Chapter 14 Basic Nursing Skills Objectives 1-4
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Vital Signs Purpose
NA’s measure, record, and report vital signs to monitor how well the vital organs of the body are functioning.
Temperature, Pulse, Respiration Rate, and Blood Pressure
What are the four vital signs measurements?
Role
The ________ of the NA is to watch and report changes in vital signs or abnormal signs, record accurate measurements, and report to the nurse. They are not to interpret data and give diagnosis.
Nurse
NAs should report to the _______ when:
The resident has a fever, the resident’s heart or respiration rate is too high or too low, and when the resident’s blood pressure changes.
Baseline Vital Signs
Vital signs measurements that are normal for a particular person.
Oral Temperature Range
97.6-99.6 degrees Fahrenheit; normal temperature 98.6 degrees
Rectal Temperature Range
98.6-100.6 degrees Fahrenheit; normal temperature 99.6 degrees
Axillary Temperature Range
96.6-98.6 degrees Fahrenheit; normal temperature 97.6 degrees
Temporal Temperature Range
97.2-100.1 degrees Fahrenheit
Tympanic Temperature Range
97.6-99.6 degrees Fahrenheit; normal temperature 98.6 degrees (same as oral)
Private
The process of taking, recording, and communicating a patient’s vital signs should be kept __________ and NAs should close the door or use a privacy curtain when taking vitals.
Body Temperature
A measurement that reflects a balance between heat created by the body and heat lost to the environment. A measure of how much thermal energy we store.
Age; infection; circadian rhythm
Factors that affect body temperature include:
______ (three letters),
illness or fighting an __________,
stress,
environmental temperatures,
exercise,
__________ rhythm
Lower
In general do the elderly have higher or lower temperatures than infants and young children?
Circadian Rhythm
The 24-hr day-night cycle with average temperature readings that fluctuate throughout the day; usually people have lower temperatures in the morning.
(F-32)/1.8
Formula to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius.
C*1.8+32
Formula to convert degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit.
Oral
What is another name for taking a temperature via the mouth
Rectal
What is another name for taking temperature through the anus/rectum?
Axillary
What is another name for taking a temperature via the armpit?
Tympanic
What is another name for taking a temperature via the ear?
Temporal Artery
What is another name for taking a temperature via the artery benath the skin of the forehead?
Digital Thermometer
This thermometer can be used for oral, rectal, and axillary temperature readings. It usually takes between 2 and 60 seconds to register the temperature. It is battery-operated and is covered by a protective sheath when used on patients.
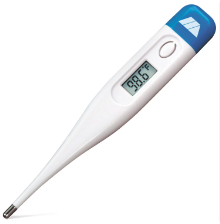
Electronic Thermometer
This type of thermometer can be used for oral, axillary, and rectal temperatures. It is battery operated and is often stored in a wall unit that can recharge it. Probe covers are used when taking temperatures. It takes between 2 and 60 seconds to register temperatures.
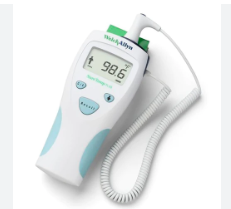
Mercury-free Thermometer
This type of thermometer is typically glass and is not battery operated or electric. It must be shaken down to below 96 degrees Fahrenheit after use and may require cleaning measures in addition to the use of a sheath. It can be used for oral, rectal, and axillary temperatures. For rectal and oral readings it should be left in place for 3 minutes and for axillary temperature readings for 8 to 10 minutes. The temperature is also shown in lines rather than digital numbers.
3
A mercury free thermometer should be held in place for ________ minutes when taking an oral or rectal temperature.
8-10
A mercury free thermometer should be held in place for ___-_____ minutes when taking an axillary temperature.
Mercury
We no longer use thermometers with __________ because it has been proven toxic to humans.
Tympanic Thermometers
These are often battery-powered and are used to take the temperature in the ear. They are very fast and take about 3 seconds to register the temperature. They can be a bit difficult to learn to perform however as the thermometer must be placed in the ear canal snugly without hurting the patient. They have probe covers.

Temporal Artery Thermometer
These thermometers are often battery-powered and function by measuring heat from the skin over the temporal artery. They can have probe covers but are also wiped down with alcohol wipes. They are held directly against the skin of the forehead and soft spot beneath ear

Infrared Thermometer
This type of thermometer is held away from the forehead and are often battery powered. It is also applied in the temporal region but is considered less accurate than temporal artery thermometers. It should have the same normal range as an oral temperature rather than the temporal range.

Sheaths or Probe Covers
What are often used to cover thermometers so they can be rescued by multiple people without spreading pathogens? (2 answers)
Tympanic Temperature
Which temperature should be taken for the fastest results?
Rectal Temperature
Which is the most accurate but also the most dangerous and invasive way to take a temperature?
Axillary Temperature
What is the least accurate way to take a temperature?
Oral Temperature
According to the textbook this kind of temperature is the most common way to record temperature data.
Non-invasive
Not inserted into the body
Green or Blue
What color should oral thermometers be?
Red
What color should rectal thermometers be?
Not
These are reasons oral temperatures should _______ be taken:
The patient is unconscious, has had a recent facial or oral surgery, is younger than 5 years old, is confused or disoriented, is heavily sedated, is likely to have a seizure, is coughing, is using oxygen, has facial paralysis, has a nasogastric tube, has sores, redness, swelling, or pain in the mouth, or has an injury to the face or neck.
Nasogastric Tube
A feeding tube inserted through the nose that goes into the stomach.
Have you had anything to eat or drink in the last 10 to 20 minutes? Have you smoked or chewed gum?
What should you ask a resident before taking an oral temperature?
Unconscious; prescribes
Rectal temperatures may be taken when:
a patient is ___________,
a doctor ___________ it,
or if the patient is a baby.
Lubricant
What should an NA apply to the thermometer or it’s probe cover before performing a rectal temperature.
½ to 1 inch
How far should a rectal thermometers be inserted into the rectum?
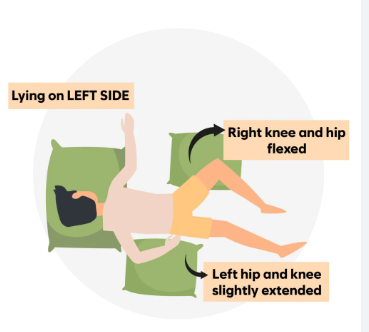
Left-lying Sim’s position
What position should a patient be placed in to have a rectal temperature performed?
Intestine Wall
NAs should not force a rectal thermometer when they meet resistance because they could be hitting the _________ _________.
Peristalsis
NAs should retain a firm grasp on the thermometer the duration of the time it takes to get a reading as _________ may cause the thermometer to move further in.
1/4-1/2 of an inch
How far should a tympanic thermometer be inserted in to the ear?
Confused; uncooperative
An axillary temperature may be performed on patients who are _______, disoriented, _______ or have dementia.
Pulse
The number of heart beats per minute (BPM)
60-100 BPM
What is a normal pulse range for adults?
Tachycardia
Fast heart rate (high count of beats per minute)
Bradycardia
Slow heart rate (low counts of beats per minute)
Radial Pulse
The most common site for measuring pulse: the pulse taken on the inner wrist where the radial artery runs under the skin.
Brachial Pulse
The pulse taken on the inside of the elbow 1-1.5 inches above the crease of the elbow.
Apical Pulse
A pulse taken by listening directly over the heart (left side of the patient’s chest just below nipple). Must be taken for a full minute.
Stethoscope
This piece of equipment is used to listen to sounds within the body. It is used when taking an apical pulse.
Higher
Do children have an a) higher or b) lower pulse than adults?
Affect
Factors that ________ pulse include:
exercise, stress, fear, medications, age, anger, anxiety, heat, infection, illness, and infection.
Respirations
The process of inhaling air into the lungs or exhaling air out of the lungs (inspirations, expirations)
Expiration
exhaling air out of the lungs
Inspiration
Breathing in
12-20 breaths per minute
Normal Respiration rate for adults
Apnea
Absence of breathing
Dyspnea
Difficulty breathing
Eupnea
Normal Respirations
Orthopnea
Shortness of breath when lying down that is relieved by sitting up.
Tachypnea
Rapid Respiration Rate
Bradypnea
Slow respiration rate
Cheyne-strokes
Alternating periods of slow, irregular respirations, and rapid, shallow respirations, along with short periods of apnea.
Telling the resident
Respiration rate is taken directly after pulse without _____________ ______ ______________ because it can affect their respiration rate.
Millimeters of Mercury (mmHg)
What unit is used for blood pressure?
Fraction
Blood pressure is recorded as a ______________.
Systolic Phase
The top number recorded in a blood pressure reading. It is the blood pressure of the arteries when the heart is at work/contracting. (Higher #). The normal range is 100-140 .
Diastolic Phase
The bottom number recorded in a blood pressure reading. It is the blood pressure of arteries when the heart relaxes. (Lower #). The normal range is 60-90 mmHg.
Hypertension
Medical term for high blood pressure. There are different categories depending on the degree of elevation.
Hypotension
Medical term for low blood pressure.
Prehypertension
This condition is when a person isn’t hypertensive but shows signs that they will likely progress to this condition in the future. It is indicated by a blood pressure of 120-140/80-90 which is on the high end of the normal range.
100-140/60-90
Normal Blood Pressure Range for adults is….
Hypotensive
When blood pressure is in the range of <100 over <60 it is called…
Hypertensive
When blood pressure is in the range of >140 over >900 it is called…
Blood; Alcohol
Factors that influence a person’s blood pressure include volume of _______, exercise, aging, stress, pain, medications, illness, obesity, and consumption of ______ or tobacco.
Atherosclerosis
The narrowing of the arteries due to the buildup of plaque and cholesterol. Its end stage is called arteriosclerosis when the arteries are hard and not at their full functioning stage. This can have a large affect blood pressure
Sphygmomanometer; Stethoscope
What two pieces of equipment are needed when taking a manual blood pressure?
A
When blood pressure is recorded which is the correct way to record systolic and diastolic measurements.
A) Systolic/diastolic
B) Diastolic/systolic
Should not
An NA __________________ take a blood pressure measurement on an arm that:
has an IV, has a dialysis shunt, medical equipment, a cast, has recent trauma, paralysis from stroke, burns, or a mastectomy on that side of the body.
Brachial Pulse
Which pulse is taken when taking a blood pressure?
Orthostatic Blood Pressure
In this type of blood pressure reading three measurements are taking. One is taken when a patient is lying down, one is taken when they are sitting up, and one is taken when they are standing up. This is to check for a drop in blood pressure when position changes.
Pulse Oximeter
A noninvasive device that uses a light to determine the amount of oxygen in the resident’s blood as well as a person’s pulse. They are clipped on the end of someone’s finger and show results digitally.
Pulse Oximeter
A noninvasive device that uses red light and infrared light to determine the amount of oxygen in the blood by detecting the percentage of hemoglobin saturated with oxygen as well as a person’s pulse rate. It can indicate if a person needs supplemental oxygen. These machines are commonly used on the finger but can also be used on the nose, ears, and toes.
SpO2
Oxygen saturation is abbreviated as _______ and is what a pulse oximeter measures.
97%-100%
What is the normal range for oxygen saturation?
cold; nail polish
Common problems that can affect pulse oximeter results include:
______ hands or feet, weak pulse, irregular heartbeat, patient moving or shivering, poor probe positioning, or dark _____-_______