ecology, biomes, and ecosystems
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
part 1 of ecology & ecosystems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
define ecology
ecology is the scientific study of how organisms interact with their environment
what two components are environmental characteristics classified as?
abiotic (physical and chemical) and biotic (living)
what 2 components does a scientific study of ecology include?
discovery of new species and how they live
what are the 4 levels of ecology?
organismal, population, community, and ecosystem
what is organismal ecology?
organismal ecology looks at how well an individual organism copes with challenges of their abiotic environment (organism and abiotic environment, least inclusive)
what is population ecology?
population ecology is the study of groups of individuals of same species living in the same area— looks at population density and growth (population = part of a whole)
what is community ecology?
community ecology is the study of species assemblages and their environmental interactions— how all species interact w/ each other (e.g. food web) (community = whole)
what is ecosystem ecology?
ecosystem ecology looks at both abiotic and biotic factors (e.g. energy flow and chemical cycling); most inclusive and complex type (ecosystem = everything)
what do abiotic factors determine? And it is not influenced by what?
abiotic factors determine which type of organism can live where and are not influenced by the organisms themselves
main energy source?
the sun
environmental temperature has a critical effect on what? At what temperature (ºC) are most enzymes of organisms destroyed?
environmental temperature has a critical effect on metabolism and most enzymes of organisms are destroyed at 45ºC
what are the cell concerns in terms of water for each organism: marine organisms. freshwater organisms, terrestrial organisms
the cells of marine organisms need to balance against high salt concentration, cells of freshwater organisms are in danger of picking up too much water and lysing, terrestrial organisms are in danger of drying out
what does soil type and nutritional load determine? How are soil type and nutritional load determined?
soil type and nutrition determine which type of plants survive in terrestrial landscapes. They are determined by their availability of nitrogen and phosphorus, and structure and pH
in aquatic ecosystems how is the growth of algae and photosynthetic bacteria limited?
in aquatic ecosystems the growth of algae and photosynthetic bacteria are limited by levels of nitrogen and phosphorous
In aquatic environments how are dissolved oxygen levels determined, and what has more oxygen: cold, fast moving water or warm, stagnant water?
In aquatic environments dissolved oxygen levels are determined by temperature and current. Cold, fast moving water has more oxygen
what are (some of) the abiotic factors that can have an effect on organisms’ use of their environment?
energy source, temperature, water, nutrients, aquatic factors, wind, storms, and fires
what are terrestrial biomes determined by?
temperature and rainfall
we want to find the earth’s global climate patterns. what do we look at?
we look at the input of radiant energy from the sun and the Earth’s movement in space
what explains why rainforests are concentrated in the tropic (zone)?
tropic near equator. air at the equator rises when heated directly by the sun. when the heated air cools, clouds and rain form.
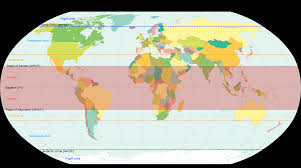
what are the two ways mountains affect climate?
mountains affect climate by decreasing air temperature as elevation increases, and blocking flow of cool, moist air from the coast
what does biome refer to
Biome refers to a major terrestrial or aquatic life zone characterized by vegetation type or physical environment, respectively
This biome occupies roughly 75% of Earth’s surface and is determined by salinity and other physical factors
aquatic biome
This biome has a salt concentration of less than 1% and includes rivers, streams, lakes, ponds, and freshwater wetlands
freshwater biome
This biome has a salt concentration of around 3% and includes oceans, intertidal zones, coral reefs, and estuaries
marine biomes
what are the (specific) abiotic and biotic characteristics of a tropical dry forest?
abiotic: warm year-round, alternating wet-dry seasons, rich soils; biotic: deciduous plants, waxy plant leaves, animals may migrate; (tropical dry = wet and dry, changing weathers)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a tropical grassland/savanna/scrubland?
abiotic: warm, seasonal rainfall, compact soils, frequent fires set by lightening; biotic: plants w/ waxy leaves, seasonal leaf loss, many animals migrate or are dormant during dry season (tropical savanna = hot, average moisture)
a biome chart can be split into 4 levels. 1 being the top of the pyramid (cold) and 4 being the bottom (hot), list the biomes from top to bottom as well as left (wet) to right (dry): temperate forest, taiga, temperate desert, tropical desert, savanna, rain forest, tundra, temperate grassland
level 1: tundra; level 2: taiga; level 3: temperate forest, temperate grassland, temperate desert; level 4: rain forest, savanna, tropical desert
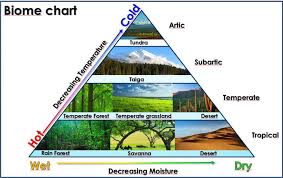
in a biome chart/pyramid there are 4 regions: temperate, arctic, subarctic, and tropical. Order them from top of the pyramid to bottom
arctic (cold, neither wet nor dry), subarctic (less cold than arctic, neither wet nor dry), temperate (warm-hot, ranges from wet to dry), tropical (hot, ranges from wet to dry)
how is a biome chart/pyramid read?
temperature increases from bottom to top and wetness decreases from left to right (coldest the top of the pyramid— think coldest at the top of a mountain—driest at the right end of the pyramid)
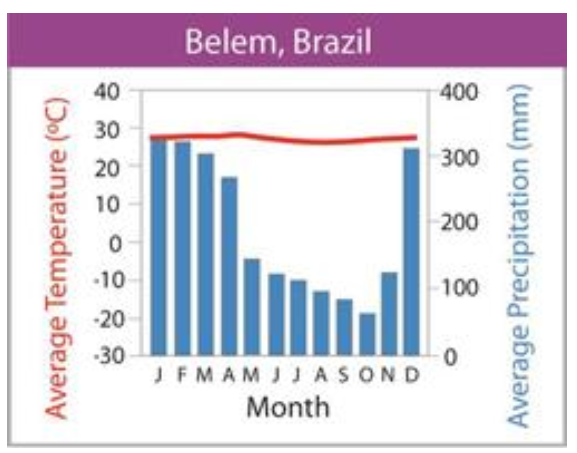
what biome does the graph depict?
tropical rain forest
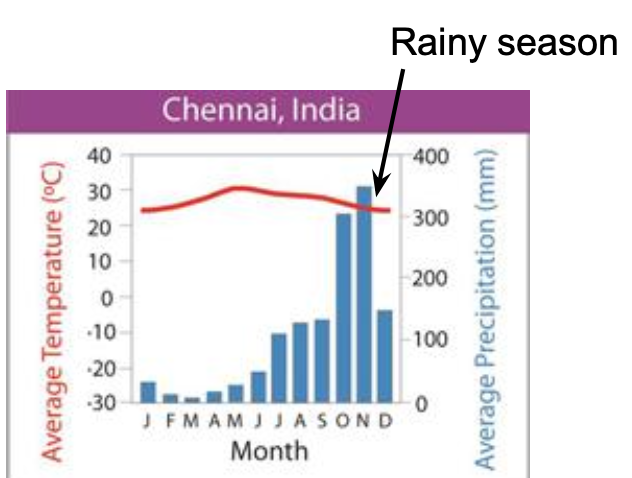
what biome does the graph depict?
tropical dry forest
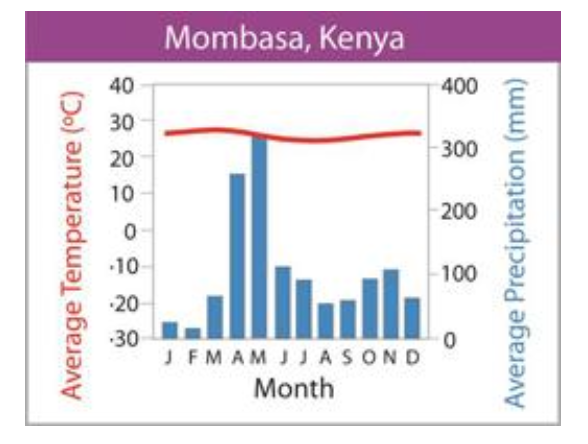
what biome does the graph depict?
tropical grassland/savanna/scrubland
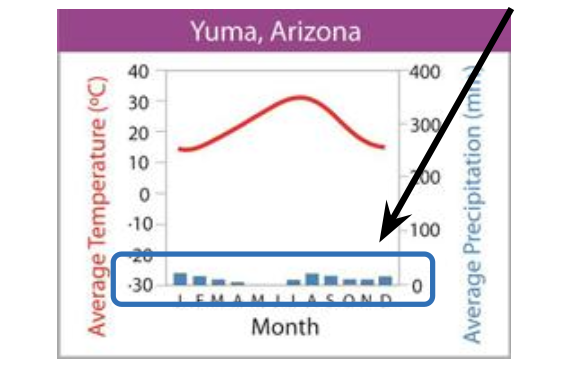
what biome does the graph depict?
desert (arrow shows precipitation, not temperature —> desert)
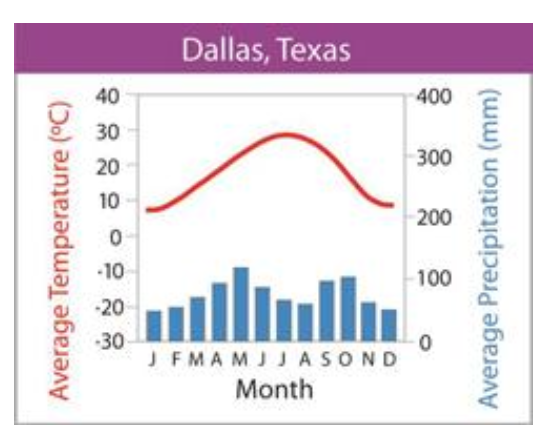
what biome does the graph represent?
temperate grassland
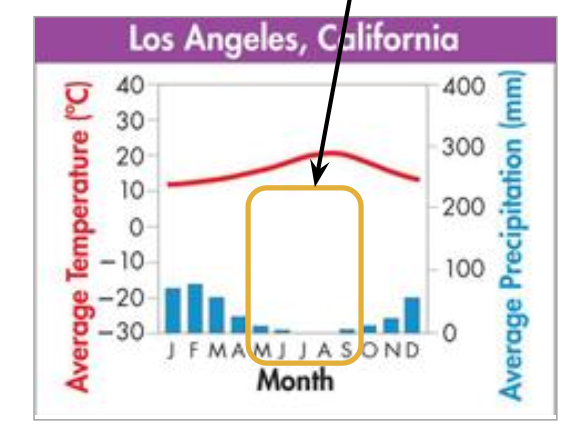
what biome does the graph represent?
temperate woodland and shrubland (arrow highlights high threat of wildfire during M-S
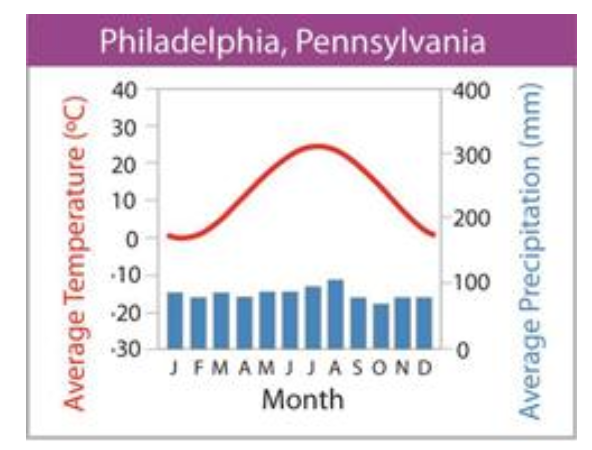
what biome does this graph represent?
temperate forest
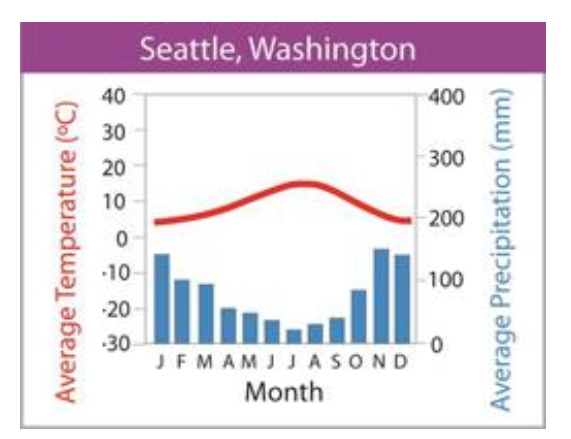
what biome does this graph represent?
northwestern coniferous forest
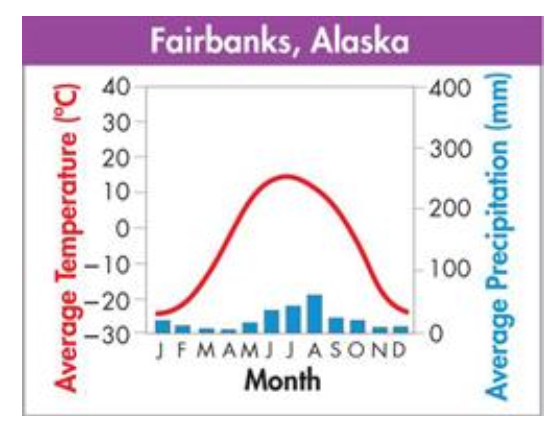
what biome does this graph represent?
boreal forest/taiga
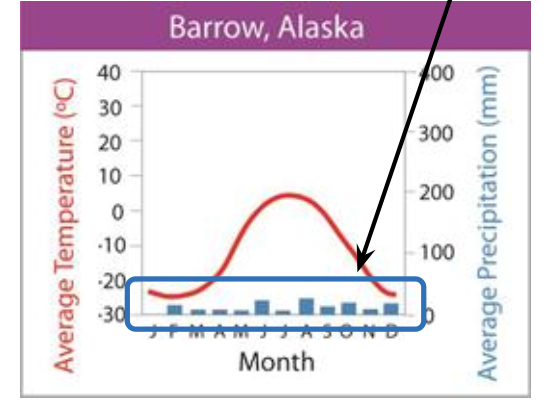
what biome does this graph represent?
tundra (arrow notes low precipitation)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a tropical rain forest?
abiotic: warm and wet year round, and soils are thin and nutrient poor; biotic: plants have large leaves and buttress tree roots, and animals are active year-round (tropical rain = warm, wet, nutrient poor, large leaves, active animals year-round)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a desert?
abiotic: low precipitation, variable temperatures, soils poor in organic material; biotic: small plant leaves, many animals nocturnal, animals get water from food (just desert is determined by precipitation)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a temperate grassland?
abiotic: warm summers, cold winters, moderate precipitation, fertile soils, occasional fires; biotic: plants resistant to grazing and fire, small animals use camouflage and burrowing (normal curve; temperate grassland = warm, moderate moisture)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a temperate woodland and shrubland?
abiotic: warm, dry summers, cool, moist winters, nutrient poor soils, periodic fires; biotic: plants adapted to drought and fire, animals commonly browsers (mix of temperate and savanna)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a temperate forest?
abiotic: cold winters, warm summers, year-round precipitation, fertile soils; biotic: deciduous trees, some animals hibernate, some migrate in winter
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a northwestern coniferous forest?
abiotic: mild temperatures, abundant precipitation in fall, winter, and spring, cool, dry summers, rocky, acidic soils; biotic: dense plant growth, tall trees, many animals with varied diets
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a boreal forest/taiga?
abiotic: long, cold winters, mild summers, moderate precipitation, acidic, nutrient poor soils; biotic: dark-green conifers, many animals have extra insulation, some migrate in winter (in subarctic category)
what are the abiotic and biotic characteristics of a tundra?
abiotic: strong winds, low precipitation, short, soggy summers, long, cold, dark winters, permafrost; biotic: small plants grow low to the ground, many animals migrate winter or have heat-saving adaptations
what are the 4 key factors in aquatic ecosystems?
water depth, temperature, currents, nutrient availability
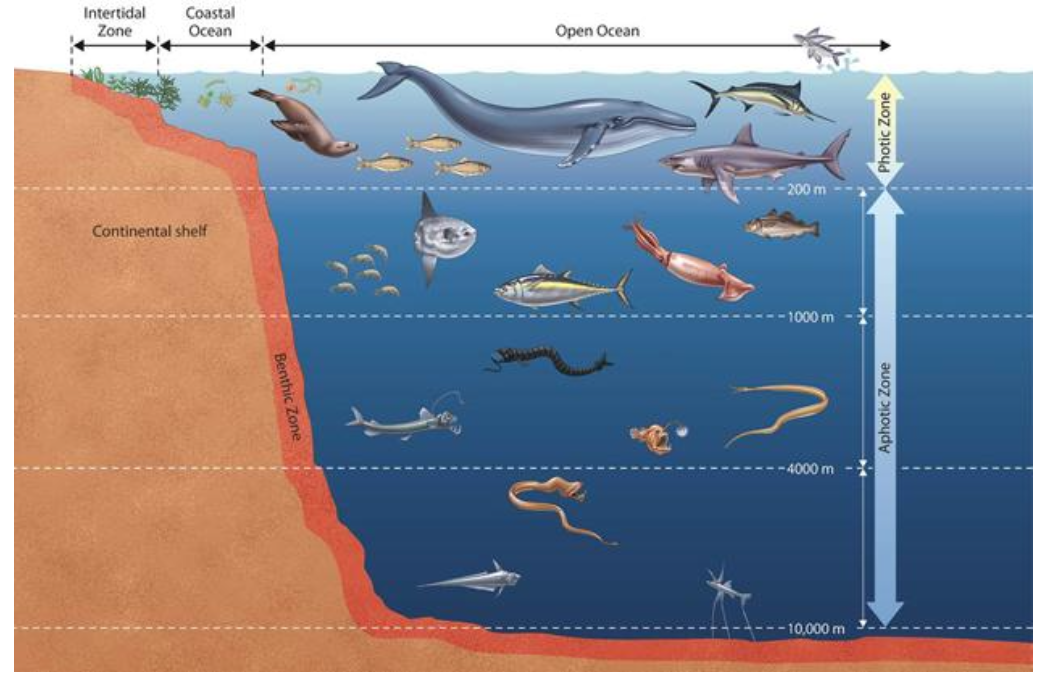
coastal ocean vs open ocean
coastal ocean extends from shore of edge to where land, sea, and atmosphere interact. open ocean refers to the open water, away from the coast and seafloor
what is an estuary?
a wetland that forms where a river meets