radiation, half life, nuclear decay
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
radioactivity
the release of high energy particles or waves
new atoms are formed
rules for graphing
divide axis evenly so data takes up most of the page
plot points clearly
label axis and include units
title should include independent variable and dependent
have a best fit line
isotopes
different atoms of the same element w a different number of neutrons in the nucleus.
the mass number will change if the # of neutrons are changed
however the # of protons and the atomic symbol are the same
atomic mass (shown on periodic table)
the average of the mass numbers of all isotopes of an atom
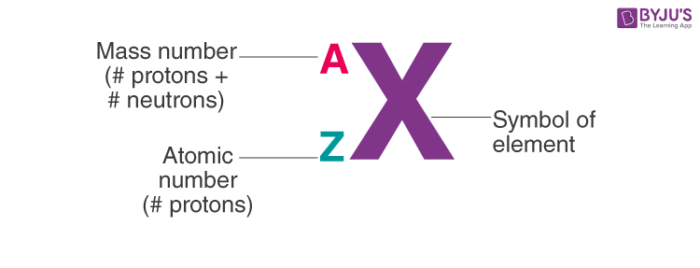
isotope notation
mass/atomic mass on top (proton + neutron)
atomic number on the bottom (proton)
Radioactive Decay
results in new atoms forming
radioactivity results from having an unstable nucleus
when nuclei break apart and release energy from the nucleus as radiation a radioactive decay has occurred
radioactive decay continues until a stable element forms
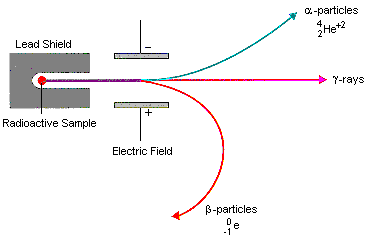
3 types of radiation
positive alpha particles are attracted to the negative plate
negative beta particles are attracted to the positive plate
neutral gamma particles didn’t move towards any plate
alpha radiation
positively charged
largest of the 3 types
same as a helium nucleus
big and slow
a sheet of paper will stop an alpha particle
release of alpha particles is called alpha decay
alpha radiation symbol
2 protons and 2 neutrons make a mass number of 4
has a charge of 2+ (2 +protons and 2 neutral neutrons)
emitted from the nucleus cuz its a He nucleus

beta radiation
negatively charged
high energy/speed electron
smaller than alpha particles
it takes a thin sheet of aluminum foil to stop a beta particle
beta decay
beta decay occurs when a neutron changes into one proton and one electron
proton stays in the nucleus
electron is released
beta radiation symbol
electrons are tiny so they have a mass number of 0
the 1 electron emitted gives a beta particle a charge of -1

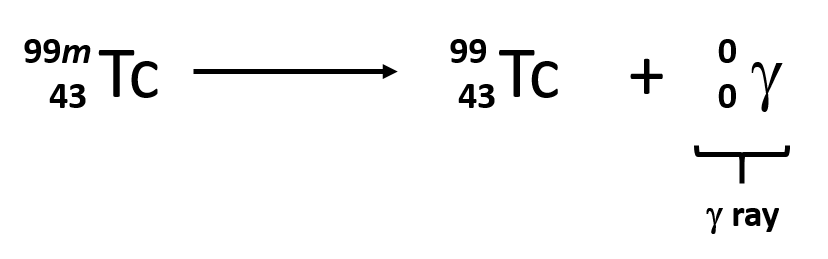
gamma radiation
a ray of high energy, short wavelength radiation
results from energy released from a high-energy nucleus
takes a thick block of lead or concrete to stop gamma rays
gamma decay
other kinds of radioactive decay can release gamma radiation
for eg. uranium-238 decays into an alpha particle but also releases gamma rays
gamma radiation symbol
has no charge or mass
star often in the reactants indicates a higher energy state cuz the products one released energy
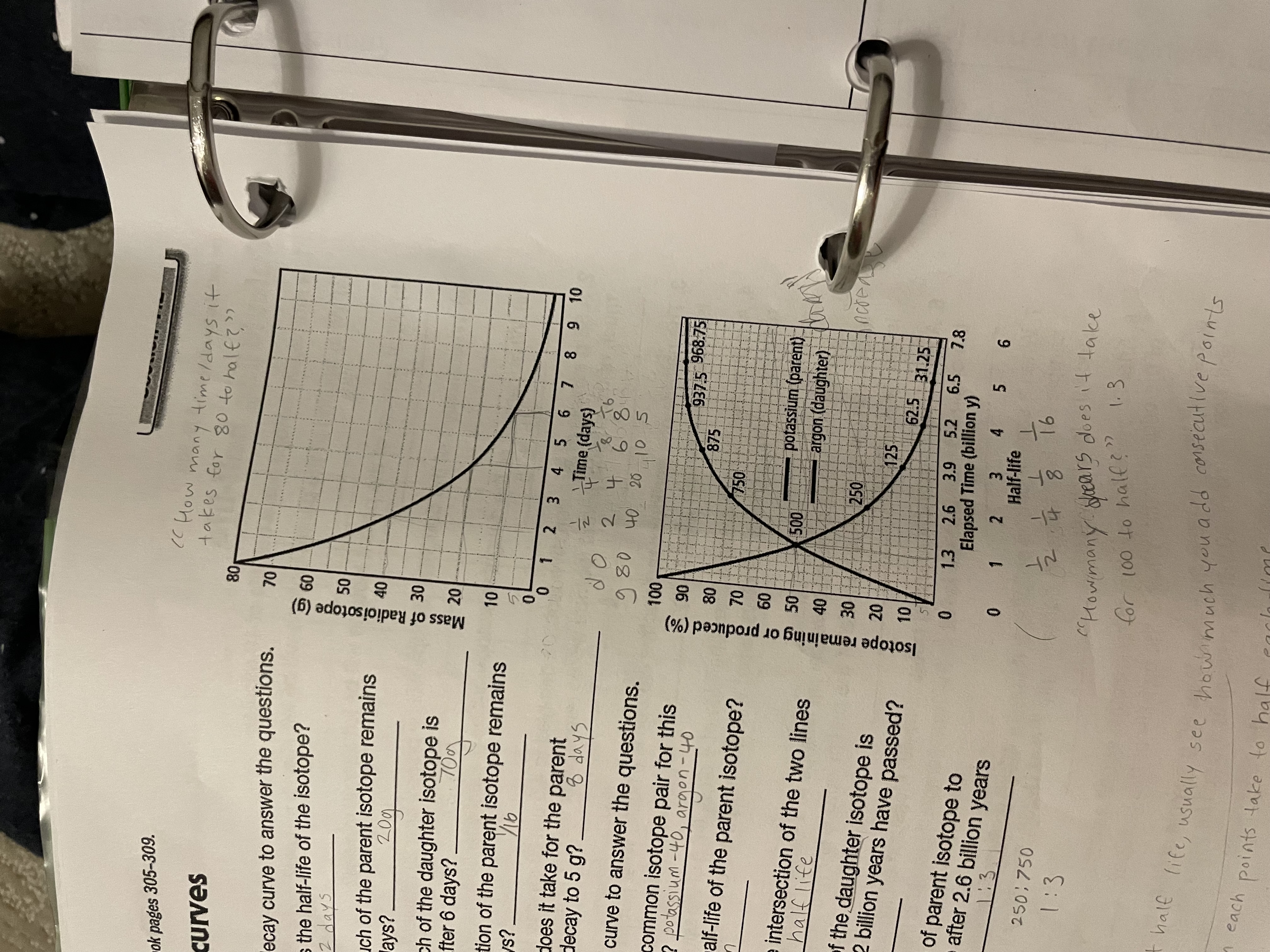
half life
how much time it takes for half of a radioactive sample to decay
is a constant rate (same half-life for each element)
parent vs daughter
parent isotope - the original radioactive material (1/4)
daughter isotope - the stable product after decay (3/4)
decay curves
show the rate of decay for radioactive elements
show the relationship between half-life and percent of the remaining original substance
total of percent should equal to 100%
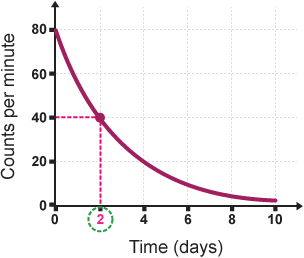
radioactive dating
method to determine the age of an object
compares the amount (NOT time) parent isotope to daughter isotope
nuclear fission
a large parent nucleus is split into smaller daughter nuclei with the release of energy.
which radioisotopes do we use in nuclear reactors
uranium 238, uranium 235, plutonium 239
first step in nuclear fission
Fire a slow moving neutron at an unstable uranium-235 nucleus.
what is produced from a nuclear fission reaction
lots of energy
2 smaller nuclei
3 more neutrons
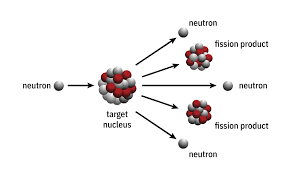
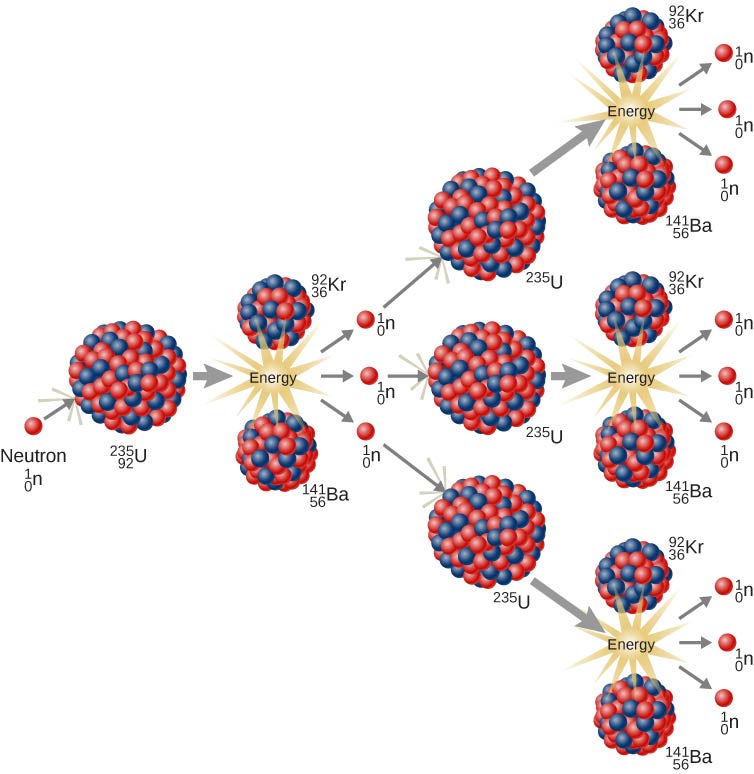
how does one nuclear fission reaction lead to a chain reaction of fission events?
The 3 neutrons attach to uranium 235
now turns into uranium 236, an even more unstable nucleus
then u-236 splits into smaller nuclei and releases energy
neutrons that keep multiplying to enable the chain reaction.
what are the safety issues with nuclear fission?
hazardous waste is produced
has a long half-life before the material is safe
hard to contain (control rods are used so too much energy isn’t overloading the reactor)
why is the reactor surrounded by a large concrete container
radioactive material produced must be stored away from living things to stop exposure to gamma rays etc.

benefits of CANDU over other reactors
more efficient than others
uses natural uranium 235 which helps produce fission rather than enriched uranium which are expensive and takes a lot of energy
uses heavy water
what is heavy water?
deuterium (water with hydrogen with 2 neutrons)
doesn’t absorb as much neutrons, hence they don’t require enriched uranium.
how does the energy produced from nuclear fuel pellets compare with other fuels?
they produce more energy per kg than other fuels
ceramic, heat resistant
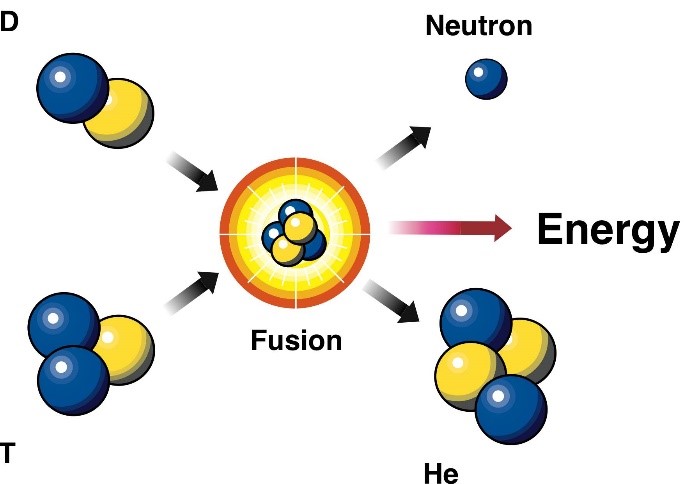
what is nuclear fusion
two small nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei
where does nuclear fusion happen in nature
in the core of the sun, stars, supernova
two hydrogen atoms join under tremendous heat and pressure to form a helium nucleus
why can’t we use nuclear fusion as an energy resource on earth?
requires extremely high temperature and pressure
do not have a safe enough source that produce the necessary conditions
scientists are working on it however
what conditions need to be met for nuclear fusion to happen?
high temp
high pressure
fusion will not happen if these conditions aren’t met.
advantages of nuclear fusion over nuclear fission as an energy resource
no radioactive waste produced
more amounts of energy released
chain reactions will not occur as they only fuse
steps of nuclear fusion that occur in stars
1 deuterium and 1 tritium nuclei combine to form an unstable helium-5 nucleus
the helium-5 breaks apart into a stable helium nucleus and an extra neutron
energy is released
which radiation is affected by electric and magnetic fields
alpha and beta
emitted from the nucleus
alpha + beta