quiz number 2 micro
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Coccus/cocci
round

Bacillus/Bacilli
rods
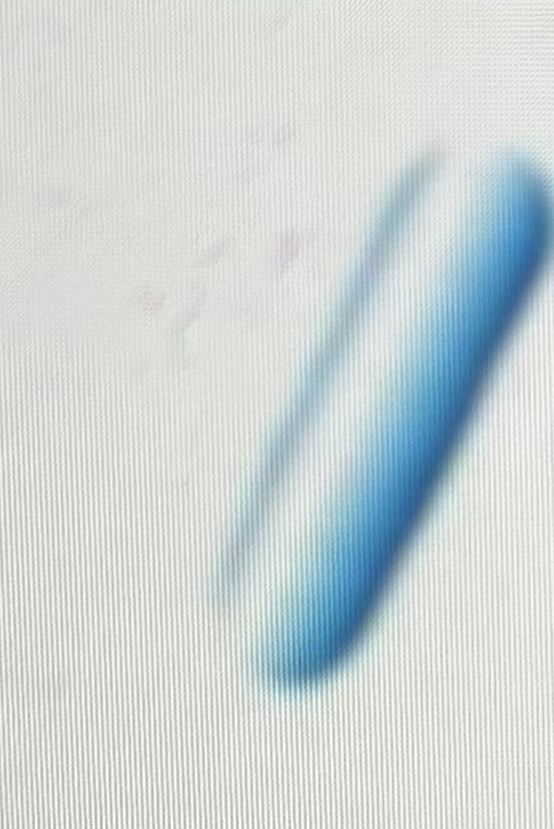
Vibrio
curved rods (like comma or lima bean)
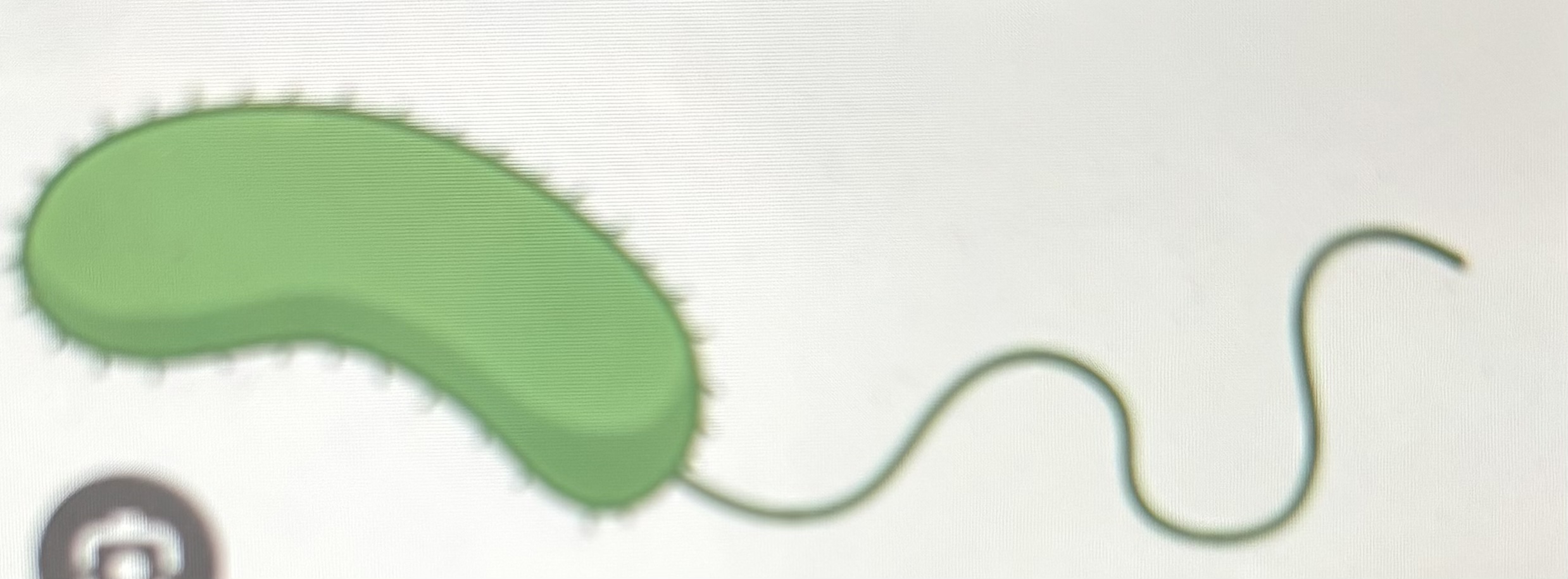
spirillum/spirilla
spirals

Spirochete
flexible spirals

single cells
photo
diplo
pairs of cells,

strepto
chain of cells,

tetrad
group of 4 cocci
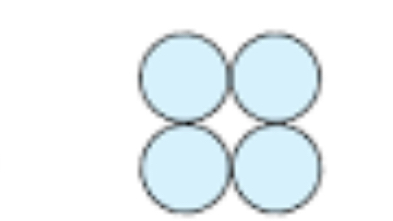
sarcina
cube of cocci
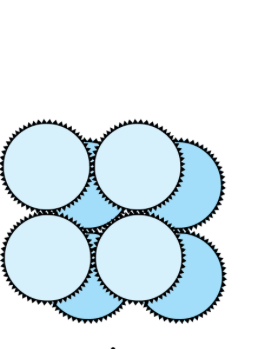
staphylo
clusters of cocci
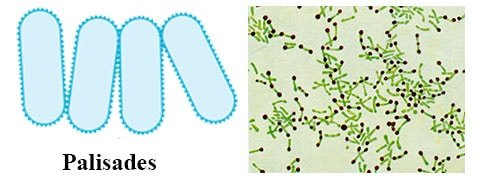
palisade/angular
bacilli side by side like a picket fence
o Know the steps in creating a bacterial smear for bacteria on solid medium:
§ Add a small drop of water onto a slide
§ Sterilize inoculating loop and let cool for at least 10 seconds
§ Touch inoculating loop to one colony to remove a very small amount of bacteria
§ Using the inoculating loop, mix the bacteria into the drop of water on your slide and spread the water/bacteria mix out into a thin layer/film
§ Allow the slide to air dry. This can be on the slide warmer.
§ Once the slide is dry, your bacterial smear is ready to be heat-fixed.
functions of heat fixing:
§ Kills bacteria
§ Causes cells to stick to the slide
§ Causes cytoplasmic proteins to coagulate = denser cell contents so more visible
o Know how to heat fix a slide using a Bunsen burner and a microincinerator
§ Bunsen burner: Pass slide quickly through tip of inner flame 2 to 3 times
§ Microincinerator: Hold smear in front of the opening of the microincinerator for about 5 seconds
o Know how to sterilize an inoculating loop using a Bunsen burner:
§ Hold loop at 60 degree angle
§ Slowly pass loop through the tip of the inner cone of the flame, starting at the base of the wire and moving to the loop until each part becomes orangish-red
o Know how to sterilize an inoculating loop using a microincinerator
§ Insert loop and wire into pre-heated microincinerator for 10 seconds and then remove
o Allow inoculating loop to cool for 10-20 seconds after sterilizing before touching bacteria
§ If you hear a sizzling sound, the loop was not cool enough and most likely killed your cells.
Chromogen
o colored molecule that is dissolved in a solvent to make a stain
Chromophore
portion of chromogen that gives color
Auxochrome
portion of chromogen that is charged and allows chromogen to interact with cell
o Basic stain
§ Positively charged (cationic)
§ Positive charge is attracted to negative charge of cell wall, cell membrane, and DNA
§ Stains cells so is more commonly used
§ Examples: Methylene blue, Crystal violet, Safranin, Malachite green
Acidic stain
§ Negatively charged (anionic)
§ Negative charge is repelled by negative charge on surface of cells
§ Stains background but not cells
§ Useful for cells that distort when heat-fixed (since no heat-fixing is required) and to see capsules around cells
§ Examples: Nigrosin, Eosin
o Know the basic procedure for staining cells using a basic stain
create a thin smear of cells on a slide, heat-fix it to the slide, and then apply the basic dye (like crystal violet or methylene blue), allowing it to bind to the negatively charged bacterial cells