Cell cycle
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Cell division
The process where 1 cell becomes 2
Why should cells divide?
Growth
Reproduction
Repair
Chromatin
Noodly DNA
Chromosome
Tightly coiled DNA
Chromatid
Half of a chromosome; there are 2 in a chromosome
Interphase + mitosis
Cell cycle
Mitosis + cytokinesis
Cell division
Mitosis
The process in which a cell divides into 2 daughter cells
Interphase
The longest phase in the cell cycle. The cell prepares itself for mitosis by growing and DNA synthesis.
G1
The cell grows and doubles its organelles. The cell still performs normal cell functions.
S
DNA is replicated.
G2
Cell continues to grow and proteins for cell division are made. Also ensures that DNA was replicated properly.
Prophase
DNA condenses and thicken, forming chromosomes. The centrioles move to the opposite poles and spindle fibres form. The nuclear membrane also dissolves.
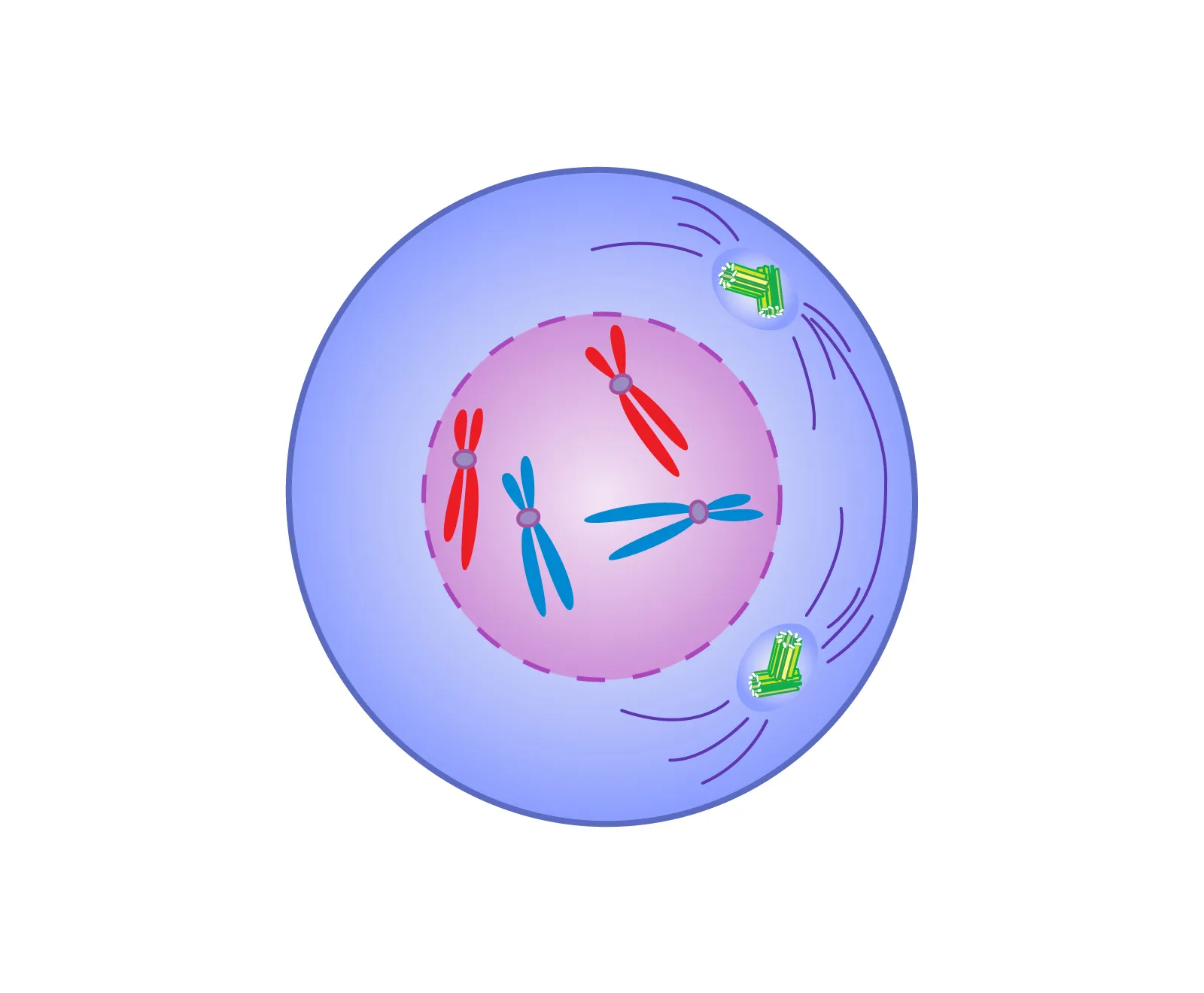
Metaphase
The chromosomes aligns themselves along the middle of the cell and the spindle fibres attach to the centromere of the chromosome.

Anaphase
The spindle fibres shorten, which pulls a sister chromatid of each chromosome to each pole. There should be the same number of chromosomes at each pole if done corrrectly.
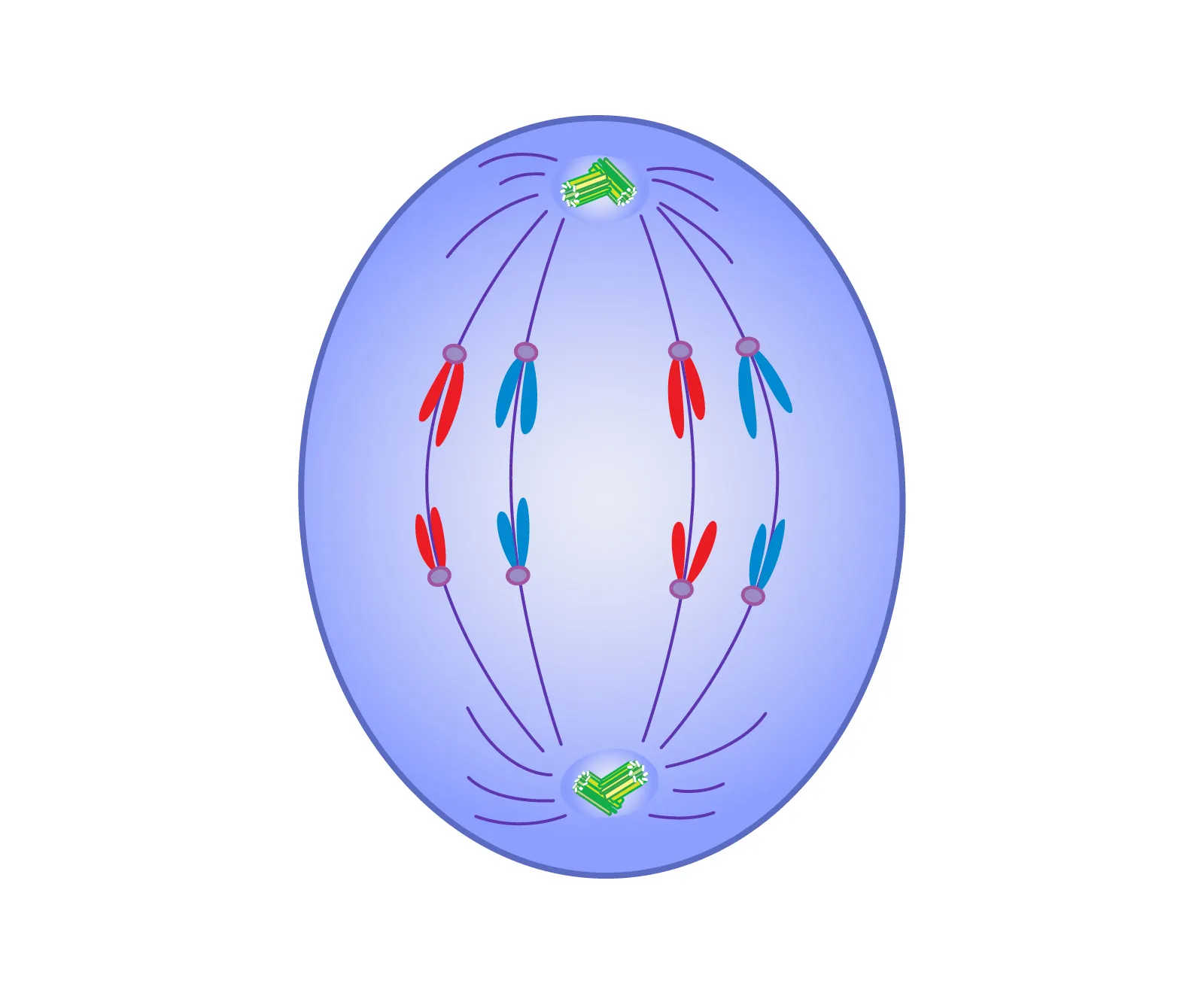
Nondisjunction
The failure of chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate properly during cell division. In meiosis, this can cause genetic conditions like down syndrome, triple X syndrome, kilnefelter’s syndrome, and turner’s syndrome.
Telophase
The chromosomes reach the opposite poles and begin to unwind. The spindle fibres dissolve and new nuclear membranes form.
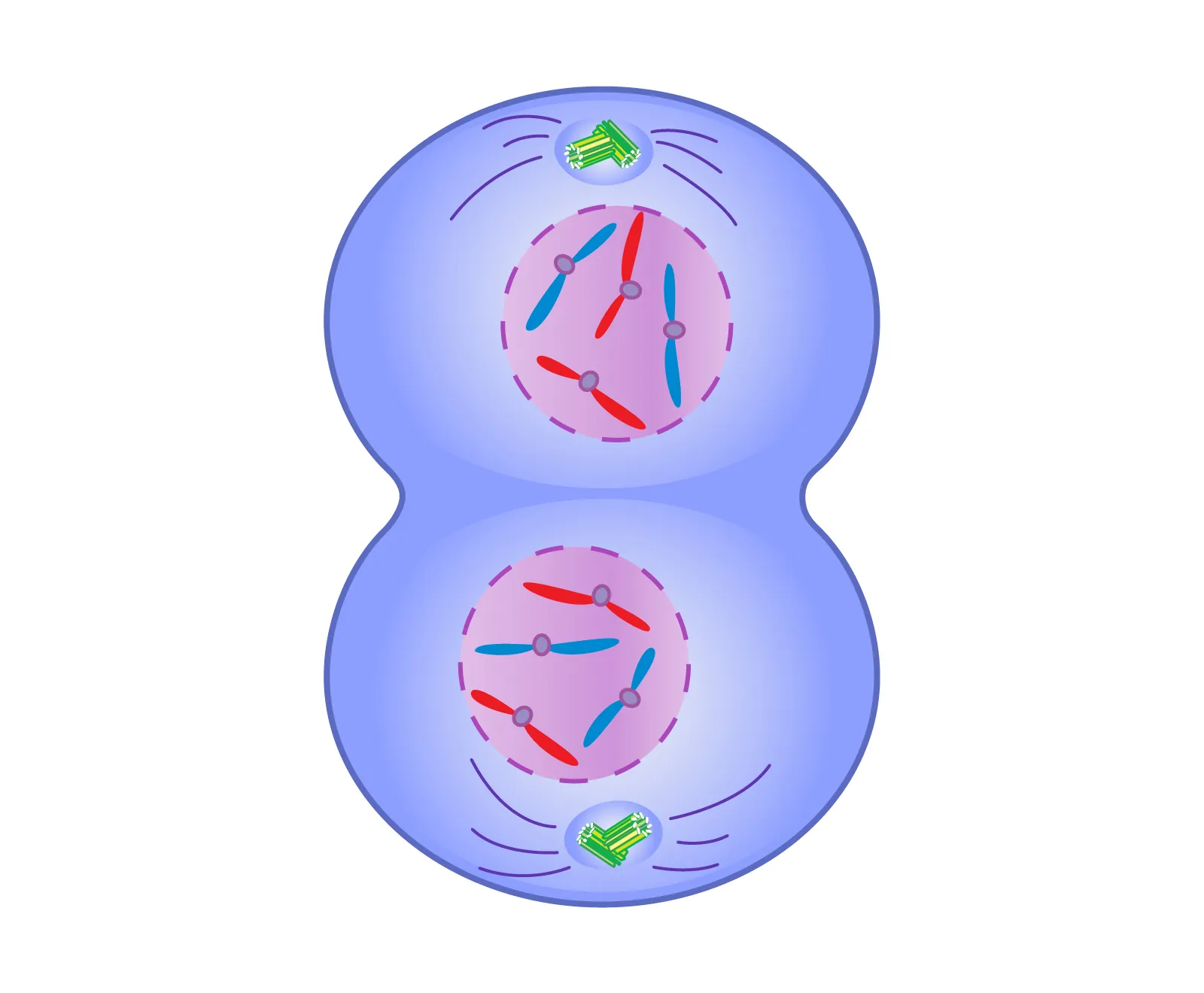
Cleavage furrow
In animal cells. A pinch forms at the middle, where the cell is spliting into two.
Cell plate
In plant cells. Vesicles gather near the center and fuse together.
Cytokinesis
Cell divides its cytoplasm into the two new identical daughter cells.
Cell division will not occur if
DNA is not replicated
DNA is damaged
Not enough nutrients to support growth