Physics Chapter 6: Gravitation
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The linear momentum and position vector of the planet is perpendicular to each other at:
(a) perihelion and aphelion
If the masses of the Earth and Sun suddenly double, the gravitational force between them will:
(c) increase 4 times
A planet moving along an elliptical orbit is closest to the Sun at distance r1 and farthest away at a distance of r2. If v1 and v2 are linear speeds at these points respectively. Then the ratio v1/v2 is
(a) r2/r1
The time period of a satellite orbiting Earth in a circular orbit is independent of
(b) The mass of the satellite
If the distance between the Earth and Sun were to be doubled from its present value, the number of days in a year would be:
(b) 1032
According to Kepler’s second law, the radial vector to a planet from the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. This law is a consequence of:
(a) conservation of linear momentum
The gravitational potential energy of the Moon with respect to Earth is:
(b) always negative
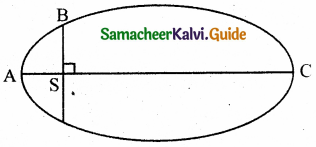
The kinetic energies of a planet in an elliptical orbit about the Sun, at positions A, B and C are KA, KB and Kc respectively. AC is the major axis and SB is perpendicular to AC at the position of the Sun S as shown in the figure.
(a) KA > KB > KC
The work done by the Sun’s gravitational force on the Earth is:
(c) can be positive or negative
If the mass and radius of the Earth are both doubled, then the acceleration due to gravity g’:
(b) g/2
The magnitude of the Sun’s gravitational field as experienced by Earth is:
(c) decreases in the month of July and increases in the month of January
If a person moves from Chennai to Trichy, his weight:
(b) decreases
An object of mass 10 kg is hanging on a spring scale which is attached to the roof of a lift. If the lift is in free fall, the reading in the spring scale is:
(b) zero
If the acceleration due to gravity becomes 4 times of original value, then escape speed:
(b) 2 times of original value
The kinetic energy of the satellite orbiting around the Earth is:
(b) less than potential energy
State Kepler’s three laws.
Law of Orbits: Each planet revolves moves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit with the Sun at one of the foci of the ellipse.
Law of area: The radial vector line joining the Sun to a planet sweeps equal areas in equal intervals of time.
Law of period: The square of the time period of revolution of a planet around the Sun in its elliptical orbit is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of the ellipse.
State Newton’s Universal law of gravitation
The gravitational force between two masses is directly proportional to the product of masses and inversely proportional to square of the distance between the masses.
Define the gravitational field. Give its unit.
The gravitational field intensity E→1 at a point is defined as the gravitational force experienced by unit mass at that point. It’s unit N kg-1.
What is meant by superposition of gravitational field?
The total gravitational field at a point due to all the masses is given by the vector sum of the gravitational field due to the individual masses.
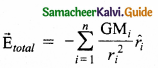
Define gravitational potential energy.
Potential energy of a body at a point in a gravitational field is the work done by an external agent in moving the body from infinity to that point.
Is potential energy the property of a single object? Justify
No, potential energy is not the property of a single system. It is due to the position of the object. Because, potential energy depends on two masses and the distance between them
Define gravitational potential.
The gravitational potential is defined as the amount of work required to bring unit mass from infinity to that point
What is meant by escape speed in the case of the Earth?
The escape speed is independent of the direction in which the object is thrown. Irrespective of whether the object is thrown vertically up, radially outwards or tangentially it requires the same initial speed to escape Earth’s gravity force. This can be written as, ve =√ 2gRE.
Why is the energy of a satellite (or any other planet) negative?
The negative sign of the total energy implies that satellite is bound to the Earth’s gravitational force. So it cannot escape from the Earth. At large distances satellite is not bound to Earth. It is completely free from gravitational force of the Earth.
What are geostationary and polar satellites?
Geostationary Satellite: It is the satellite which appears at a fixed position and at a definite height to an observer on earth.
Polar Satellite: It is the satellite which revolves in polar orbit around the earth
Define weight.
The weight is defined as the downward force whose magnitude ‘w ’ is equal to that of upward force that must be applied to the object to hold it at rest or at constant velocity relative to the Earth.
How will you prove that Earth itself is spinning?
When the position of a star is observed over a night, it appears to move in circular motion about the pole star. This fact proves that Earth itself is spinning.