TV4101 - RI - Thorax - Mediastinum
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What is the mediastinum?
All the organs along the middle of the thorax between the lungs
What can we see in the mediastinum?
What can’t we see in the mediastinum on normal RG?
Visible
- Cranial mediastinal width
- Trachea
Not visible
- Lymph nodes
- Oesophagus
Cranial Mediastinum width
Extends where?
From the first ribs to the cranial aspect of the heart
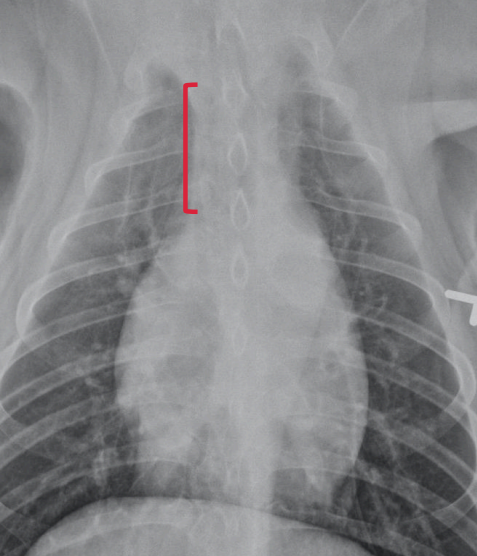
Cranial mediastinum – normal anatomy
The structures in the cranial mediasnum are all?
Structures include?
soft tissue opacity (except the trachea) so they efface.
Trachea, oesophagus, blood vessels, lymph nodes
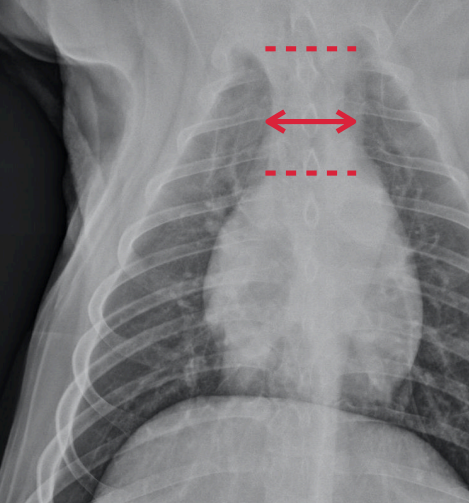
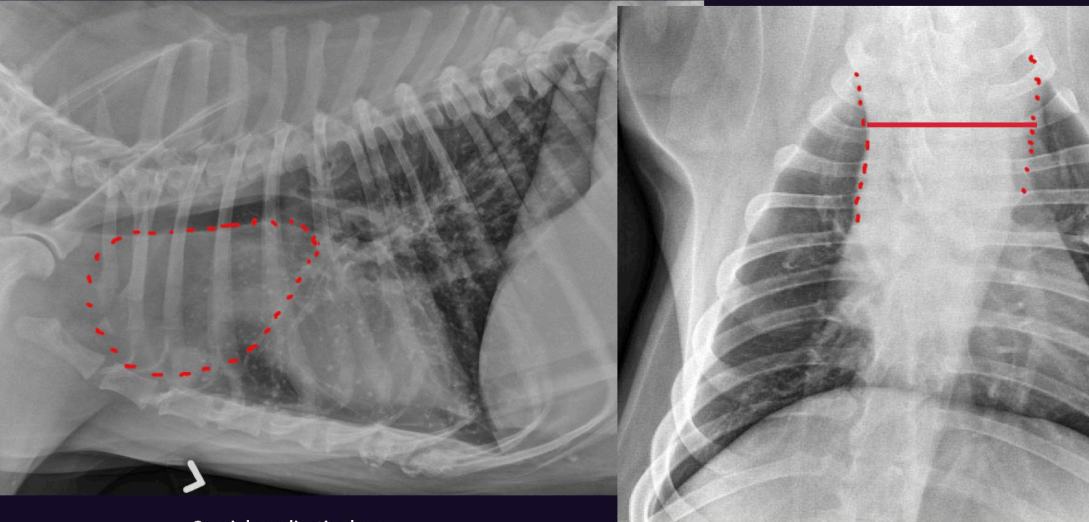
Cranial mediastinal width
Which view?
How to measure?
• Measured on the VD view
• Locate the first ribs and the cranial border of the heart
• Measure the width half way between these structures
Cranial mediastinal width
What is normal?
Why would it be wider if not diseased?
• Normal is <2 mes the width of the vertebra
• Wider in brachiocephalic and obese dogs
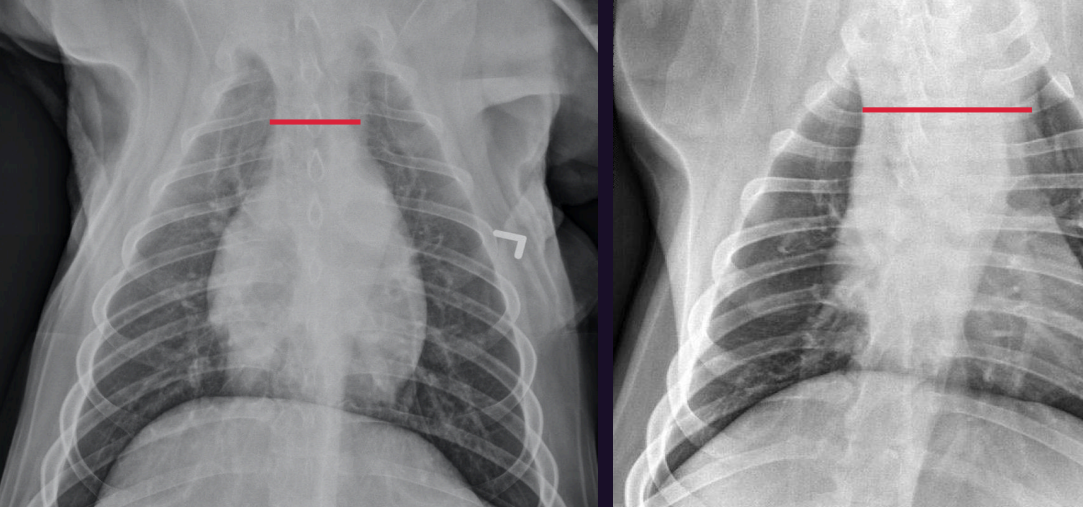
Which is abnormal, why?
Right - Too wide
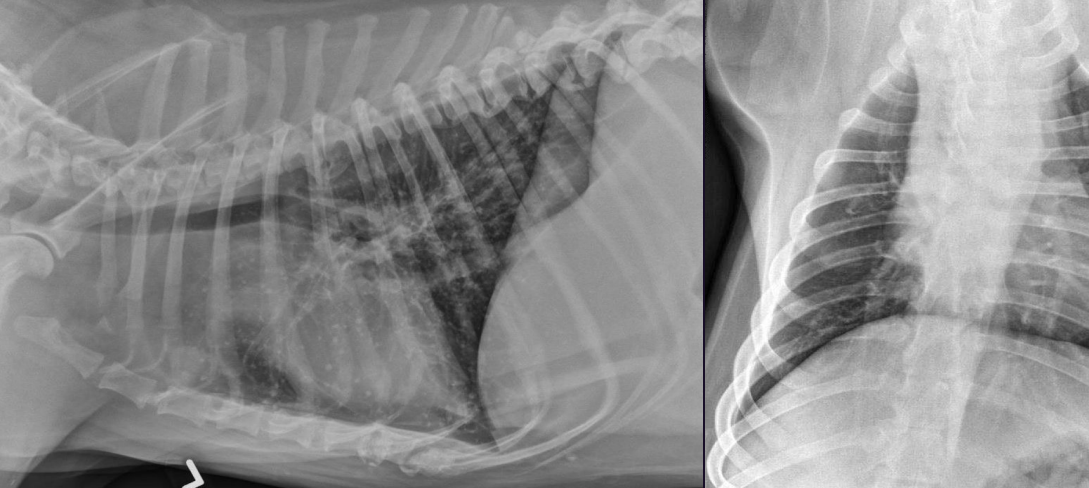
What can we see here?
Cranial mediastinal mass
Cranial mediastinal mass DDx?
• Lymphoma
• Thymoma
• Less common – other neoplasia (eg ectopic thyroid), cyst, abscess, granuloma
Not all cranial mediastinal masses are?
What is a cause that isn’t uncommon?
Neoplasia
Mediastinal cysts are not uncommon and are benign & of no clinical signicance
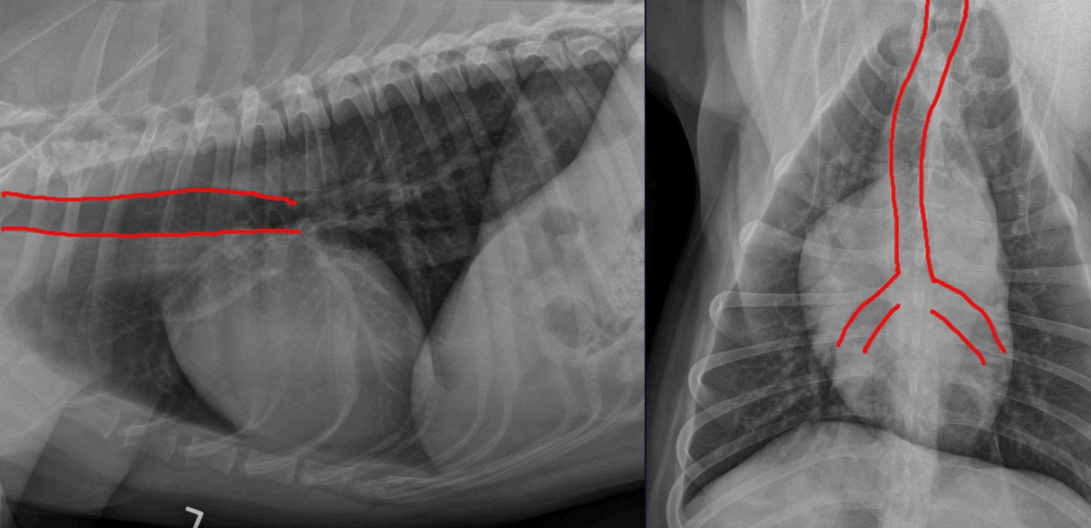
What can we see here?
Any features?
The trachea
The trachea is normally to the right of midline on the VD view
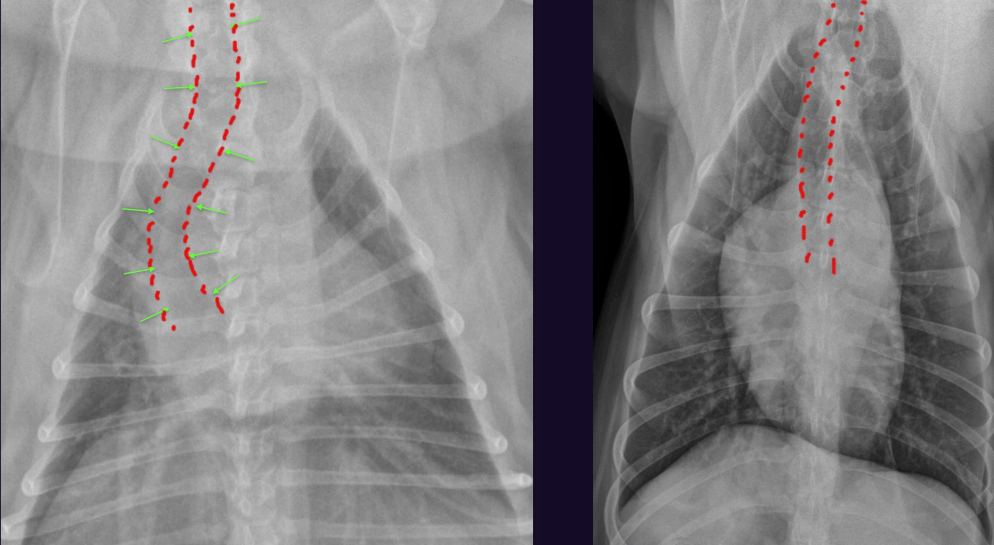
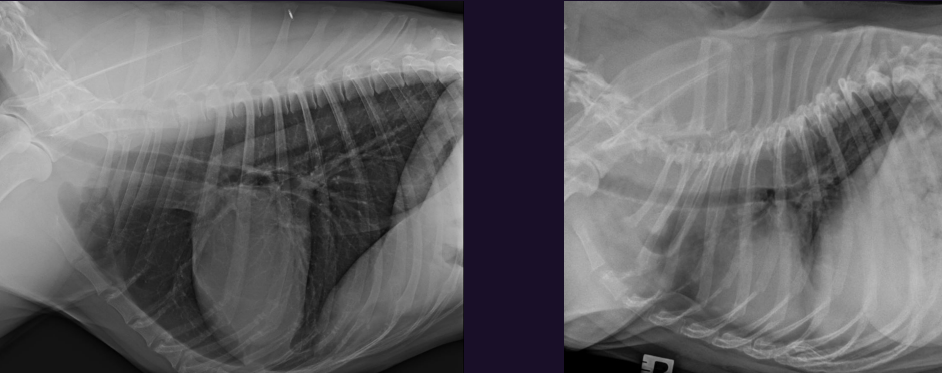
Describe each of these photos, both of these animals came in and are healthy
Left - Normal brachiocephalic – curves more rightward (DDx heart base mass (very unlikely)
Right - normal non-brachiocephalic
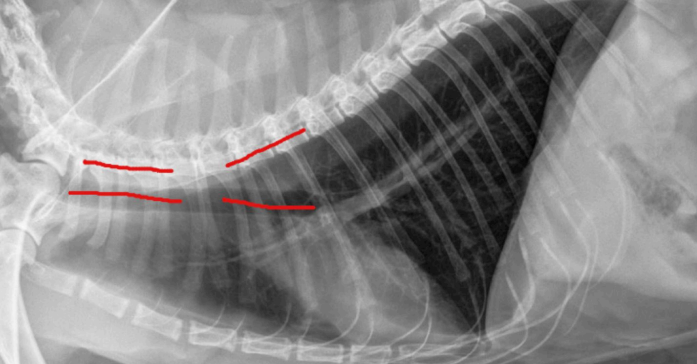
Trachea - describe each of these photos
Left - Trachea with greater angle with spine → deep chested dog
Right - Trachea is parallel to the spine → barrel chested dog

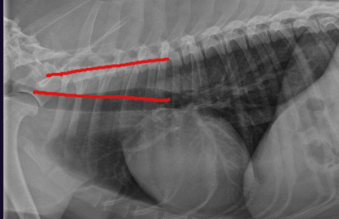
What can we see here?
Normal cat trachea
Cranial trachea is parallel
Caudal trachea at angle to spine due to natural lordosis
What can we see here?
Normal dog trachea - thoracic spine in dog is straight so the angle with the trachea is constant
Trachea - abnormalities inc?
•Tracheal hypoplasia
•Tracheal collapse
•Tracheal displacement
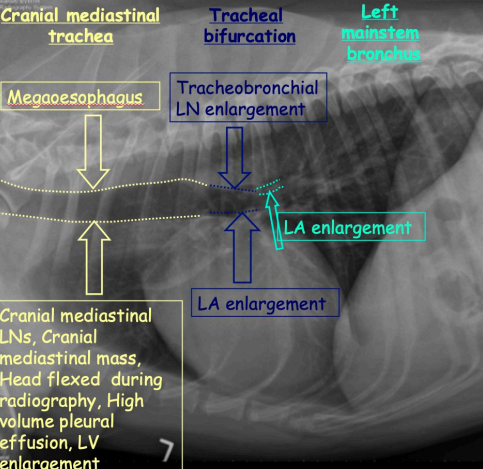
Tracheal Displacement at different regions and causes inc?
Cranial mediastinal trachea
Megaoesophagus
Cranial mediastonal LNs or mass
Head flexed during RG
High vol pleural effusion
LV enlargement
Tracheal bifurcation
Tracheobronchial enlargement
LA enlargement
Left mainstem bronchus
LA enlargement
Tracheal Hypoplasia
Physical change on RG?
Why does it occur?
How to measure?
Generalised decrease in width of the trachea
Part of brachiocephalic airway syndrome
Congenital but CX worse in pups
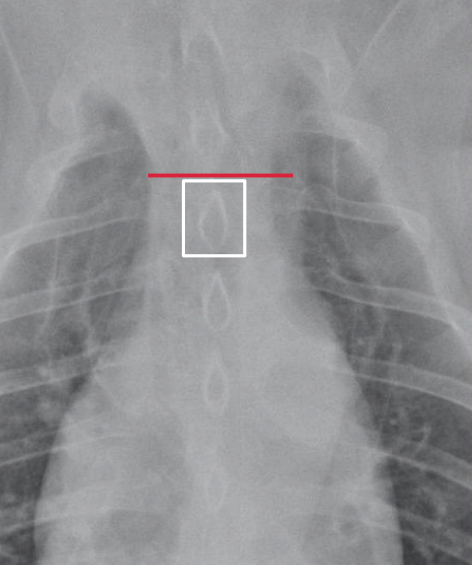
Measured by the ratio of the tracheal width to the
width of the thoracic inlet
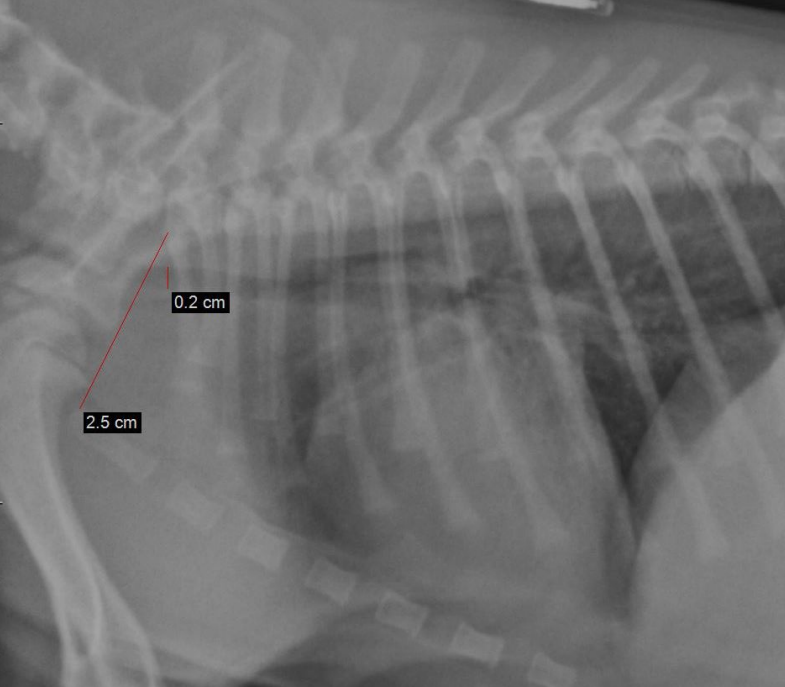
What this?
Tracheal hypoplasia The trachea to thoracic inlet ratio is 8%.
Tracheal Hypoplasia
Trachea width : Thoracic inlet ratio?
• Normal = 20% +/-3%
• Bulldog = 13% +/-4%
• Other brachiocephalic = 16% +/-3%
Tracheal collapse
Signalment?
Caused by?
CX?
In middle-aged to old small breed dogs
Due to chondromalacia (softening of the tracheal rings)
Chronic cough
Tracheal collapse - How to Image?
• Endoscopy of the trachea is the best
• Fluoroscopy is the best imaging method
• Radiographs are not sensitive
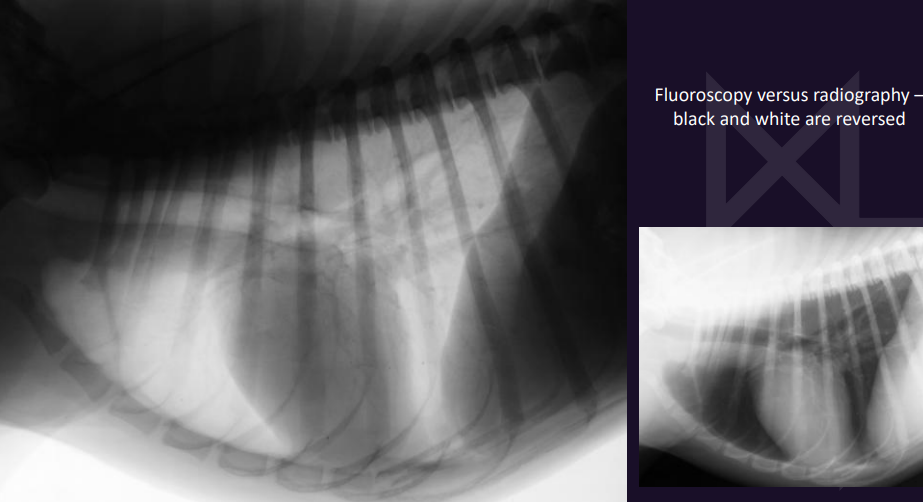
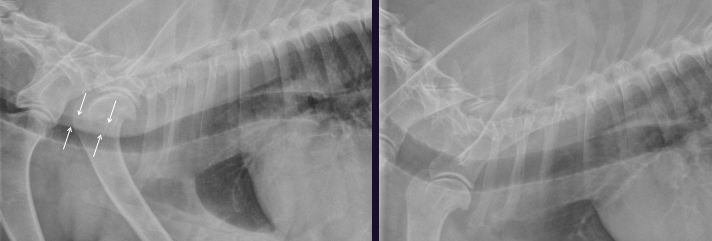
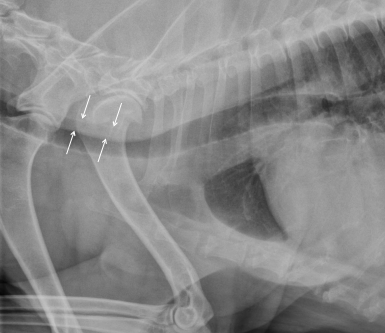
What is this? Same dog btw
Ass with?
Left - Redundant dorsal tracheal membrane
Right - Normal trachea (same dog on the other lat view)
Can be associated with tracheal collapse if they have a chronic cough, but can also be seen in normal dogs
Redundant dorsal tracheal membrane - large breed versus small breed dog
If this is seen in a large breed dog it is likely normal superimposiotin of the oesophagus as tracheal collapse is very rare in large breed dogs.
3 Lymph Nodes we need to think about?
Sternal LNs
Cranial mediastinal LNs
Tracheobronchial LNs
3 Lymph Nodes - Sternal LNs
Features?
At the level of S2 in dogs, and S3 in cats.
They drain the abdomen and mammary glands.
3 Lymph Nodes - Cranial mediastinal LNs
Features?
They efface with the soft tissue in the cranial mediastinum so they are not seen until they cause a cranial mediastinal mass.
3 Lymph Nodes - Tracheobronchial LNs
Lymph nodes at the carina
They displace the caudal aspect of the trachea ventrally.
They can be difficult to tell apart from le atrial enlargement, but patient presentation is helpful.
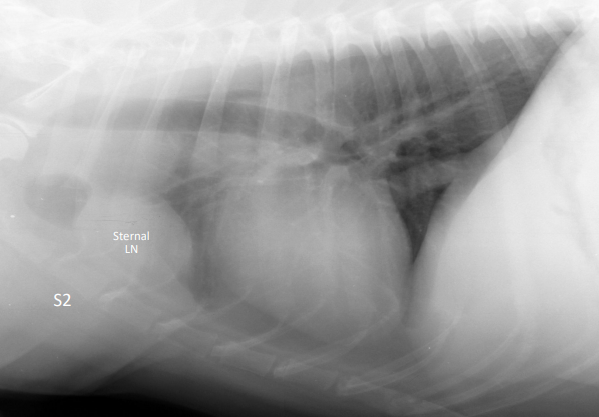
What can we see?
Very large sternal LNs
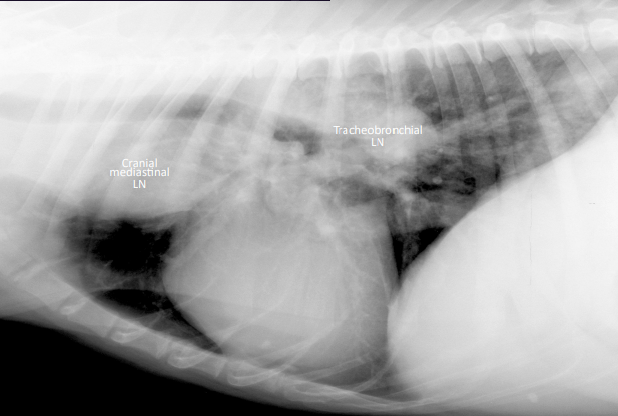
What can we see?
Large tracheobronchial and cranial mediastinal LNs
Large LNs Ddx?
• Mulcentric neoplasia - lymphoma, hisocyc sarcoma
• Disseminated fungal infection
Metastasis from the draining area eg mammary neoplasia to the sternal LNs
Reactive hyperplasia from the draining area - this only applies to the sternal LNs (peritonitis, haemoabdomen due to benign or malignant causes). Mild enlargement due to reactive hyperplasia of the other LNs (cranial mediastinal & tracheobronchial LNs) is not seen.
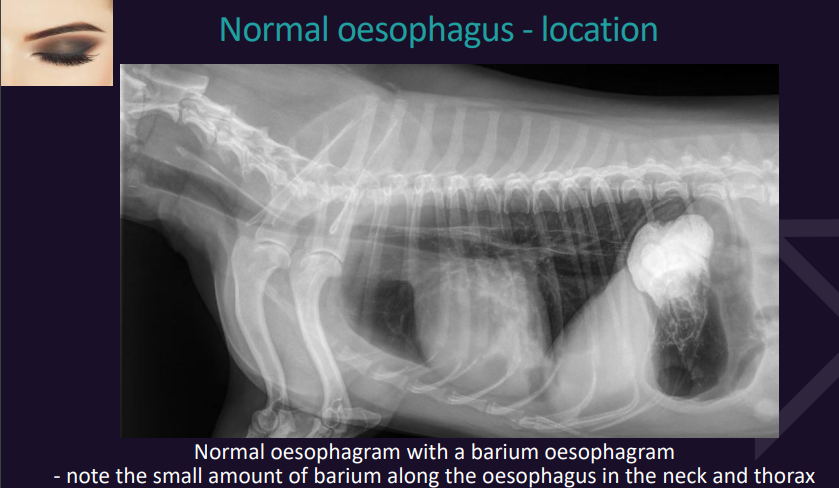
Oesophagus
Normal oesophagus - location
VD view?
Lateral view?
VD view it is superimposed on the midline/mediastinum and often not seen even if it is abnormally large
Better assessed on the lateral view.
What is this?
How can we tell?
Oesophageal foreign body
Not a lung mass as it is not seen on the VD (and therefore must be superimposed on the spine on the VD (ie midline)).
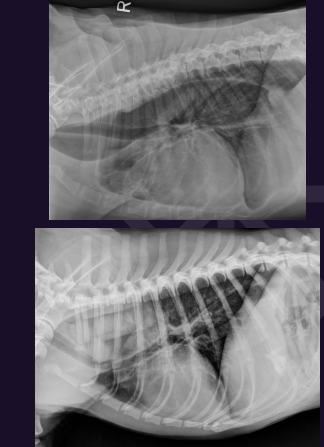
What is this?
Types and features?
Megaoesophagus
•Generalised
Transient due to GA or sedation
Pathology – such as idiopathic, oesophagitis, myasthenia gravis, myopathy, hypoadrenocorticism, hypothyroidism, toxin (lead, OP)
Focal
Vascular ring anomaly (VRA)
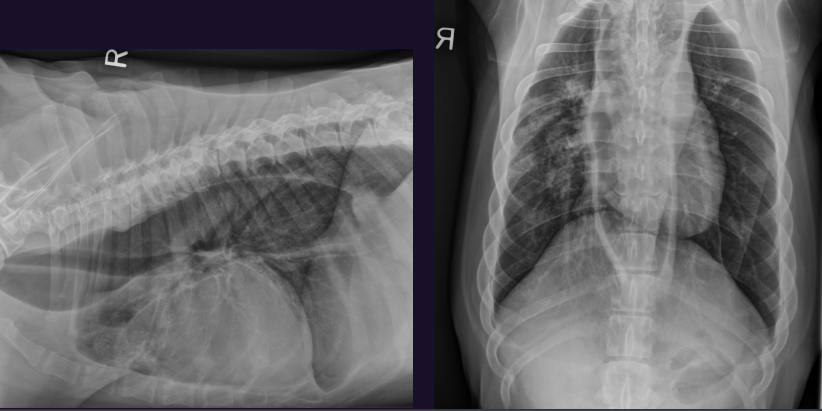
What is this?
Megaesophagus - generalised
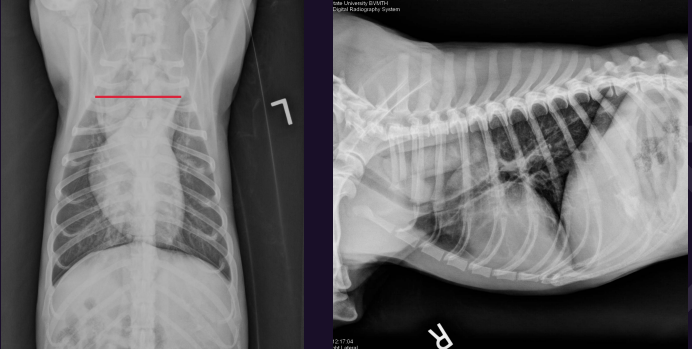
What is this?
Megaesophagus - focal
Pneumomediastinum
What view to assess?
The key to idenfying pneumomediasnum is seeing?
Lateral view only
Separation of the blood vessels on lateral view
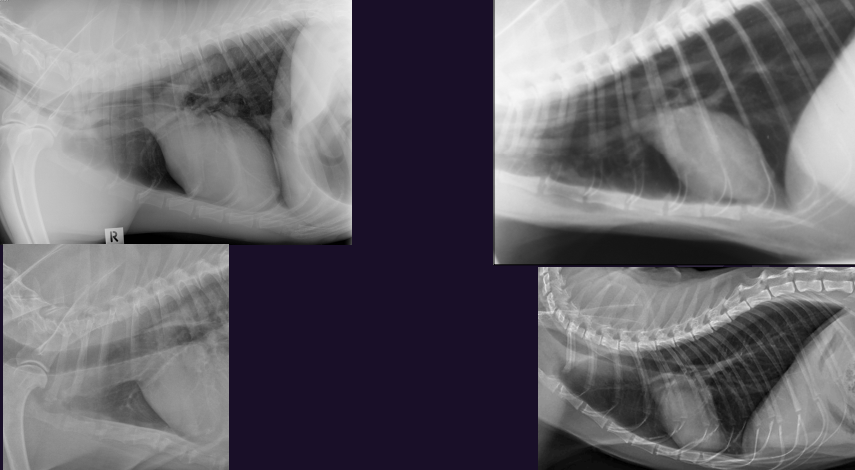
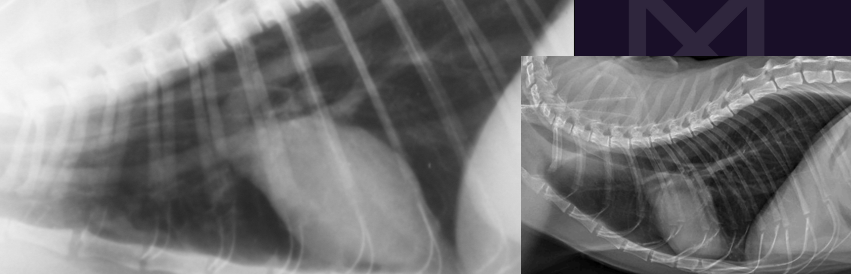
Which is abnormal?
What is it?
Left - Pneumomediastinum
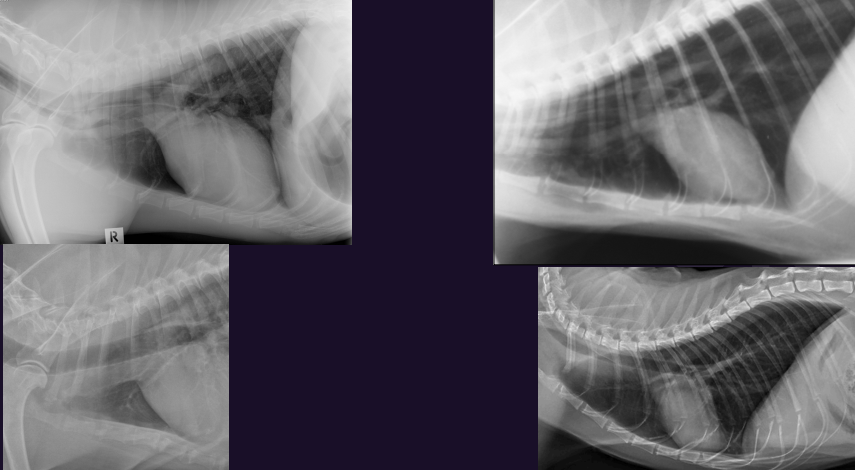
What is this?
Pneumomediastinum
Other mediastinal things to think abt?
Pneumomediastinum
Mediastonal Shift
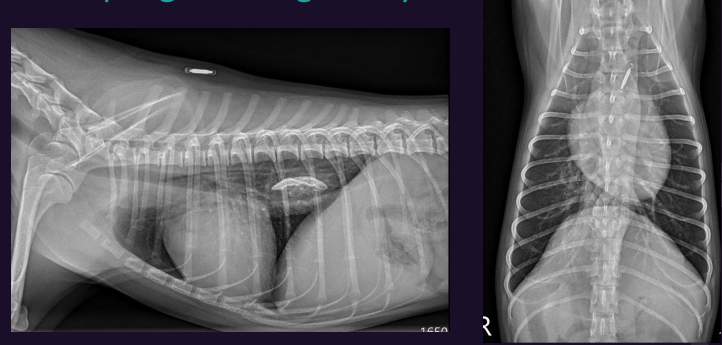
Normal thymus - seen in young puppies and sometimes kittens
Mediastinum Anatomy
Communications?
Cranially - Neck via thoracic inlet
SC gas in neck → enters mediastinum
Gas from mediastinum → cranially into neck (Rare)
Caudally - Retroperitoneum via aortic hiatus in diaphragm
Gas from mediastinum (pneumomediastinum) → retroperitoneum (rare)
Pneumomediastinum
Causes?
Significance?
TX?
• Gas in the mediasnum
• Caused by blunt trauma (HBC) or rupture of the trachea or oesophagus
Clinically insignicant, but can cause pneumothorax which is clinically signicant (Pneumothorax can’t make pneumomediastinum)
Can also cause pneumoretroperitoneum, subcutaneous emphysema
Pneumomediasnum is not specically treated
Mediastinal Shift
Causes inc?
Appearance on RG? What view to use?
• One side has increased volume à heart shis away eg tension pneumothorax
• One side has decreased volume à heart shi towards that side eg lung atelectasis, occasionally with regular pneumothorax
•Heart ‘shifts’ to the left or right
•Assess on the VD only
•The VD has to be PERFECTLY straight
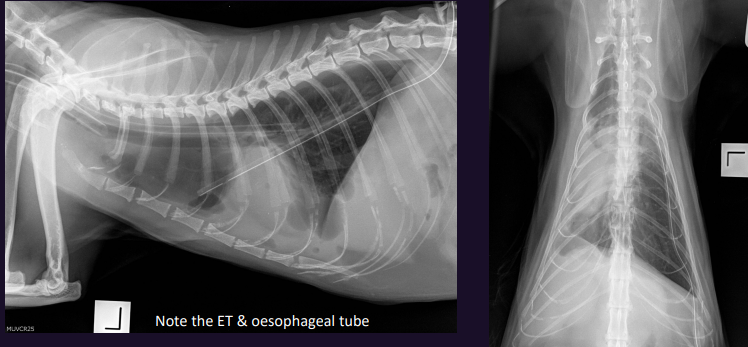
What is this?
Mediastinal shift
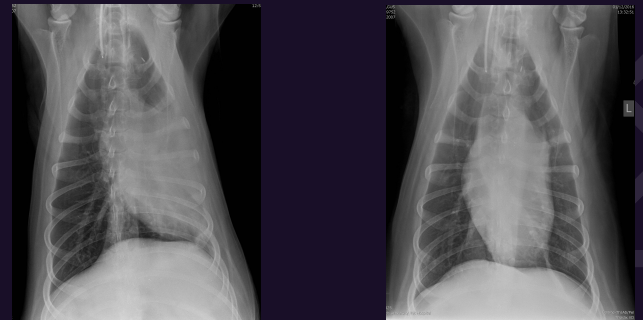
What is this? Sam animal btw
Left - Mediastinal shift as an artefact from positioning (Rotated VD view)
Right - Normal positioning as not rotated
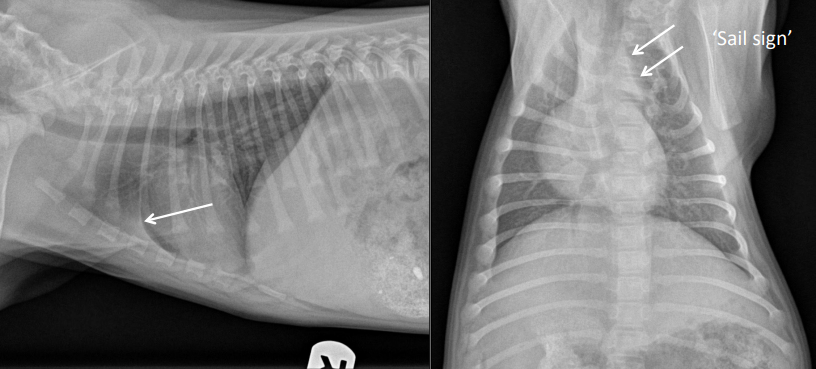
What is this?
Normal thymus in a puppy