3.1 - articular cartilage
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
fibrous
cartilaginous
synovial (diarthrodial)
what are the 3 types of joints?
synovial
hyaline cartilage is a _________ type of joint
distribute joint leads
decrease friction
what are the 2 purposes of hyaline cartilage
biphasic
collagen-PG solid matrix (25%)
freely moving interstitial fluid (75%)
articular cartilage is made up of ________ material
chondrocytes
the purpose of ______________ is to manufacture, secrete, and maintain organic component of extracellular compartment (the MATRIX)
MATRIX
the ______________ provides the structural components supporting the internal mechanical stresses that results form loads being applied to the joint cartilage; it is these structural components, together with water, that determine the biomechanical behavior of the tissue
collagen fibrils; PG
the MATRIX = ___________ and ____________
90; flexion
Peter Pidcoe extra fact:
by the time you hit ________ degrees of knee _________, the entire patella has hit the condyles at some point
collagen
___________ is the most abundant protein in the body
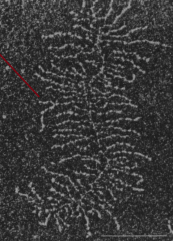
densely packed → less dense → radial orientation → grows into bone where it is anchored
how is the collagen distributed in this picture
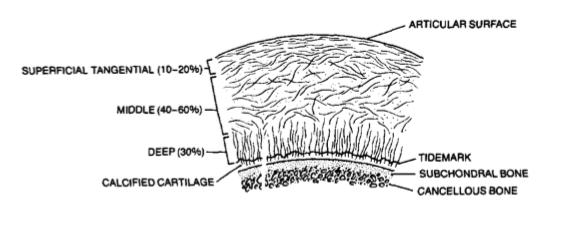
hyaline bone
annular ligament
Peter Pidcoe extra fact:
where in the body does cartilage not attach to bone?
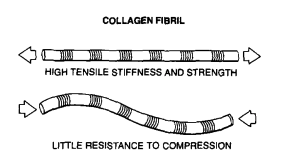
tension
collagen is stronger in (tension or compression)
anisotropic
collagen is ___________ meaning it has different mechanical properties when loaded along different axes
proteoglycan with bottle brush GAGs attached to protein core
what is this
glycosaminoglycan
GAG stands for
age
proteoglycans change with _________
10:1 → 2:1
(could be from cartilage maturation or result from increased functional demand)
chondroitin sulfate - keratan sulfate ration is _________ at birth and _______ as an adult
water
_________ is the most abundant component of articular cartilage and is most concentrated near articular surface
70
_____% of the intermolecular space is water
avascular
articular cartilage is (vascular or avascular)
load; pressure
chondrocytes; synovial fluid
mechanical; lubrication
the significance of water being in the intermolecular space is:
free to move when _______ or ______ gradient applied
permits diffusion of nutrients/waste products between _________ and ________
also controls __________ behavior and joint __________
negatively; Na+ and Ca+; repulsive
GAGs are (positively or negatively) charged so they attract ________ and _________ molecules which increases the _________ force
more (becuase water want to leave to dilute the outside)
if there is (less or more) salt on the outside, it will decrease the stiffness of the GAG structure
interstitial fluid flow
intrinsic behavior of solid matrix
what are the 2 reasons behind articular cartilage being viscoelastic
creep
stress relaxation
what are the 2 material responses when articular cartilage is put under stress
creep
__________ is where a constant force is applied → rapid initial deformation then slow to equilibrium
stress relaxation
______________ is where a constant deformation (or position) is applied → high initial stress then decreased stress
fluid flow (exudate); solid matrix
_________ controls creep and in equilibrium _________ supports the load
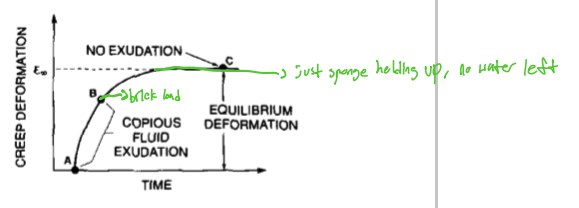
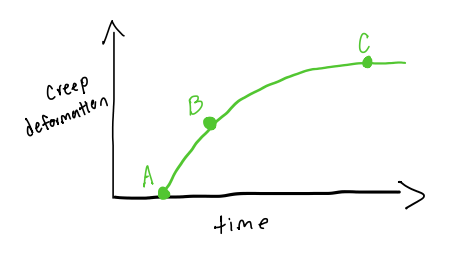
A to B
what points indicate the copious fluid exudation
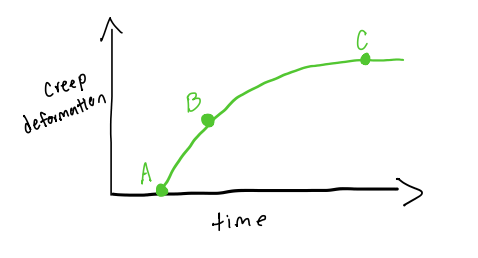
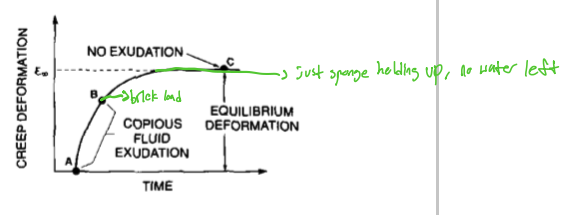
C
what point indicates no exudation
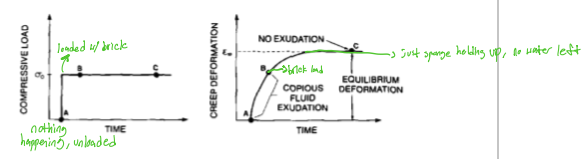
creep elongates progressively overtime, compressive load goes from 0-100 BAM
difference between a compressive load graph and a creep deformation graph
joy to the world and give thanks to pidcoe

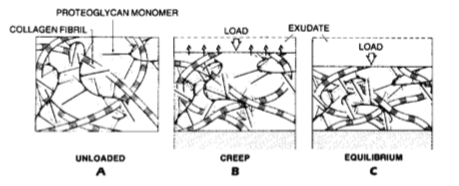
unloaded
creep
equilibrium
indicate which image is showing
creep
equilibrium
unloaded
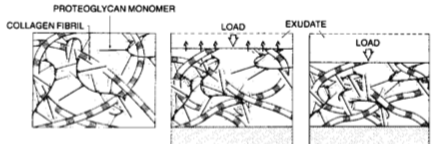
exudation; redistribution
the method behind stress relaxation is that stress rises due to fluid __________ and stress relaxes due to fluid ____________
more
Peter Pidcoe extra fact:
old cartilage has (less or more) permeability
less
Peter Pidcoe extra fact:
young cartilage has (less or more) permeability
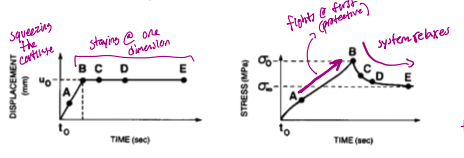
the displacement increases at first and then stays at one dimension
stress relax will increase more before it relaxes, takes more time
what is the difference between the displacement graph and stress relaxation graph
low (this means it is hard to push liquid through)
articular cartilage has (low or high) permeability
harder (increases the frictional drag → makes tissue stiffer → difficult for fluid to move)
does a higher load on the joint articular cartilage make is easier or harder for fluid to move
low
fluid in the joint space is reabsorbed during the (low or high) load
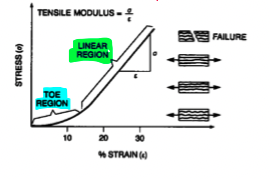
pull out
the toe region of the stress strain graph is due to collagen fiber “__________”
dec; inc (essentially means that pH can affect cartilage so lay off the salt)
increased water content leads to (dec or inc) compressive strength and (dec or inc) permeability
inc
if there is (dec or inc) permeability, this means that the structure has decreased ability to support loads
collagen-PG matrix changes with age
repetitive and massive movement of interstitial fluid may cause PG “washout”
cumulative stress of impact loading (low or high)
excessive stress concentrations int eh body (hot spots, too much at one spot)
4 causes of collagen network disruption
congenital acetabular dysplasia
slipped capital femoral epiphysis
intra-articular fx
meniscectomies → modify load pattern
ligament rupture → allows excessive movement and abnormal stresses
RA and joint space hemorrhage (hemophilia) can contribute to a breakdown in collagen-PG matrix integrity
what are 6 examples of excessive stress concentrations in the body that can lead to collagen network disruption