Physics Mod 3 Waves & Thermo Dynamics
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Waves & Thermo Dynamics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What is a wave?
A disturbance that travels through a medium or space, transferring energy through matter or space
What causes a wave?
Created when a source of energy causes a vibration
Vibration is the up and down, back and forth motion
Examples of waves
Water
Light
Sound
Microwaves
Radio waves
X-rays
Ultraviolet (UV)
Seismic
Electromagnetic waves (EM)
Waves that DO NOT require a medium to transfer energy, travel at the speed of light in a vacuum!
E.g: Radio waves, Microwaves, infrared radiation, light, ultraviolet, X-rays, gamma rays
Mechanical waves
Waves that require a medium to transfer energy
E.g: Sound waves, Water waves, seismic waves
A medium
Something that a wave travels through, this could be solid, liquid or gas
In a sound wave, the medium is air
In an earthquake, the medium is the ground
Where light comes from
Comes from the sun, reflected off our eyes.
→If it can travel through a vacuum, it doesn’t need a medium
Transverse waves
The particles of the medium vibrate at 90 degrees or perpendicular to the direction that the wave is travelling
2 Groups of Transverse waves
Electromagnetic waves
Mechanical Waves
Longitudinal Wave
The particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction that the wave is travelling
All longitudinal waves are mechanical
Example: Slinky, Sound
Wave parts
Trough, Crest, Wavelength, Amplitude
Wavelength in Transverse
The distance between two identical consecutive points on a wave, such as crest-to-crest, trough-to-trough
Amplitude in Transverse
The max extent from the resting position of the medium to the crest or trough
Wavelength in Longitudinal
From one compression to another, or from one rarefaction to another
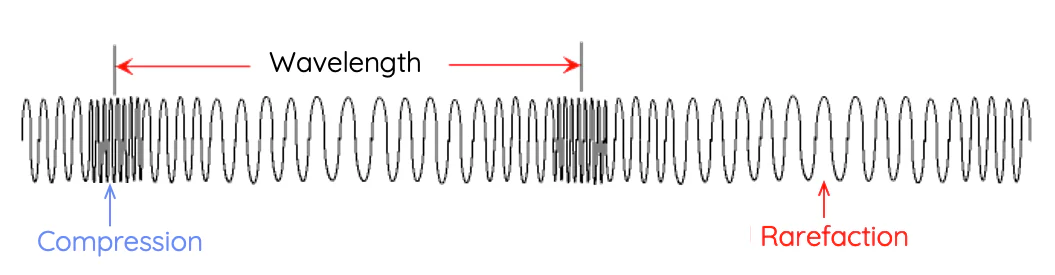
Compression
The space in a medium in which molecules are close together
Rarefaction
The space in a medium where molecules are more spead out
Amplitude in Longitudinal
The biggest move from one molecule to another
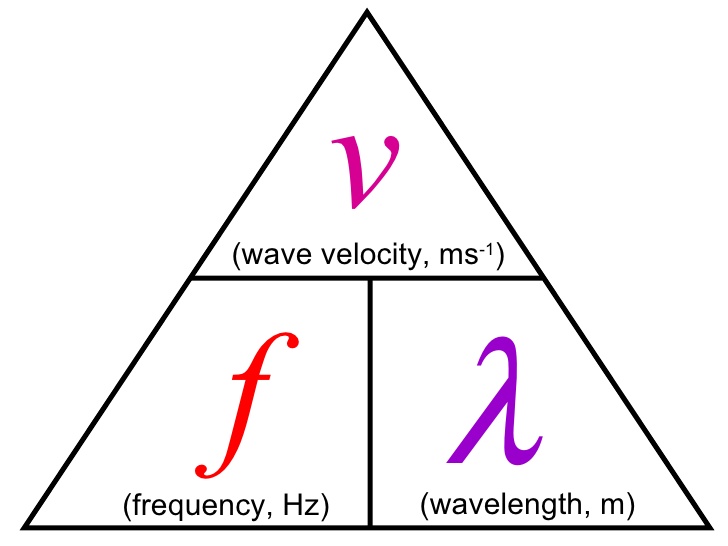
Frequency
The number of waves that pass a given point in 1 second, measured in Hertz
Wave number and its equation
The number of wavelengths per unit distance.
k = 2 π / λ
where
K: wavenumber
λ: wavelength (m)
Seismic waves
Caused by the sudden movements of materials within the earth, such as an earthquake
tsunami
a series of ocean waves with very long wavelengths, caused by large scale distrubances of the ocean
Period
Time per wavelength (in seconds)
Relationship between frequency and period
Indirect relationship
Frequency increases, period decreases
Frequency decreases, period increases
Equation for frequency
frequency = velocity / wavelength
Why do mirrors show reflections?
All objects which can be seen either
→Produce their own light (candles, lightbulb)
→ Reflect light (moon, table, you)
A mirror is smooth & shiny, it reflects light rays in one direction
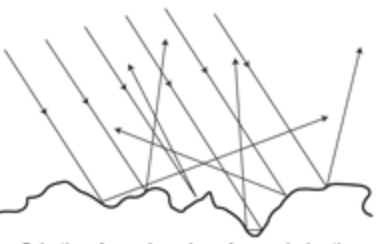
Diffuse scattering
When a surface looks smooth, but in detail it is rough and reflects light rays in all directions.
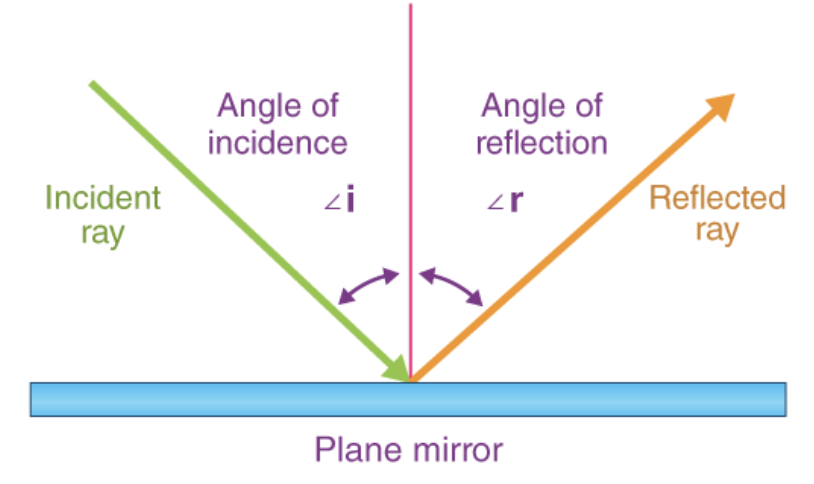
Law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
2 types of curved mirrors
Convex and Concave
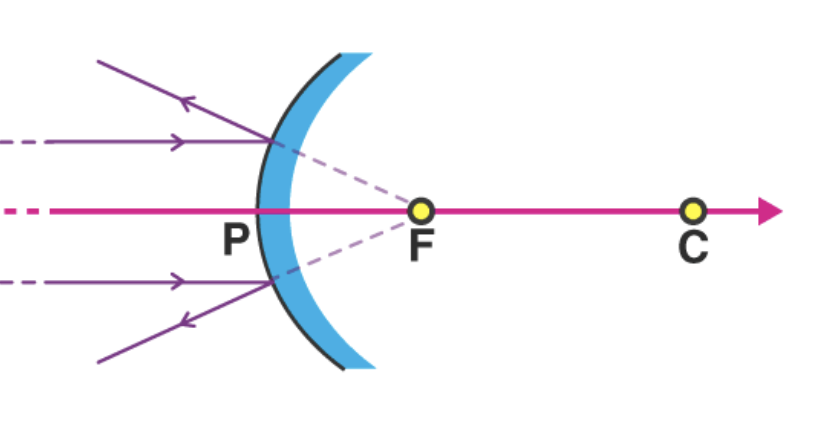
Convex mirror
Bend outwards and are dome-shaped, obeys the law of reflection and forms an image smaller than the object
→ produces a virtual image
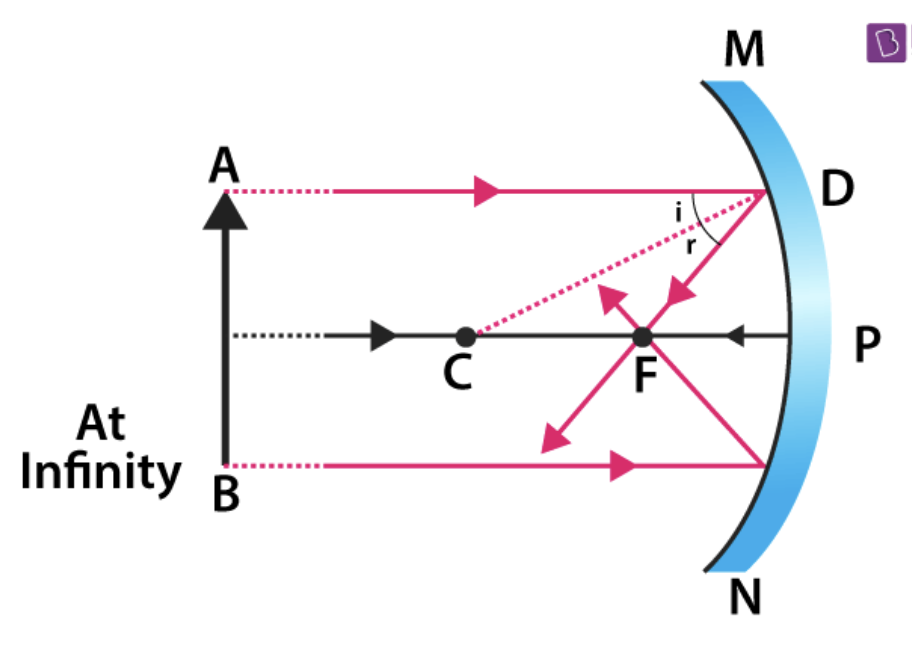
Concave mirror
Bend inward and are bowl-shaped, obeys the law of reflection and produces a reflected image larger than the object (magnifies)
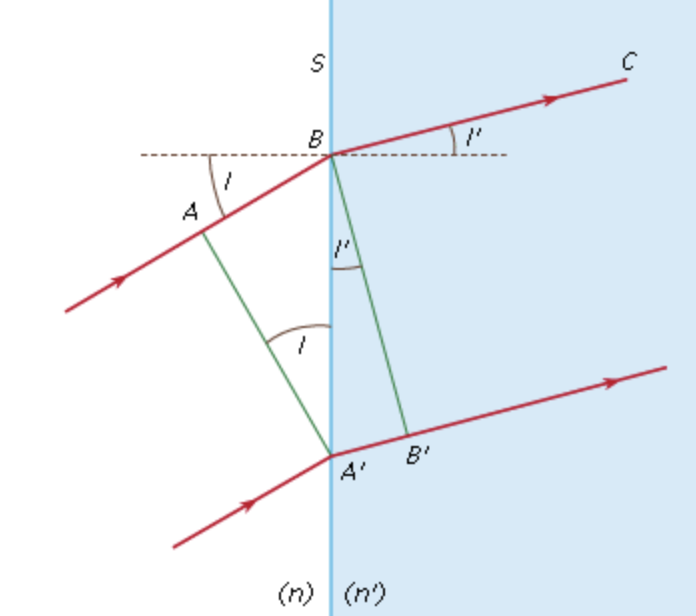
Refraction
the bending and changing of speed. For example, light beams bend when it transitions from one medium to another (glass, water, air)
Law of Refraction (aka Snell’s law)
Formula: n₁ sin(θ₁) = n₂ sin(θ₂)
When beam first strikes prism → ray bends towards the normal
When beam exits the prism → ray bends away from the normal
Diffraction definition
The spreading out of waves as they pass through a gap
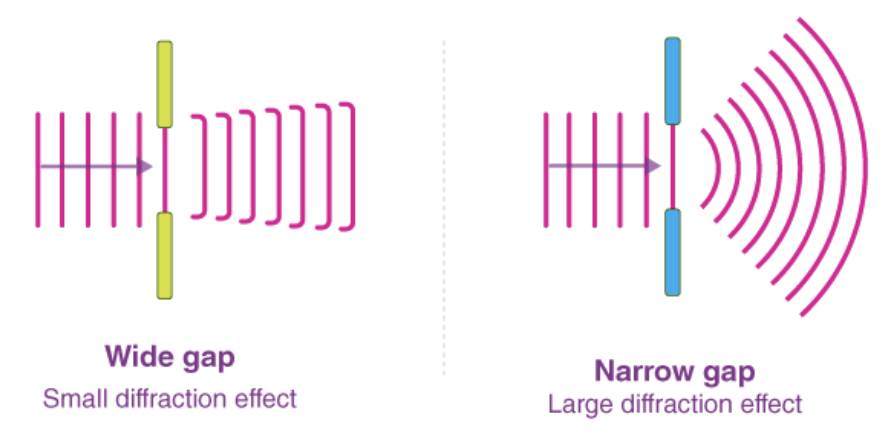
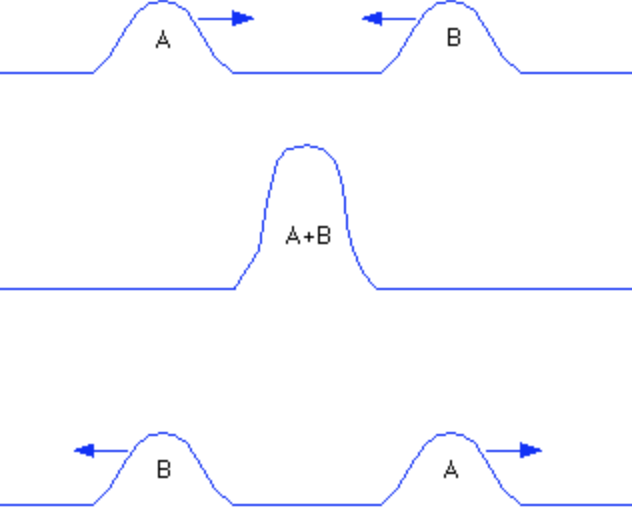
Superposition - constructive interference
When 2 crests/troughs collide, this creates a super crest or super trough, meaning the slinky will double the height
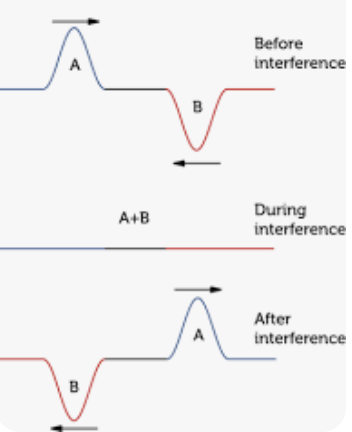
Destructive interference
When a crest and trough with equal size collide, they produce a cancellation
Factors affecting a harmonic
Mass of object, tension
Types of harmonics
1st harmonic (fundamental frequency), 2nd harmonic (first overtone), 3rd harmonic (second overtone)
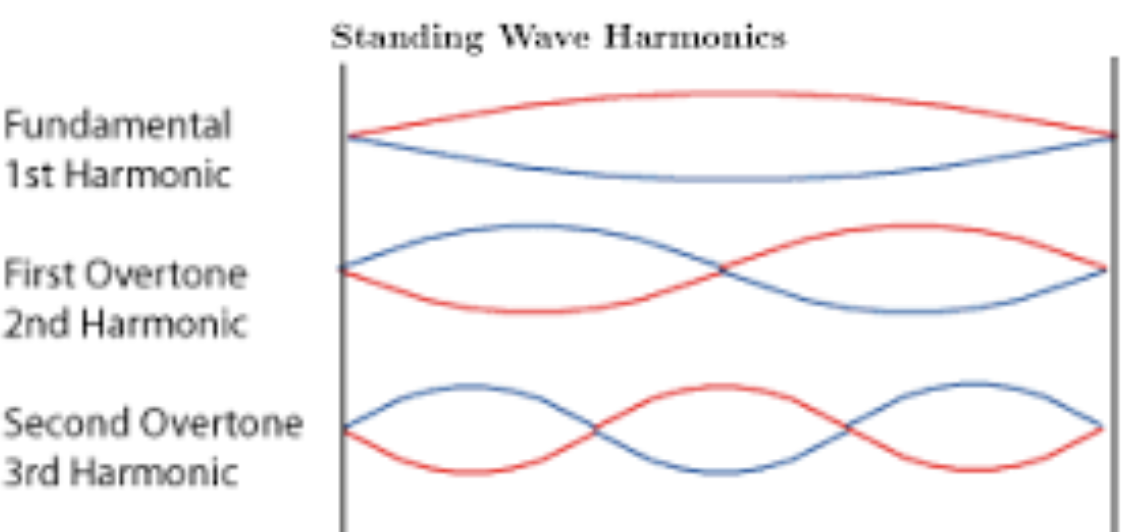
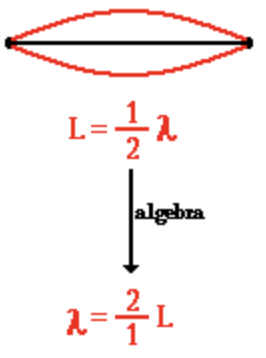
1st Harmonic
2 nodes, 1 antinode, ½ wavelength
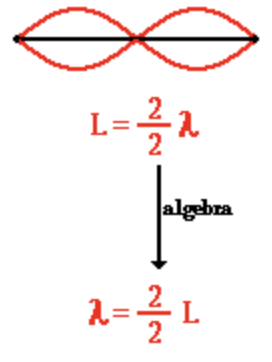
2nd Harmonic
3 nodes, 2 antinodes, 1 wavelength
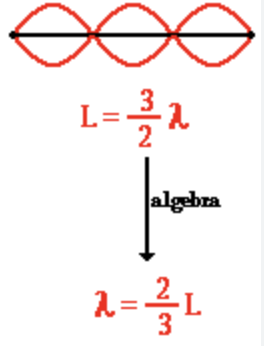
3rd Harmonic
4 nodes, 3 antinodes, 1.5 wavelength
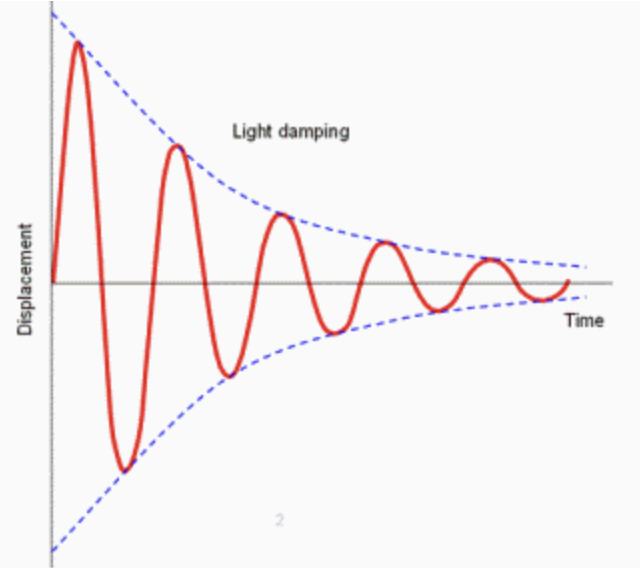
Damping
A reduction in the amplitude of a wave as a result of energy absorption or destructive interference. For example, a child’s swing will eventually come to rest due to friction and air resistance→ the swing’s motion has been dampened.
Resonance
The tendency for one vibrating object to start another object vibrating if its frequency is close to the second object’s natural frequency (all objects have a natural frequency).
For example: singing at a very high pitch to break a glass
What happens when a building with a natural frequency of 0.02 Hz is disturbed
It would sway back and forth at 0.02 Hz
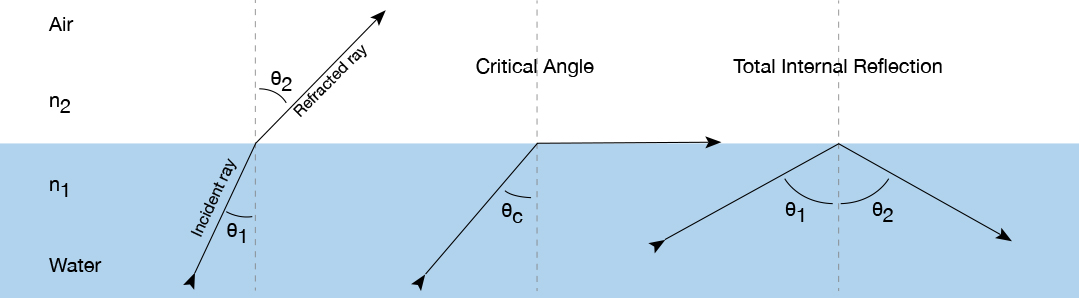
Critical angle
When the angle of refraction is 90°. The light must travel from a denser medium to a less dense medium. At this point onwards, any further increase in the angle of incidence will cause total internal reflection.
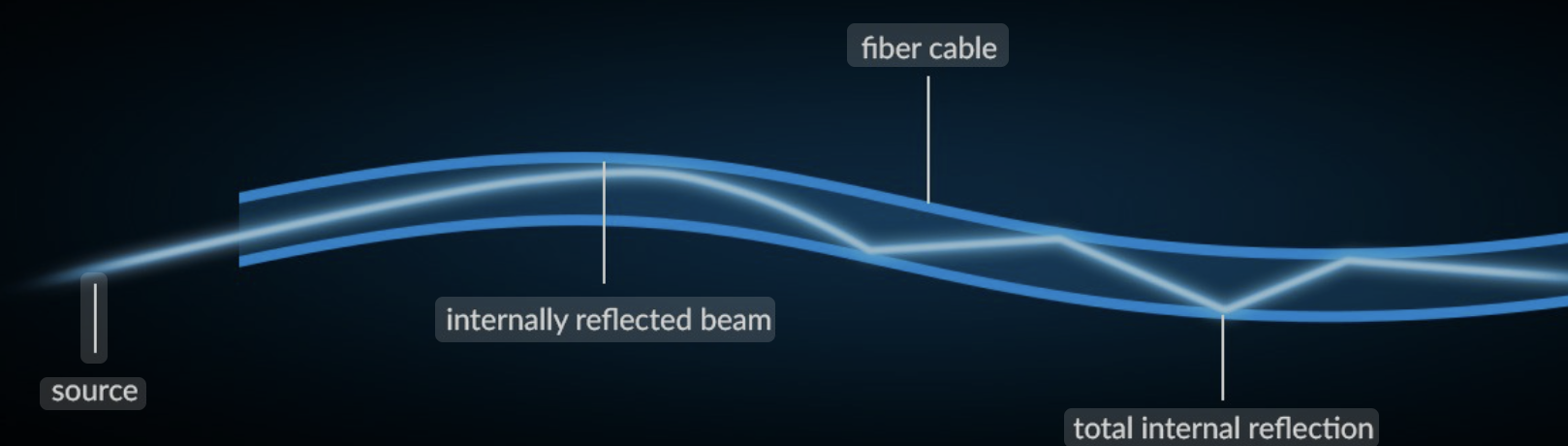
How do optical fibres work?
By trapping light within a plastic core, using the principle of total internal reflection
Total internal reflection
The light ray is reflected back into the denser medium, occurs when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
Dispersion of light
A phenomenon where white light splits into different colours, because white light is made up of multiple colors, each colour has a different wavelength.
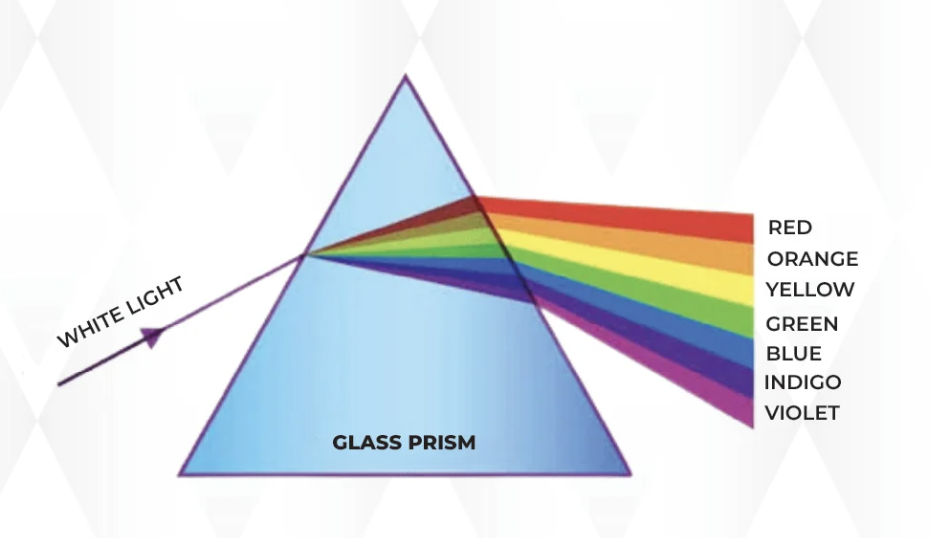
7 colours in the dispersion of light
red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, violet
Inverse Square Law definition
As the distance from the source doubles, the brightness of the field goes down by a quarter
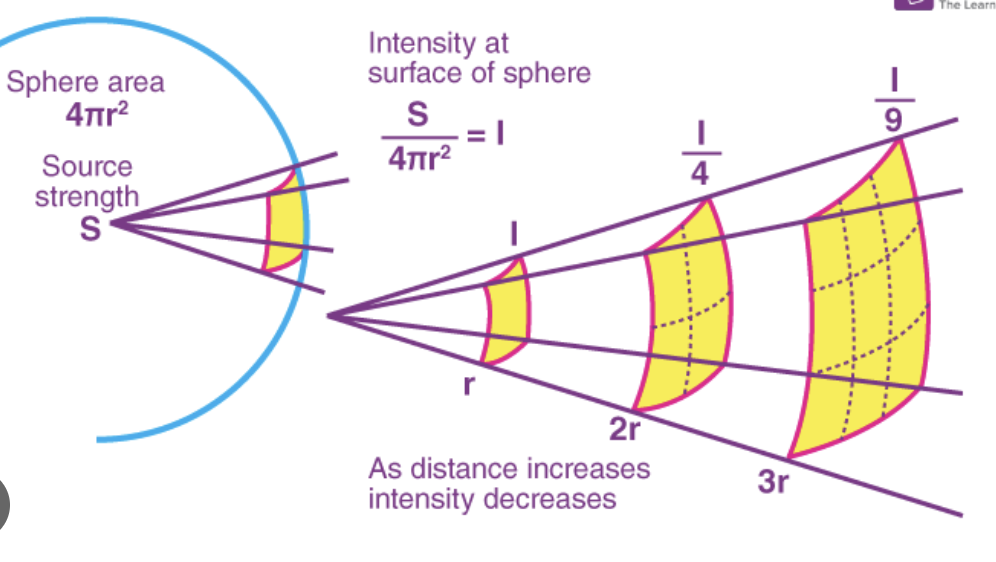
Inverse square law formula
Intensity is proportional to 1/r²
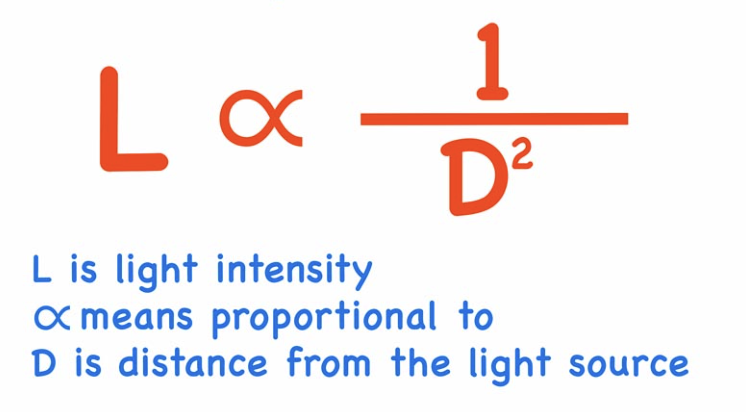
Things that follow the inverse square law
gravitational fields
electrical fields
light intensity
sound intensity
Thermal energy(aka heat energy) vs Temperature
Temperature measures the average kinetic energy of each particle in a substance, indicating how hot or cold it is, while thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of all particles in the substance, representing the sum of their energies.
A hot bath: high thermal energy, low temperature
A sparkle: low thermal energy, high temperature (1500 degrees Celsius)
What is Thermodynamics?
A study of relationships involving heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and energy transfer
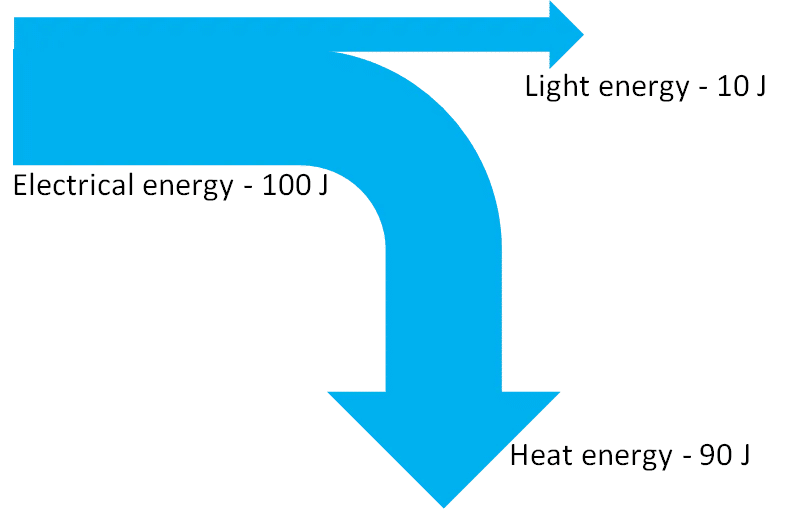
1st Law of thermodynamics
Law of conservation of energy: energy cannot be created nor destroyed
2nd Law of thermodynamics
There is a limit to the availability of energy.
no such thing as 100% efficient
follows the concept of entropy (Entropy = energy degradation)
3rd Law of thermodynamics
States that it's impossible to reach absolute zero (0 Kelvin)
0th Law of thermodynamics (4th law)
Thermal Equilibrium.
For example, under the ocean, fish, sand, and corals are the same temperature
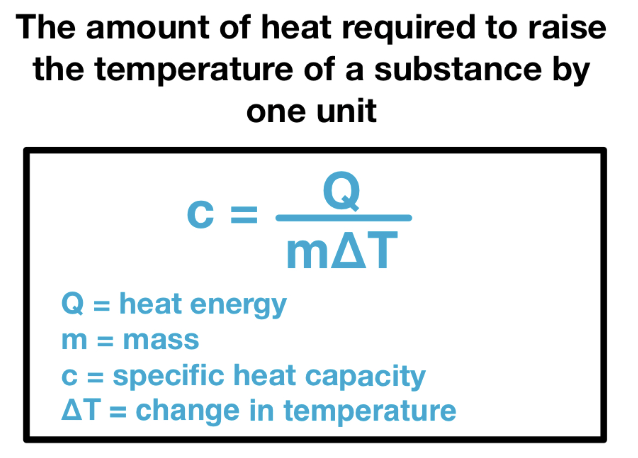
Specific Heat Capacity
The amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by one unit. That’s why we need to heat water twice the amount of time to get the same temperature as a pot of oil that’s been heating for 1 minute.