Biology - B1 (Cell Level Systems) *GCSE OCR HIGHER*
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Aerobic respiration
- A form of respiration that uses a plentiful supply of oxygen to release energy from glucose
- The reaction transfers energy from a chemical store (glucose) to another chemical energy store called ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
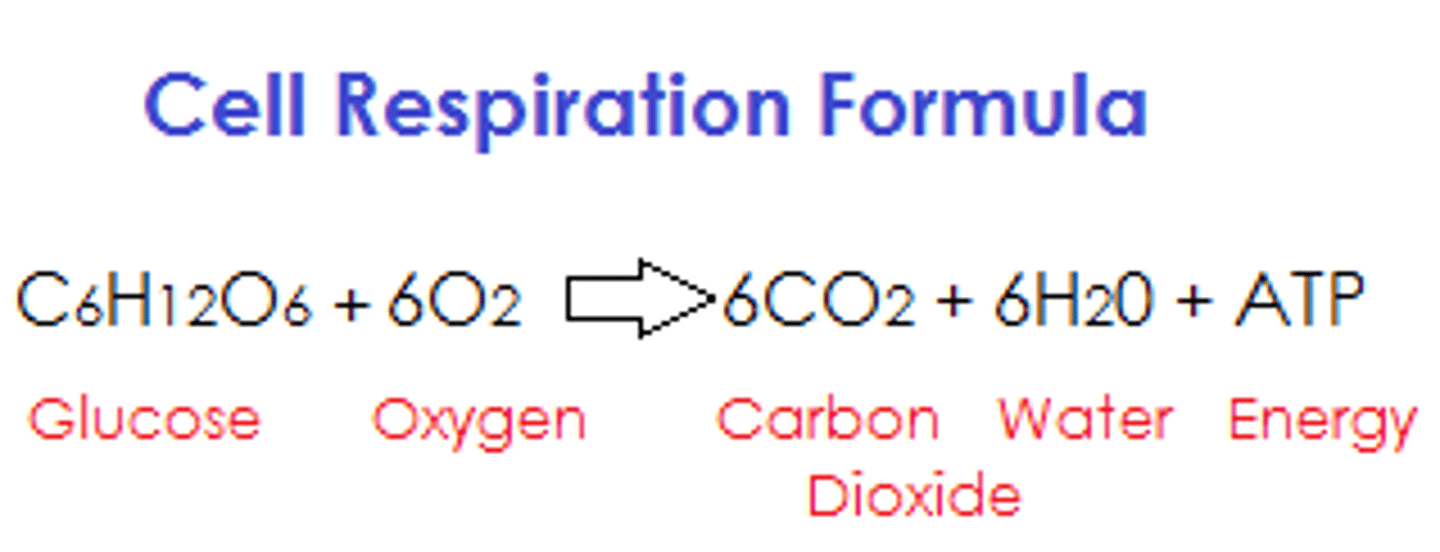
Anaerobic respiration
- A form of respiration that releases energy from glucose when there is an oxygen debt
- Glucose is not broken down properly and poisonous lactic acid is produced
- Glucose -> Lactic acid
C6H12O6 -> 2C3H6O3
Amino Acids
Small molecules that make up a protein
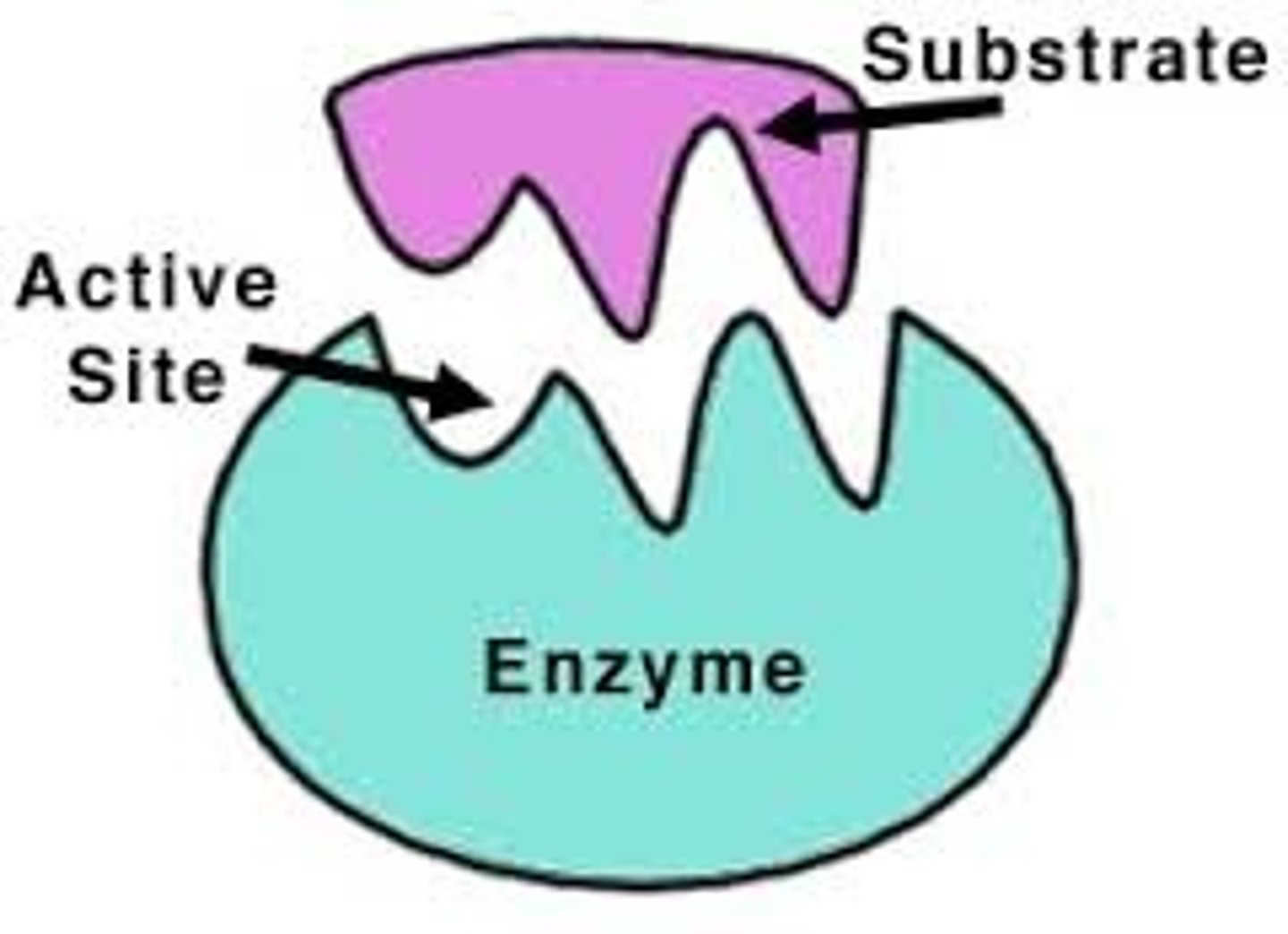
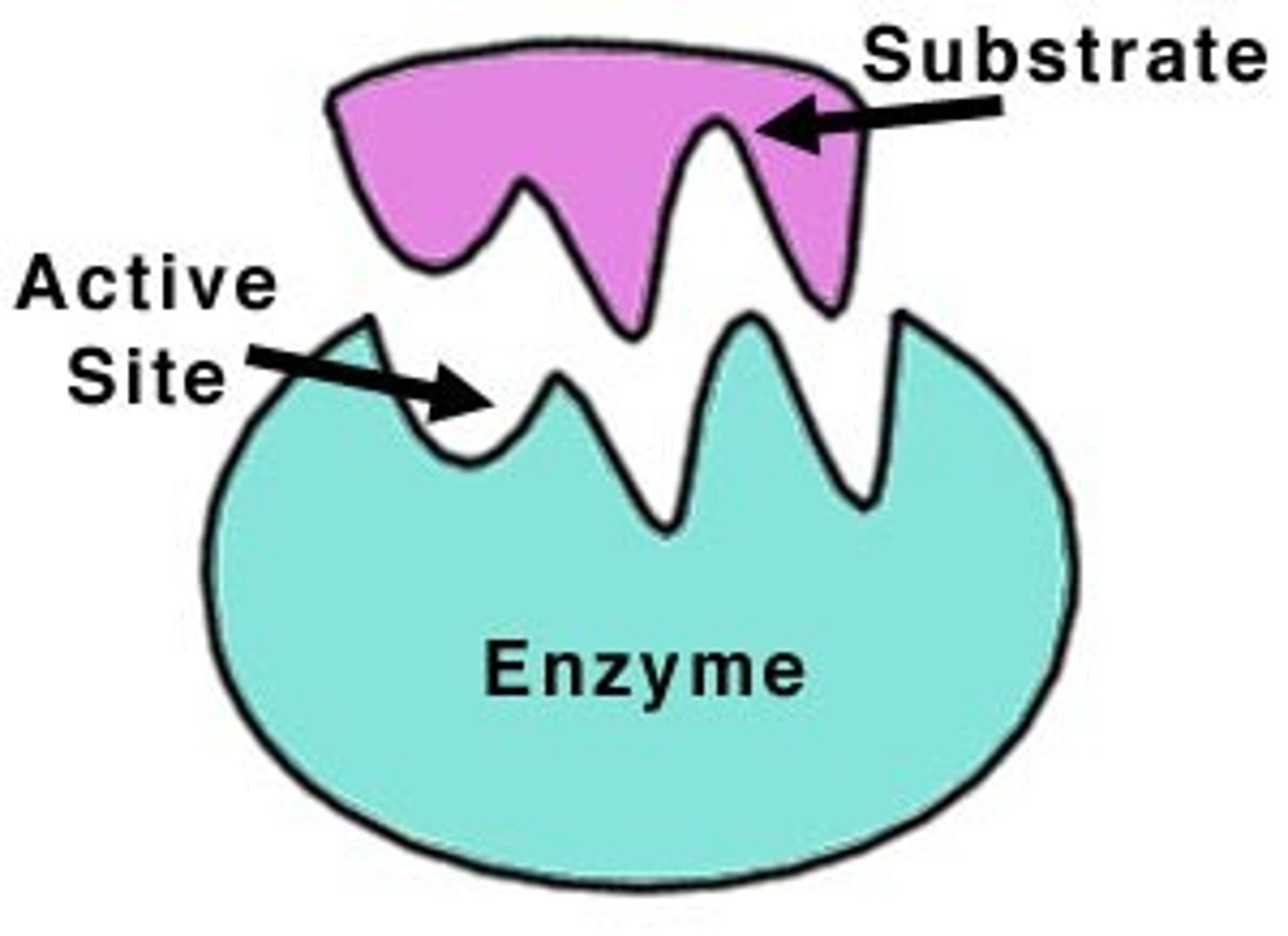
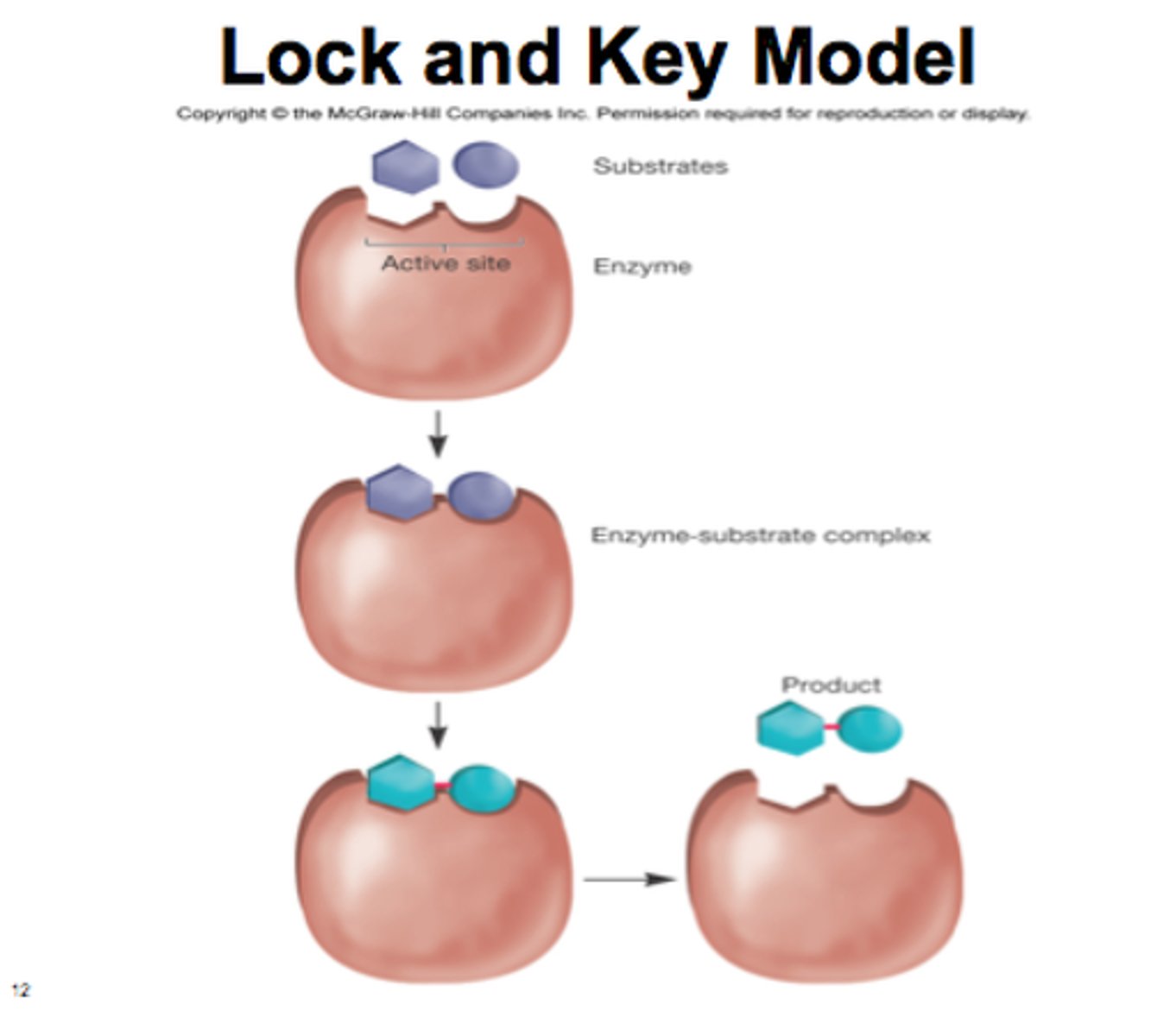
Active Site
The part of the enzyme which is specific to the substrate and has a complementary shape to it
Amylase
- An enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars
- It is produced in the pancreas and salivary glands
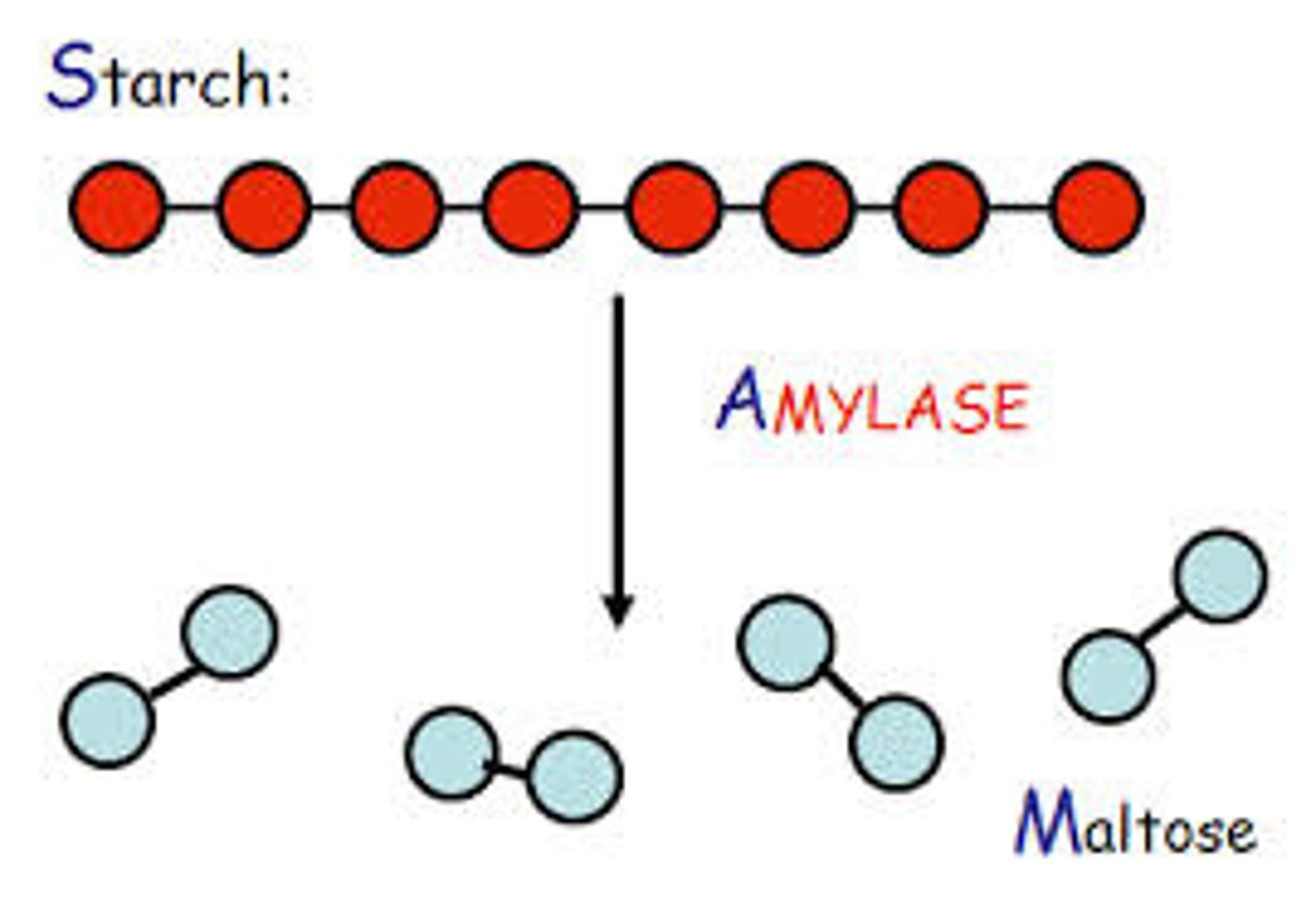
Carbohydrate
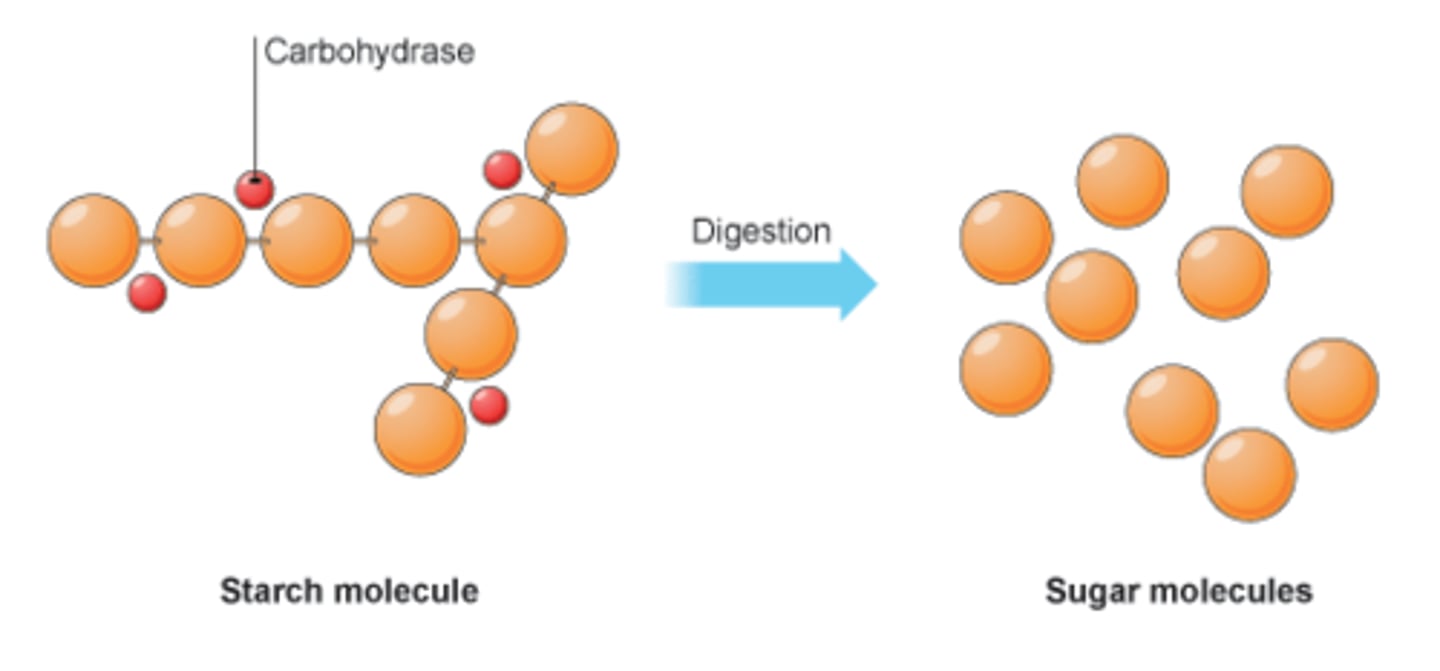
- A large molecule that is synthesised from simple sugars
- They are polymers
- Starch is a carbohydrate polymer which can be broken down by amylase
- Carbohydrase breaks down carbohydrates
Cell Membrane
- A selectively permeable barrier which controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell
- It also has receptor molecules on the surface for cell-to-cell signalling
Cellular Respiration
- A continuously occurring chemical process which is universal and occurs in all living cells
- It occurs in the mitochondria = more mitochondria tells you how active the cell is
- It is exothermic and releases energy (in the form of ATP) from the breakdown of organic compounds such as glucose
Cell Wall
- Surrounds cell using tough fibres (cellulose)
- Supports the cell (wall is rigid)
Chloroplasts
- The organelles that are the site of photosynthesis
- They contain chlorophyll (a green pigment) which absorbs light energy
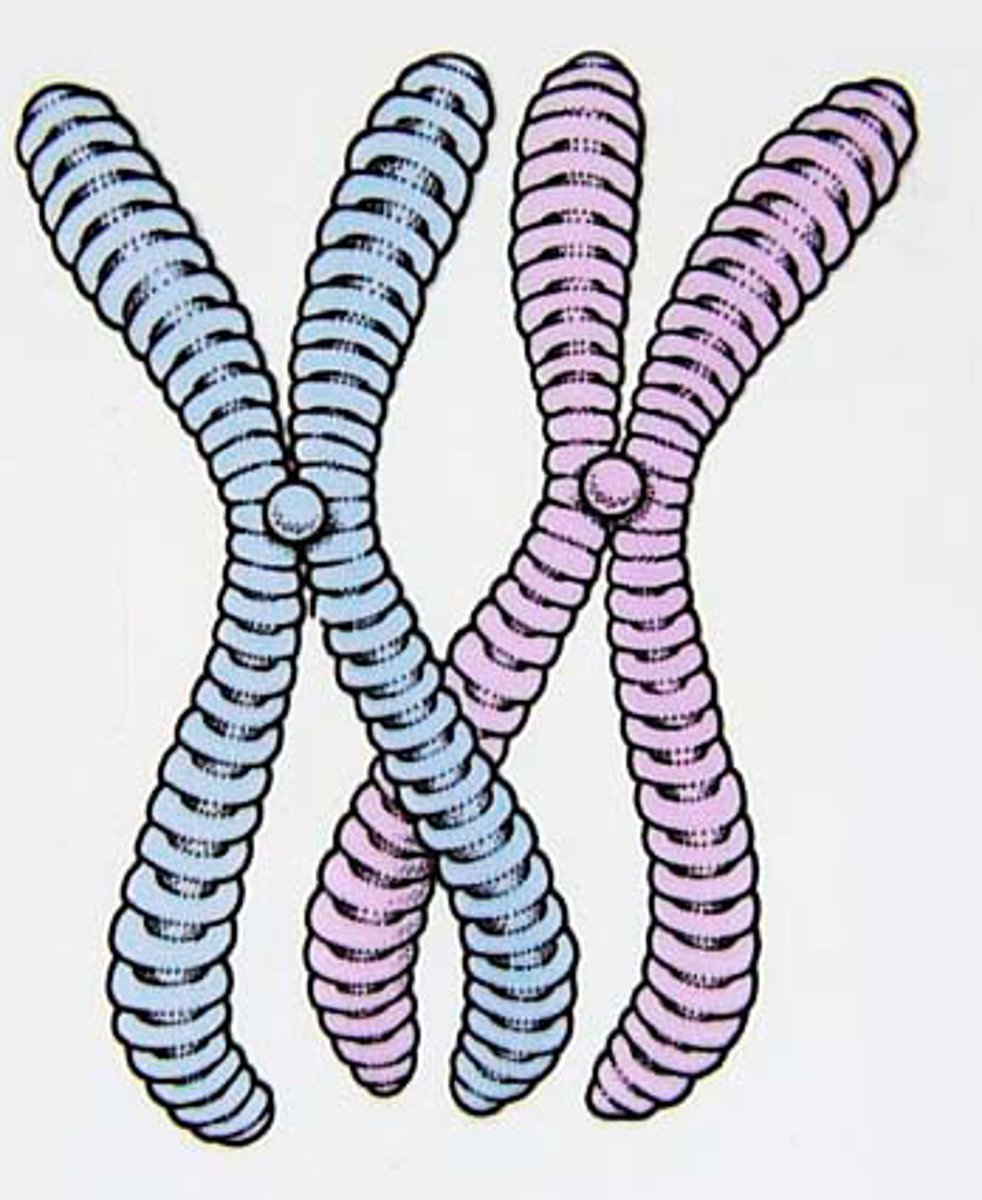
Chromosome
A long, coiled molecule of DNA that carries genetic information in the form of genes
Cover Slip
A small piece of glass placed on top of the specimen to protect it from the lens
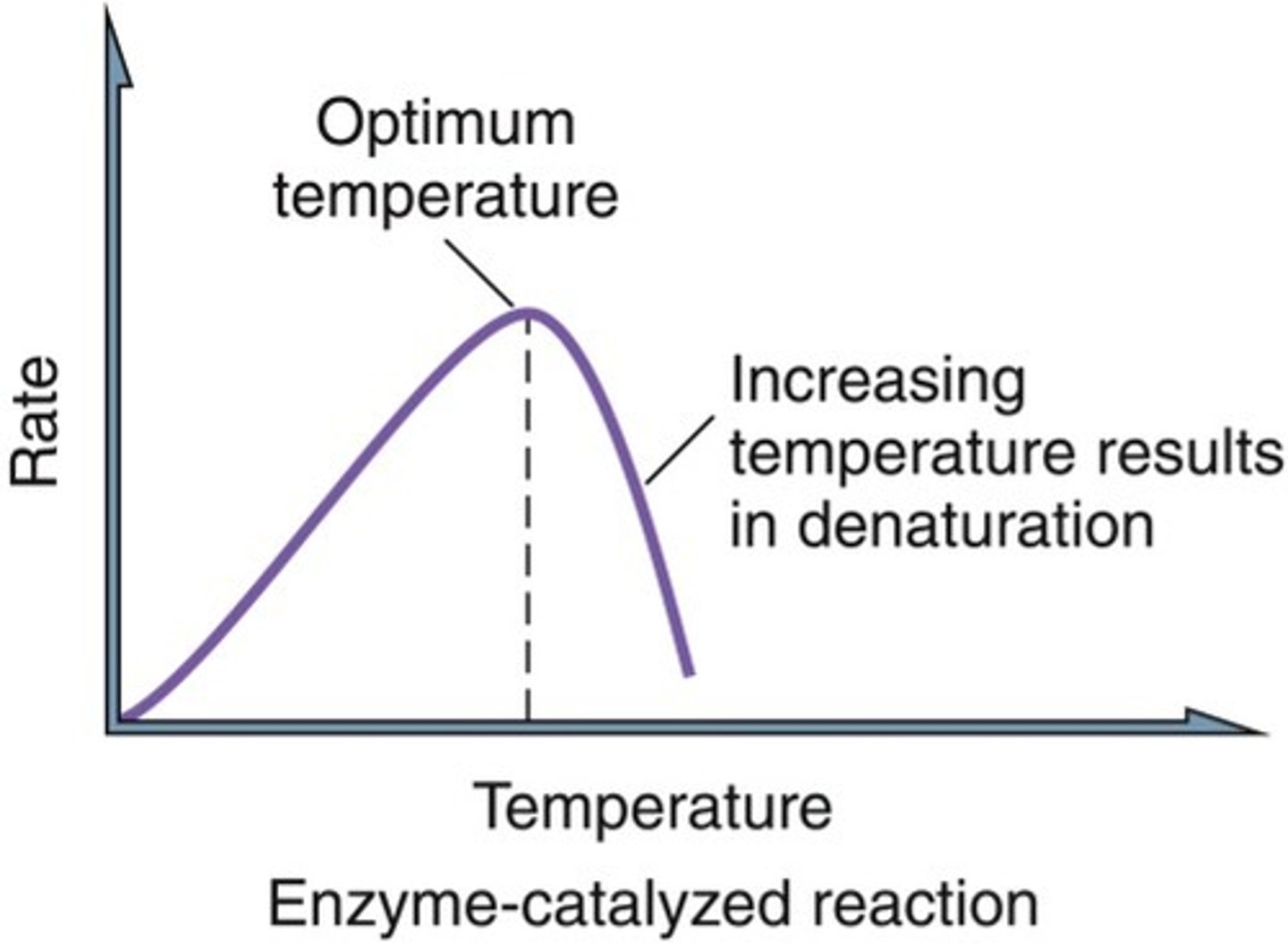
Denaturation
The permanent change in the shape of an enzyme's active site that stops the enzyme functioning normally
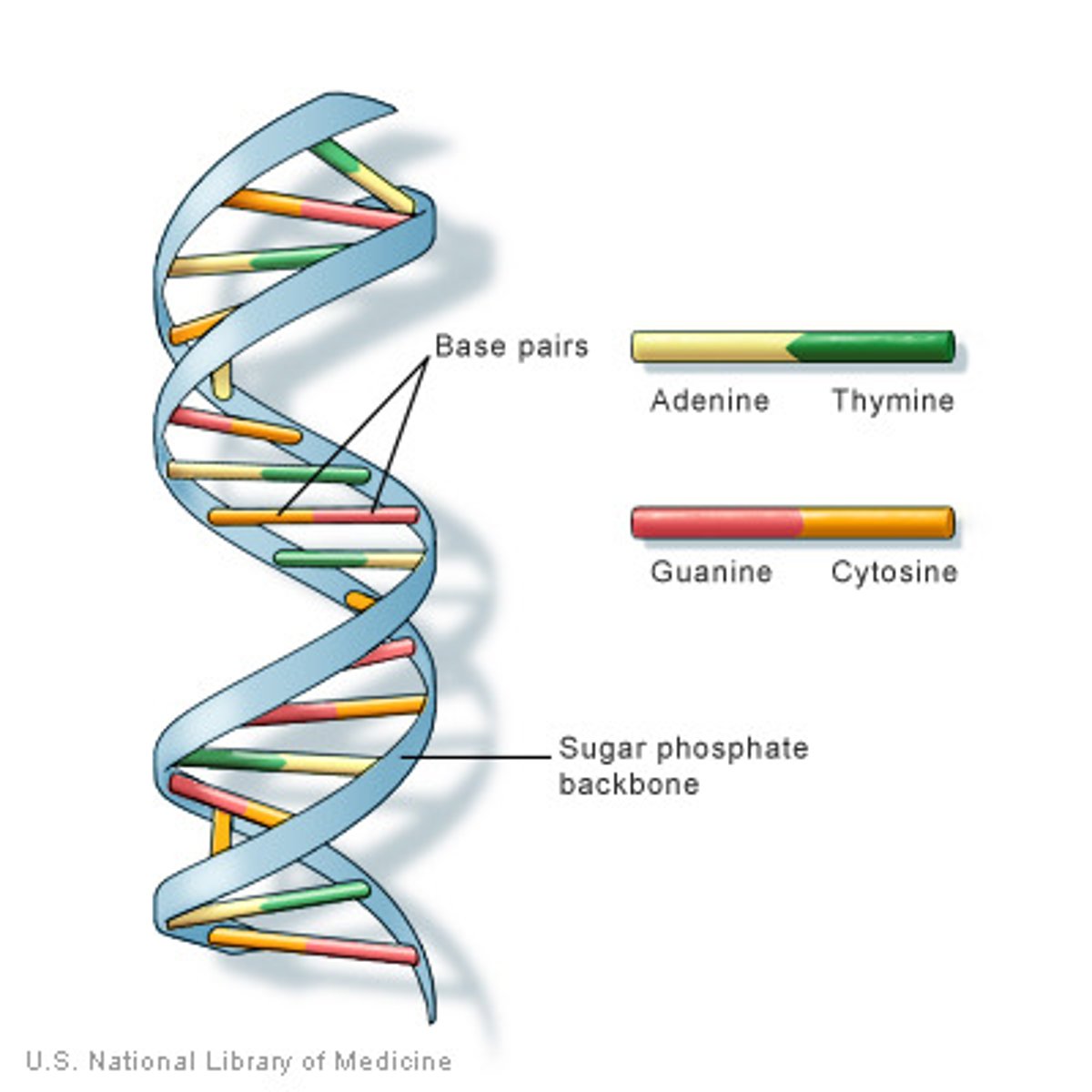
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
- It is found in the nucleus
- Each long molecule of DNA is a chromosome
- You have 46 chromosomes / 23 pairs
- Short sections of DNA that code characteristics are genes
Enzymes
- Biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions
- They are made of proteins
- They build larger molecules from smaller ones = protein synthesis
- They break down larger molecules to smaller ones = indigestion
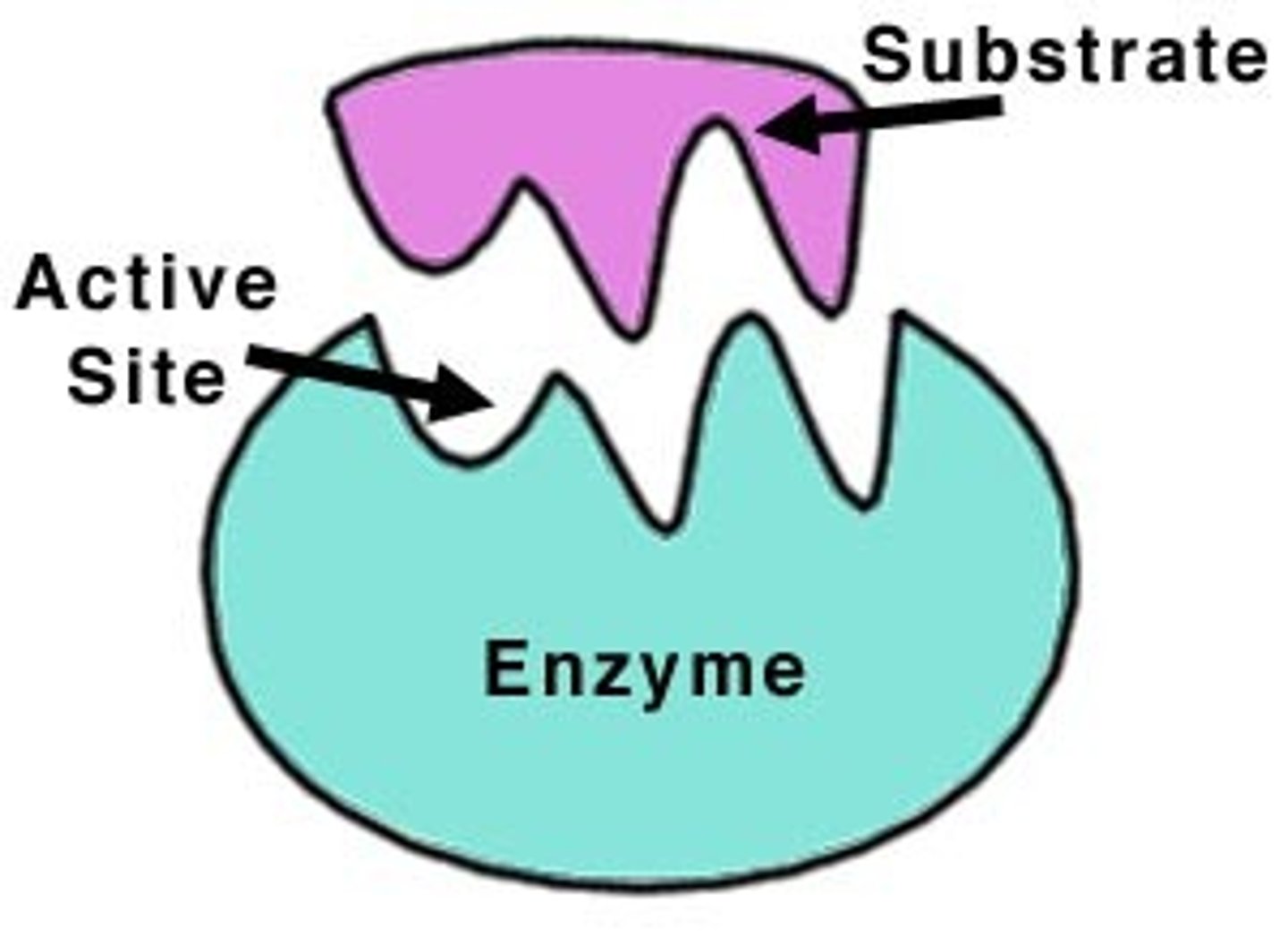
Enzyme specificity
- Enzymes will only act on specific substrates that have a complementary shape to the active site of the enzyme
Eukaryotic cell
- A type of cell found in plants and animals that has a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles
- Contains genetic material in the nucleus
- They are large and complex (10um to 100um)
- Plant cells and animal cells are eukaryotic
Exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy, usually in the form of light or heat
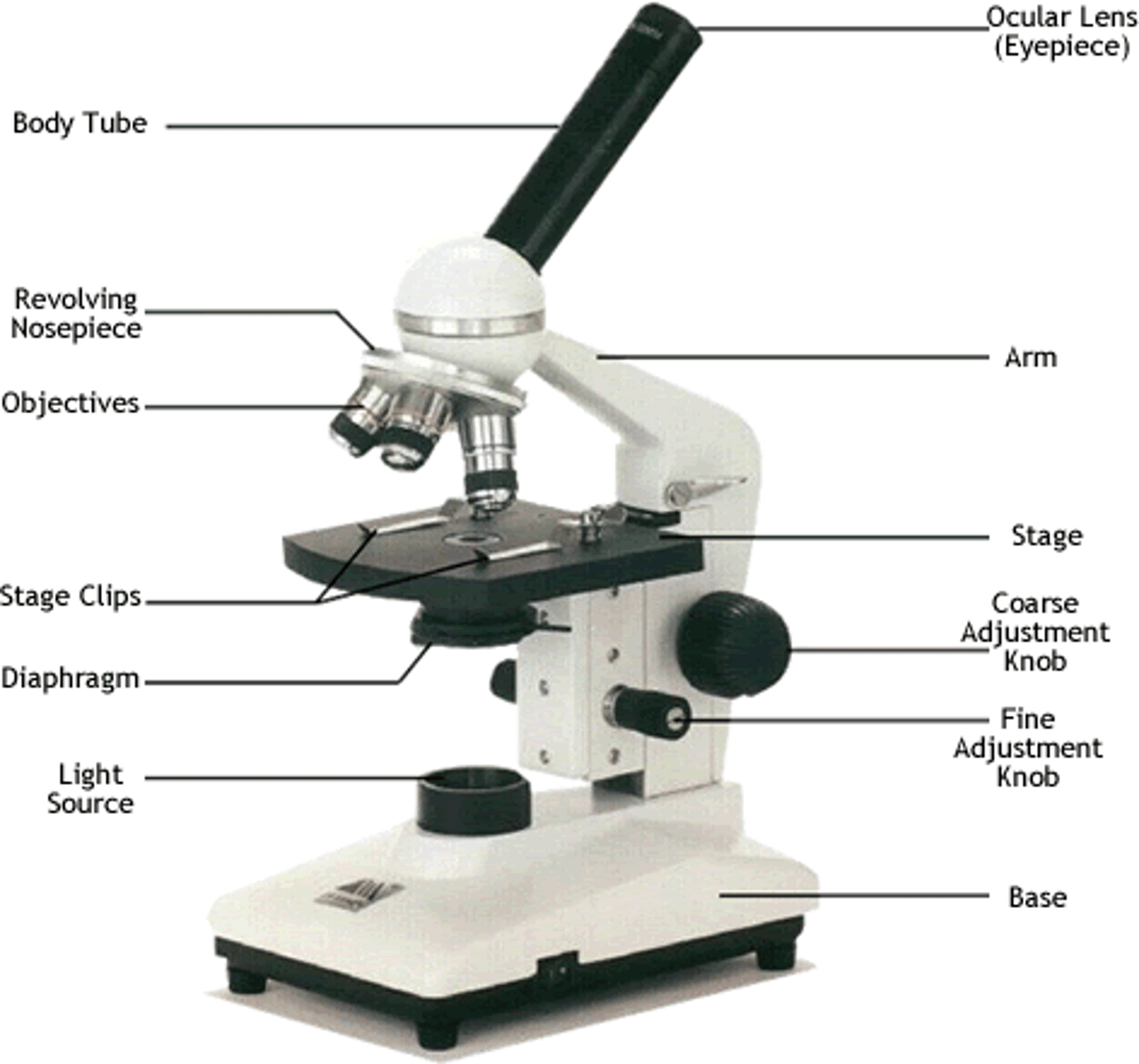
Eyepiece lens
The lens that further magnifies the image produced by the objective lens
Fatty Acid
- A carboxylic acid that has a long carbon chain
- Fatty acids react with glycerol to make lipids
Genetic Material
The material that stores the genetic information
Light Microscope
- A microscope that used light to produce an image of a specimen
- It passes light through an object placed on a slide, on the stage, then through 2 glass lenses
- Resolution = 0.2 um (2 x 10^-7m)
- Benefits: Cheap / Small / Portable / Natural colour seen / Living + Dead specimens used
- Total Magnification = Eye piece lens magnification X Objective lens magnification
Limiting Factor
A factor that when in short or inadequate supply limits the rate of a reaction
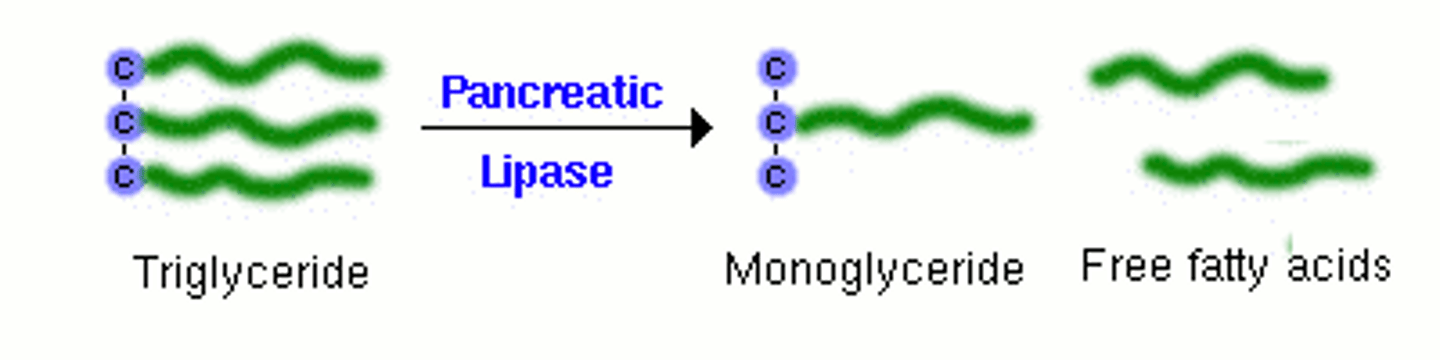
Lipase
An enzyme that breaks down lipids into fatty acids and glycerol
Lipid
- A large molecule that is synthesised from three fatty acids and a glycerol molecule
- Lipase enzymes break down the lipids
Lock and key hypothesis
A theory that describes how substrates must be the correct shape to fit the active site of an enzyme
Magnification
- How many times larger the image appears relative to the original object
- Magnification = image size / actual size
Mitochondria
- The organelle which is the site of aerobic respiration
- It contains enzymes required for cellular respiration
Monomer
- A small molecule which can be bonded to other identical monomers to form a large polymer
- Monomers usually contain a carbon-carbon double bond, C=C
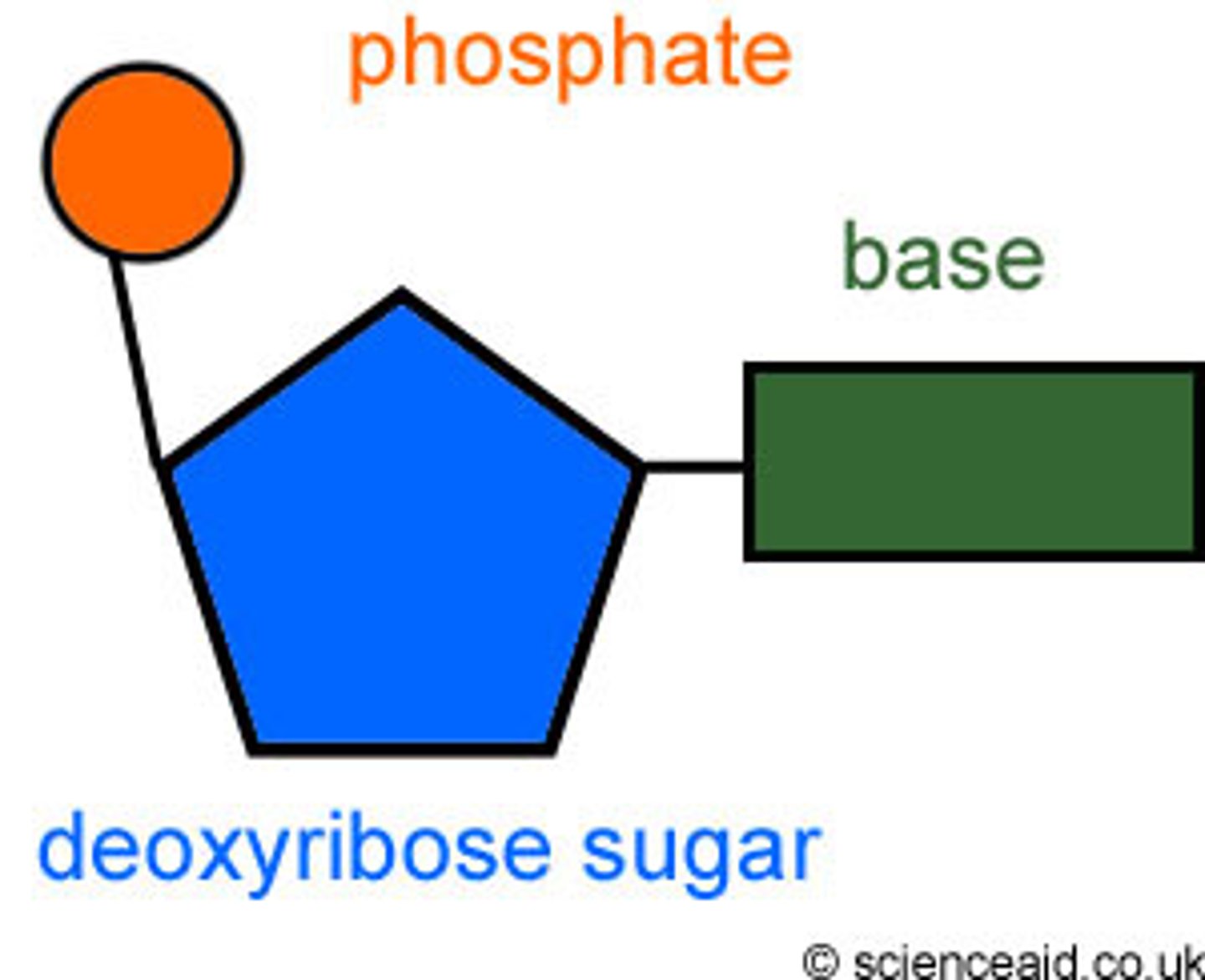
Nucleotide
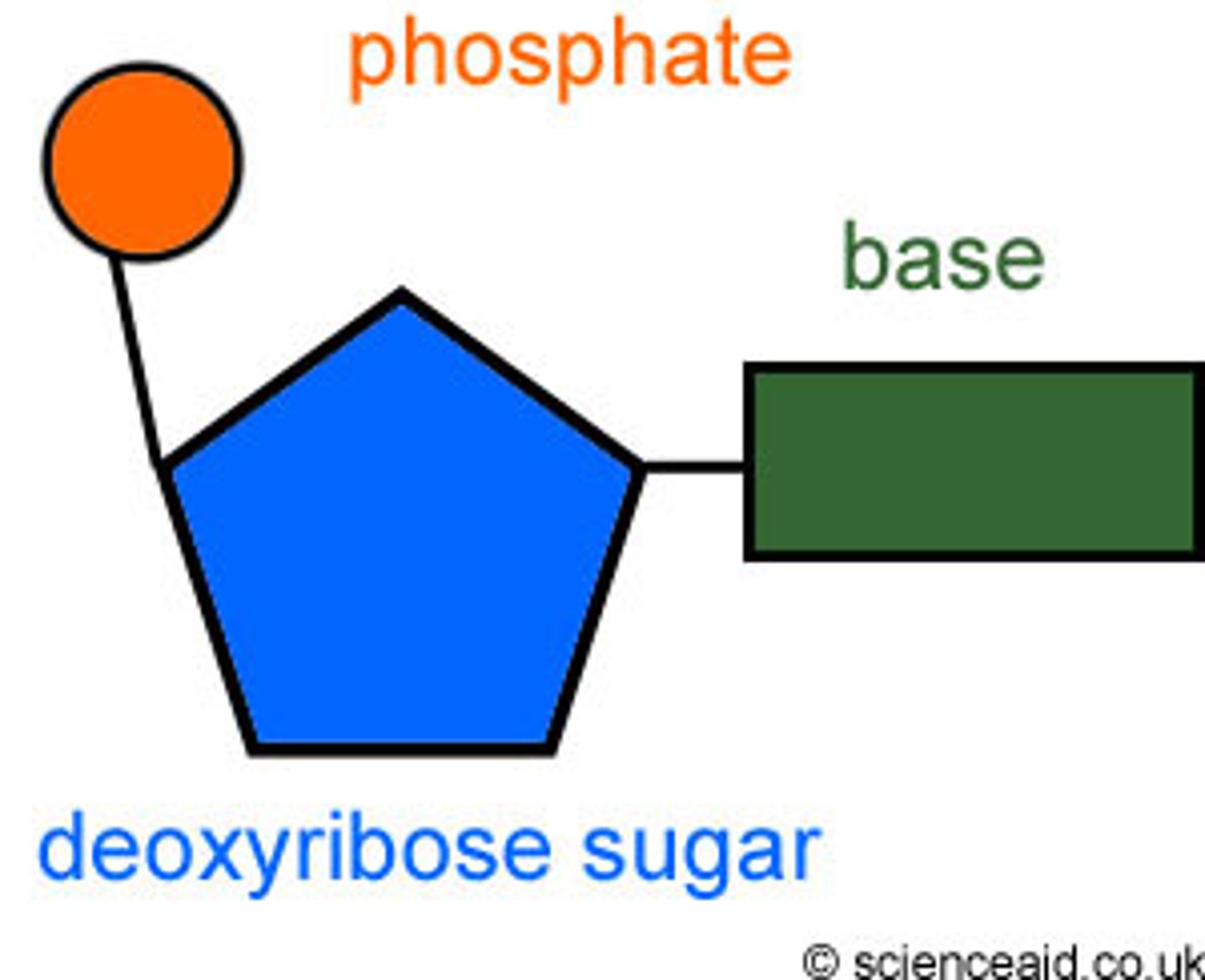
- The monomers of DNA that consist of a common sugar, a phosphate group and a base attached to the sugar
- The chemical base can be one of A, C, T or G
Nucleus
- An organelle found in most eukaryotic cells that contains the cell's genetic material (chromosomes)
- It contains instructions to make a new cell
- It controls the activities and appearance of the cell
Objective Lens
The lens found closest to the specimen that magnifies the image
Palisade Mesophyll
A specialised plant tissue that carries out photosynthesis
Permanent Vacuole
- An organelle found in plant cells which stores cell sap
- It helps maintain the cell's turgidity
- It contains a watery solution of sugars and salts
Photosynthesis
- An endothermic reaction
- It takes place in the chloroplasts of a plant (it gives the plant its green pigment)
- Light energy is used to split water into oxygen and hydrogen ions
- Carbon Dioxide + Water → Glucose + Oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Photosynthetic organisms
- Organisms that are the main producers of food and therefore biomass for life on earth
Plasmid
- A circular loop of double-stranded DNA that is found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells
- It is free to move unlike chromosomal DNA
- It stores extra genes
Polymer
Many small molecules (monomers) chemically joined together to make 1 large molecule
Prokaryotic cell
- A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles e.g. bacteria
- It does not contain a nucleus, genetic material float in the cytoplasm
- They are simple cells (1 to 10 um)
Protein
- A large molecule synthesised from amino acid monomers
- The order in which the amino acids are joined determines the protein synthesised
- Protease enzymes break down proteins into amino acids
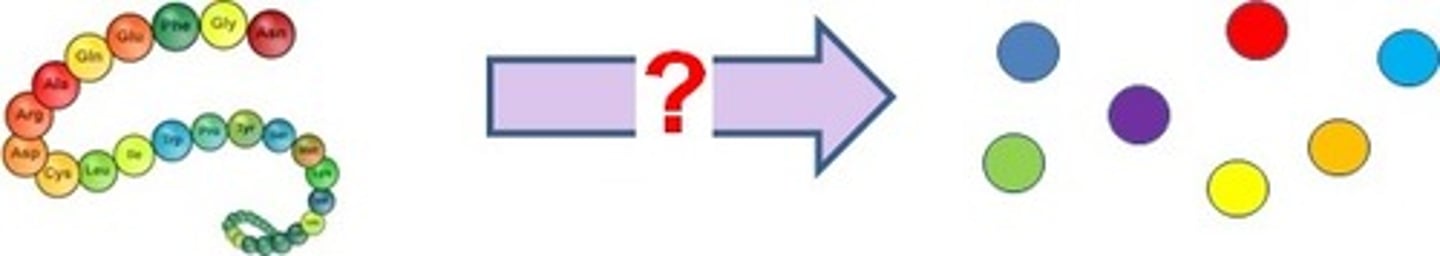
Protein Synthesis
The formation of proteins from amino acids which takes place in the ribosomes
Resolution
The ability to see two cells as two separate entities (measured in dpi)
Ribosomes
Organelles which are the site of protein synthesis
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
- A microscope that uses reflected electrons to produce an image of a specimen
- It creates a 3D image with a lower resolution
- Resolution = 0.5 - 4 x 10^-9 m
- Limitations = Expensive / Not portable / Black and white images / Specimens are dead

Slide
A thin piece of glass on which the specimen is placed
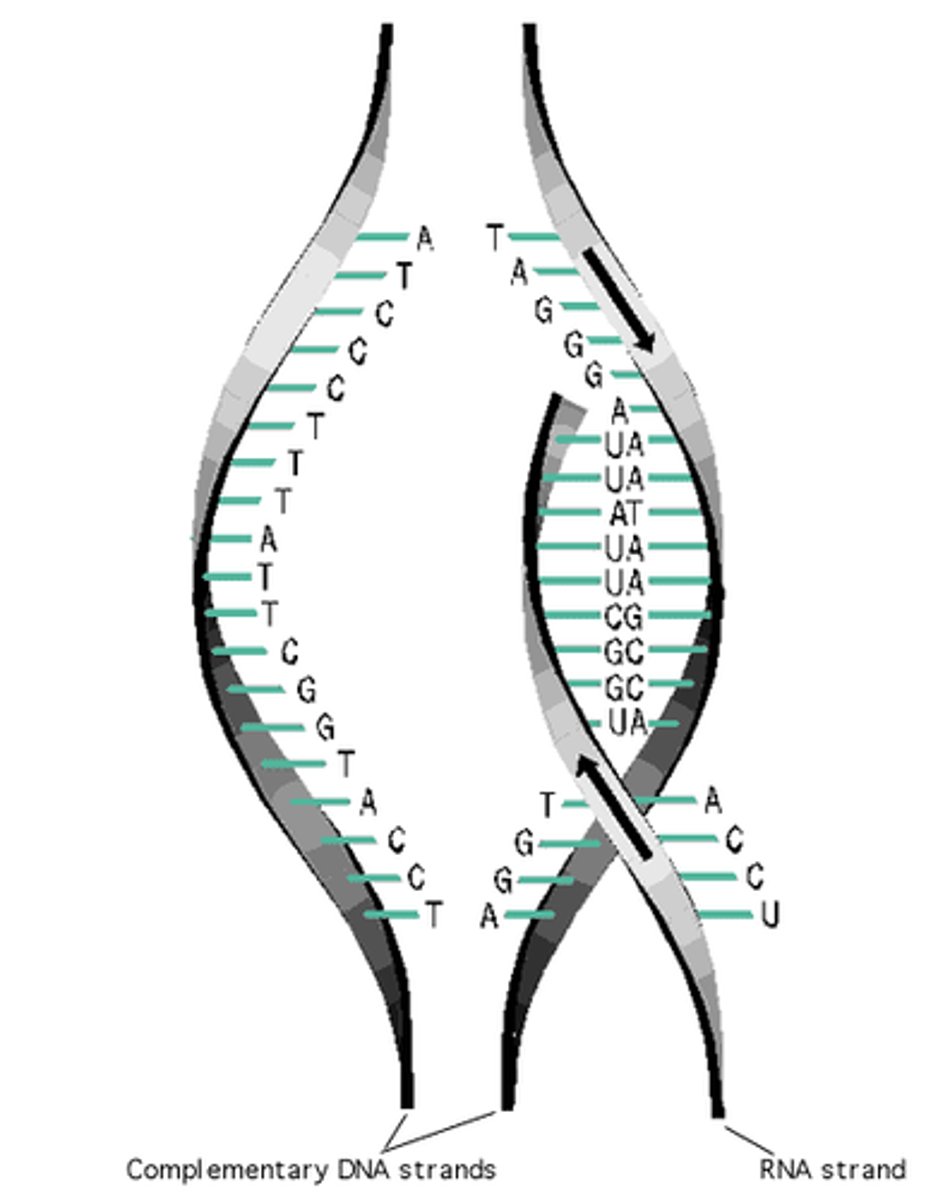
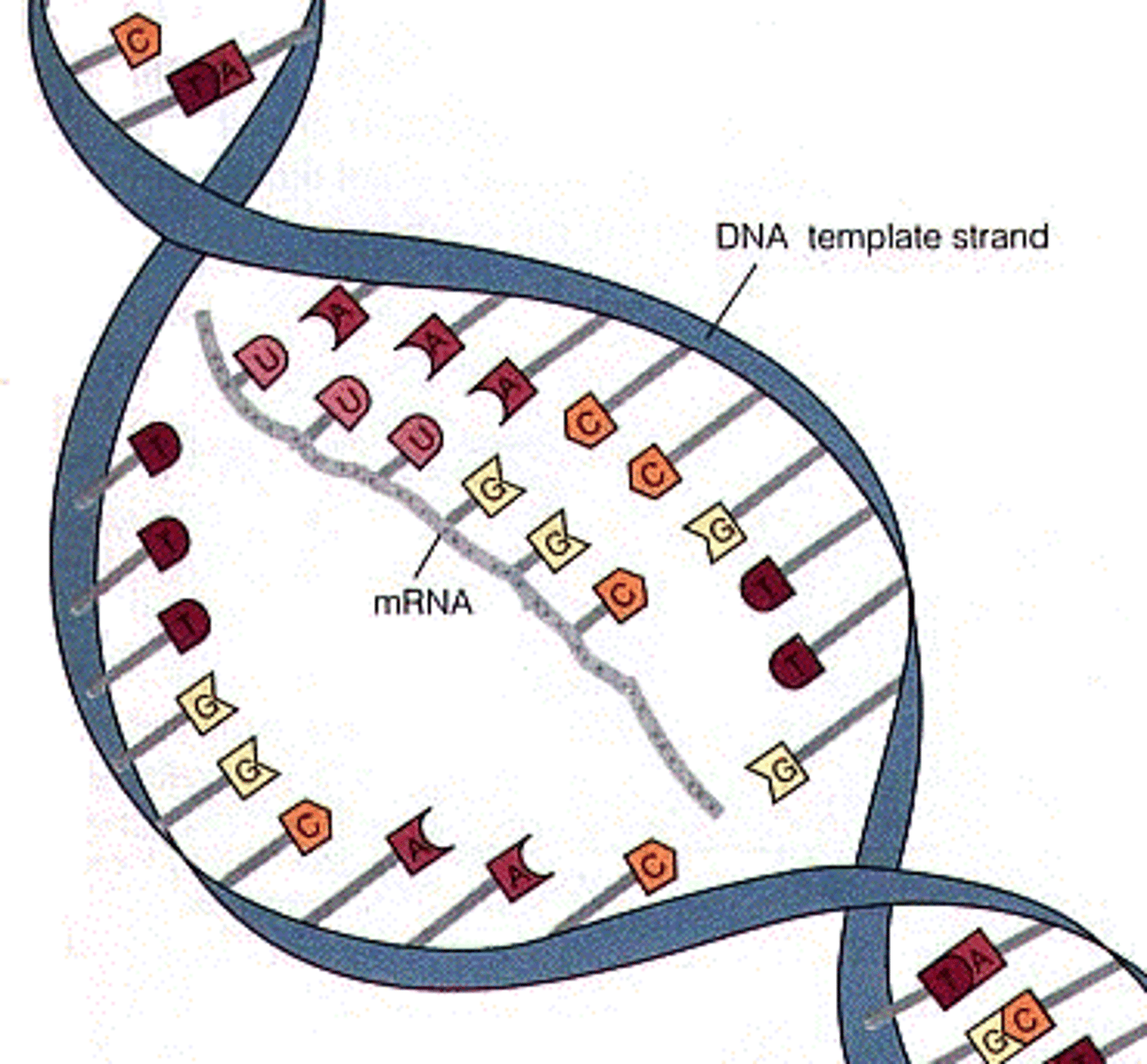
Transcription
The unzipping of the DNA molecule around the gene, copying it to mRNA in the nucleus
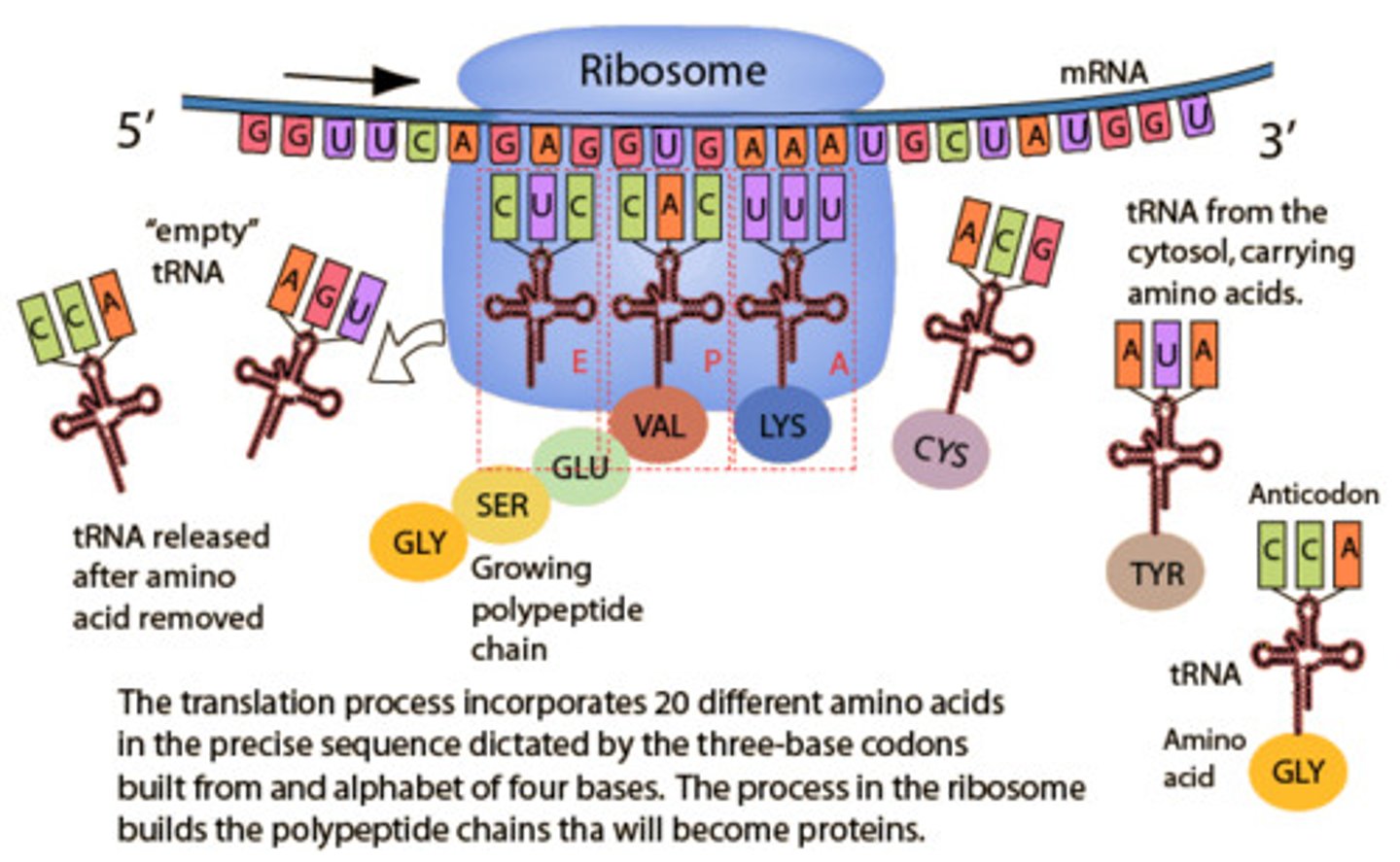
Translation
Translating the mRNA sequence to an amino acid sequence during protein synthesis
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
- A microscope that uses transmitted electrons to produce an image of a specimen
- It creates a 2D image with a higher resolution so details of organelles can be seen
- Resolution = 1 x 10^-10 m
- Limitations = Expensive / Not portable / Black and white images / Specimens are dead

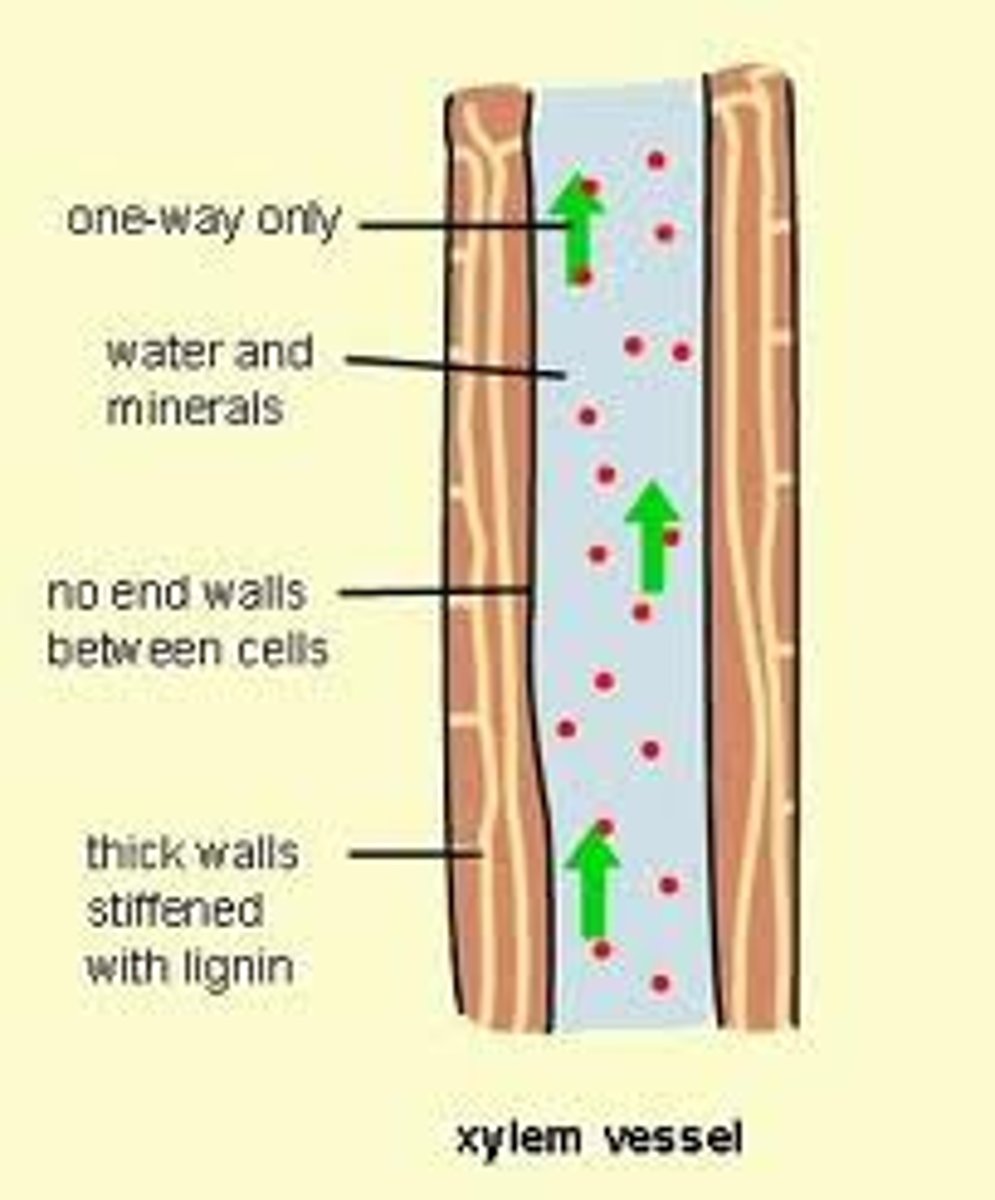
Xylem
A specialised plant tissue that transports water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the leaves of the plant
Parts of Plant Cells
Chloroplast, Chlorophyll, Cell wall, Cell membrane,
Vacuole, Mitochondria
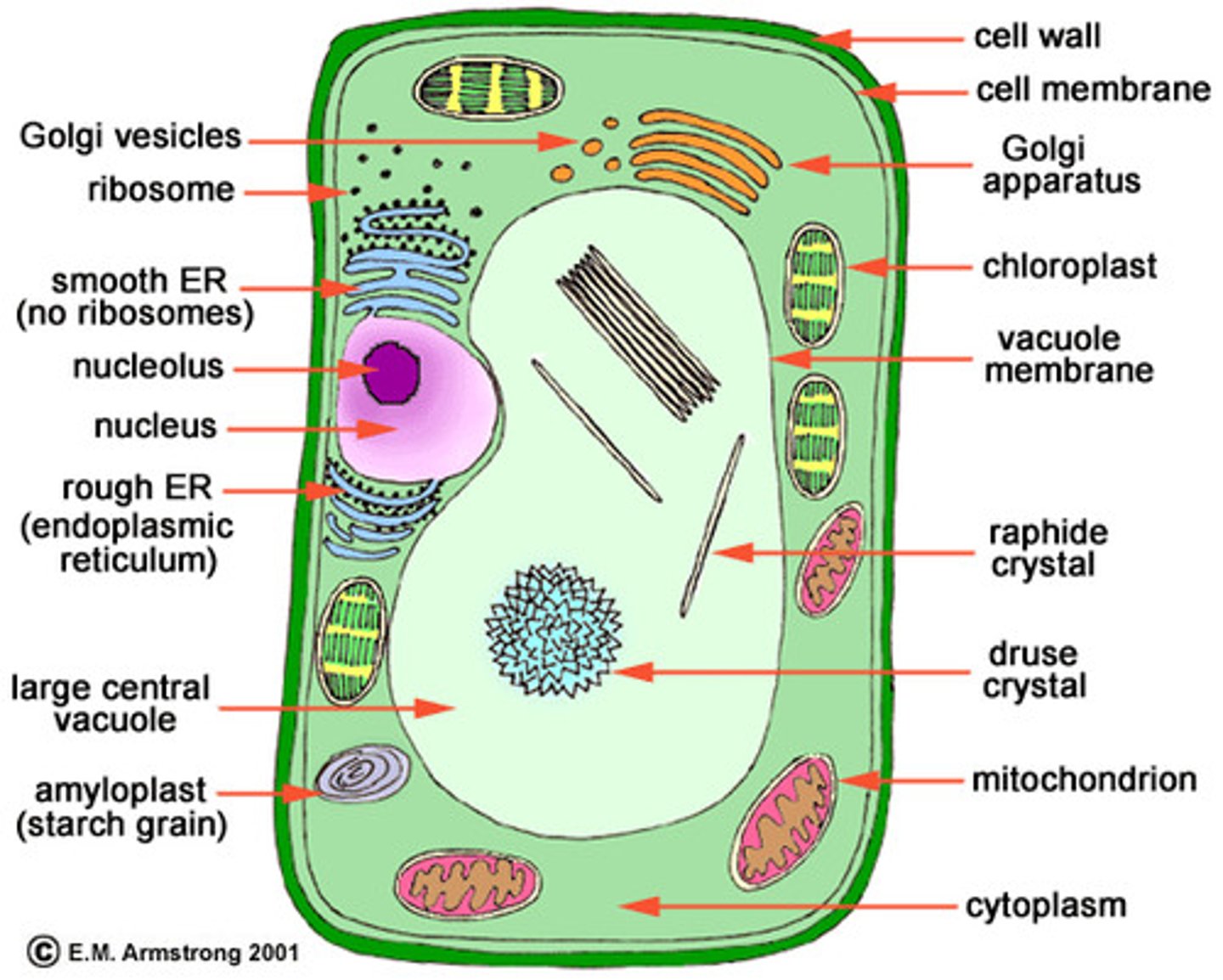
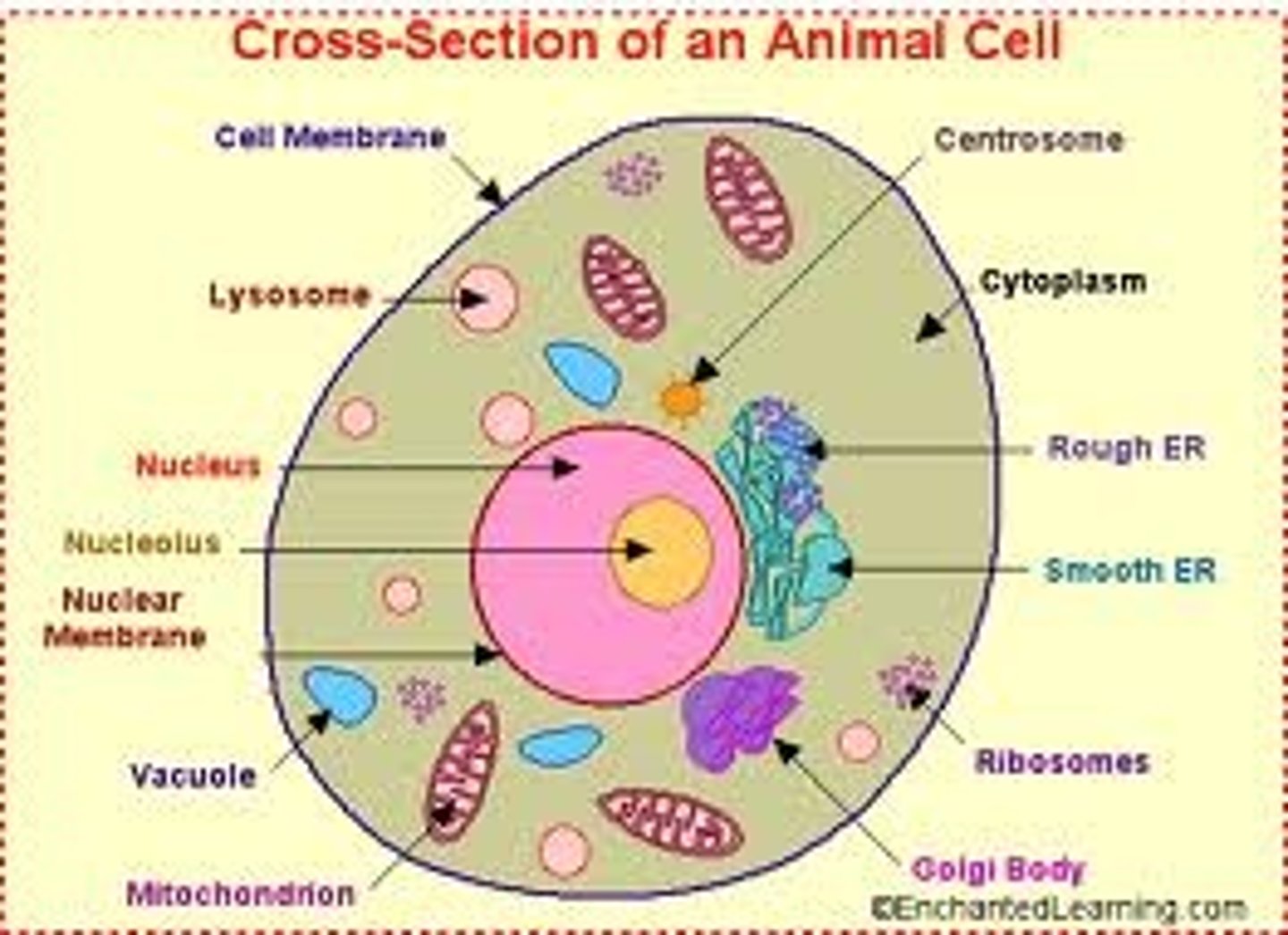
Parts of Animal Cells
Nucleus, Cell membrane, Mitochondria, Cytoplasm
Parts of Prokaryotic Cells
- DNA/genetic material, Cell wall (surrounds cell using tough fibres (cellulose)
- Made of peptidoglycan (holds/protects cell), Ribosomes
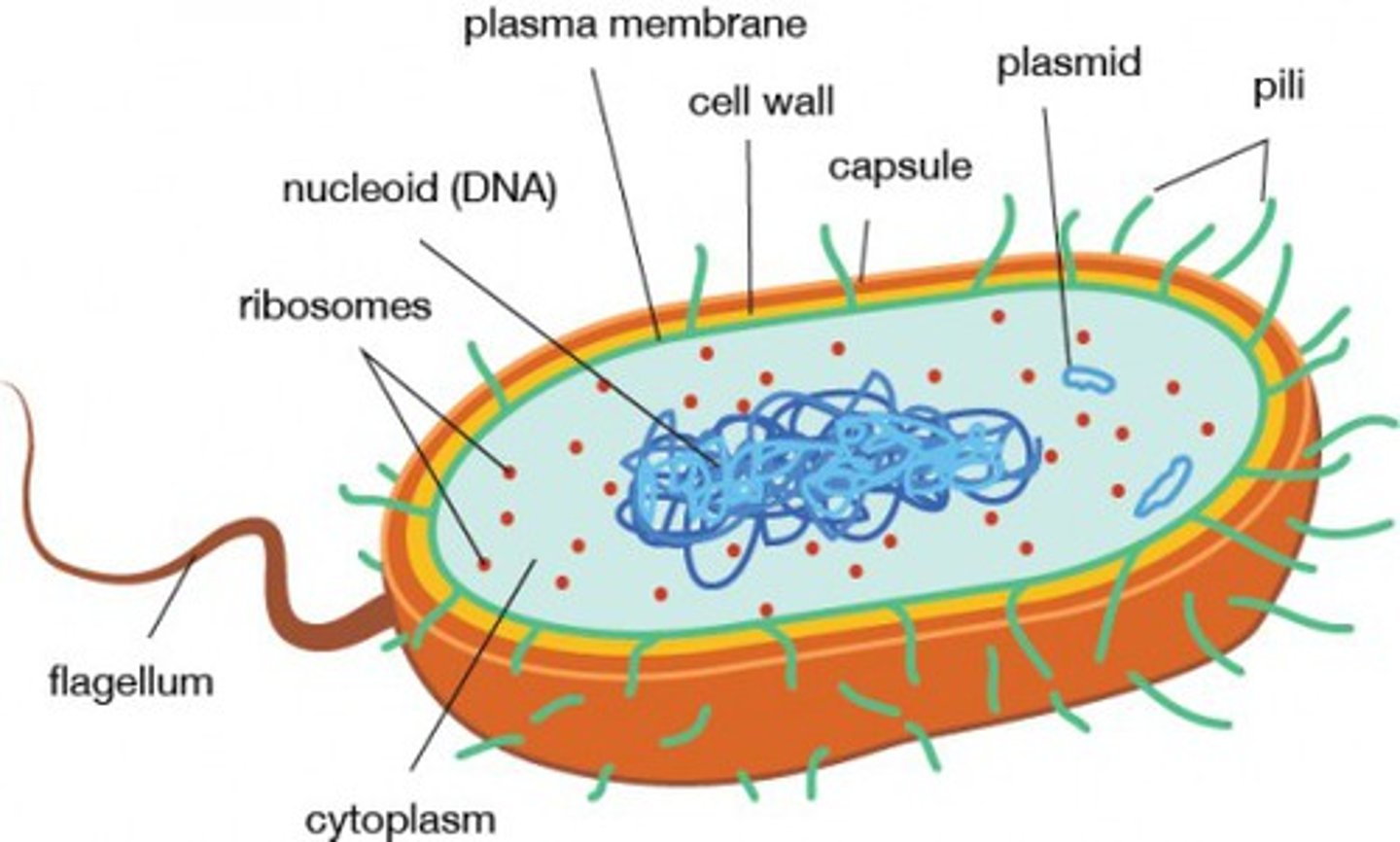
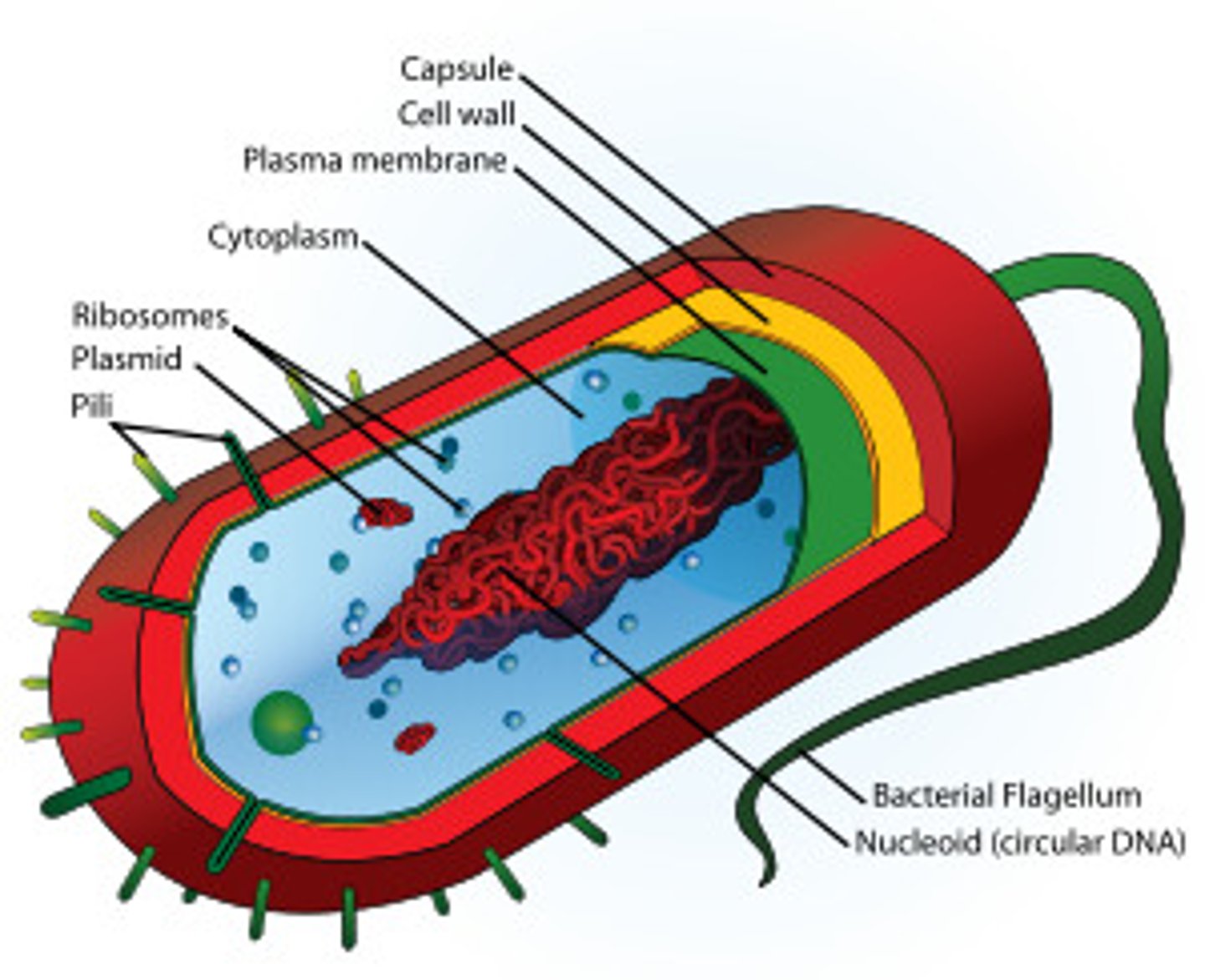
Parts of Bacteria Cells
- A single-celled organisms that lack a nucleus
- Every cell carry's out the seven life processes
- Flagella, Pili, Slime capsule, Plasmid
Cytoplasm
A jelly like substance where chemical reactions take place
Chlorophyll
Transfers sun energy (light) used in photosynthesis (only green part in plants
Flagella
Taillike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement in liquid
Pili
- Tiny hair-like structures that help the cell attach to structures
- They transfer genetic material between other bacteria
Slime Capsule
- Mucous layer on the outside of prokaryotic cells, used for sticking cells together
- It offers protection from drying out and poisonous substances
Seven life processes
- Movement
- Reproduction
- Sensitivity
- Growth
- Respiration
- Excretion
- Nutrition
Staining Cells
- Many cells are colourless so staining cells make them easier to see
- To apply the stain: Place cell on slide, add one drop of stain, place cover slip on top, tap gently to remove air bubbles
- Methylene Blue = easier to see nucleus of animal cell
- Iodine = easier to see nucleus of plant cell
- Crystal Violet = stains bacterial cell wall
Structure of DNA
- It is a polymer made up of four nucleotides, each consisting of a phosphate group and a common sugar which has one of four different bases attached: Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C) and Guanine (G)
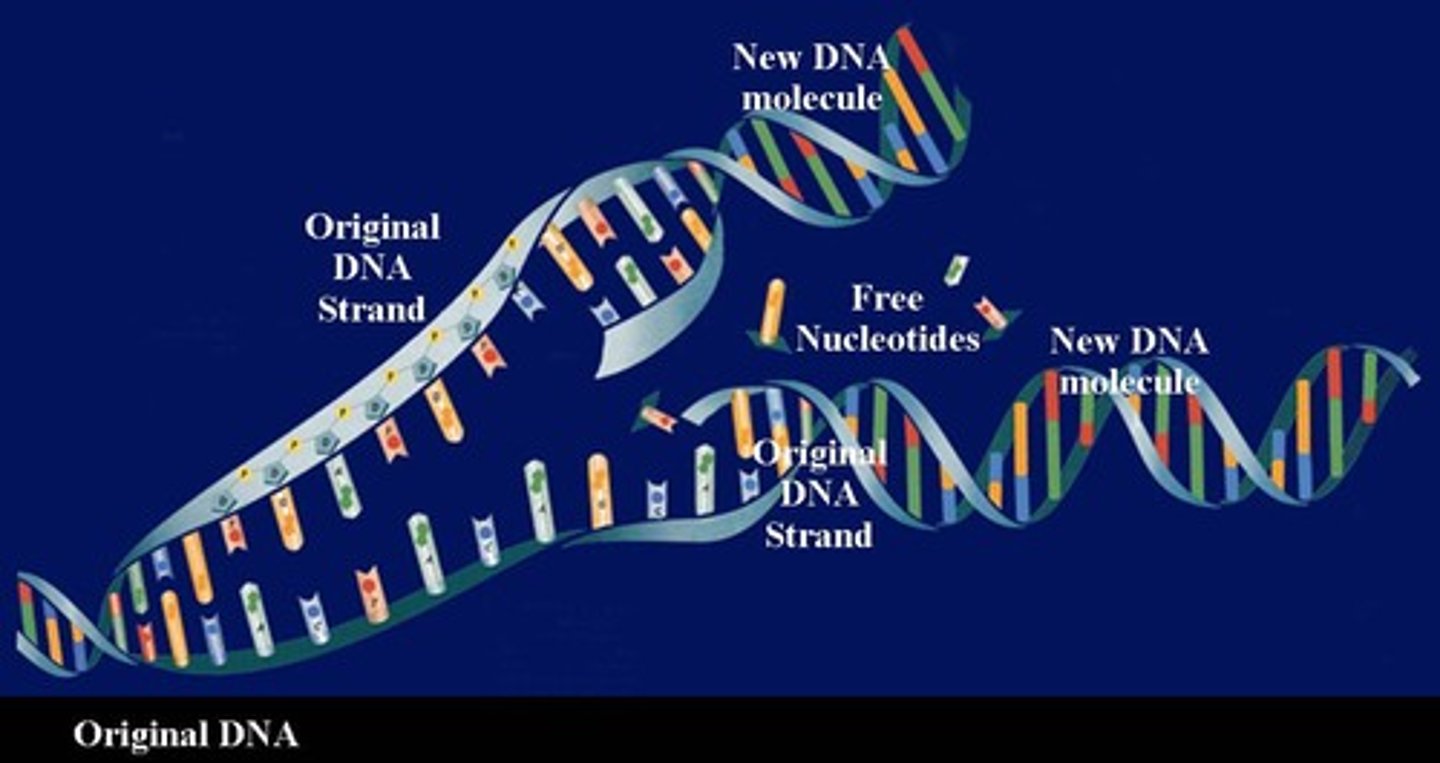
How a Copy of DNA is Made
- DNA cannot leave the nucleus
- A copy of DNA is made by mRNA produced in transcription
- The DNA unzips into two separate strands
- The strands act as a template and complementary bases attach
- The new strands detach and the DNA zips up
mRNA (messenger RNA)
- The form of RNA which is created as a blueprint from DNA
- It carries instructions for making a protein
- It is small so it can move out the nucleus
How a Protein is Made
- They are made of Amino Acids
- They are made by translation
- the mRNA attaches to a ribosome which read the nucleotides on the mRNA in 3 groups called base triplets (codons)
- The amino acids join together, making a protein
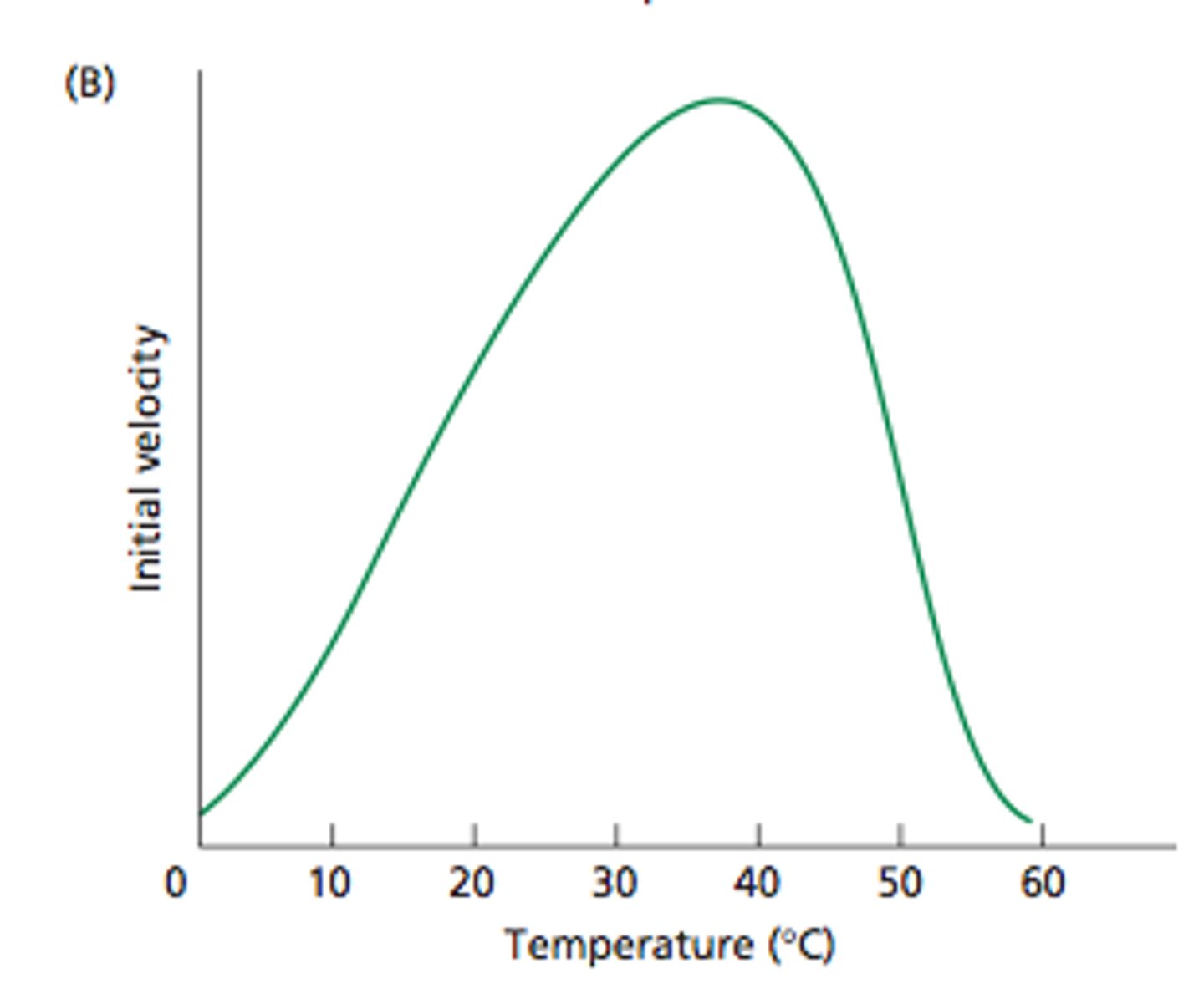
Factors Affecting Enzymes - Temperature
- At high temperatures the enzymes and substrates move faster and collide more
- If temperatures become to high, the amino acid chains in the proteins start to unravel, changing shape of the active site
- The enzyme becomes denatured and the change is irreversible
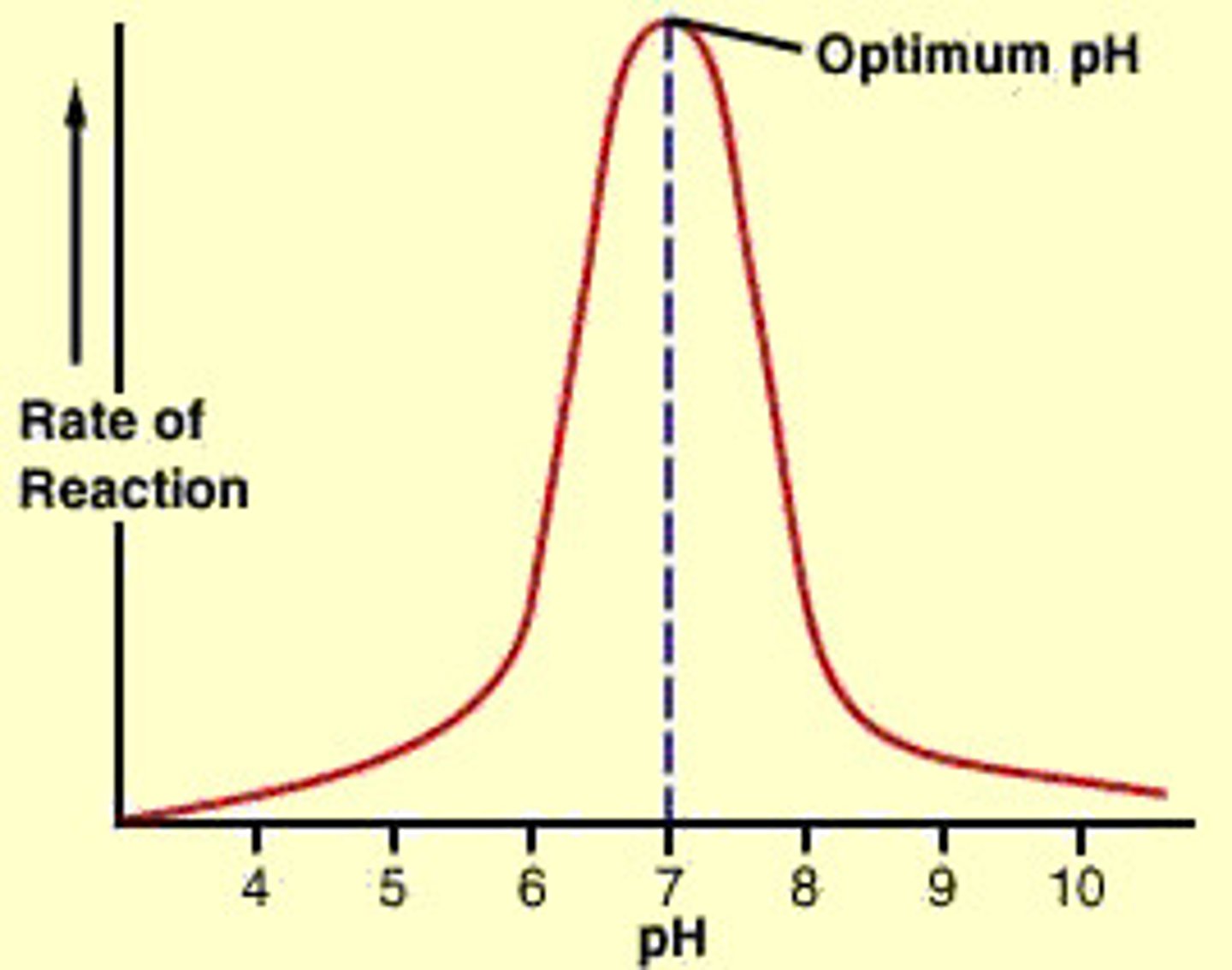
Factors Affecting Enzymes - pH
- Each enzyme has an optimal pH
- A change in pH affects interactions between the amino acids in the chain
- This changes the shape of the active site resulting in a change in the chemical formula
- The enzyme becomes denatured and the change is irreversible
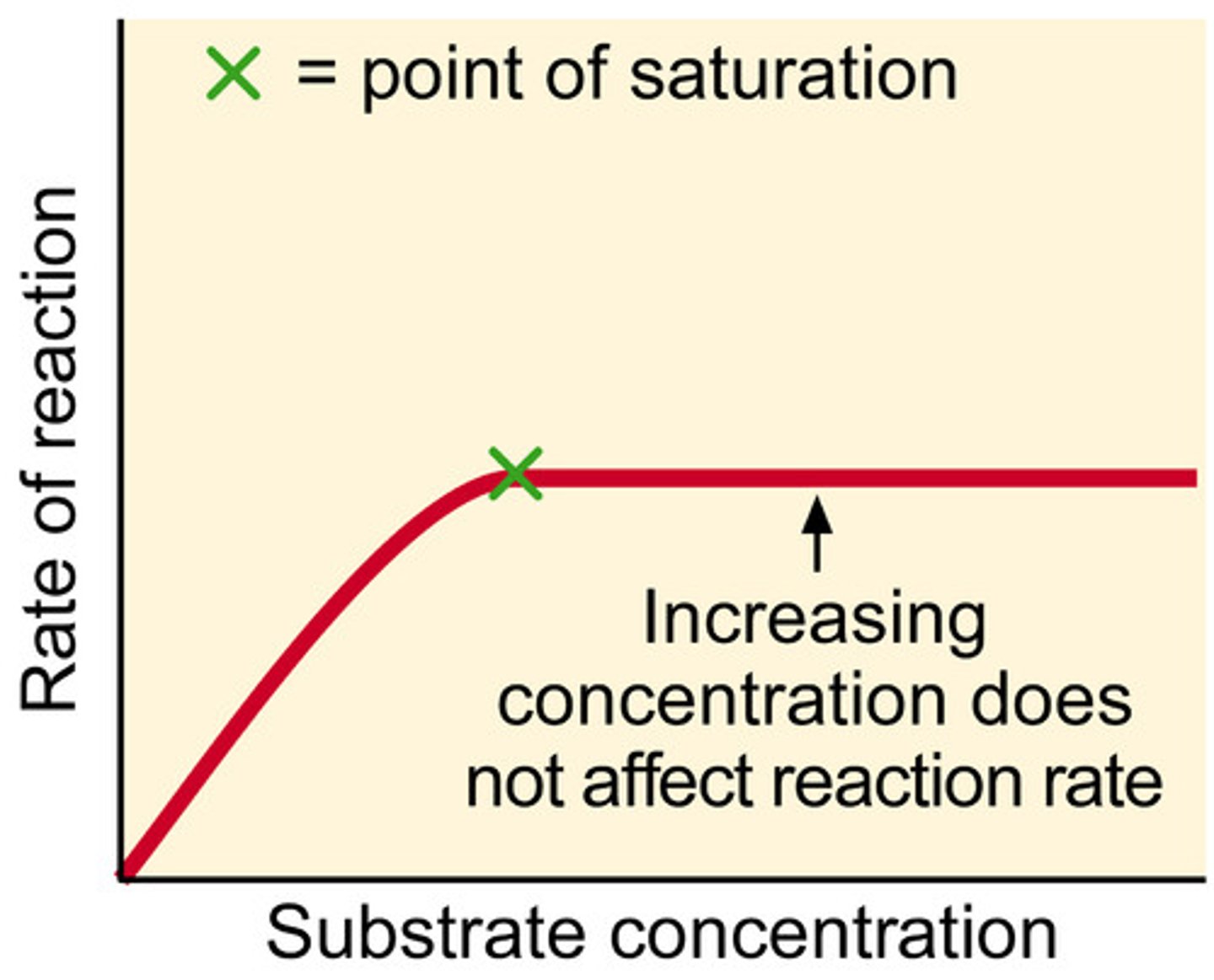
Factors Affecting Enzymes - Substrate Concentration
- The higher the substrate concentration, the faster the rate of reaction
- If there are too many substrates, all enzymes are bound to a substrate so the rate of reaction is at its maximum = There aren't enough enzymes
Factors Affecting Enzymes - Enzyme Concentration
- The higher the enzyme concentration, the faster the rate of reaction
- The rate of reaction is limited by the substrate concentration
- If no new substrates are added the reaction will stop
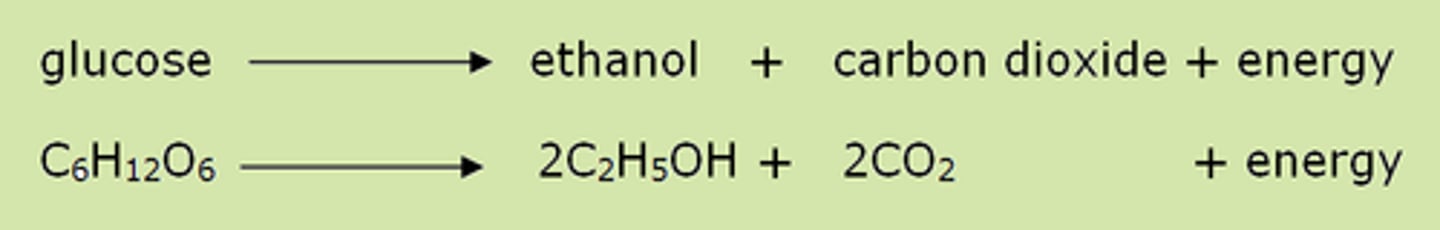
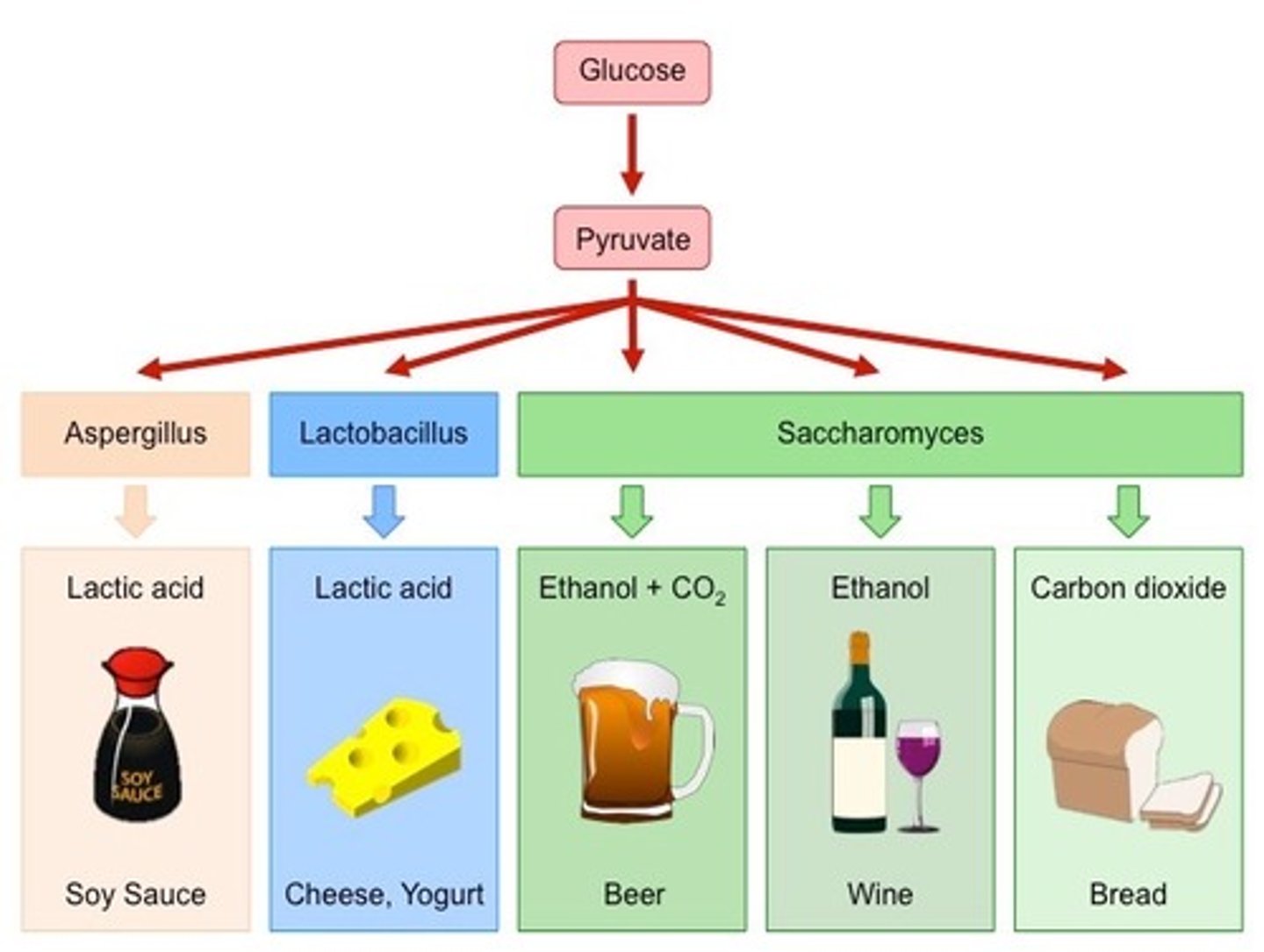
Fermenation (Anaerobic Respiration)
- In plant and yeast cells pyruvate is converted into carbon dioxide and ethanol
- Ethanol is produced instead of lactic acid
- Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon Dioxide
C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Test for Starch (Test for Chlorophyll)
- Add Iodine to the sample
- If it goes blue/black, starch is present
- If it stays brown, starch is not present
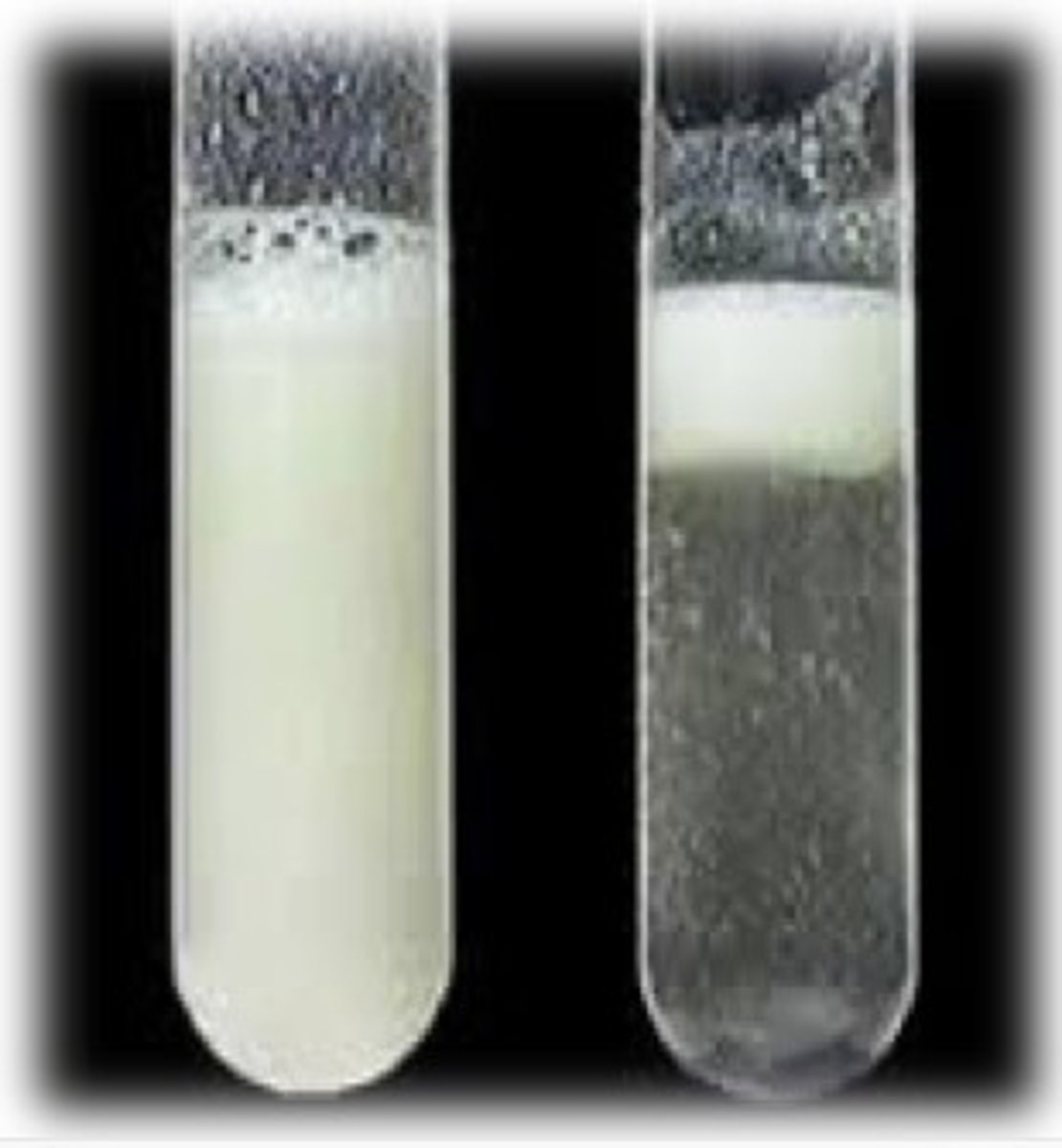
Test for Fats
- Add ethanol to the sample
- Mix and add water
- If it goes cloudy, fats are present
Test for Proteins
- Add Biuret to the sample
- If it goes mauve/lilac, proteins are present
- If it stays blue, no proteins are present
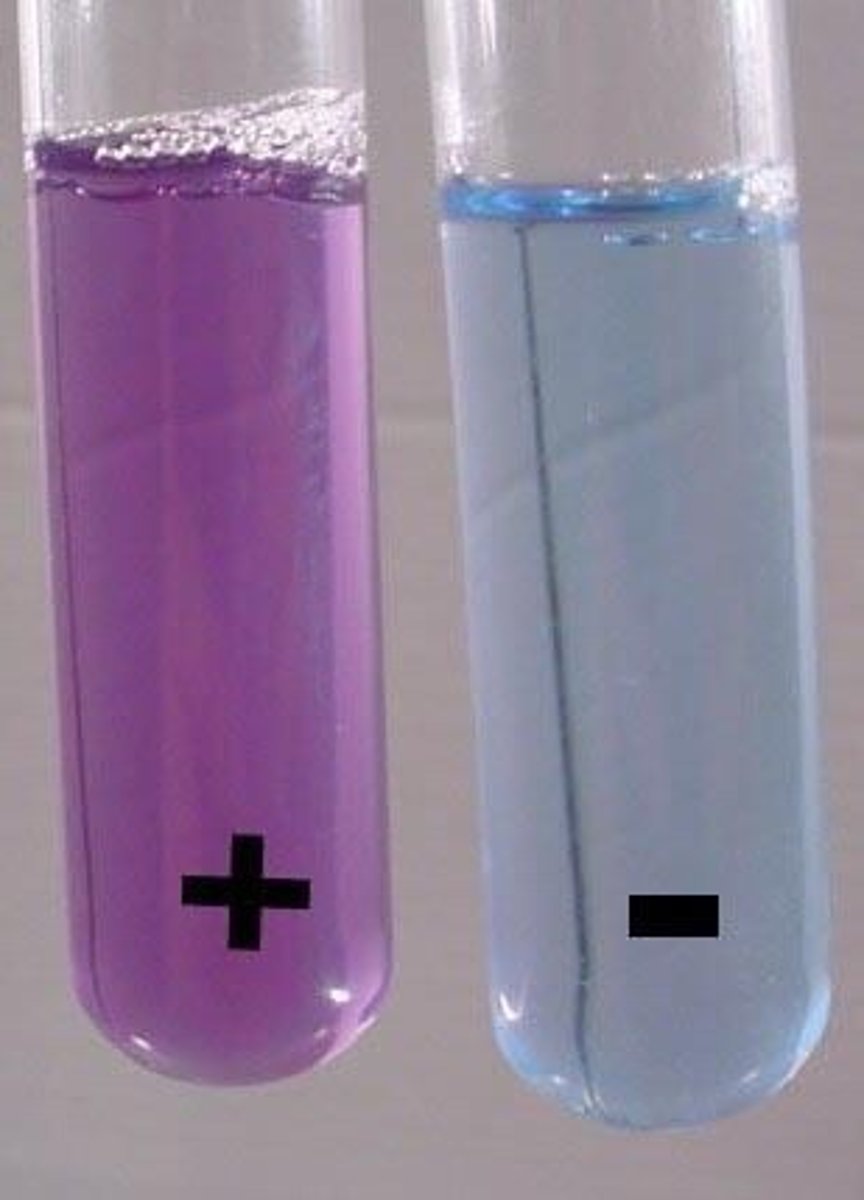

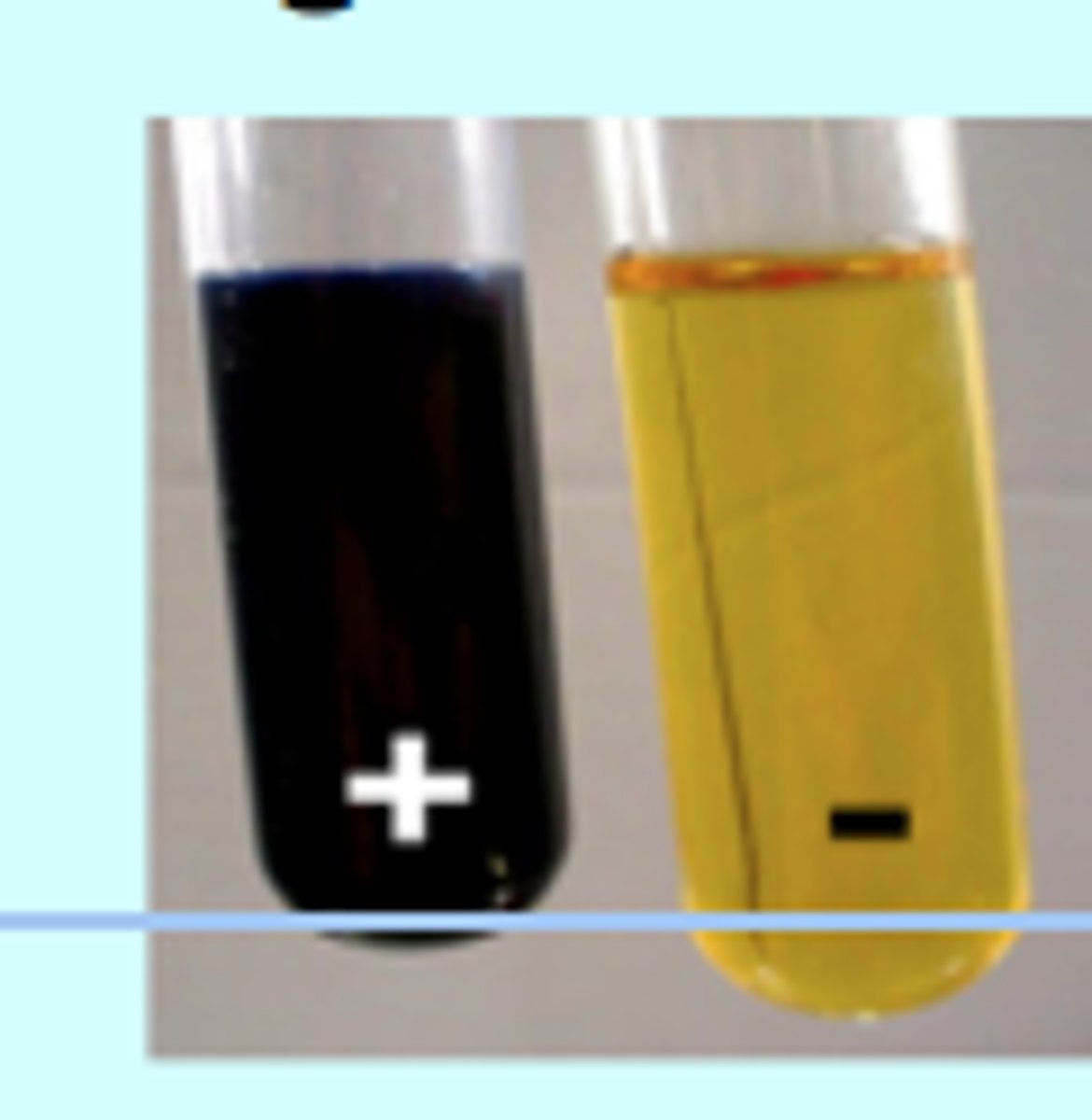
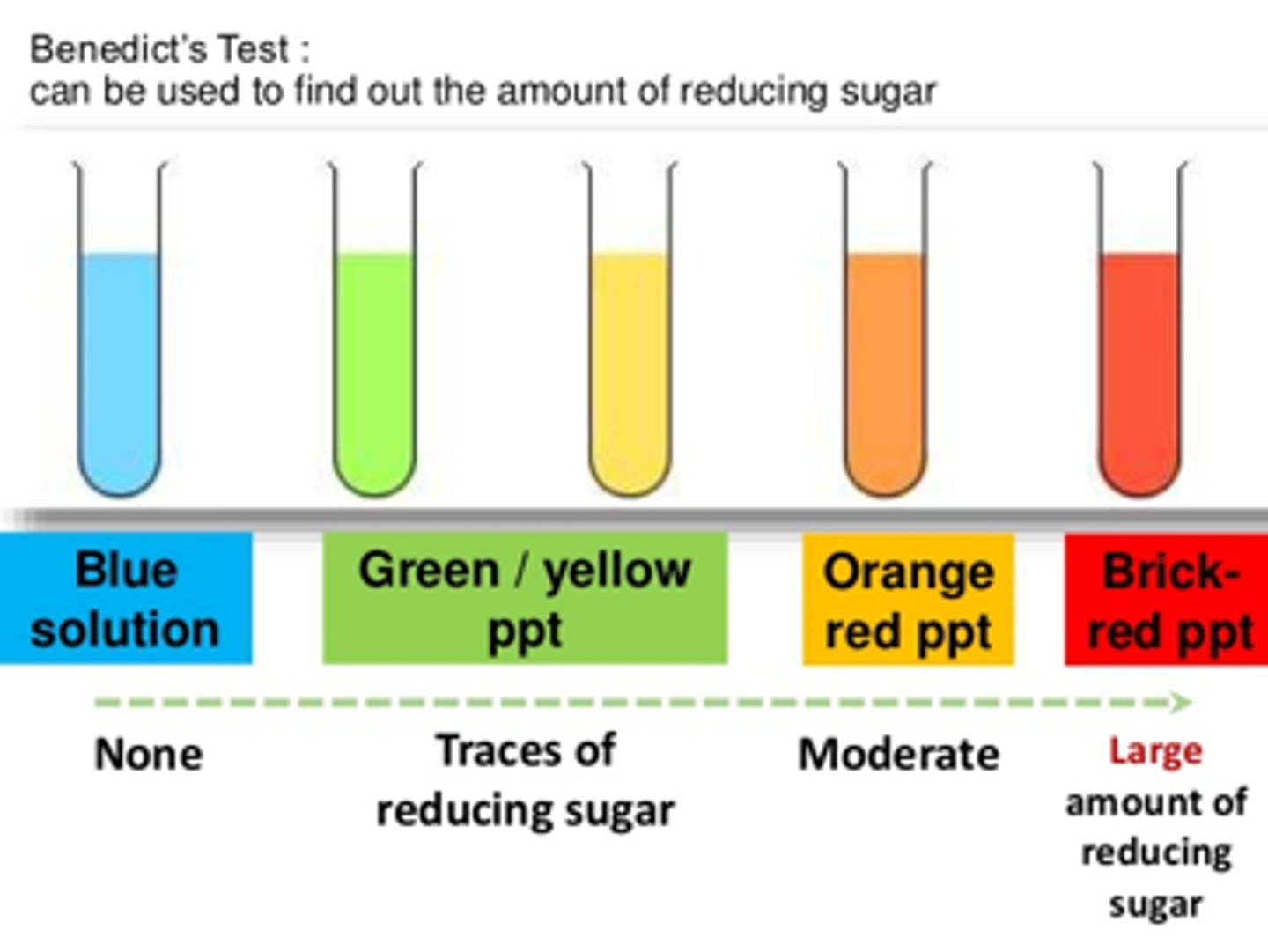
Test for Sugars (Glucose)
- Add Benedicts solution/reagent to the sample
- Place it at 80° for 5 minutes
- If it has an orange / red precipitate, sugars are present
- If it stays blue, sugars are not present
Test for Carbon Dioxide (In a Plant)
- Take a de-starched plant and place it inside a polythene bag with a pot of soda lime (it absorbs can=bon dioxide)
- Place the plant in the sunlight for 7 hours and test for starch

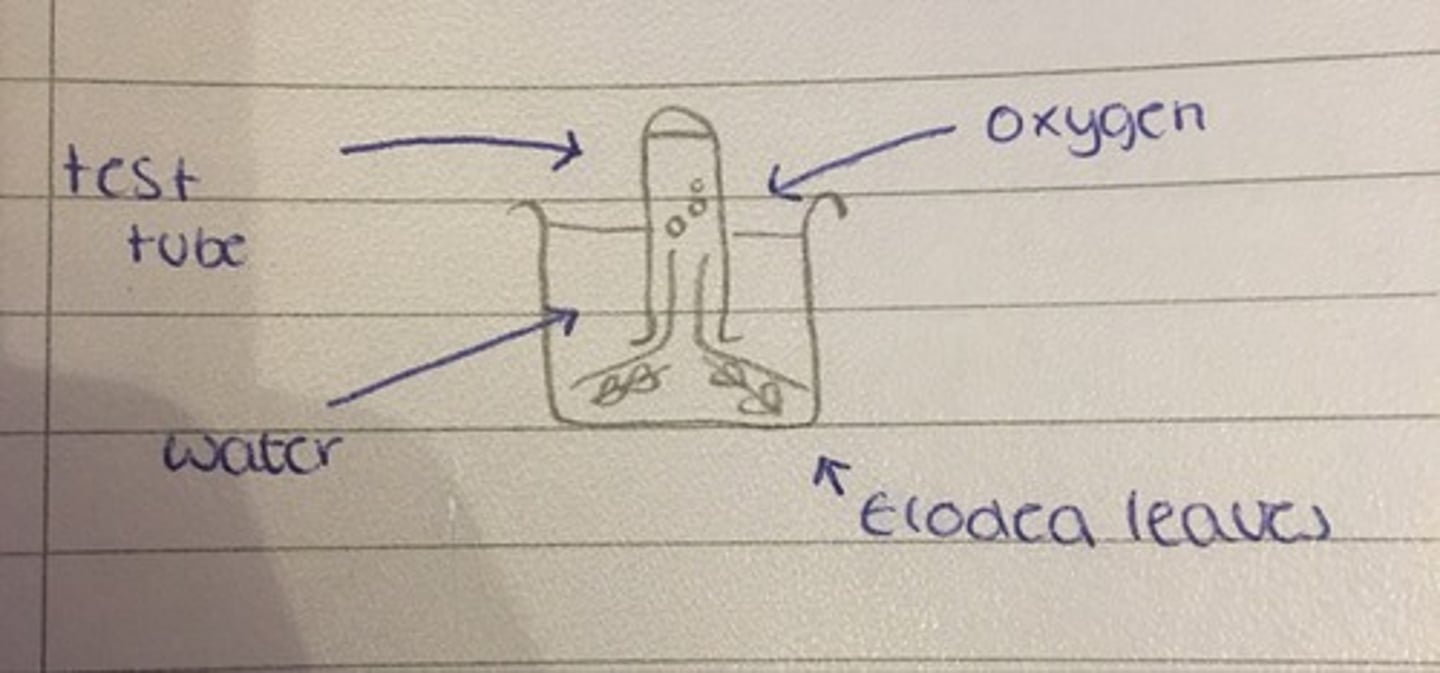
Test for Oxygen (In a Plant)
- Place an upturned test tube above an aquatic plant
- When you have collected the gas, check for oxygen using a glowing splint
- The glowing splint will relight with oxygen
Factors affecting Photosynthesis
- Light intensity
- Carbon Dioxide Concentration
- Temperature
- Rate = 1/time
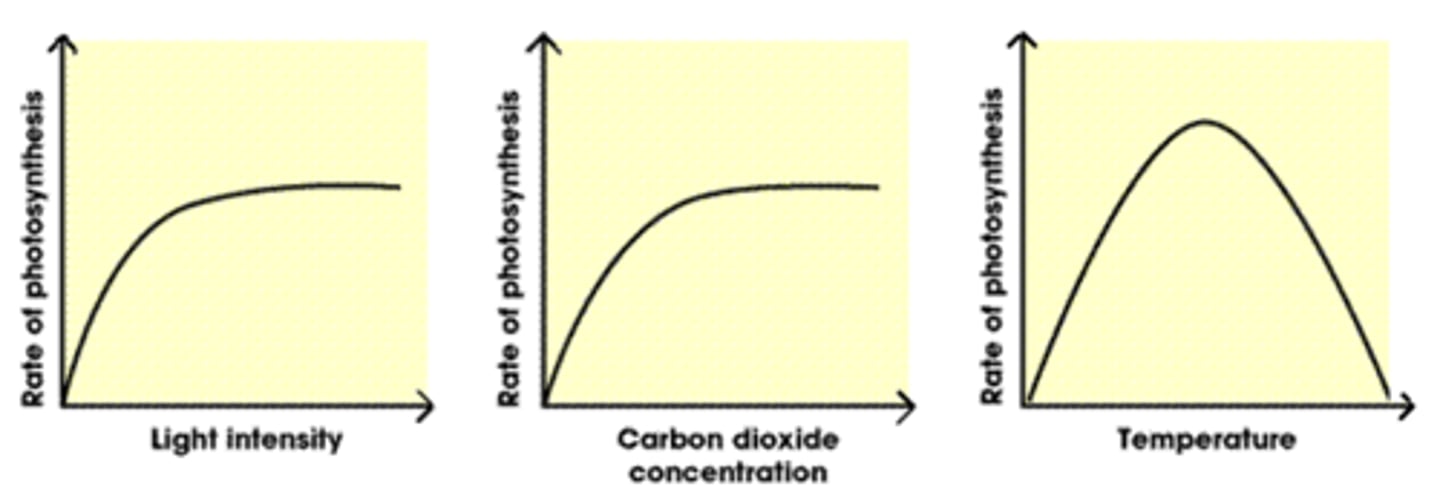
Rate of Photosynthesis
- Using an aquatic plant (Elodea = Pondweed) you test the volume of oxygen given off per minute
- You count the number of bubbles produced per minute
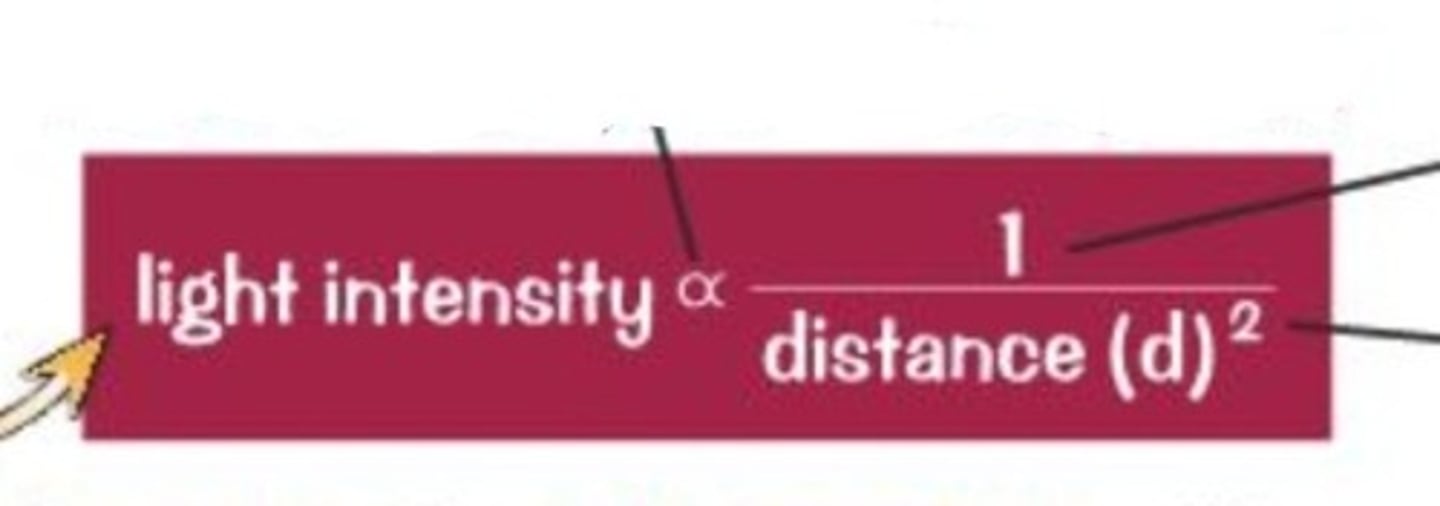
Inverse Square Law
Relative Light Intensity = 1 divided by distance from light source ^2