Supporting Processors and Upgrading Memory
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Processor
Central component determining computing power in systems.
Intel
Major processor manufacturer known for various families.
AMD
Processor manufacturer popular in gaming and hobbyist markets.
Processor Speed
Rate at which a processor executes instructions.
Lithography
Manufacturing process size, affecting performance and power.
Socket
Physical interface for connecting processor to motherboard.
Chipset
Set of components managing data flow between processor and peripherals.
Multiprocessing
Using multiple processors to execute tasks simultaneously.
Multithreading
Single processor executing multiple threads concurrently.
Multicore Processing
Multiple processing units within a single processor.
Dual Processors
System using two separate processors for increased performance.
Memory Cache
Small, fast memory storing frequently accessed data.
Virtualization Support
Processor capability to run multiple operating systems.
Overclocking
Increasing processor speed beyond manufacturer specifications.
Hybrid Processors
Processors supporting both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures.
64-bit Processors
Processors capable of handling 64-bit data.
Intel Core i3
Entry-level processor for desktops and laptops.
Intel Core i5
Mainstream processor for desktops and laptops.
Intel Core i7
High-end processor for demanding applications.
Intel Core i9
Top-tier processor for high-performance desktops.
ARM Processors
Low power processors used in mobile devices.
Thermal Compound
Material applied to improve heat transfer from CPU.
ESD Strap
Wristband preventing electrostatic discharge during installation.
Socket Lever
Used to secure or release the processor.
Socket Load Plate
Raises when the socket lever is lifted.
Processor Protective Cover
Removed before installing the processor.
Processor Alignment Notches
Align with socket posts for correct installation.
Thermal Compound
Applied to enhance heat transfer from processor.
Cooler Assembly
Installed on top of the processor for cooling.
Cooler Posts
Support the cooler assembly during installation.
4-Pin CPU Fan Header
Connects cooler fan power to the motherboard.
BIOS/UEFI Setup
Used to verify processor recognition by the system.
AMD Processor Installation
Requires aligning pins with socket holes.
Intel Processor Installation
Involves pushing down lever to lock processor.
Clipping Mechanism
Secures the cooler in place on the processor.
Heavy Coolers
May require a plate under the motherboard.
Lighter Coolers
Use locking pins turned counter-clockwise.
Processor Pins
Must sit slightly into socket holes.
Cooling Assembly Replacement Parts
Includes processor and thermal compound.
Processor Notches
Ensure correct orientation during installation.
Power Cable Reusability
Can be reused when replacing a processor.
Thermal Compound Application
May be pre-applied or need manual application.
Processor Installation Verification
Check alignment using gold triangle and right-angle mark.
Socket Orientation
Align processor with four empty pin positions.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Temporarily holds data and instructions for CPU.
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Loses data quickly; requires frequent refreshing.
DIMM
Dual inline memory module for desktops.
SO-DIMM
Small outline DIMM used in laptops.
DDR
Double Data Rate; faster than earlier DIMMs.
DDR3
Uses 240 pins; incompatible with other DIMMs.
DDR4
Faster, uses 288 pins, single notch design.
DDR5
Faster than DDR4; offers 64 Gb DRAM.
Memory Channels
Single, dual, triple, or quad configurations.
Single Channel
Access one DIMM at a time.
Dual Channel
Access two DIMMs simultaneously, doubling speed.
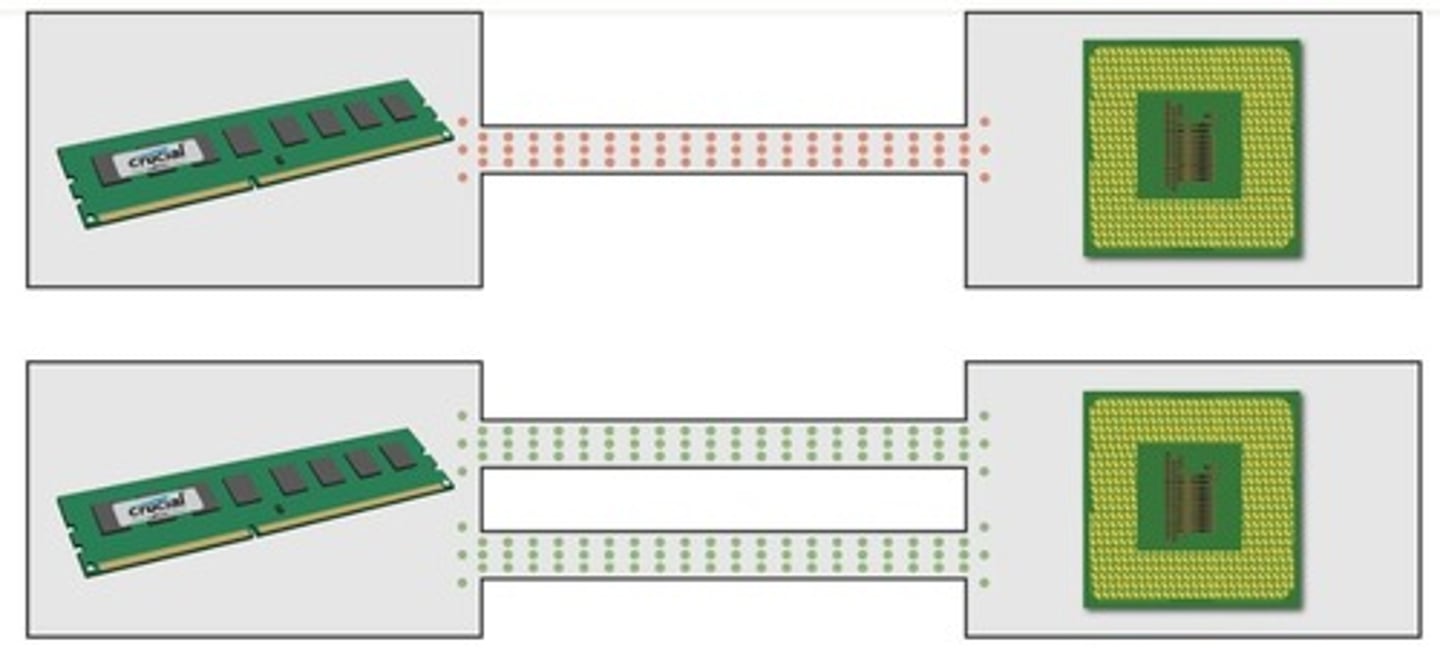
Triple Channel
Access three DIMMs at once.
Quad Channel
Access four DIMMs simultaneously.
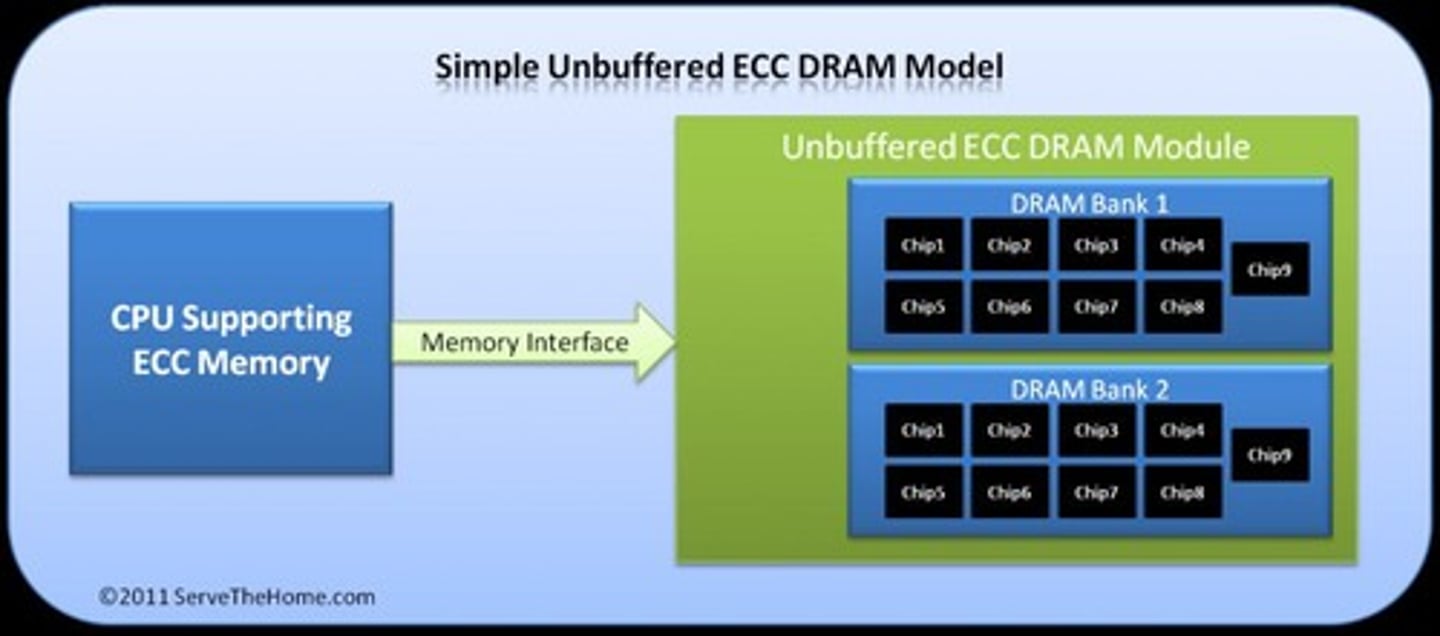
ECC
Error-correcting code for reliability in DIMMs.
CAS Latency
Measures timing for reading/writing data.
Buffering
Holds data to amplify signal before writing.
Registered DIMM (RDIMM)
Uses registers to improve server performance.
Virtual RAM
Uses hard drive space to enhance RAM.
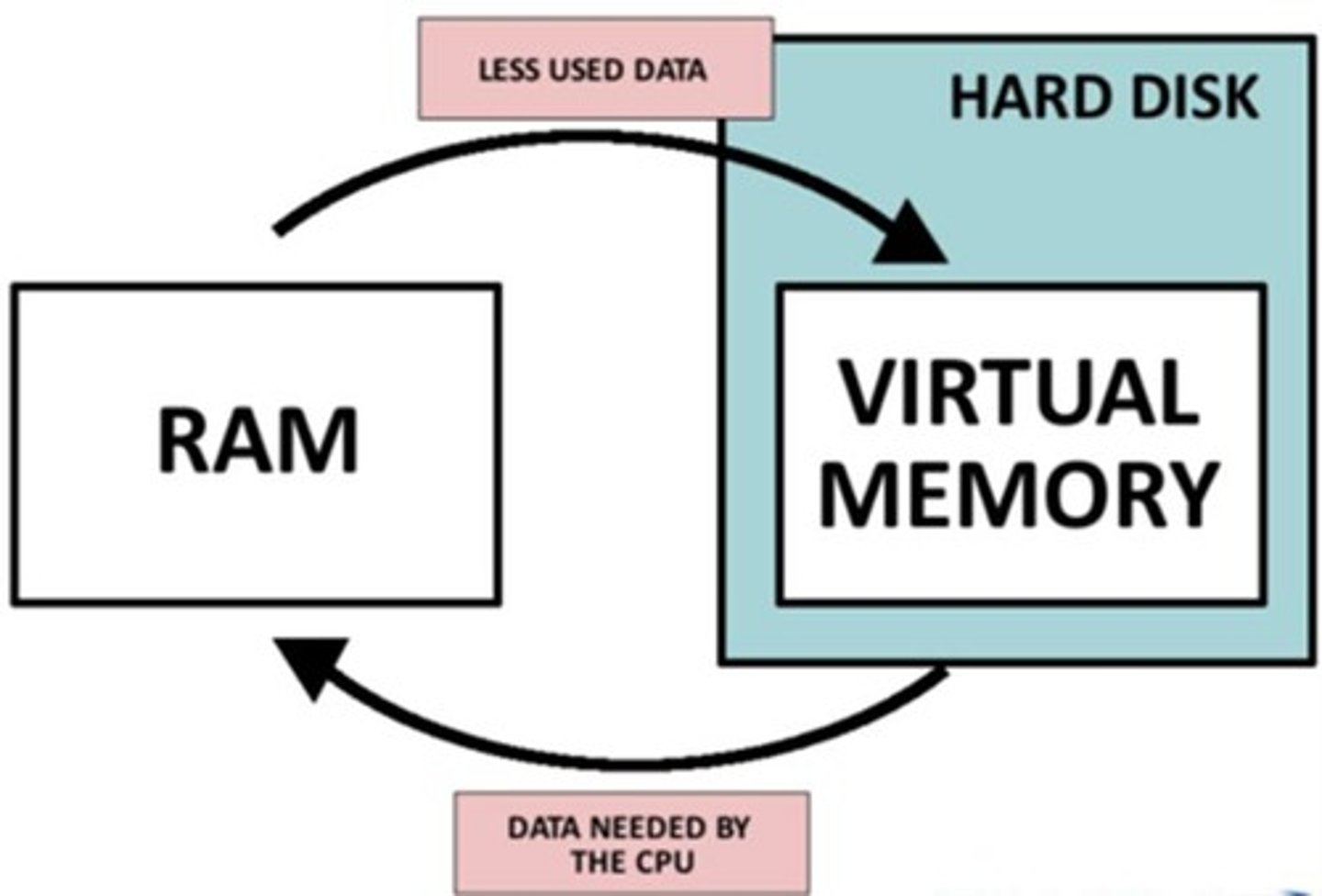
Pagefile.sys
File for storing virtual memory in Windows.
Memory Upgrade
Adding RAM to improve system performance.
Insufficient Memory Error
Occurs when RAM is inadequate for tasks.
DIMM Speed Measurement
Measured in MHz or PC rating.
PC Rating Calculation
Speed x 8 bytes for bandwidth.
Motherboard Color-Coding
Indicates DIMM slot configuration for channels.
DIMM Capacity Factors
Includes channels, RAM amount, speed, and features.
Motherboard Limitations
Determines maximum supported memory capacity.
32-bit Windows Memory Limit
Supports up to 4 GB of RAM.
64-bit Windows Memory Requirement
Requires 2 GB for installation.
Windows 10 Pro Memory Support
Can support up to 2 TB of RAM.
DIMM Module
Dual In-line Memory Module used in computers.
Memory Slot Identification
Check slots for type and capacity.
Memory Module Manufacturer
Brand that produces memory components.
Dual Channel Configuration
Requires matching DIMMs for optimal performance.
Triple Channel Configuration
Uses three matching DIMMs for efficiency.
Buffered Memory
Memory with additional buffering for stability.
Unbuffered Memory
Standard memory without buffering.
Memory Speed Mixing
All modules perform at the slowest speed.
ESD Strap
Prevents electrostatic discharge during installation.
BIOS/UEFI
Firmware interface to verify memory recognition.
Memory Installation Precautions
Handle modules carefully and avoid connectors.
Laptop Memory Upgrade
Ensure compatibility with laptop specifications.
DIMM Orientation
Use notches for correct installation alignment.
Power Off Procedure
Turn off and unplug before installation.
Memory Research Tools
Websites to match modules with motherboards.
Memory Module Imprint
Label showing specifications of the memory.
Motherboard Documentation
Guide detailing memory compatibility and limits.
Memory Slot Colors
Indicates type of memory supported by motherboard.
Memory Upgrade Process
Select, purchase, and install new memory.