Performance Diction I--Final Exam
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Language Diction
the study of two aspects of language—articulation and pronunciation
Articulation
the process of forming or shaping the individual sounds of a language by the movements of the articulators
Pronunciation
the selection of sounds and syllabic stress
International Phonetic Alphabet “IPA”
developed by the International Phonetic Association in the late 19th century
IPA is a series of symbols that each represent a certain speech sound
the symbols are “universal,” designed to represent the same sound across all languages
Orthographic Letter
symbols we use to communicate language in written form
each individual symbol is called an orthographic letter
Orthographic Spelling
symbols we use to communicate language in written form
individual symbols combined into larger groupings are called orthographic spellings
IPA Symbol
the symbols we use to represent individual linguistic sounds
IPA Spelling
differentiated from orthographic letters and spellings by the use of square brackets
IPA symbols combined into larger groupings
IPA Transcribing
the act of changing an orthographic spelling into International Phonetic Alphabet
IPA Transcription
the product which results from the act of IPA transcribing
Phoneme
an individual speech/language sound
Syllable
a unit of spoken language that is larger than an inividual phoneme and consists of one or more sounds with or without consonants
Accent/Stress
the syllable within a word that receives more emphasis, either being louder or longer, or both
Primary Stress
the syllable within a word that receives the most emphasis
marked with an apostrophe before the syllable “‘“
Secondary Stress
the syllable within a multi-syllable word that receives the second most emphasis
marked with a comma before the syllable “,”
Penultimate
the second-to-last stressed syllable
Antepenultimate
the third-to-last
Vocal Tract
the passageways and spaces in the body which are critical to vocal action
(lungs, trachea, larynx, pharynx, nasopharynx, nasal cavity, oral cavity, articulators)
Articulators
body parts within the vocal tract which are used in the formation and articulation of speech sounds
(tongue, lips, jaw, alveolar ridge, velum)
Velum
the soft palate or the soft back part of the roof of the mouth
Hard Palate
the rigid portion of the roof of the mouth
Alveolar Ridge
the ridge on the top of the mouth behind the upper front teeth where the roofline of the mouth ascends upward
Uvula
the tissue that descends from the back edge of the velum
Vowel
a speech sound that is produced without any major interruption of the airflow through the vocal tract and can be sustained
Pure Vowel
a vowel that consists of one single sound from beginning to end
Diphthong
a vowel unit that consists of two pure vowel sounds that occur in the same syllable, flowing smoothly from one to the next
Triphthong
a vowel unit that consists of three separate vowel sounds in the same syllable, flowing smoothly from one to the next
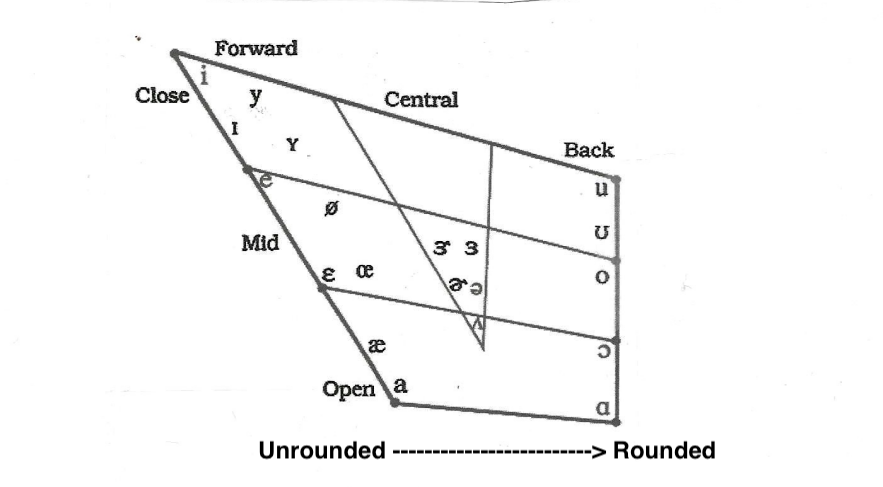
Forward Vowels
vowels produced with the highest point of the arch of the tongue forward in the mouth, near the teeth ridge of hard palate
Central Vowels
vowels which are produced with the highest point of the arch of the tongue centrally located in the mouth
Back Vowels
vowels which are produced with the highest point of the arch of the tongue toward the back of the mouth
Closed Vowels
vowels which are produced with the least amount of space between the highest point of the arch of the tongue and the roof of the mouth
Mid Vowels
vowels which are produced with a moderate amount of space between the highest point of the arch of the tongue and the roof of the mouth
Open Vowels
vowels which are produced with the most space between the highest point of the arch of the tongue and the roof of the mouth
Rounded Vowels
vowels that require the corners of the mouth to be drawn toward one another
Unrounded Vowels
vowels that require the lips to be less rounded
Vowel Diagram
a graphic which represents the positioning of the tongue for various vowels used in speech
developed by Daneil Jones in the early 20th century
Consonant
a speech sound that is produced with some type of interference or interruption of the air stream as it moves through the vocal tract
Place of Articulation
refers to the location within the vocal tract where the interruption of the airflow occurs
Manner of Articulation
refers to the method of interruption of the air flow, whether by a complete or partial interruption
Plosive (Stop-Plosive) Consonant
the airflow is completely prevented from passing through the mouth or the nose and then is released suddenly
[p b t d k g]
Fricative Consonant
the air flow is partially interrupted, producing a noisy sound and creating a quality of friction
[f v s z h ð θ ʃ ʒ]
Nasal Consonant
the vocal tract is blocked within the oral cavity and the lowered velum allows air to travel through the nasal passageway
[m n ŋ]
Lateral Consonant
the tip of the tongue lifts to touch the teeth and alveolar ridge and the breath flows past one of both sides of the tongue
[l]
Consonant Glide
characterized by movement of the articulators from one position to another, smoothly linking speech sounds
[ɹ j w hw]
Affricative Consonant
produced by a stop followed by a fricative consonant forming a single sound
[tʃ dʒ]
Voiced Consonants
pronounced with vocal fold vibration
[m n ŋ l j ɹ]
Unvoiced Consonants
produced without vocal fold vibration
[h]
Cognates
pairs of consonants that have the same manner of articulation, one being voiced and the other being unvoiced
[p b], [t d], [k g], [f v], [s z], [ʃ ʒ], [θ ð], [w hw], [tʃ dʒ]
Digraph
a combination of two or more orthographically spelled letters that represent a single sound
“th” and “ch” in english
Consonant Blends
groups of two or more consonants that appear together without a vowel in between and each of the letters makes its own sound
“bl, br, cl, cr, dr, fl, tr, tw, scr, shr, spl, mp, ft, ld, sp, lf,” etc.
Vowel Modification
a process used to aid singing efficiency, which requires a slight intentional alteration of a vowel from its most speech-like state to one that allows for a more optimal sung sound
Vowel Harmonization
a process used in singing to make slight intentional alterations in vowel sounds that are in proximity in a phrase to create a more pleasing vocal line
Consonant Assimilation
unintentional slight alterations in consonants which are caused by other consnants in proximity
Syllabification
the period between syllables of IPA transcription
Syllabification Rules
1. every syllable must have at least one vowel
2. v/cv
3. vc/cv
4. keep digraphs and consonant blends together
5. prefixes and suffixes should stay intact and kept as a whole (ex. “march/ing”)
6. silent “e” stays with preceding syllable
7. when word ends in a consonant + le pattern it forms its own syllable (ex. “mar/ble”)
[i]
tongue placement: forward & closed
pronunciation: “heat”
[Ɪ]
tongue placement: forward & close
pronunciation: “mitten”
[e]
tongue placement: forward & mid
pronunciation: “chaos”
[ɛ]
tongue placement: forward & mid
pronunciation: “met”
[æ]
tongue placement: forward & open
pronunciation: “cat”
[a]
tongue placement: forward & open
pronunciation: “a-ha!”
[u]
tongue placement: back & closed
pronunciation: “hoot”
[ʊ]
tongue placement: back & closed
pronunciation: “book”
[o]
tongue placement: back & mid
pronunciation: “obey”
[ɔ]
tongue placement: back & open
pronunciation: “only”
[ɑ]
tongue placement: back & open
pronunciation: “father”
[ʌ]
tongue placement: central & open
pronunciation: “up”
[ə]
tongue placement: central & mid
pronunciation: “around”
[ɝ]
tongue placement: central & mid
pronunciation: “heard”
[ɚ]
tongue placement: central & mid
pronunciation: “inner”
[p]
place of articulation: lips
pronunciation: “pepper”
[b]
place of articulation: lips
pronunciation: “baby”
[t]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “test”
[d]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “dark”
[k]
place of articulation: tongue & velum
pronunciation: “crank”
[g]
place of articulation: tongue & velum
pronunciation: “grand”
[tʃ]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “church”
[dʒ]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “judge”
[f]
place of articulation: teeth & lips
pronunciation: “fruit”
[v]
place of articulation: teeth & lips
pronunciation: “vase”
[θ]
place of articulation: tongue & teeth
pronunciation: “north”
[ð]
place of articulation: tongue & teeth
pronunciation: “these”
[s]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “source”
[z]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “xylophone”
[ʃ]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “shirt”
[ʒ]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “azure”
[h]
place of articulation: glottis/larynx
pronunciation: “house”
[m]
place of articulation: lips
pronunciation: “make”
[n]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “nonsense”
[ŋ]
place of articulation: tongue & velum
pronunciation: “song”
[l]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “lemon”
[hw]
place of articulation: lips
pronunciation: “where”
[w]
place of articulation: lips
pronunciation: “wobble”
[ɹ]
place of articulation: tongue & velum
pronunciation: “more”
[j]
place of articulation: tongue & alveolar ridge
pronunciation: “year”
[ɛ:i]
pronunciation: “late”
[o:ʊ]
pronunciation: “boat”
[a:Ɪ]
pronunciation: “might”
[a:ʊ]
pronunciation: “hound”
[ɔ:Ɪ]
pronunciation: “alloy”