Ochem things to memorize
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Alkane
single bonded carbons and hydrogens
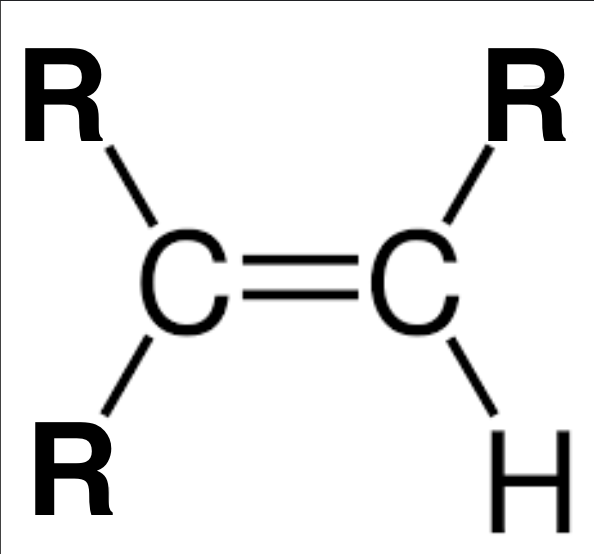
Alkene
1 double carbon bond, no other functional groups
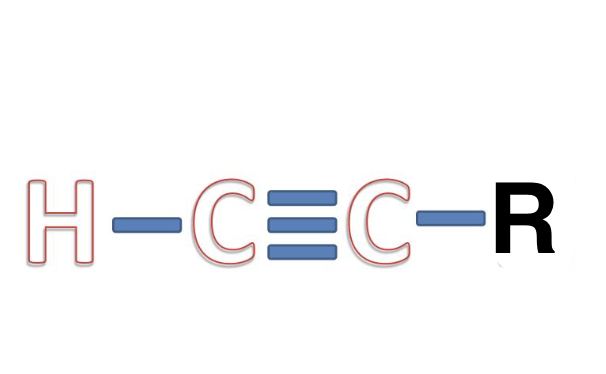
Alkyne
triple carbon bond, no other functional groups
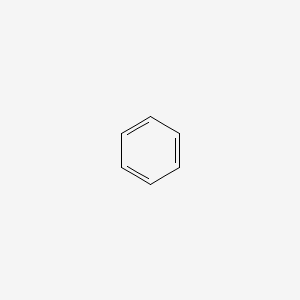
Aromatic
hexagon carbons, alternating double bonds
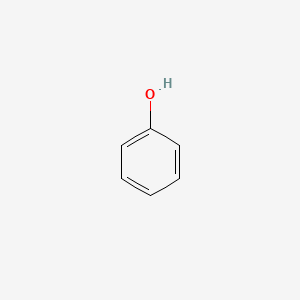
Phenol
aromatic with an OH group
Alkyl Halide
R-F, R-Cl, R-Br, R-I
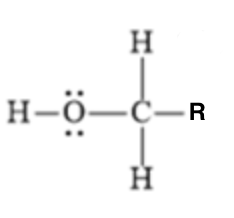
alcohol
R-OH
Ether
R-O-R
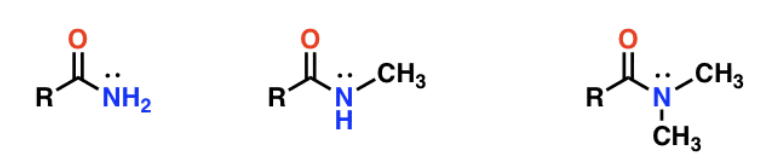
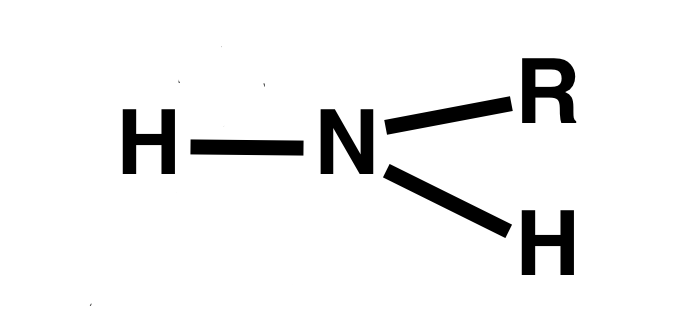
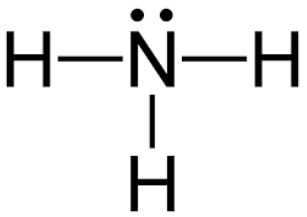
Amine
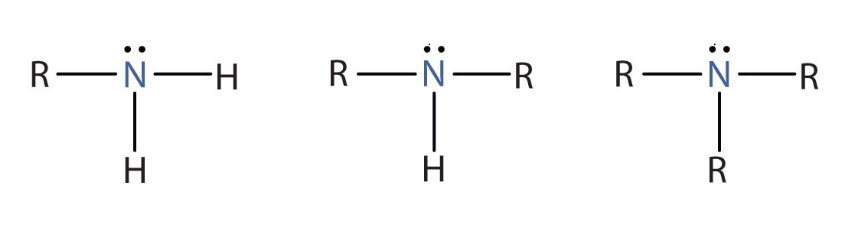
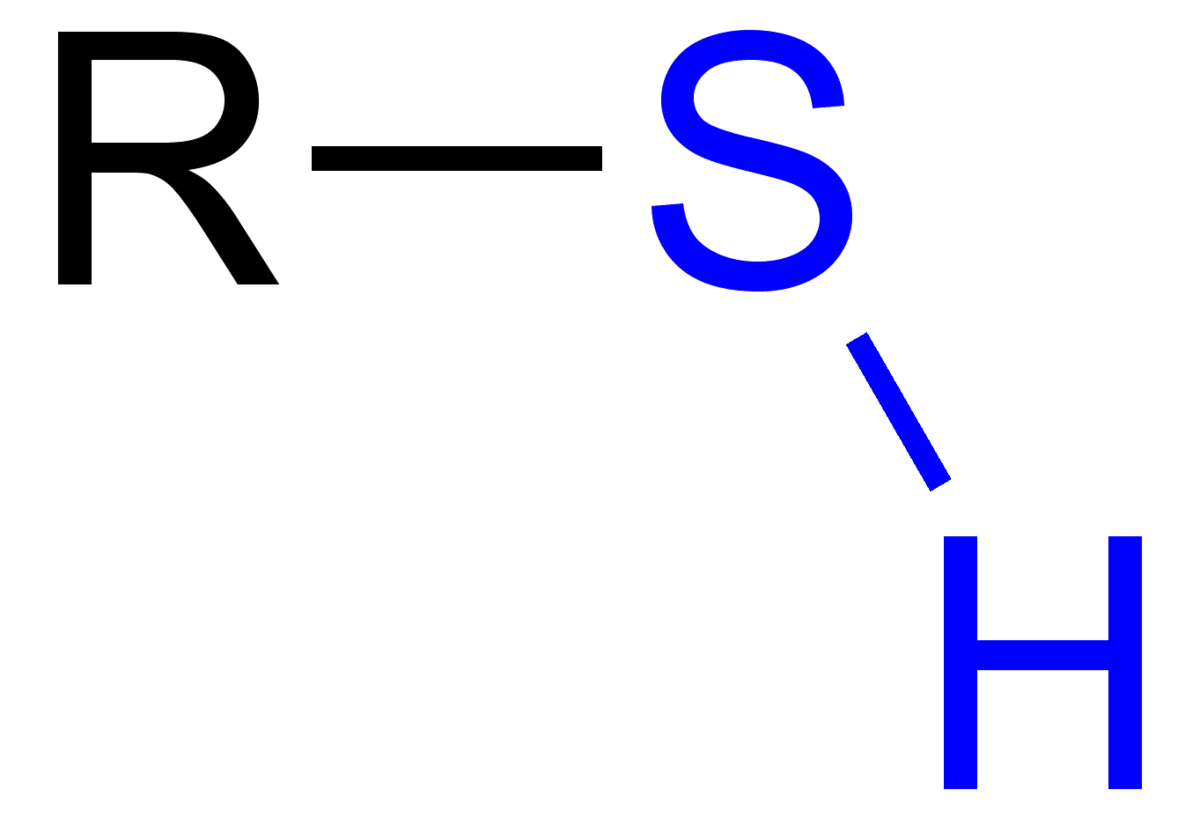
Thiol
R-SH
Sulfide
R-S-R
Disulfide
R-S-S-R
Aldehyde
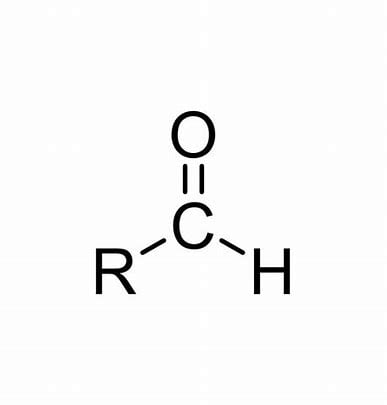
Ketone
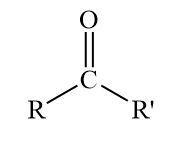
Carbonyl
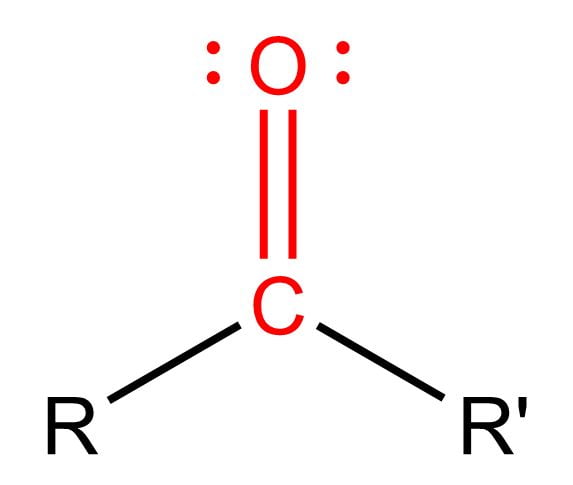
Carboxylic acid
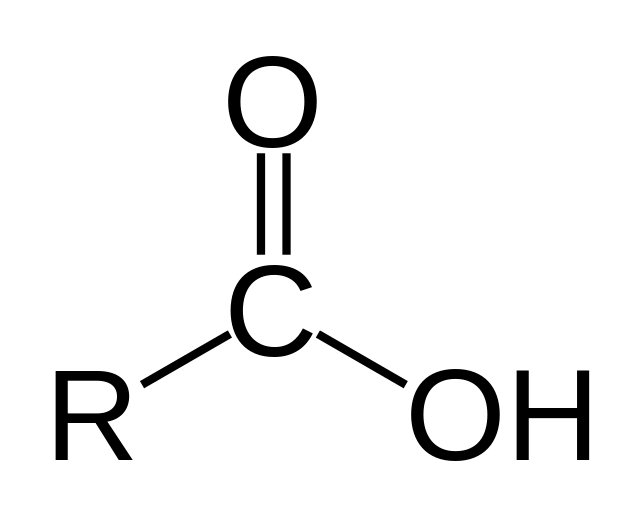
Ester
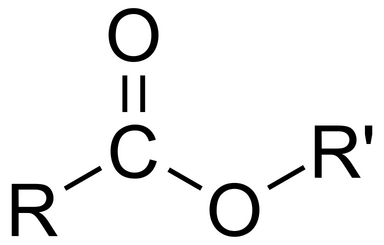
Amide
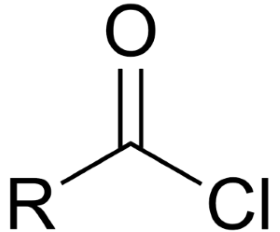
Acid chloride
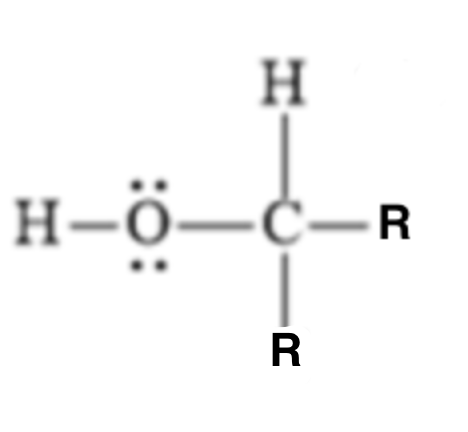
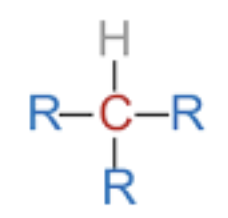
Primary
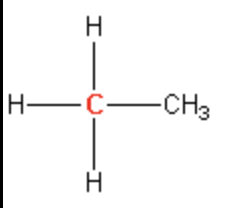
secondary
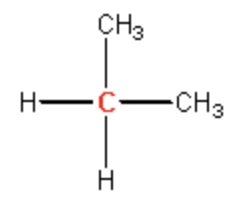
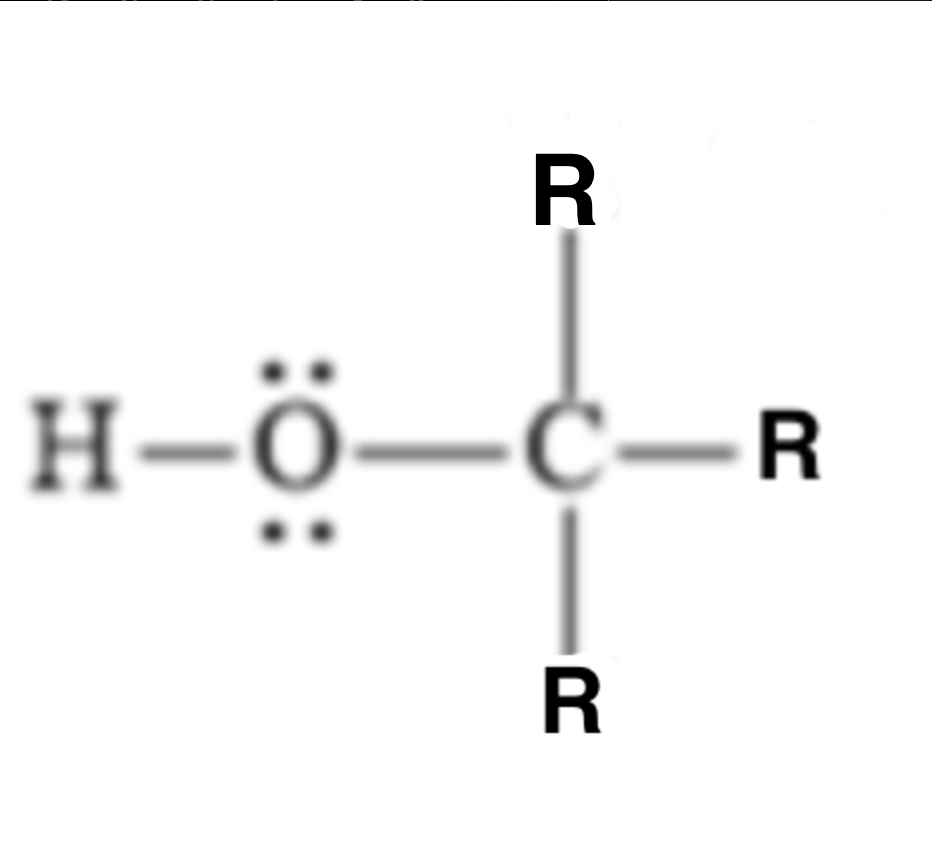
tertiery
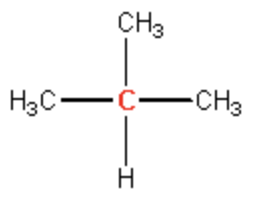
quatrinary

Electrophile
Lewis acid that accepts electrons
Nucleophile
lewis acid that donates electrons
Ka
Base/Acid, 10^(-pKa)
pKa
-logKa
-10
pKa?
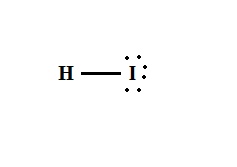
-9
pKa?
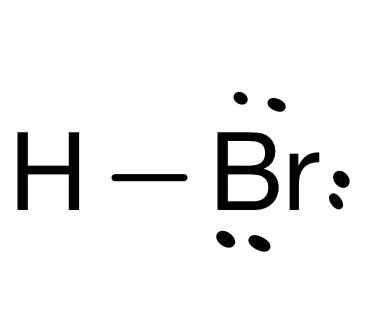
-8
pKa?
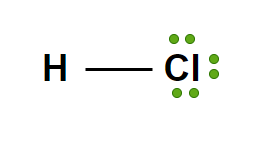
4
pKa?
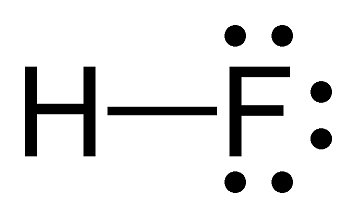
5
pKa?
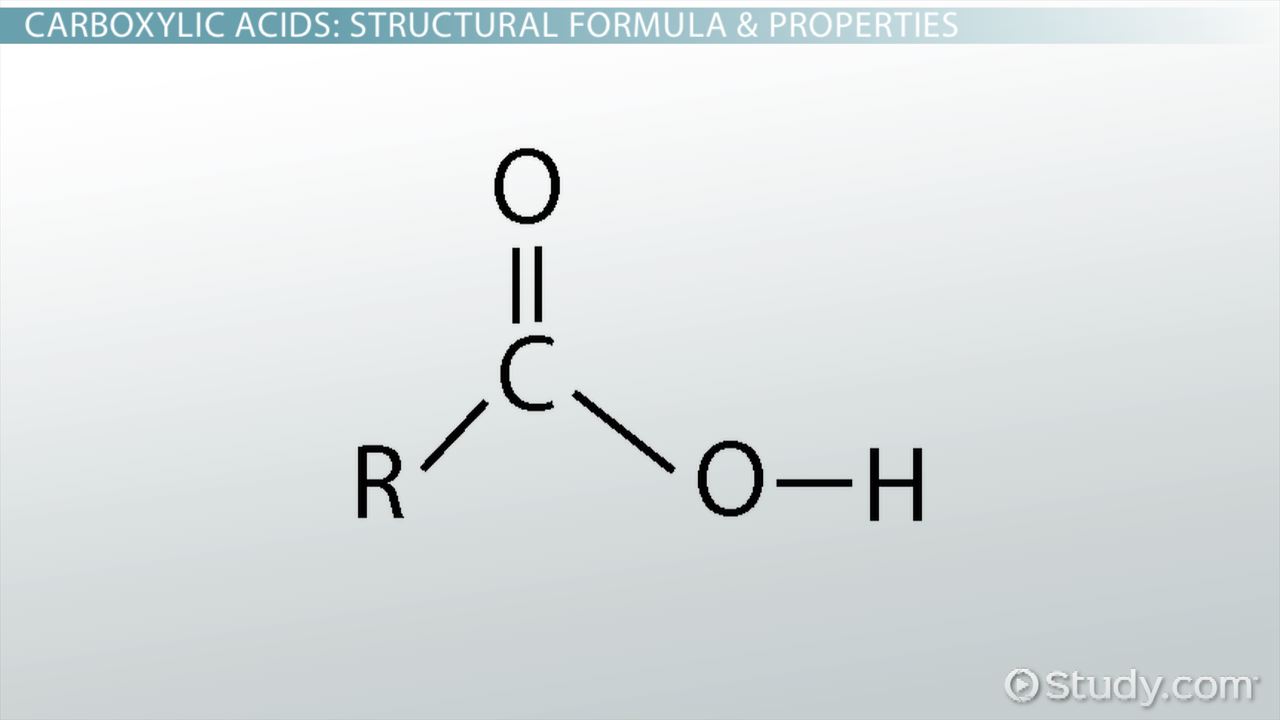
10
pKa?
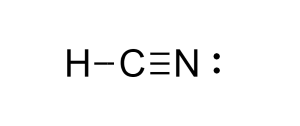
10
pKa?
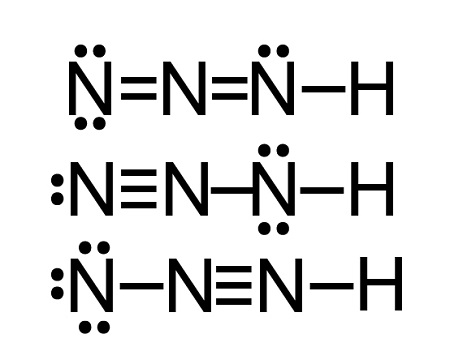
10
pKa?
10
pKa?
15
pKa?
16
pKa?
17
pKa?
18
pKa?
23
pKa?
35
pKa?
36
pKa?
36
pKa?
36
pKa?
42
pKa?
42
pKa?
50
pKa?
Isomer
Same atoms, different arrangement
resonance
Same atoms, same arrangement, different charges or bonds
Dichloromethane
CH2Cl2
Diethyl ether
Et2O
Methanol
CH3OH
Ethanol
CH3CH2OH
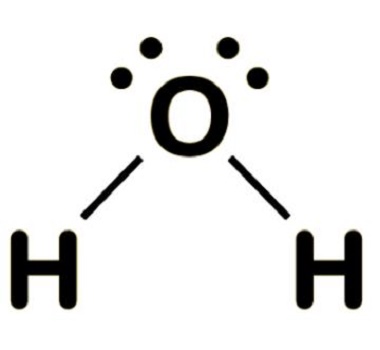
Water
H2O
Acetone
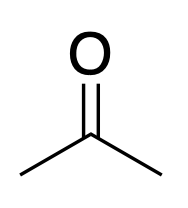
Acetonitrile
CH3CN
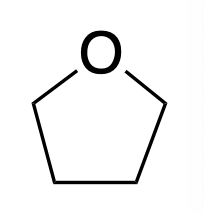
Tetrahydrofuran
THF
Dimethylformamide
DMF
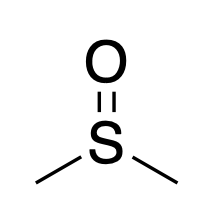
Dimethylsulfoxide
DMSO
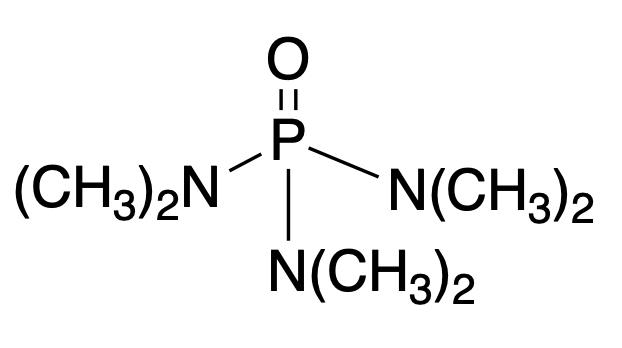
Hexamethylphosphorictriamide
HMPA
DMSO
THF
Acetonitrile
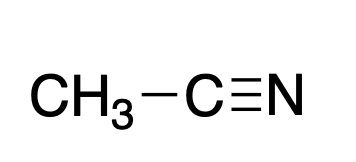
DMF
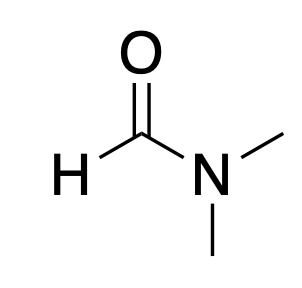
HMPA
Protic
Favors sn1, e-1 reactions, has an -OH group, unimolecular
Aprotic
Favors sn2, e-2 reactions, bimolecular
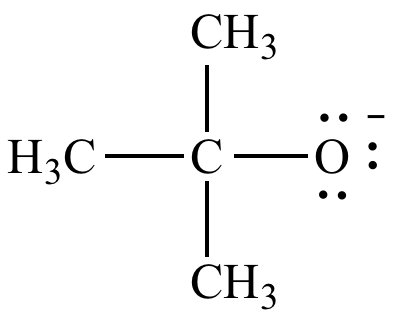
tBuO-
tert-butoxide
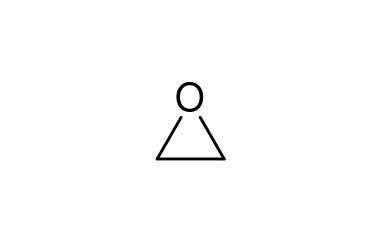
oxirane
1°
What NEVER undergo sn1 or E1 because it is too high in energy? and mostly undergo SN2
Always undergoes E2 regardless of solvent or carbon attatchments (unless primary carbon then ONLY bulky bases)
Bulky bases (and generally strong bases)
3°
NEVER undergoes Sn-2
Alkene product is monosubstituted
Sn1 is favored in protic solvents over E1 in 2° and 3° when the
alkene product is more than monosubstituted
E1 is favored in protic solvents over sn1 in 2° and 3° when
weak base
CH3CO2-
weak base
CN-
weak base
N3-
weak base
SH-
strong base
CH3O
strong base
CH3CH2O-
strong base
tBuO-
strong base
R-
strong base
NH2-
pyridine
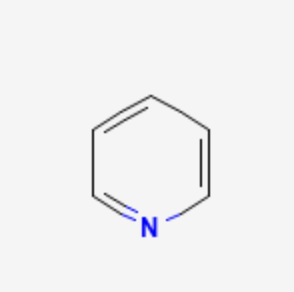
SN2
SOCl2 or PBr3 in pyridine
E2
POCL3 in pyridine