Chapter 6 - Adaptations to Aquatic Biomes
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Which of the following provides the strongest molecular evidence supporting the evolutionary relationship between whales and terrestrial ungulates?
Comparative analysis of DNA sequences
The discovery of Indohyus most directly supports which inference about whale evolution?
The transition from land to water in whale evolution occurred gradually through semi-aquatic intermediates.
Which morphological change most directly facilitated the whale’s ability to maintain high-speed movement in water?
Reduction and modification of pectoral and pelvic girdles
At what temperature does liquid freshwater reach its maximum density?
4°C
Which of the following best explains why ice floats on liquid water?
The molecular structure of ice creates more open space between water molecules.
Why does seawater remain unfrozen at temperatures slightly below 0°C?
Salt lowers the freezing point of water by disrupting hydrogen bonding.
Which statement correctly describes the relationship between temperature and density in water?
Density decreases as temperature decreases below 4°C.
Which statement about the relationship between salinity, temperature, and density is correct?
Cold, salty water is denser than warm, fresh water.
Which is not an adaptation for buoyancy?
Maintaining similar bone density to terrestrial organisms
Viscosity is best described as:
The thickness of a fluid that resists movement of objects through it
Which organisms experience the greatest relative effects of viscosity and adhesion?
Zooplankton
How does a fusiform body shape help aquatic animals?
It reduces drag and friction while moving through water
In small aquatic organisms, structures like antennae and feathery projections primarily:
Generate drag to prevent sinking
Which statement correctly compares the experience of viscosity between large and small aquatic animals?
Small zooplankton are more affected by viscosity than large fishes
A fish and a zooplankton of similar shape are moving through water. Relative to the fish, the zooplankton experiences:
More drag due to viscosity and adhesion
Which of the following is not a characteristic of deep-water habitats?
Increased photosynthetic activity
How do many deep-living fish cope with the pressure?
By lacking air in their bodies
Hydrothermal vents provide deep-sea organisms with:
Hot water and high concentrations of sulfur and other minerals
In the symbiosis between tube worms and chemosynthetic bacteria, the bacteria:
Convert sulfide gas and CO₂ into organic compounds used as food by the tube worms
Bioluminescence in deep-sea organisms is primarily used to:
Attract prey and mates
Why is water considered a powerful solvent?
It has the ability to dissolve many substances
The polar nature of water molecules comes from:
The slightly negative oxygen end and slightly positive hydrogen ends
Water allows substances to react chemically to form new compounds because:
It acts as a medium in which molecules can move and collide
Water molecules are attracted to other polar compounds because
They have a polar charge distribution
Which statement best explains why dissolved minerals in water are accessible to living systems?
Minerals are carried by water in a solvated form
What does the term saturation refer to in the context of mineral solubility?
he upper limit of solubility of a mineral in water
Why does calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) often precipitate out of ocean water?
It has low solubility in ocean water and exceeds saturation
Over millions of years, precipitation of calcium carbonate contributes to:
Formation of limestone deposits
Which gases are primarily responsible for the formation of acid deposition?
Sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide
What happens to sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide once they enter the atmosphere?
They convert into sulfuric acid and nitric acid
What is the main difference between dry and wet acid deposition?
Dry sticks to surfaces; wet falls as precipitation
How does acid deposition affect aquatic ecosystems?
It lowers the pH, making water more toxic
Why is acid deposition especially harmful to soil and vegetation?
It leaches nutrients and damages leaves
A lake downwind from several coal-burning factories suddenly shows a drop in pH from 7 to 3. What is the most likely cause?
Acid deposition from industrial emissions
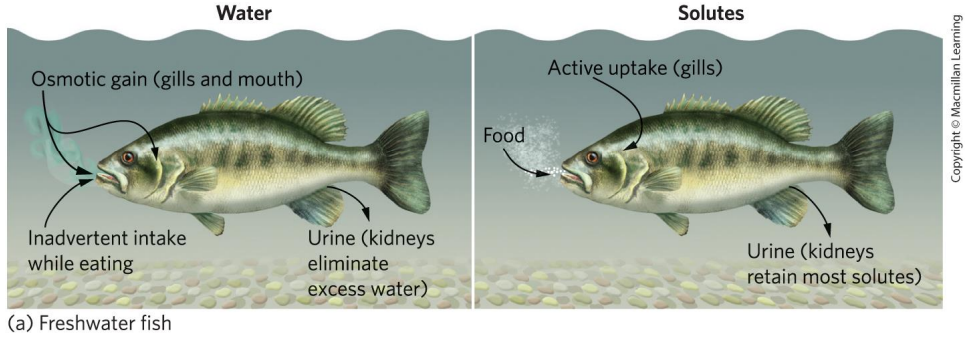
Explain osmoregulation in freshwater fish
salt concentration within body is higher than surrounding water
use gills and kidneys to actively uptake and retain solutes
do not need to uptake a ton of water
large amounts of dilute urine excreted
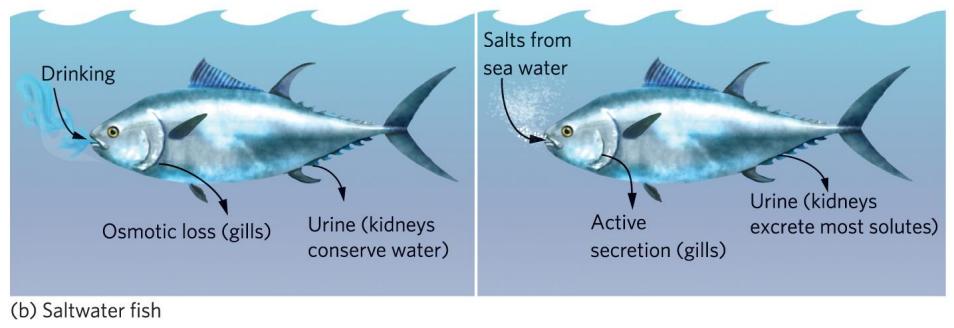
Explain osmoregulation in saltwater fish
salt concentration within body is lower than surrounding water
use gills and kidneys to actively secrete salt
must uptake large amounts of water
excretes highly concentrated urine
Why do sharks retain some of their urea in their bloodstream?
sharks produce ammonia from protein digestion, which is then converted into urea
the stored urea increases the solute concentration which helps offset the challenge of being hypoosmotic
How do mangrove trees ensure water continues to move into their roots despite being surrounded by salt water?
By increasing osmotic potential using organic solutes like amino acids and sugars
What happens to the salty solution excreted by mangrove leaf glands?
It evaporates, leaving salt crystals on the leaf surface