Module 4 Test Prep
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Gene Expression
take DNA and create a protein from it
-regulated at every level
What places can gene expression be regulated?
Eukaryotic gene expression is regulated during transcription, which happens in the nucleus, and during translation, which happens in the cytoplasm
Do all cells in your body have the same DNA? How does that work?
Yes!
Your eyes have the DNA to make hair but they don’t, because part of the DNA is turned off
What are the molecules DNA is wrapped around?
Histones
How can DNA be turned off?
-Tying histones together keeps them inaccessible
-DNA methylation makes DNA inaccessible
DNA Methylation? Ex.?
Transfer of a methyl group to DNA
-When a woman has 3 X chromosomes, one of them is deactivated by a methyl group being added, and it becomes a Barr body
How is DNA made accessible?
By modifying the histones to be separated
Can DNA be unwound?
Only when it is accessible.
What happens when DNA is unwound?
RNA is made using DNA as a template
What is RNA
ribonucleic acid
-composed of nitrogenous bases Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine
There are many different kinds
Transcription
Process where DNA is copied into RNA
Translation
Process where RNA is used to create proteins
What types of RNA are involved during translation?
Ribosomal RNA- makes up much of the ribosome
Transport RNA- transports the amino acids to the ribosome
Messenger RNA- carries instructions for putting together chains of amino acids (proteins)
How many types of tRNA are there? Does tRNA have codons?
61
tRNA does not have codons like mRNA
-it has anticodons
Codons
Mrna is divided into units of 3 called codons
-codons code for a specific amino acid
What is the START codon? how many stop codons?
AUG for methionine is the start codon
There are three stop codons
How many amino acids only have one codon? What is the max number of codons amino acids have?
Two amino acids only have one codon.
The max number of codons amino acids have is 6
How is mRNA destroyed once it is no longer needed?
RNAi destroys RNA
-mRNA will continue to create polypeptides, but once a satisfactory amount is produced, it needs to be stopped or there can be consequences
Many proteins are only needed for a short time. How are proteins removed once they are no longer needed?
The protein is tagged with ubiquitin and taken apart
Genome
the complete set of genes present in a cell or organism
Mutation
Change in DNA sequence
Somatic mutation
Occurs after conception…therefore not passed onto children
Point Mutation
single base pair is added, deleted, or changed.
-ex: transition or transversion
Occurs at a single “point”
Transition
Point mutation where a purine is turned into another purine (A to G)
or a pyrimidine is turned into another pyrimidine (C to T)
Transversion
Point mutation purine is turned into a pyrimidine
ex: A turned to anything but G
-C turned to anything but T
Nonsense mutation
Point mutation that results in a nonsense codon (premature termination)
Silent mutation
Point mutation that does not change the amino acid, even though the codon has changed
Frameshift Mutation
The insertion or deletion of a nucleotide base
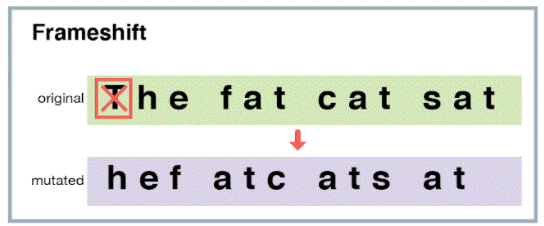
Missense mutation
Results in a different amino acid being encoded…may change the function of the protein
Deletion
Loss of one or more nucleotides…entirely removed instead of replaced
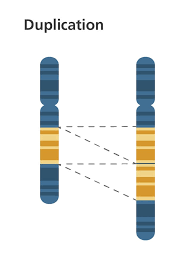
Duplication
DNA segment is copied…results in extra copies of chromosome
Inversion
When dna segment breaks away and reattaches in a reversed order
Translocation
DNA segment breaks off and attaches to another chromosome
Gene therapy
Treats or prevent disease by correcting the genetic issue
-viruses with a lysogenic cycle insert DNA
What is the issue with gene therapy?
modified viruses insert DNA, though sometimes the viruses interrupt other genes when inserting the DNA
How do you analyze DNA?
To do this DNA must be chopped into pieces with restriction enzymes
Gel electrophoresis
Process where DNA is separated and analyzed
How is DNA moved during Gel electrophoresis?
DNA is negatively charge, so when an electric current is applied to DNA it moves towards the positively charged electrode
STR
short tandem repeated DNA sequences
Who inherits STRs?
Males inherit STRs on the Y chromosome from their fathers
LAC operon
inactivates the repressor
TRP operon
activates repressor
Pharming
genetically modifying plants and animals so that they produce a desired substance to be used as pharmaceuticals
Offers promised for Parkinson’s disease
Stem Cell Research
Viruses with a ____ cycle destroy their host cell
Lytic cycle
HIV contains
Single stranded RNA that acts as a template for DNA synthesis
Glow in the dark kittens
GMOs
About ___% of DNA is composed of introns
5%
How are you going to do on this exam?
GREAT