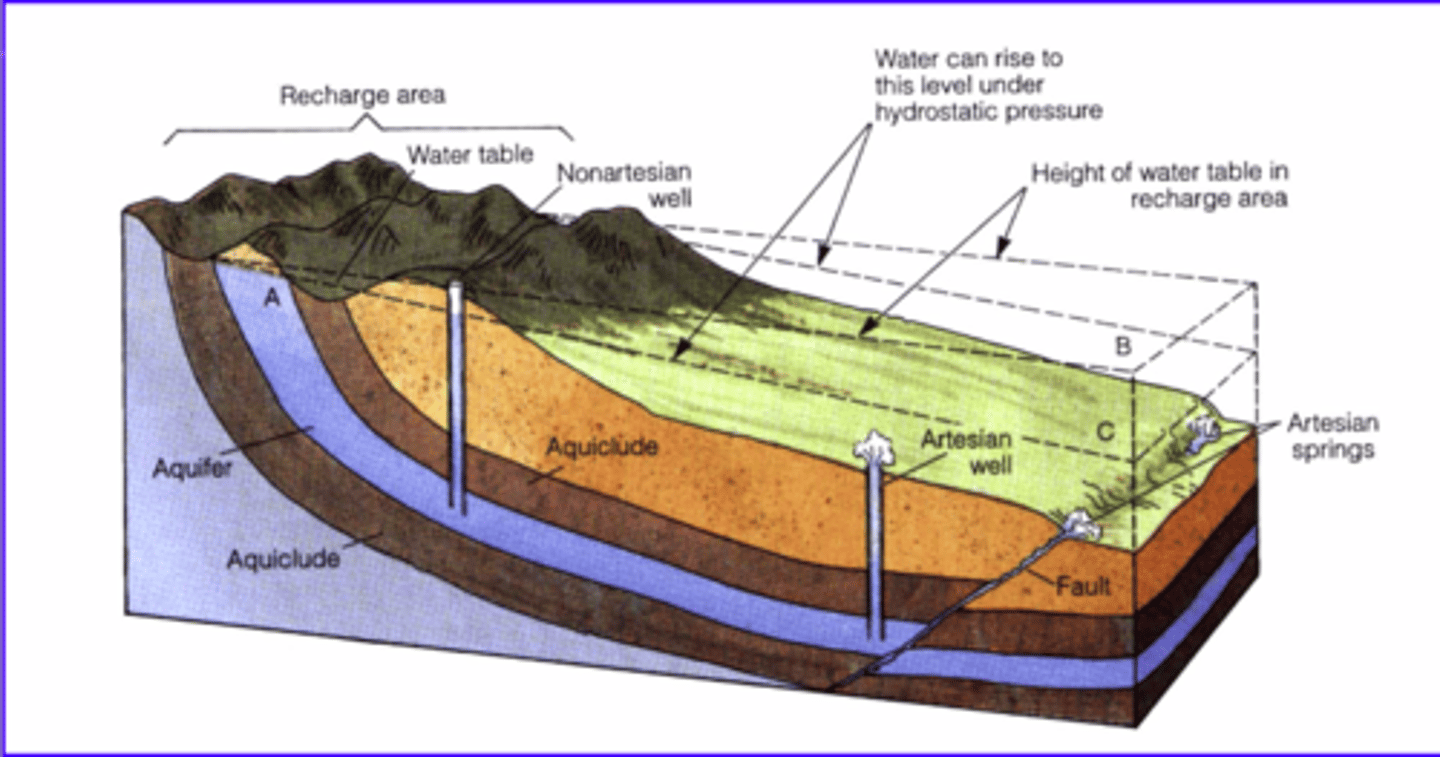
Water Table Diagram 2
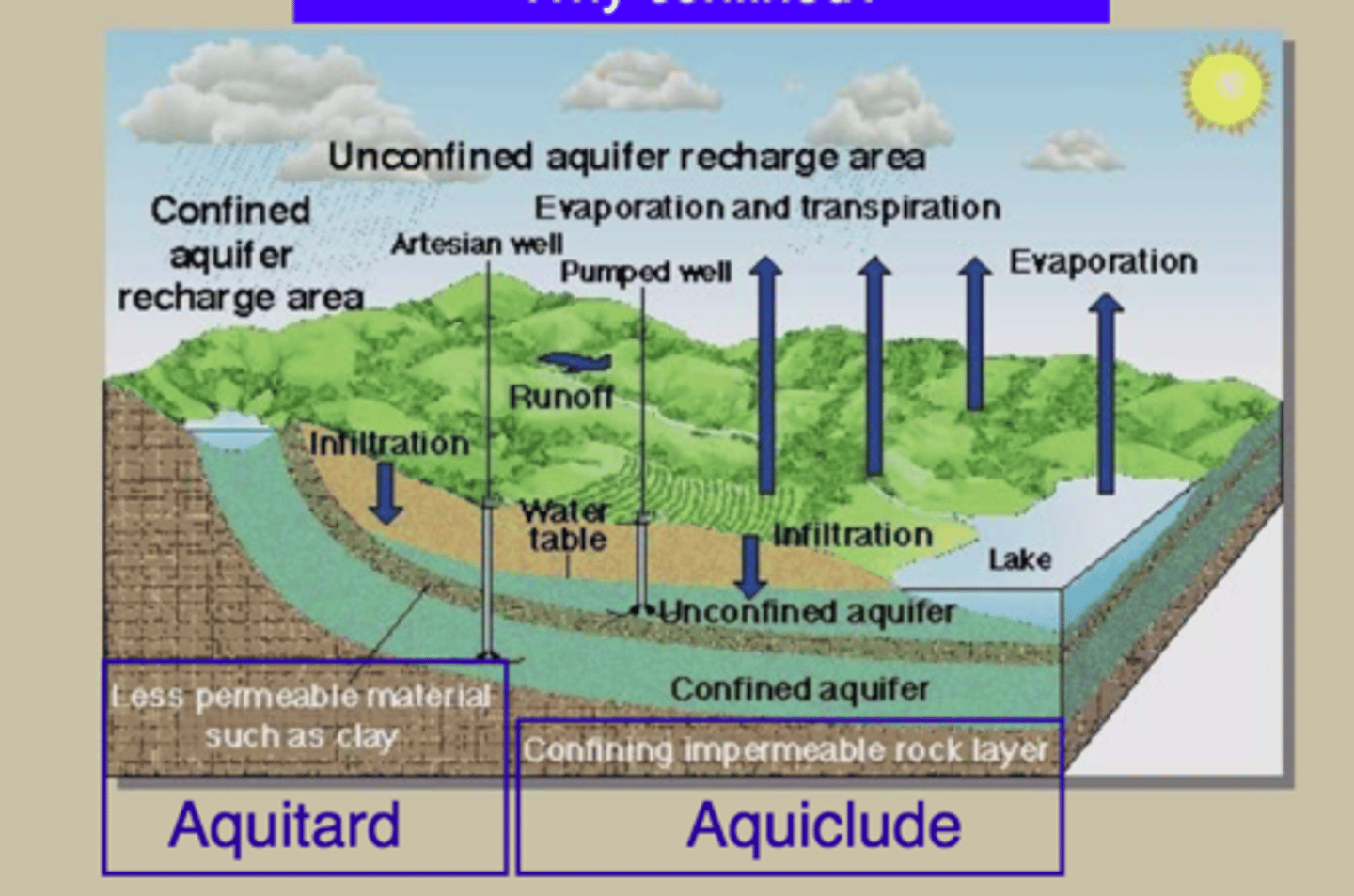
How much of the Ogalla Aquifer's water has been pumped?
30%
How large would the Ogalla aquifer be if it was above ground?
Twice as large as all of the great lakes
How much of US cattle, corn and cotton does the aquifer sustain?
205
What are the three causes of sinkhole collapse?
Erosion, Groundwater withdrawal, Surface loading
What's the difference between unconfined and confined groundwater in WI?
Mostly Unconfied - thin glacial outwash
Mostly confined - bedrock
What are the two big us groundwater problems?
Near the coast - saltwater intrusion
in the west and florida - Subsidence
What are some groundwater pollutants? (3)
Industrial Chemicals
Domestic and Municipal Chemicals
Agricultural Chemicals
What are some other controls on temperature? (4)
Specific Heat (continentality versus maritime influence)
Latent Heat Exchange with Phase Change (Hurricane)
Ocean currents and global circulation patterns
Elevation
What is required for precipitation? (2)
Moist air masses
Lifting mechanisms (Descending air, no precipitation)
What are lifting mechanism? (4)
Orographic lifting
Convergent lifting
Frontal lifting
Convectional lifting
What is orographic lifting?
What happens when surface winds blowing toward mountains are forced to rise
What is convergent lifting?
What happens when surface winds blow into the same area from different directions
What is frontal lifting?
WHat happens when a cold/warm air advances into a warm/cold mass
What is convectional lifting?
What happens when unequal surface heating creates bubles of air that are warmer than the surrounding air
What clouds are caused by convectional lifting?
Cumulus and Cumulonimbus
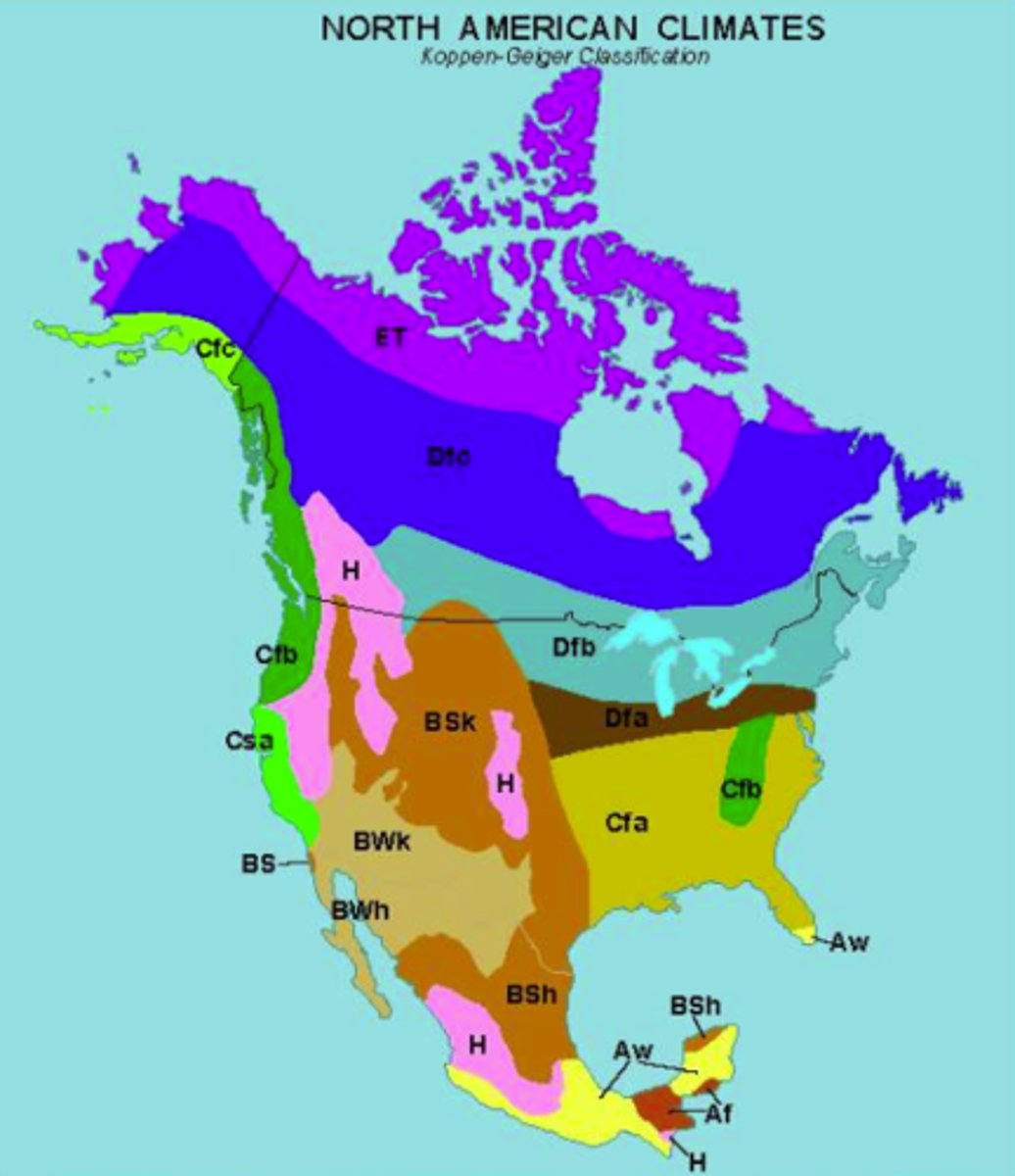
North American Climates
Who is Alexander von Humboldt?
Modern Climatology and Instrumentation
Who founded the isotherm?
Alexander von Humboldt
What is the Koeppen system?
Biogeographic link between climate regions that fit to vegetation regions
Climate controls on Biome Distribution
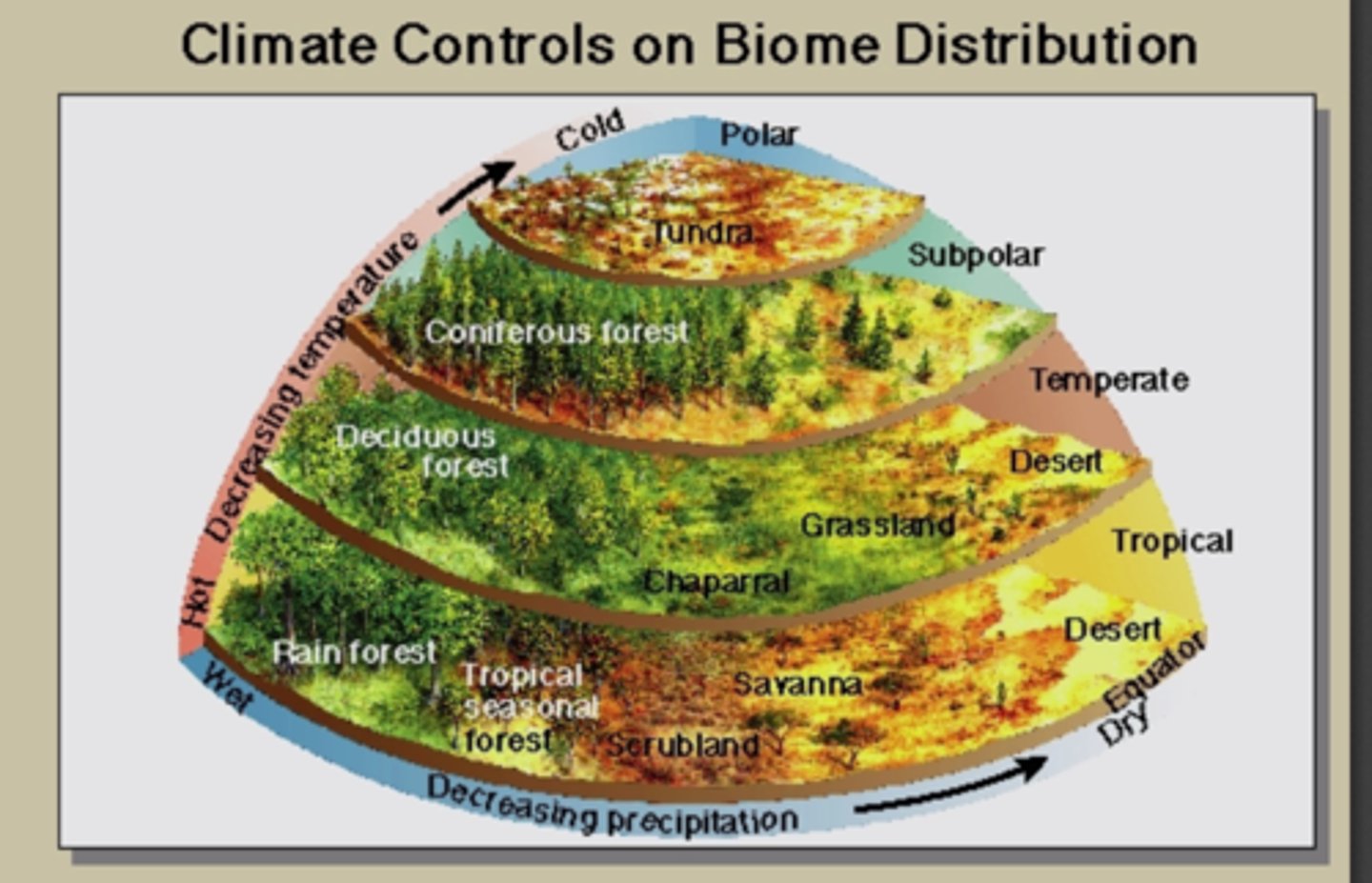
What are A climates?
Tropical, hot humid year round
What are B climates?
Arid Climates, annual moisture-deficit
What are c climates?
Warm, humid climates. seasonally hot
What are d climates?
Cold, snow-forest climates
What are e climates?
Poloar Climates
What are h climates?
Highland climates
What are Af, Aw, and Am climates in order?
No Dry Seasons, short dry season, dry winter
What are the Bs, Bw climates in order?
Semiarid, Arid
What are the Cf, cw, and cs climates in order?
No dry season, dry winter, dry summer
What re the df and dw climates in order?
No dry season, dry winter
What is Dynamism?
Change is the norm
What are three responses to change beyond tolerance limits?
Adapt, Migrate, Die
What is a biome?
A large, regional scale, stable terrestrial ecosystem complex characterized by specific plant and animal communities
What does climate trigger in plants?
A metabolic response
What does climate trigger in animals?
homeostatic, physiological and behavioral response
What does climate control?
The available water/energy available to run ecological systems
Biome Triangle
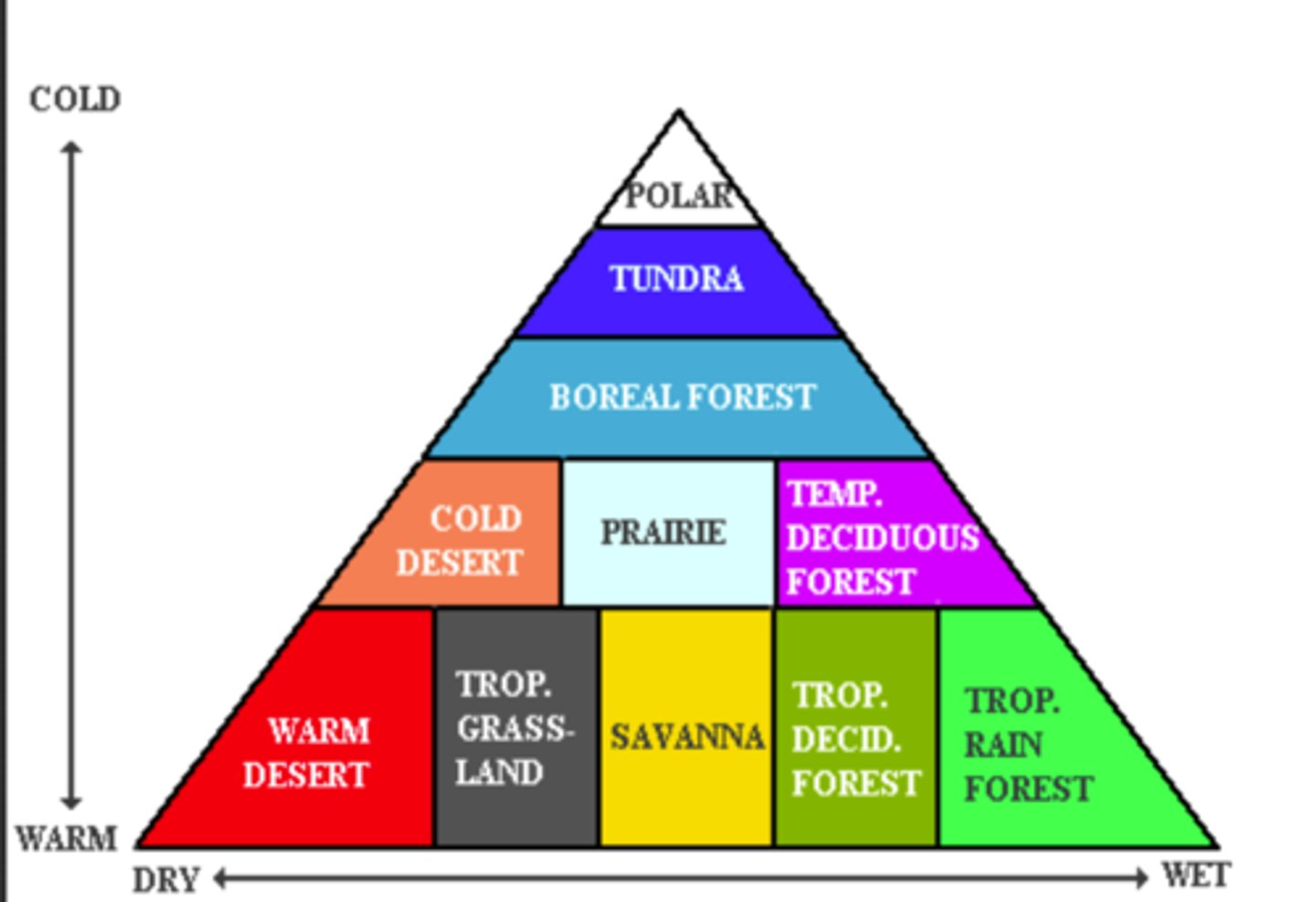
What is climate a major control on?
Biomass, NPP, biodiversity
What did Alexander von Humboldt study?
Phytogeography with a main focus on plants
Why are all plants autotrophs?
Only they convert solar energy to chemical energy
What are all creatures?
Heterotrophs
WHat forms the base of the ecological pyramid?
Plants
What causes the size of the biome pyramid?
The size of the pyramid base is a funciton of available energy and water ergo climate is the major driving mechanism
What is plant's link to the hydrologic cycle? (4)
The major biological storage facility
Input from soils
Output to atmosphere
Influence groundwater recharge (influence on infiltration ratio)
What is plant's link to the lithosphere?
Protect soils from erosion
What is plant's link to soils (pedosphere)?
Organic matter in soils comes mostly from plants
How many plant species are there?
> 420,000
What are lianas?
Vines
What are epiphytes?
Plants growing on other plants to get closer to the sun
What are bryophytes?
Mosses
What is stratification?
The number of canopies
What are the periodicity? (3)
Deciduous
Evergreen
Semi-deciduous
What leaves are cold adapted?
Needles
What are features of hot and wet adapted plants?
Big and broad, oriented , drip point, waxy
What are some qualities of dry adapted?
Tiny, dusty
North American Terrestrial Biomes
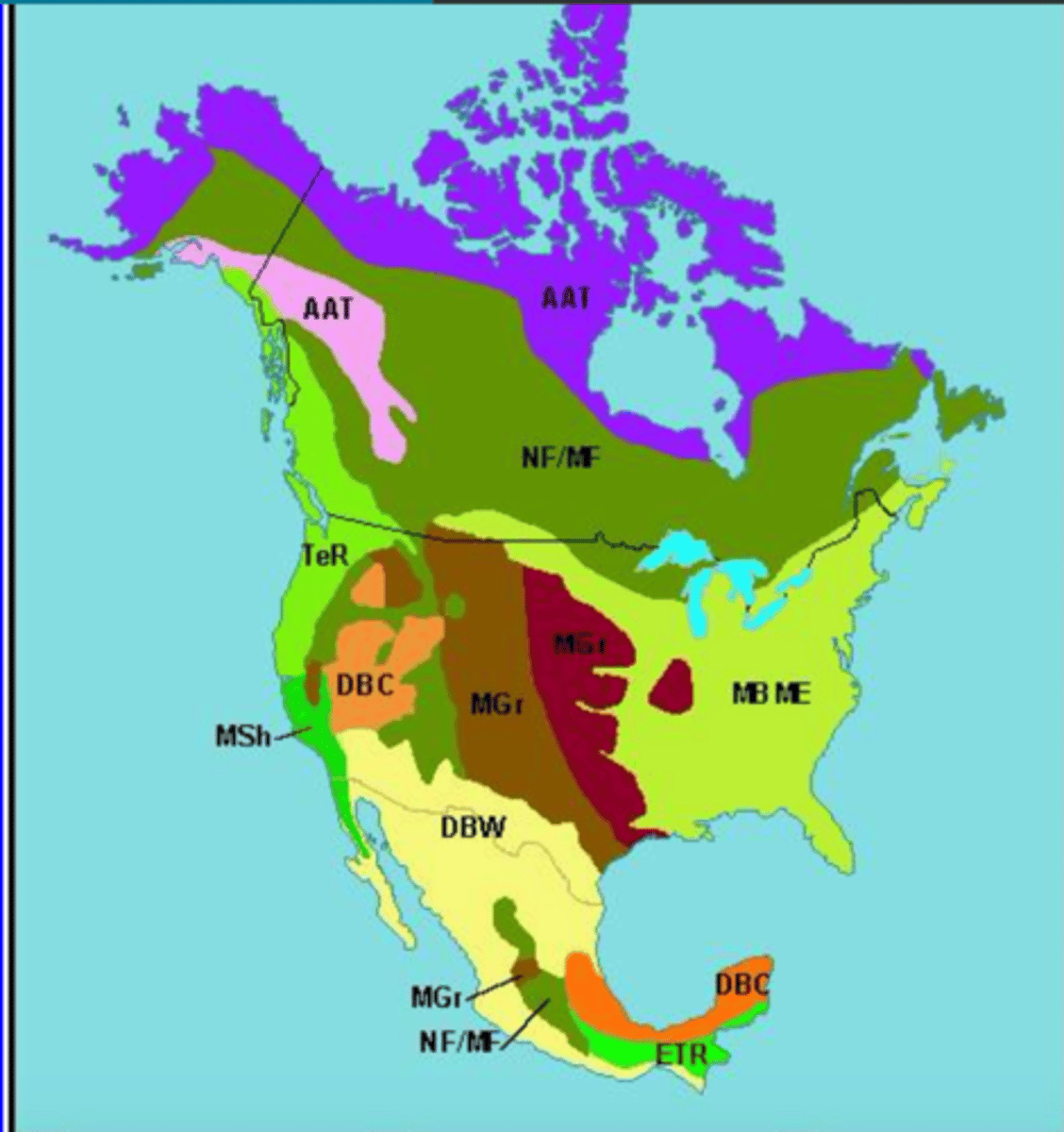
What letters are for Forest biomes?
A, C, D
What letters are for Savanna biomes?
A, C, D transitional to/adjacent to B