Cognition Lecture 16 - Events
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
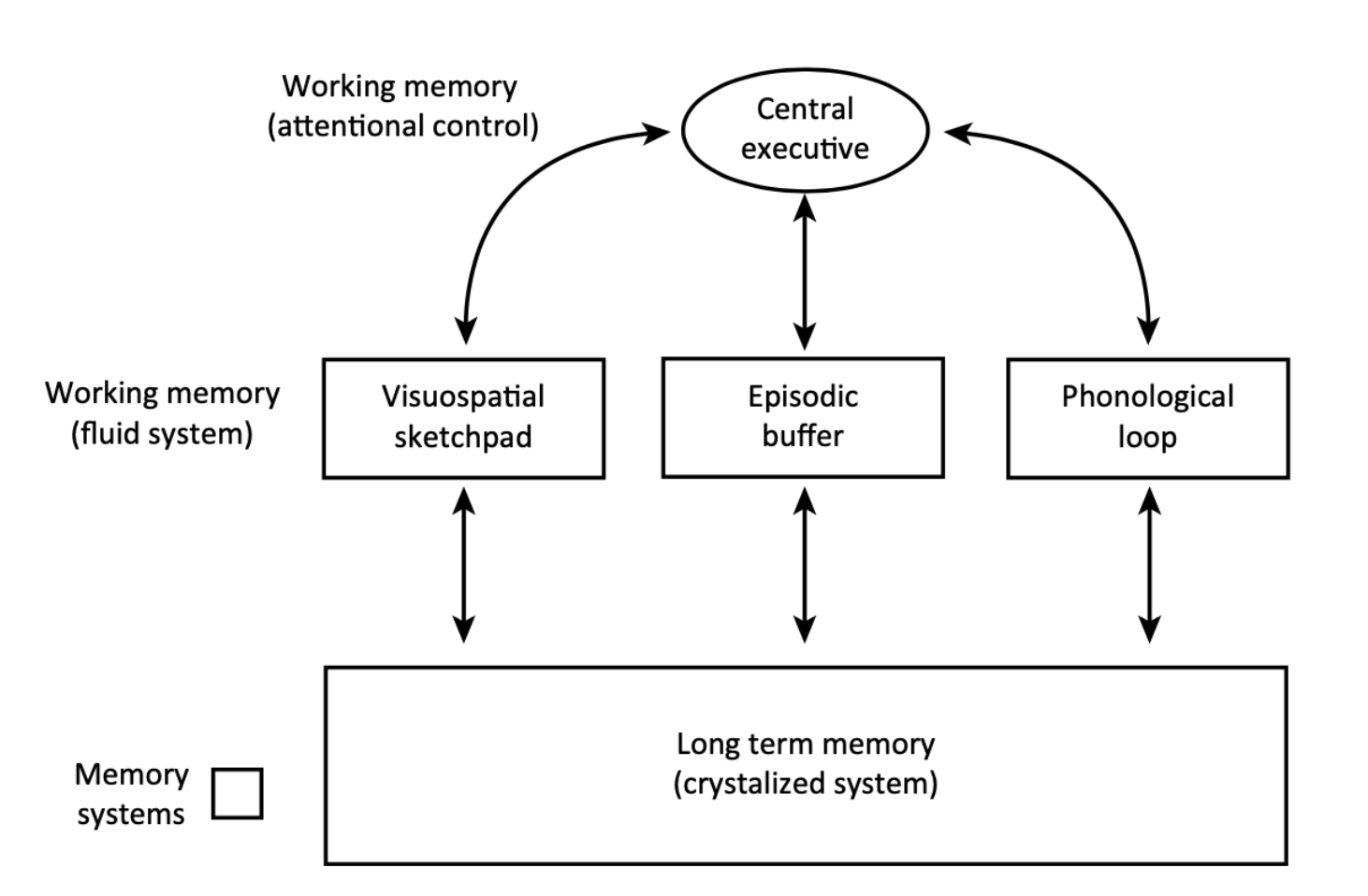
Working memory vs Long Term Memory
“Systems of Memory” framework
Classical view: information storage is separated from the information-processing units
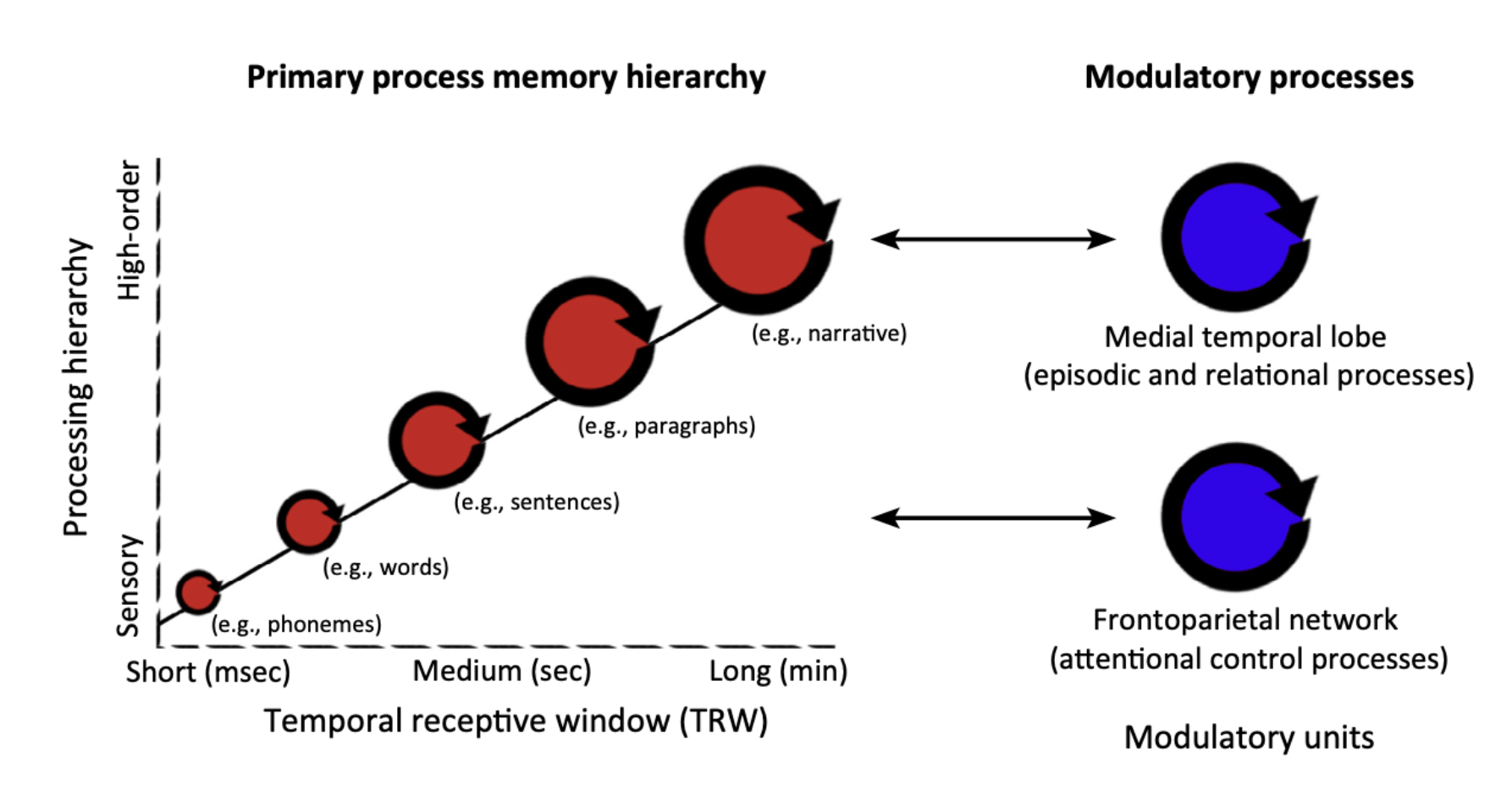
Hierarchical Process Memory
The past is continuously being integrated with the present
In language, we need to integrate each word with preceding words and sentences with each other
Hierarchical Process Memory (cont)
Organization based on temporal processing windows
HPM: no separation between information storage and processing, memory is integrated with processes
(cont)
Scrambling stories to confuse your brain
If a brain region has a specific (or maximum) time-integration window for stimuli, it would be disrupted by scrambling above that specific timescale
(cont 2)
Different regions integrate information over different timescales
Temporal receptive windows (TRW) are the time equivalent of retinotopic spatial receptive fields
(cont 3)
Electrophysiology evidence in non-human primates
Temporal receptive windows (TRM) are the temporal equivalent of retinotopic spatial receptive fields
Experiencing the World as Stories
Our naturalistic sensory input is complex, but structured
*TV show example
Quantifying the Elements of a Story
From words to sentences to scenes to events
Events: points in the movie when there is a major change in topic, location, or time
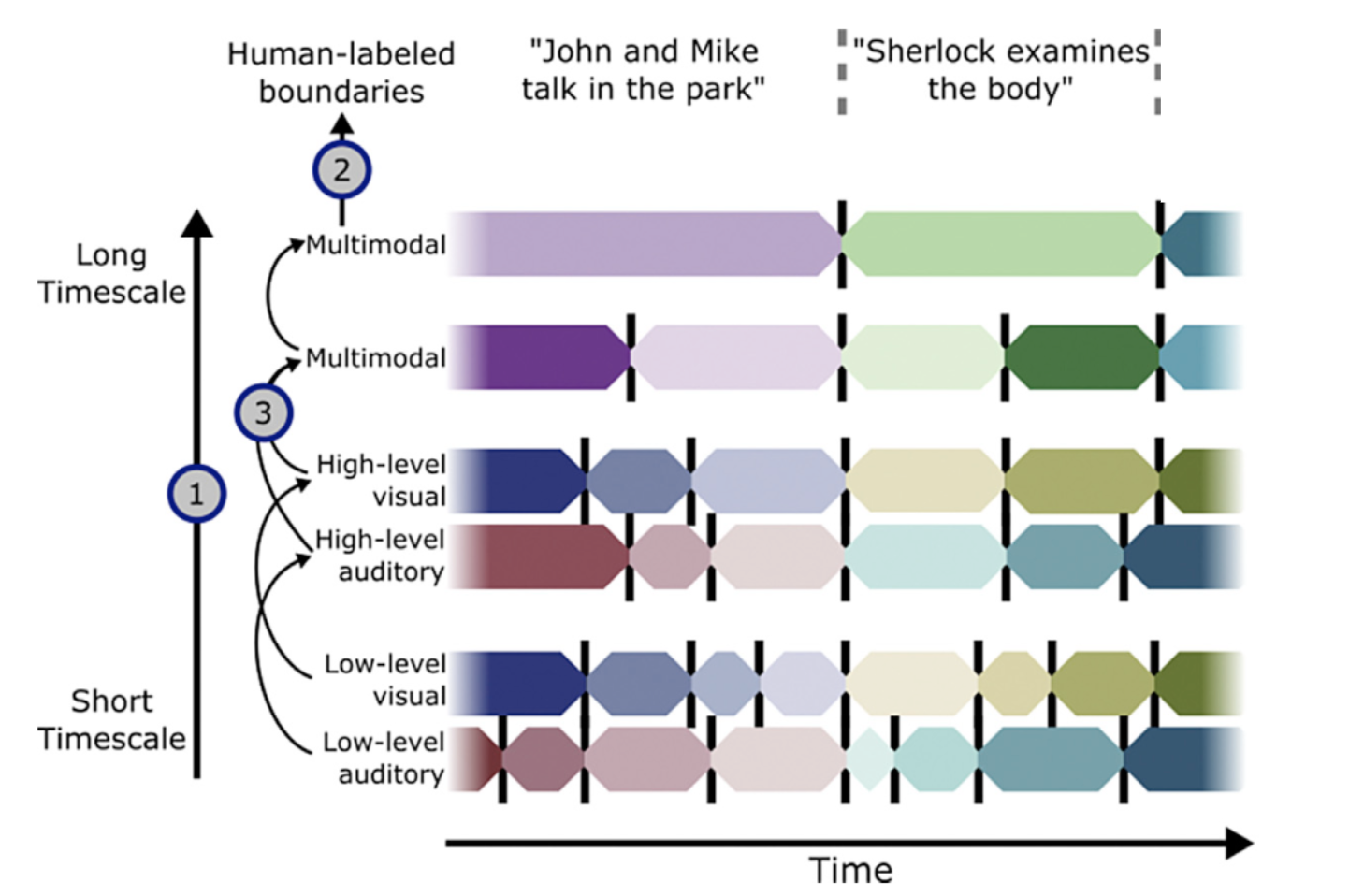
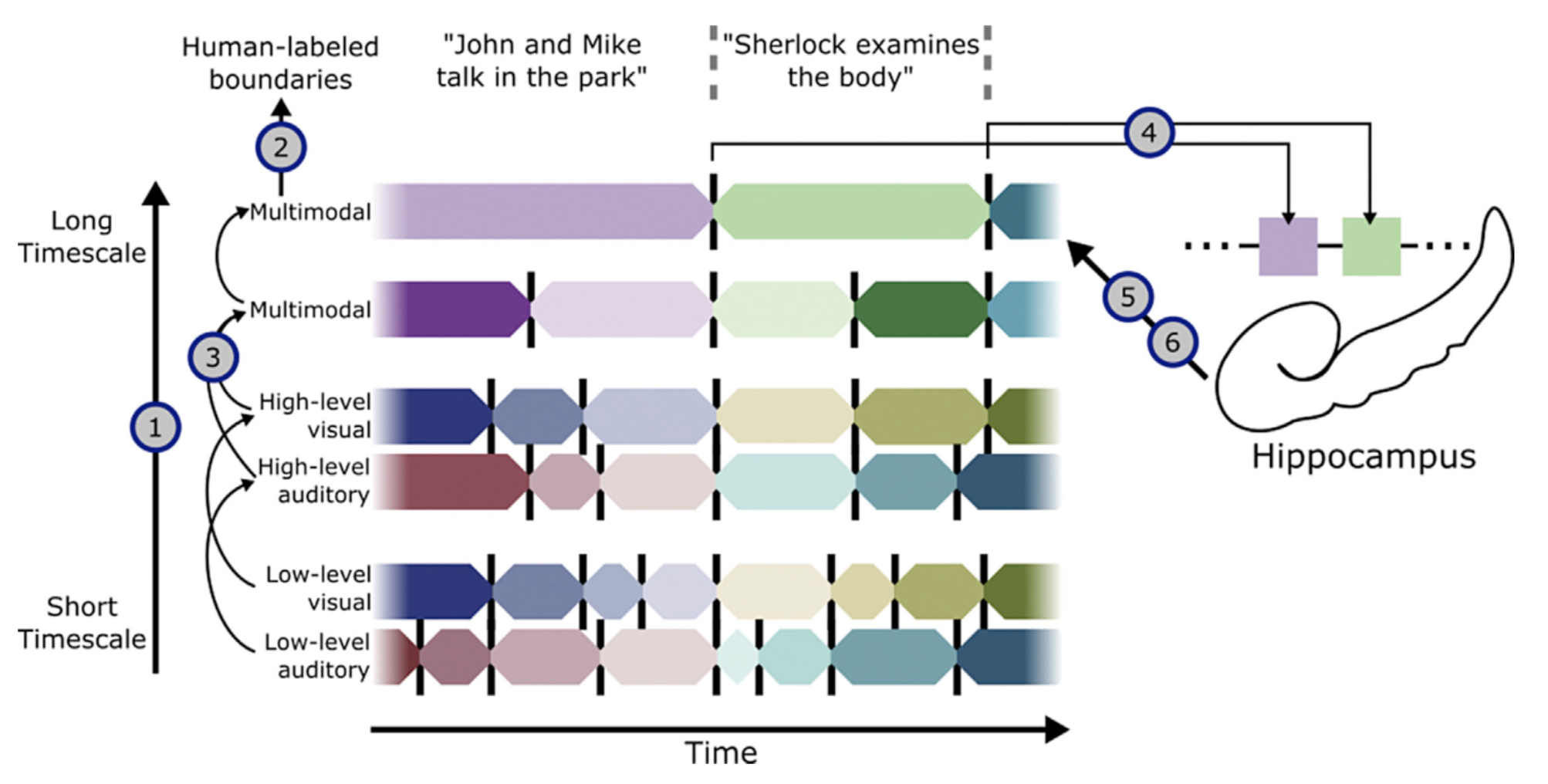
Events in Naturalistic Cognition
Consistent chinks of narrative experience
Event boundaries
point in the narrative / neural response with a major change in topic, location, or time
Assumption 1
an event is semantically consistent and elicits a consistent pattern of neural activity
Assumption 2
each event pattern is unique and brain regions transition between events (and patterns)
Neural Event Discovery: HMM
Hidden Markov Model for (neural) event segmentation
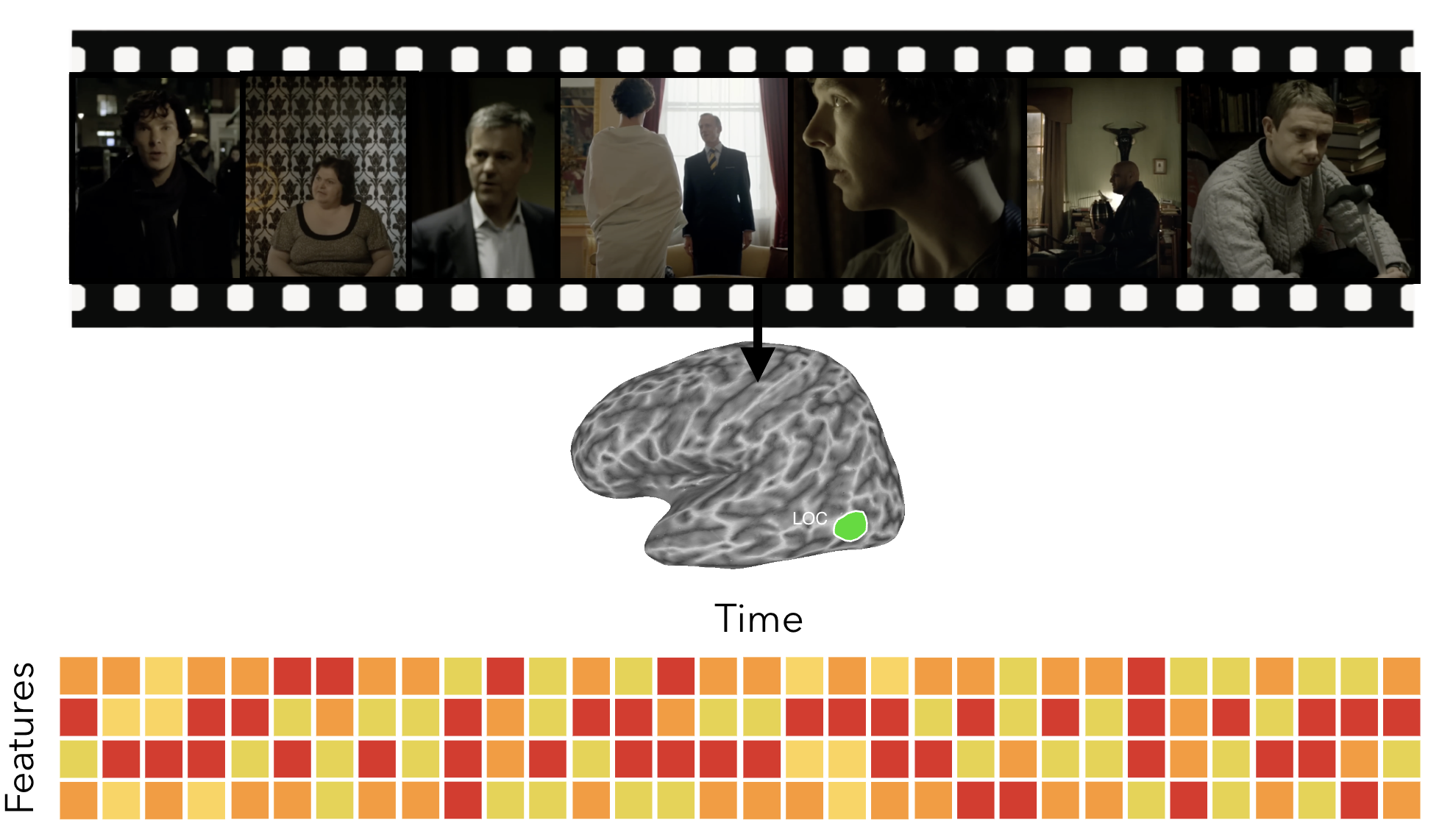
Number of Neural Events Varies Across Cortex
Posteromedial cortex (PMC) event structure similar to perception
The brain is building increasingly complex, longer TRW patterns that better reflect structure in the world
Correlated with the region’s temporal receptive window (TRW)
Why are event boundaries important?
Event boundaries trigger hippocampal encoding signals
Strength of encoding signal is correlated with reinstatement quality and with better memory for the event
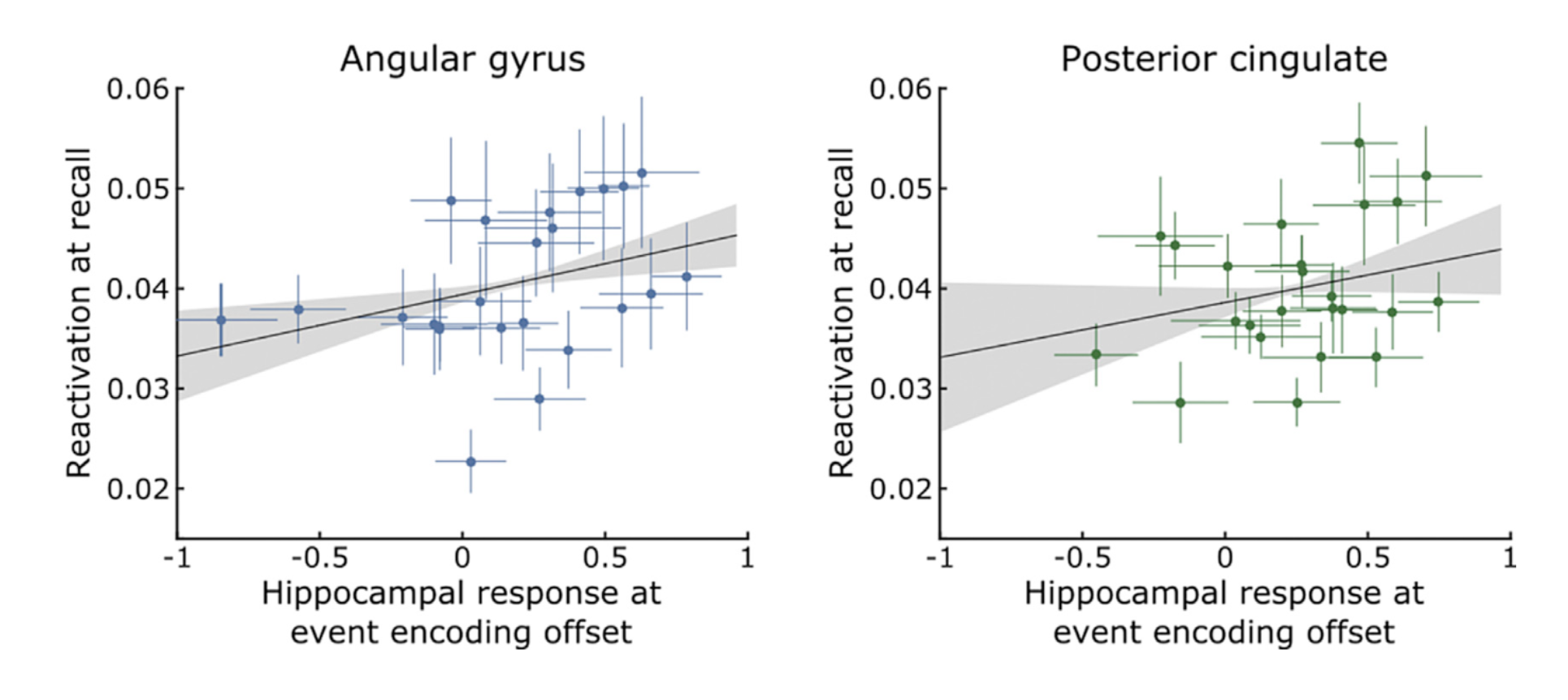
Important takeaway
When an event ends, information in high-level cortical regions is stored as episodic memory
Real Life Experience is a Stream of Events
And they are encoded from / reinstated to cortex at boundaries