NURS 202: Unit 8 (Lab 8 Review) - Nutrition and Oral, Head, Face, and Neck, and Nose, Mouth, and Throat (good luck on clinicals!)
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Special Diets
- Regular diet
- NPO
- DAT
- Clear fluids
- Full fluids
- Soft/low residue
- Low sodium
- Low cholesterol
- Diabetic
Regular Diet
A diet with no dietary restrictions
NPO (nil per ora) Diet
A diet where the patient can't eat or drink anything for a certain period of time
DAT (Diet as Tolerated) Diet
A diet where the patient decides how to progress back to a regular diet
Clear Fluids Diet
A diet where a patient can only drink drinks that can be seen through (Ex. Water)
Full Fluids Diet
A diet where a patient can only drink clear fluids, dairy, fruit juices, pureed vegetables, refined cereals, and thickened fluids
Soft/Low Residue Diet
A diet where a patient can only eat puree and mechanical soft (soft-textured foods)
Low Sodium Diet
A diet specifically designed for patients with hypertension
Low Cholesterol Diet
A diet specifically designed for patients with elevated cholesterol levels
Diabetic Diet
A diet that specifically pays attention to sugar levels
Key Points for Assisting with Nutrition
- Stimulate appetite
- Have equipment available
- Sit patient upright
- Provide patient with adequate time to eat or chew
Dysphagia
Difficulty swallowing
Aspiration Precautions
- Observe for dysphagia
- Offer small bites
- Provide verbal cueing if needed
- Observe for fatigue
- Keep patient upright for at least 30 mins after eating
- Assist with mouth care
- Document
Key Points on Patient Nutrition
- Know that certain patients need certain diets
- Encourage food intake by patients
- Take precautions to avoid aspiration
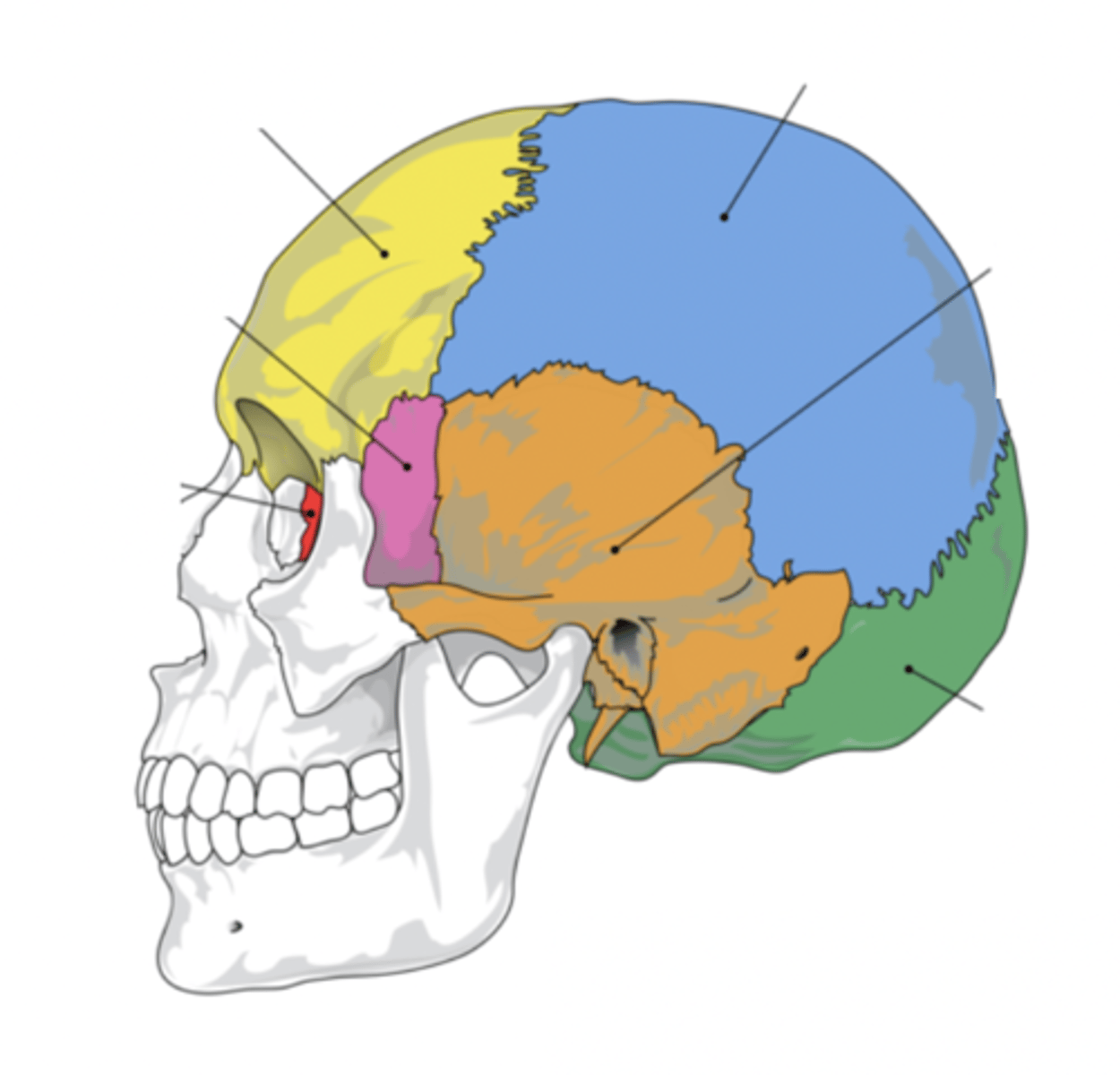
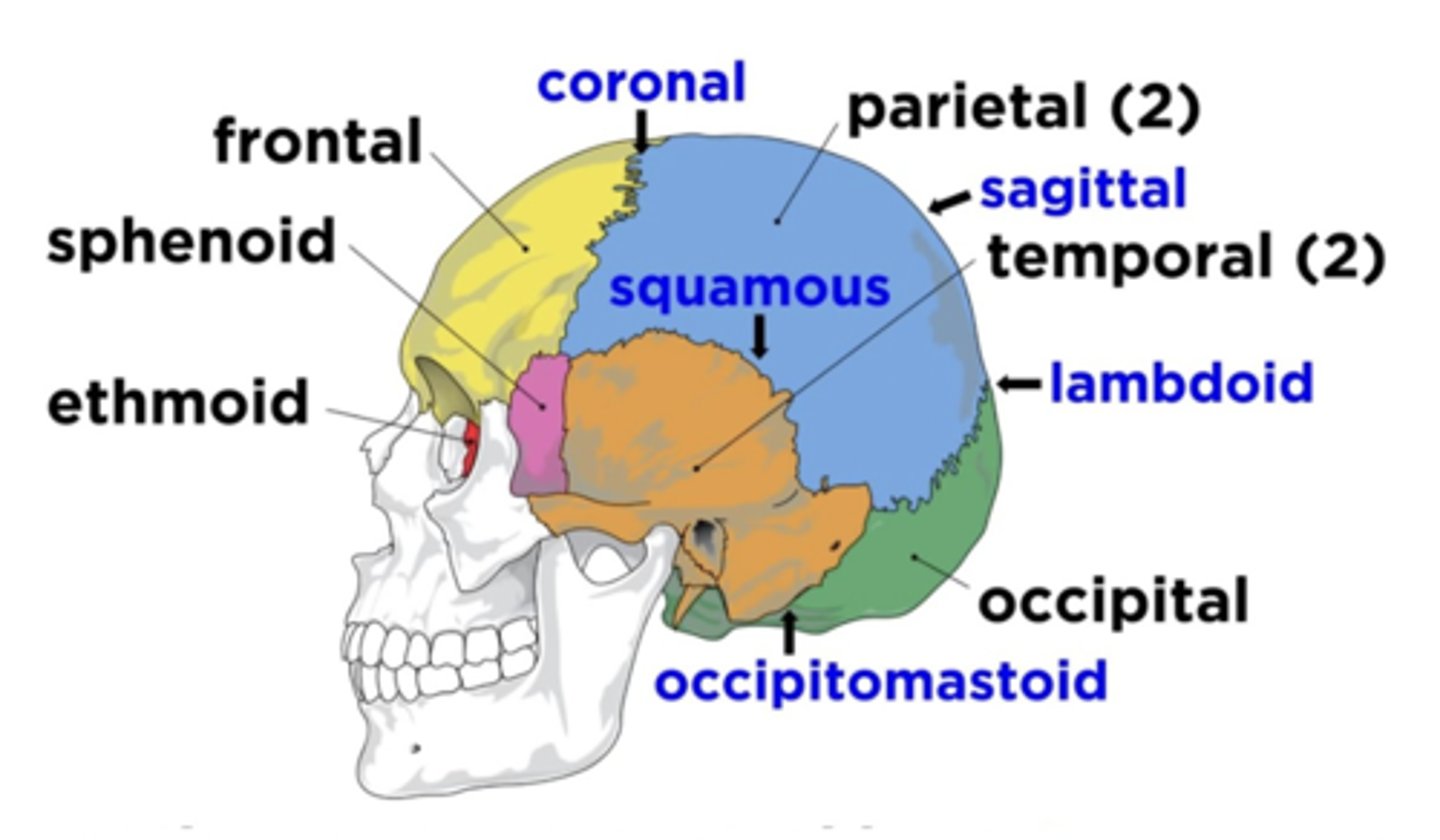
Cranial Bones (8)
- Ethmoid
- Frontal
- Sphenoid
- Temporal (2)
- Occipital
- Parietal (2)
(EFSTOP)
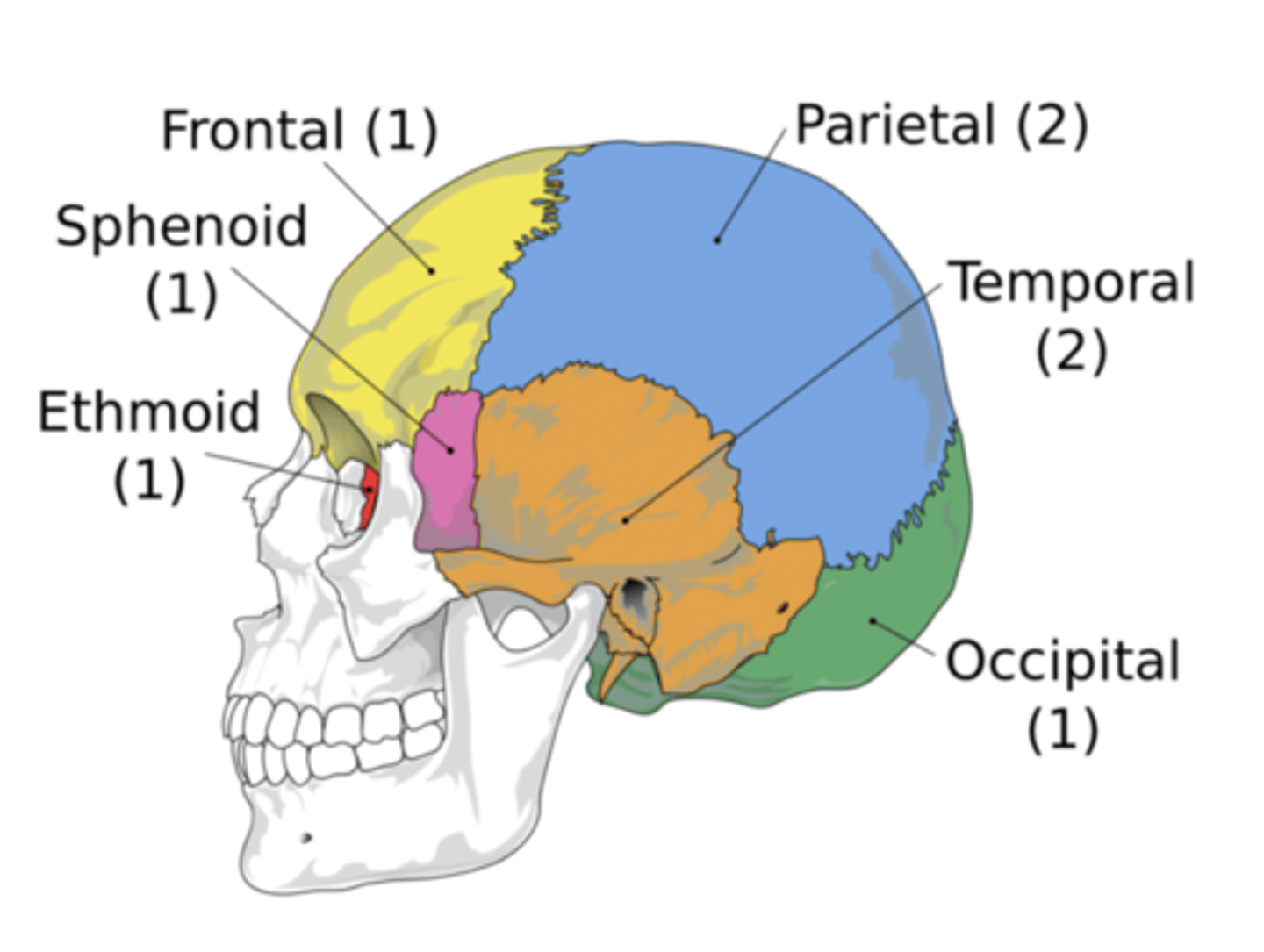
Ethmoid Bone
Forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium (red)
Frontal Bone
Bone that forms the forehead (yellow)
Sphenoid Bone
Forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit (pink)
Temporal Bone (2)
Bone that forms parts of the side of the skull and floor of the cranial activity (orange)
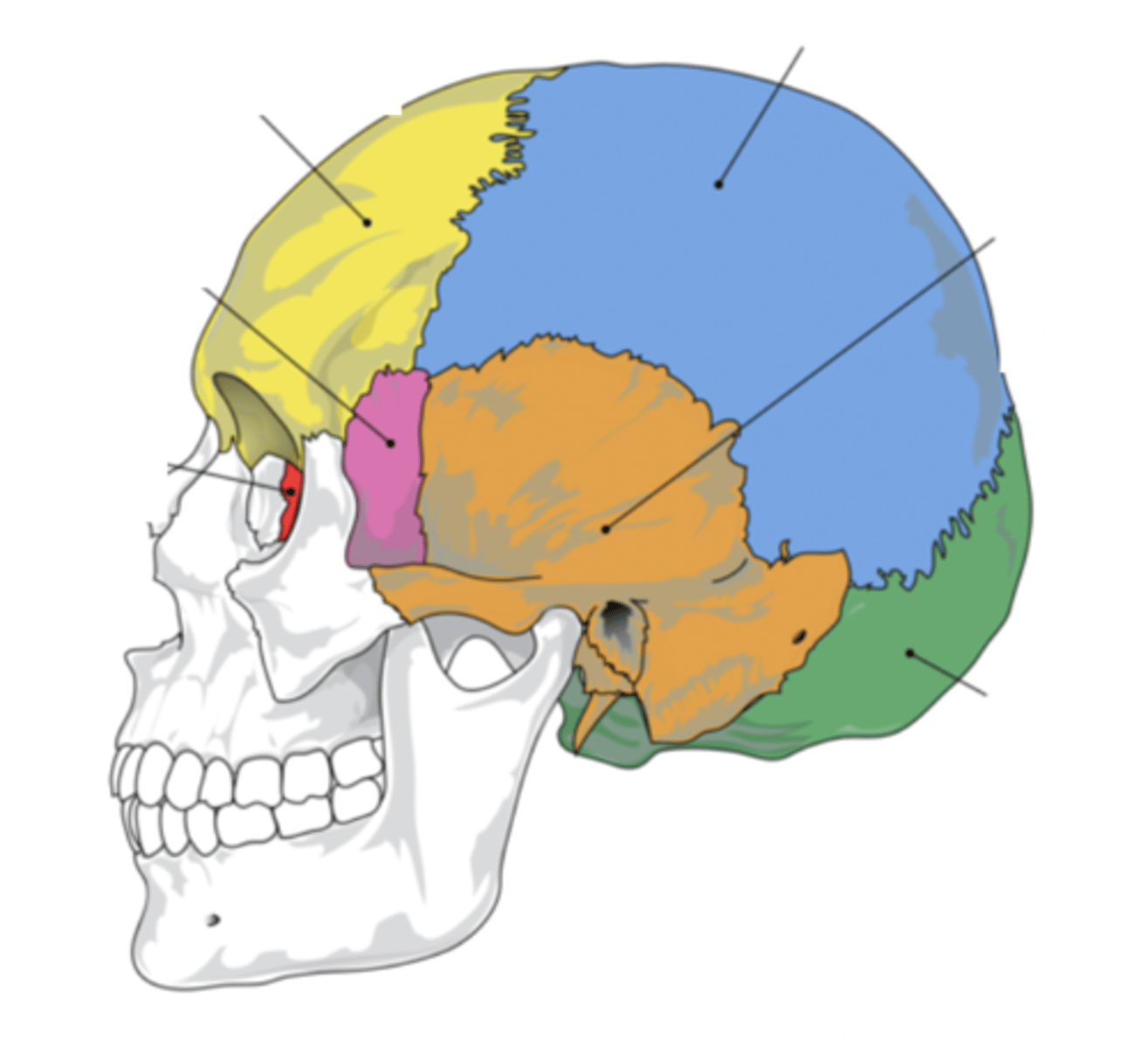
Occipital Bone
Bone that forms the back of the head (green)
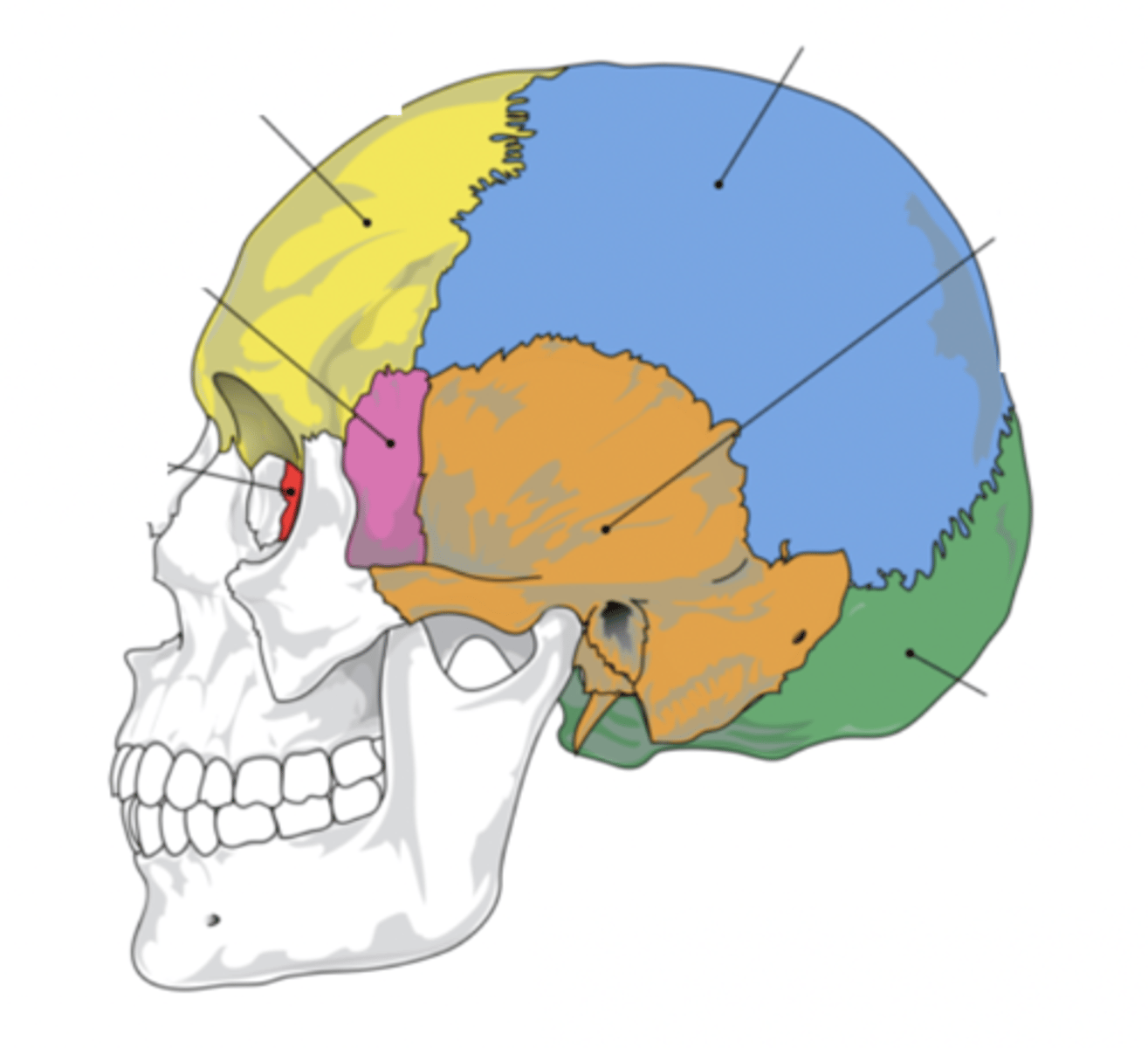
Parietal Bone (2)
Either of two skull bones between the frontal and occipital bones and forming the top and sides of the cranium (blue)
Facial Bones (14)
- Maxilla (2)
- Mandible
- Lacrimal (2)
- Palatine (2)
- Inferior conchae (2)
- Vomer
- Nasal (2)
- Zygomatic (2)
(Many Mammals Like Playing In Very Nice Zoos)

Maxilla Bone (2)
Upper jaw bone (yellow)
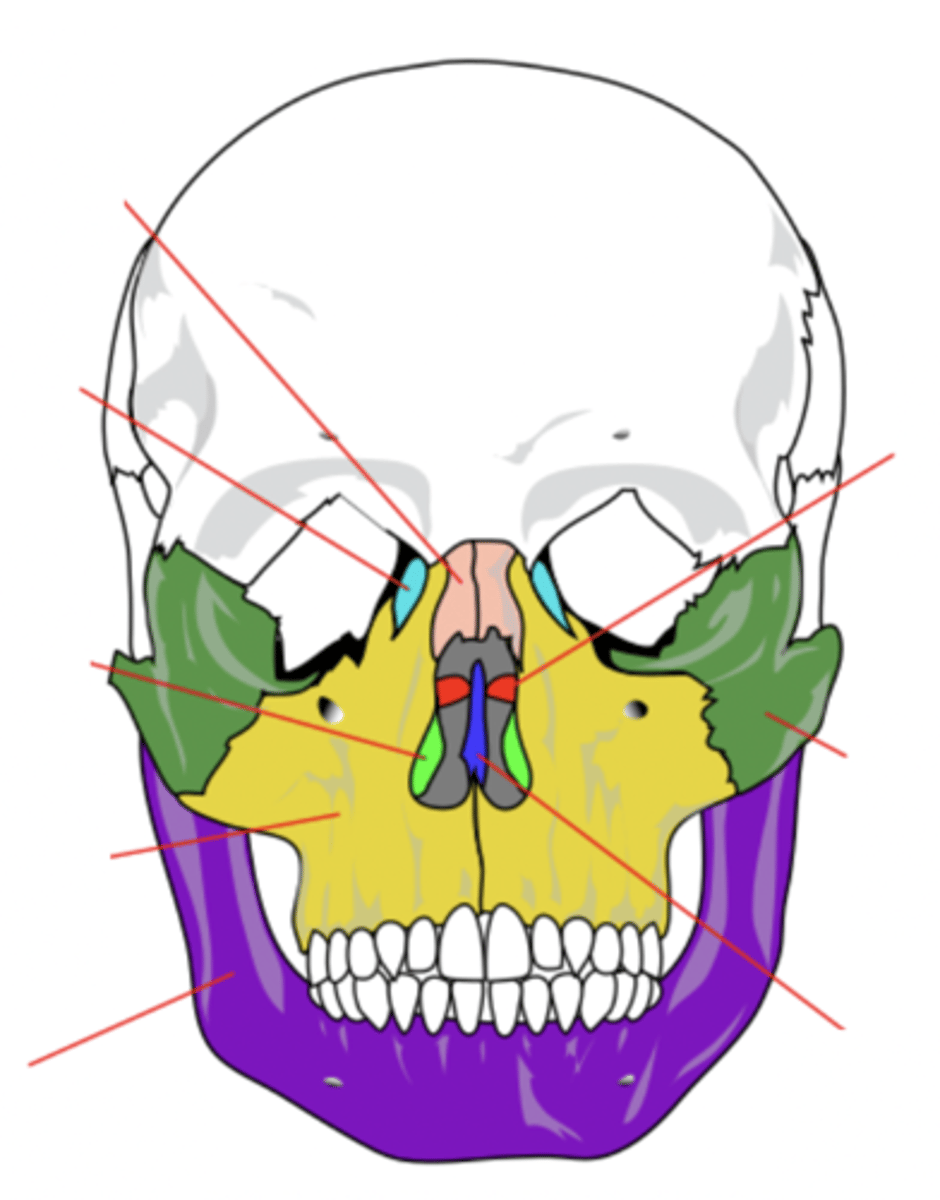
Mandible Bone
Lower jaw bone (purple)
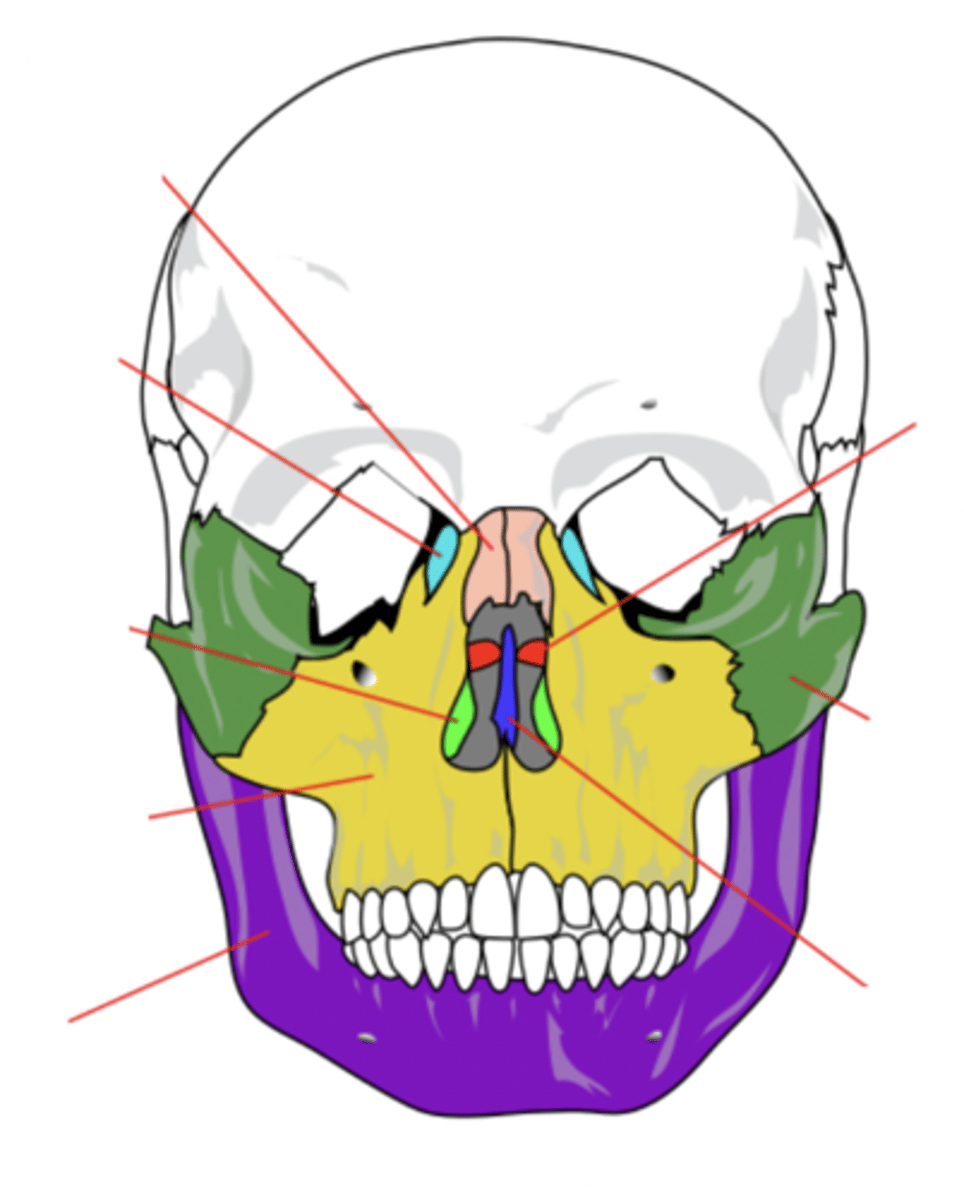
Lacrimal Bone (2)
Small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts (light blue)
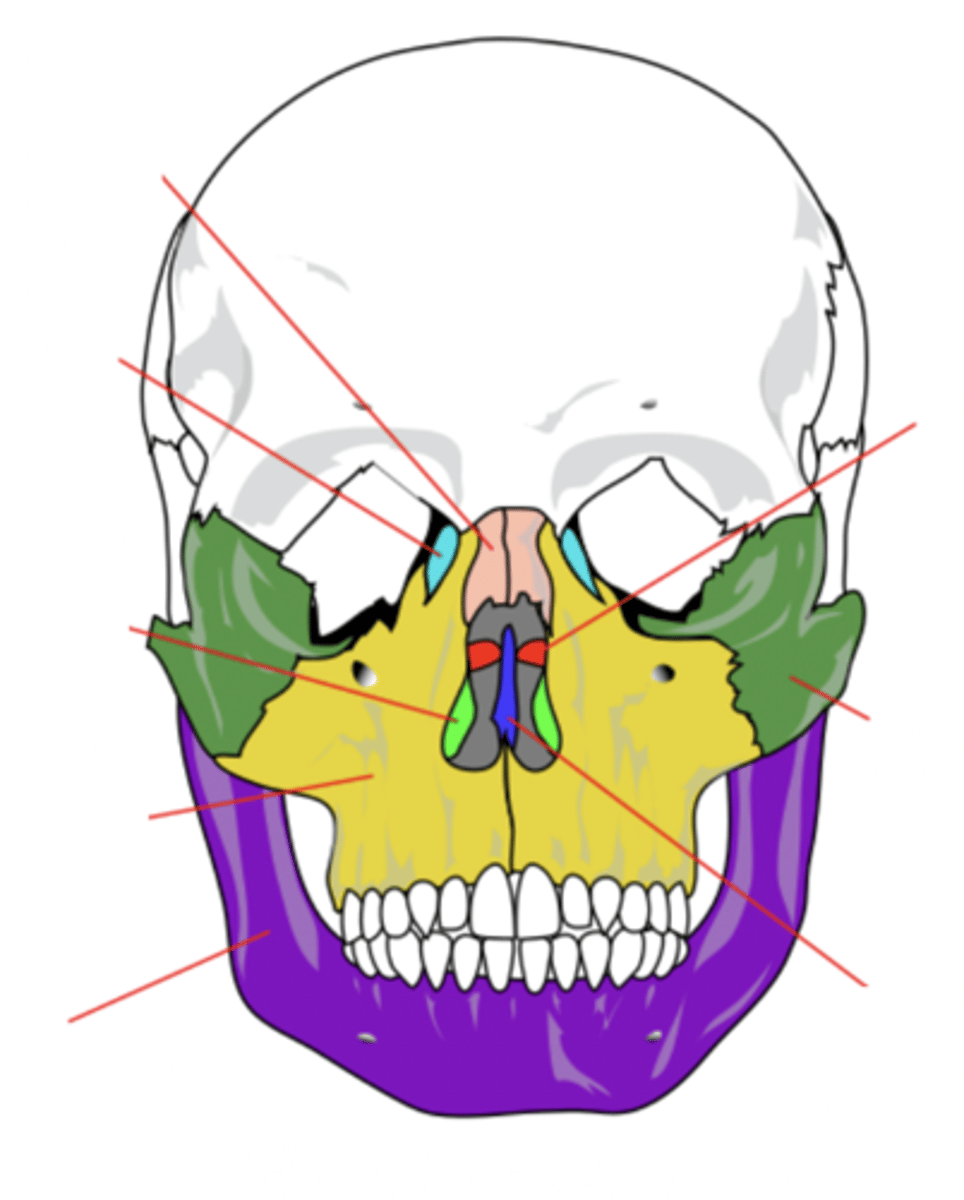
Palatine Bone (2)
Bone that forms the hard palate and parts of the nose and orbits (red)
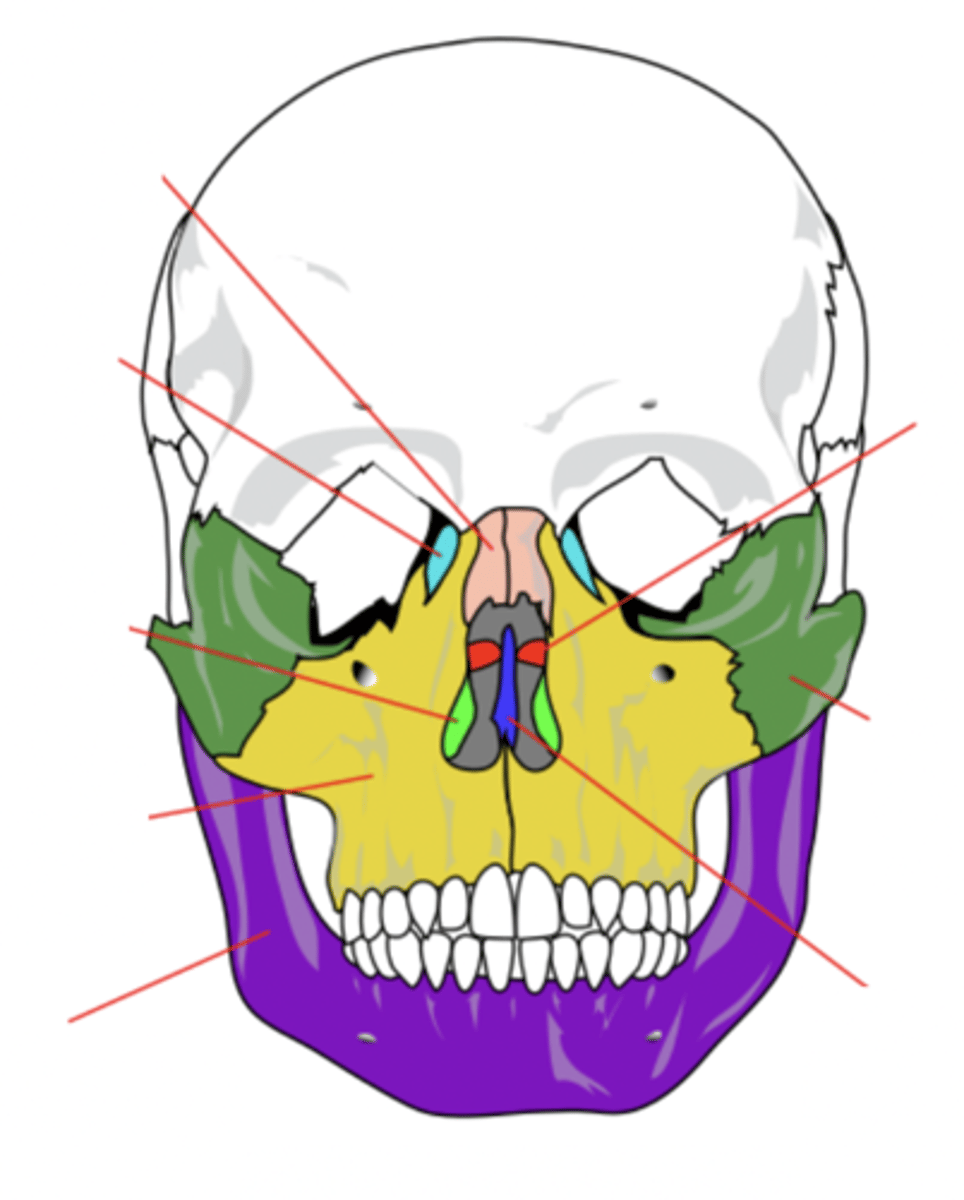
Inferior Conchae Bone (2)
The thin, scroll-like bones that form part of the interior of the nose (light green)
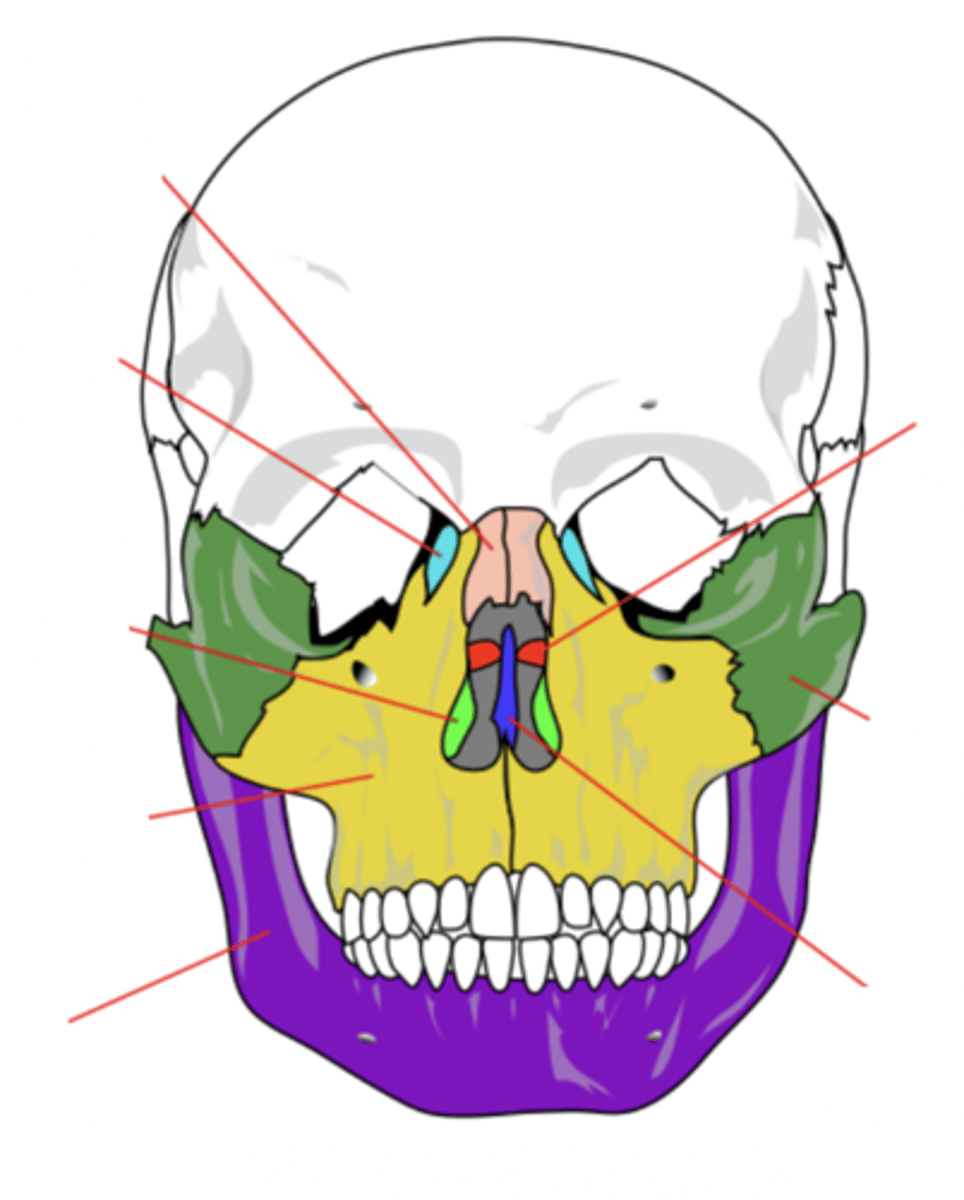
Vomer Bone
Bone that forms the inferior portion of the nasal septum (blue)
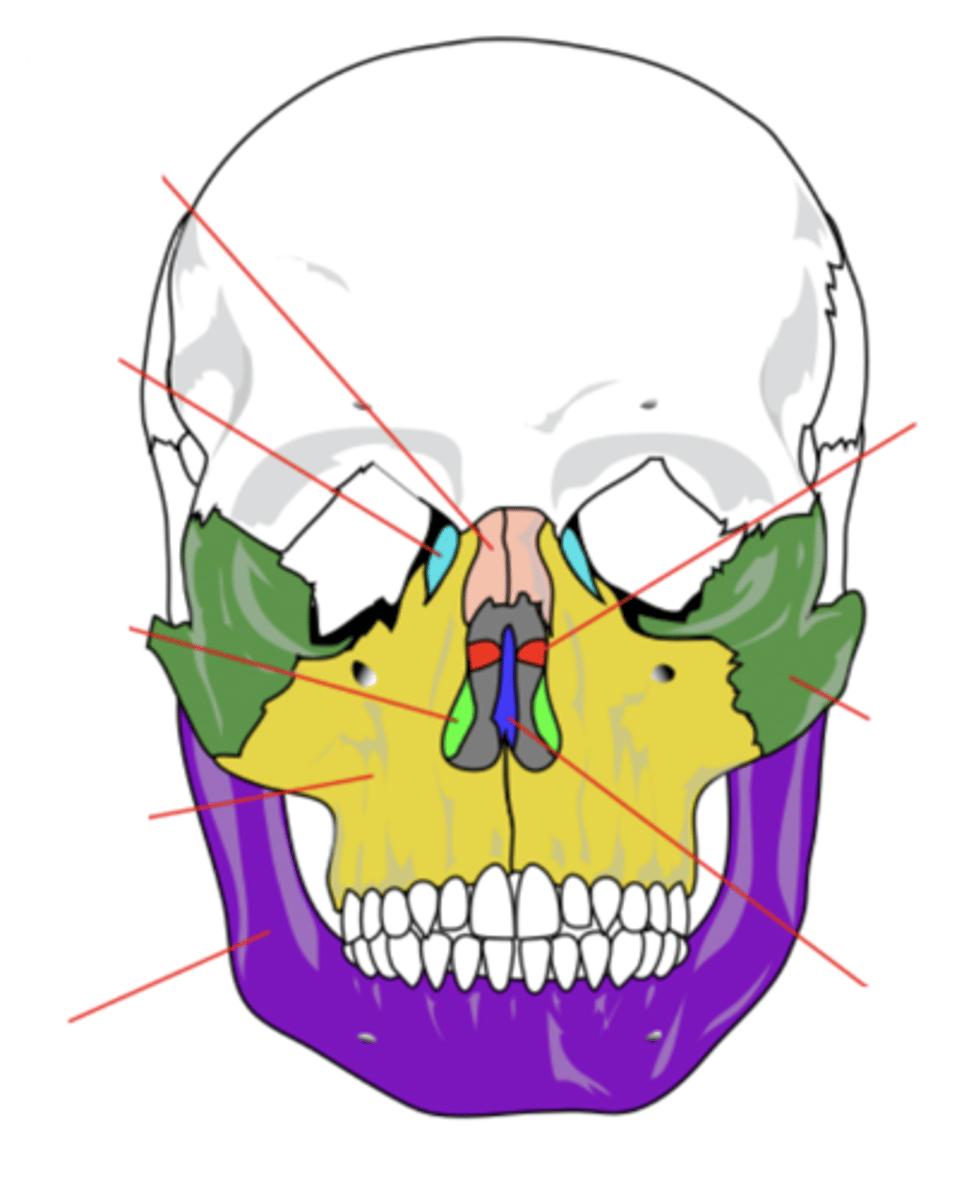
Nasal Bone (2)
Bone that forms the bridge of the nose (pink)
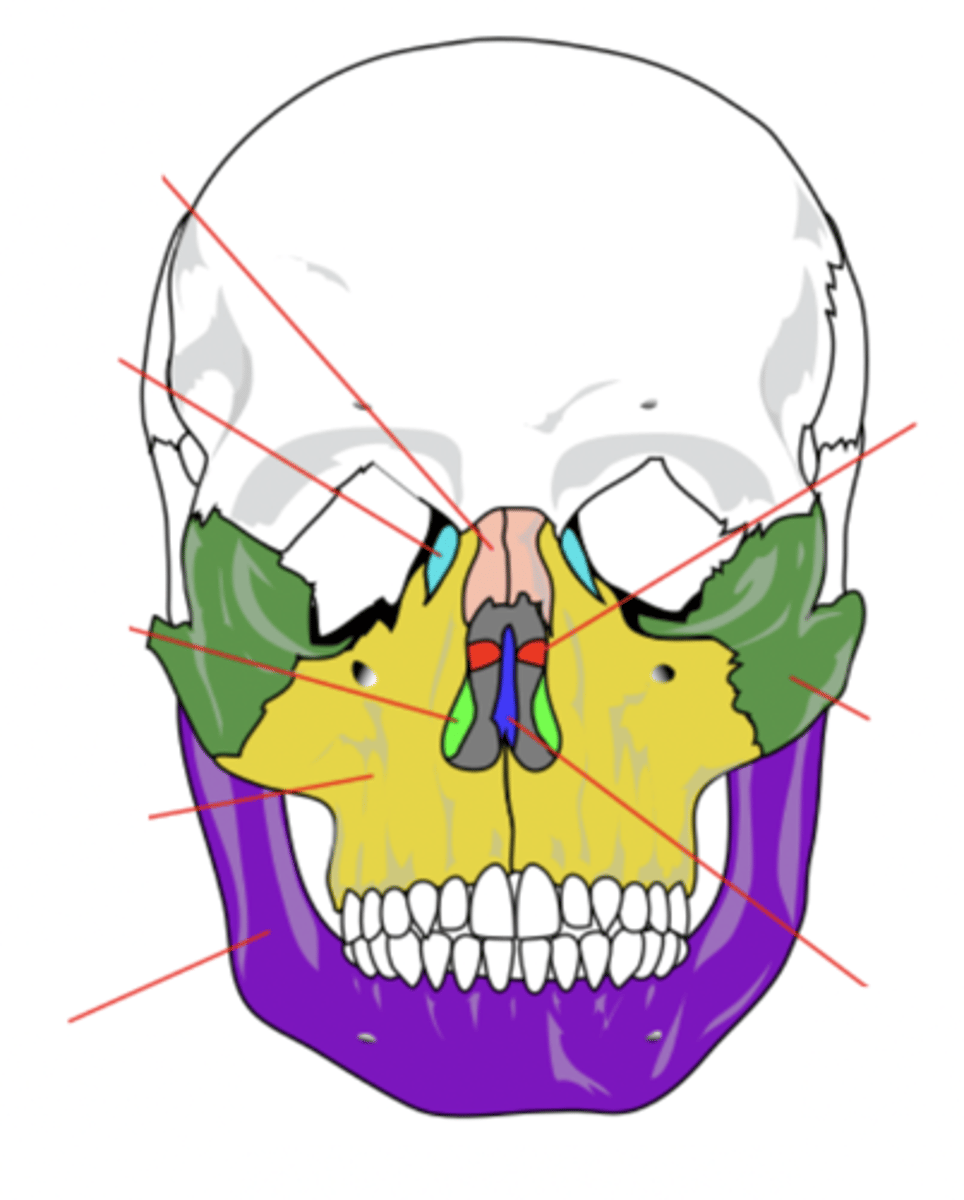
Zygomatic Bone (2)
Cheek bone (green)
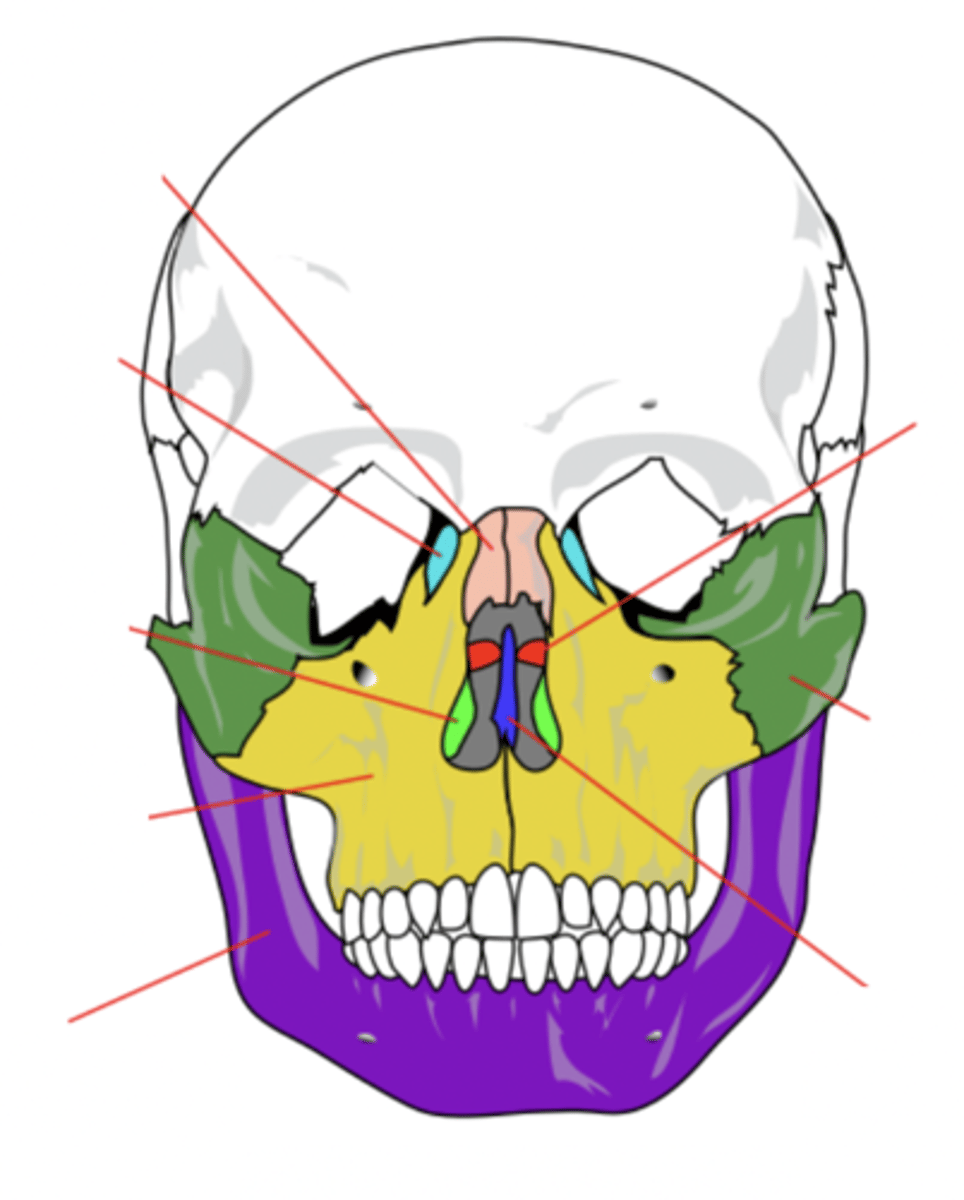
4 Main Sutures of the Skull
- Saggital
- Lamboid
- Coronal
- Squamous
(SLCS)
Saggital Suture
Suture that separates the left and right parietal bone
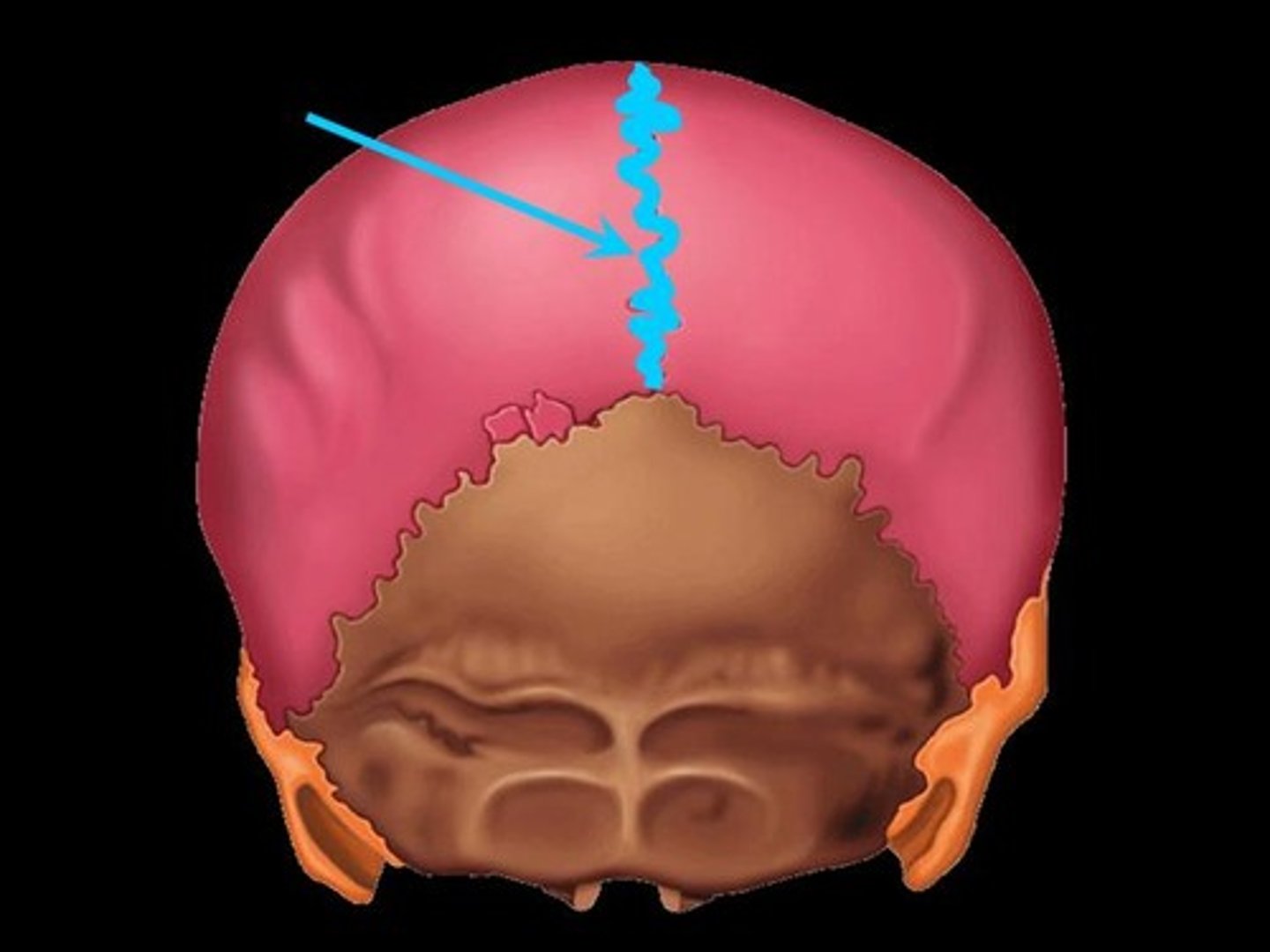
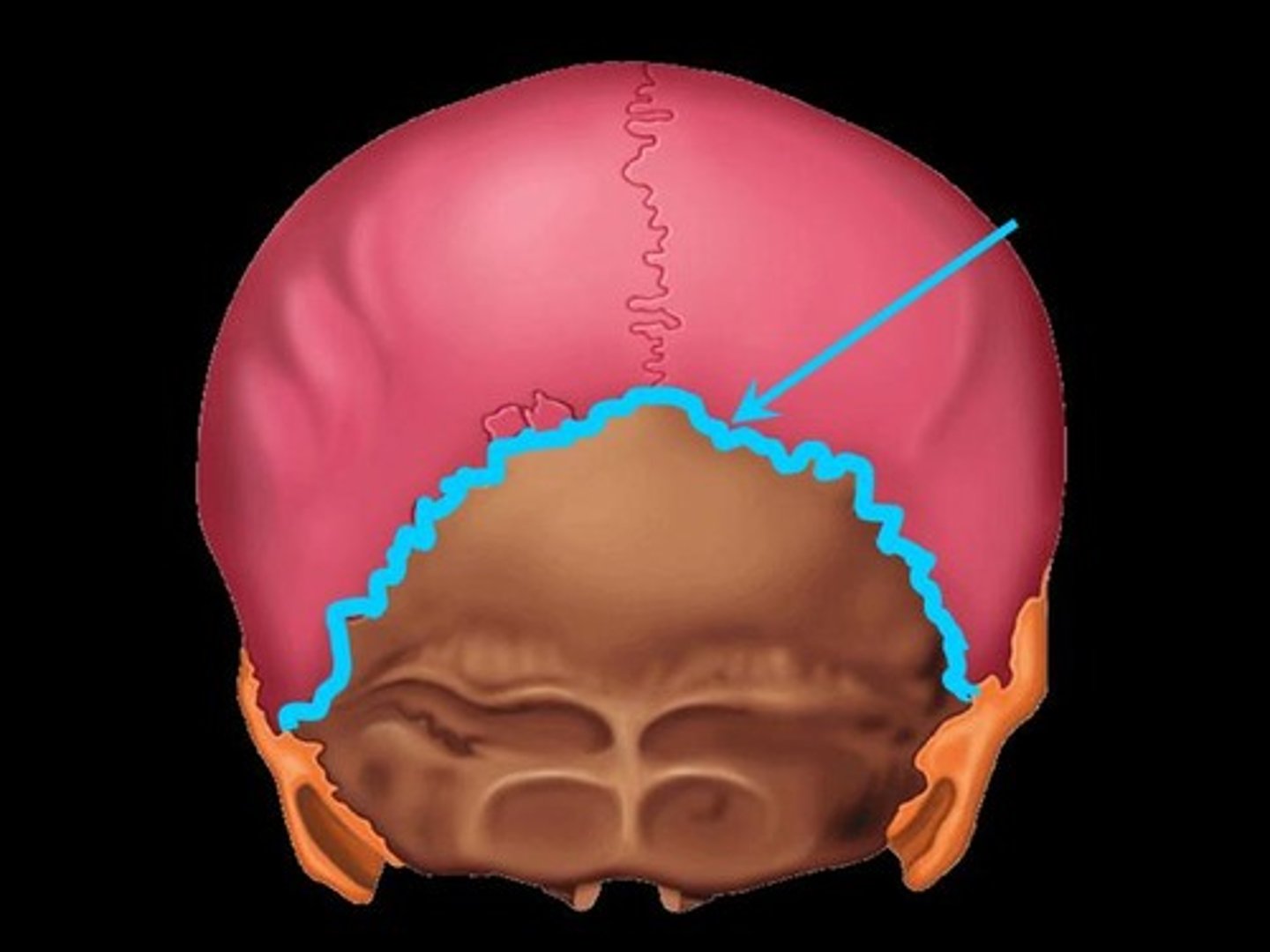
Lamboid Suture
Suture between the occipital and parietal bones
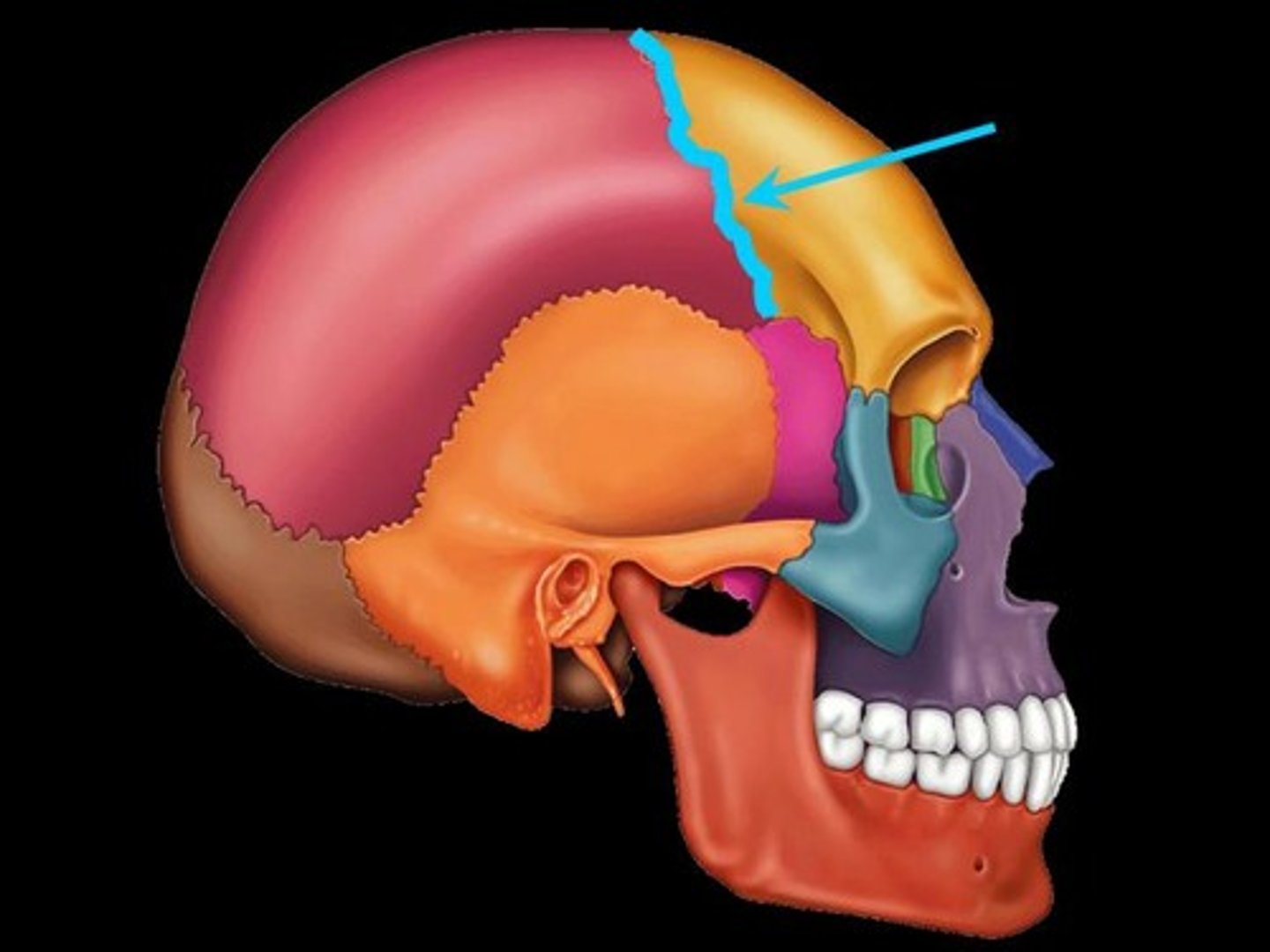
Coronal Suture
Suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
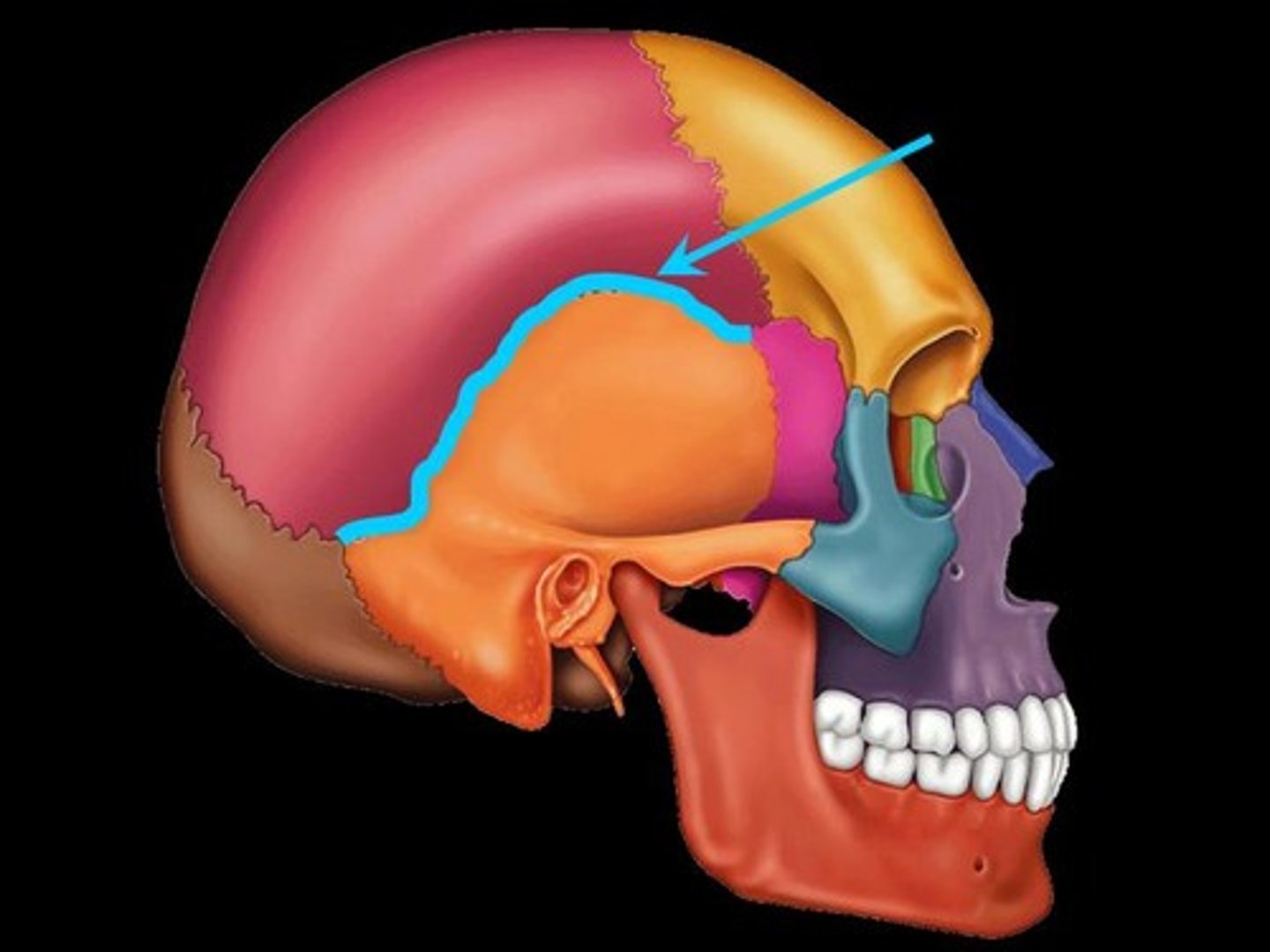
Squamous Suture
Suture between parietal and temporal bones
Function of Head and Face
- Serves as attachment for muscles; allows us to move our head, chew food, express emotions
- Houses delicate organs
- Entrance to digestive and respiratory systems
- Protect, support, and stabilize the brain
(SHEeP)
Anterior Triangle
The area that lies in front, between the sternomastoid and the midline of the body, with its base up along the lower border of the mandible and its apex down at the suprasternal notch
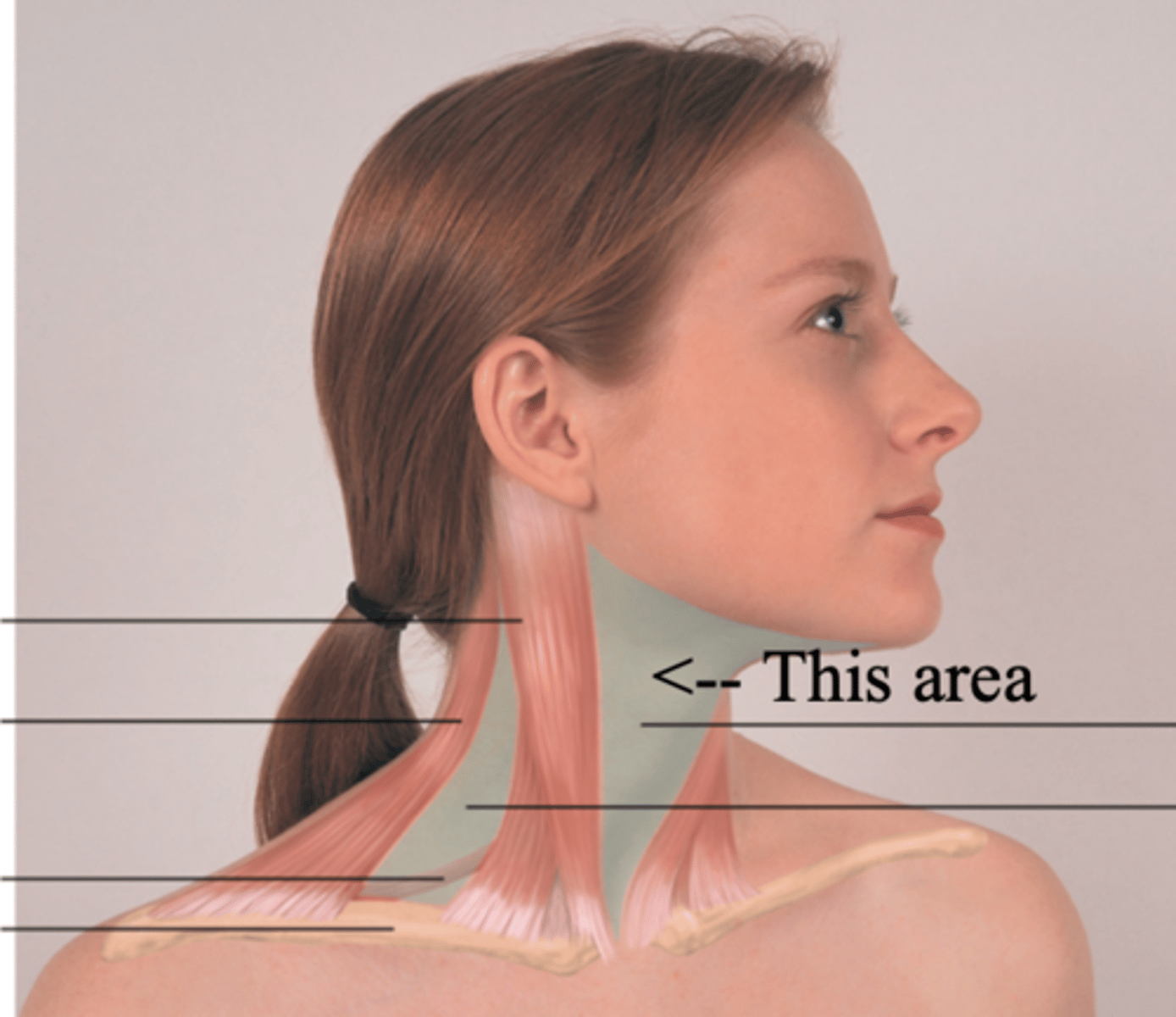
Posterior Triangle
The area of the neck between the sternocleidomastoid muscle and trapezius muscles
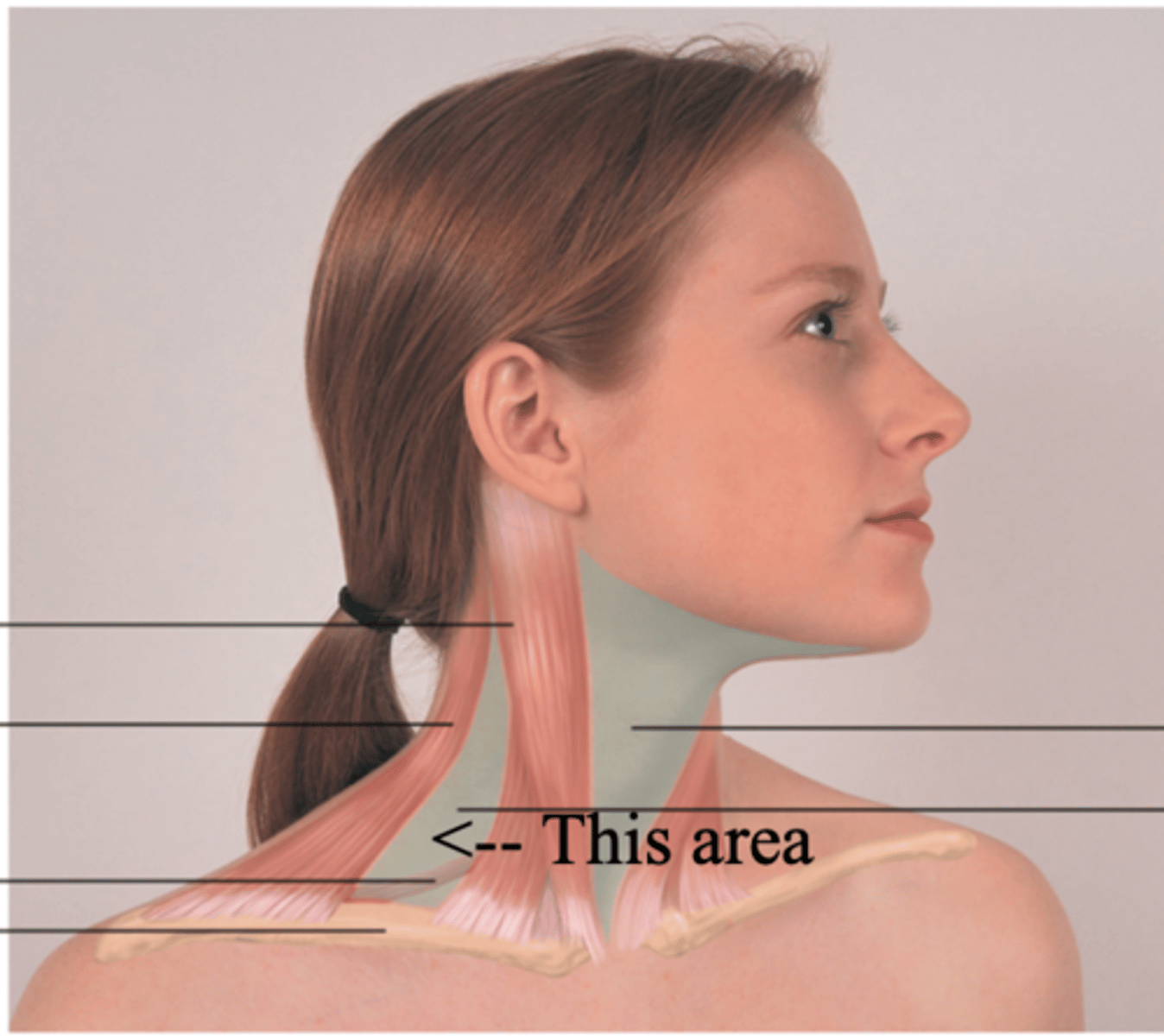
Functions of the Neck
- Continuation of the digestive and respiratory system
- Support the passage for many structures to and from the brain
Thyroid Gland
A gland found in the neck that secretes calcitonin, T3, and T4 hormones
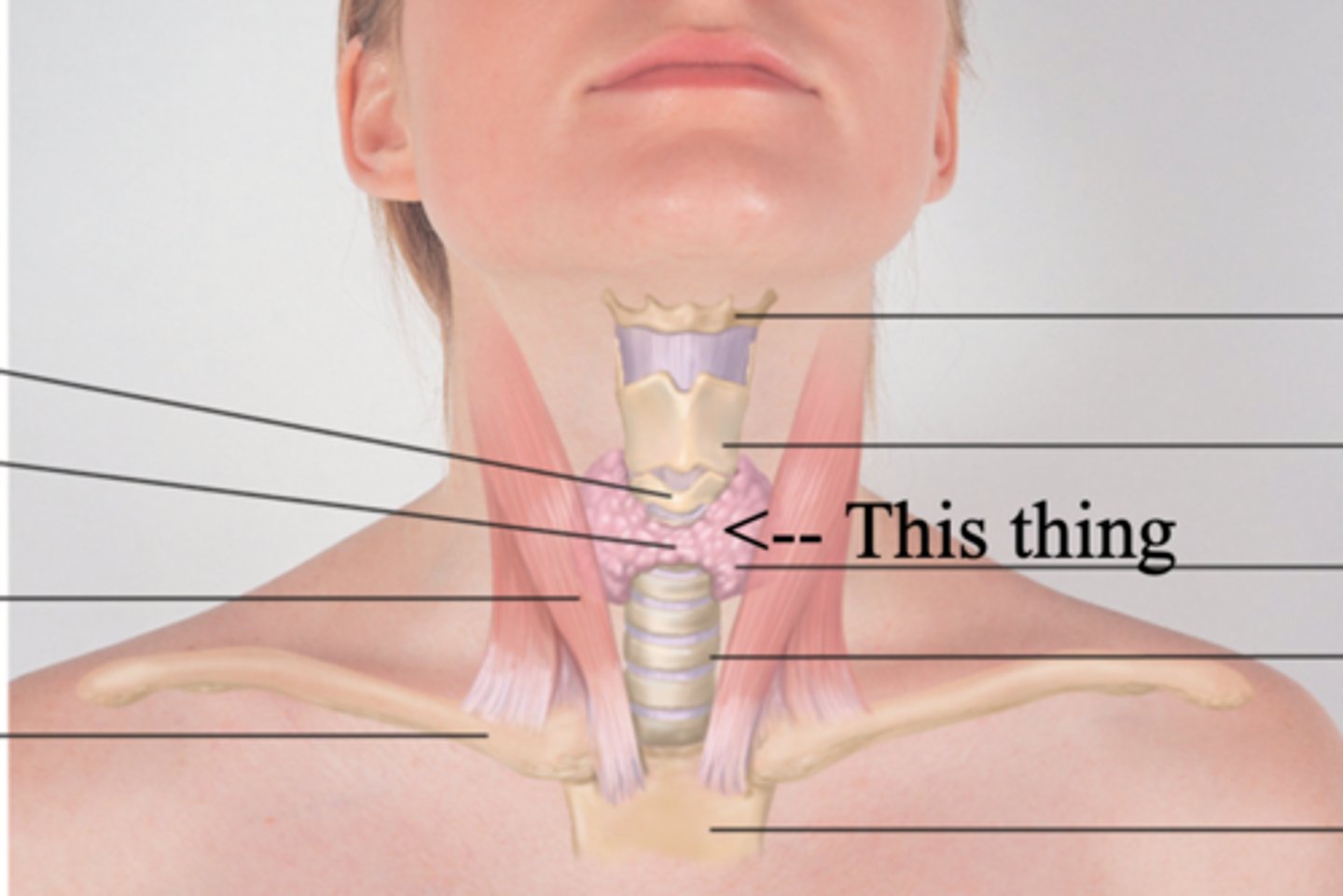
T3 and T4 Hormones
Hormones that stimulates rate of cellular metabolism
Calcitonin
Hormone that lowers blood calcium levels
Major Lymph Nodes in the Neck (FUN!)
- Preauricular
- Posterior auricular
- Occipital
- Submental
- Submandibular
- Jugulodigastric (tonsil)
- Superficial cervical
- Deep cervical chain
- Posterior cervical
- Supraclavicular
(Party People Often Sell Sardines Just So Dogs Pee Silver)
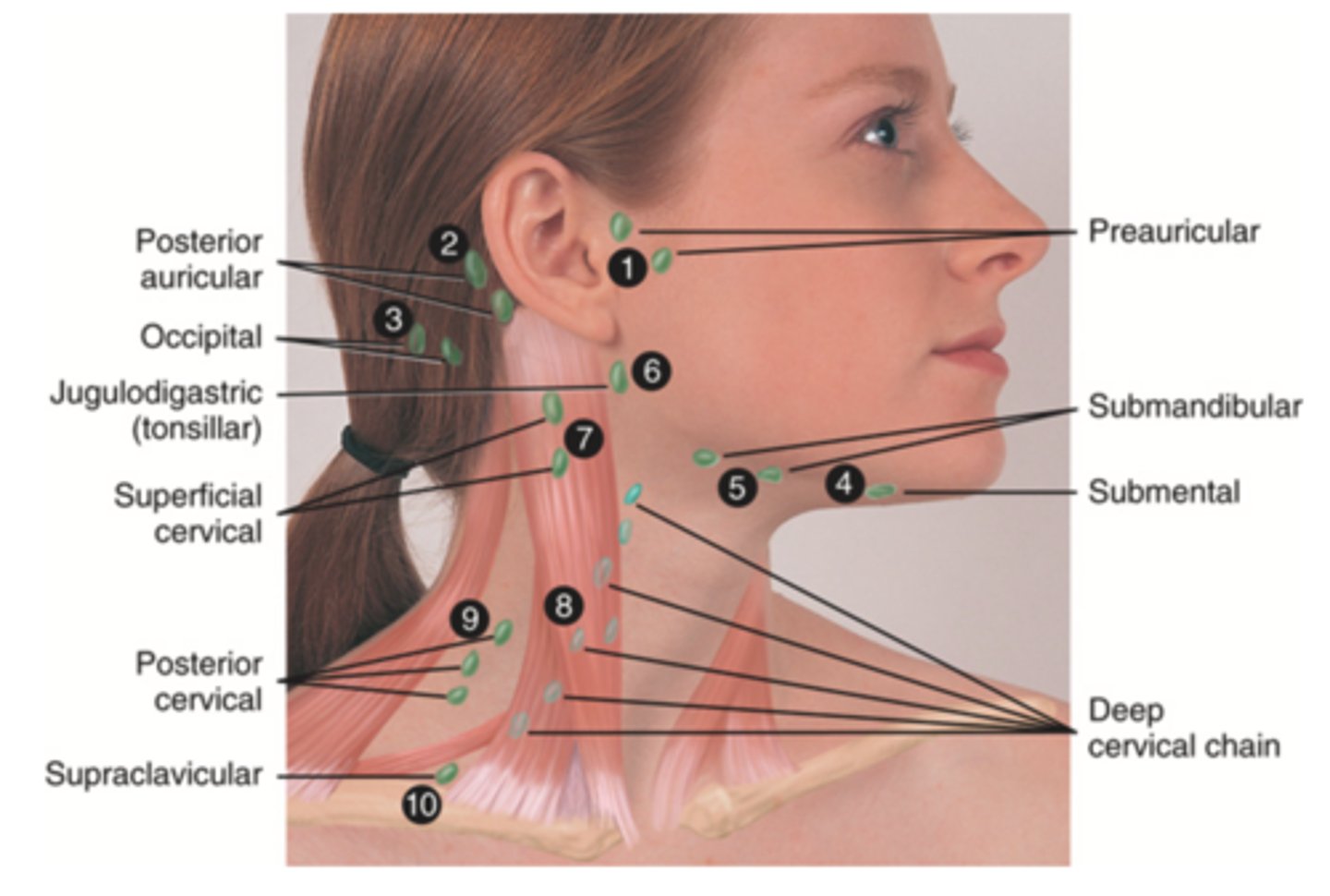
Preauricular Lymph Node
Lymph node in front of the ear (1)
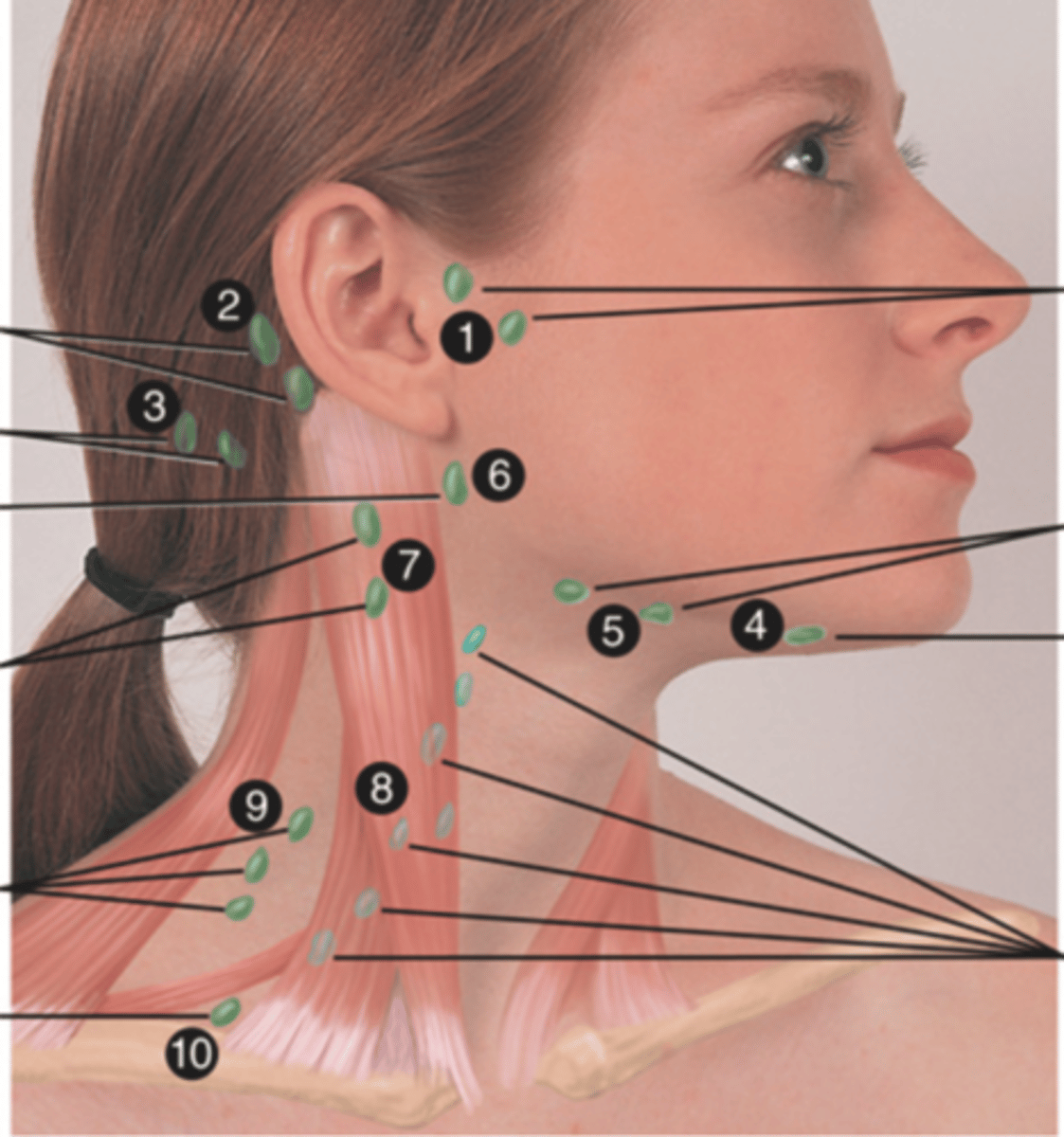
Posterior Auricular Lymph Node
Lymph node behind the ear (2)
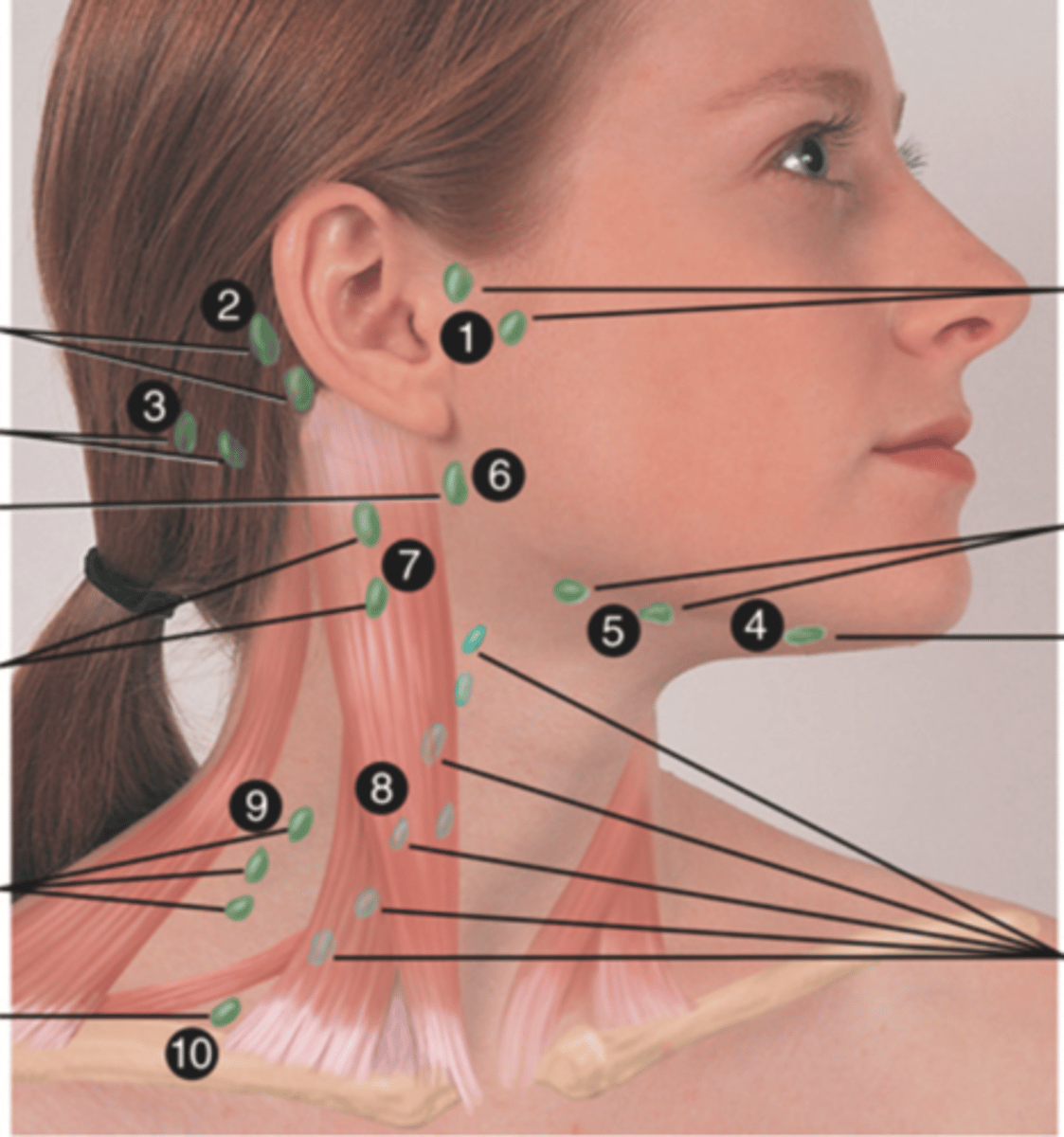
Occipital Lymph Node
Lymph node at the base of skull (3)
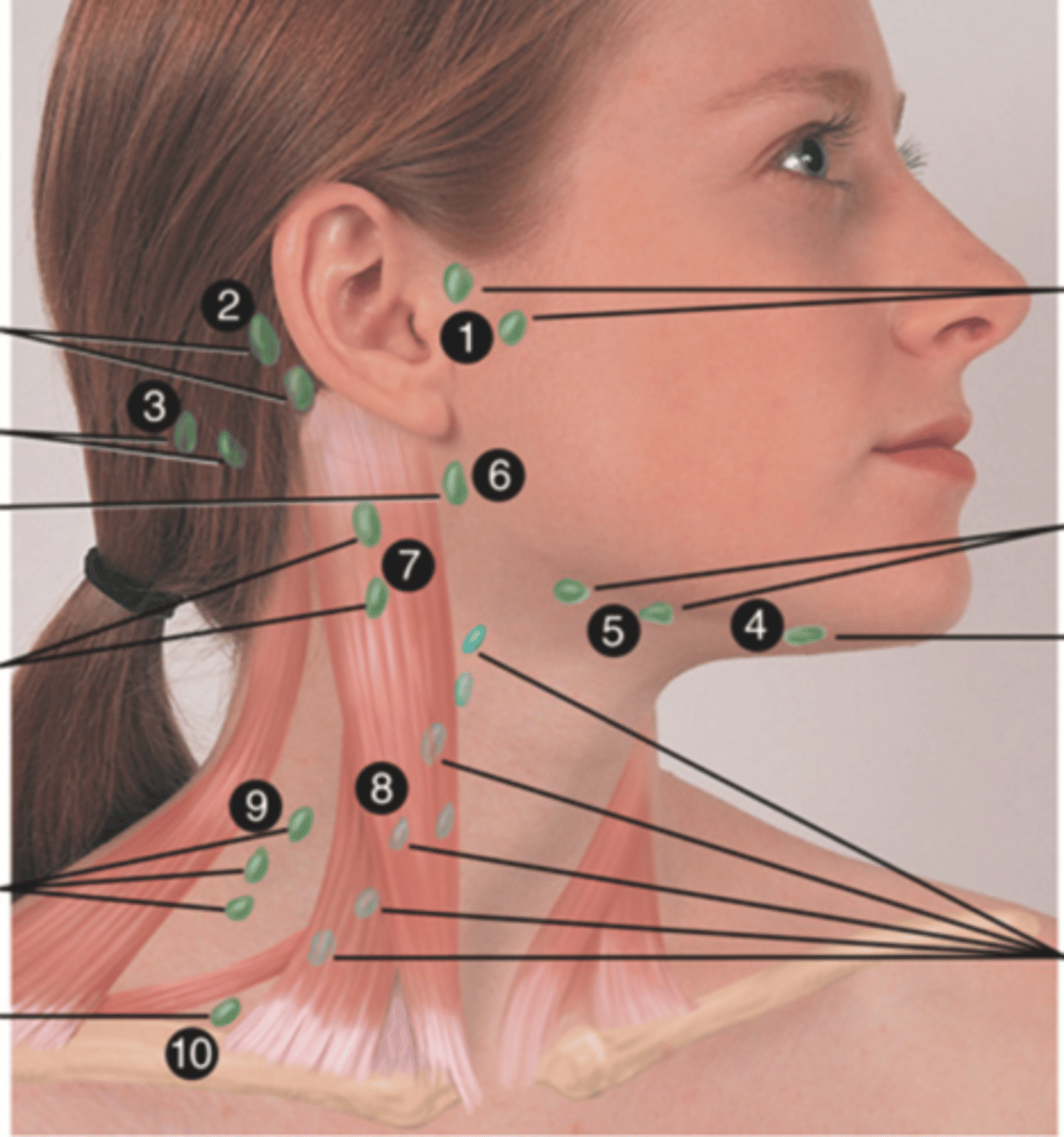
Submental Lymph Node
Lymph node under the chin (4)
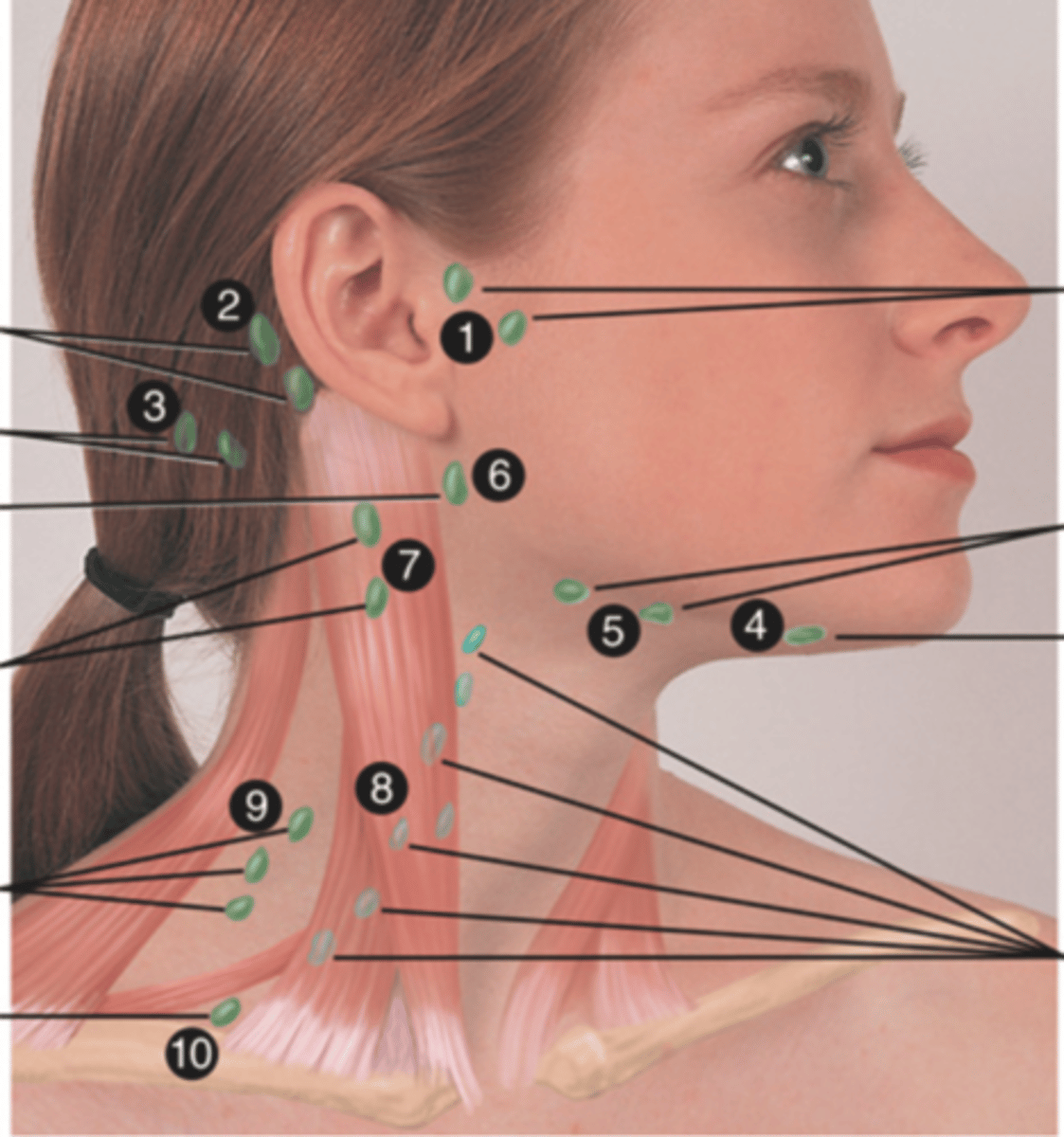
Submandibular Lymph Node
Lymph node along base of mandible (5)
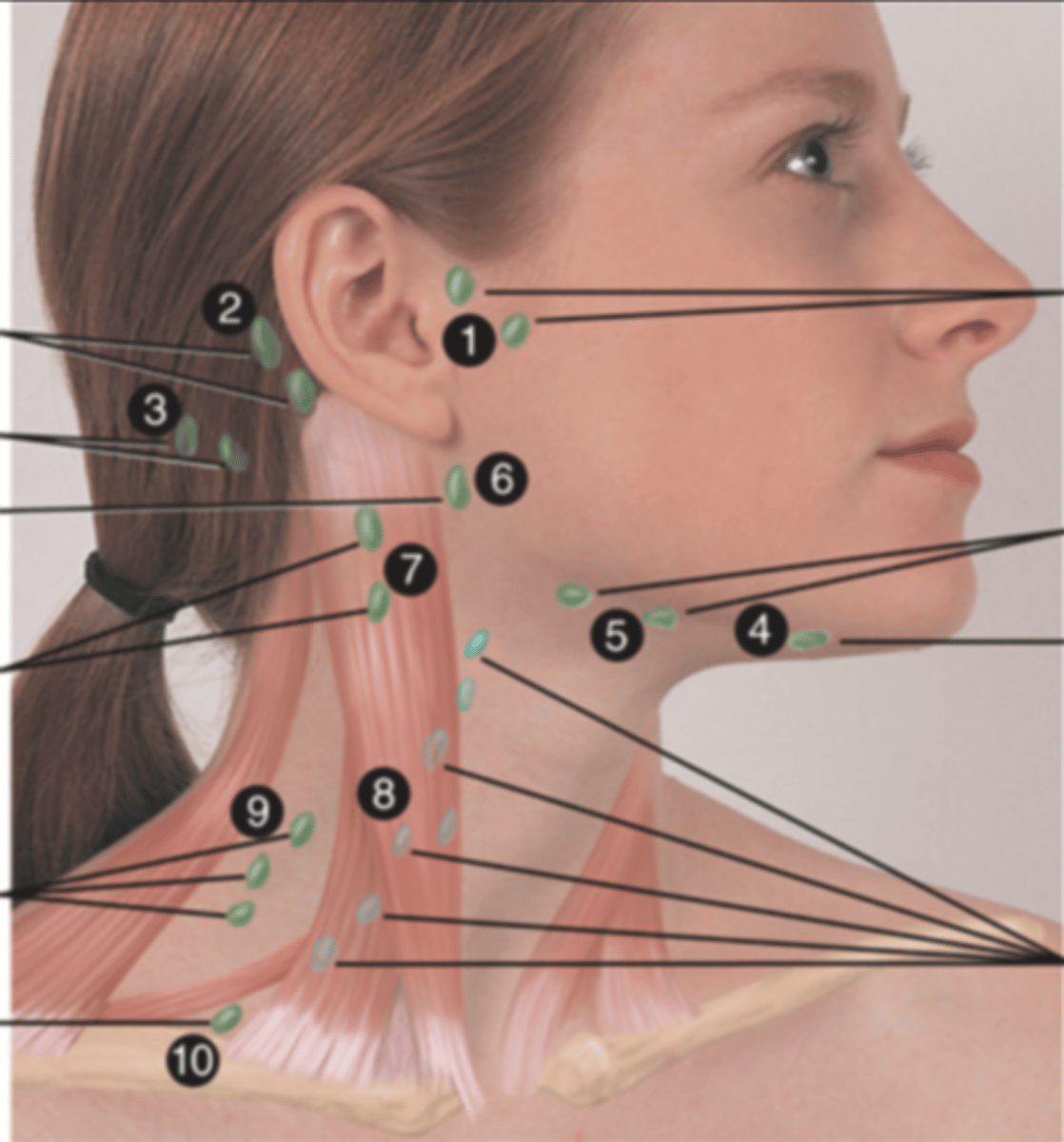
Jugulodigastric (Tonsil) Lymph Node
Lymph node under the angle of the mandible (6)
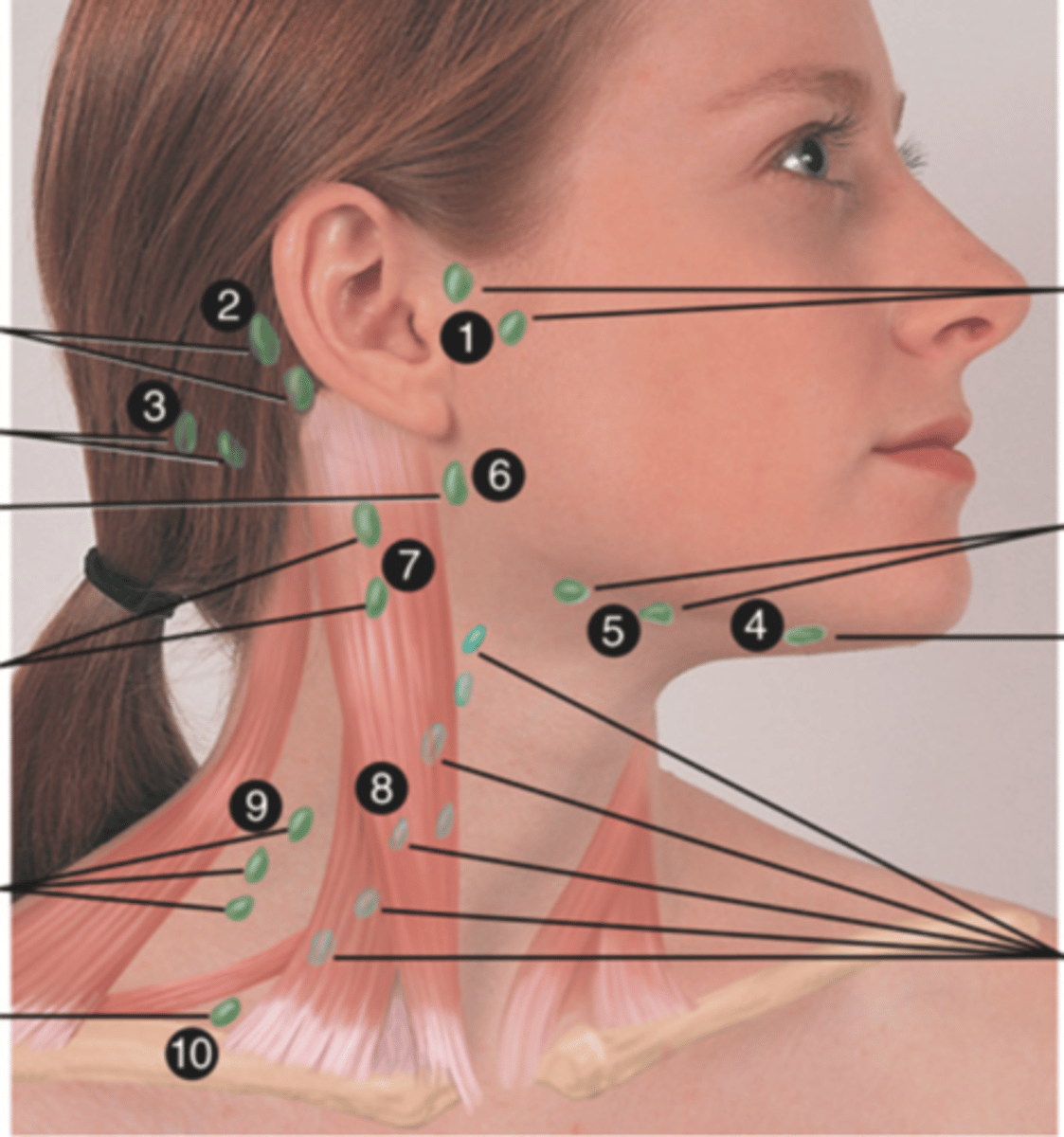
Superficial Cervical Lymph Node
Lymph node overlying the sternomastoid muscle (7); can feel enlarged even when there are no problems
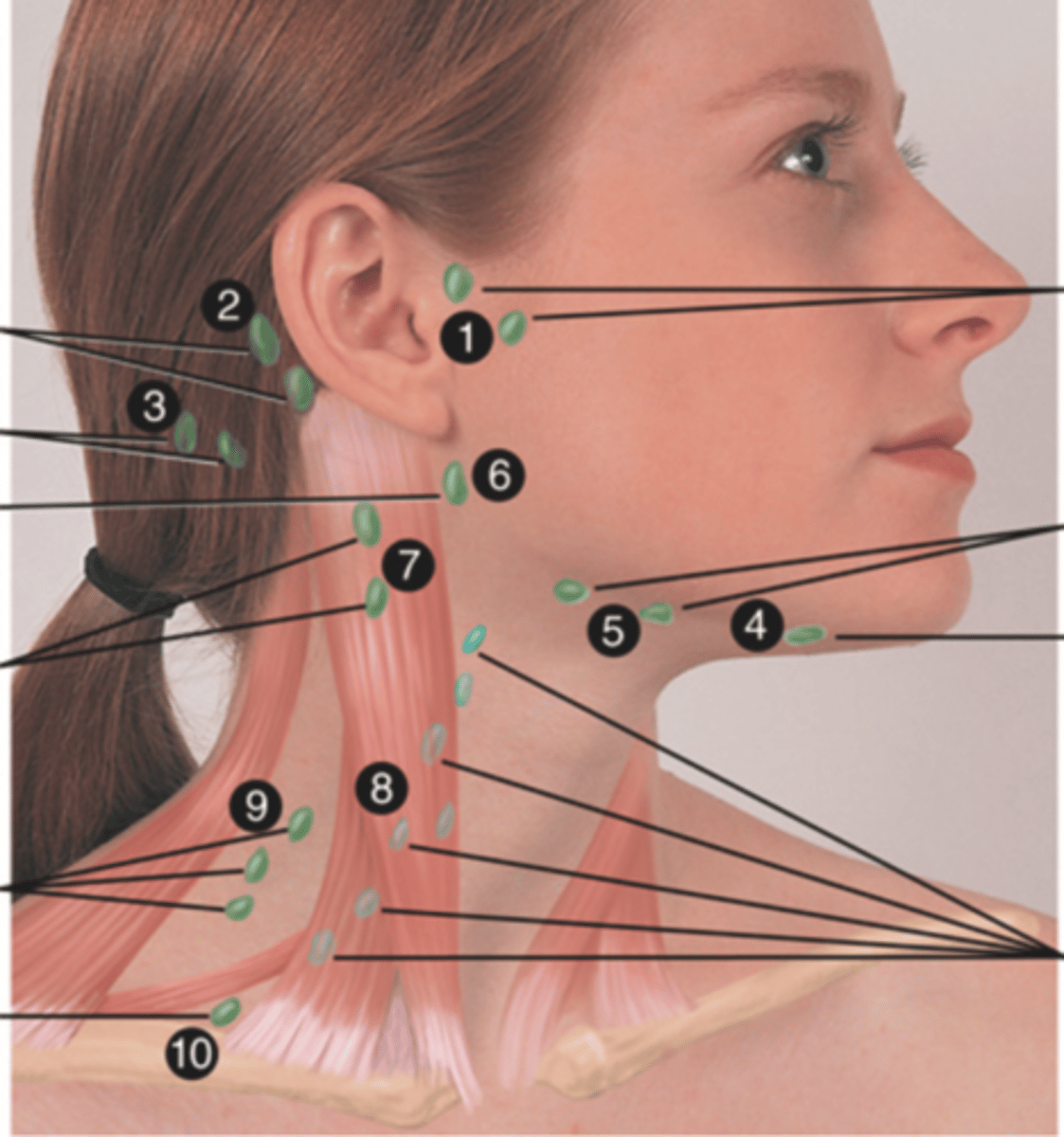
Deep Cervical Chain Lymph Node
Lymph node located on the posterior triangle of the neck (8)
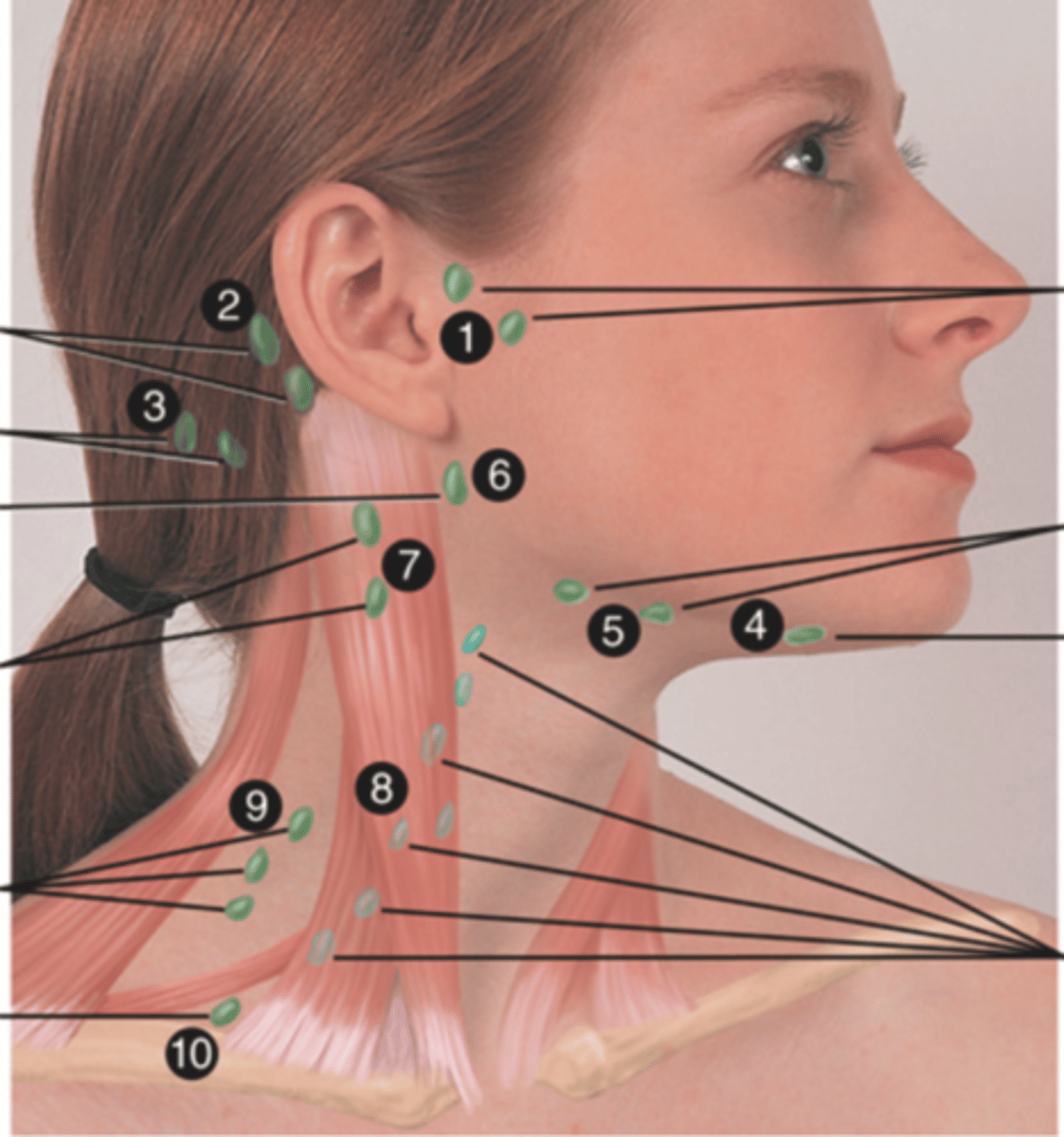
Posterior Cervical Lymph Node
Lymph node in the posterior triangle along the edge of the trapezius muscle (9)
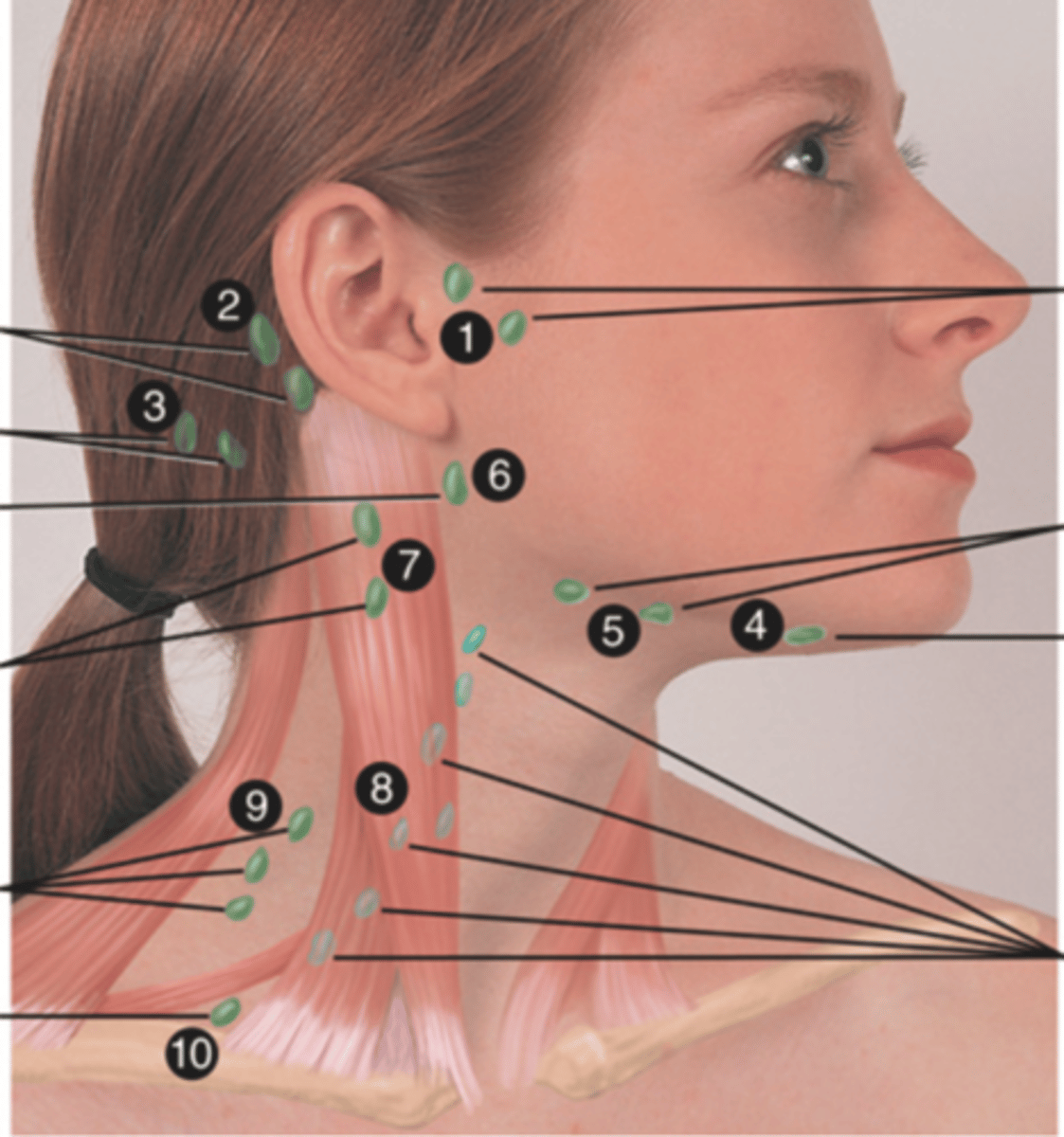
Supraclavicular Lymph Node
Lymph node just above and behind the clavicle, at the sternomastoid muscle (10)
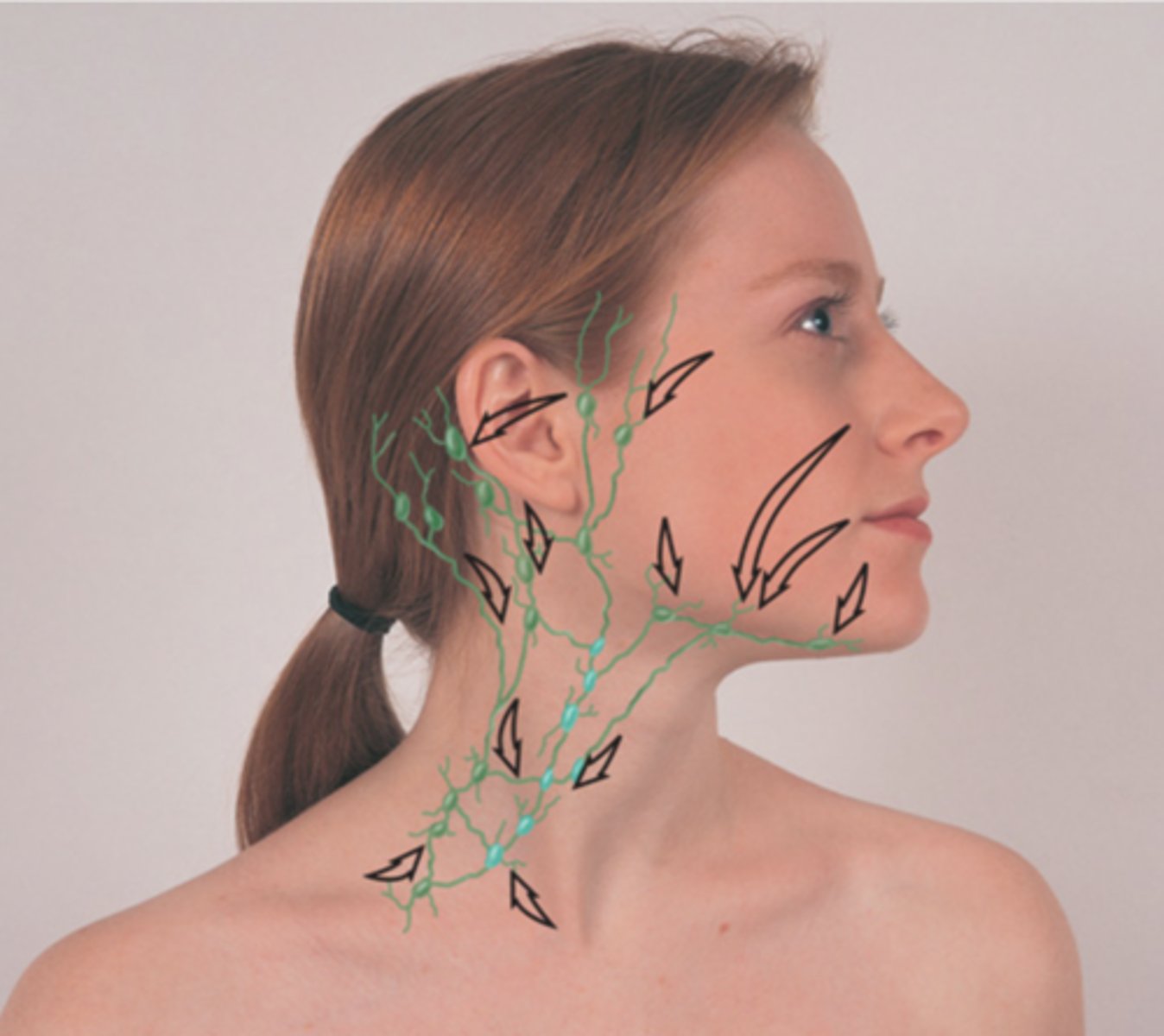
Functions of the Lymphatic System
- Manages interstitial fluid
- Part of the immune system
- Absorbs fat from the gut
Subjective Data to Assess for the Head, Face, and Neck
- Headaches
- Head injury
- Dizziness
- Neck pain or limited motion
- Lumps/swelling
- History of surgery
(Heavy Horses Die Naked Like Humpty)
Objective Data to Assess for Head and Face
- Size and shape (inspect and palpate)
- Temporal area (inspect and palpate)
- Facial structures (inspect)
(STF)
Objective Data to Assess for Neck
- Symmetry
- ROM
- Lymph nodes
- Trachea
- Thyroid gland (advanced skill; can auscultate for bruit)
(Inspect and palpate for all)
(Seven Rangers Like Talking Trash)
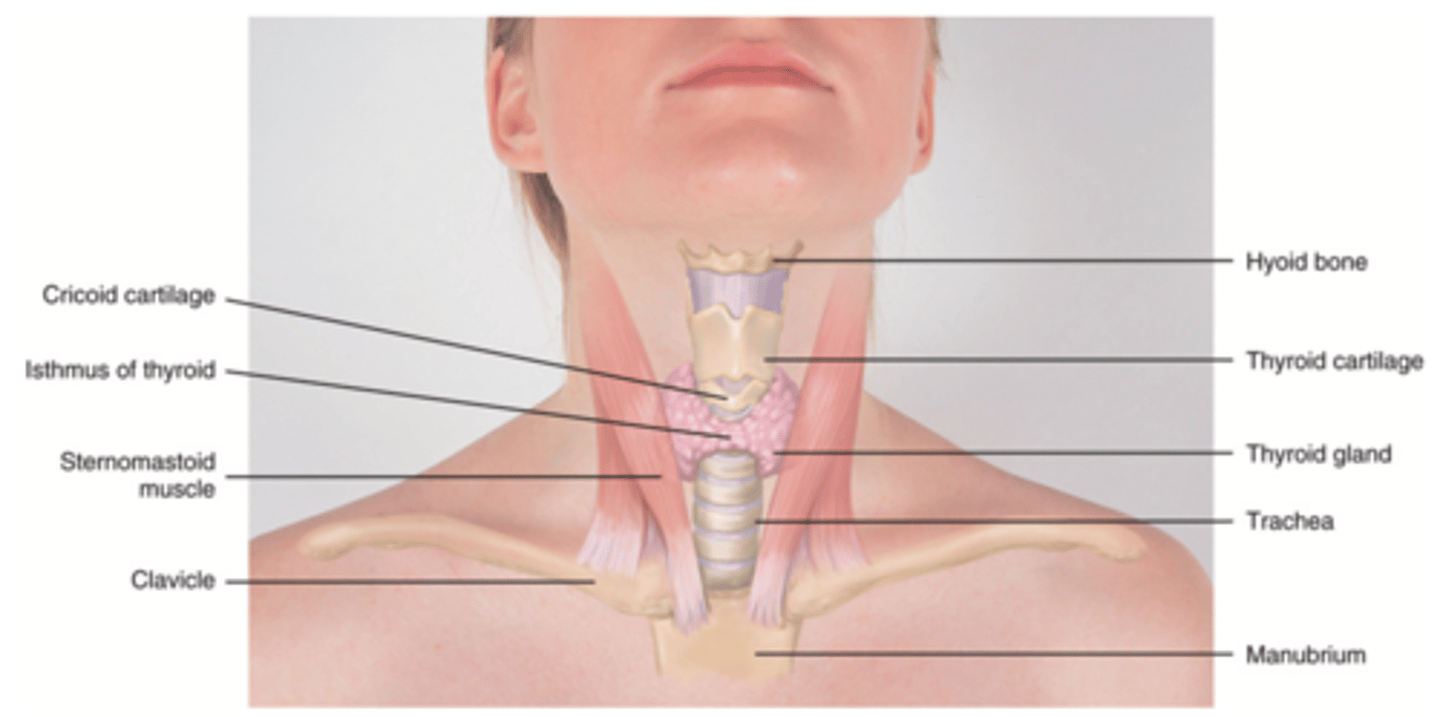
Bruit
Blowing, swooshing sound heard through a stethoscope over an area of abnormal blood flow
Developmental Considerations for Infants and Children when it comes to the Head, Face, and Neck
- Do not palpate fontannels
- Head is larger than chest until 2 years of age
- Lymphatic system is well developed
- Puberty
Developmental Consideration for Older Adults when it comes to the Head, Face, and Neck
Decreased subcutaneous fat
Key Points on Head, Face, and Neck
- Inspection and palpation are key
- State the names of the lymph nodes as you palpate them
- Remember to assess the trachea and the thyroid
Nose
Organ of smell
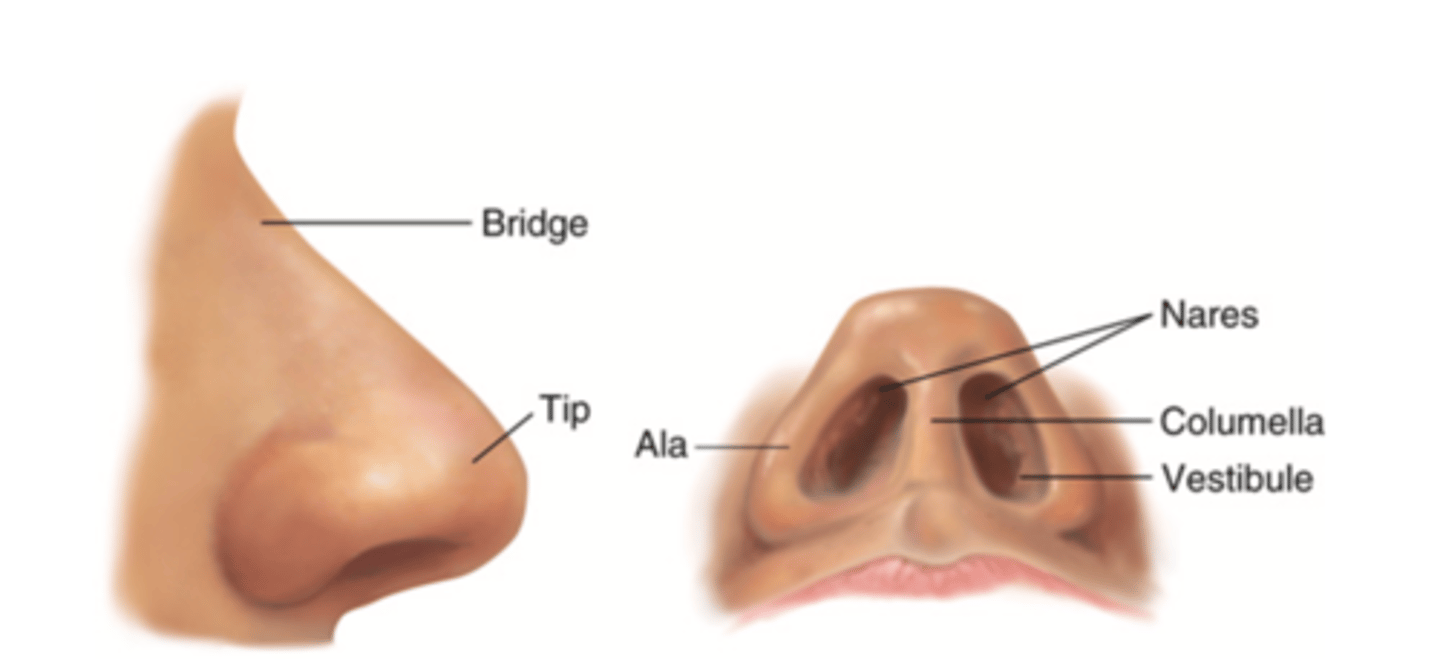
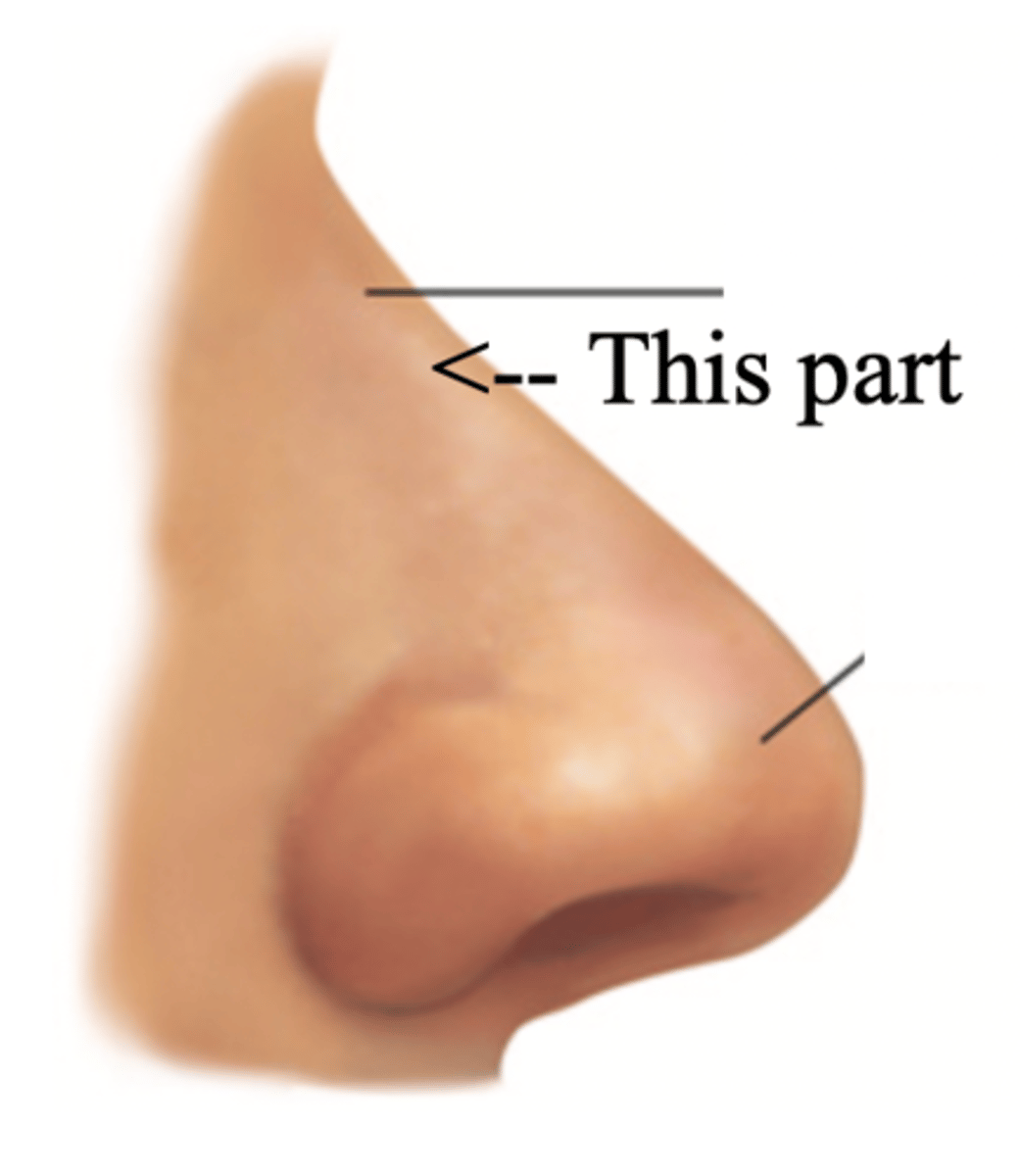
Bridge
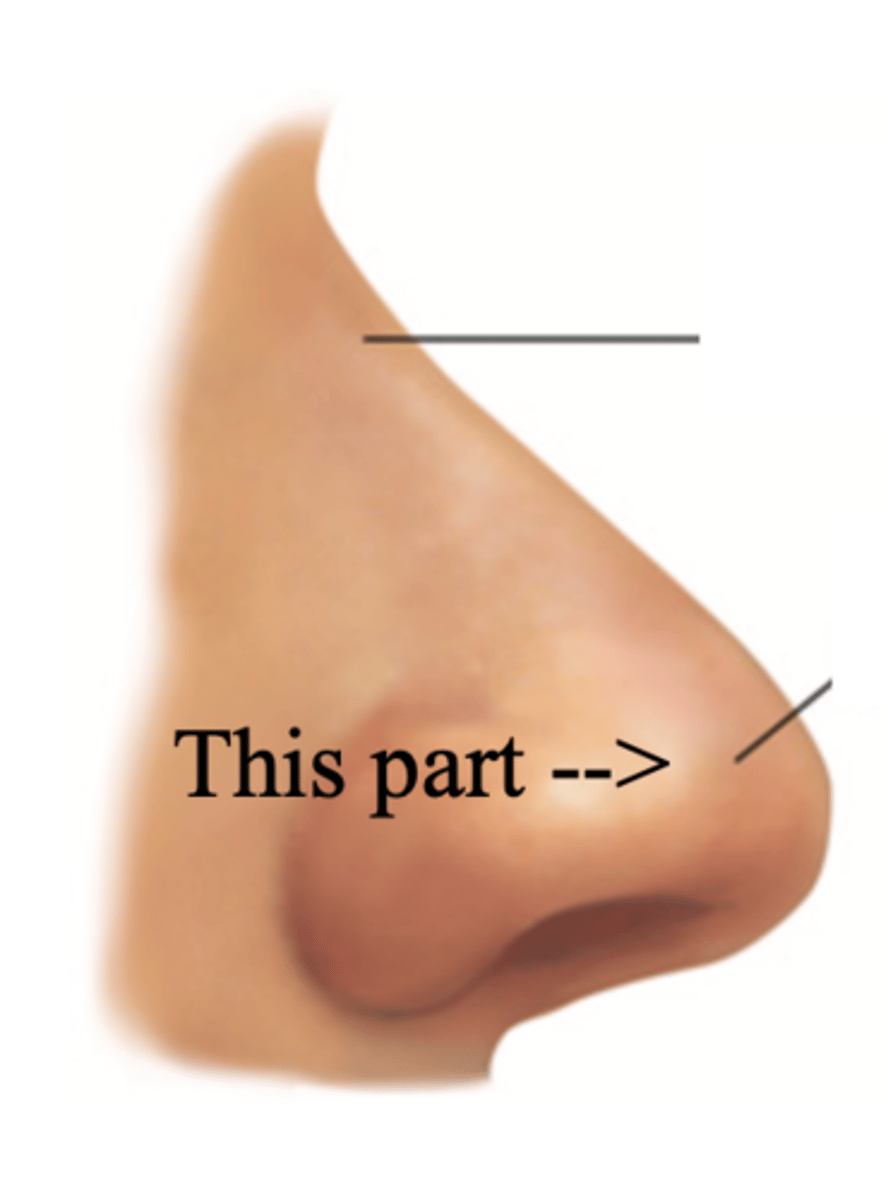
Tip
Ala
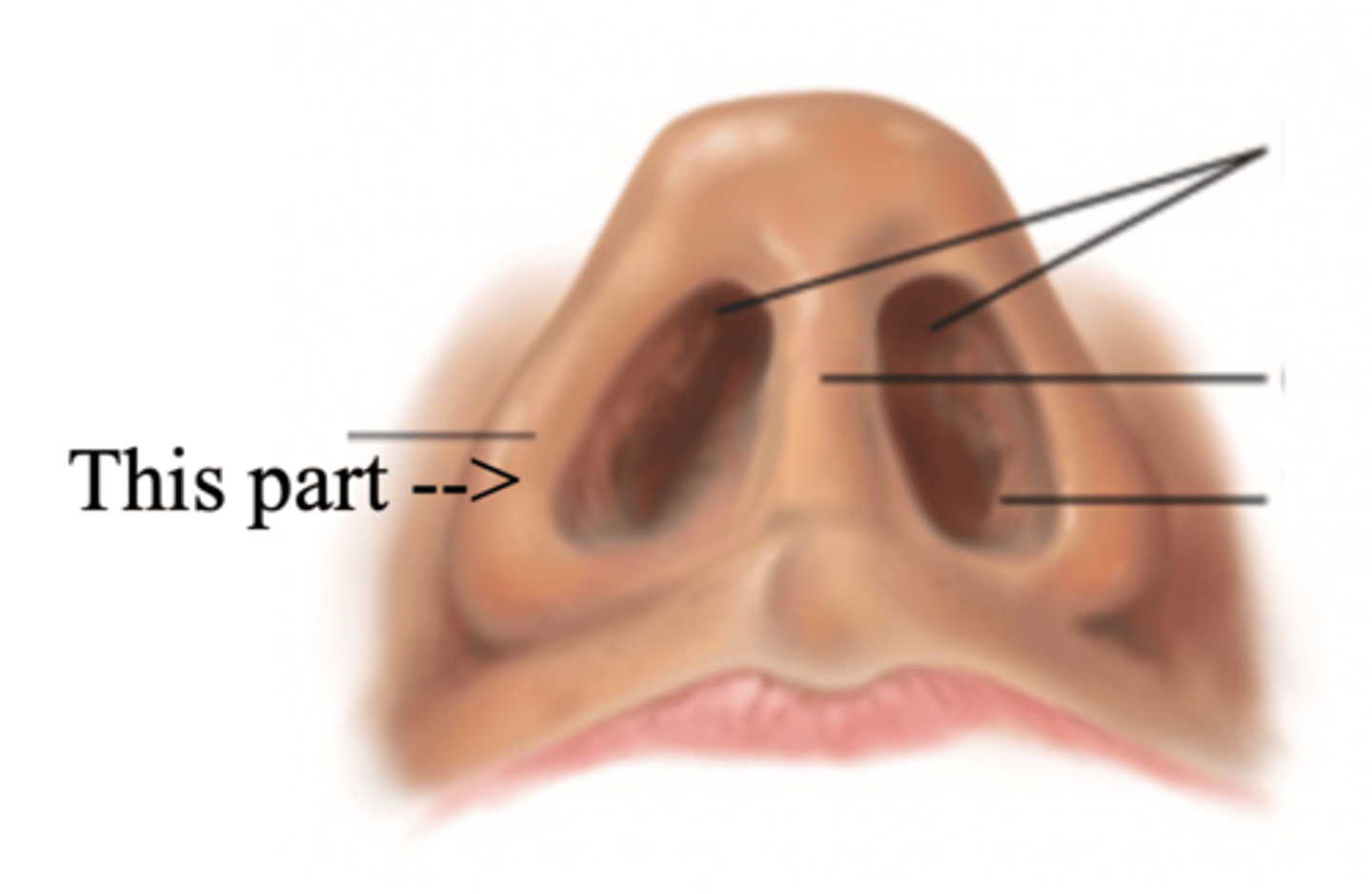
Nares
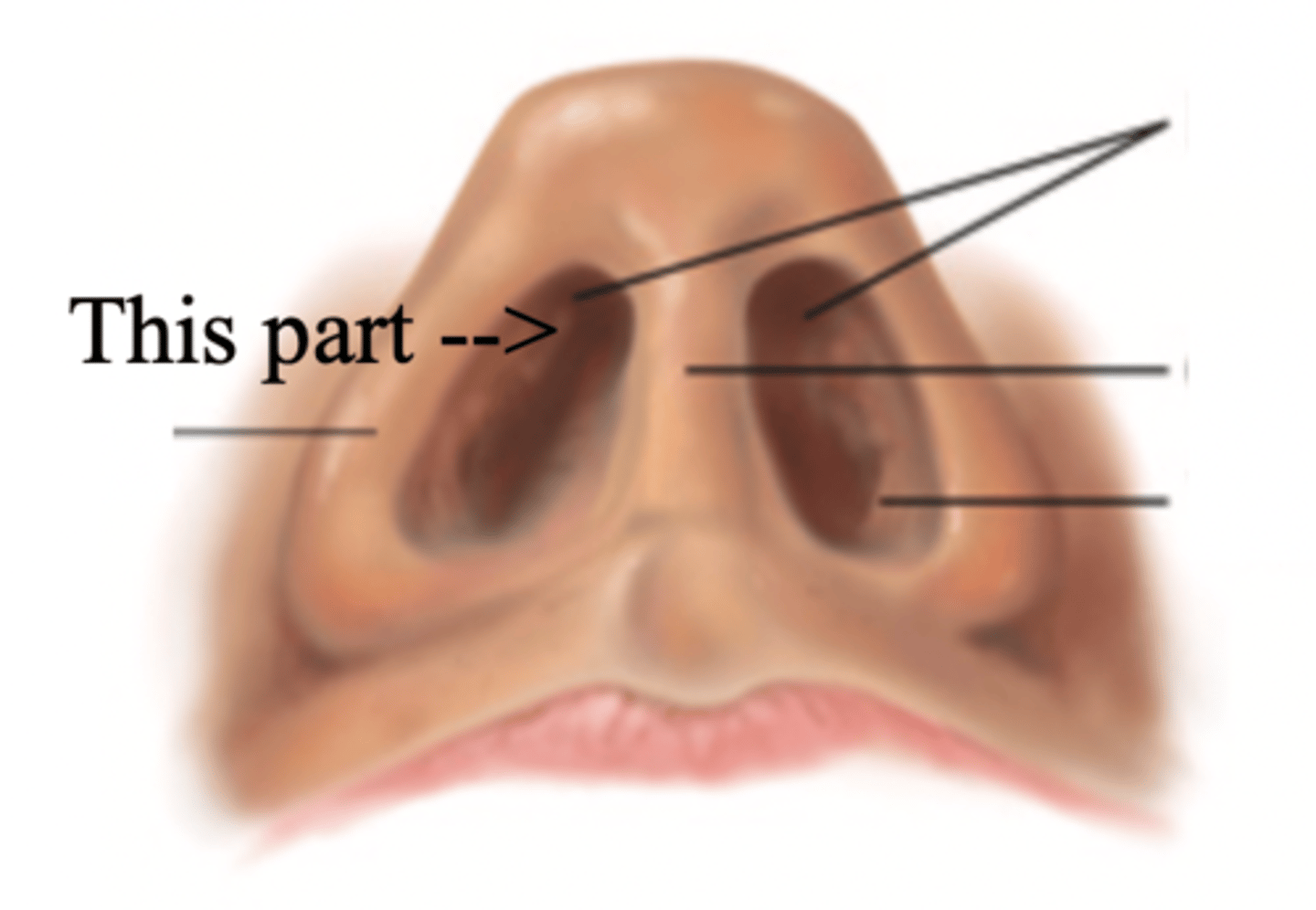
Columella
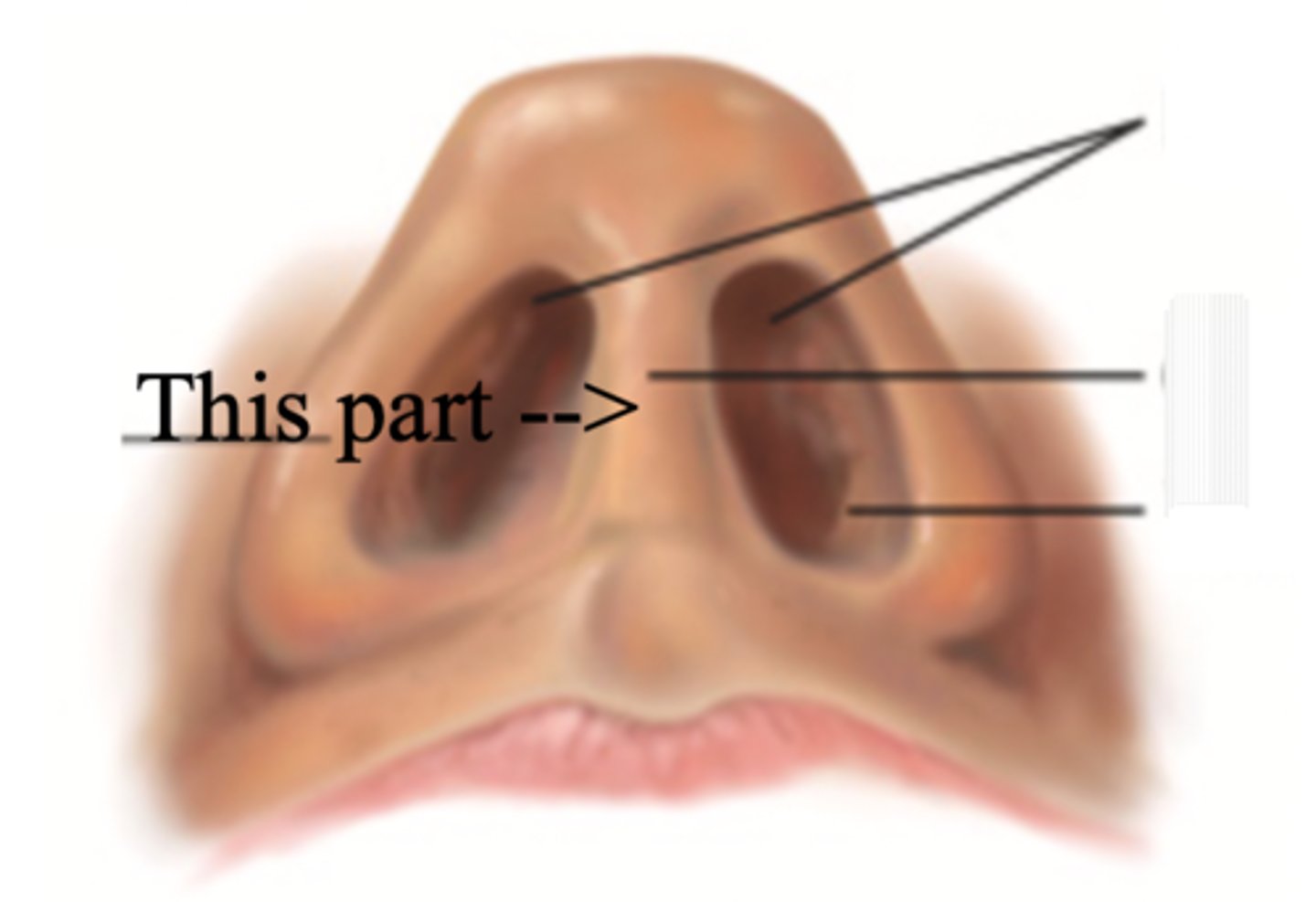
Vestibule
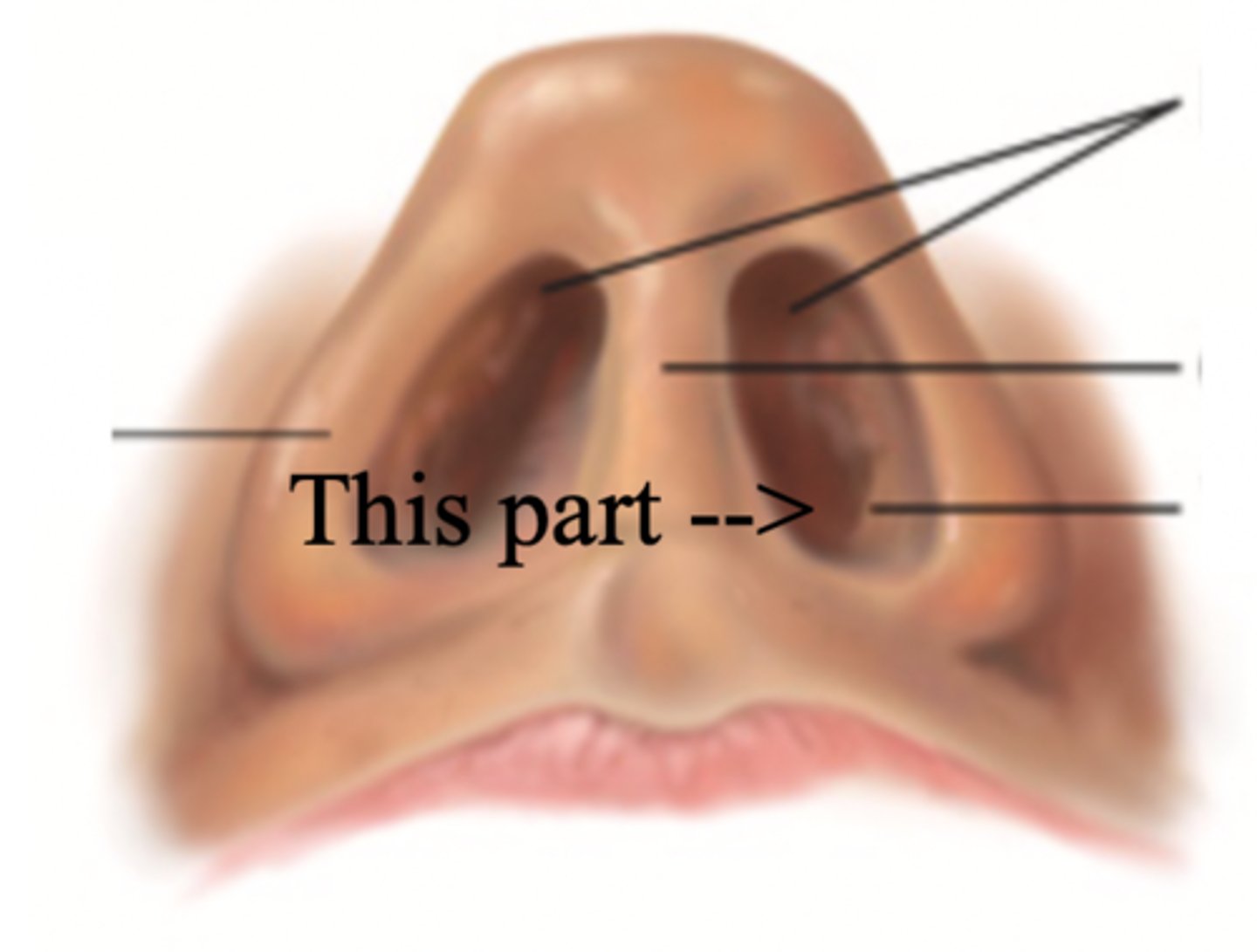
Nasal Cavity
Hollow space behind the nose
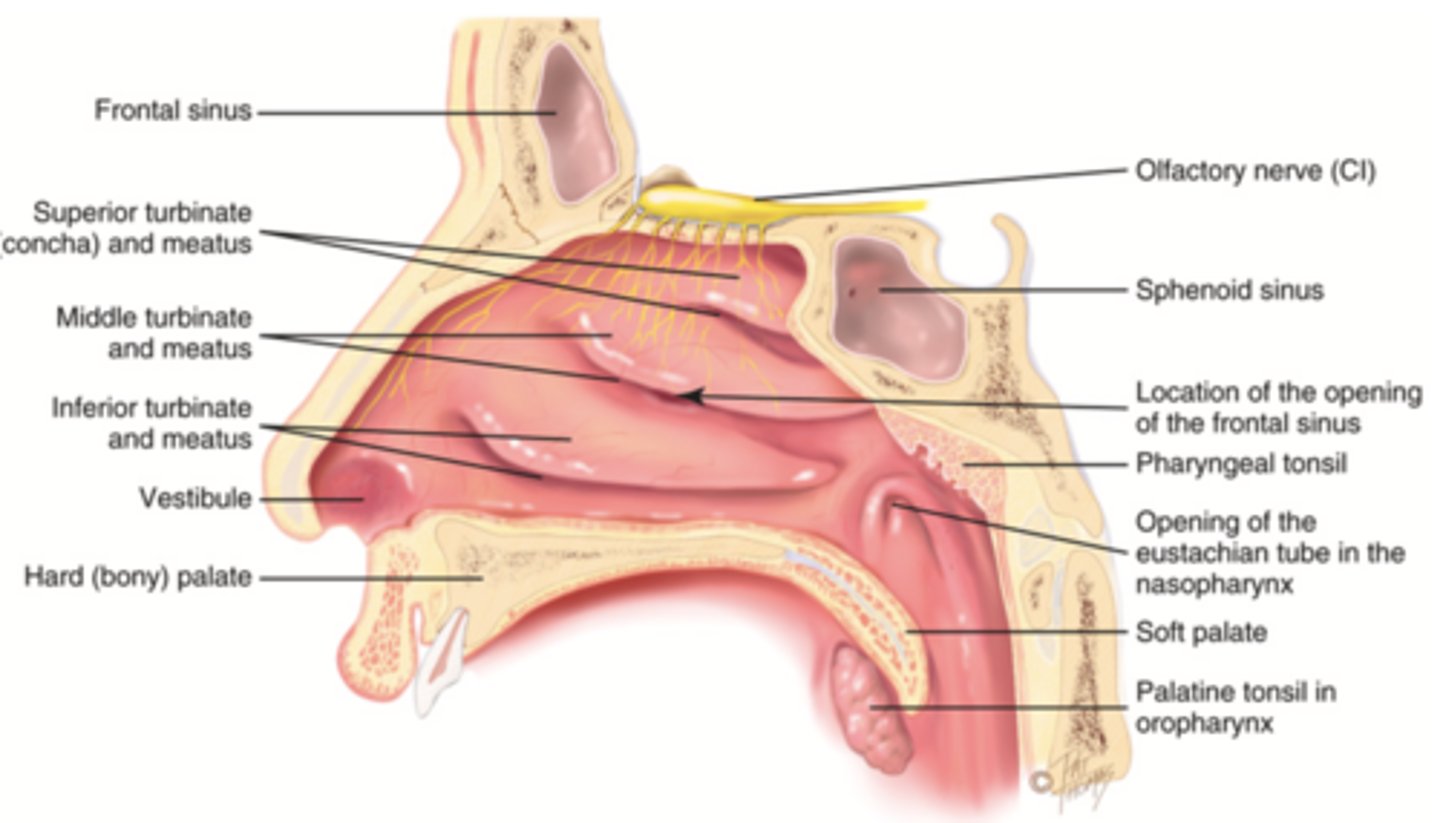
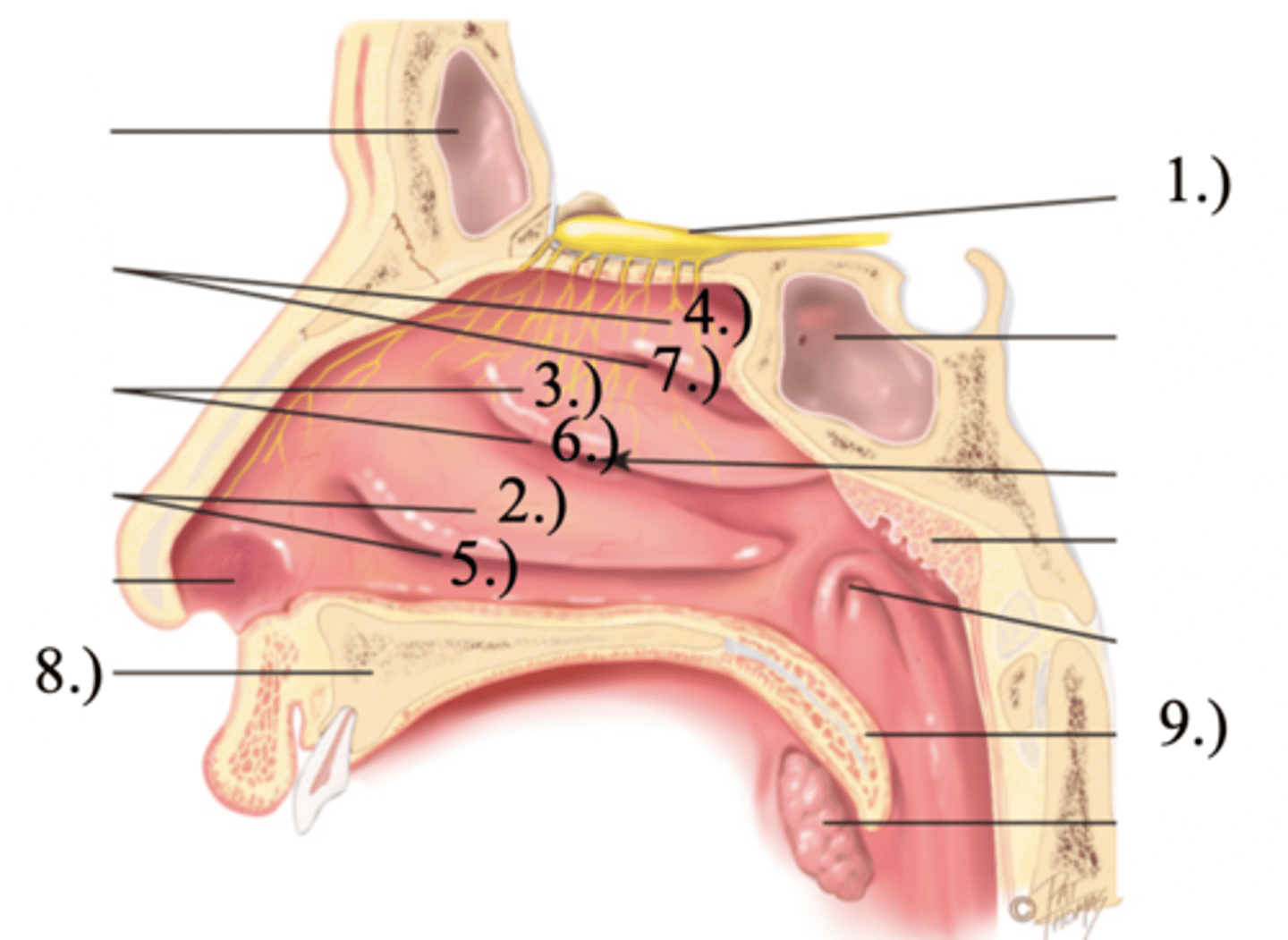
Turbinates (Conchae)
- Bones that protrude into the nasal cavity- that increases surface area for filtering dust and dirt particles by the mucous membrane
- There's an inferior, middle, and superior one (2.), 3.), 4.))
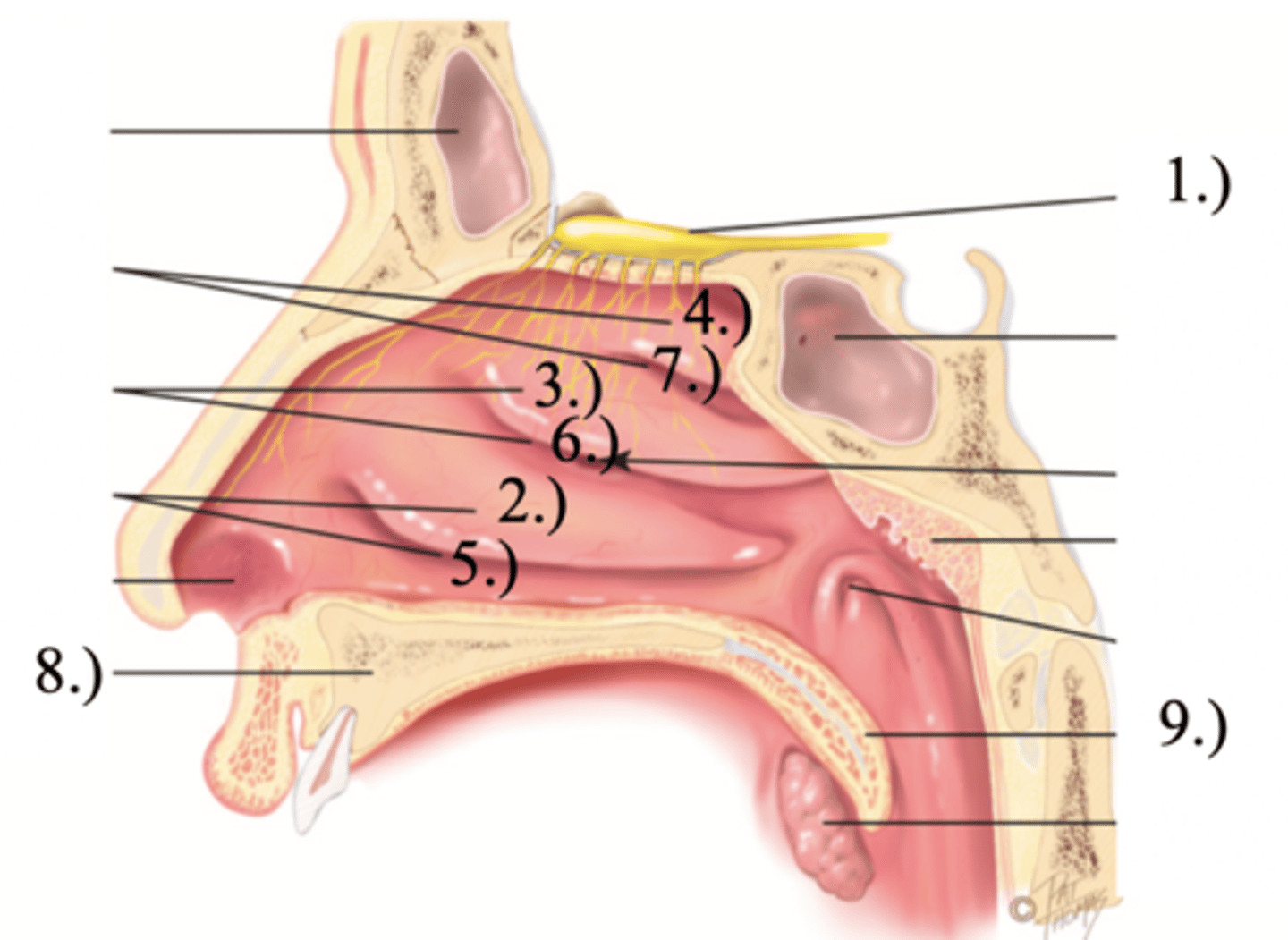
Olfactory Region
A dime-sized area at the top of each nasal cavity that houses sensors responsible for smell (1.))
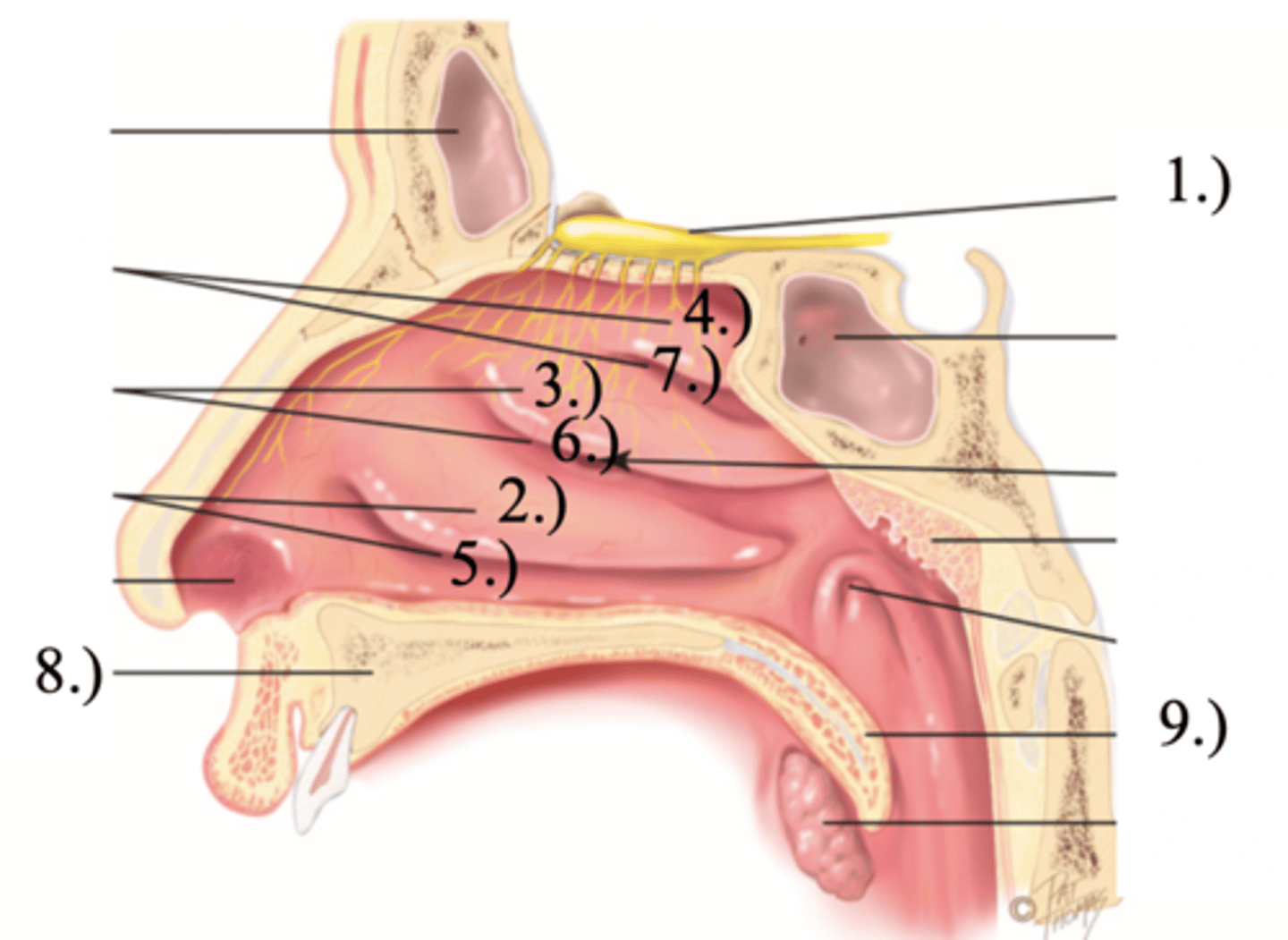
Hard (Bony) Palate
Anterior palate portion that is supported by the palatine processes of the maxillae and the palatine bones (8.))
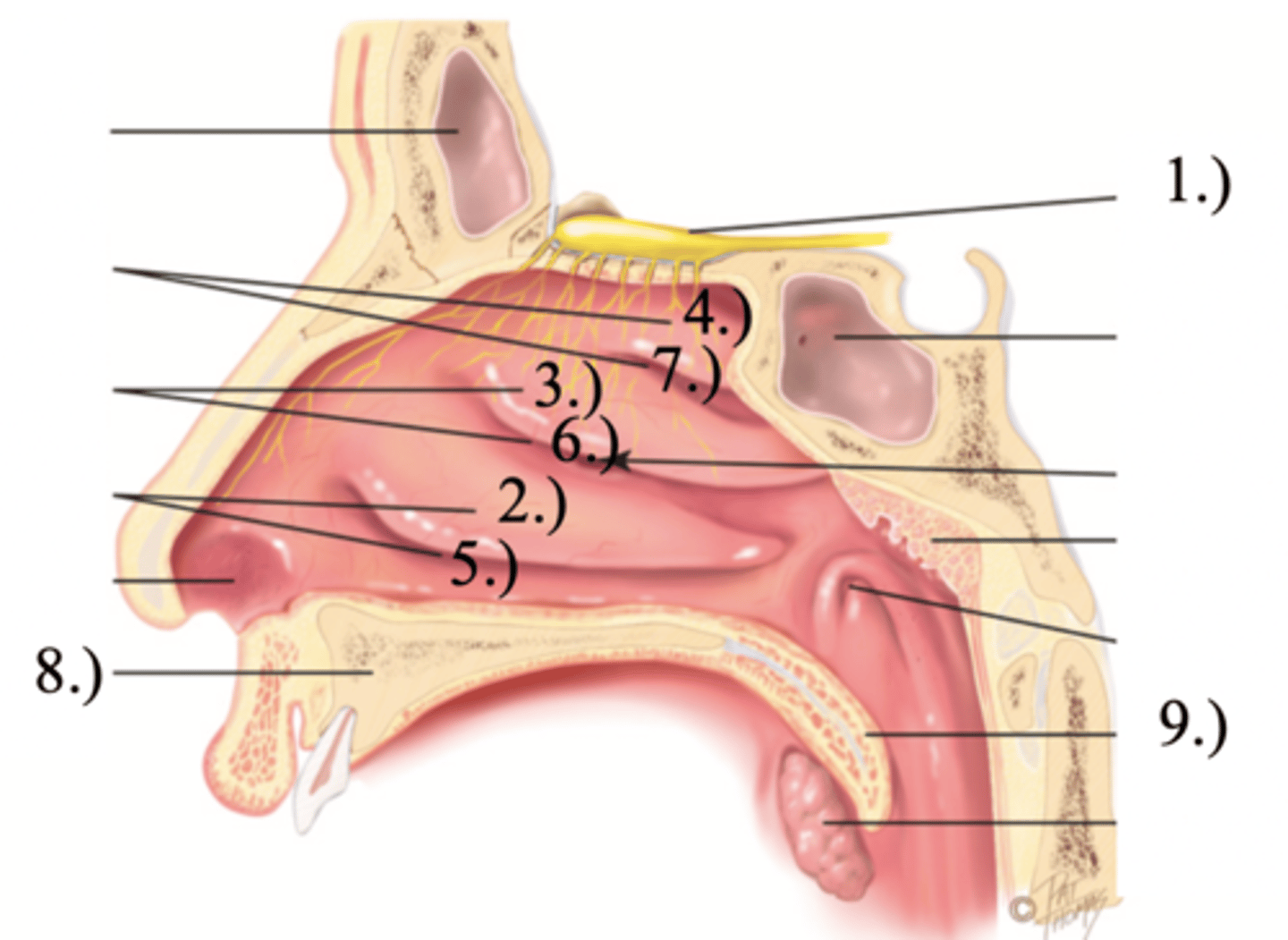
Meatuses
- Constricted passageways in the nasal cavity that produce air turbulence
- There's an inferior, middle, and superior one
(5.), 6.), 7.))
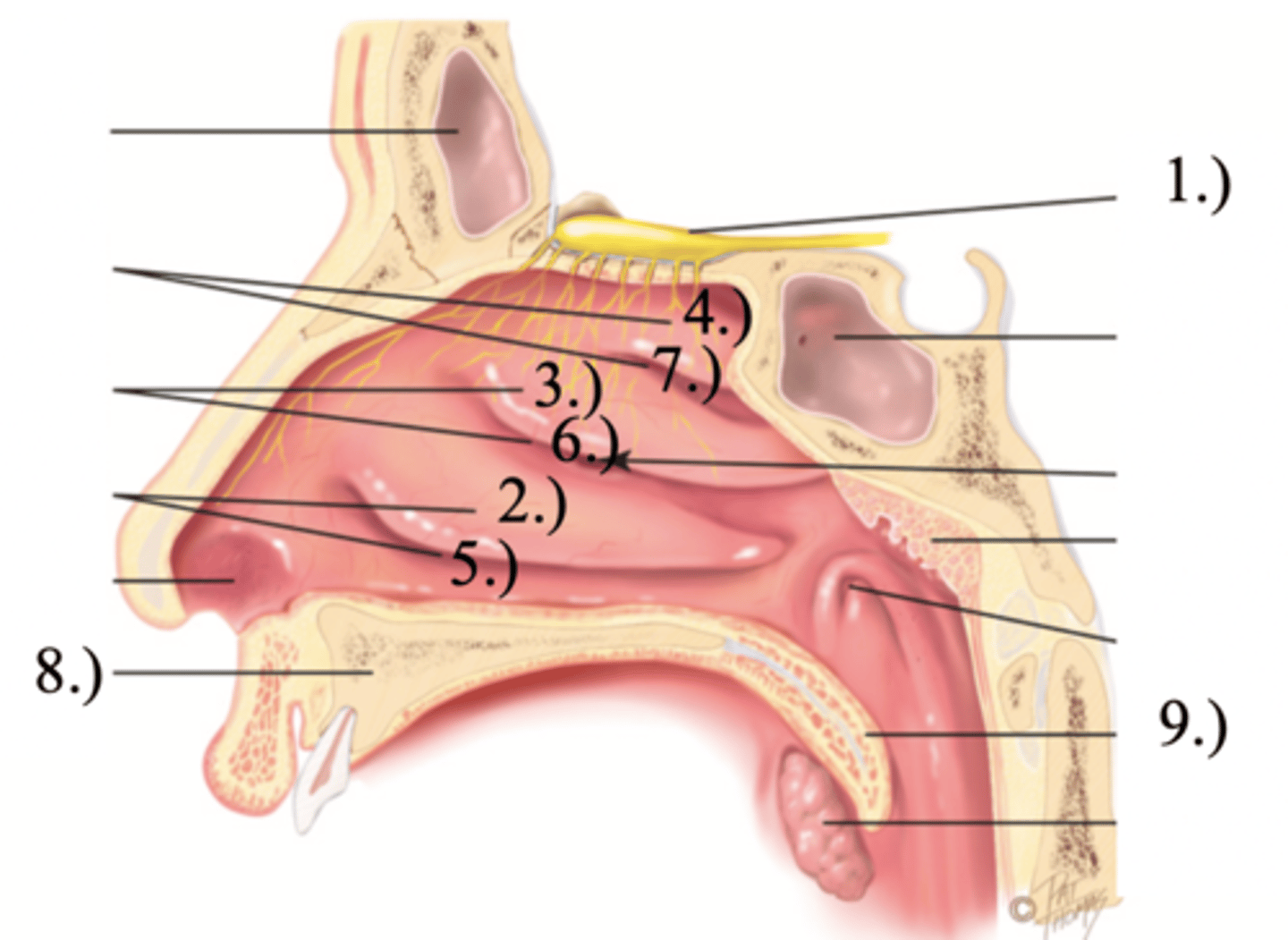
Soft Palate
Posterior palate portion, not supported by bone (9.))
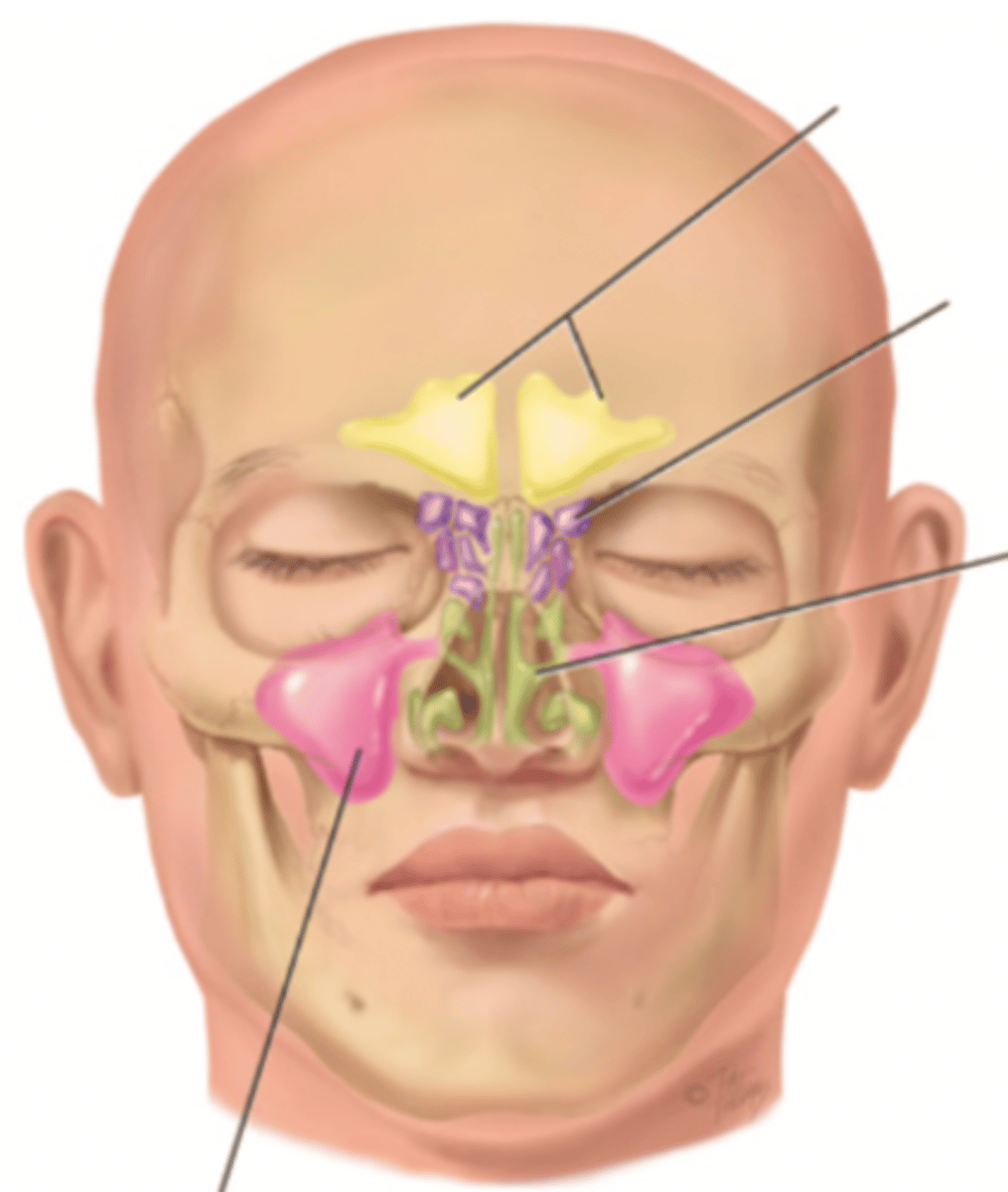
Paranasal Sinuses
- Frontal
- Ethmoid
- Sphenoid
- Maxillary
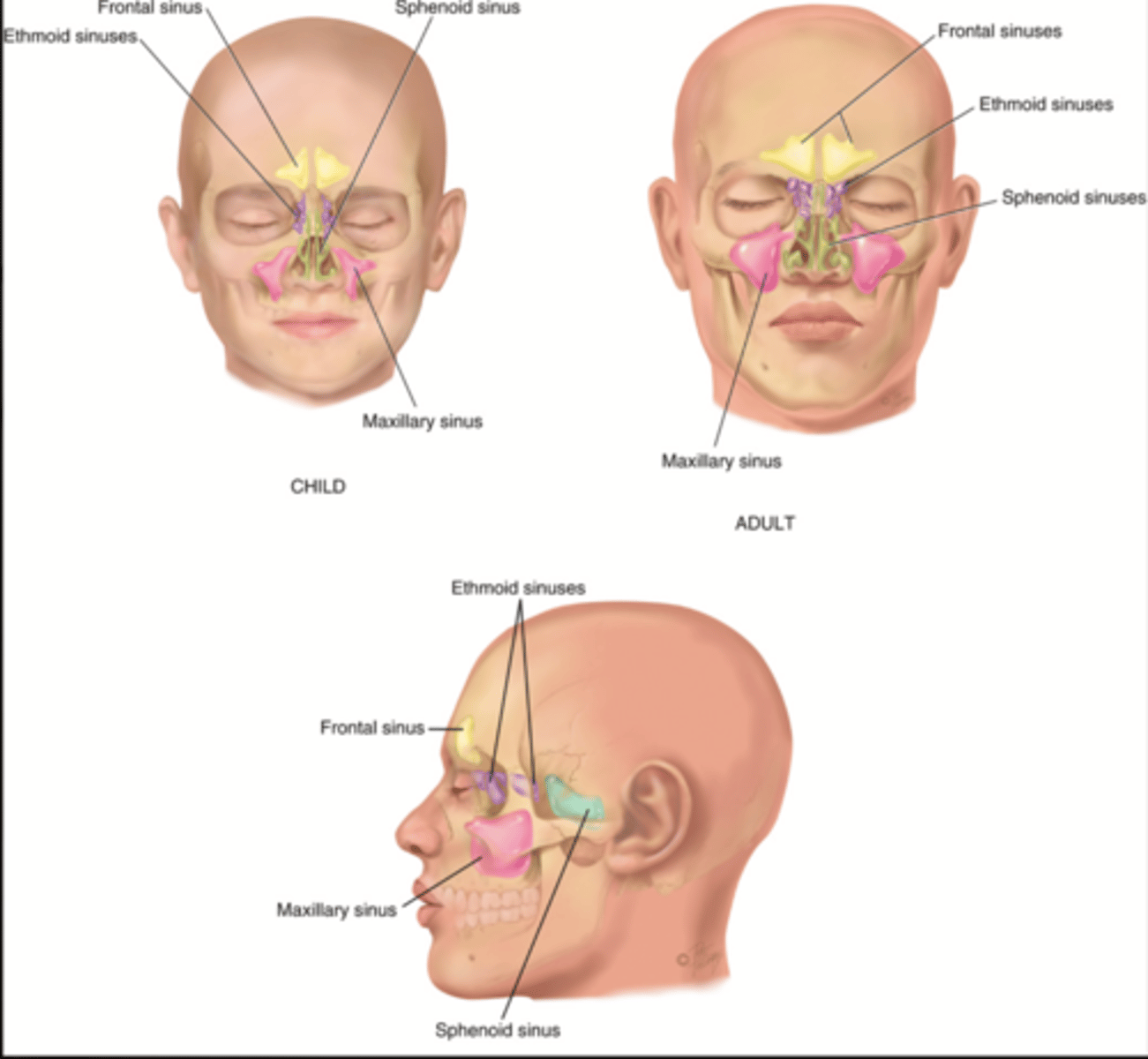
Frontal Sinus
Cavity within the frontal bone (yellow)

Ethmoid Sinus
Mucosa lined air spaces located above the sphenoid sinus and below the frontal sinus (purple)
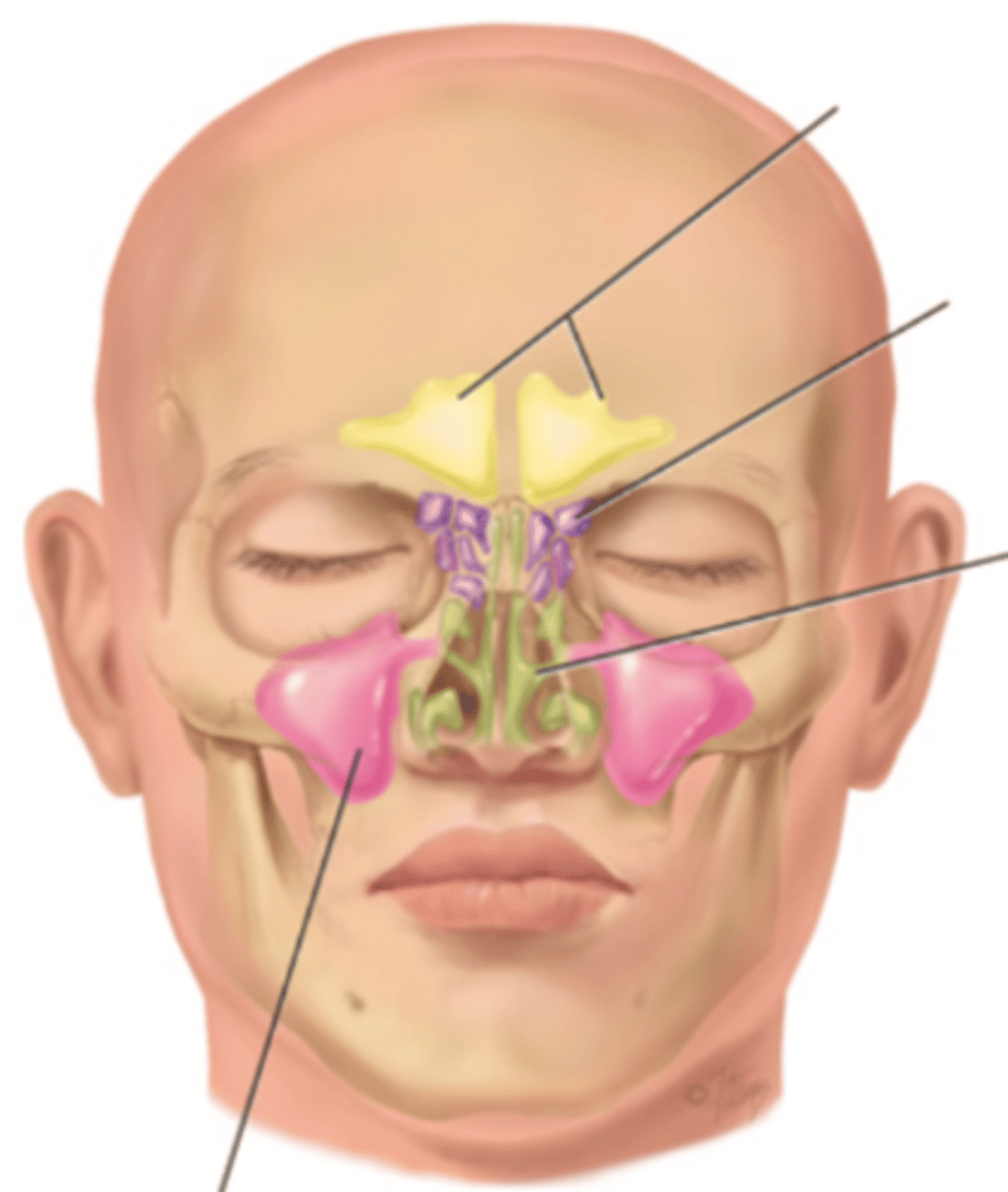
Sphenoid Sinus
Sinus above and behind the nose (green)
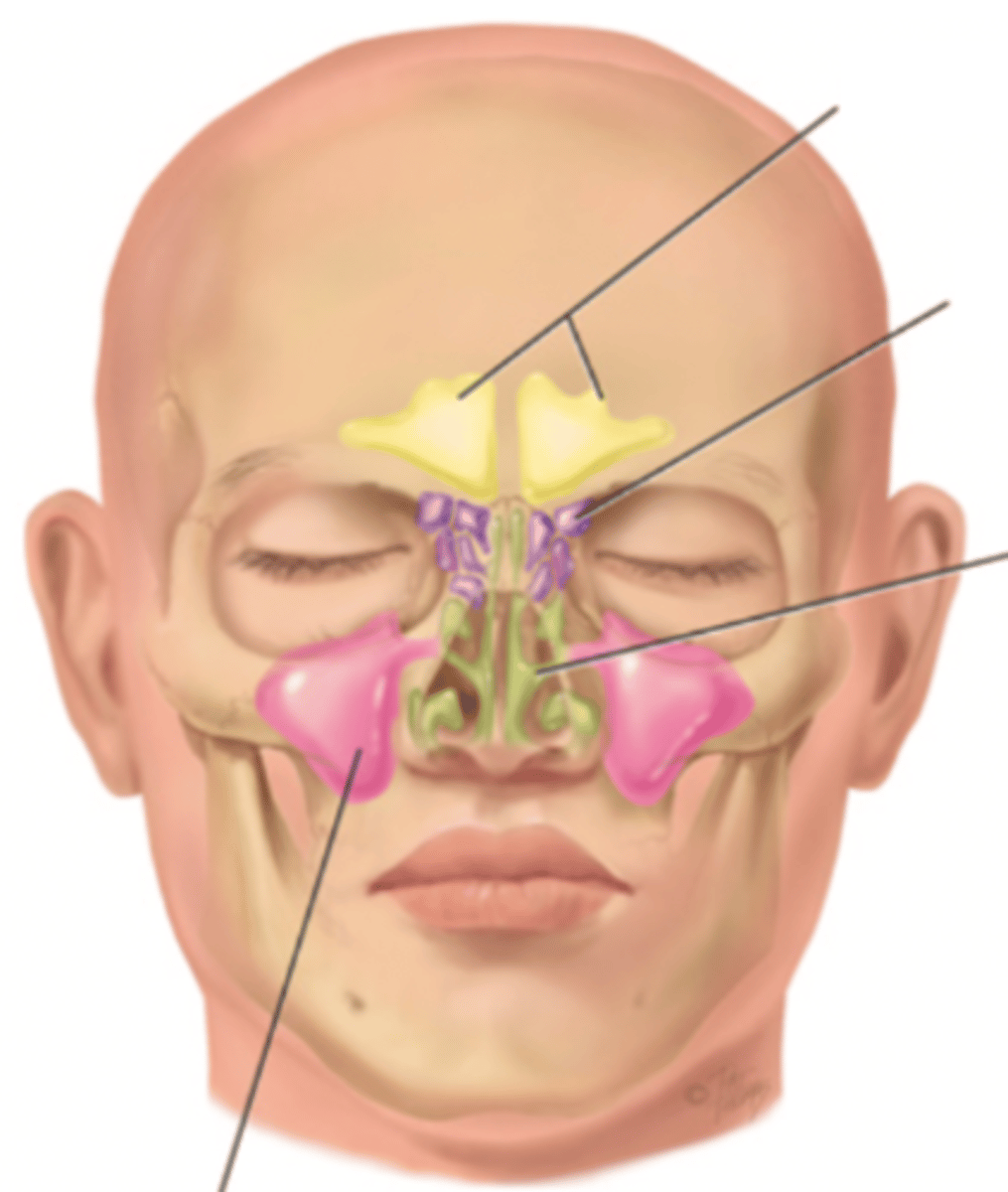
Maxillary Sinus
Sinus on either side of the nasal cavity below the eyes (pink)
Functions of the Nose
- First part of respiratory system
- Warms, moistens, and filters air
- Sense of smell
- Sinuses lighten skull and produces sound and mucus
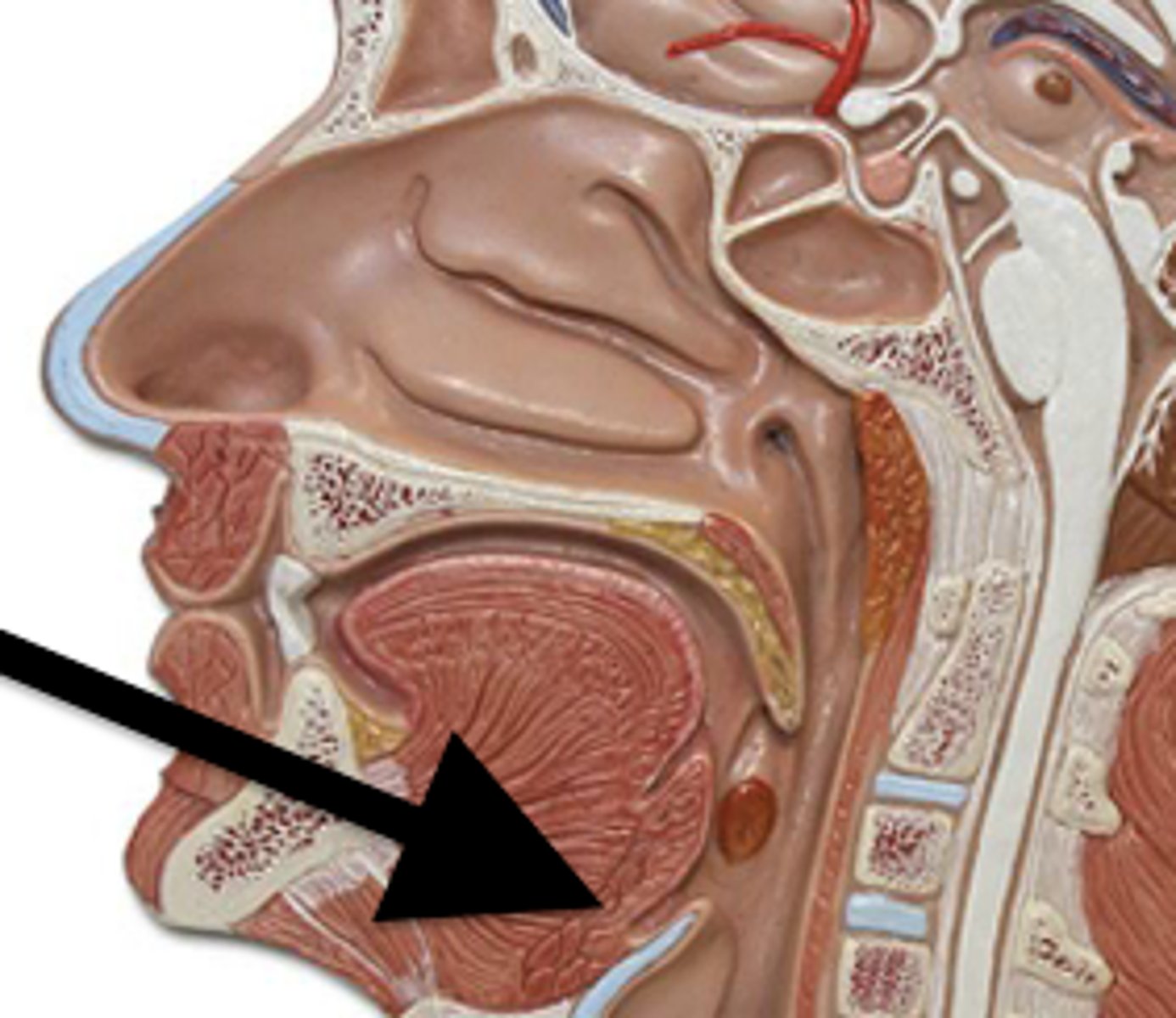
Oral Cavity
Mouth
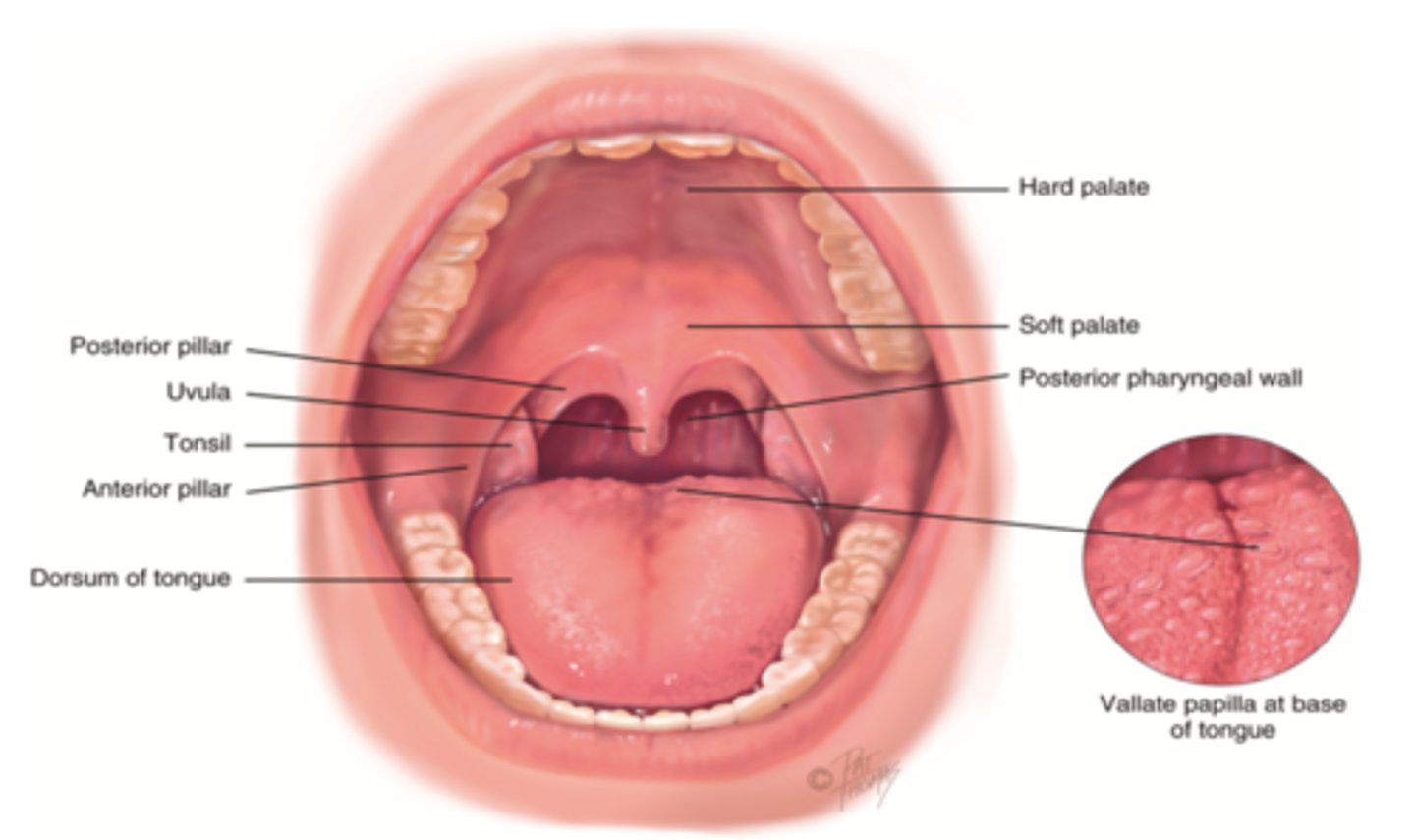
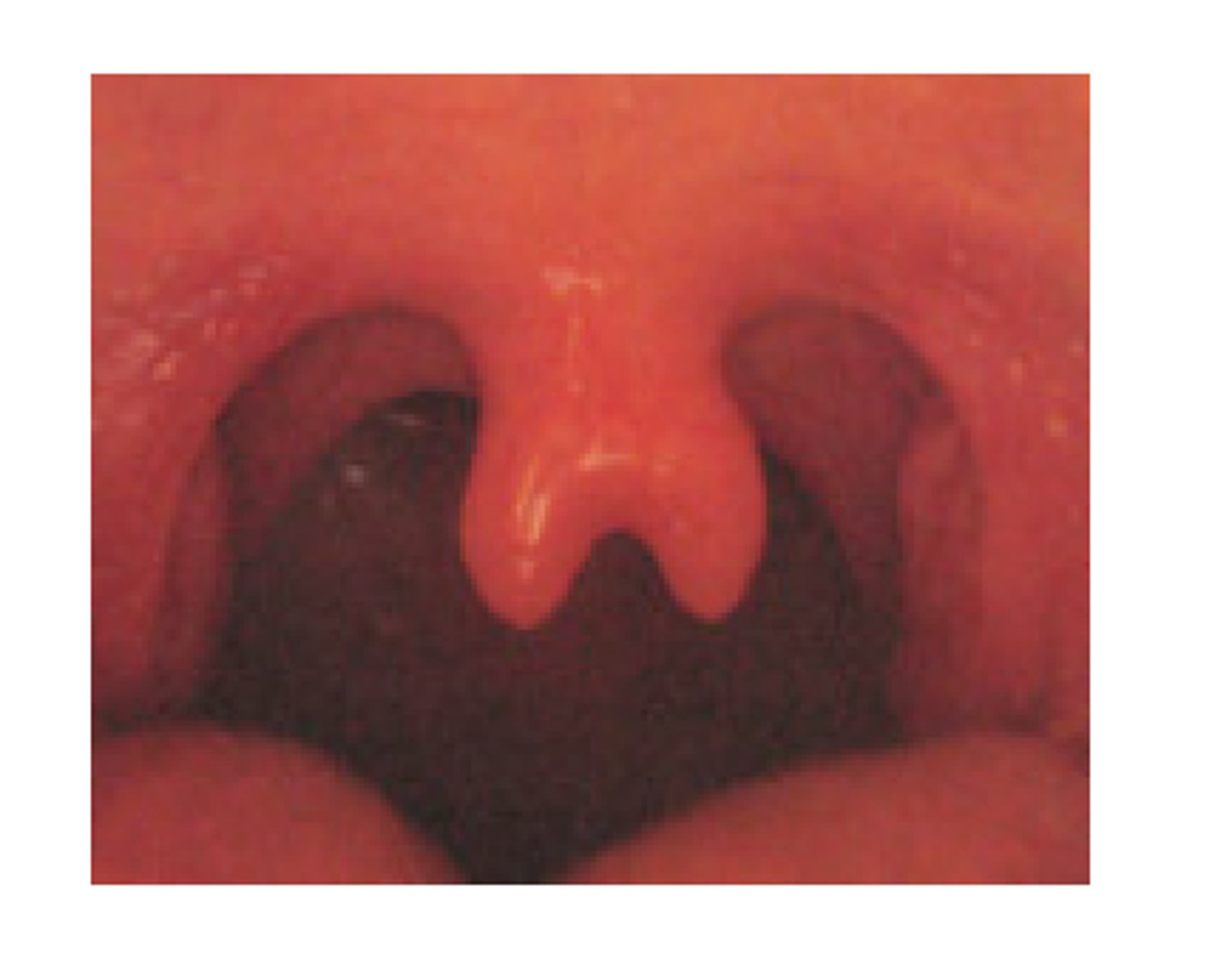
Uvula
Soft tissue hanging from the middle of the soft palate
Amount of Teeth in Adults
32
Amount of Teeth in Babies
20
Salivary Glands
- Parotid
- Submandibular
- Sublingual
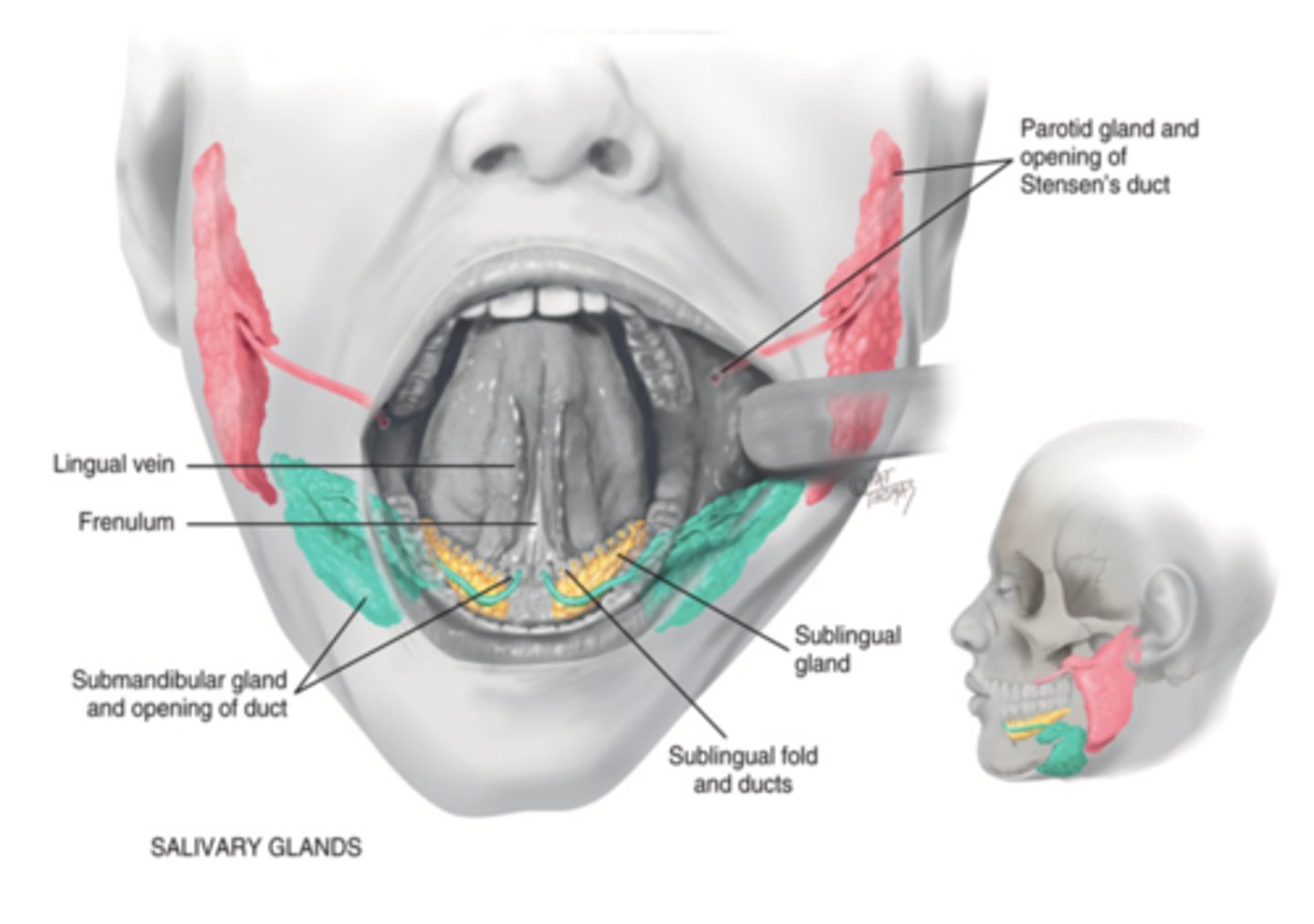
Parotid Gland
Salivary gland within the cheek, just anterior to the ear (red)
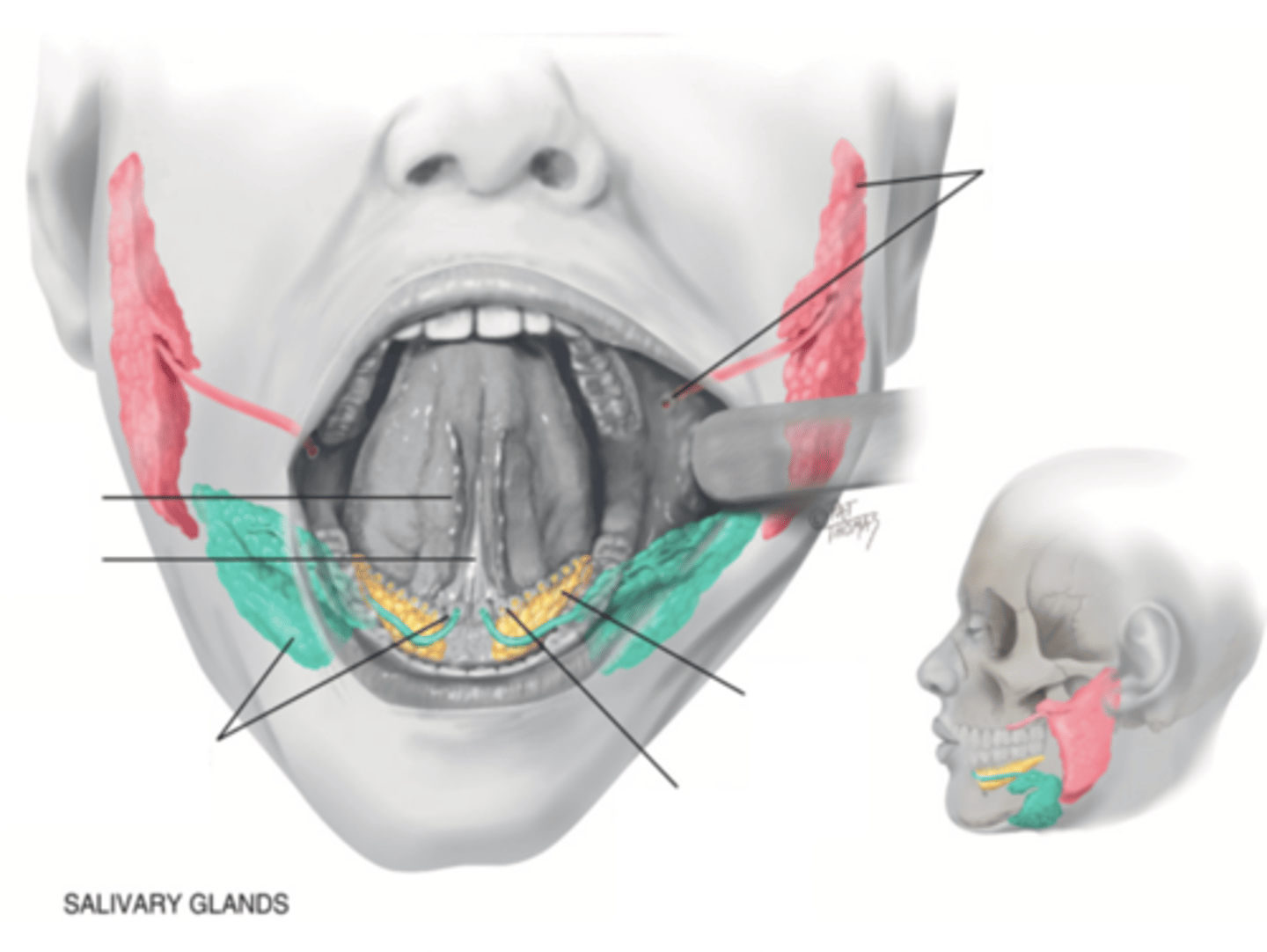
Submadibular Gland
Salivary gland under the mandible (green)
Sublingual Gland
Salivary gland under the tongue (yellow)
Functions of the Mouth
- First part of the digestive system
- Formation of speech
- Sense of taste
Pharynx (Throat)
Passageway for air, leads to trachea
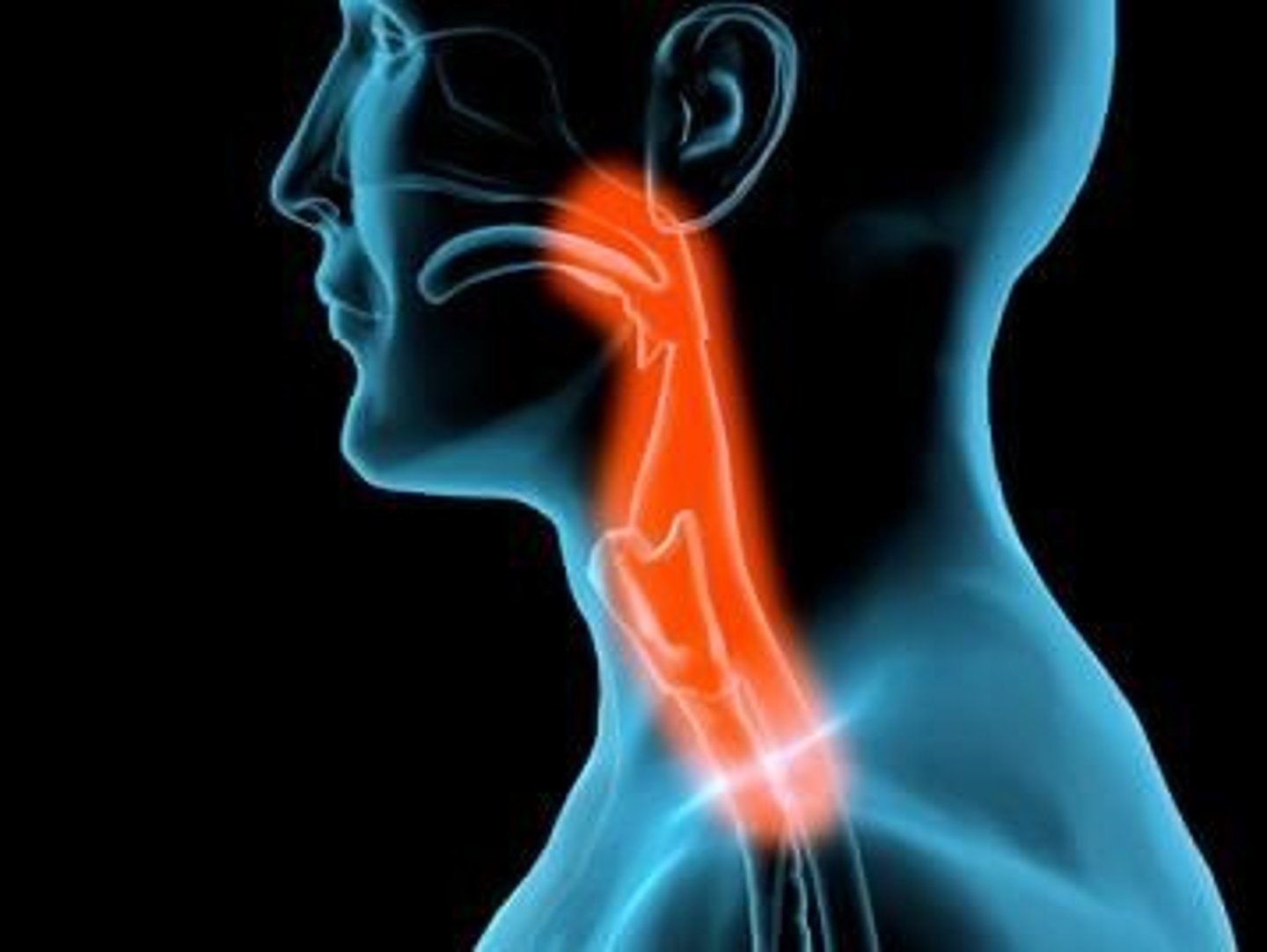
Function of Throat
- Passageway for food
- Passageway for air
- Tonsils are part of the immune system
Nasopharyx
The portion of the pharynx that extends from the nostrils to the soft palate
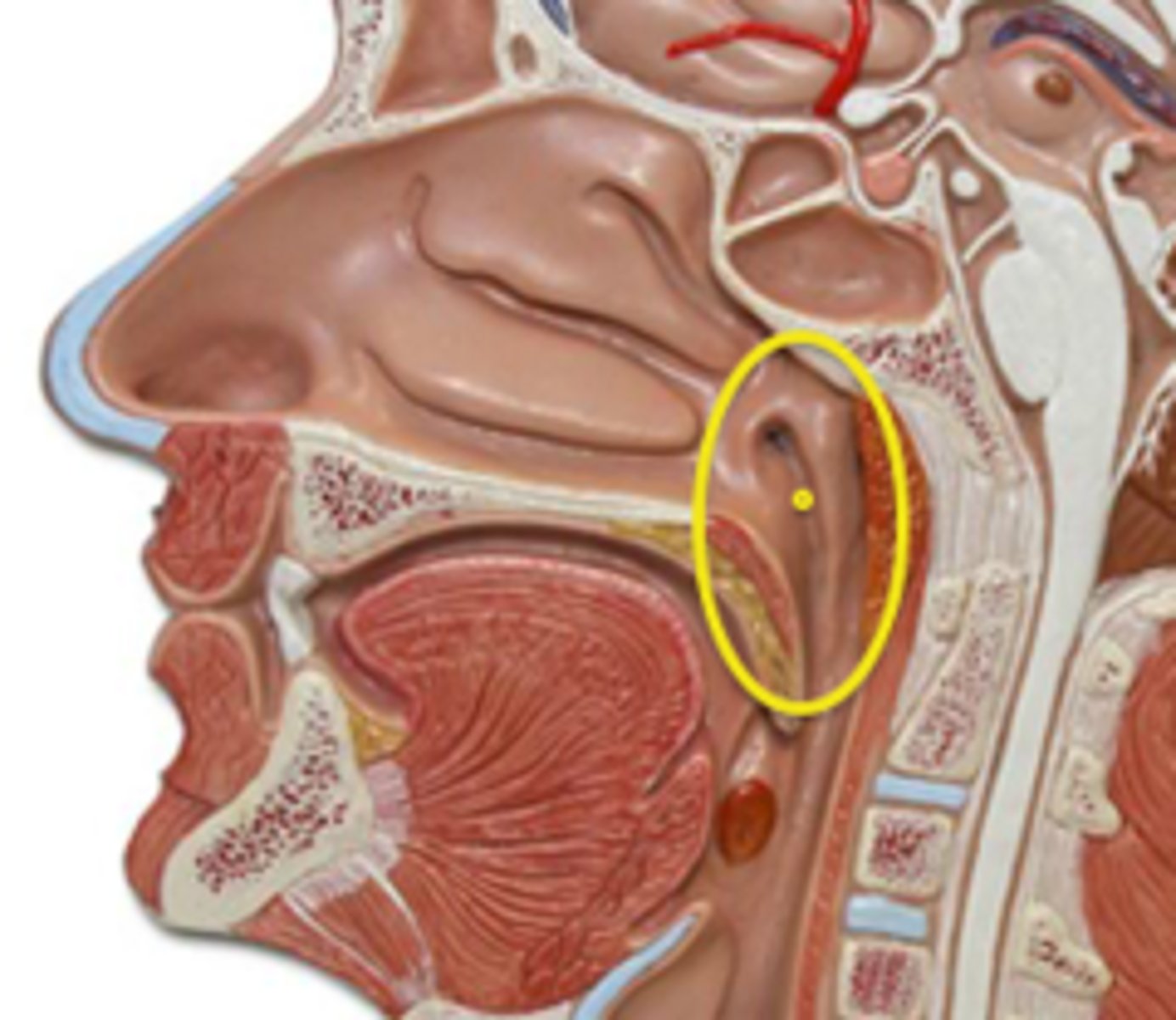
Oropharynx
Central portion of the pharynx between the roof of the mouth and the upper edge of the epiglottis
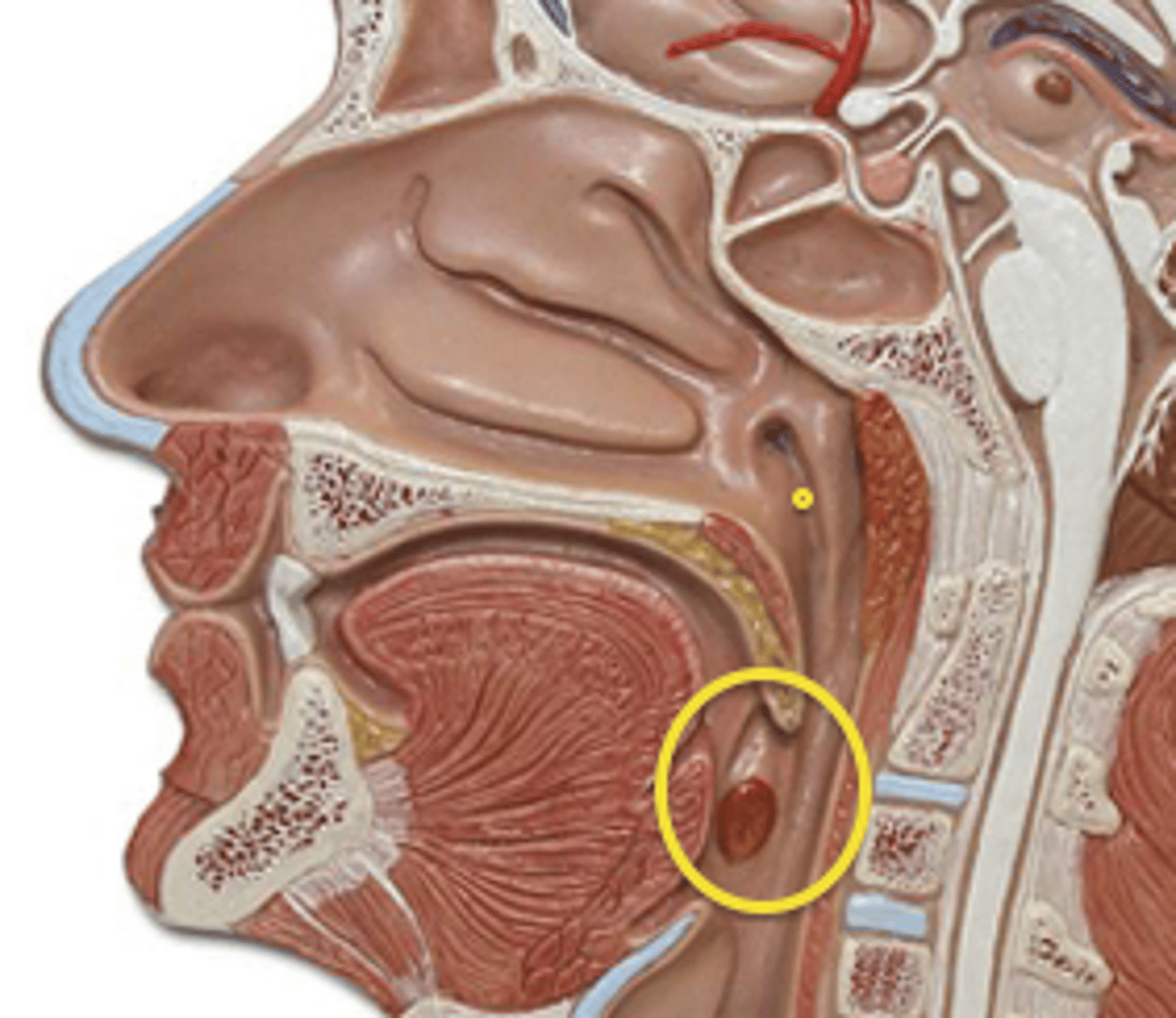
Tonsils
Masses of lymphatic tissue in the back of the oropharynx
3 Tonsils in the Mouth
- Palatine
- Adenoid
- Lingual
Palatine Tonsil
One of a pair of almond-shaped masses of lymphatic tissue in the oropharynx
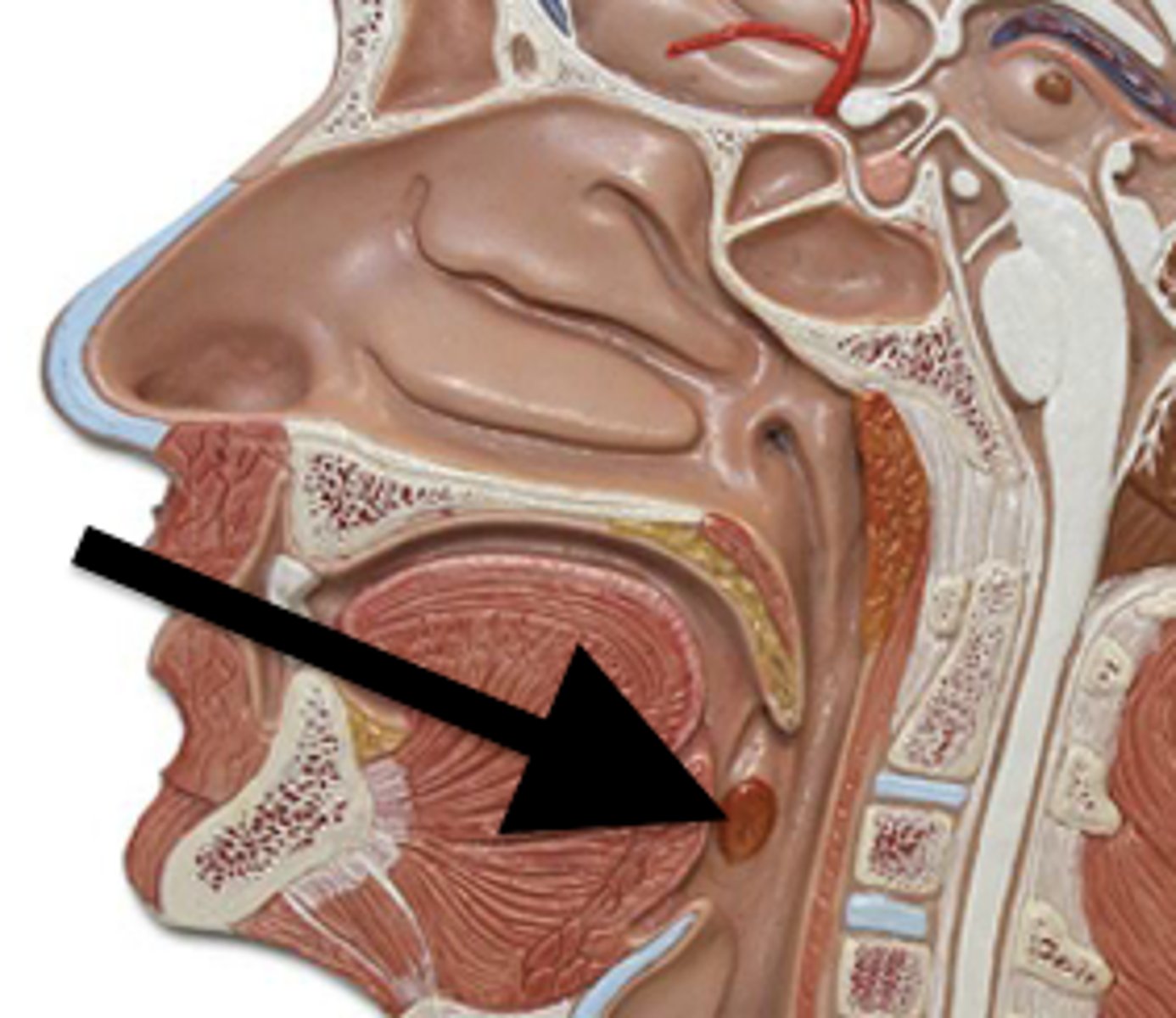
Adenoid Tonsil
Pharyngeal tonsil
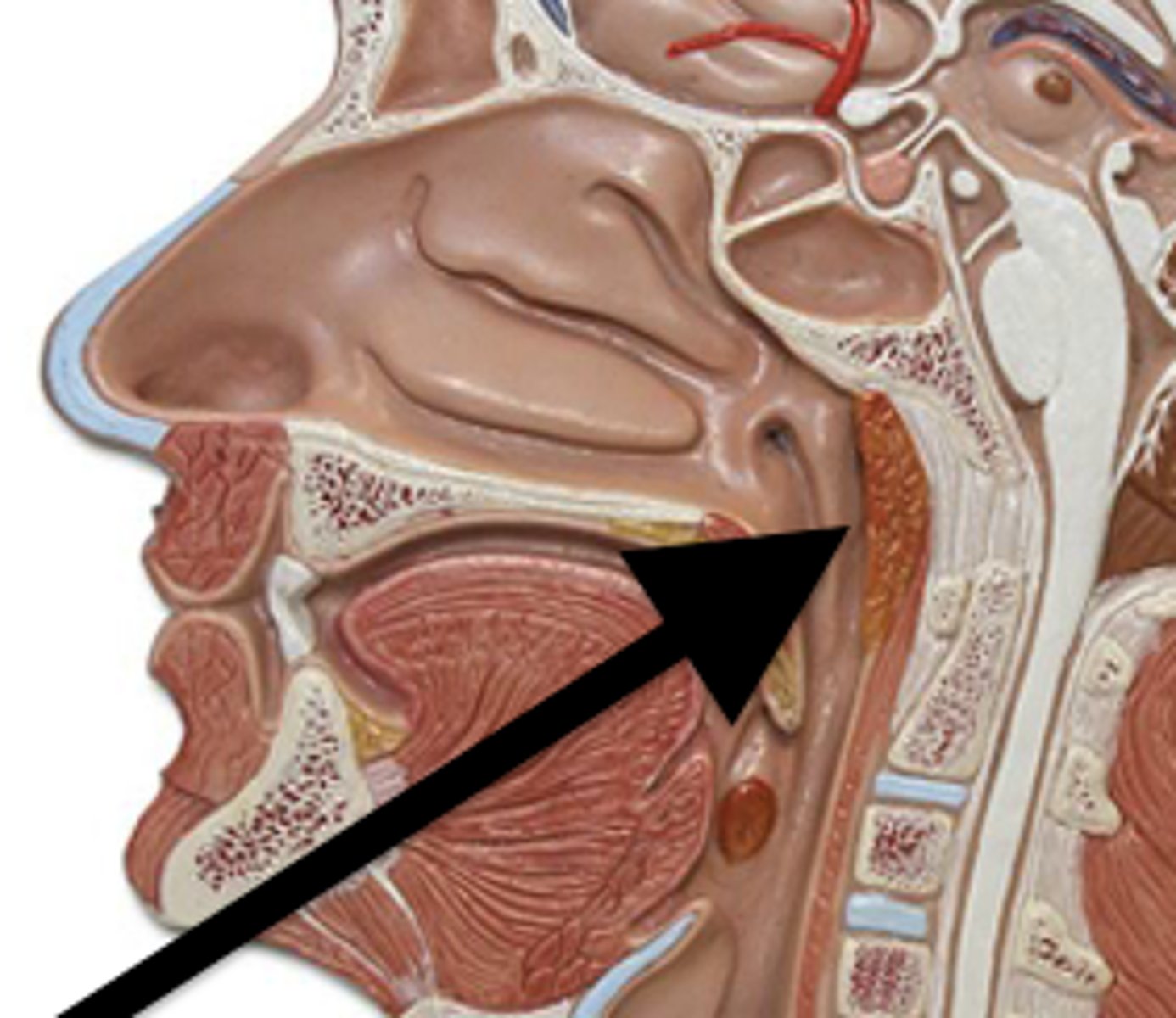
Lingual Tonsil
Tonsil located at the base of tongue
Subjective Data to Assess for the Nose
- Discharge
- Frequent colds
- Sinus pain
- Trauma
- Epistaxis
- Allergies
- Altered smell
(Dangerous Falcons Smell Trouble Everywhere and Are Astute)
Subjective Data to Assess for Mouth and Throat
- Sores/lesions
- Sore throat
- Bleeding gums
- Toothache
- Sugar consumption
- Bruxism
- Hoarseness
- Dysphagia
- Altered Taste
- Tobacco consumption
- Alcohol consumption
- Sleep apnea
- Self-care behaviours
(Sharp Shooters Buy Tiny Shiny Bows and Horses Date Alligators To Aggravate Small Snakes 🐍)