Nucleic Acids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
DNA full name
deoxyribonucleic acid
RNA full name
ribonucleic acid
nucleic acid structure
made up of nucleic acid monomers (nucleotides)
DNA function
encodes instructions to make protein with a specific sequence of amino acids
RNA function
intermediate messenger molecule that transports the information from DNA to make the protein synthesis possible
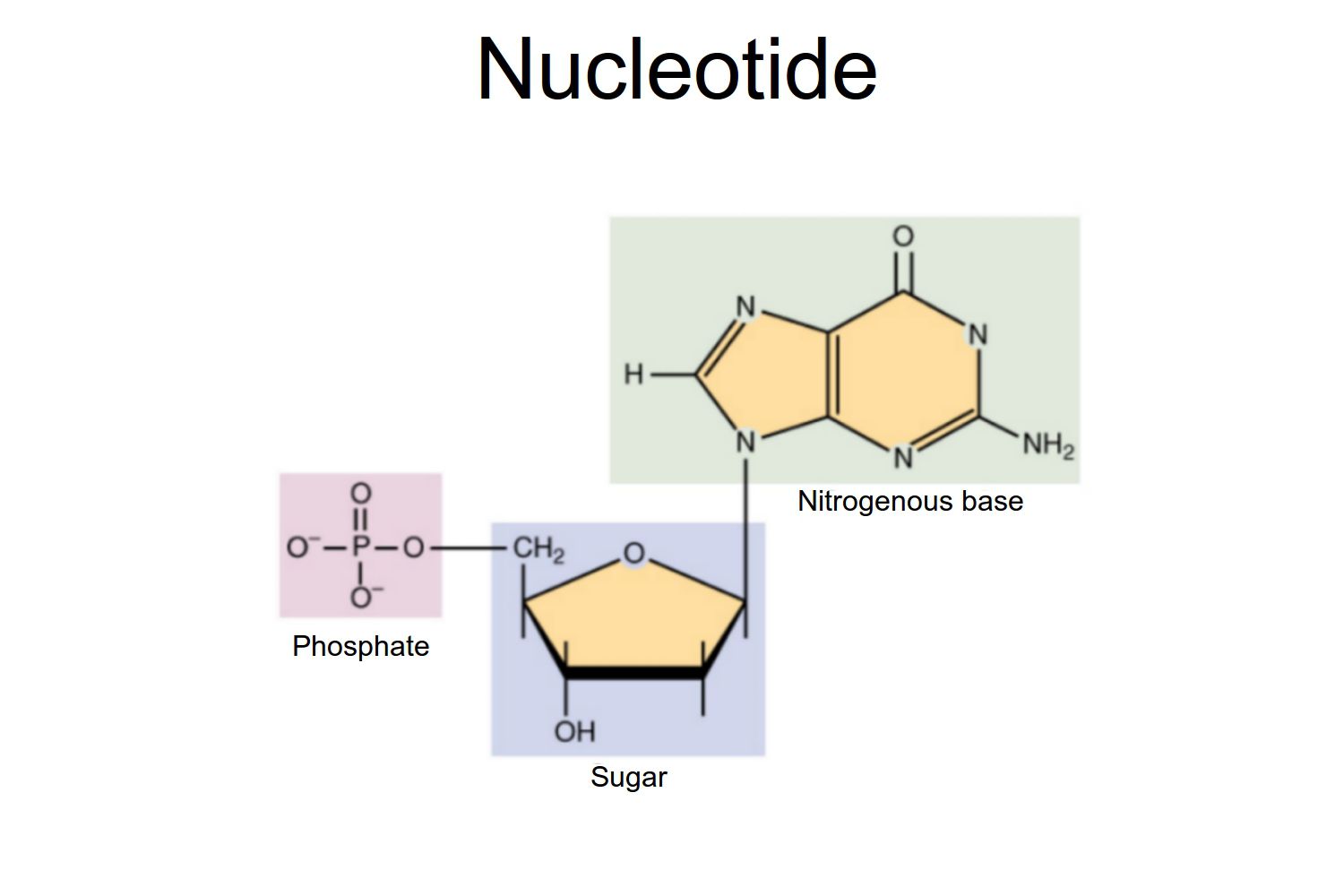
nucelotides structure
composed of:
a sugar (pentose, 5 carbon ring)
phosphate
nitrogenous base
sugar and phosphate makes the “backbone” of the DNA/RNA
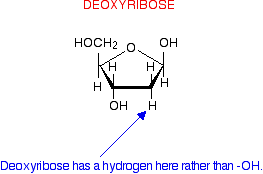
deoxyribose
sugar in DNA
H (hydrogen) at the 2nd carbon
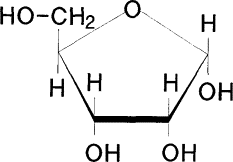
ribose
sugar in RNA
OH (hydroxyl) group attached to the 2nd carbon
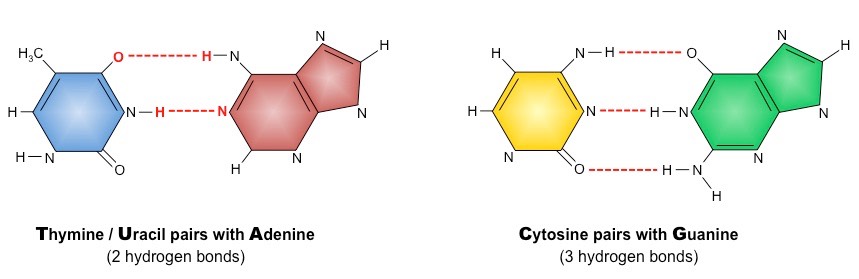
nitrogenous bases
thymine
cytosine
adenine
guanine
difference between purines and pyrimidines
purines - two ring structures
pyrimidines - one ring structure
nitrogenous base structure
adenine bonds with thymine (apples, trees) - 2 H bonds
cytosine bonds to guanine (cars, garages) - 3 H bonds
the hydrogens produced will bonded to each other to form DNA’s double helix/spiral structure (just like secondary protein)
phosphodiester bond
covalent bond that connects DNA/RNA nucleotides together, forming the sugar phosphate backbone from monomers
occur with a condensation rxn
genes function
segments of DNA that are instructions for making proteins
how does genes direct protein synthesis
enzymes copy genes and make an RNA molecule (mRNA) which travels to ribosomes as a messenger because DNA is too large to leave the nucleus
ribosomes “read” RNA and make protein
nitrogenous bases that are purines
adenine and guanine
nitrogenous bases that are pyramidines
cytosine and thymine