Heme: Anemia
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
What is leukocytosis?
increase in WBCs
What is leukopenia?
decrease in WBCs
What is the normal range of Hgb?
males 14-18 g/dl
females 12-16 g/dl
What is the normal range of Hct?
males 42-52%
females 37-47%
What is the normal range of MCV?
80-100 um
What is the best test to classify anemias?
MCV
What is the normal range of MCH?
30-34 pg/cell
What is the normal range of MCHC?
31-37 g/dl
What is the normal range of WBC?
5-10 K/uL
What is the normal range of platelets?
150,000-450,000 /uL
What can contribute to an increased reticulocyte count?
post bleeding, post hemolysis, response to therapy (iron, b12, folic acid, etc)
What can contribute to a decreased reticulocyte count?
anemia, decrease erythropoietin, post radiation therapy
What are the youngest circulating platelets?
reticulated platelets
What is the role of Hgb?
O2 & CO2 transport
How many chains is Hgb made up of?
4: 2 a-chains, 2 B-chains
What are granulocytes?
neutrophil, eosinophil, basophil
What are agranulocytes?
lymphocytes, monocytes
What is the most abundant cell type? (45% of BV)
erythrocytes
What leukocyte is the 1st cell recruited to sites of infection/inflammation and the most abundant circulating phagocytes?
neutrophils
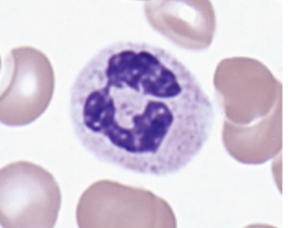
What leukocyte plays a role in resisting parasitic worm infections?
eosinophils
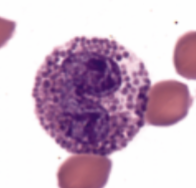
What leukocyte appears only in the blood, responds to inflammation, and release histamine?
basophils
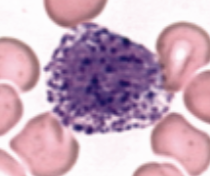
What leukocytes are phagocytic, differentiate into circulating macrophages, and present foreign antigens to lymphocytes?
monocytes
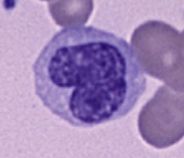
What leukocyte differentiates into T cells and B cells?
lymphocytes
What is anisocytosis?
abnormal variation in size
What is poikilocytosis?
abnormal cell shape
What is the range to classify microcytic anemia?
MCV < 80 fL
What is the range to classify macrocytic anemia?
MCV > 100 fL
What is the range to classify normocytic anemia?
MCV 81-99 fL
Someone with anemia may present to the clinic with complaints of:
fatigue, nail defects, tachycardia, dyspnea, pale skin
What labs do you order when checking for anemia?
CBC w/ diff (dec H&H), RBC indices, Reticulocyte count, fecal hem occult, urinalysis
If the reticulocytes are low where is the problem?
bone marrow (decreased RBC production)
If the reticulocytes are high where is the problem?
not in the marrow; reflects appropriate compensation response
Where is iron primarily absorbed?
duodenum
What protein is designed to store iron in the cells?
ferritin
What happens to ferritin in the presence of iron deficiency?
decreases
What is the most useful test for iron deficiency?
ferritin; no other cause of low ferritin
What measures the amount of free iron in the serum?
Serum Iron (Fe)
What is an indirect measure of transferrin, which holds iron in the serum?
TIBC (total iron binding capacity)
What happens to transferrin in the presence of iron deficiency?
increases
What anemia results from under production of RBCs due to lack of adequate amount of iron?
iron deficiency anemia
What type of anemia does iron deficiency present as?
hypochromic, microcytic anemia
What is the most common cause of anemia?
iron deficiency
What is the most common cause of iron deficiency anemia?
chronic blood loss
What are signs of iron deficiency anemia?
asymptomatic, fatigue, SOB, weakness, pallor, palpitations, HA, tinnitus, dizziness
What are the unique manifestations of iron deficiency anemia?
glossitis, angular cheilitis, koilonychias, pica
What would be seen in an iron study done on a pt with iron deficiency anemia?
dec Hgb, low MCV, low MCH, high RDW, low reticulocytes, low serum iron, high TIBC, low ferritin, decreased % transferrin saturation
What vitamin can enhance absorption of iron?
Vit C
What tx can you give to manage Iron Deficiency Anemia?
Oral iron supplements, correct underlying problem, IV iron, blood transfusion
What anemia is genetic and characterized by mutations that result in a reduction or absence of one or more globin chains?
Thalassemia
Thalassemia can result in?
hemolysis
What is a classic finding of Thalassemia?
microcytosis out of proportion to the degree of anemia; normal iron studies
What will be seen on an iron study of a pt with Thalassemia?
normal values
How many B-globin genes are there? Where are they located?
2; chromosome 11
If you inherit only one abnormal Beta allele (b/b+) or (b/bo) what happens?
pt has Thalassemia trait or is a silent carrier
What happens if you inherit both abnormal B-Globin alleles (bo/bo)?
Thalassemia Major: marked hemolysis, profound anemia, and transfusion dependency
How many a-globin genes are there? Where are they located?
4; chromosome 16
What happens if there is a deletion of 1 a-globin gene (-a/aa)?
silent carrier of SCD
What happens if there is a deletion of 2 a-globin genes (-a/-a) or (--/aa)?
Thalassemia trait or Thalassemia minor
What happens if there is a deletion of 3 a-globin genes (--/-a)?
Hgb H disease: Hgb precipitates → hemolysis → splenomegaly
Hgb H disease presents as what type of anemia? What can be seen in a blood smear?
moderate/severe microcytic anemia
hypochromic, targets cells, basophilic stippling
What happens if there is a deletion of 4 a-globin genes (--/--)?
Thalassemia major or hydrops fetalis: total hemolysis
What is the Gold Standard test for diagnosing Thalassemia?
Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
What symptoms would a pt with Thalassemia have?
asymptotic or S/sx of anemia
What would you seen on a PE of a pt with Thalassemia?
hepatosplenomegaly, jaundice
What would you see in the lab smear of a pt with Thalassemia?
microcytosis, hypochromica, stippled cell, target cell, elliptical cell
Upon Hgb electrophoresis, what would lead to a dx of B Thalassemia?
inc levels of Hgb F and A2
Management of Thalassemia is only required for severe symptoms. If needed what would you do to treat it?
chronic transfusion therapy, iron chelation, splenectomy
What is the only curative measure for Thalassemia Major?
allogeneic stem cell transplant
Why can thalassemia trait be confused with iron deficiency anemia?
low MCV
Thalassemia trait is most prevalent in what population?
Asian, Mediterranean, and African population
Thalassemia trait presents as what type of anemia?
mild (no tx), asymptomatic, mild/moderate microcytic hypo chromic anemia
When should you suspect thalassemia?
low MCV w/ iron deficiency r/o, pt fails to respond to Fe replacement
What would the labs look like in a pt w/ Thalassemia?
low MCV, high RBC, normal RDW, normal or inc iron studies
What type of anemia would lead poisoning anemia present as?
microcytic hypochromic anemia w/ basophilic stippling
What are S/sx of lead poisoning?
vague non-specific sx, appetite changes, wt loss, anemia, learning disability, cranial nerve paralysis, seizures, coma
What would a lead level above 10 mcg/dl indicate?
toxicity
What would a lead level above 45 mcg/dl indicate?
chelation therapy
What would a lead level above 70 mcg/dl indicate?
medical emergency
What is the tx for lead poisoning?
prevention, chelation (promote excretion), supportive care
Normocytic anemia of blood loss can be caused by?
chronic and acute blood loss
Hemolytic anemia is caused by?
accelerated destruction of erythrocytes resulting in anemia (can be intra or extravascular)
What would the labs look like for a pt w/ hemolytic anemia?
CBC: normocytic anemia, inc total Bilirubin, inc LDH, dec haptoglobin, markedly inc reticulocytes
What is the most common RBC enzyme defect?
G6PD deficiency
G6PD deficiency is what type of inherited trait?
X-linked
G6PD deficiency most commonly affects what populations?
Mediterranean, Africa, China
What can be seen in a blood smear of a pt w/ G6PD deficiency?
Heinz Bodies
What forms Heinz Bodies?
inappropriately oxidized Hgb precipitates
What prompts hemolysis in G6PD deficiency?
“bite cells” formed by abnormal “pitted” Hgb from the RBC in the spleen
When does hemolysis occur in individuals w/ G6PD deficiency?
only under oxidative stress
What symptoms would you see in a pt with G6PD deficiency when they are in steady state?
asymptomatic
What test would you order to dx G6PD deficiency?
quantitative enzyme assay
What causes autoimmune hemolytic anemia (AIHA)?
antibodies and complement develop against RBCs resulting in their destruction
Warm Antibody AIHA is due to what?
-this form is most common
antibodies that are active at room temp (IgG)
Cold Antibody AIHA is due to what?
antibodies that are active in the cold (IgM)
What is the mainstay of treatment for Warm AIHA?
corticosteroids
What is the treatment for Cold AIHA?
supportive measures
When should a direct Coomb’s test (DAT) be ordered?
once hemolysis is suspected
What is a DAT used for?
distinguish immune from non-immune causes of hemolytic anemia using pt’s RBCs
What indicates that a DAT is positive (+)?
agglutination
What does a + DAT result indicate?
warm AIHA