Alternate Unit Cells
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flash Card for Lecture 3 of Solid State and Diffraction
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is a binary solid
A solid structure formed from just two constituents.
Name the 3 most common binary solids and state there coordination number
-Tetrahedral (4 coordinate)
-Octahedral (6 coordinate)
-Cubic (8 coordinate)
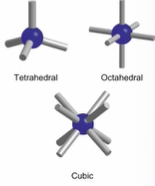
What does coordination number refer to
Refers too the number of atoms in contact with the atom in interest
What does coordination geometry refer to
Refers too the shape of the polyhedron formed by neighbouring atoms
Describe the Coordinate geometry of NaCl
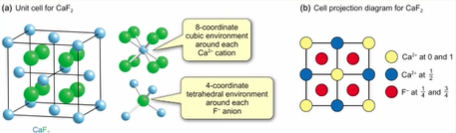
What do interstitial sites refer to
Refers to the empty spaces between atoms in a crystal lattice. Smaller atoms can occupy these spaces
For CCP arrangement what are the two interstitial sites we can have, describe the difference between the two.
For CCP arrangements we can either have octahedral (O) or tetrahedral (T) holes.
T sites are smaller than O sites, so which we find is likely to be dictated by the size of the second type of ion
What does a ternary solid refer to
Refers to solids that are formed by more than two substituents
For predicting structures what 3 assumptions must we make, and why
-Assume ions are hard spheres, allows us to ignore the electron cloud.
-Ions should be in contact with ions of the opposite, due to the fact they are experiencing electrostatic forces of attraction and ignores the fact these may be weak
-The most stable structure maximises the number of cation-anion contacts, this is because it’d mean its more electroneutral meaning more stable
How do we predict the structure of a solid using its ions.
Determine the radius ratio of ions :
positive ion / radius of negative ion
Then compare to a data set to get the structure.
Why is this method only predictive and not concrete
-This is only a general prediction and not a concrete rule due to the fact that in some ions there may also be significant covalent interactions which significantly affect the structure adopted. This occurs when the ionic character of the two ions are not particularly strong.