Biology - Microscope
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microscope
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Microscope
An instrument which is used to make small objects look bigger or magnify small objects which are invisible to the naked eyes
Magnification
Magnification is the number of times the image of the object is enlarged (magnified) as compared to the specimen.
Magnification formulae
Magnification= size of drawing (image) /Actual size of specimen (object) SI unit XNumber
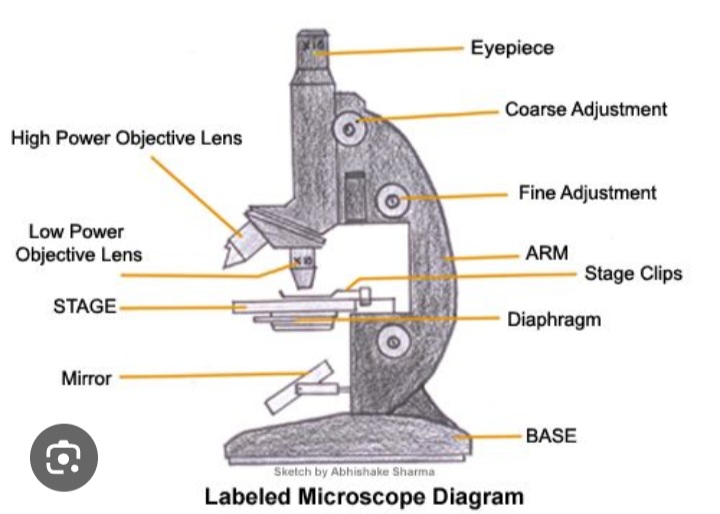
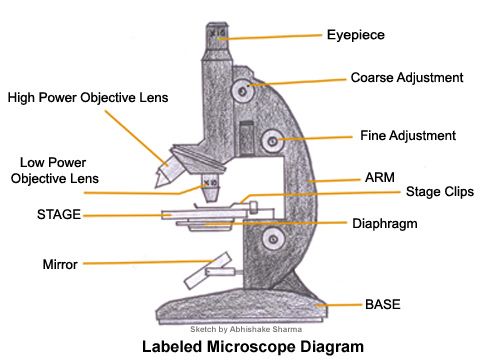
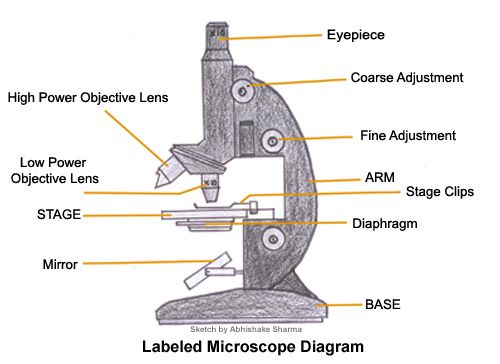
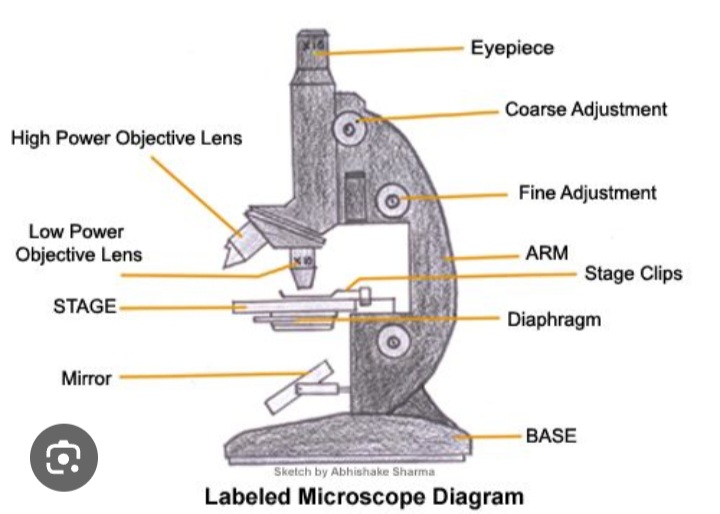
Eye piece
Contains the lens that magnifies the specimen
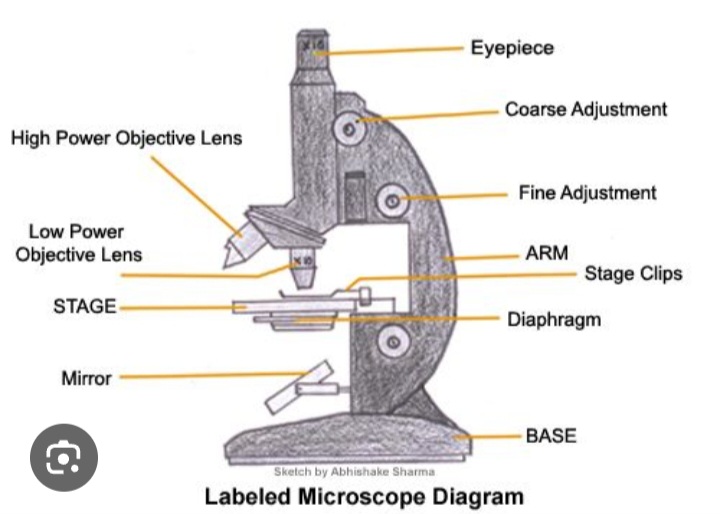
Tube
Hold the lenses of the eyepiece and the objective at the correct working distance from each other
Coarse adjustment wheel
Moves the tube up and down to bring the specimen into focus
Fine adjustment wheel
Used for final focusing when observing under high power magnification
Rotating nosepiece
Holds objectives with low power and high power lenses on rotating disc
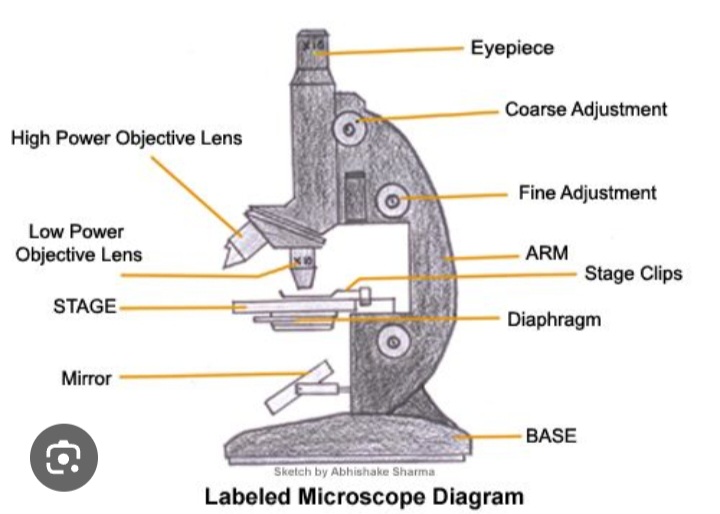
Objective lens
Enlarges the image from lower to higher power magnification
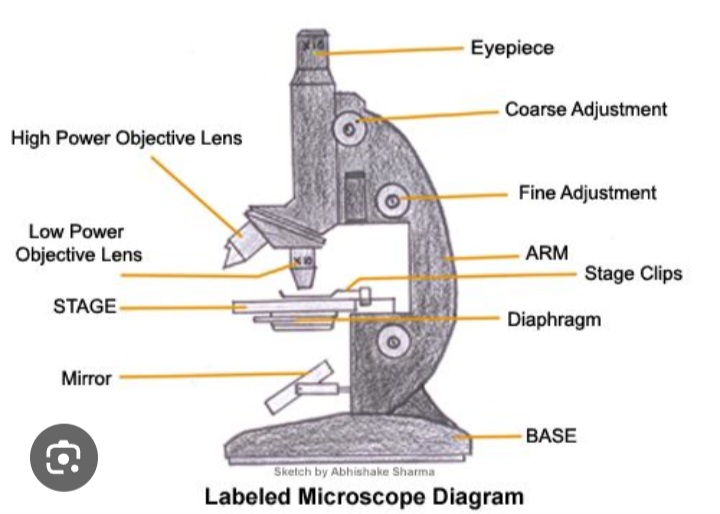
Arm
Joins the base and stage to the tube and supports the adjustment wheel.
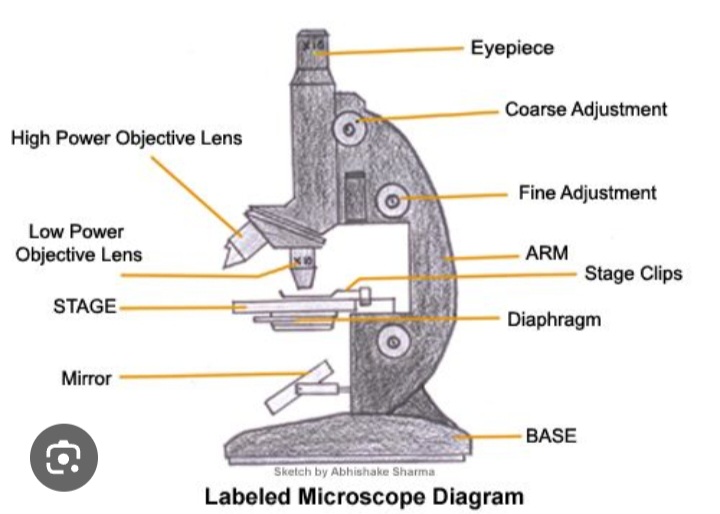
Stage
Supports slides over an opening which transmits light from a mirror or electric light source below it
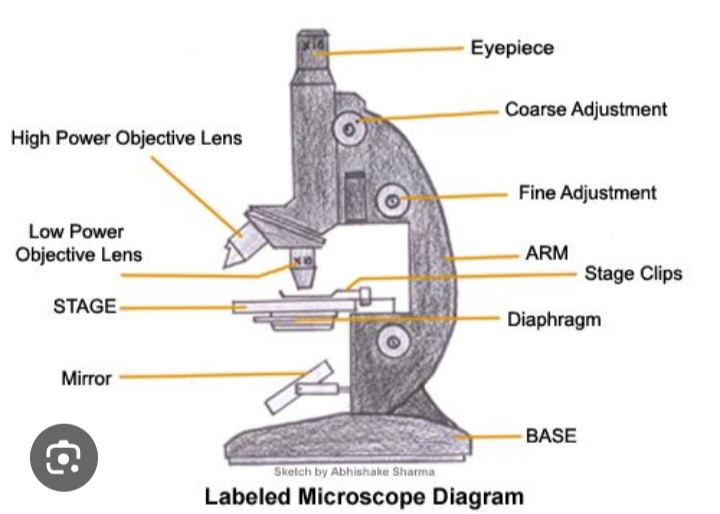
Diaphragm
Controls the amount of light directed onto and passing through the object.
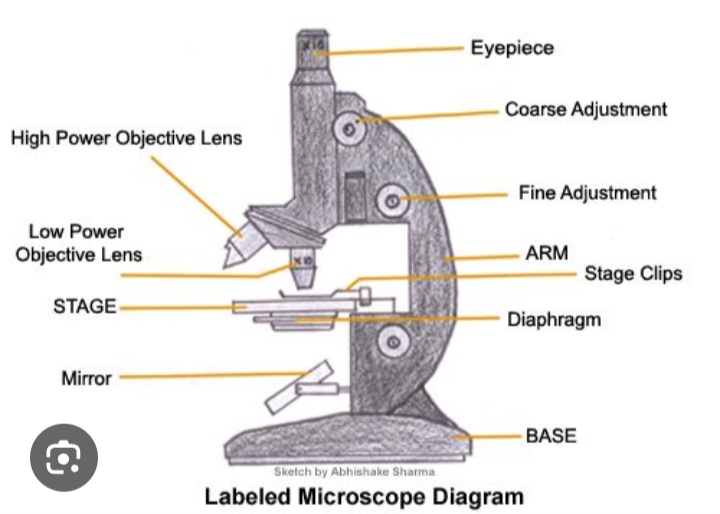
Mirror/light source
Directs light upward through the condenser and the opening on the stage.
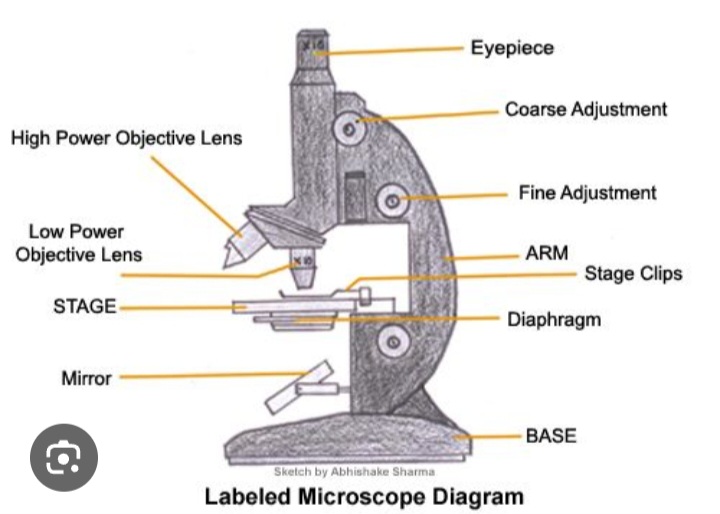
Base
Provides a firm support for the weight of the microscope
Biology
The study of living things (organisms).
Respiration
The release of energy from food substances inside living cells.
Aerobic respiration
Energy release in the presence of oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration
Energy release in the absence of oxygen.
Autotrophic nutrition
The type of nutrition where an organism makes its own food.
Heterotrophic nutrition
The type of nutrition where an organism obtains food from other organisms.