class 10- Central banks & monetary policy.
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are the 3 functions of central banks?
STATE INSTITUTIONS=
manage finances of state
manage currency to allow economic activity
unique lender of last resort to banks, governments & economy.
Central banks and emergency finace:
try to prevent emergencies instead of reacting.
signaling to markets that they will not be able to make money by selling off a currency on financial markets:
3 examples: 2008, 2012, 2020.
On an international level?
provider of last resort= hegemon’s central banks
What do central banks engage in when the manage the economy?
MONETARY POLICY.
ensure enough loney in circulation.
ensure banks have enough
ensure governments have acces to finance.
act through primary interest rate
What are the 3 main goals of the central bank?
PRICE STABILITY= low inflation
ECONOMIC STABILITY= smoothing
FINANCIAL STABILITY= preventing economic crashes.
What is the fisher equation?
real interest rate= nominal interest rate- inflation rate
What is disinflation?
= decrease in the rate of inflation
Who are the winners & losers from inflation?
winners=
anyone earning money
debt payers
losers=
anyone who has money
investors, savers, creditos
pensions (fixed benefits)
who are the winners & losers from deflation?
winners=
anyone who has money
investors, savers, creditos
pensions (fixed benefits)
real value of assets increase
losers=
anyone earning money
debt payers
society= consumption drops → delays.
If inflation is too high…
If unemployemt too high
→ central banks can…
too high → raise interest rate.
unemployement → lower interest rates
The measurement approach: (pros/ cons)
Central bank pays attention to prices in order to change interest rates. (rise when prices rise…)
PRO: evidence based, works without paying attention to money supplu.
CON: suffers blind spots (didnt think housing was part of inflation)
The WS/ PS model approach:
Central bank think inflation caused by how workers and firms bargain over prices.
PROS: goes beyond economic shocks to look at how firms and workers react
CONS: suffers from blind spots: ignores financial markets = unrealistic
How can firms & workers cause inflation?
baraganing power of firms increases over consumers= greedflation.
of workers over firms: wage increase that doesnt result from increased productivity.
When increase in price of oil:
downwards shift PS curve
prices rise
real wages fall
positive baragaing gap
peristently higher inflation
Inflation can be caused by supply and demand shocks:
supply shock ?
solution= windfall taxes on firms
demand shock =cannot boost production → rise prices.
solution= fiscal policy investments to increase supply or higher interest rates
Philipps curve
inflation and unemployement curve
moderate inflation is okay as long as employement goes with it
baragining power and inflation:
bargaining power can increase inflation over time
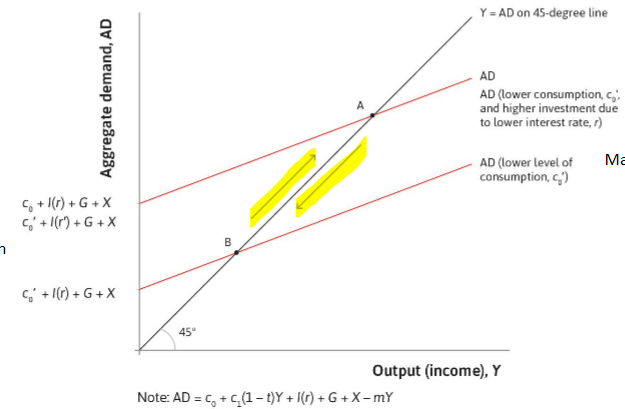
How does the central bank stimulate investment?
lowering real interest rate.
AD curve shifts upwards
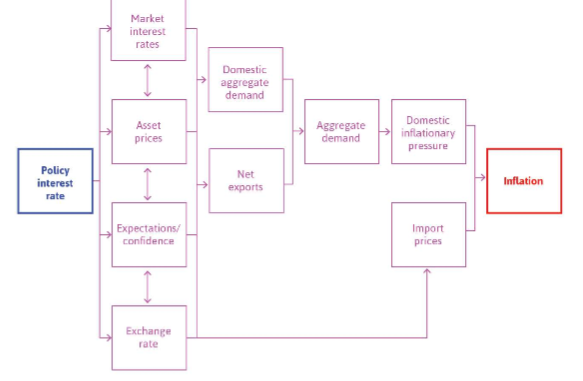
Transmission mechanisms
asset prices: interest rate goes down → asset prices go up
Exports: interest rate goes down → exports go up
expensive imports drives up inflation.
Can interest rate go below 0%?
no “zero lower bound”
should use fiscal policy
if not use quantitative easing
Do Monetary and fiscal policy work together?
Ideally yes → work in same direction as they share the same path.
created success in US.
What does the effectivness of central banks depend on?
transmission mechanisms
interaction with fiscal policy
capacity constraints (zero lower bound)