LO5 ORAL PATHOLOGY
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Humoral Immunity
Which type of immunity is mediated by antibodies?
Impetigo
caused streptococcus pyogenes and staphylococcus aureus seen in young children, extremely infectious
Scarlet fever
occurs in children mostly, high fever with generalized red skin rash caused by a toxin released by the bacteria, petechia and strawberry tongue
Rheumatic fever
a childhood disease that follows a group A B-hemolytic streptococcal infection. a heart valve damage may occur requiring patient to be have premedication before DH treatment.
Tuberculosis
caused by the organism Mycobacterium tb, persistent caugh producing sputum and blood.
Actinomycosis
draining abscsses usually originating in the mandible; lumpy jaw
Syphilis
transmitted by sexual contact and direct contact (auto-inoculation)
mucous patches, oral lesions, grayish-white plaque
What are some signs of secondary stage of syphilis?
gumma: a firm mass, non infectious, destructive lesion that can result in perforation of the palatal bone.
What are some signs of tertiary stage of syphilis?
hutchinson’s incisors and mulberry molars
What are some dental abnormalities cause by congenital syphilis?
penicillin
treatment of syphilis
NUG Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
What is a painful, erythematous gingivitis with necrosis of interdental papillae associated with immunosuppression?
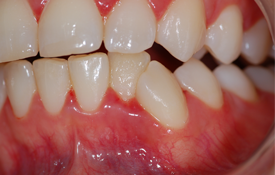

Pericoronitis
inflammation around the crown of a partially erupted, impacted tooth. mainly on a lower third molar. OPERCULUM (flap of skin)
Acute Osteomyelitis
commonly the result of a chronic periapical abscess. acute inflammation of the bone and bone marrow.
Chronic Osteomyelitis
a long standing inflammation of bone (painful and swollen); on rad eventually become opaque
Candida albicans fungal infection
What is often related for dentures improper care and immuno compromised?
Pseudomembranous Candidiasis
What is a white curdlike material on the mucosal surface and red underneath?
Denture Stomatitis (Chronic Atrophic Candidiasis)
What is the most common type of candidiasis?
Angular Cheilitis
erythema or fissuring at the labial commissures caused by candida or nutritional deficiency
Median Rhomboid Glossitis
an erythematous, often rhomboid-shaped, flat to raised area on the midline of the posterior dorsal tongue
Chronic Hyperplastic Candidiasis ( candidal leukoplakia)
a white lesion that does not wipe off the mucosa
deep fungal infections
oral lesions are chronic and non healing, primarily involve the lungs. clients should be assessed before aerosol generating procedures are used during debridement
Neoplasia
What is uncontrolled, abnormal growth of cells in the body (benign or malignant)?
human papilloma virus
What is a small DNA virus with an affinity toward squamous epithelium?
sexual interaction or auto inoculation
How can HPV be spread?
Verruca Vulgaris (Common Wart)
well-circumscribed, pedunculated or sessile, cauliflower-like appearance, finger like projections. colour from white to pink
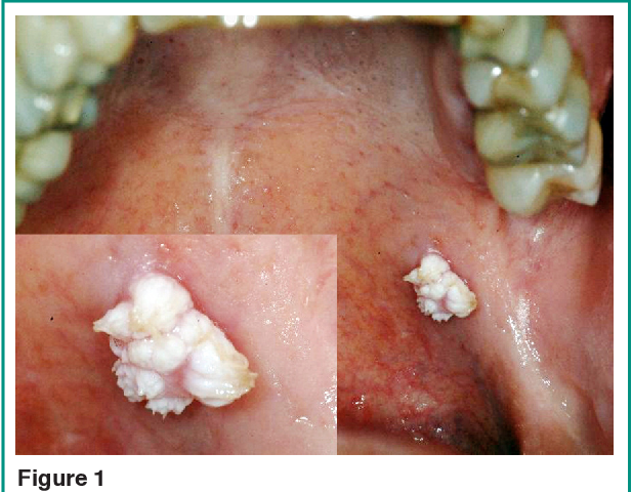

Condyloma Acuminatum
A benign papillary lesion caused by a papillomavirus, bulbous pink massess that can occur anywhere in the oral mucosa.


Multifocal Epithelial Hyperplasia (Heck Disease)
presence of multiple whitish to pale pink npdules distrubuted throughout the oral mucosa. most common in children
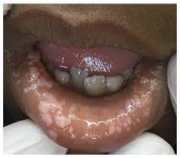

Primary herpetic gingivostomatitis
initial infection with herpes simple virus, painful tiny vesicles
recurrent herpes simplex infection
tends to persist in a latent state. affects the trigeminal nerve; herpes labialis
prodromal symptoms
pain, burning, or tingling sign that a lesion will soon appear
herpetic whitlow
a painful infection of the fingers caused by a primary or secondary infection
Varicella-Zoster Virus
what virus is responsible for causing chicken and shingles
secondary chickenpox in an adult
What is herpes zoster shingles?
mono epstein barr virus
What is known as “kissing disease”?
Hairy Leukoplakia
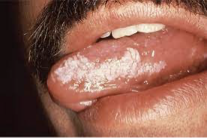
an irregular corrugated white lesion most commonly on the lateral border of the tongue.

herpangina
characterized by dysphagia and sore throat, resolves within a week
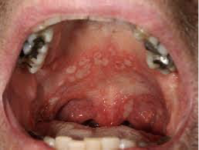

coxsackievirus infection
usually occurs in children, oral painful elsions resolves within 2 weeks
also called (hand foot and mouth disease)


measles
koplik spots( small red macules in the oral cavity with blueish colour) highly contagious
sexual contact, infected blood, breastmilk
how is HIV transmitted?
CD4 T-helper lymphocytes
which cells does HIV attacks or infects?
window of infectivity
antibodies may not be detectable for 6 months or up to a year or longer
Viral load
test such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are used to measure the amount of HIV circulating in serum
Oral candidiasis (thrush)
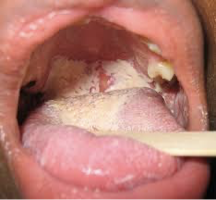
signals the beginning of progessively severe immunodeficiency

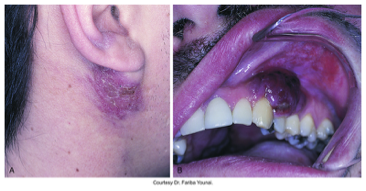
Kaposi Sarcoma
An opportunistic neoplasm that may occur in patients with HIV infection located on the palate and gingiva, dark purple lesion

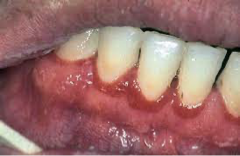
Linear Gingival Erythema

Necrotizing Periodontitis
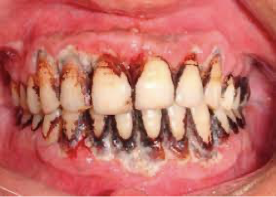
intense erythema and extremely rapid bone loss

Aphthous Ulcers
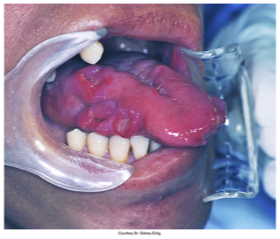
increase number of these in patients with HIV, deep persistent and painful. responds to STERIODS.

Salivary Gland Disease
bilateral parotid gland enlargement may occur in patients who are HIV+