MOD 9 - Exposure and IQ in DR
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Contrast Resolution
the ability of the imaging system to express slight attenuation differences (brightness) between similar adjacent tissues
High contrast resolution
images will have sharp differences between structures but not be able to differentiate similar attenuating tissues (such as muscle, water and fat imaged together)
smaller grey scale
Low contrast resolution
images will have dull differences between structures but better at defining these similarly attenuating tissues
extensive grey shades
Spatial Resolution
the measure of a system's ability to accurately demonstrate small objects as distinct, often considered high detail or high resolution
Spatial Resolution is dependent on
the fixed spatial resolution determined by the detector element size
Method of Spatial Resolution Measurement
Line Pair Testing and Spatial frequency (determined from pixel pitch)
Modulation Transfer Function (MTF)
Spatial Frequency
tests the system's ability to distinguish adjacent small objects as separate using the 'line pair' test tool that contains pairs of thin wires with increasing narrow spaces between the lines
spatial frequency =
line pair = defined as both the solid line and the adjacent space
higher spatial frequency =
higher spatial resolution
higher spatial frequency of the anatomy
smaller in size = more difficult to image
Modulation Transfer Function (MTF)
the ability of a system to accurately demonstrate small objects accurately
most common method of describing spatial resolution
MTF range and meaning
MTF range = 0-1
0 = the object is not represented at all
1 = ideal, system expresses very small objects exactly as they exist
lower MTF =
high spatial frequency objects = harder to image and thus look blurrier
can MTF be 1
No, MTF can never be 1 in diagnostic imaging due to a variety of geometric factors and detector element size limitations
Image Noise
a blanket title that defines all destructive data being included in an image
Electronic Noise (dark current noise)
inherent noise in digital imaging systems due to the use of electrical devices
Quantum Mottle
another form of image noise, that is directly related to dose and receptor exposure
Quantum Mottle in images and dependent on what
shown as brightness fluctuations and is photon-dependent
quantum mottle with low exposure
incident beam lacks sufficient energy = high absorption (photoelectric effect) → insufficient beam transmission = increased noise and patient dose
signal-to-noise ratio
ratio of useful diagnostic image and noise
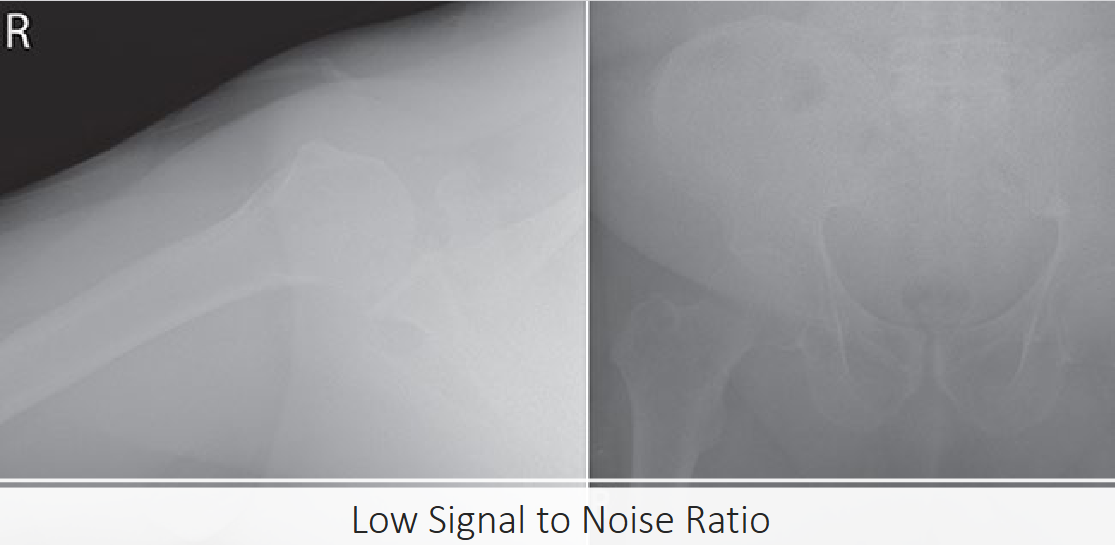
low-signal-to-noise ratio
noisy images that are produced when the detector pixels do not receive sufficient signal to produce an accurate sample
Dynamic Range
DR system's wide grey scale to express its deep contrast resolution
Exposure Latitude
a DR algorithm which is associated with a histogram of ideal exposure intensities that during processing can correct a wide variation in actual exposure
Exposure Latitude cannot “fix“
excessive noise caused by quantum mottle
Detector Saturation
when the detector elements are flooded with transmitted photons (high exposure) and the differential attenuation required for radiographic is lost
Detective Quantum Efficiency (DQE)
represents the detector absorption efficiency for a wide range of photon energies
DQE is dependent on
detector materials and design
DQE and kV
increased kV = low DQE that requires the extra kV to produce a good image
high DQE =
fewer x-ray photons are required to produce an image
which material provides the highest DQE
amorphous selenium (a-Se)
Windowing
a post-processing function which allows the viewer to alter the grayscale display to improve visualization of different densities