Immunization and Immune Testing Flashcards - ch 14
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards about Immunization and Immune Testing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Acquired Immunity
Immunity acquired through normal life experiences or medical procedures (immunization).
Natural Immunity
Acquired immunity through normal life experiences, not induced through medical means.
Artificial Immunity
Immunity produced purposefully through medical procedures (immunization).
Active Immunity
Immunity developed as a consequence of a person's own immune response to a microbe (same as vaccination).
Passive Immunity
Immunity resulting from receiving preformed immunity made by another person.
ex. mother to newborn
Vaccination
The process of inducing active immunity to protect against disease.
Variolation
An early method to prevent smallpox.
Edward Jenner
Developed the vaccine for smallpox.
Vaccinia virus
Cow pox virus used in smallpox vaccine.
Attenuated vaccines
Vaccines with reduced virulence; pathogen no longer causes disease (Modified, weakened Live vaccine).
Inactivated vaccines
Vaccines made from infectious agents that have been inactivated or killed.
Toxoid
A type of inactivated vaccine using inactivated toxins.
ex. tetanusand diphtheria to induce immunity.
Subunit vaccine
A type of inactivated vaccine using only parts of the infectious agent.
ex. Hep. B
Conjugated vaccine
A type of inactivated vaccine that links polysaccharides to proteins.
ex. prevnar
Adjuvant
Substance mixed with a vaccine to enhance the immune response (e.g., Alum).
additive added to vaccine to jumpstart vaccine
Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)
Antibodies that are all exact clones of each other, binding to the same epitope of the same antigen.
Hybridomas
Immortal B cells created by fusing a B cell to a myeloma cell, used to produce monoclonal antibodies.
Antibody titer
Measurement of antibody produced for a particular epitope.
Serial Dilution
Method to measure antibody titer.
Rising titer
A second blood sample has more antibody than the first blood sample.
Seroconversion
Change in titer from zero antibody before illness to significant titer while disease progresses.
Precipitation Reactions
Involve soluble antigens and require IgM- or IgG- class antibodies.
detects: Ag in pt. sample and Ab in serum sample
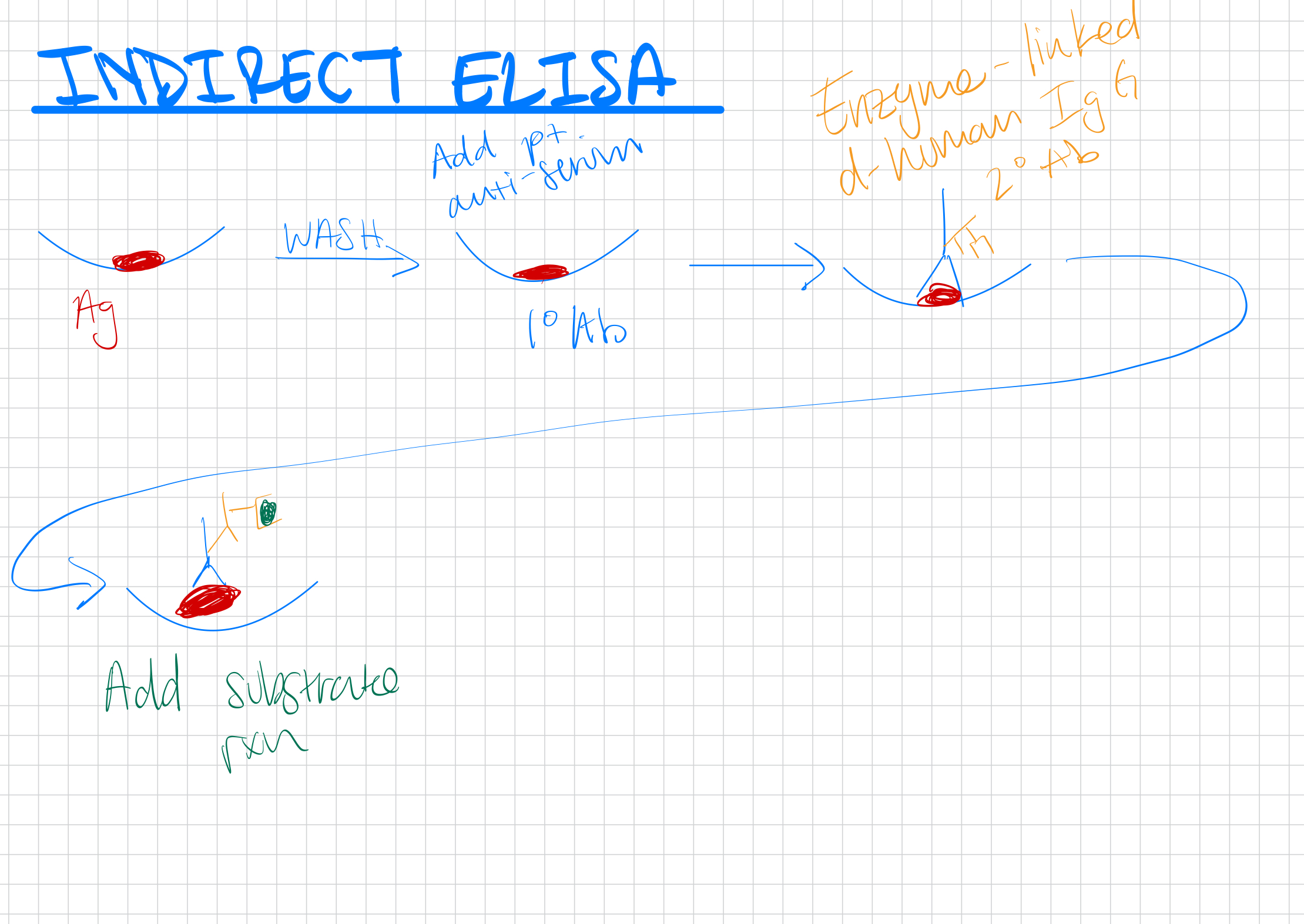
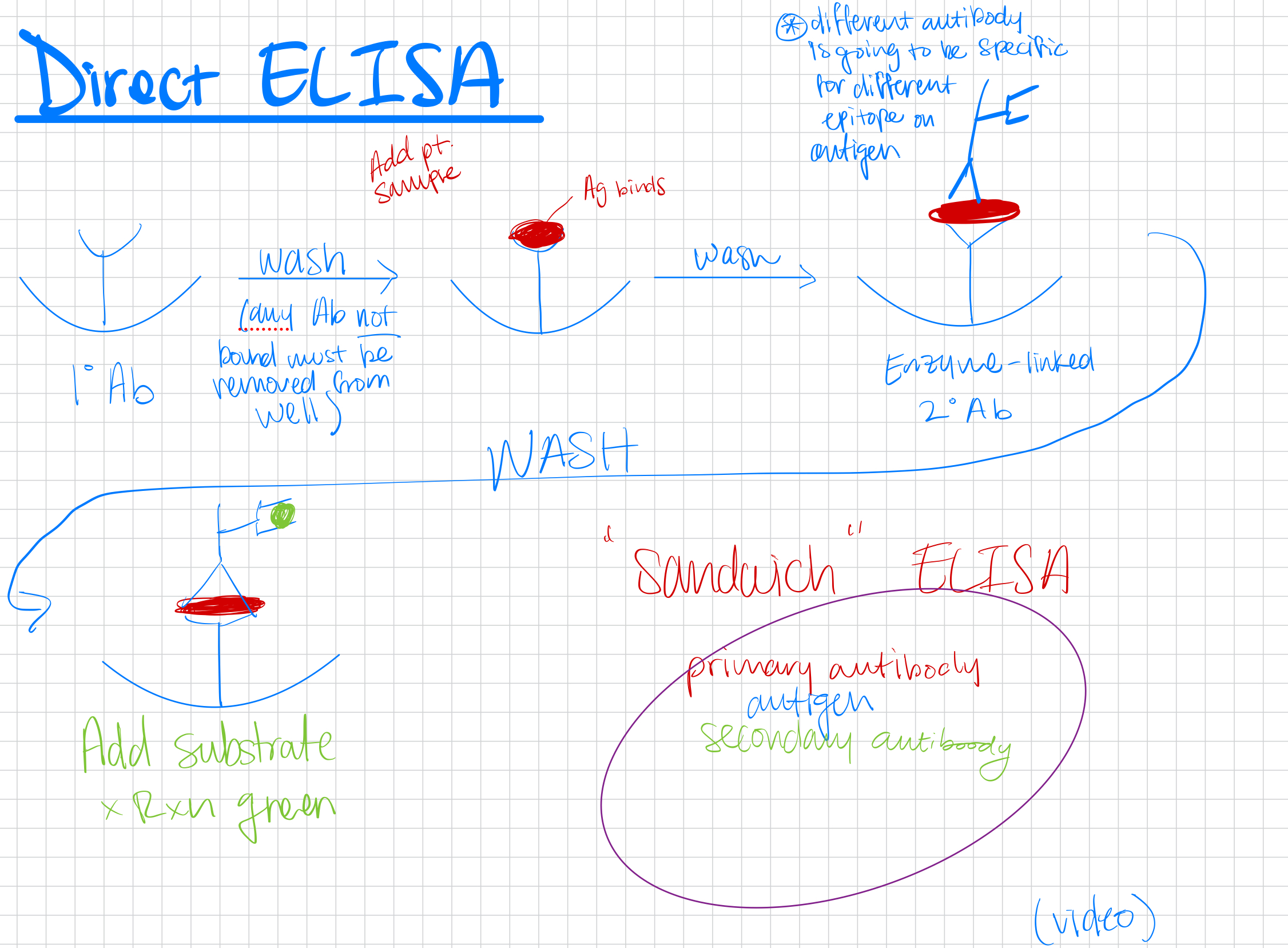
ELISA
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; used to detect antigens or antibodies in a sample.
Direct ELISA
Detects antigen in a patient sample using known antibody.
Indirect ELISA
Detects antibodies in a sera sample using known antigen.