American Federal System & Texas State Constitution CH 2 Tx POl
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Federalism
Division of powers between a central authority and constituent political units (gov and states)
Powers of States
-Establish local gov. schools
-regulate trade w/ states
-conduct elections
-provide for public safety
Necessary and Proper Clause vs 10th Amend.
McCulloch v. Maryland established Elastic Clause (able to stretch powers as needed) & national Supremacy (fed. over state) (state tax on fed. bank)
Powers of Government
-Declare war and create armed forces
-establish foreign policy
-reg. interstates/foreign trade
-copyright/patent laws
-establish postal offices
-coin money
Interstate Commerce Clause
- Applied to goods across state lines left most reg. to states (legit barriers?)
-State courts decide on legitimacy of trade barriers (only safety issues affect commerce)
Equal Protection & Due Process Claus (14th amend.)
Bill of rights provides civil liberties fed cannot deny; 14th amendment made some of those civil liberties upheld by state and gov
Civil Liberties
Freedom of speech/religion, no segregation in schools, protection of self-incrimination in criminal proceedings
Power to tax/spend to promote general welfare
National Gov. provides money to state/local gov. with standards for how it is spent (grants)
Dual Federalism
- 19-20th century
National gov delegated most power to states & provided civil rights
- Little financial assistance
= states dominate (declined after civil war)
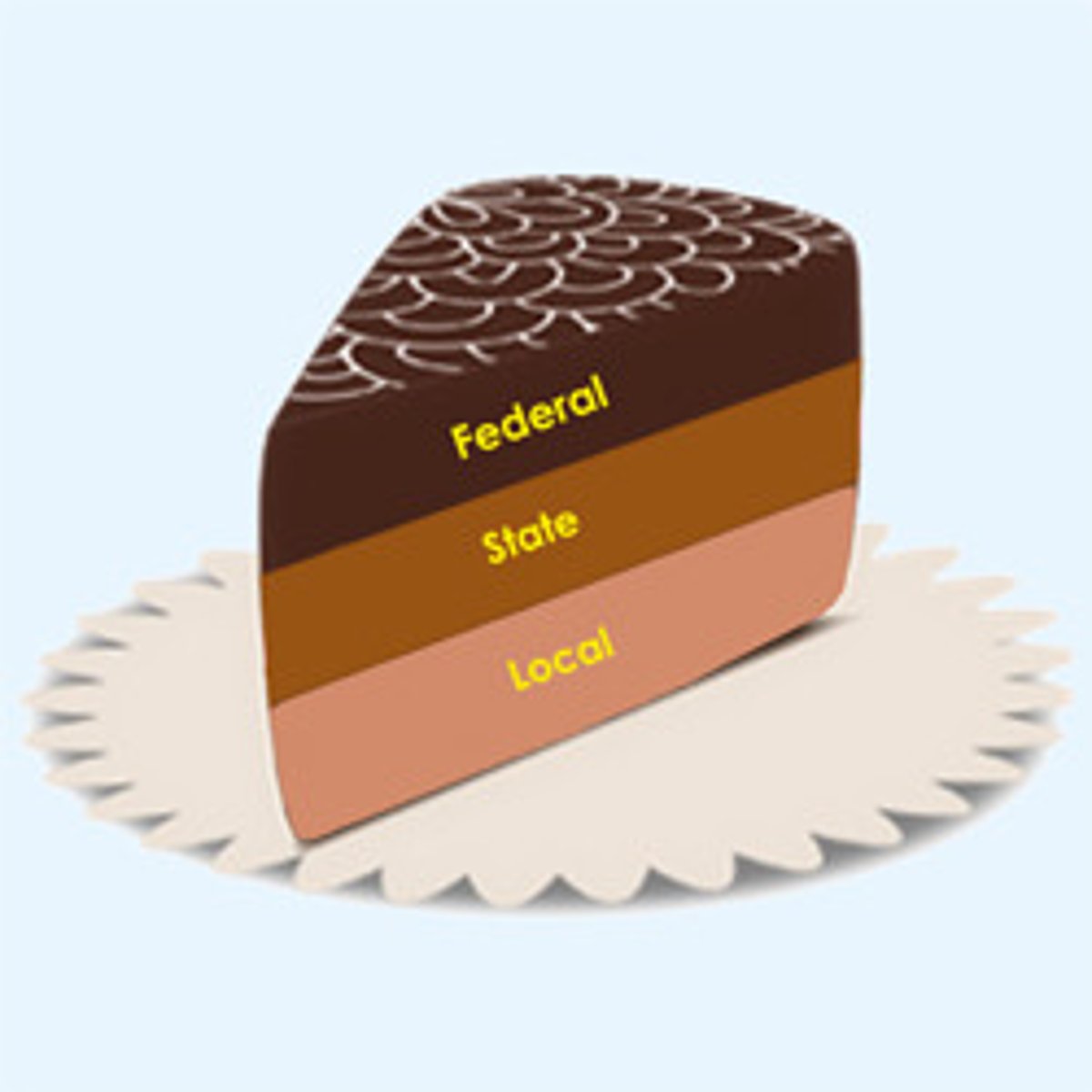
Cooperative Federalism
- Great Depression
-cooperation between state and gov to meet increasing needs of citizens during severe hardship

Creative Federalism
- 1960-1980 (great society)
- gov sought end poverty and lift all citizens up
-States gave more power to spent grant money while reducing amount available to spent
Full Faith and Credit Clause
Acts, records, and judicial proceedings in any state must be recognized by other states (relationship b/w states)
Privileges and Immunities Clause
States cannot violate basic rights/privileges of nonresident/ citizen of diff. State (relationships b/w states)
categorical grants
fed grants with strings attached for specific use of money (coercive federalism)
27 Amendments
1-8 civil rights
10- power to states
13- no slavery
14- equal due process
15- equal rights
16- income tax
19- women's rights
24- no poll tax
26- voting age 18

Popular sovereignty
- root power in people
- legit constitutions should articulate will of people
(Texas bill of rights and Preamble)
Social Contract Theory
Individual possess inalienable rights and willingly submit to gov. To protect these rights
Principles of Constitutional Government
- Popular sovereignty
-social contract theory
- divide and assign power a (limit gov.)
Characteristics Common to State Constitutions
- Legislature: propose laws, set tax budget, oversee state departments
- Governor: Limited power, call special sessions, veto, fill vacancies
- Judiciary: interpret law (civil and criminal), elected in
Plural Executive System
Executive power divided among statewide elected officials in Texas (limit gov by fragmenting exec.)
Texas Bill of Rights
Texas grants more civil rights than the US Constitution
Supreme Law of the State
State law cannot violate the state constitution, making the state superior to local government
Evolution of Texas Constitution: 1824-1876
Texas constitutions reflecting political climates and historical events
Tx constitution under Republic of Mexico
-Federalist concept
-established Catholicism as official religion
-didn't legalize slaves
Tx constitution under Republic of Texas
-Unitary system of gov.
-freedom of religion
-limited gov. (no armies unless approved, 3yr term)
-legalized slavery
Tx Constitution of Statehood
-women granted property rights
- limited exec.
Tx Constitutions during Civil War and Reconstruction
1861- no freeing slaves + ability to secede
1866- free slaves + no more secession
1869- carpet bag constitution (more power to gov, equal voting rights, centralized gov)
Tx Constitution of 1876 (present)
- traditionalistic +individualistic
-reestablished elections for offices
-restricted powers of legislature and governor
Culture Drives Institutions
Texas constitutions influenced by attitudes towards former Mexican government and Southern traditional beliefs
Important Sections of Texas Constitution
-(1) Bill of rights: basic + no suspension of writ of habeas
- (2) Power of Gov: specific separation of powers
- (3) Legislative Department: bicameral that are elected + requirements
- (4) Executive Department: all elected positions and terms
- (5) Judicial Departments: has multiple courts+ requirements for judges
- Additional (6- suffrage/who cant vote, 7- free public school, 9&10- creation of counties, 11- amending Tx constitution)
Ideal Characteristic of Constitutions
-Brief and explicit
- Embody general principles of gov,
- Broad outlines of gov. Subject to interpretation
-Be broad and flexible
-Grant power to specific agencies and hold officials accountable
-Formal amendments should be infrequent, deliberate and significant
Common State Constitutions are...
- Weak executives, strong legislatures
-Have articles of taxation and finance
- Prohibit deficit expenditures unless voted
- Contain large amount of detail
Amending Tx constitution
the Texas State Legislature must propose the amendment in a joint resolution of both House and Senate (2/3 vote)
Amendment Initiatives
requires collection of prescribed number of signatures on petition to propose amendment (by people)
Constitutional Convention
legislature submits questions to voters to propose amendments (more for general revisions)
Constitutional Commissions
created by acts of legislature to submit a report to legislature for recommended changes
Criticisms of Texas Constitution
Length
Organization (lack of)
Detail
Inflexibility
Unclear wording
Why hasn't the Tx constitution been revised?
Conservative nature of Texas does not support broad changes (previous attempts have failed)