Chapter 1 Physical Quantities, Units and Measurements
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Value of Physical Quantities
Quantity = Numerical Magnitude + Unit
7 Base Units
Length, Mass, Time, Electric Current, Thermodynamic Temperature, Luminous Intensity, Amount of Substance
Length
metre (m)
Mass
kilogram (kg)
Time
second (s)
Electric Current
ampere (A)
Thermodynamic Temperature
kelvin (K)
Luminous Intensity
candela (cd)
Amount of Substance
mole (mol)
Prefixes
Used to represent powers of 10
tera (T)
10¹²
giga (G)
10⁹
mega (M)
10⁶
kilo (k)
10³
deci (d)
10⁻¹
centi (c)
10⁻²
milli (m)
10⁻³
micro (µ)
10⁻⁶
nano (n)
10⁻⁹
Diameter of Typical Atom
10⁻¹⁰ m
Types of Physical Quantities
Scalars and Vectors
Scalars
Have only magnitude
Vectors
Have magnitude and direction
Example of Scalar
Speed
Example of Vector
Velocity
Numerical Representation of Vectors
If motion is in one line, use ± symbols to represent direction. We must write in the direction that is positive or negative.
Graphical Representation of Vectors
Use arrows to represent a vector. The direction of the arrow is the same as the vector. The length represents the magnitude of the vector if drawn to scale.
Result of Addition of Vectors
resultant
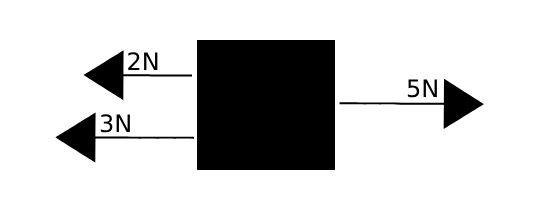
Vectors upon the same line
5N - (2N+3N) = 0N
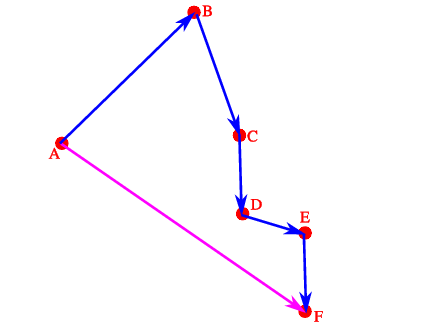
Vectors not upon the same line
Write the scale (1u:1u)
Draw a reference line (Vertical or Horizontal)
Choose a starting point on the reference line
Draw a straight line from the start point to end point and that will be the answer (Pink Line)