CHAP 10.1: Liquids & Solids
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Intermolecular forces determine the _ of a substance.
Phase
Intermolecular forces occur between particles in a substance. These particles can be:
both atoms & separate molecules
Intermolecular forces are primarily responsible for:
holding together molecules in a material
The phase of a substance depends on the relative magnitudes of the molecular ___ and the energy of intermolecular attractions.
kinetic energy (KMT Kinetic Molecular Theory)
In general, the type and magnitude of intermolecular forces that are present in a substance will determine that substance's:
physical properties ONLY
What is produced as a result of rapidly fluctuating induced dipoles and instantaneous dipoles?
Dispersion Force
- Powerful dipole-dipole force
- special type of dipole-dipole interactions BUT not an actual bond
- very electronegative atom is bonded to this
Hydrogen Bonding
O-H, N-H, F-H
Hydrogen Bonding Types
Which molecule would exhibit the strongest dipole-dipole interactions?
HCl
HBr
HI
HAt
HCl
Which molecule would exhibit the strongest dipole-dipole interactions?
CH4
CH3Cl
CCl4
They are all nonpolar
CH3Cl; has the strongest net dipole, and will therefore participate in the strongest dipole-dipole interactions.
Dispersion forces are a type of:
intermolecular force
van der Waals force
electrostatic interaction
Arrange the following molecules in the correct ascending order of boiling point.
HCl HI HF
HCl < HI < HF; the strength of intermolecular forces follows the trend: dispersion < dipole-dipole <hydrogen bonding.
Dispersion forces occur due to:
the temporary asymmetry of electron density
Which molecule will engage in the strongest dispersion forces?
CF4
(carbon tetrafluoride)
CCl4
(carbon tetrachloride)
CBr4
(carbon tetrabromide)
CI4
(carbon tetraiodide)
Bc of mass and size causing the induced dipole to last longer:
CI4
(carbon tetraiodide)
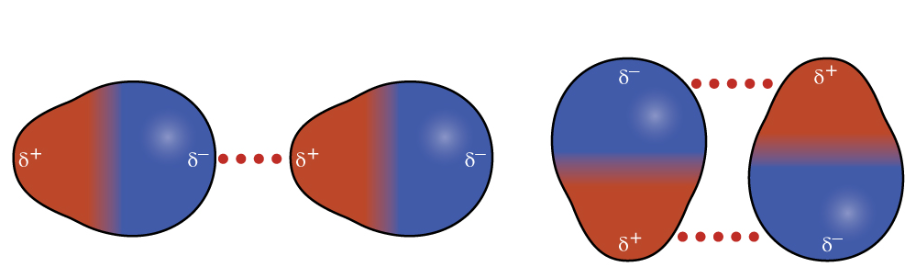
Polar molecules have attractive dipole-dipole interactions when the dipoles are arranged in which of the following geometries?
head-to-tail: ←←
side-to-side, antiparallel: ↑↓
Dipole-dipole interactions occur when the positive end of one polar molecule is near the negative end of another.
ICl is a polar molecule and Br2 is a non-polar molecule. Which molecule will have a higher boiling point?
ICl
Dipole-dipole attractions increase in magnitude with:
increasing bond polarity (bc As covalent bonds become more polar, dipoles become greater in magnitude, and thus the resulting dipole-dipole attractions increase in magnitude.)
(The stronger the bond polarity (i.e., the greater the difference in electronegativity between the atoms),
The larger the dipole moment,
Which results in stronger dipole-dipole interactions.)