physio- female reproductive system
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
the age that reproductive organs become functional
define puberty
the repetitive cycle that happens when there is no gestation
the period between 2 ovulations
what is the estrous cycle?
production of egg cells
production of sexual hormones- estrogens and pregesterone
what are the functions of the ovaries?
GnRH
what is 1?
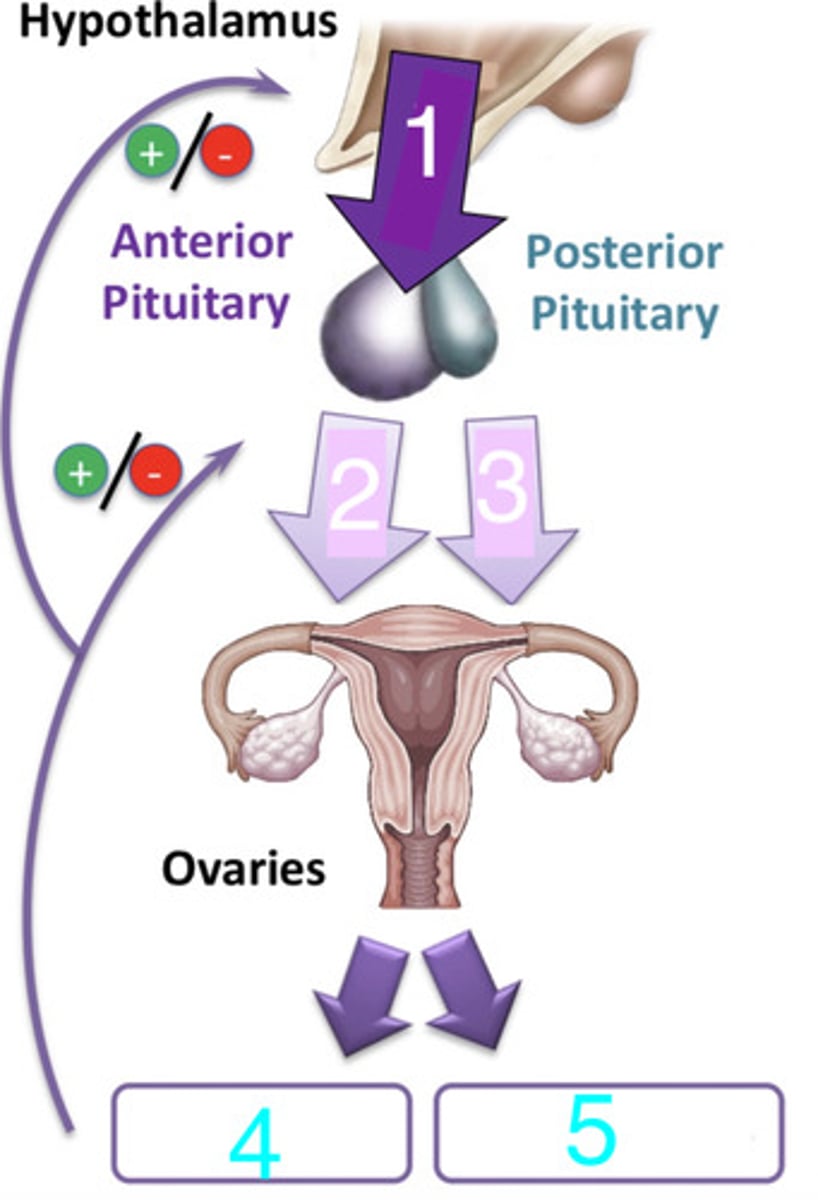
LH and FSH
what are 2 and 3?
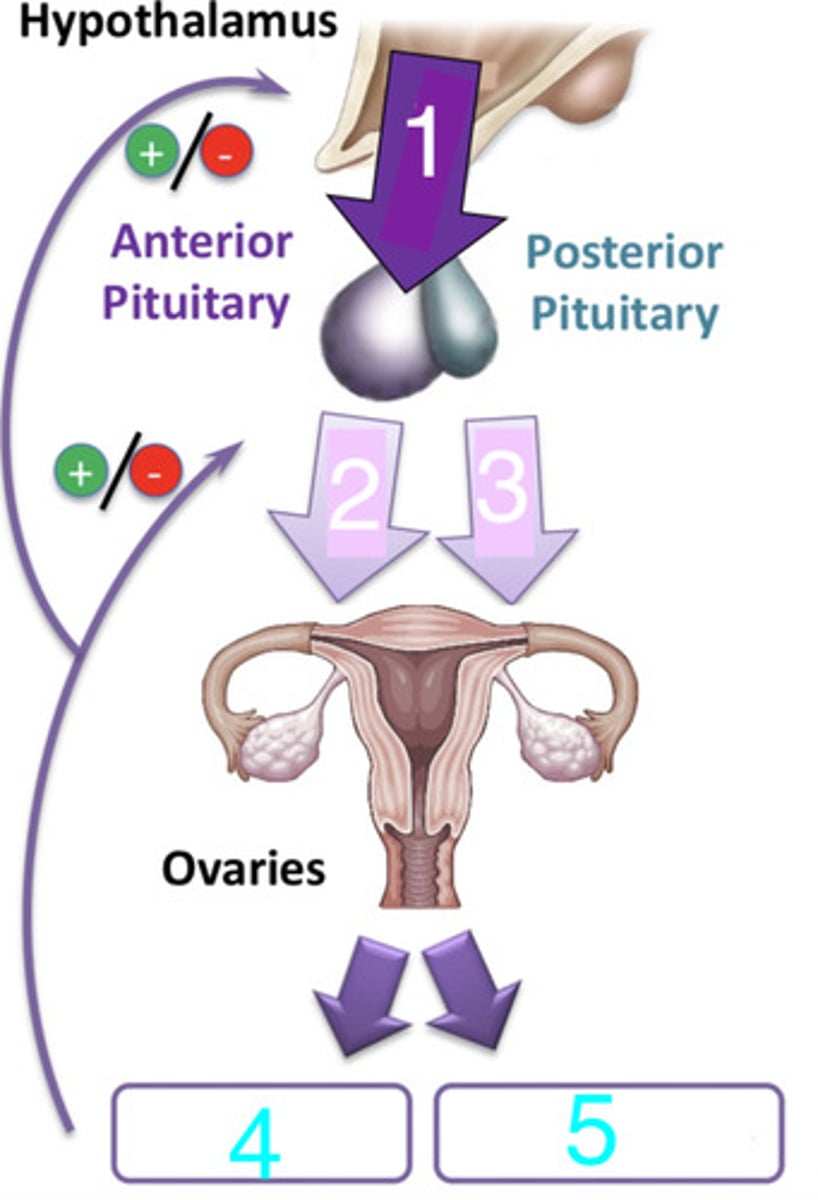
progesterone and estrogen
what are 4 and 5?
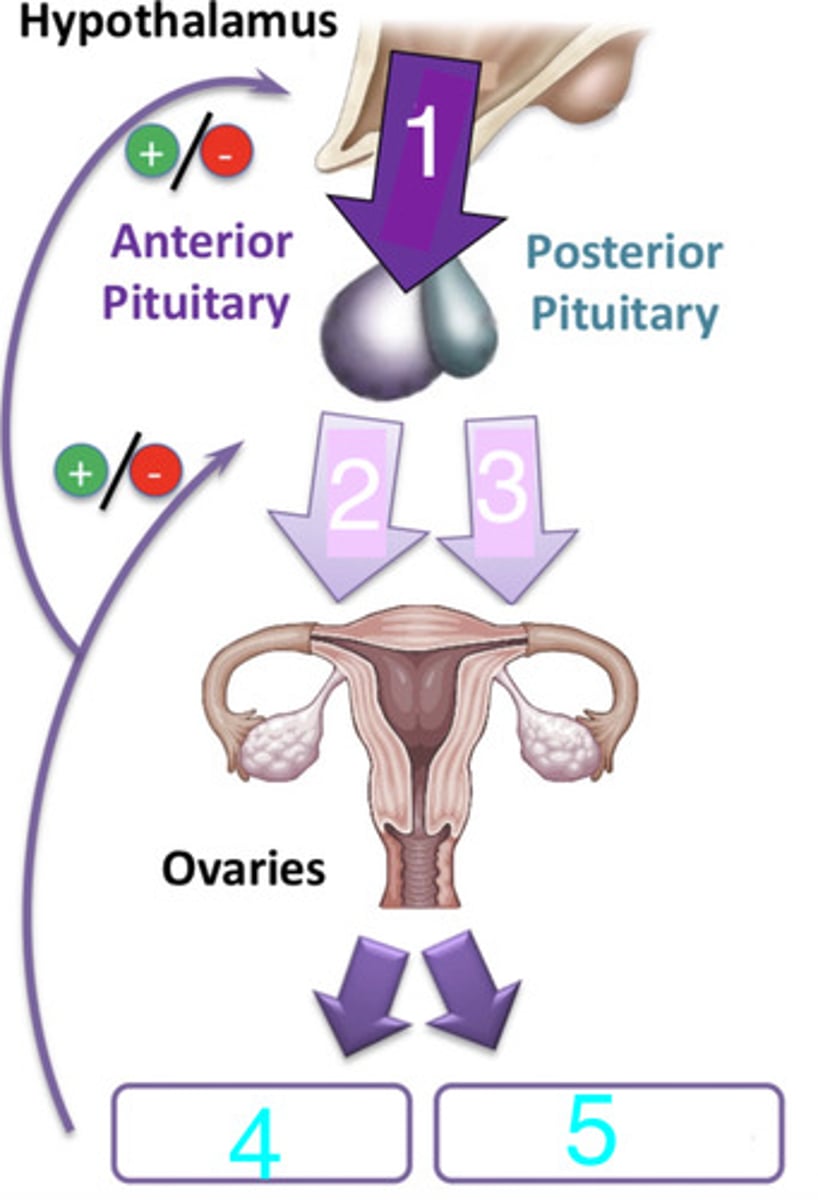
FSH and LH
what hormones from the anterior pituitary cause the release of sexual hormones (estrogens and progesterone) from the ovaries?
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)
what hormone from the hypothalamus triggers the anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and LH?
steroid hormones
what type of hormones are progesterone and estrogen?
liposoluble- they are steroid hormones
are progesterone and estrogen hydrosoluble or liposoluble?
cholesterol
progesterone and estrogen are _______ derived
prepare the uterus for pregnancy and the breasts for lactation
what is the main role of progesterone?
aromatase
what is responsible for conversion of androgens into estrogens?
converts androgens (testosterone) to estrogens
what does aromatase do?
promote growth and proliferation of specific cells that are responsible for secondary sexual characteristics
what is the main role of estrogens?
ovaries
progesterone and estrogens are synthesized in the ______
granulosa and theca cells
what cells of the ovaries produce the hormones?
progesterone and androgens- which are then converted to estrogens by aromatase (also produced by these cells)
in the ovaries, granulosa and theca cells produce ______
convert cholesterol to progesterone and produce aromatase
what exactly do granulosa cells do?
convert cholesterol to androgens
what do theca cells do?
theca cells
what cells of the ovaries make androgens?
granulosa cells
what cells of the ovaries make progesterone and aromatase?
-ovum is surrounded by one layer or granulosa cells
-FSH stimulates early growth of primary follicle
-ovum grows with LH and FSH stimulation
-more granulosa layers are added due to FSH and LH stimulation
what is occurring during follicular growth?
granulosa cells
what ovary cells are targeted by FSH?
theca interna, androgens
LH targets ____ cells of the ovary, which produce ____
positive, a peak of LH
LH and FSH cause synthesis of progesterone and estrogens in the ovaries, and this estrogen gives ______ feedback to the anterior pituitary, causing......
the peak of LH (due to positive feedback by estrogens)
what event causes ovulation?
FSH also increases, and the 2 hormones (FSH and LH) cause the follicle to swell, LH converts granulosa and theca cells into progesterone secretors and causes final follicular growth until it breaks and releases the egg
how does the LH peak cause ovulation?
LH
which hormone allows the final follicular growth, leading to the release of the egg?
LH
a peak in ______ causes ovulation
the phase after ovulation, where the granulosa and theca cells become luteal cells. they enlarge and fill with lipids, creating the corpus luteum. granulosa cells make more progesterone and theca cells make more androgens that become estrogens
what is the luteal phase?
granulosa, progesterone
during the luteal phase, _____ cells make more ______
albicans
after the corpus luteum, it becomes the corpus _______
theca, granulosa
LH acts on ____ cells, while FSH acts on _____ cells
androgens
theca cells produce ______
aromatase and progesterone
granulosa cells produce ______
positive feedback from estrogens from the ovaries
what causes the peak of LH?
inhibin, negative, to the anterior pituitary to secrete less FSH
during ovulation, granulosa cells release ______, which sends _____ feedback to the _____
less
during the luteal phase, is more or less LH acting on the theca cells?
low LH levels
what causes the atrophy of the corpus luteum?
progesterone, estrogens, inhibin
the corpus luteum secretes....
negative, hypothalamus and anterior pituitary (to inhibit secretion of GnRH, LH, and FSH)
the inhibin from the corpus luteum sends _____ feedback to the _____
hormone production is stopped- no more release of estrogen, progesterone, inhibin
what happens when the corpus luteum dies?
now, there is no more negative feedback to the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary, so they being to release GnRH, FSH, and LH, so the cycle begins again
when the corpus luteum dies and stops releasing hormones, what does this cause?
non-primate female mammals
which animals have an estrous cycle?
period of sexual receptivity (aka heat)
what is estrus?
humans and other primates
which animals have a menstrual cycle rather than an estrous cycle?
high estrogen in the receptive period
why would there be bleeding in animals experiencing estrous cycles?
because the endometrium of the uterus is shed
-in estrous cycle, the endometrium is reabsorbed, so bleeding does not occur
why do animals with a menstrual cycle bleed?
the follicular phase
what is proestrus?
follicular phase and ovulation
what is occurring during estrus?
metestrus and diestrus
the luteal phase is separated into what 2 phases?
not a phase, but a period of no cycling between diestrus and proestrus
what is anestrus?
diestrus
at what phase is progesterone released the most?
proestrus
estrogen levels peak during what estrous phase?
24-48 hours later
ovulation occurs how long after the LH peak?
corpus luteum, progesterone
during diestrus, the ______ is producing high levels of _______
PGF2a, uterus
regression of the corpus luteum
towards the end of diestrus, if the female is not pregnant, _____ is released from the ______. this causes ______
FSH
right after ovulation, the metestrus phase is occurring, and we observe a rise in what hormone?
it is limited to a "heat" period called estrus
for animals with an estrous cycle, is sexual receptivity limited or can it occur any time?
ovulation
the "heat" period, or period of sexual receptivity, is occurring close to what part of the cycle?
high levels of estrogen
why might an estrous animal bleed?
luteal phase
during what phase is progesterone production the highest?
progesterone
what hormone gives negative feedback to the hypothalamus in relation to GnRH?
estrogen
what hormone gives positive feedback to the hypothalamus in relation to GnRH?
inhibit, which stops the negative feedback and restarts the cycle
does PGF2a stimulate or inhibit progesterone secretion?
high levels of progesterone, without pregnancy, stimulates the uterus to produce PGF2a, which inhibits progesterone, stopping the negative feedback, and restarting the cycle
what occurs to allow the cycle to restart?
PGF2a
when there is no pregnancy, ________ inhibits progesterone secretion
estrogen
during the follicular phase, there are high secretions of what hormone?
high levels of estrogen during proestrus give positive feedback to the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus, causing high levels of FSH and LH (mostly LH) to swell the follicle until is breaks and releases the egg
ovulation occurs because....
decrease
after ovulation, estrogen levels _______ (Increase or decrease)
animal is standing to be mounted, the vulva is enlarged and "winking"
what are the physical signs of estrus?
the corpus luteum regresses due to PGF2a release from uterus
what happens after ovulation if the female is not pregnant?
to begin growth of new follicles
why does FSH peak during diestrus?
metestrus
in the cow, what phase does ovulation occur (this is different than other species)?
pregnancy, lactation, disease, stress, malnutrition, etc
what are some causes of anestrus?