9.3 - Growth in Plants
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
Types of plant tissues
Dermal tissue: outer covering that protects
Ground tissue: thin-celled walls that have functions related to storage, photosynthesis, support, secretion
Vascular tissue: xylem and phloem, used for transport and support
All arise from meristematic tissue: small clusters of undifferentiated cells that can specialize into types of plant tissues
Plant tissues and meristems
Apical meristem
Occurs at tips of roots and stems
Responsible for primary growth up and down (growing taller, extending roots)
Results in soft tissue (non-woody stems, roots)
Lateral meristem
Occurs at roots and stems
Responsible for secondary growth (growing in diamter)
Vascular cambium: produces more vascular bundles, which is a major component of wood
Cork cambium: occurs within bark and produces cork cells
Factors influencing plant growth - hormones
Functions of membrane proteins: junction, enzymes, transport, recognition, anchorage, transduction (hormone binding)
Many cells produce the same hormone that has many different effects depending on location of the receptor cell
Protein receptors in or on a specific plant cell receives stimulus from the environment, such as light
The protein receptor becomes activated
Activated protein receptor initiates a metabolic pathwya
Metabolic pathway produces a hormone
The hormone travels through the phloem
Plant hormone
Tropism: growth or movement in response to environmental stimuli (chemicals, gravity)
Phototropism: plant growth in response to light
Necessary because it allows plants to compete for light or to maximize their exposure to light
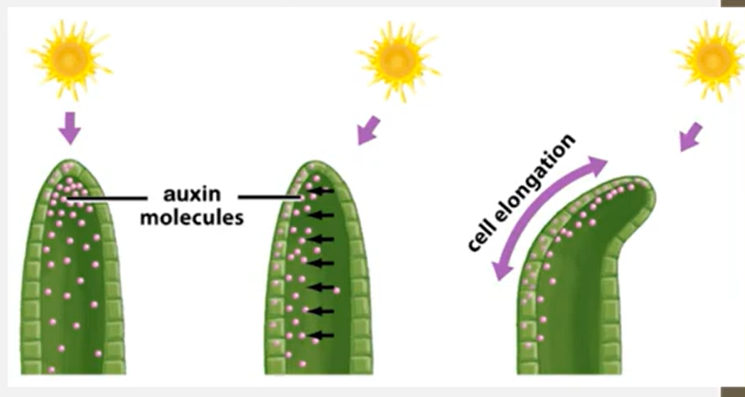
Auxin is a plant hormone that is equally distributed in the plant cells
To bend towards light, auxin is actively pumped OUT of the cell that are closest to the light
Auxin accumulates in the space between cells
Auxin diffuses into the cells that are farthest from the light (passive)
Increased auxin levels activates genes that code from a specific enzyme
The enzyme causes the cell walls of the cells farthest from light to elongate
Elongation of cells away from the light cause the plant to bend toward the light
Auxin also helps…
Stimulation of mitosis in meristematic tissue
Differentiation of xylem and phloem
Development of roots
Micropropagation
Using cells from the shoot apex (apical meristem, non-differentiated cells) to produce more individual plants
A way to help preserve populations of endangered plants