2- Auxiliary Retention Systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what are auxillary retention systems?
elements that provide retention to the restoration
they retaina core in a tooth with loss of coronal structure
What are the types of auxiliary retention systems?
Pins- vital
Posts- non vital
what are pins?
Small metal rod driven into dentin on one side, other is embedded in sealing material to aid retention
When is the use of pins indicated?
significant loss of coronal structure due to caries or trauma
when preparation design alone doesnt provide enough retention
always in dentin, never enamel or pulp
Vital teeth
When is the use of pins not indicated?
For restoring teeth with severe malocclusion
If direct resto not possible due to anatomy or functional considerations
What should we evaluate on the periapical x ray to correctly place the pins?
location of position and size of the pulp chamber
thickness of dentin
inclination of crown axis relative to root axis and adjacent tooth
What should we evaluate on the location of pins to correctly place the pins?
place midway between pulp and tooth surface
keep 2mm away from pulp and periodontium
at cervical third of molars and premolars
as close as possible to line angles
0.5mm away from axial or vertical wall cavity
on flat surfaces
which areas should we not interfere with when inserting pins?
cavity walls or matrix
pulp chamber
isthmus
furcation areas
small amounts of dentin
mesiofacial corners of molars
222 rule
length of pin inside dentin and remains outside should be 2mm- if not- fractures or disinserts pin
what are disadvantages of pins?
doesn’t increase the strength of restorative materials- may even decrease- induces stress- cracks, microleakage, pulpal damage
external or pulpal perforation
perforation in periodontium
chance of microleakage
looseness in duct- due to drill defects
fracture of drill
what are posts?
only placed in teeth that have RCT with large portions of tooth missing- one part inside canal other protrudes into crown
what procedural accidents may occur during the post space preparation?
strip perforation- in apical portion of root
increased risk of root fracture if oversized channel
how are posts classified? (5) according to…
modulus of elasticity
technique of clinical use
manufacturing method
its shape
composition
How are posts classified according to the modulus of elasticity?
Higher MOE- rigid- e.g metallic and ceramic
Lower- flexible- fiberglass and carbon fiber- MOE similar to dentin- this avoids stress and root fractures

How is force distributed in posts with different modulus of elasticity?
When materials with different mechanical properties are combined
Stresses concentrate in the weaker one at the root apex- causes fracture
If both have similar elasticity- act as a monoblock- distributing forces evenly
In what 3 techniques are posts used?
Direct- ready made in diff sizes, shapes and compositions
Indirect- made in lab using impression of root canal
Semi direct- mix impression of root canal and prefabricated fiber post and composite
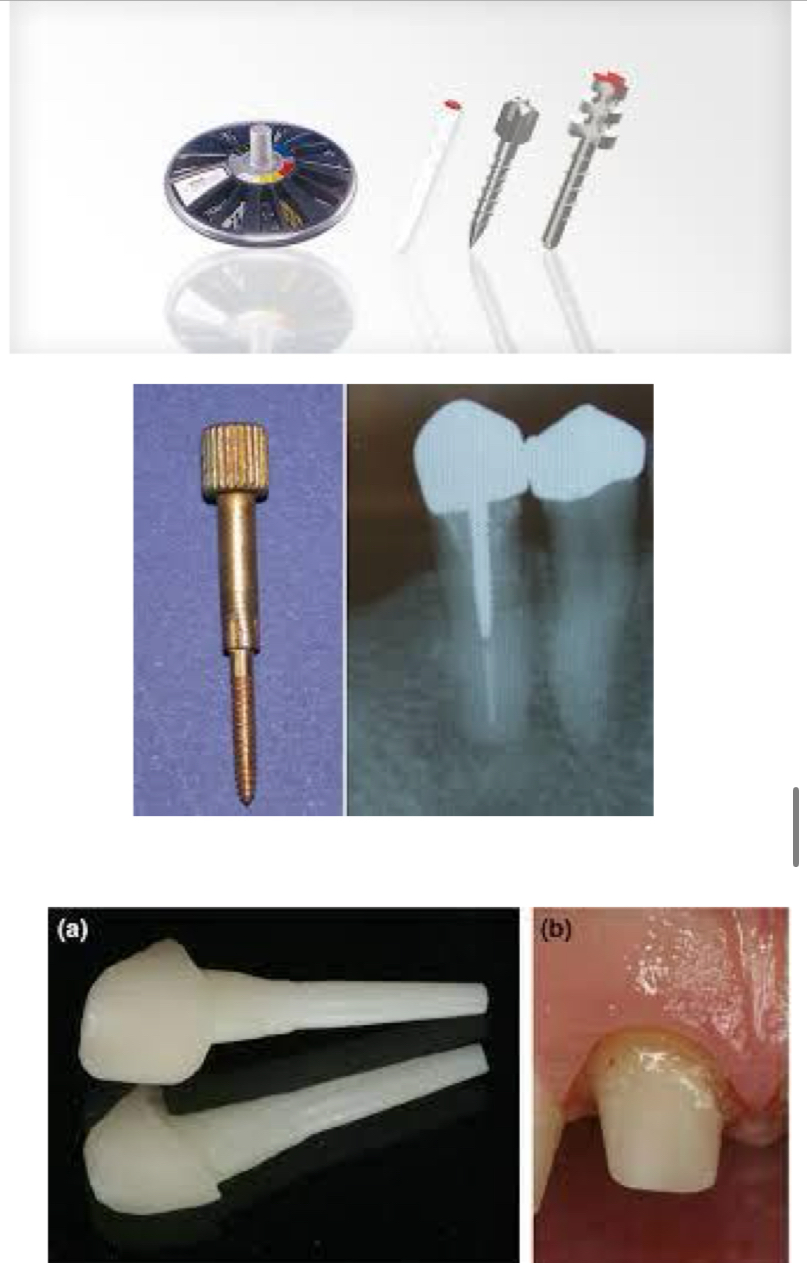
What is an emdocrown?
Type of crown designed for a tooth that’s undergone RCT or has significant structure loss
endocrowns are anchored within tooth structure extends in pulp chamber for stability
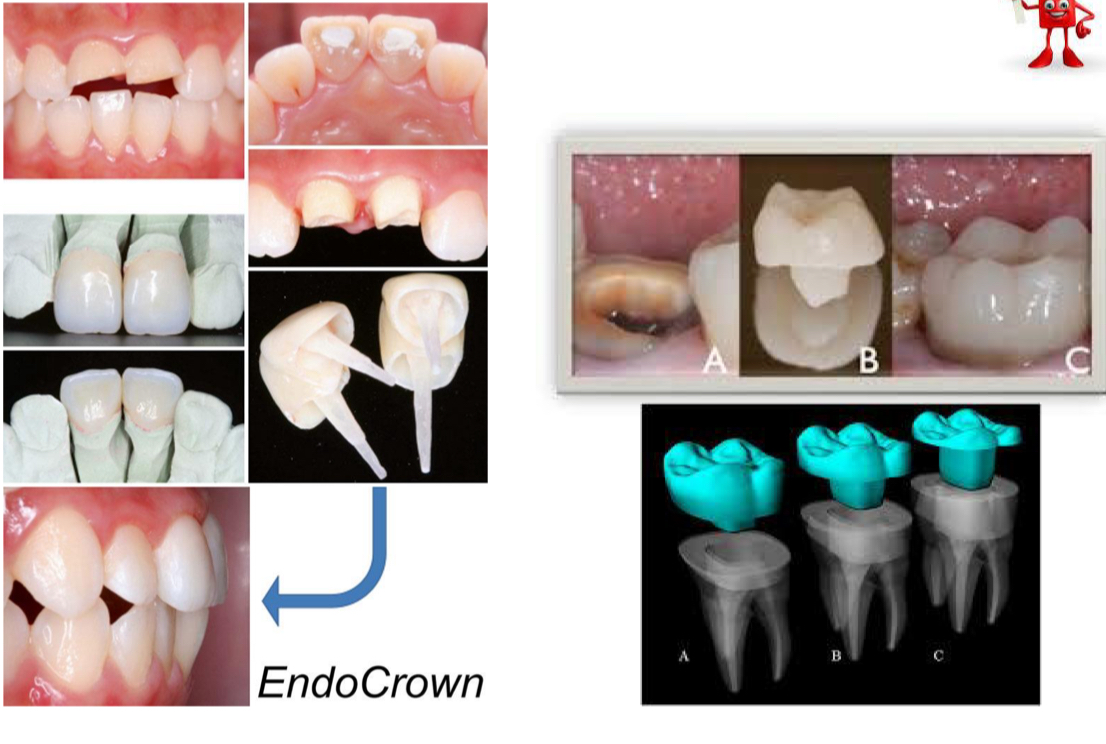
How are posts classified by shape?
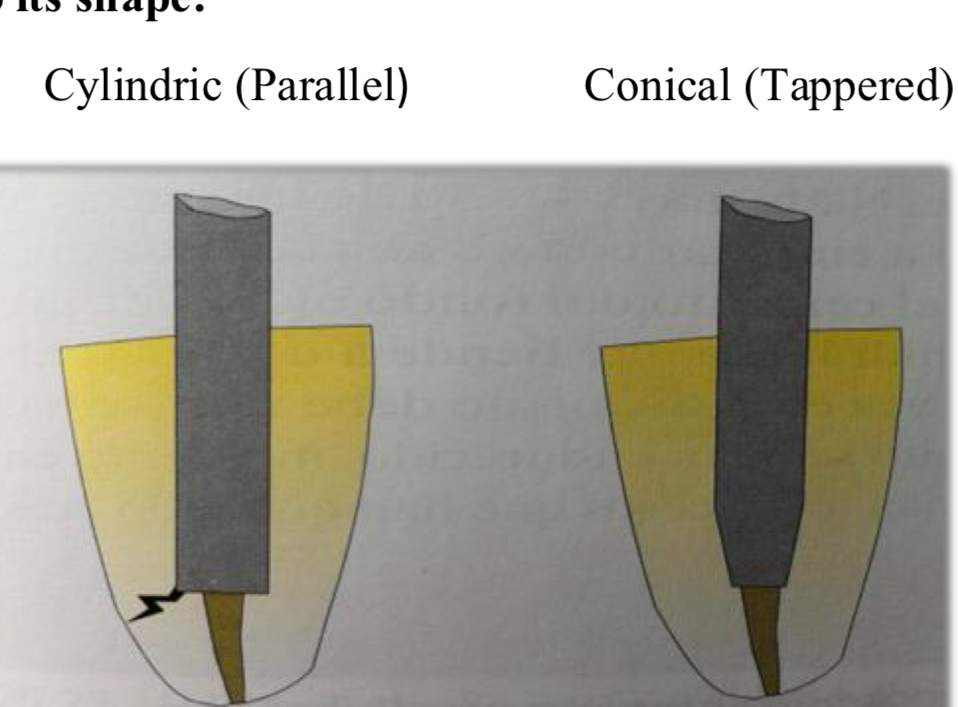
Conical (tapered)- less retentive than cylindrical but more anatomical in apical zone- don’t thin in roots
Cylindrical (parallel)- good retention but need to prep apical zone of canal for adaptation- risk of fractures and perforation
Double taper- more ret than conical, has 3 parts- coronal- cylindrical so retains filling material, middle- conical, has taper, apical- minor taper- usually made of quartz fiber

What are accessories?
Bundled glass fiber reinforced composite
Many fine individual posts 0.3mm diameter
Remove sleeve- fibers spread inside the root canal, adapting to its exact shape- translucent so aesthetic
How can posts be classified according to its composition?
Metallic
Ceramic
Carbon fibre
Glass fibre- 42% longitudinal glass fiber, 29% epoxy resin, 29% inorganic particles, can either transmit lighti or not
What are morphological requirements to place a post?
No cavities, fractures or resorption
Enough length and thickness
Straight root, round wide canal
In multi radicular teeth- choose thickest, longest most straight root
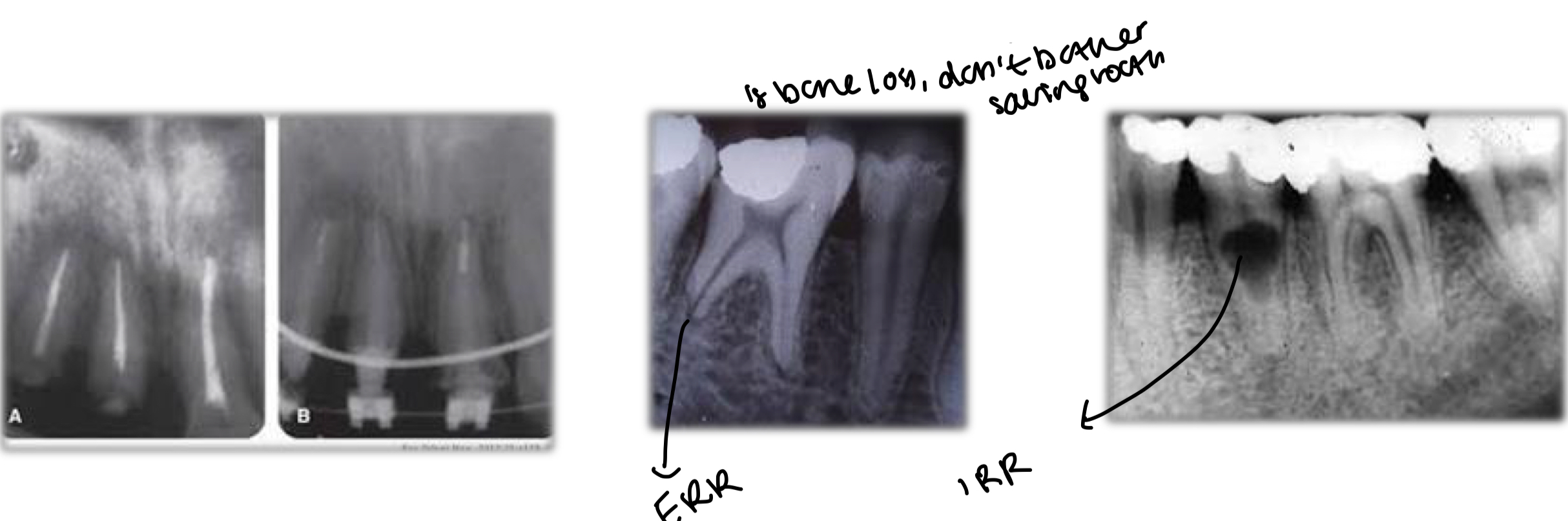
In which root should posts be placed?
Upper molars- palatine
Lower molar- distal
Upper premolar- palatine
Lower premolar- single
What are the clinical requirements to place a post?
X ray
Correct RCT
Good apical sealing
No radiolucent lesions
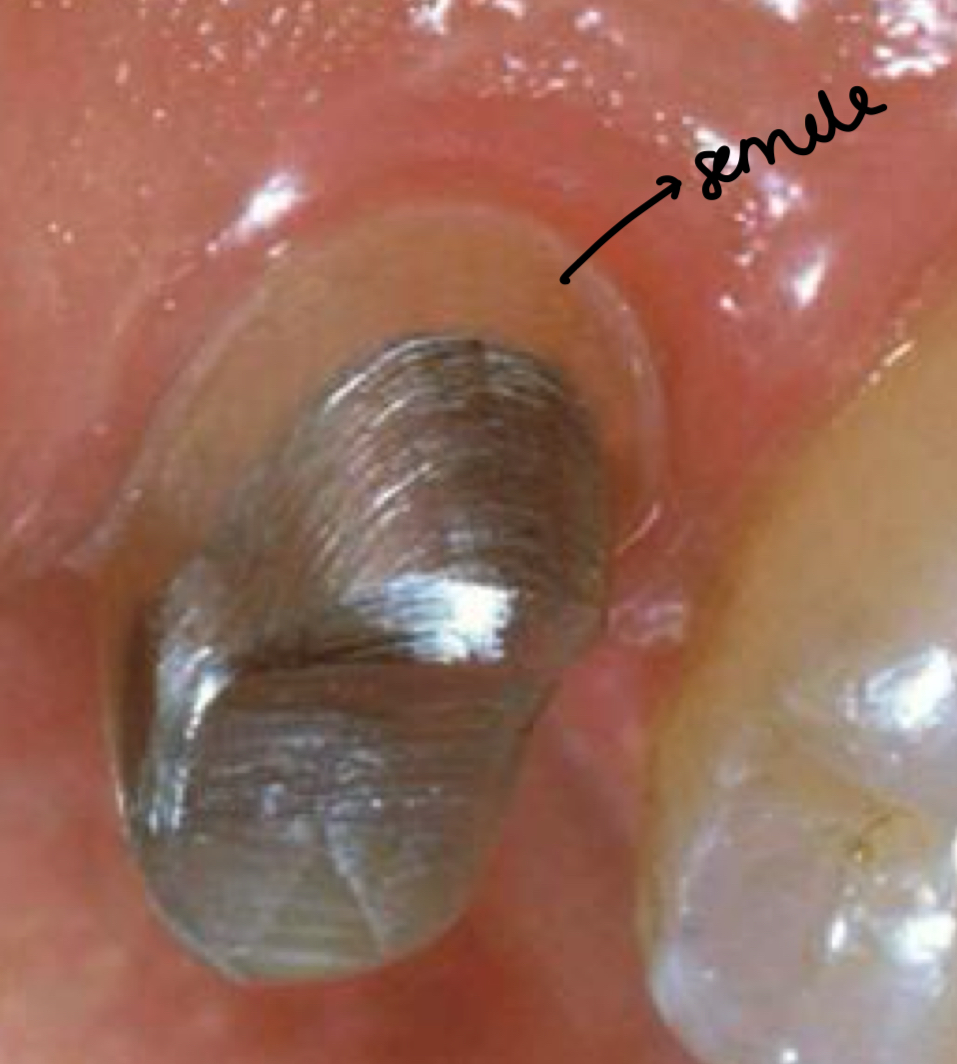
2mm of supragingival ferrule
If bone crest is below post due to bone loss- no resto
What are the requirement of the post length in order to place a post?
Post enters up to 2/3 of root, leaves 4mm to apex, 2mm to dentin wall
Longer post- greater retention
Length equal or more than clinical crown
In periodontal teeth- length=half length of root surrounded by bone
How do you place a direct prefabricated glass fibre post?
X ray, clinical eval, isolation- only use rubber dam when inserting post not when removing gap to avoid perforations
Post space preparation- create a correct entry, then use Gates-Glidden drills #2, #3 to remove GP, drill corresponding to the chosen post size, insert post, adjust and cut to desired length
Surface treatment of post and canal with acid etch and alcohol
Dual adhesive system inside canal
Apply fluid composite and place post, polymerise
Manufacture cure with same composite or hybrid
What are the challenges when a direct fibreglass post bonds to root dentin?
Limited vision and access
Residual GP
Hard to apply and cure adhesives in root canal
Hard to rinse etchings
Solvent may not completely evaporate