Chemistry (H) Final Exam 24-25
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Physical Change
A change in size, shape, or state to the physical properties of a substance where no new substance is made.
Physical Property
A characteristic of a substance that can be observed with sense and determined without destroying matter.
Chemical Change
A change in a substance’s physical and chemical properties, creating a new substance.
Chemical Property
A characteristic of a substance which indicates how a substance reacts with something else. Matter will be changed into a new substance after the reaction.
Malleability
The ability to be hammered into a thin sheet.
Chemical Formula
A representation of different chemical compounds.
Element
A collection of particles consisting of atoms that are all the same.
Atom
A particle of matter.
Pure Substance
Matter that has only one set of chemical and physical properties.
Product
The substance formed as a result of a chemical reaction.
Period
-Horizontal row of chemical elements
-Do not have similar properties
-First Element in a Period: Extremely active
-Last Element in a Period: Inactive gas
Metal
-Left and middle sections (trans.) of the period table
-Elements which loose electrons easily
-High thermal and electrical conductivity
-Ductile, Malleable, Lustrous, High tensile strength
Atomic Number
-How many protons an atom, of an element, has.
-Located near the top left corner of an element
-Unique to each element, no two elements have the same atomic number
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a substance changes from a liquid state to a gas at a given pressure.
Homogeneous
Components evenly mixed together and part cannot be seen separate (pure).
Heterogeneous
Components unevenly distributed (impure).
Mixture
Two or more pure substances mixed together. Each substance in the mixture retains its own set of chemical and physical properties.
Compound
Two or more elements chemically bonded together.
Particulate Level
Observing matter at the level of their atoms and molecules.
Macroscopic
Observing matter that is large enough to be observed by the unaided eye.
Reactant
The original substance which undergoes a chemical or physical change during a reaction.
Atomic Mass
-The mass of both protons and neutrons combined in a nucleus.
-Located on the top right of an element.
Ionic Bond
-An atom attracts electrons a lot more than another
-The electron is considered to be transferred from one atom to the other.
-Between a metal and non-metal
-Big differences in electronegativity
Halogens
-Most reactive non-metal (7 valence electrons)
-Never found free in nature
-Reacts with Alkali metals to form salt
-Located in group 17
Noble Gases
-Colorless gases that are extremely un-reactive
-Inactive due to the outermost shell being full (8 Valence Electrons)
-Inert: don’t form with other elements to form compounds
Molecule
A particle with two or more atoms joined by a chemical bond.
Subscript
A number printed below the line type which indicates the total atoms of a given element in a chemical compound.
Coefficient
The number placed in front of a chemical formula to indicate the number of molecules of a substance involved in the reaction.
Percent Composition
-Percent by mass of each component in a material.
-Part mass/Total mass x 100
Stoichiometry
The study of quantitative relationships between the amounts of reactants use and amounts of products formed by a chemical reaction.
Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance.
Proton
A positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom.
Neutron
An uncharged subatomic particle found in the nucleus of an atom (except for hydrogen).
Synthesis Reaction
-A compound made from simpler material.
-A + B → AB
Decomposition Reaction
-A compound broken down into simpler compounds, or all the way down to the elements that make it up.
-AB → A +B
Single Replacement Reaction
-One element that starts out by itself replaces another element in a compound, kicking it out.
-A + BC → B + AC
Double Replacement Reaction
-The positive and negative ions in two compounds switch places.
-AB + CD → AD + BC
Combustion Reaction
-A compound containing carbon and hydrogen (and sometimes oxygen) combines with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water.
-Burning
-CxHy(O2) + O2→ CO2 +H2O
Non-metals
-Elements lacking the characteristics of metals.
-Poor conductors of heat and electricity.
-Not ductile or malleable.
-Many are gasses, solids are brittle and break easy.
Combustibility
-Burning.
-The property of a substance that can burn or react with an oxidant to produce light and heat.
Polar Covalent Bond
-Separated Positive and negative charges in the same bond
-Electrons shared unequally between atoms
-Occurs between non-metals with different electronegativities
-0.4 < EN < 2.0
Non-Polar Covalent Bond
-Two electrons are shared equally
-Strong bonds within a Molecule, weak attractions between molecules
-Low melting/boiling points
-Generally wont dissolve in water
-Poor electrical conductors
Metallic Bond
-Electrons shared among atoms
-Occurs between metals
-Metal cations in a ‘sea’ of electrons
-Malleable, ductile, lustrous, electrical conductors
Ductility
The ability to be pulled into wires.
Independent Variable
The variable being tested (x-axis).
Dependant Variable
The data measured in response to the changed caused by the independent variable (y-axis).
Electrons
Negatively charged subatomic particle.
Constant
A value that doesn’t change or vary.
Control
A standard variable not exposed to the experimental treatment. Used as a comparison point.
Valence Electron
The electrons of an atom located in the outermost shell.
Groups
The vertical Columns (location) of elements that share similar chemical properties (Same number of VA).
Balancing Equations (solving)
1) Write equation
2) Add coefficients (a,b,c,d..)
3) Break it down (algebraically)
4) Atom inventory
Predicting Products (solving)
-Single Replacement: A+BC→B+AC
-Double Displacement: AB+CD→AD+CB
-Combustion Reaction: CxHy (o2) → CO2+H2O
Stoichiometry (Solving)
-Grams to grams: Molar mass
-Moles to moles: Mole ratio
-Moles to grams: Mole ration > molar mass
-Grams to liters: Molar volume > molar mass > mole ration
Molar Mass
1) Rewrite the numbers of atoms of each element separately
2) Multiple the number of atoms of one element by the atomic mass of that element
3) Add the sums together
Unit: g/mol
Naming Ionic Compounds (Solving)
1) Identify cation and anion
2) Name the cation first, by its elemental name
3) Name the anion by using the first syllable of its elemental name followed by ‘ide’
4) Write the name of the cation first and the name of the anion second
Electronegativity and Determining Bond type (Solving)
-Find the electronegativity for each atom and subtract the two values (biggest ones always first, or absolute value).
-Ionic: >2
-Polar Covalent: between 0.5 to 1.9:
-Non-Polar Covalent: 0.4 or less
Reactivity of Metals (Solving)
-Metal reactivity (activity) series: List of metals from most to least reactive.
-Metal: M & Ion: I
-M/I: If the metal is above the Ion, it WILL react
-I/M: If the Ion is above the metal, it WILL NOT react
Types of Chemical Reactions (Solving)
-Synthesis: A+B→ AB
-Decomposition: AB→ A+B
-Single Replacement: A+ BC →AC + B
-Double Replacement: AB+CD→ AD+ CB
-Combustion: Substance + O2 → CO2 + H2O
Particulate Level Models (solving)
1) Each element is represent by a different type of circle
2) Determine a key
3) Include ‘+’ and ‘→’ symbols
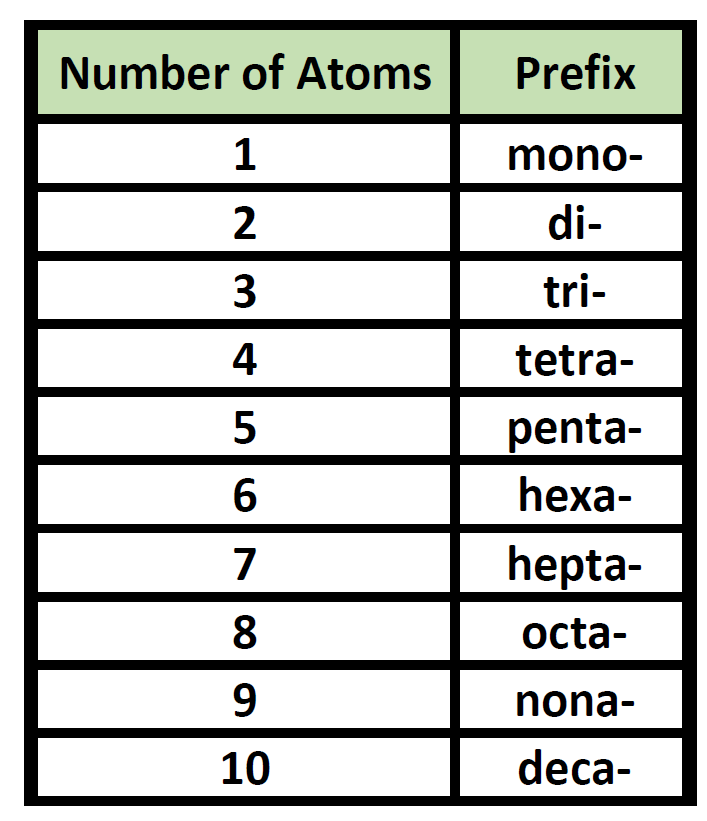
Naming Covalent Compounds (solving)
-Use numerical prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element.
-Change the ending of the second element to ‘ide’