managerial accounting exam 3
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
The concept of capital budgeting
Convincing your company to lend you/your department the
resources for an investment to expand/improve your business.
Time value of money
a dollar today is worth more than that same dollar in the future
cost of capital
average rate of return a company must pay creditors and stockholders for use of their funds. also known as the discount rate.
payback method focuses on
cash Flows (NOT NOI), and DOES NOT USE Time Value of Money
what is the payback method?
How many years (or partial years) does it take to pay back the initial
investment? If given NOI, you must add back depreciation to get cash flows to calculate the
payback period
net present value
calculate NPV of all cash outflows and inflows using the
discount factor associated with the discount rate and the year of the cash outflow/inflow
if NPV is positive
project is acceptable because the internal rate of return is greater than the required rate of return
if NPV =0
project is acceptable because the internal rate of return is equal to the required rate of return
if NPV is negative
project is rejected because the internal rate of return is less than the required rate of return
internal rate of return (IRR)
IRR is the discount rate that makes the net present value
(NPV) of all cash flows equal to zero in a discounted cash flow analysis
simple rate of return focuses on
incremental NOI (NOT CASH FLOWS), and DOES NOT USE Time
Value of Money
simple rate of return
also called accounting rate of return. Calculated by dividing the
annual incremental NOI by the initial investment. It approximates the IRR
When evaluating performance, you should
not compare actual results at one activity level to a budget at another activity level
True or False: Performance reports help managers identify the difference between actual results and planned
results
True
activity variance
explains the change in revenue and expenses when the master budget
Revenue or spending variance
explains the change in revenue and expenses related to
a change in cost behaviors. Compare Actual Results with Flexible Budget.
Favorable (F)
Will increase net operating income
Unfavorable (U)
Will decrease net operating income
management by exception is used when
evaluating variances that need to be investigated further
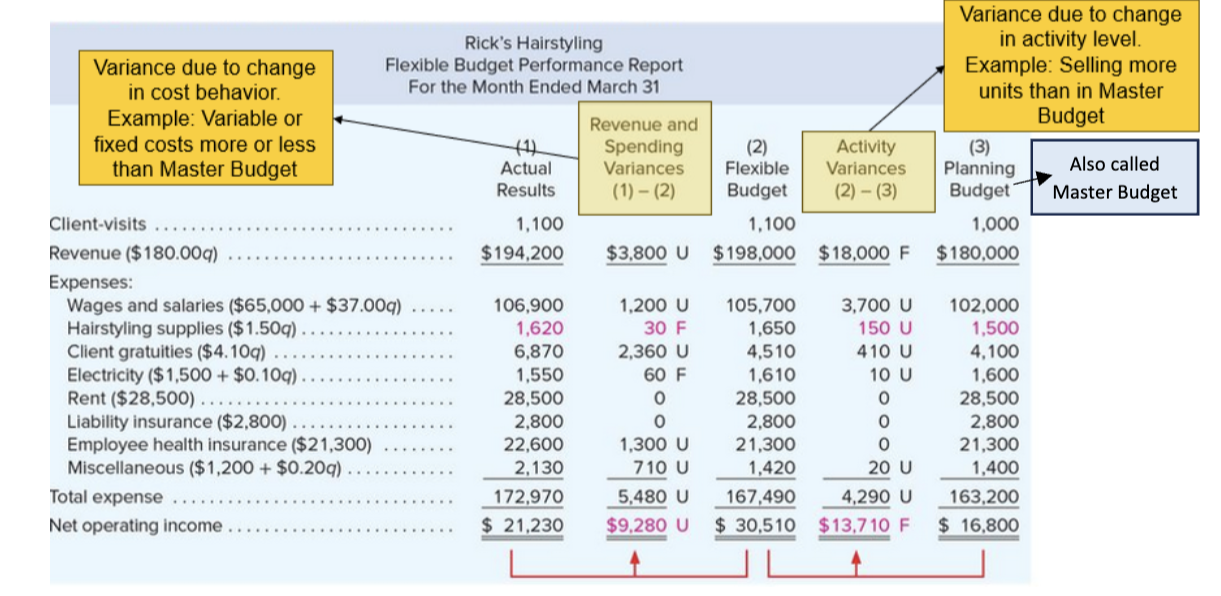
Step 1 in flexible budget performance report
complete master (planning) budget before the period begins (before march in the example)
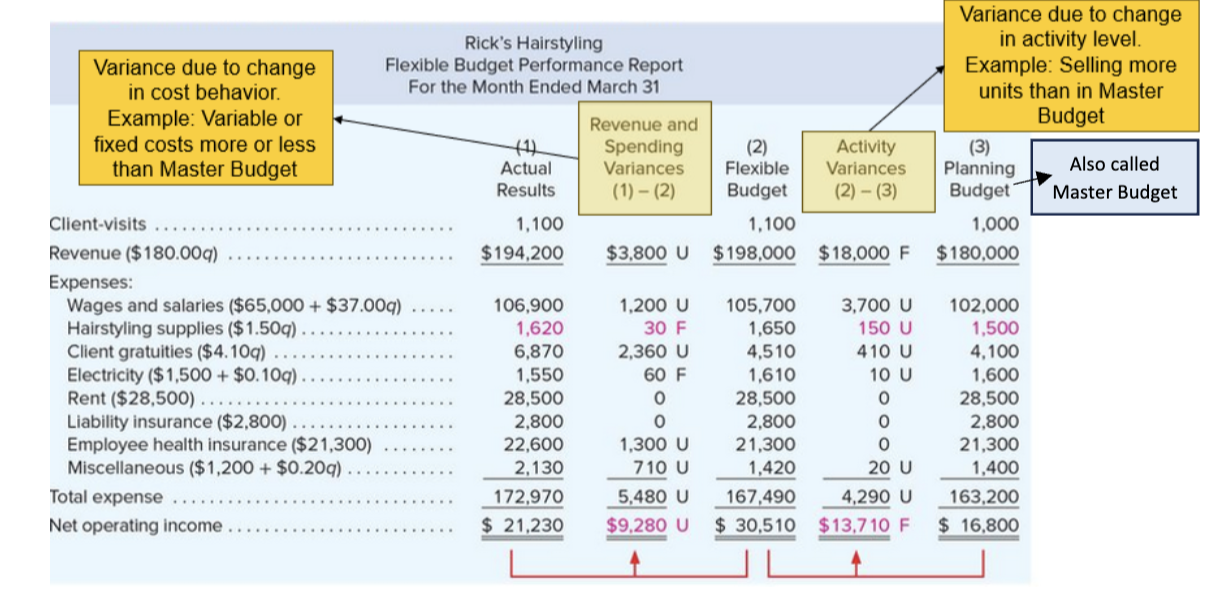
Step 2 in flexible budget performance report
add actual results for the period (march)
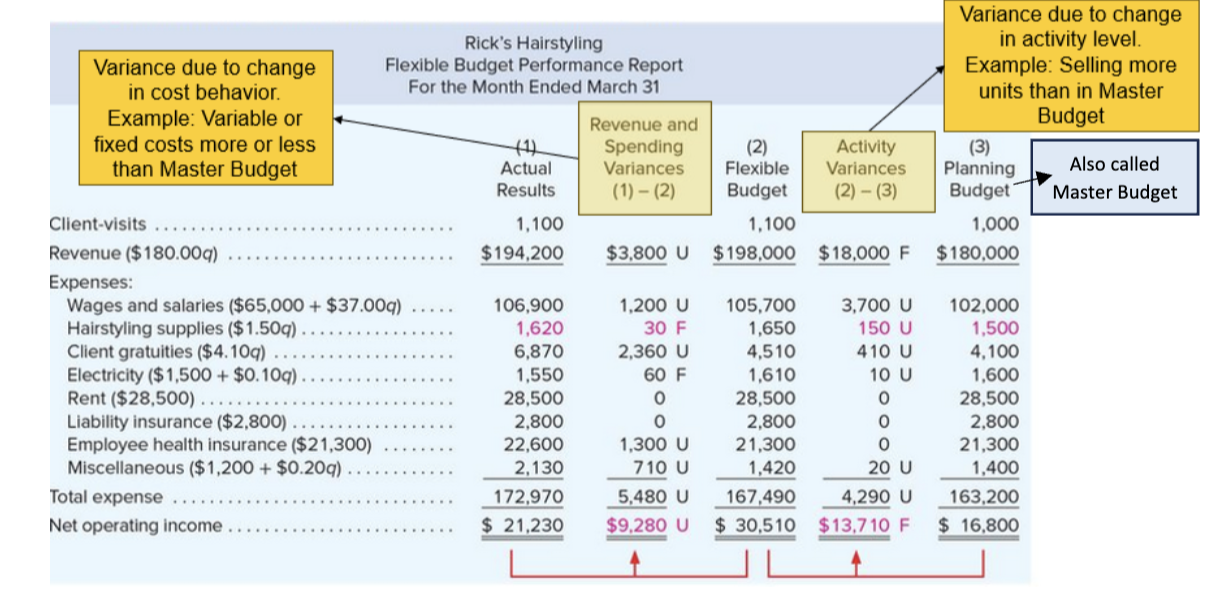
Step 3 in flexible budget performance report
Complete Flexible Budget using the Actual Activity Level (Client visits of 1,100 in the above example). The flexible budget tells us what should have happened based on the actual level of activity
Step 4 in flexible budget performance report
Calculate Activity Variances (Flexible Budget minus Master Budget). Enter as absolute values and identify each line-item variance as Favorable (F) or Unfavorable (U) depending on how they affect NOI. The Activity Variance is the Master Budget variance due to change in the activity level. Also called Master Budget
Step 5 on flexible budget performance report
Calculate Revenue and Spending Variances (Actual Results minus Flexible Budget). Enter as absolute values and identify each line-item variance as Favorable (F) or Unfavorable (U) depending on how they affect NOI. The Revenue and Spending Variance is the Master Budget variance due to changes in cost behaviors
calculate total variance=
Revenue and Spending Variance +/- Activity Variance. In the above example, $9,280 U plus $13,710 F = Overall Variance of $4,430 F. Or calculate as Actual Results NOI of $21,230 less Master Budget NOI of $16,800 equals Overall Variance of $4,430 F.