Nucleotide Metabolism - Lecture 4
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Catabolism
set of reactions by which simple molecules (biomolecules or monomers) undergo combustion to generate energy
Metabolic pathways
these pathways are both interdependent and tightly regulated
Metabolic pathways - shared intermediates
many of these among many pathways
Metabolic pathways - distinct regulatory enzymes
these enzyme(s) are used for each metabolic pathway
intermediates for cellular respiration
majority of pathways generate these for cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
series of metabolic pathways that convert carbon fuels into CO2 and H2O to generate energy
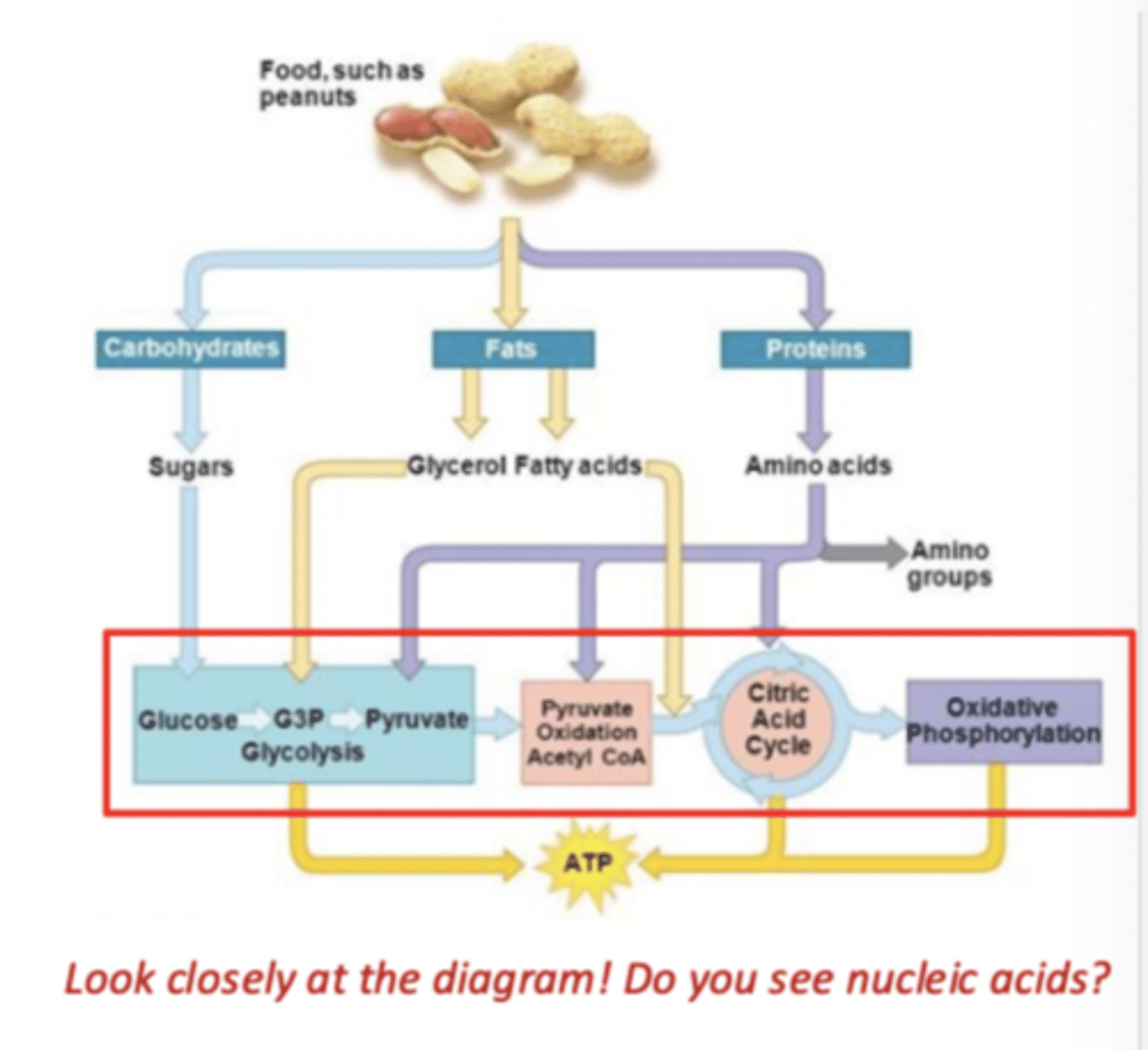
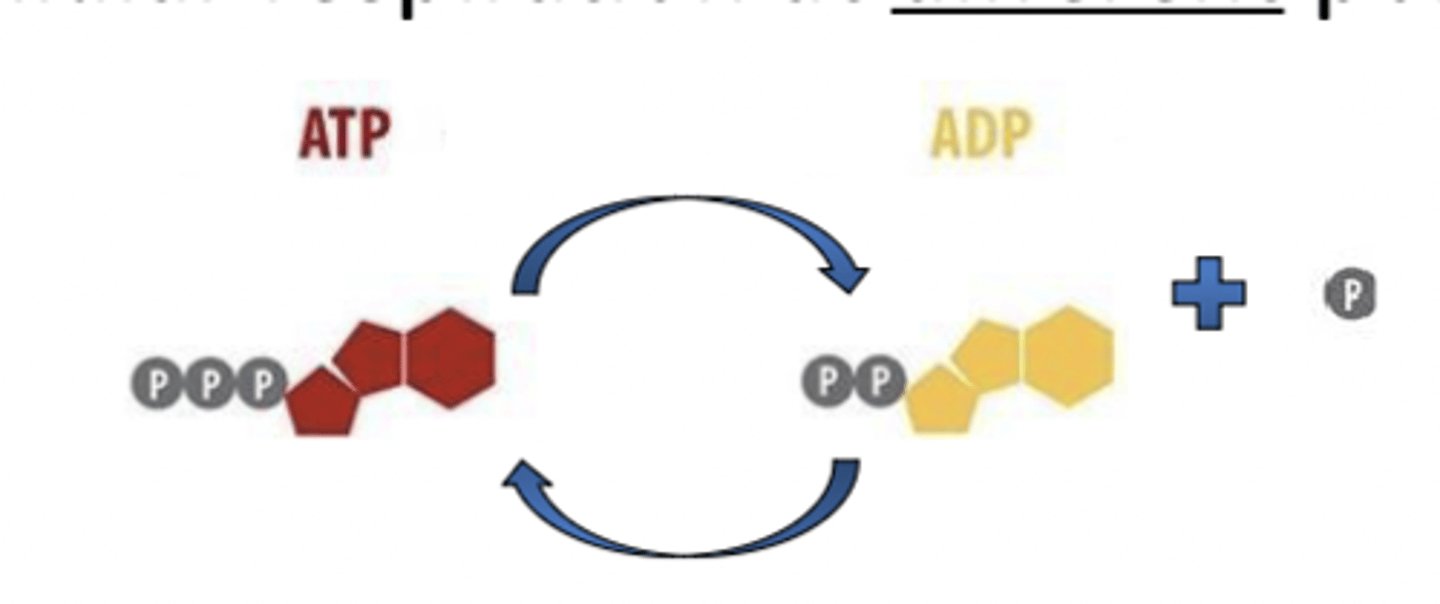
Cellular respiration - ATP
Energy used from carbon fuels to power ___ regeneration
Cellular respiration - biomolecule monomers
biomolecule ________ (or components) enter cellular respiration at different points
Where Nitrogenous Base Metabolism Occurs
occurs within liver mitochondria
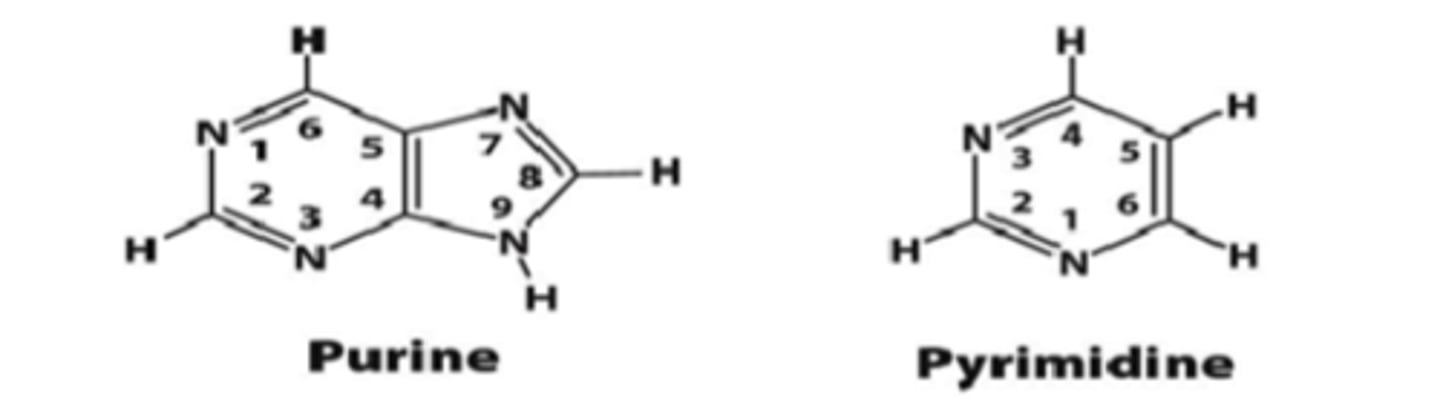
Nitrogenous Base Metabolism
pathway differs depending on the type of nitrogenous base (purine or pyrimidine)
Nitrogenous Base Metabolism - urine
final products from either pathway can be excreted from body into _____
Nitrogenous Base Metabolism Pyrimidine Four steps
Deamination
Dehydration
Hydraulic ring opening
Hydrolysis
Schematic of the pyrimidine pathway!
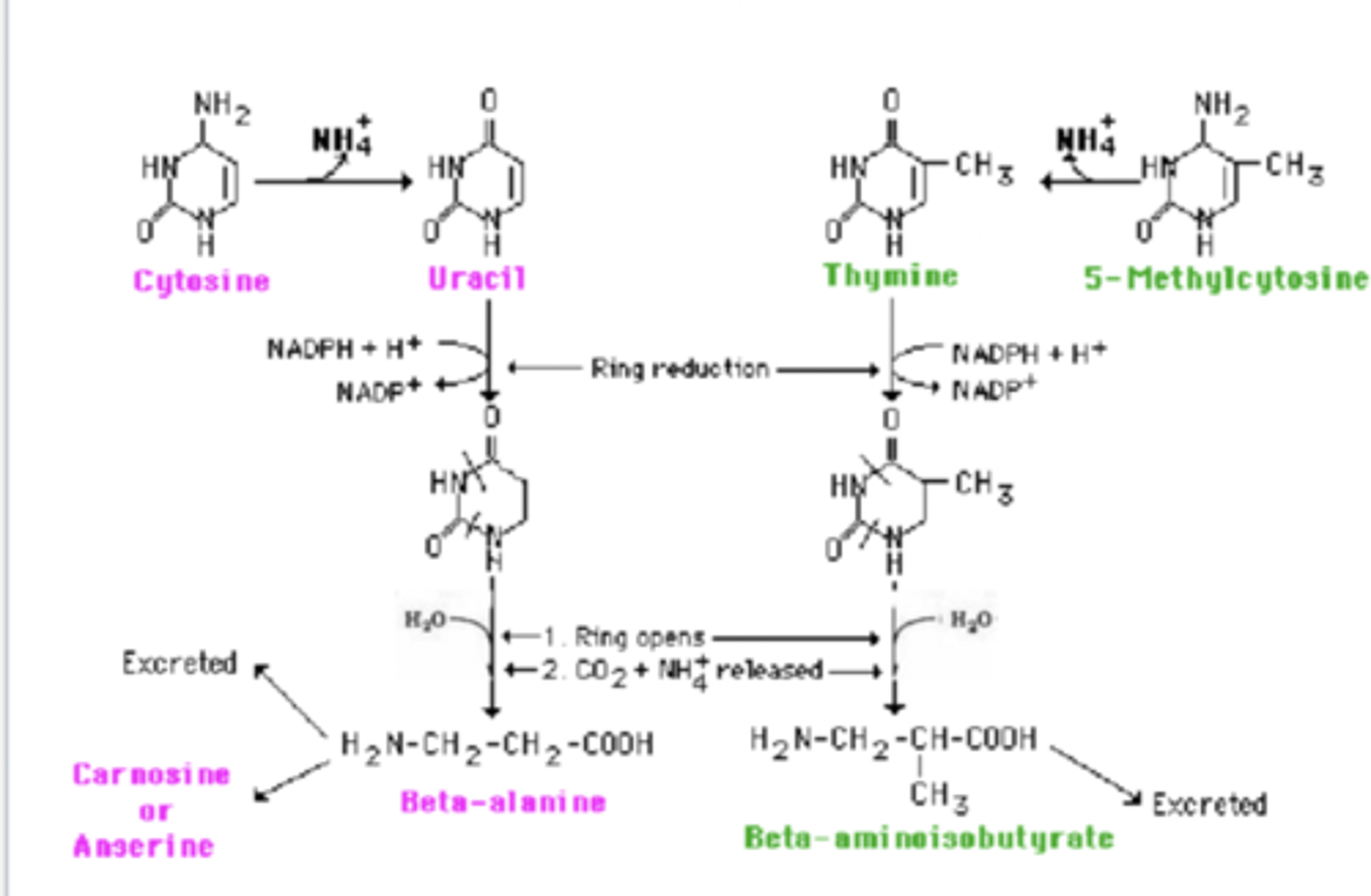
What happens to B-alanine
converted into malonyl CoA or excreted into urine
can also be converted to acetyl CoA for citric acid cycle
malonyl CoA
an intermediate of fatty acid synthesis
What happens to Β-aminoiosbutyrate
converted into succinyl CoA or excreted in urine
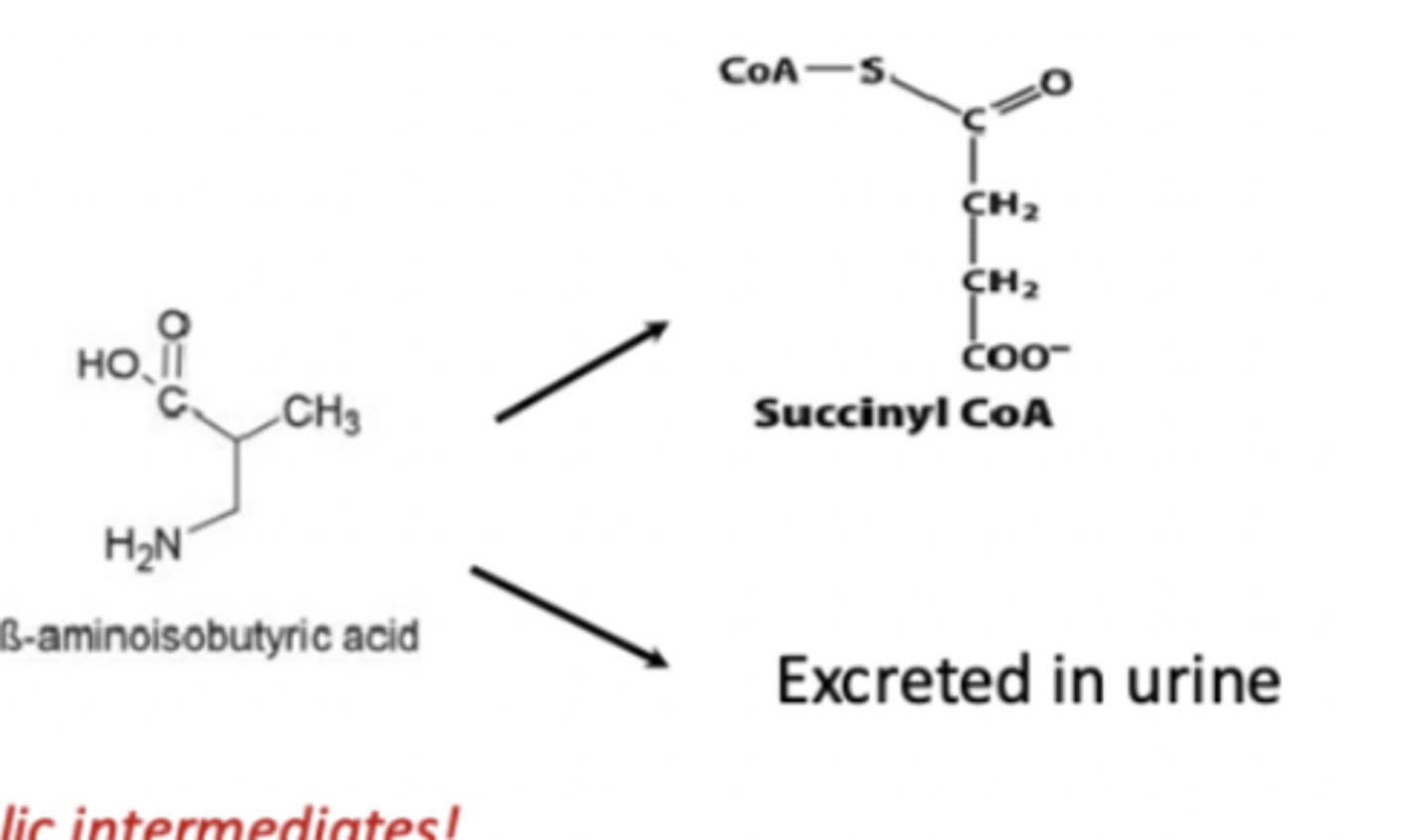
Succinyl CoA
intermediate of the citric acid cycle
Acetyl CoA and succinyl CoA
both major metabolic intermediates
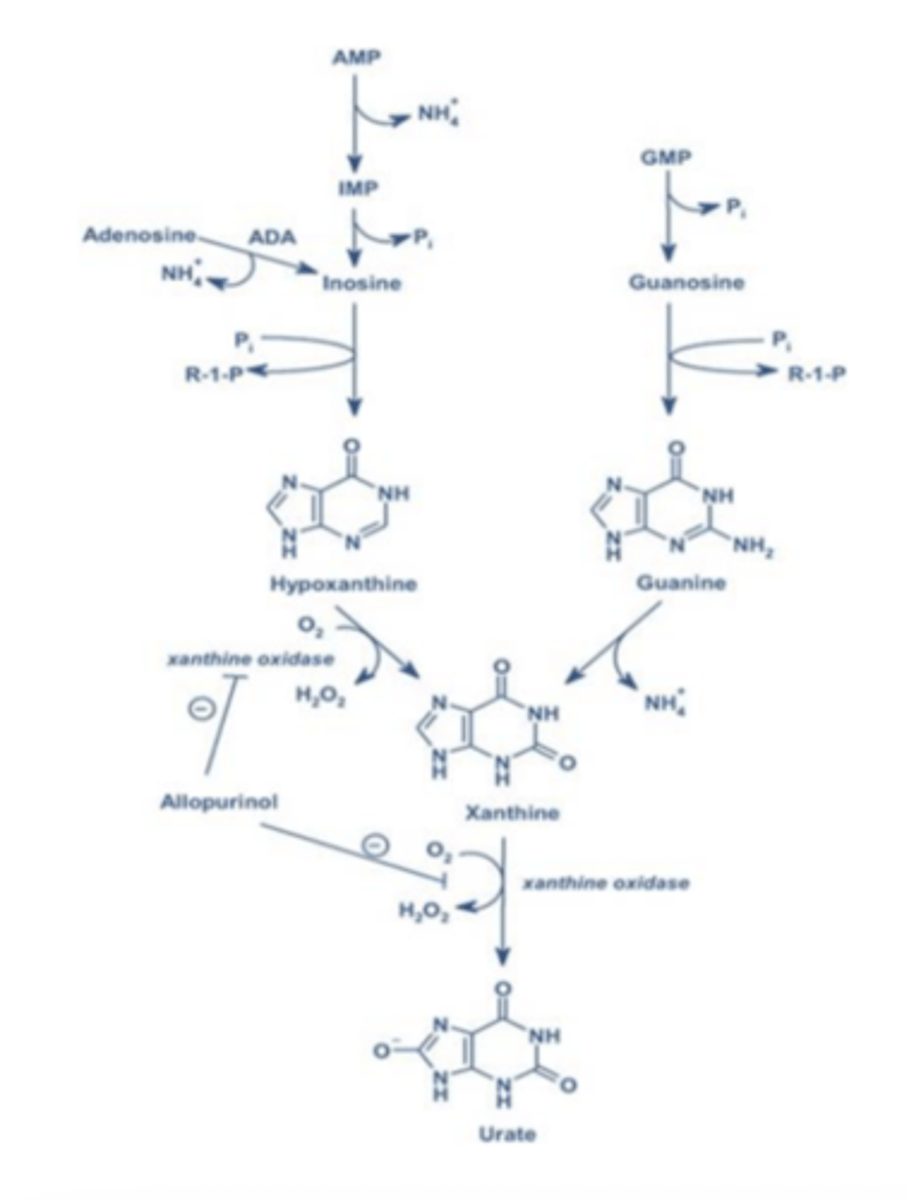
Steps of Nitrogenous Base Metabolism: Purines
1. Deamination
2. Inosine cleavage
3. Oxidation
Schematic pathway of purine catabolic pathway
Uric acid destination
this acid is sent to kidneys via bloodstream, then excreted in urine
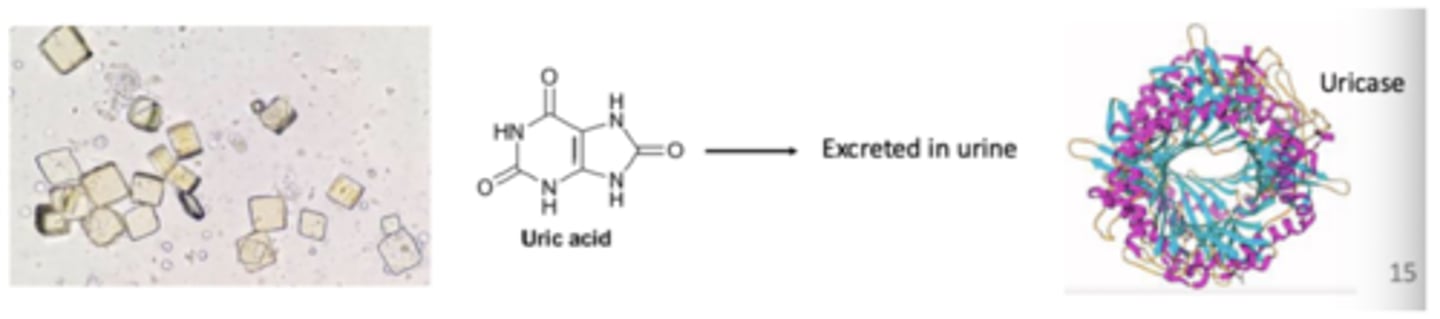
Normal plasma levels
between 2.4 and 7 mg/dL
- if higher, crystallized and precipitates out, depositing into joints
Allantoin
most animals oxidize uric acid into _________ - improves stability
Regulation of nitrogenous base metabolism
impacted by nitrogen availability; sensing glutamate and glutamine
Regulation of nitrogenous base metabolism - Rate limiting enzynme
primarily controls the pathway of nitrogenous base metabolism
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase
Rate limiting enzyme for pyrimidine
- transcription factor p53 suppresses gene expression
Xanthine Oxidase
rate limiting enzyme for purines
- transcription factor ModE suppresses gene expression (purine analogs)
Purine analogs (like allopurinol)
prescribed to control enzyme activity
If ribose, enters pentose phosphate pathway as ribose 5-phosphate
Generates intermediates for glycolysis or gluconeogenesis
Reactions parts of the pathways non-oxidative phase
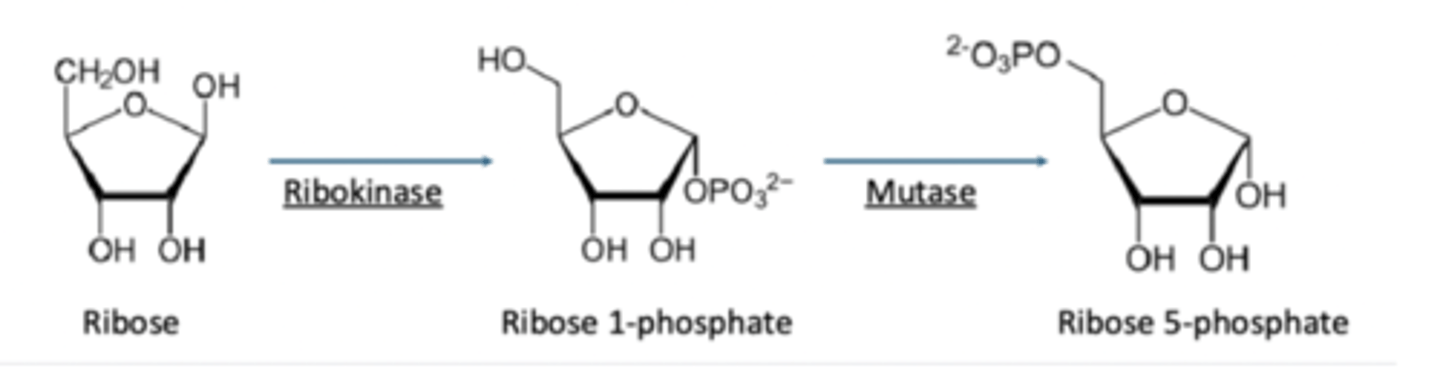
Pentose phosphate pathway
Important set of reaction that generates NADH and pentoses
- links glycolysis (and cellular respiration) with nucleotide synthesis
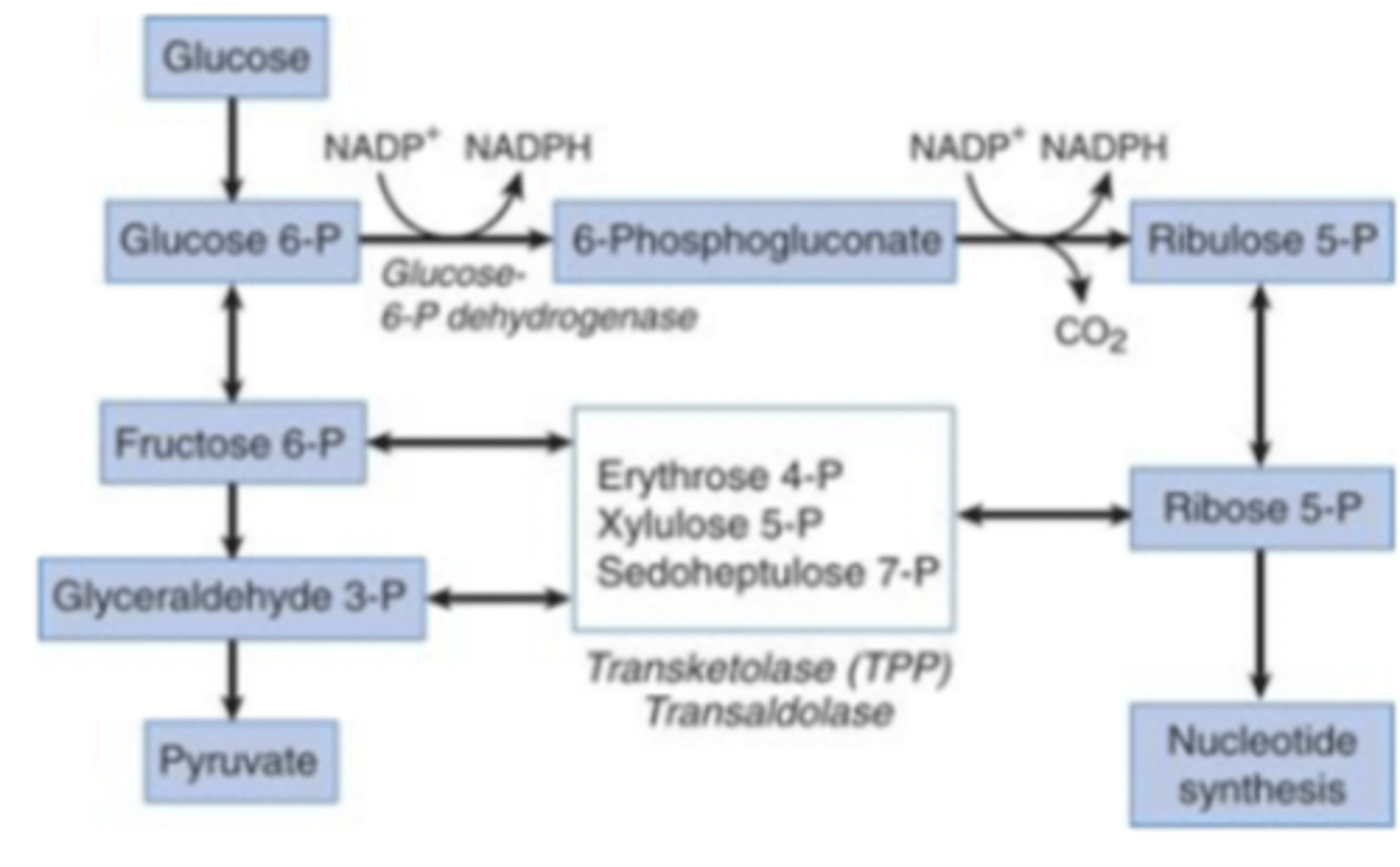
NADPH
coenzyme with reducing power; can chemically reduce other molecules)
Where the pentose phosphate pathway operates
operates in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Highest activity of pentose phosphate pathway in human
highest activity of this pathway in humans is in the liver, adipose tissue, and red blood cells
Why pentose phosphate pathway unusual
This pathway is unusual because no ATP is produced or used
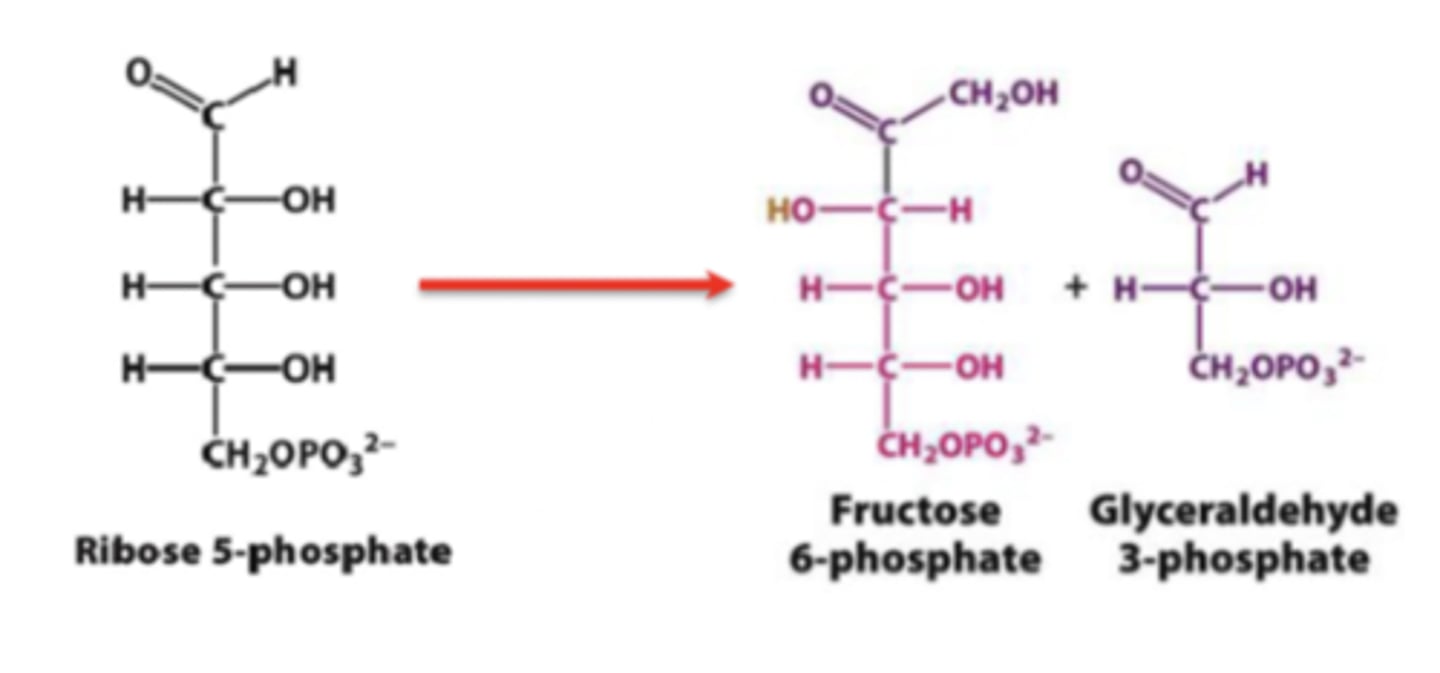
How nucleotide sugar is metabolized
During nonoxidative phase, ribose 5-phosphate converted into fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
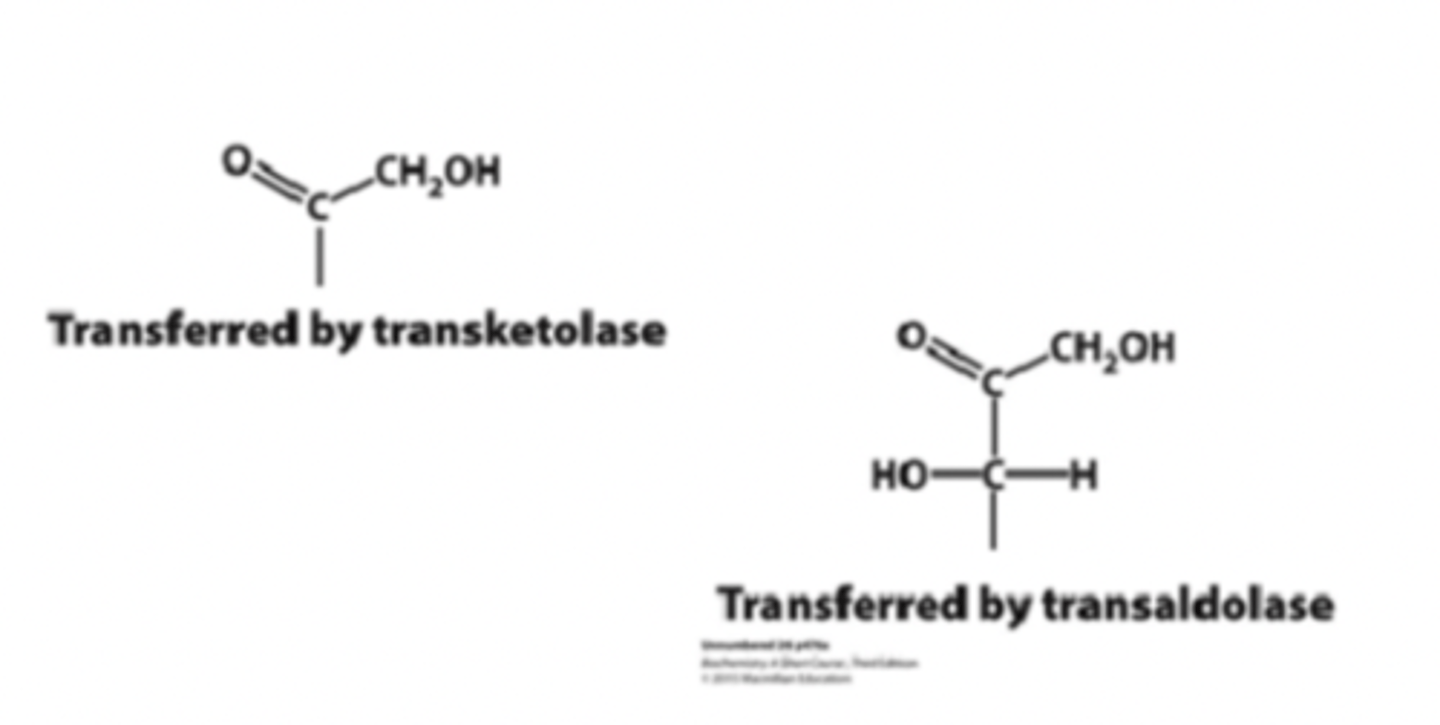
Enzymes Transketolase and transaldolase
two enzymes required for metabolism of nucleotide sugar
Metabolism of nucleotide sugar products
products of this metabolism directed into glycolysis (generates ATP) or gluconeogenesis (generates glucose), depending on the cells needs
Deoxyribose metabolism
sugar cleaved by deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase (DERA)
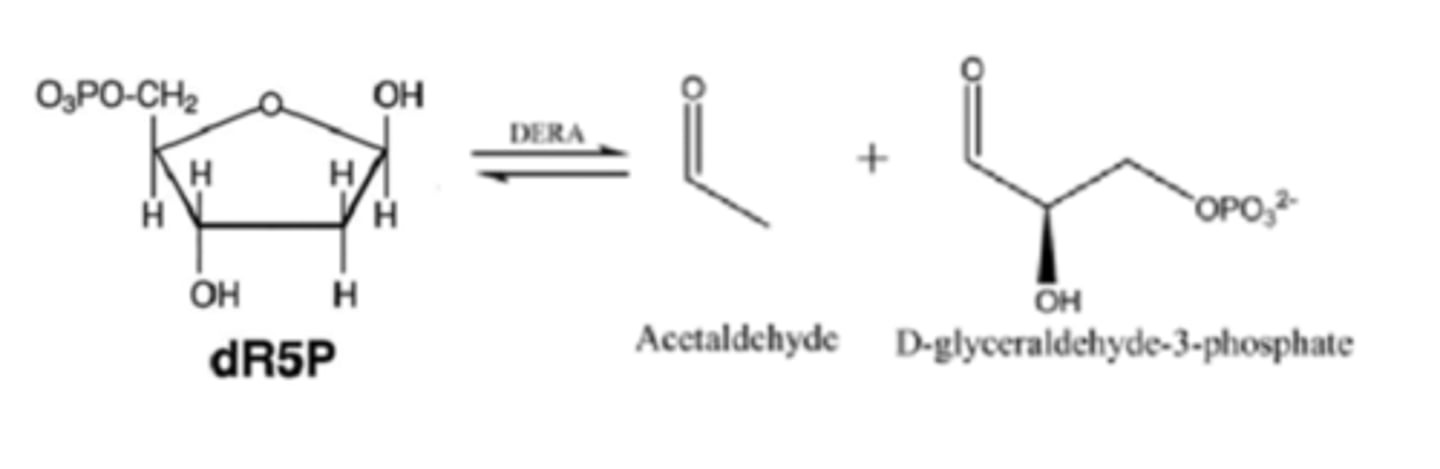
What deoxyribose metabolism produces
generates acetaldehyde and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
acetaldehyde and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
intermediates of alcoholic fermentation and glycolysis, respectively
Where deoxyribose-phosphate aldolase (DERA) enzyme is in humans
this enzyme in humans is mainly expressed in the liver, lungs, and colon