1 - INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY (BRS) 2025
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
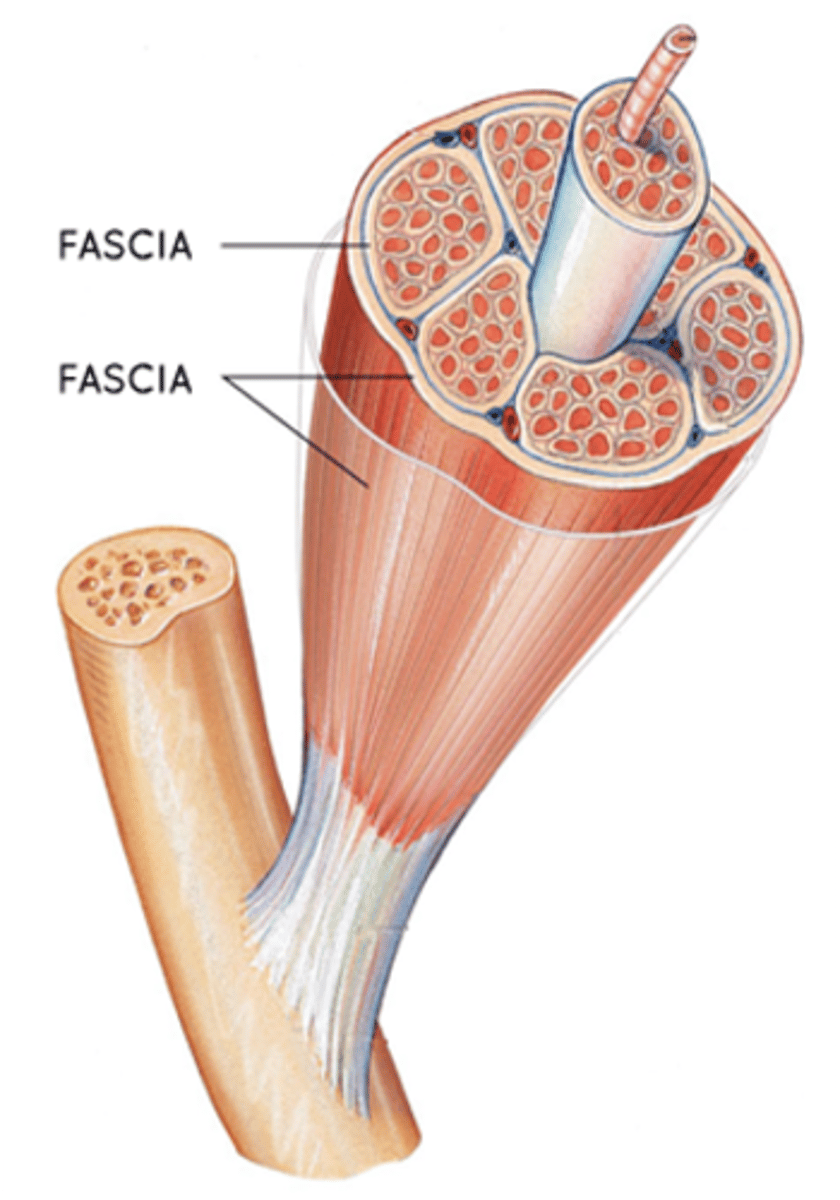
This is a fibrous sheet or band that covers the body under the skin and invests the muscles
Fascia
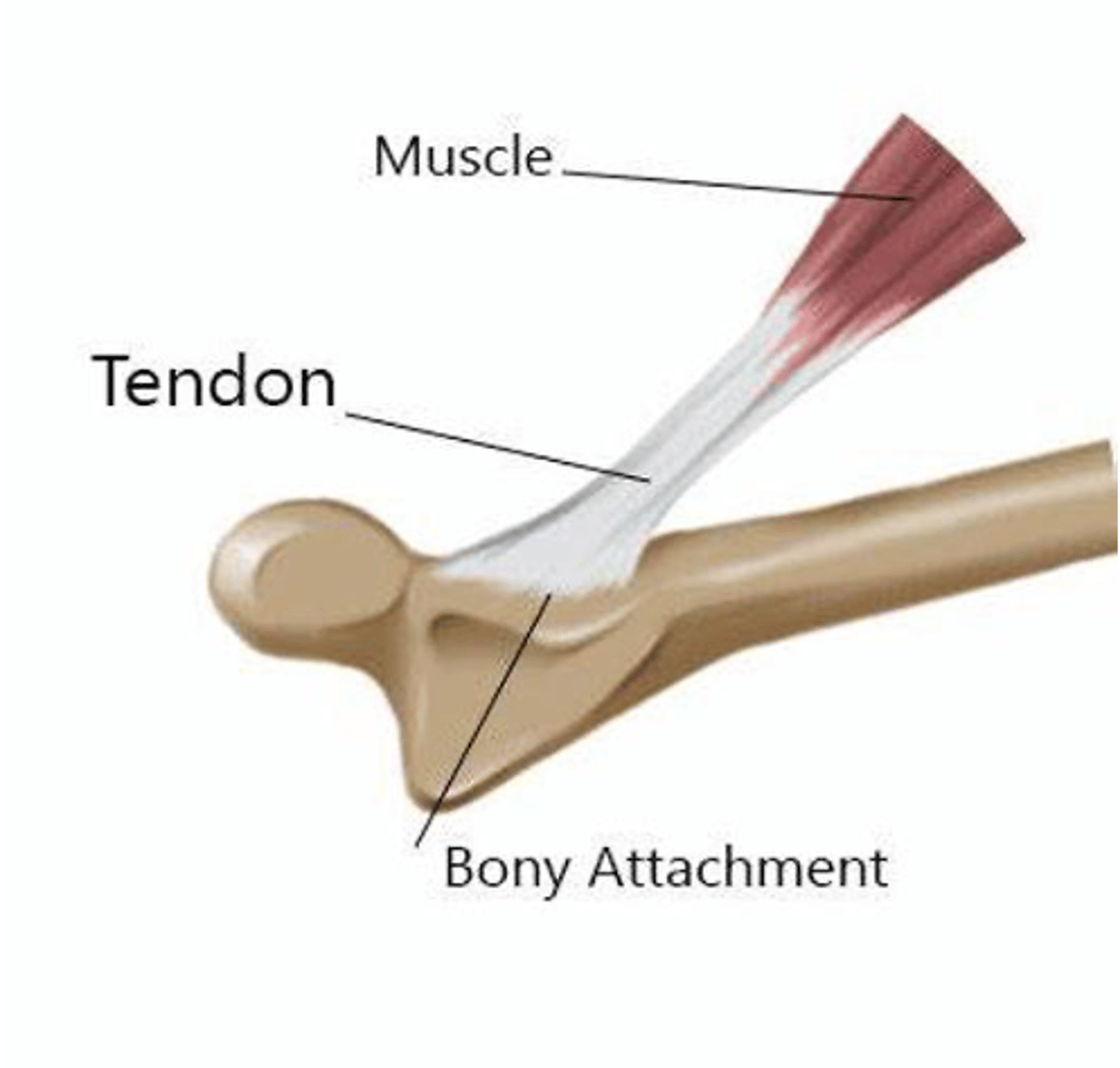
This structure connects muscles to bones or cartilage
Tendon
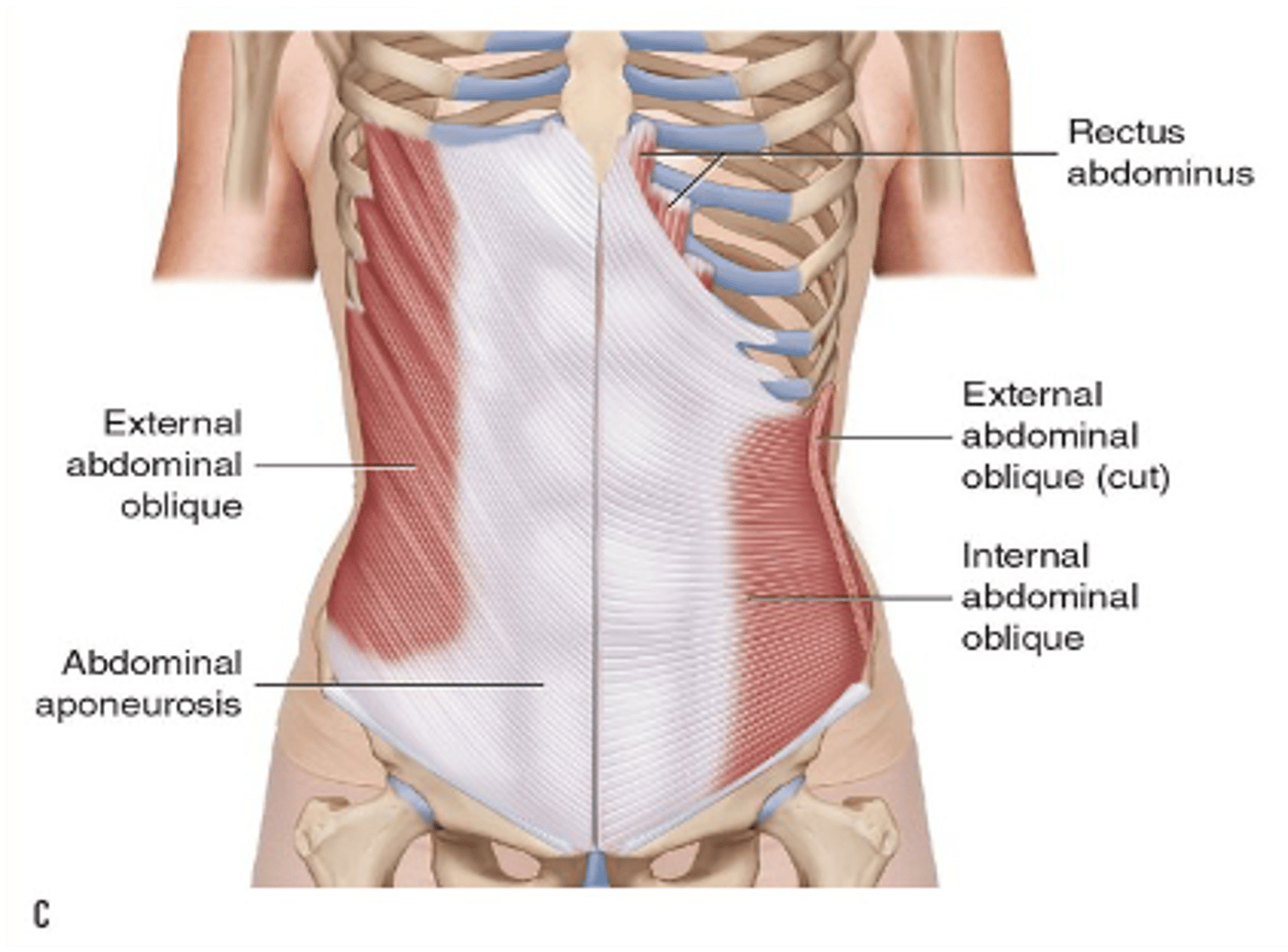
This structure serves as the origin or insertion of a flat muscle
Aponeurosis
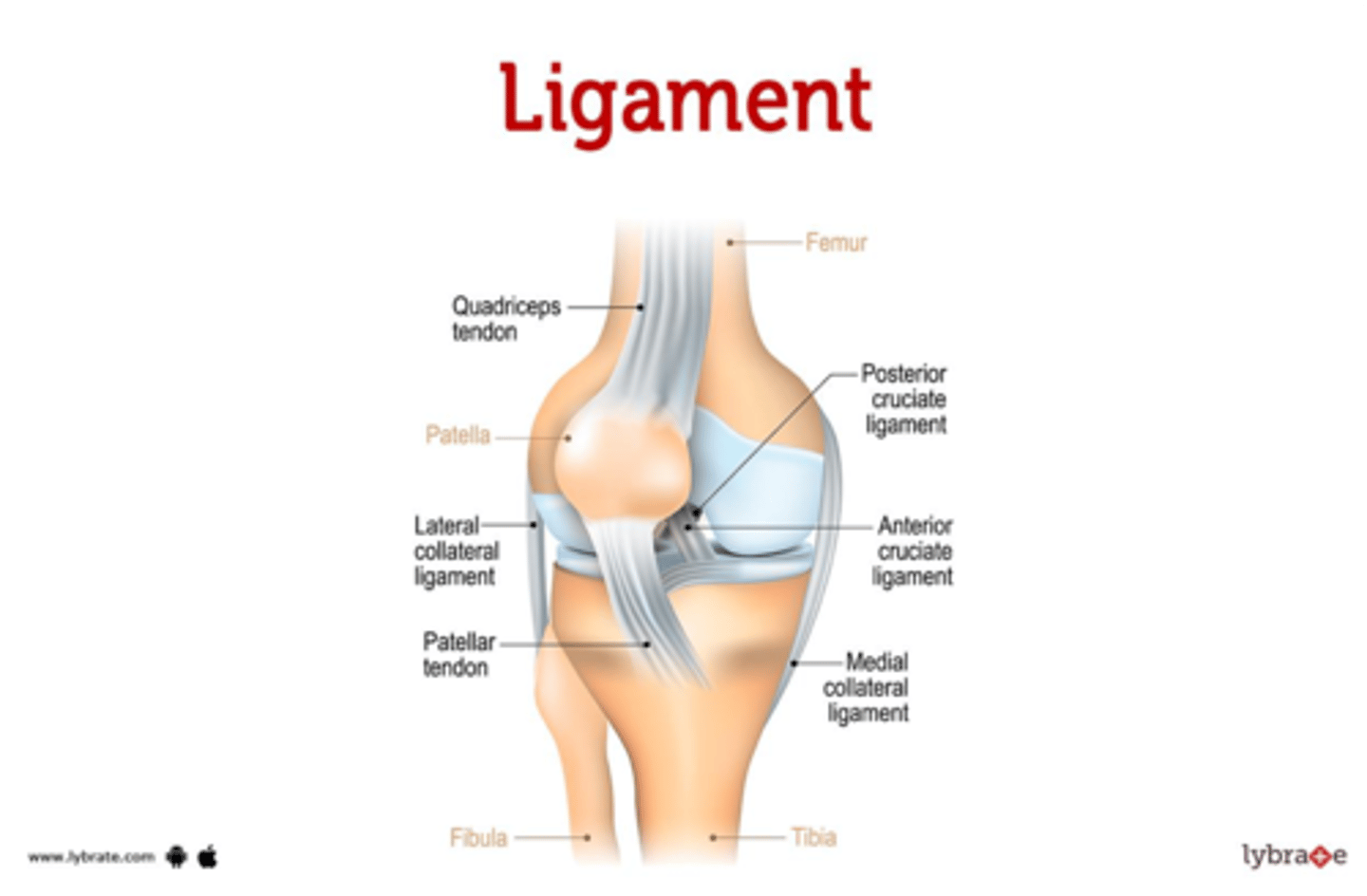
This supporting structure connects bones to bones or cartilage
Ligament
These structures are tubular sacs filled with synovial fluid that wrap around the tendons.
Sinovial Tendon Sheaths
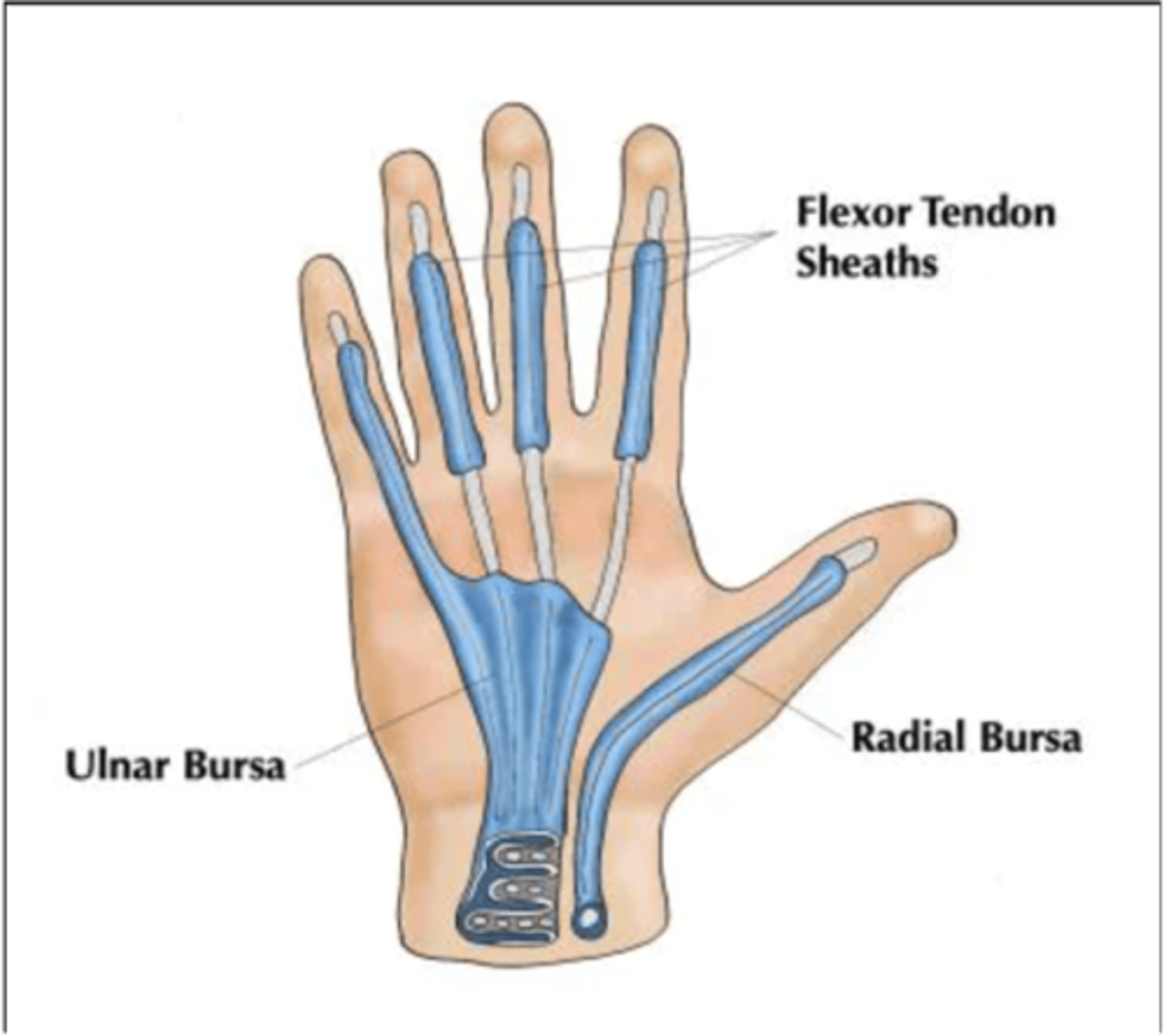
Smooth muscles located in these 2 structures are innervated only by sympathetic nerves
Wall of blood vessels;
Arrector pili muscles in hair follicles
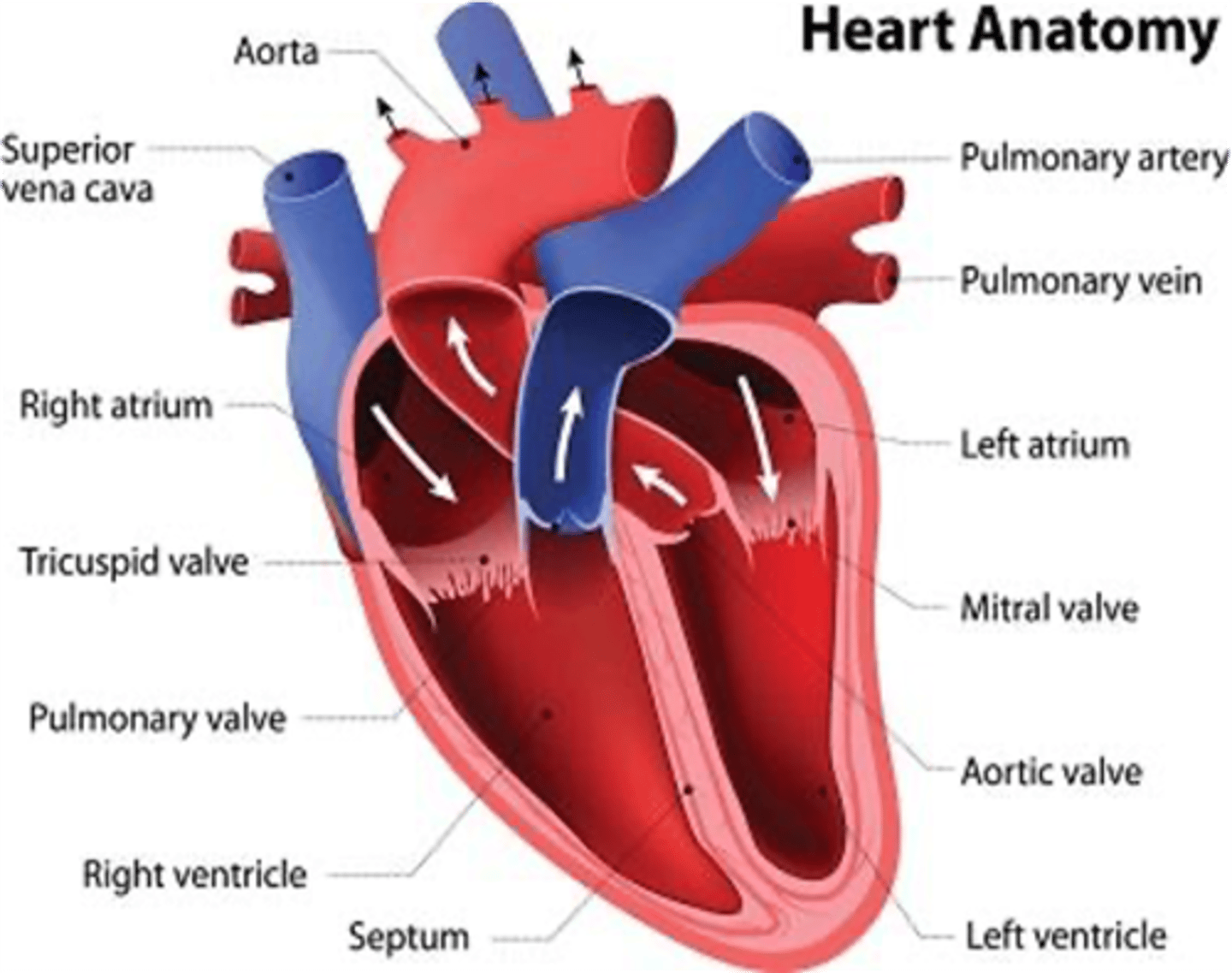
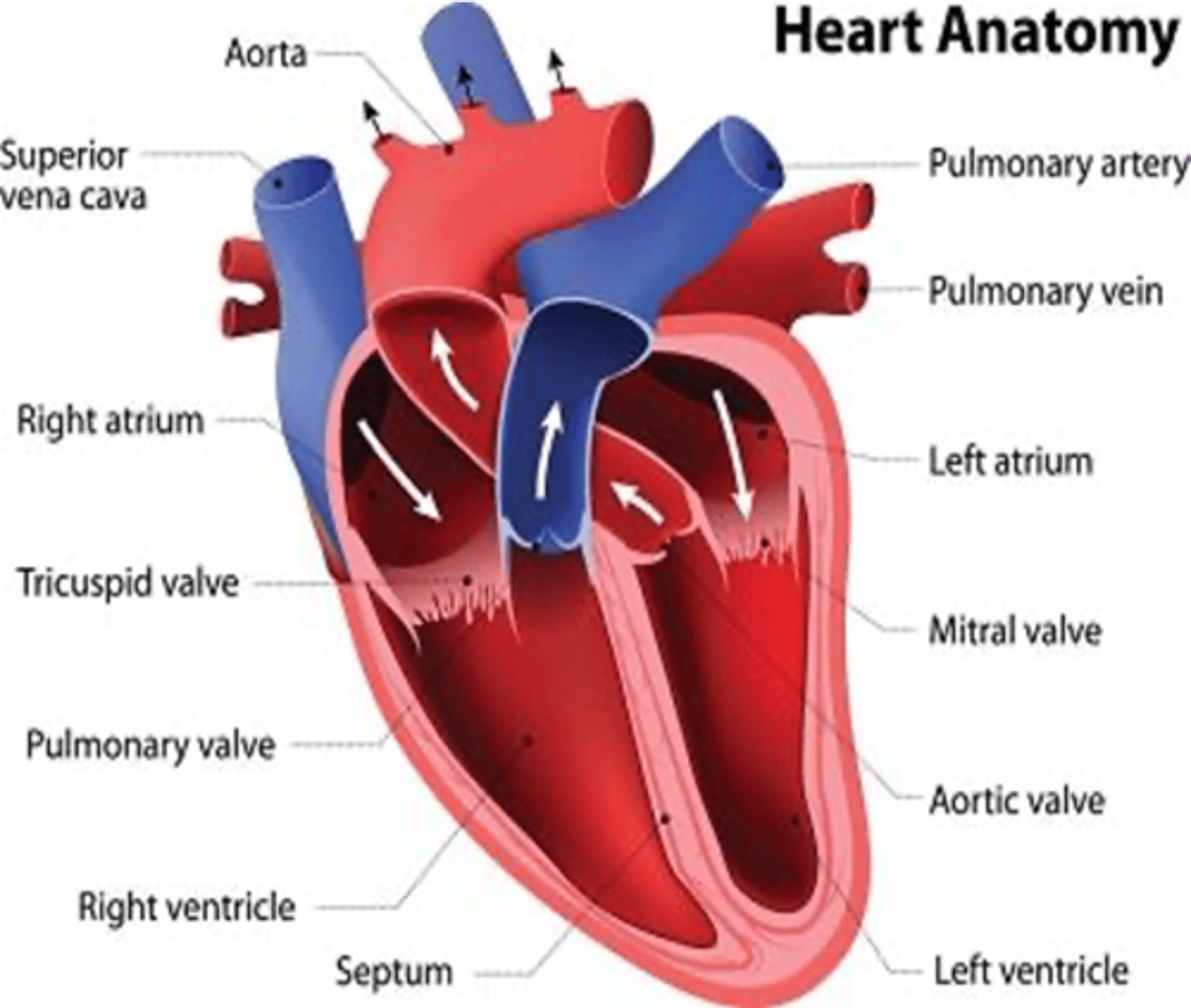
What blood vessel carries oxygenated blood back to the heart?
Pulmonary Veins
4 vessels carry blood back to the heart:
1. Superior vena cava
2. Inferior vena cava
3. Coronary sinuses
4. Pulmonary veins
-The first 3 vessels carry DEOXYGENATED blood back to the heart while the pulmonary veins carry OXYGENATED blood from the lungs to the heartREMEMBER:Pulmonary veins are the ONLY VEINS in the body that carry OXYGENATED BLOOD, rest of the veins carry DEOXYGENATED BLOODPulmonary arteries are the ONLY ARTERIES in the body that carry DEOXYGENATED BLOOD, rest of the arteries carry OXYGENATED BLOOD
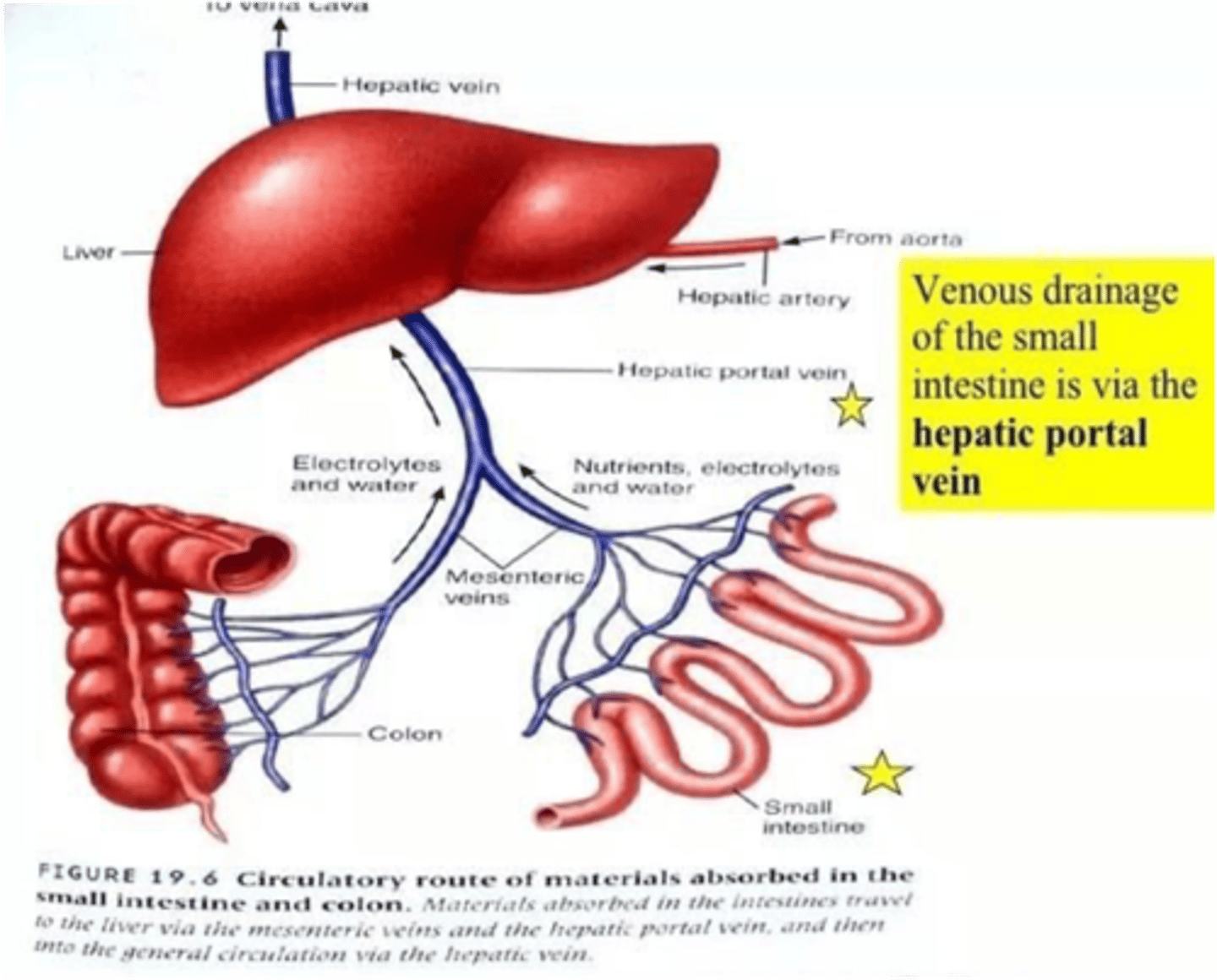
These blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood with nutrients from intestines to the liver
Portal veins
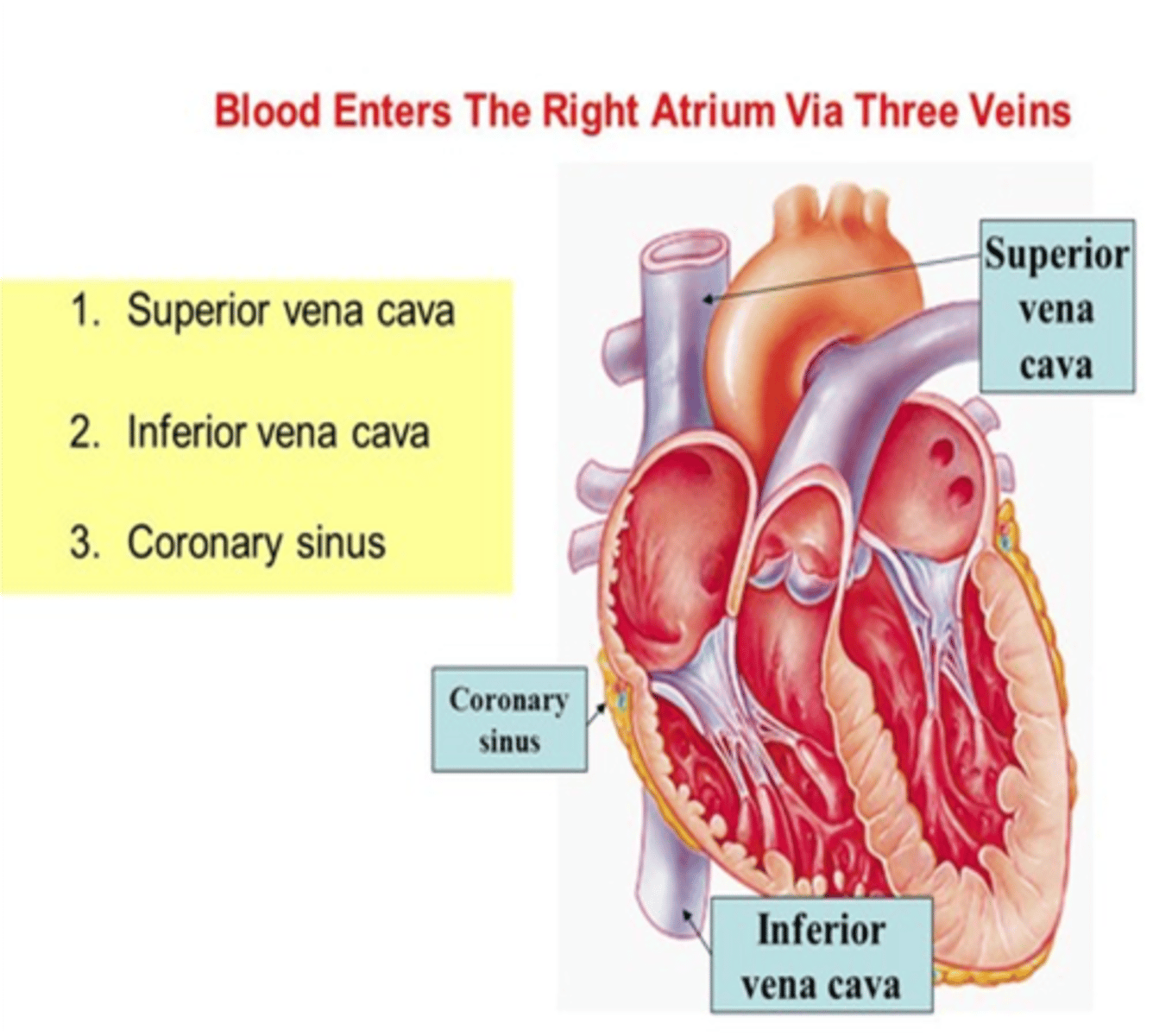
What 3 blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood to the right atrium
-Superior Vena Cava
-Inferior Vena Cava
-Coronary sinus
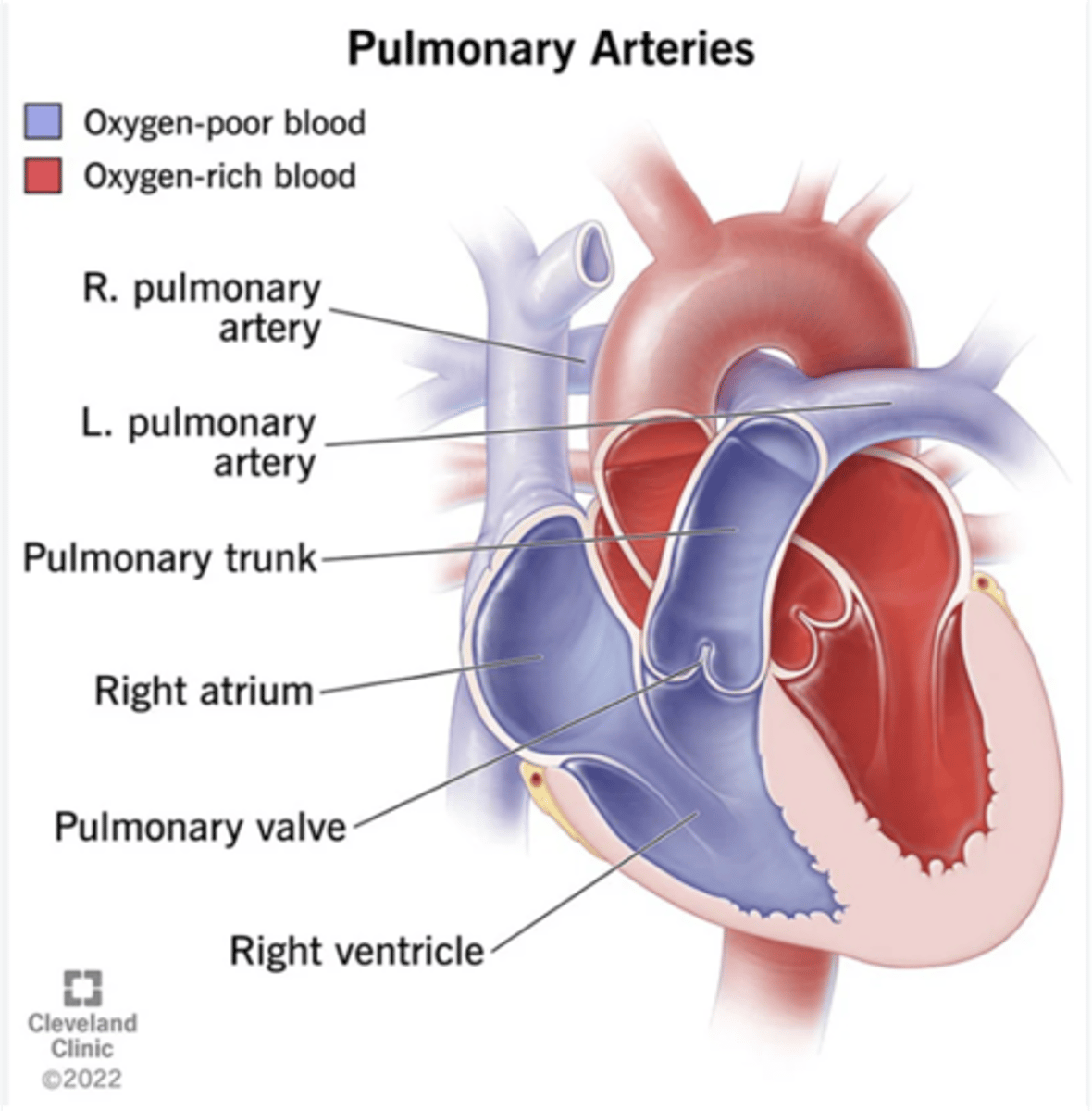
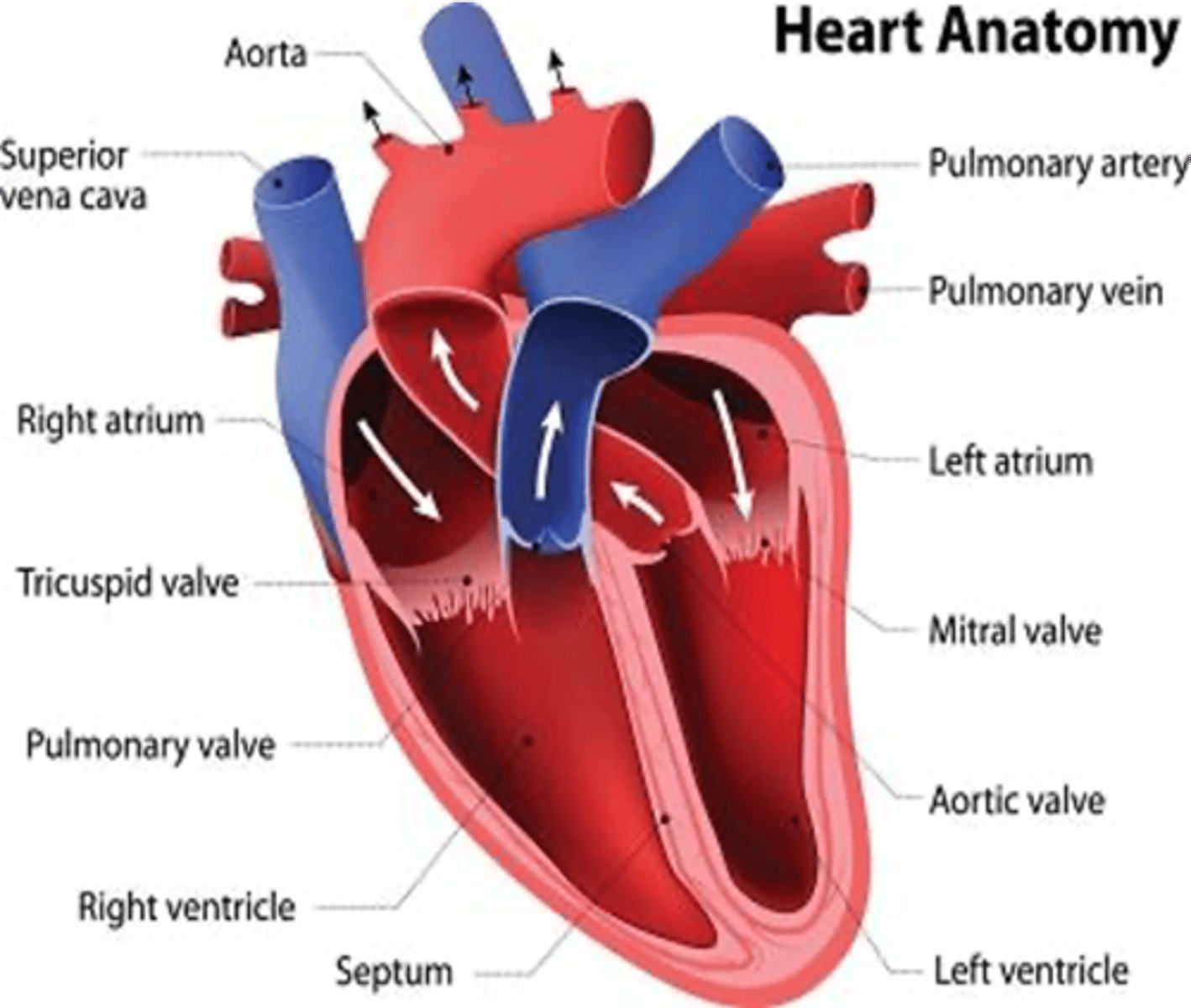
These blood vessels carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygen renewal.
Pulmonary arteries
What part of the neuron carries impulses away from the cell bodies
Axons
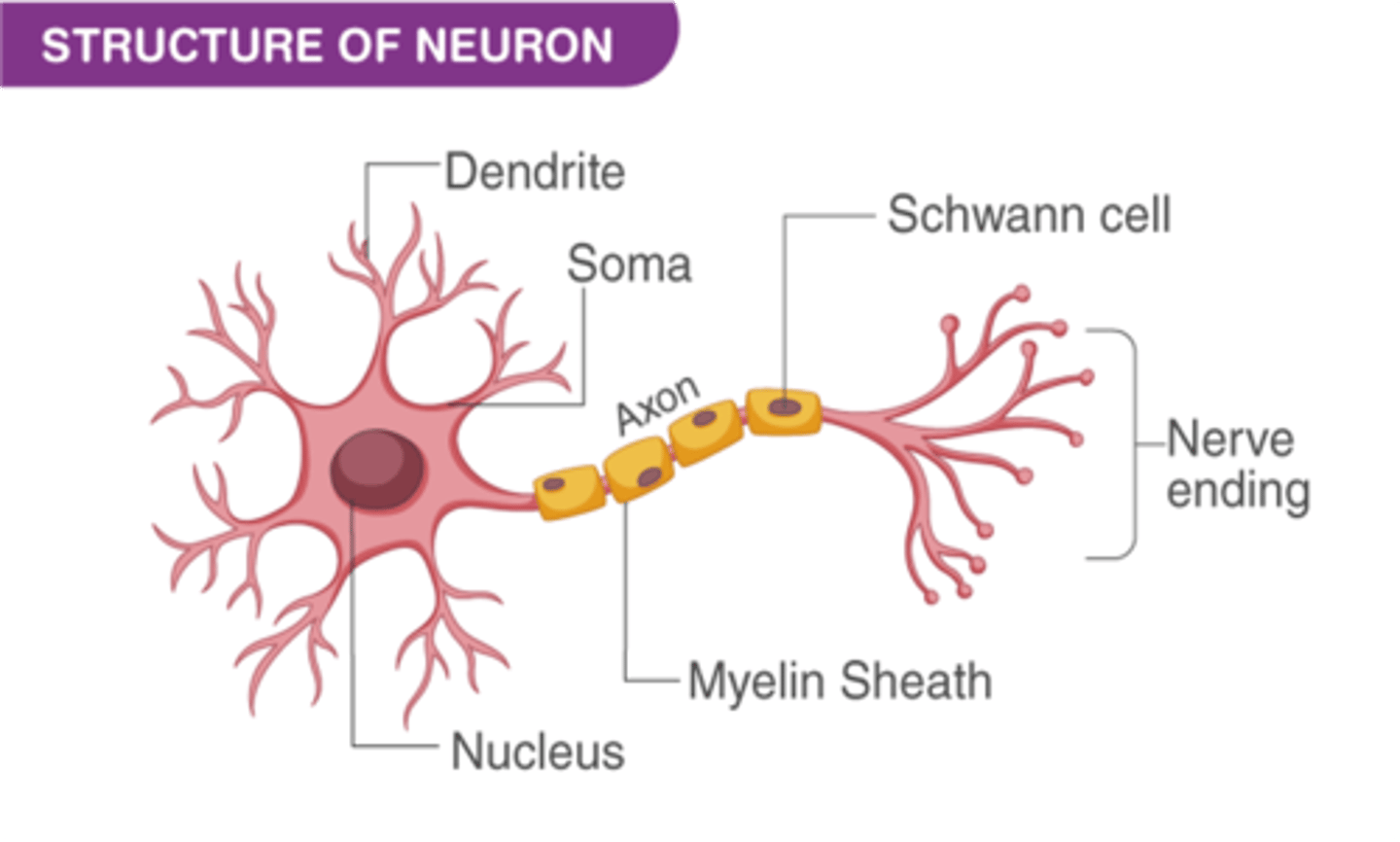
What part of the neuron carries impulses towards the cell bodies
Dendrites
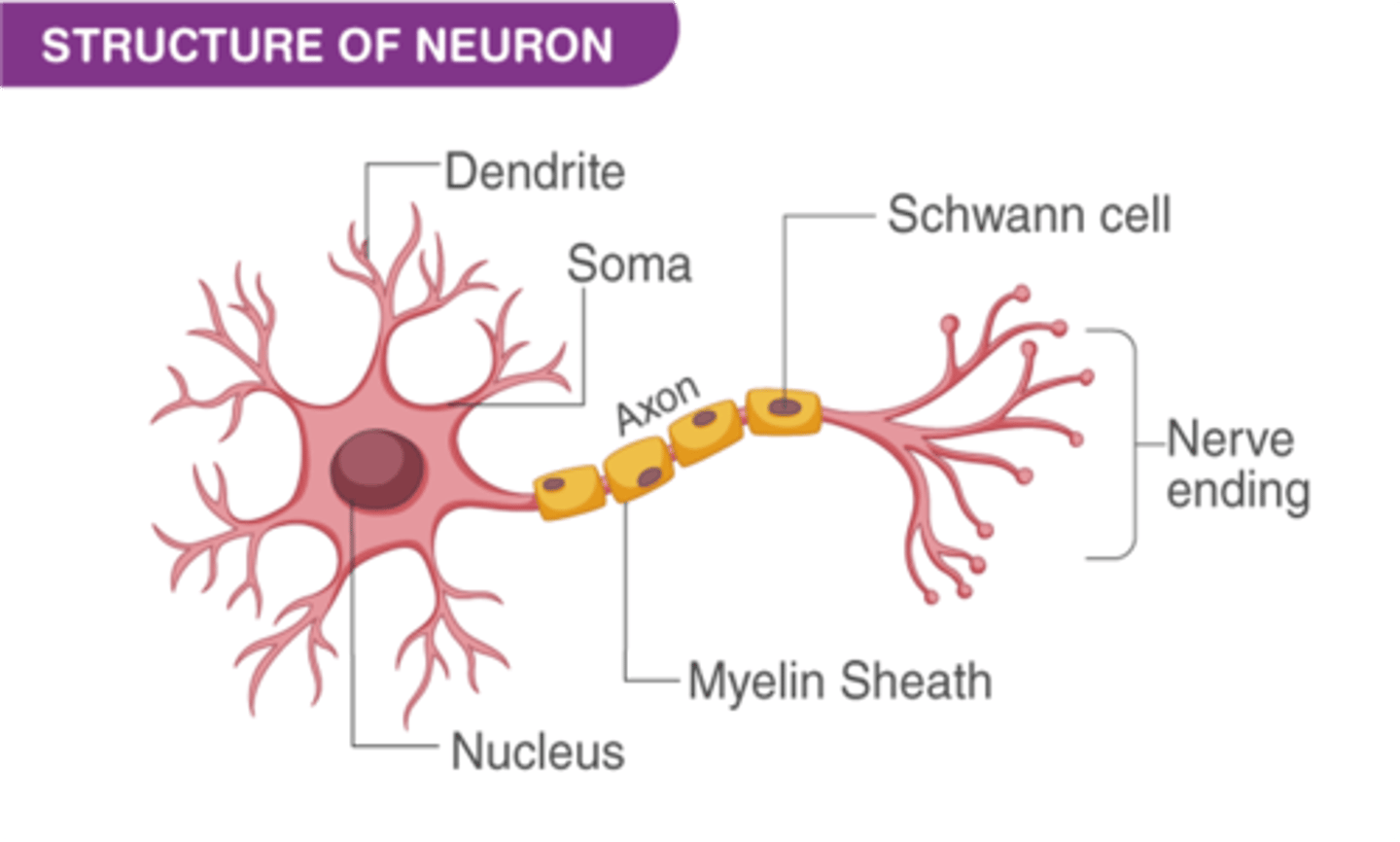
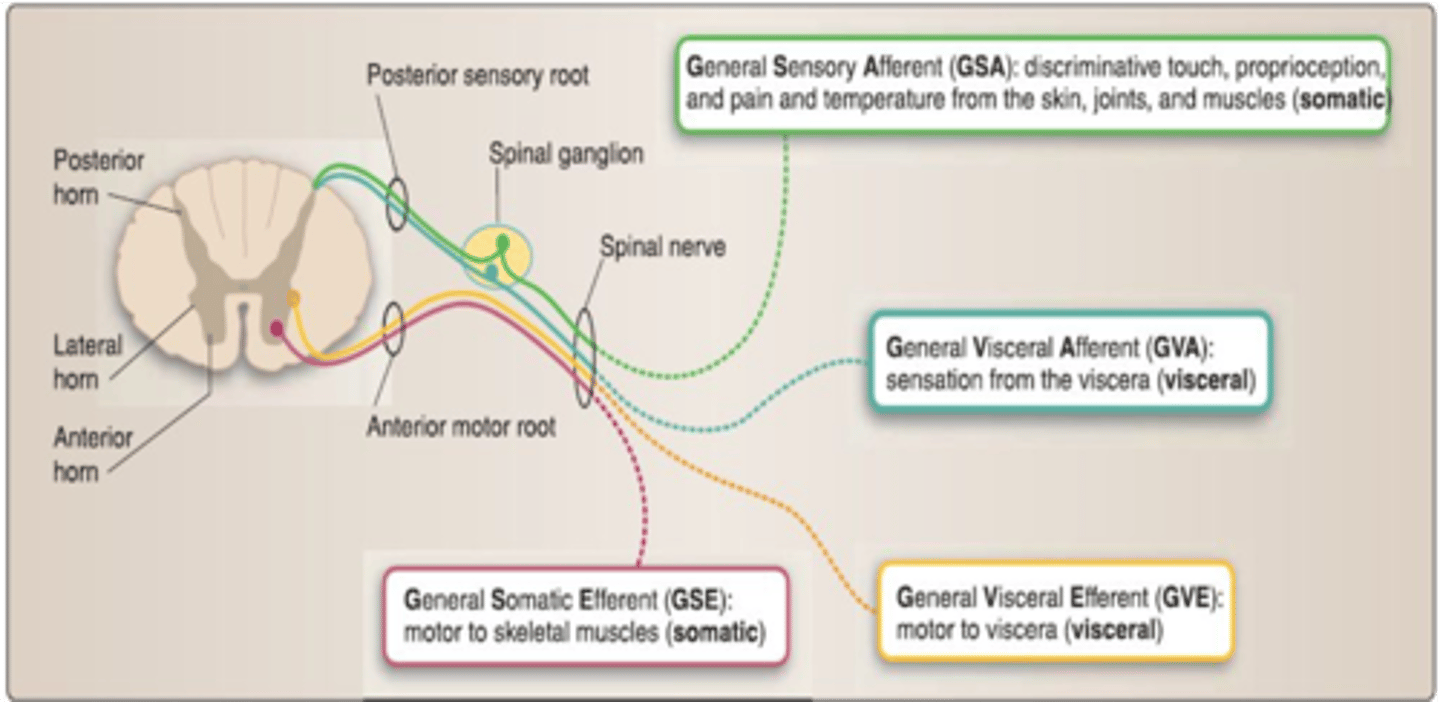
This classification of nerves DO NOT carry sensory impulses and are responsible to innervate skeletal muscles
General Somatic Efferent Nerves
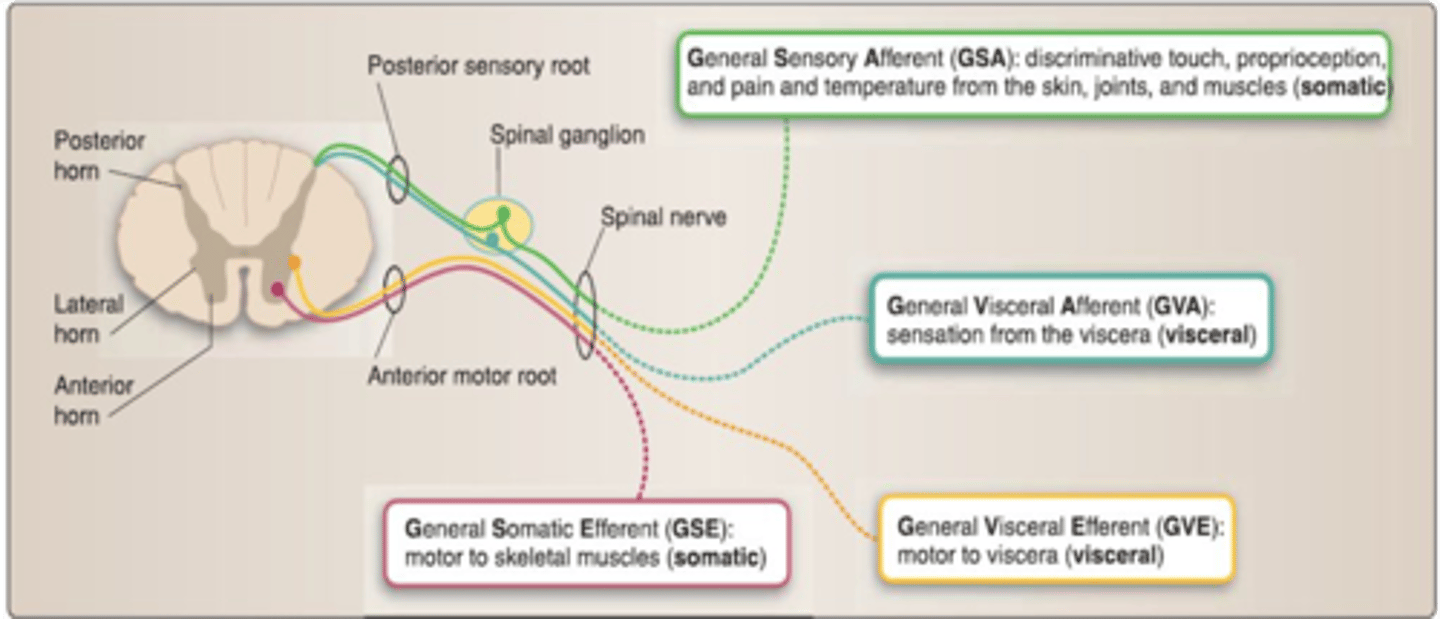
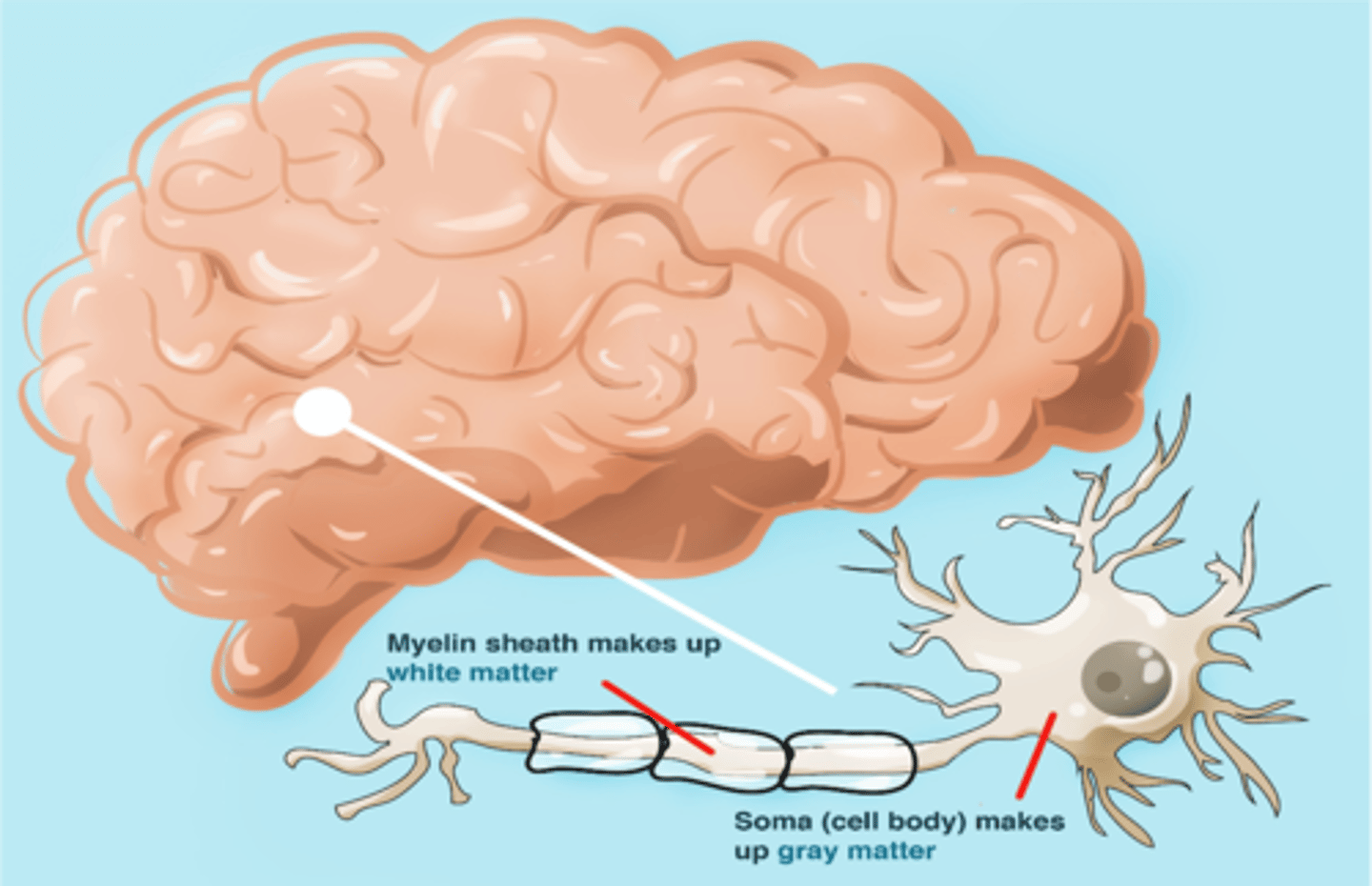
This structure surrounding the axons are responsible for making the white matter white.
Myelin sheath
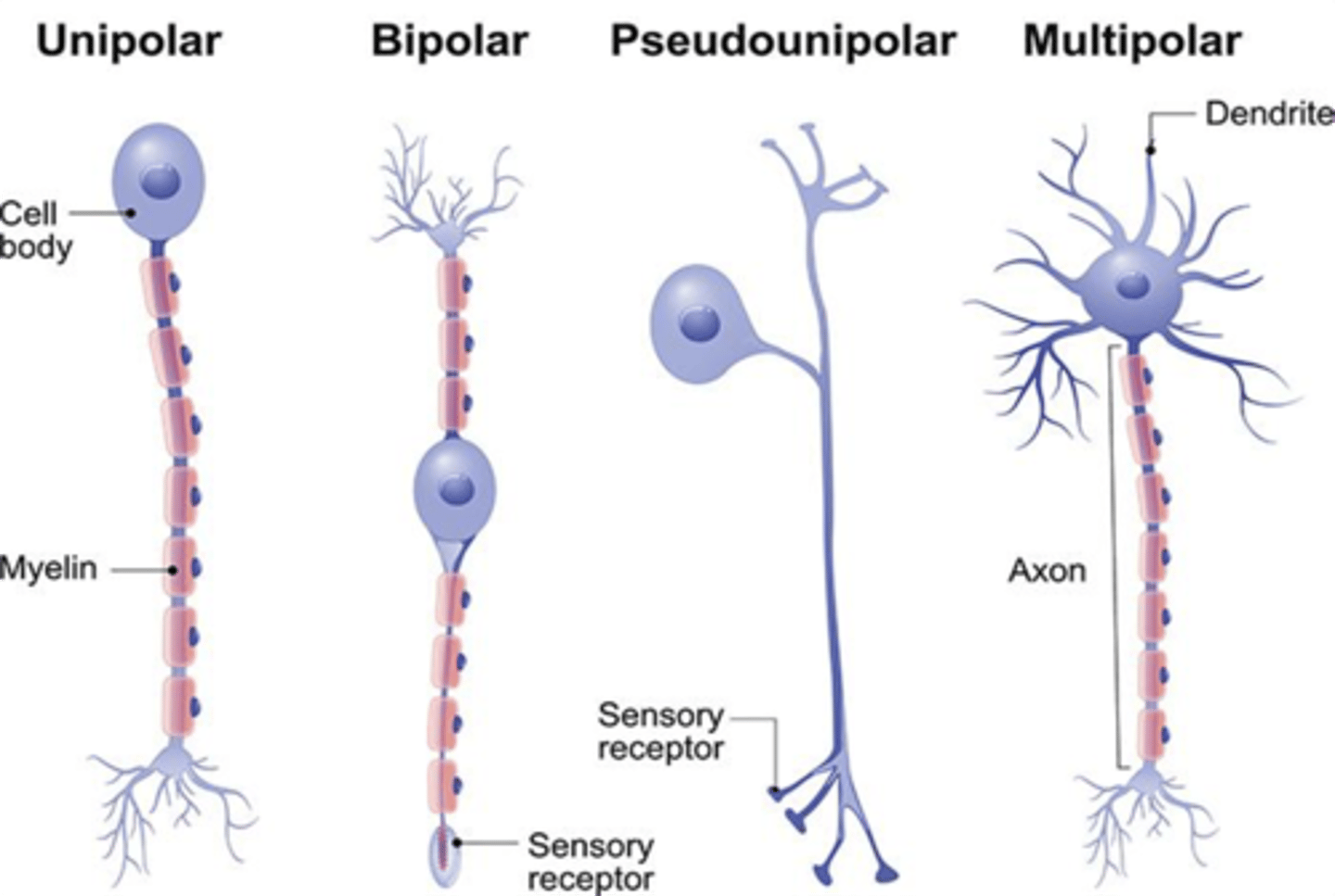
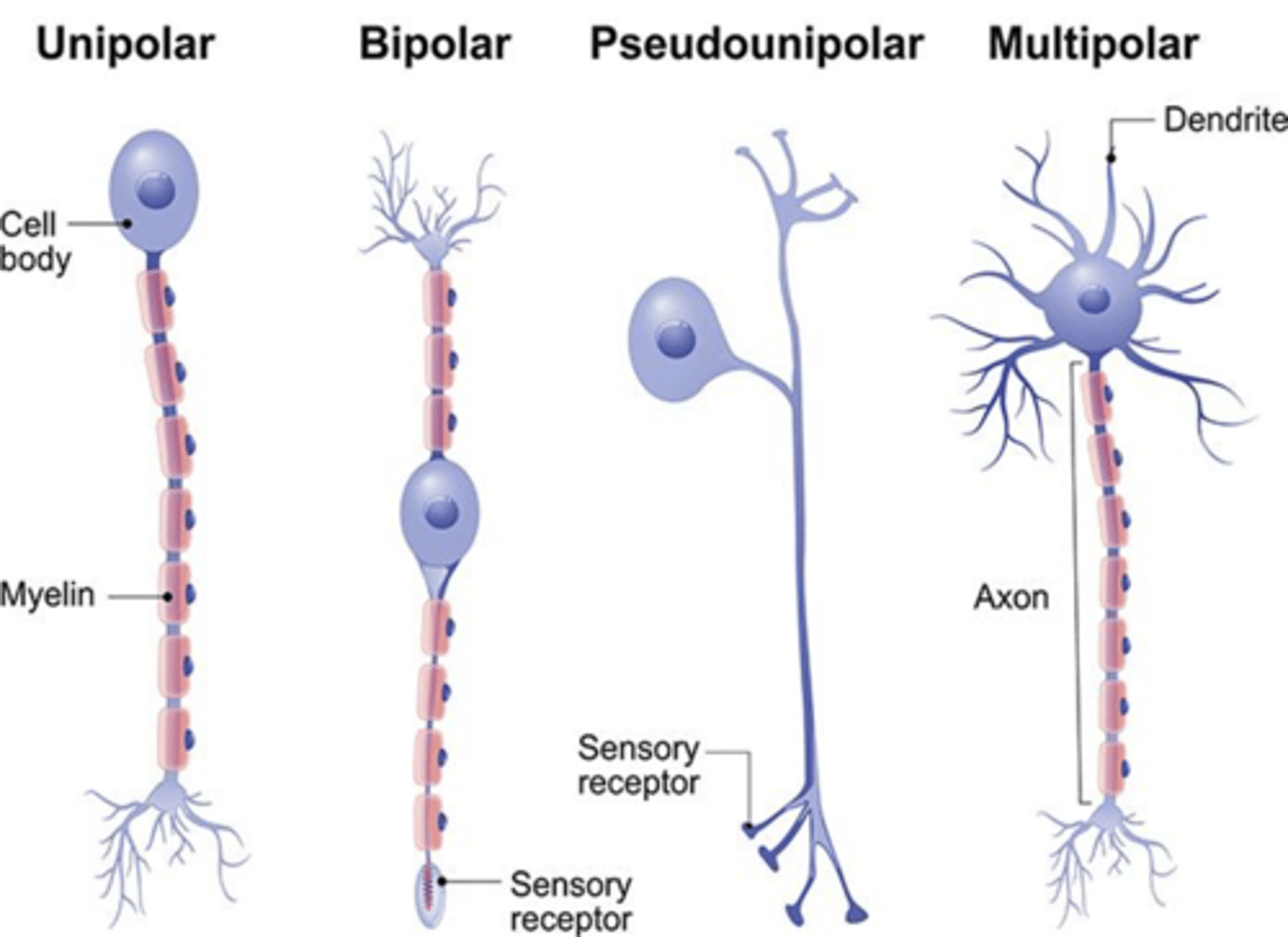
This type of neuron (based on morphology) contains several dendrites and one axon
Multipolar neurons
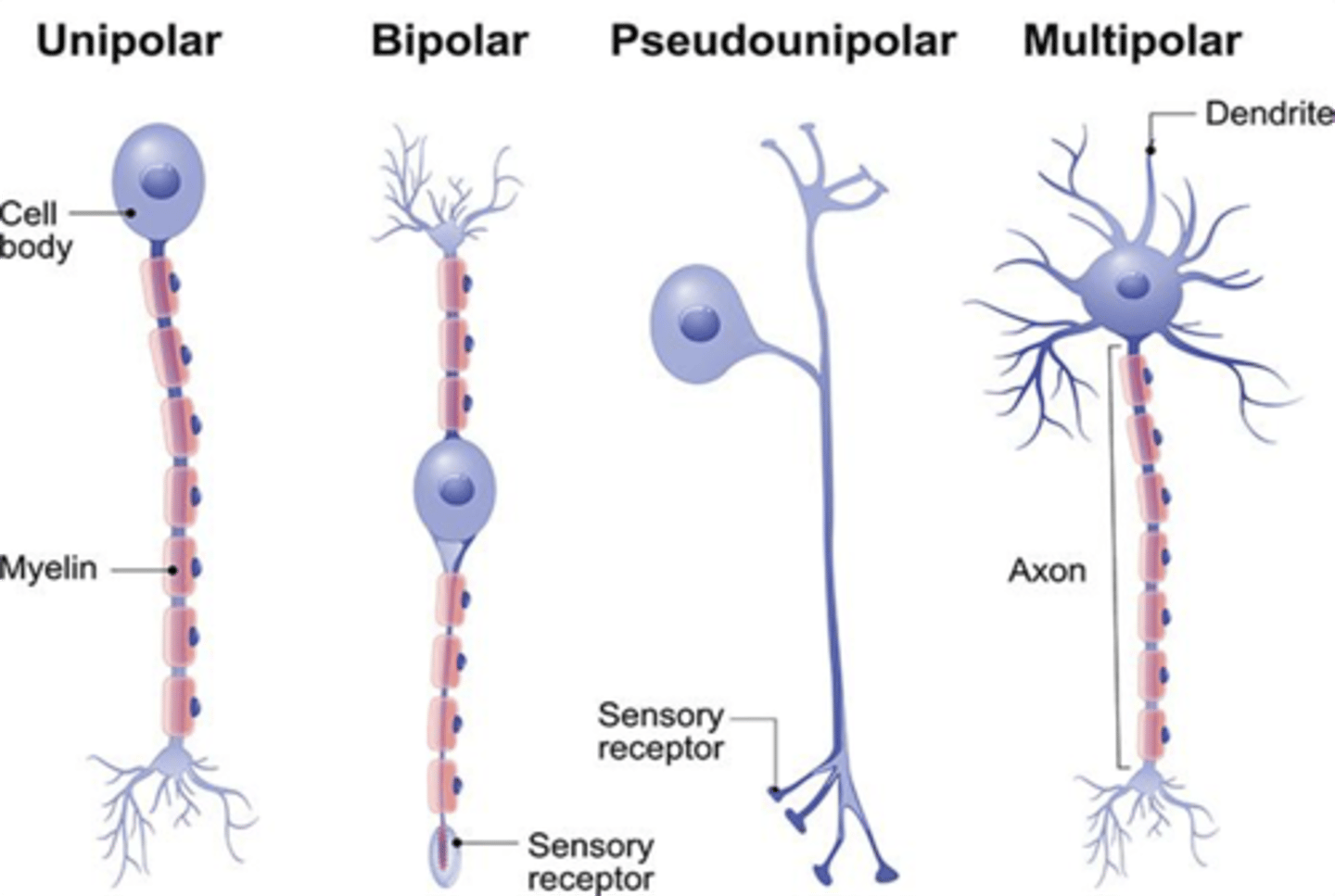
What kind of neurons (based on morphology) are found in the dorsal root ganglion?
Unipolar or Pseudounipolar Neurons
There are 3 types of neurons based on morphology:
1. Multipolar
2. Bipolar
3. Pseudounipolar
-Most typical morphology is the MULTIPOLAR NEURONS. Multipolar neurons have multiple small processes (dendrites) and one long process (axon) projecting from its cell body. BIPOLAR NEURONS, on the other hand, have two processes located on the cell body's opposing sides: one process serving as dendrite, one process serving as axon.Lastly, PSEUDOUNIPOLAR NEURONS, have
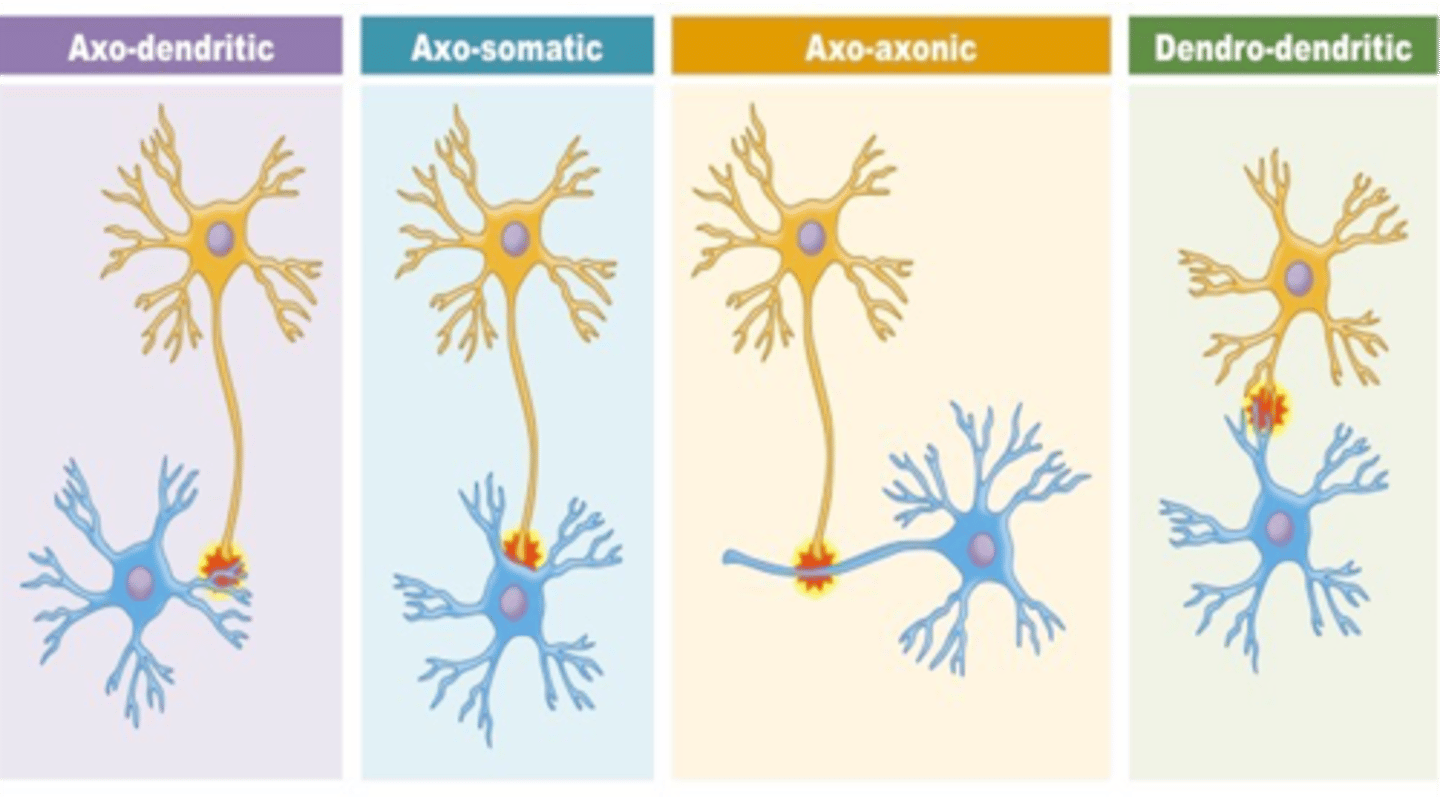
2 most common types of synapses
Axosomatic and Axodendritic Synapses
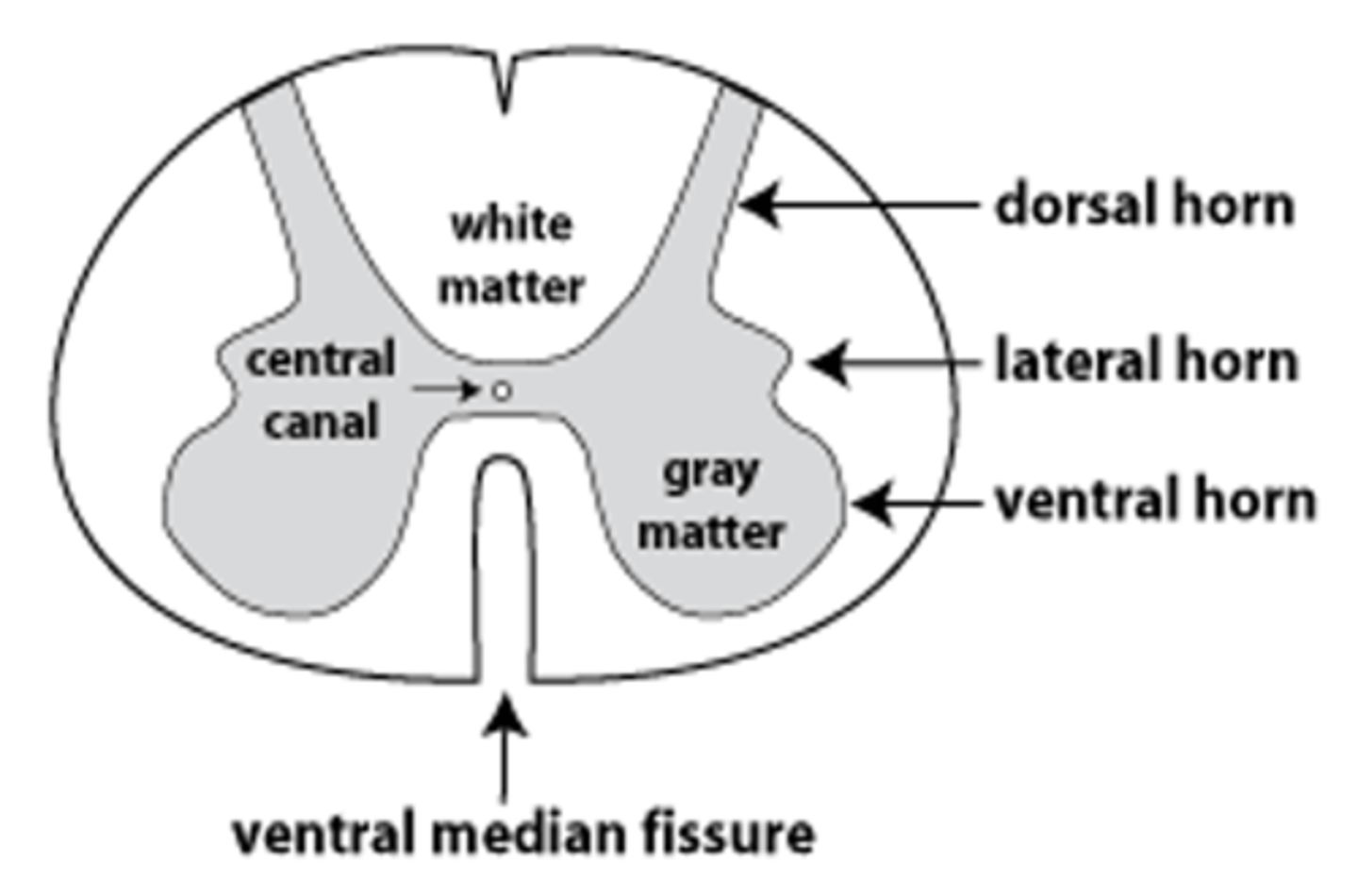
The lateral horns are found in what levels of the spinal cord?
T1-L2, S2-S4
The cell bodies of the sympathetic nervous system are primarily found in the lateral horns of the spinal cord, specifically at level T1-L2, and S2-S4.
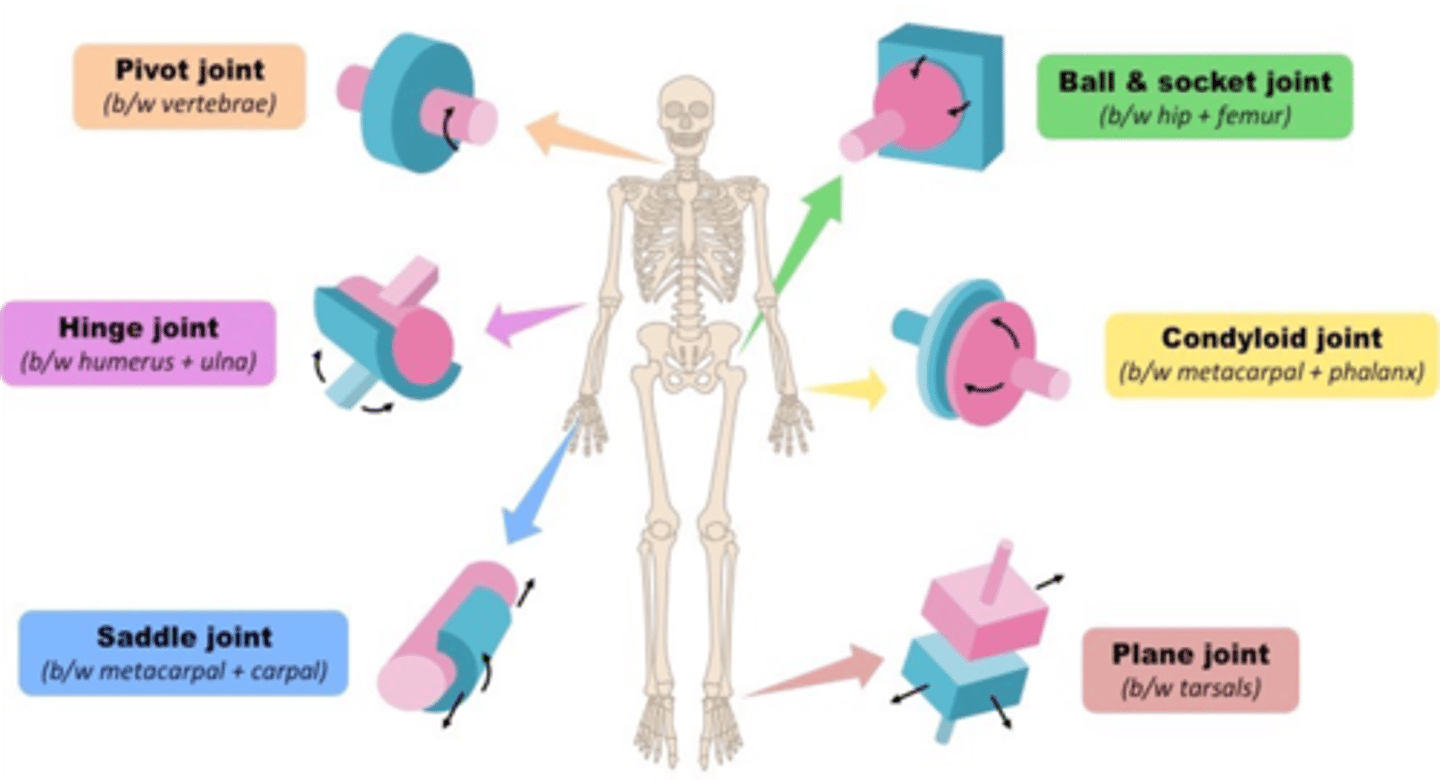
What is the only pivot joint found in the neck?
Atlantoaxial joint
"A pivot joint (also called a trochoid joint) is a joint consisting of a shaft/axis upon which another bone moves around. Imagine the earth rotating upon its axis.
In the entire human body, there are only 3 pivot joints.
1. Located in the neck is the atlantoaxial joint. This is the reason why the 2nd cervical vertebra is called the axis. Because the atlas (first cervical vertebra) rotates around the dens (also called the odontoid process) of the axis (second cervical vertebra).
2. Located in the wrist is the DISTAL radioulnar joint where the distal radius rotates around the distal ulna during pronation and supination.
3. Located in the elbow is the PROXIMAL radioulnar joint where the radial head rotates around the proximal ulna during pronation and supination."
The atlanto-occipital joint is an example of _________ joints
Condylar (ellipsoidal)
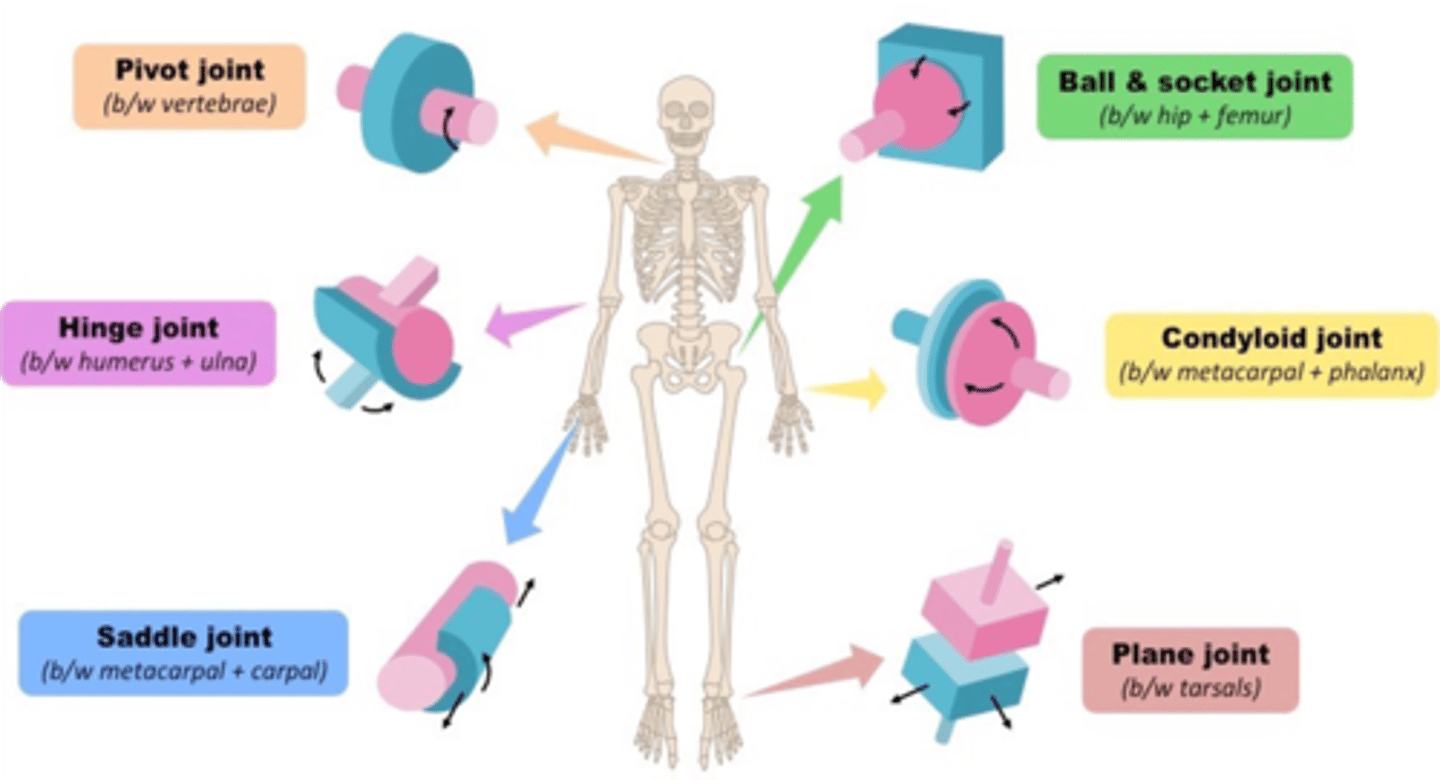
The carpometacarpal joint of what finger is an example of a saddle/sellar joint?
Thumb (first finger)
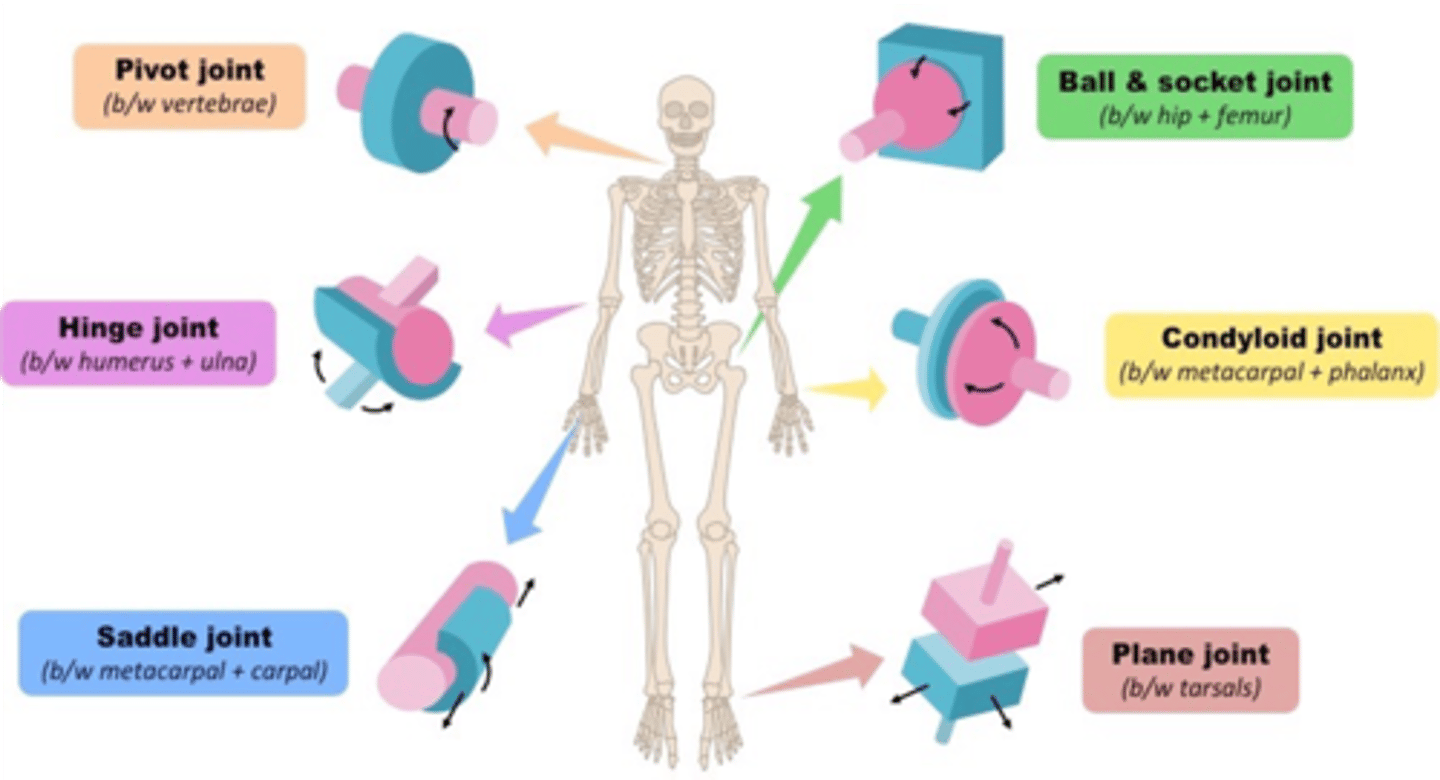
The proximal tibiofibular joint is an example of what joint?
Plane (gliding) joint

What type of nerve fibers carry sensation from the skin?
General Somatic Afferent (GSA) fibers
This type of fiber (based on morphology) are sensory neurons but are not somatic sensory neurons
Bipolar neurons
The only vein that carries oxygenated blood?
Pulmonary vein
The only artery that carries deoxygenated blood?
Pulmonary artery
The stomach mixes food with mucus and gastric juice to form what substance/mixture?
Chyme
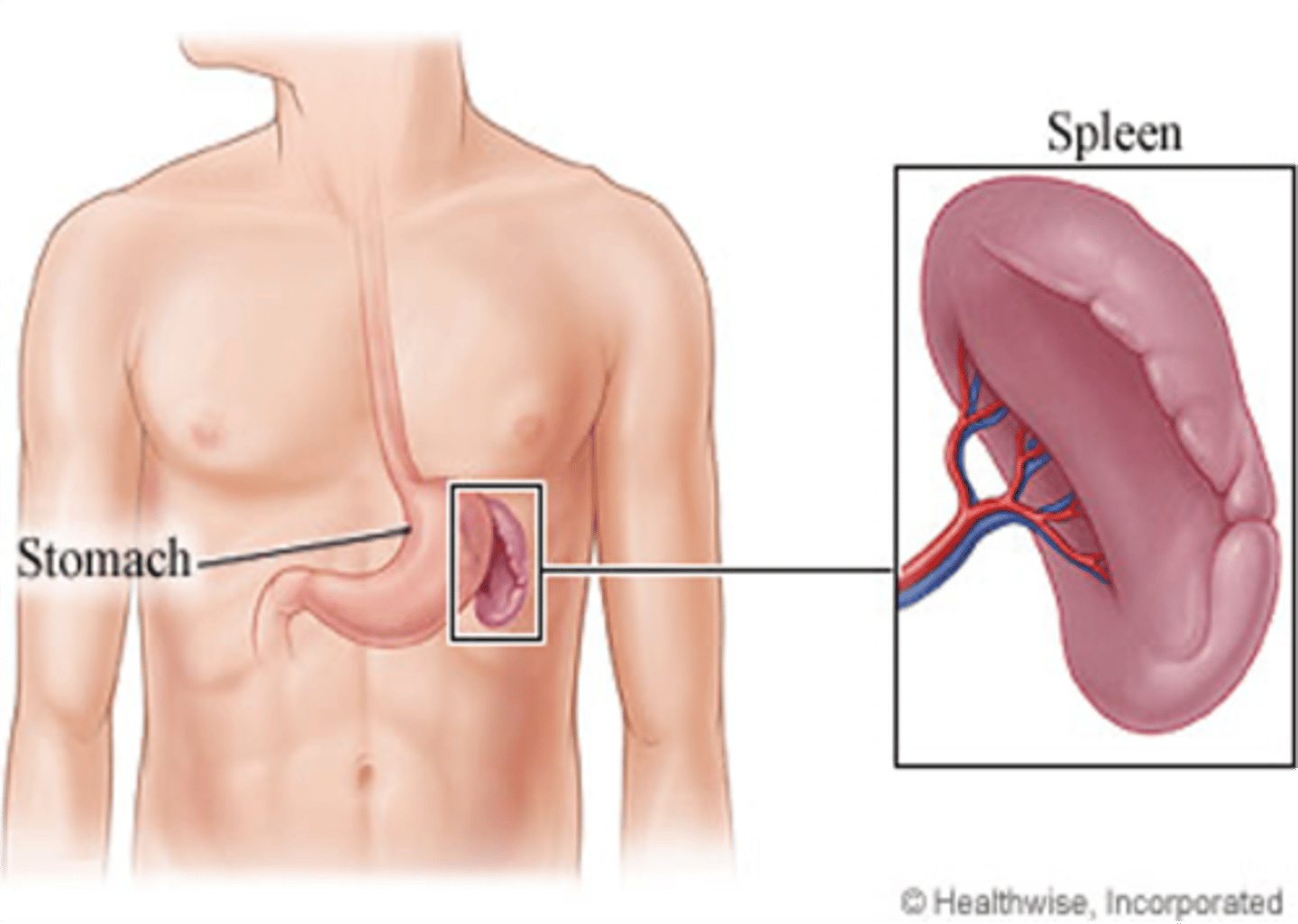
This organ filters blood to remove particulate matter and cellular residue, stores red blood cells, and produces lymphocytes
Spleen
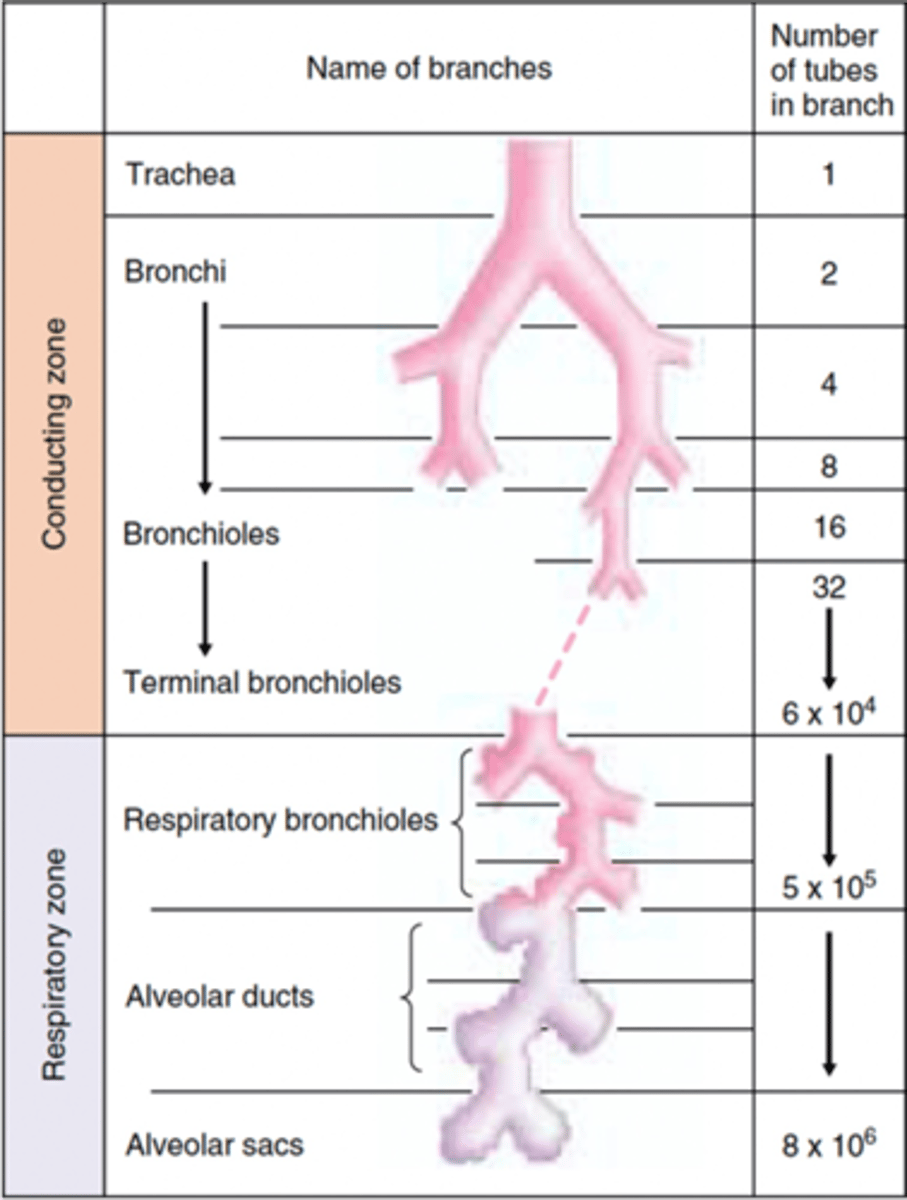
The conducting zone of the respiratory system ends at what type of bronchioles?
Terminal bronchioles
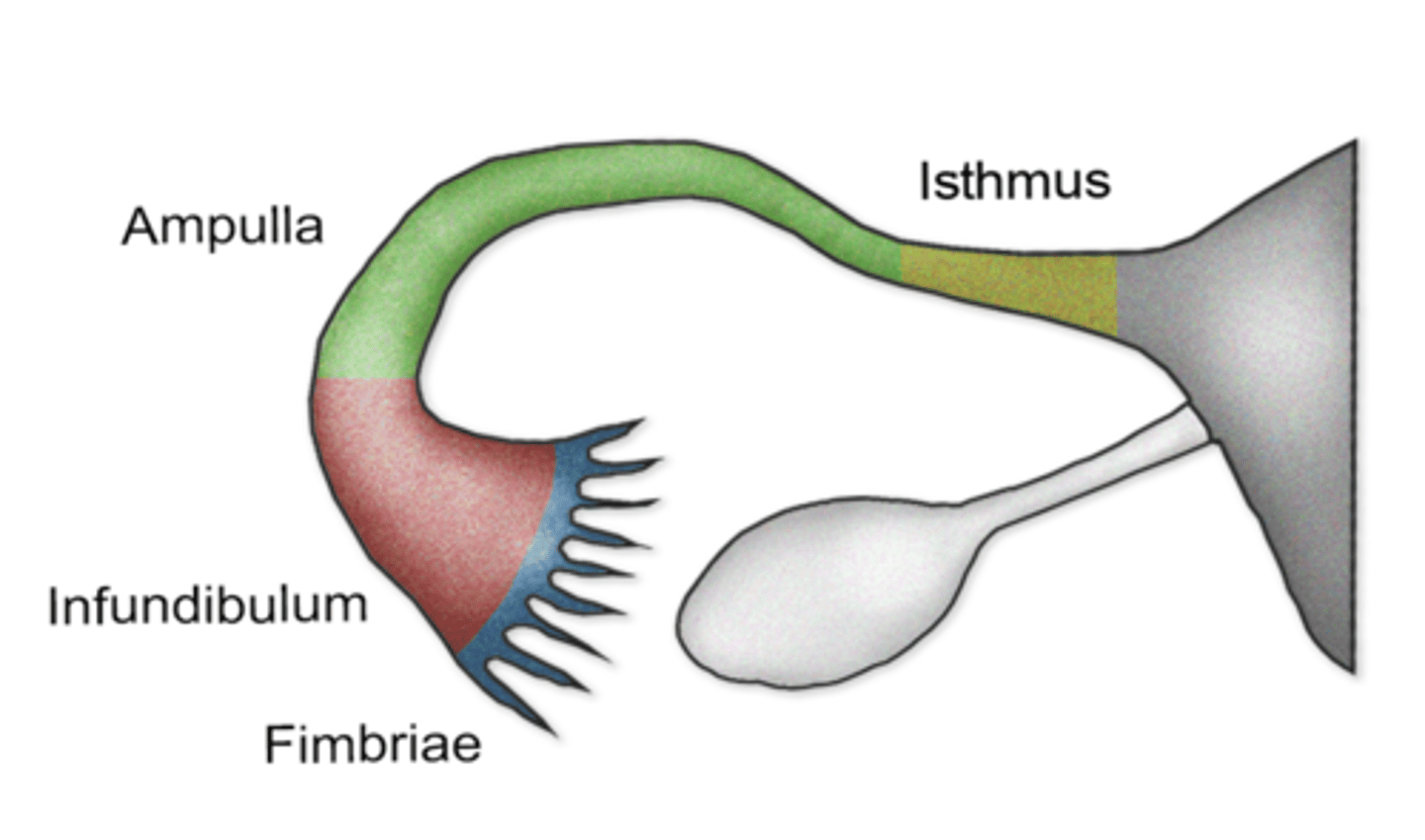
Fertilization usually occurs in what part of the uterine tube
Ampulla
A blastocyst becomes embedded or implanted in the wall of the uterus during what phase of the menstrual cycle?
Progestational (secretory) phase
This retroperitoneal organ is a purely endocrine gland
Adrenal (Suprarenal) gland
Retroperitoneal Organs
S - Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands
A - Aorta + Inferior Vena Cava
D - Duodenum (2nd and 3rd segments)
P - Pancreas
U - Ureters
C - Colon (Ascending + Descending)
K - Kidneys
E - Esophagus
R- Rectum
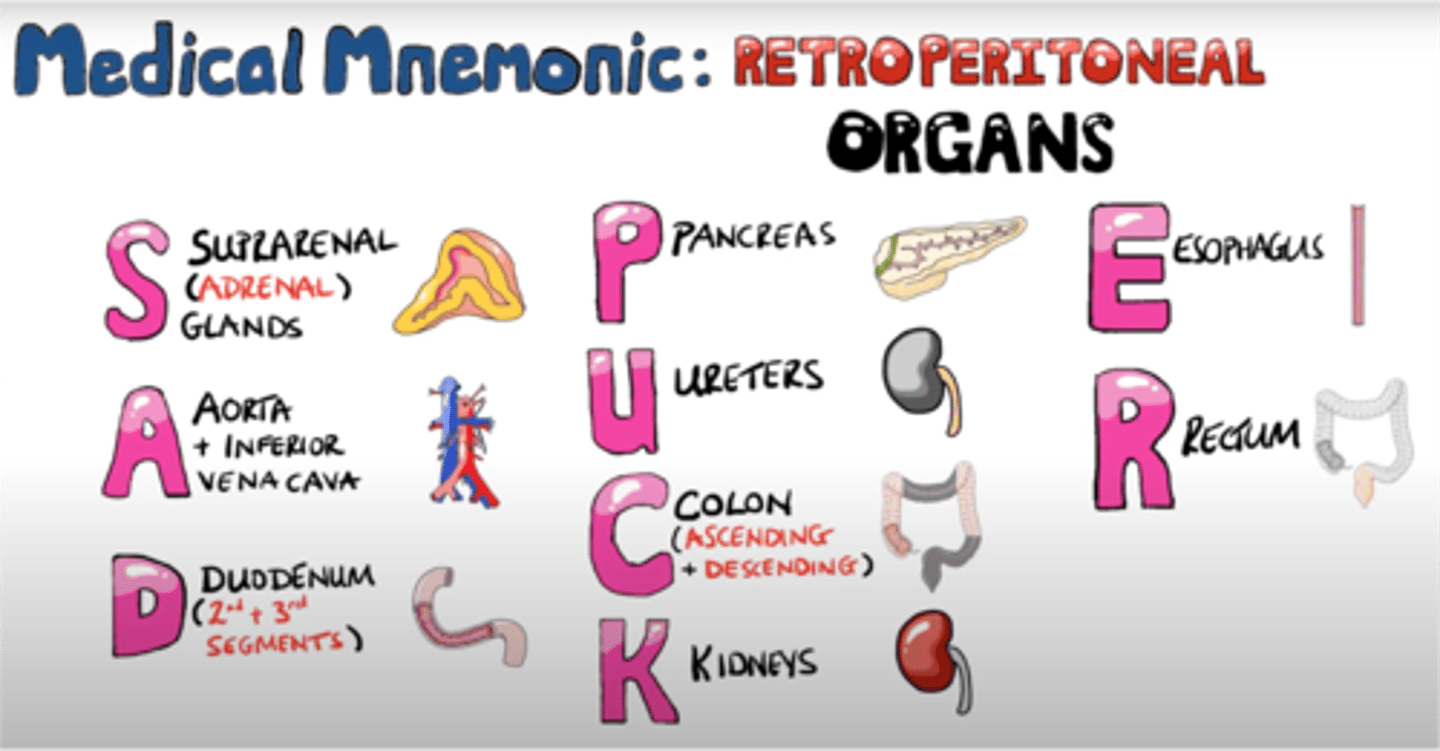
This retroperitoneal organ is a both an endocrine and an exocrine gland
Pancreas
Two types of exocrine glands in the skin
-Sweat glands
-Sebaceous glands
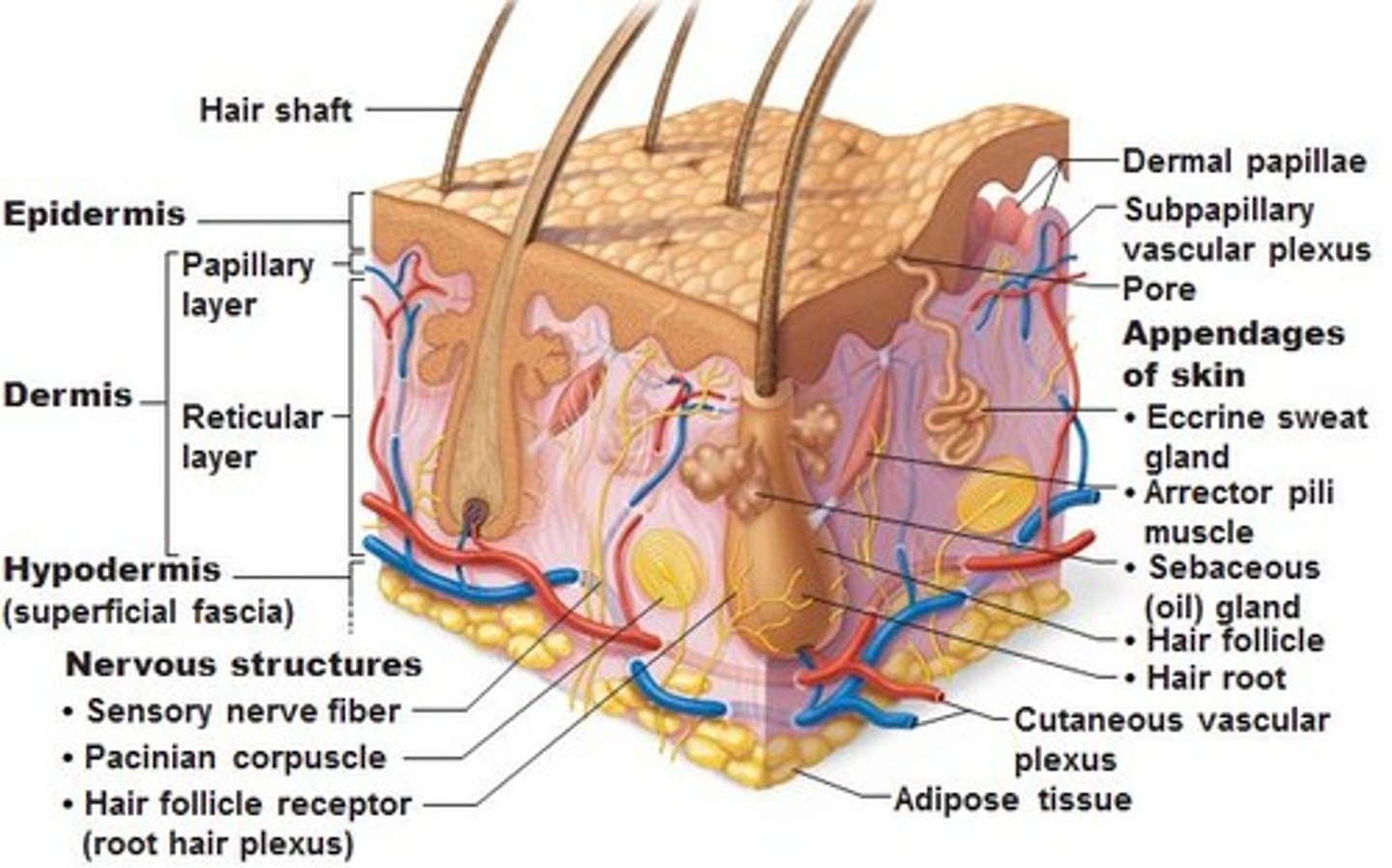
What glial cell is affected in multiple sclerosis?
Oligodendrocytes
What vitamin is produced in the skin
Vitamin D