Experiment 1: Isolation, Cloning and Transformation of Plasmid DNA
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Isolation, Cloning and Transformation of Plasmid DNA Overall Purpose of the Experiment
To transform a strain of E.coli DH5-alpha to be resistant to both ampicillin and kanamycin by creating a recombinat pUC18 plasmid by restriction digestion and cloning
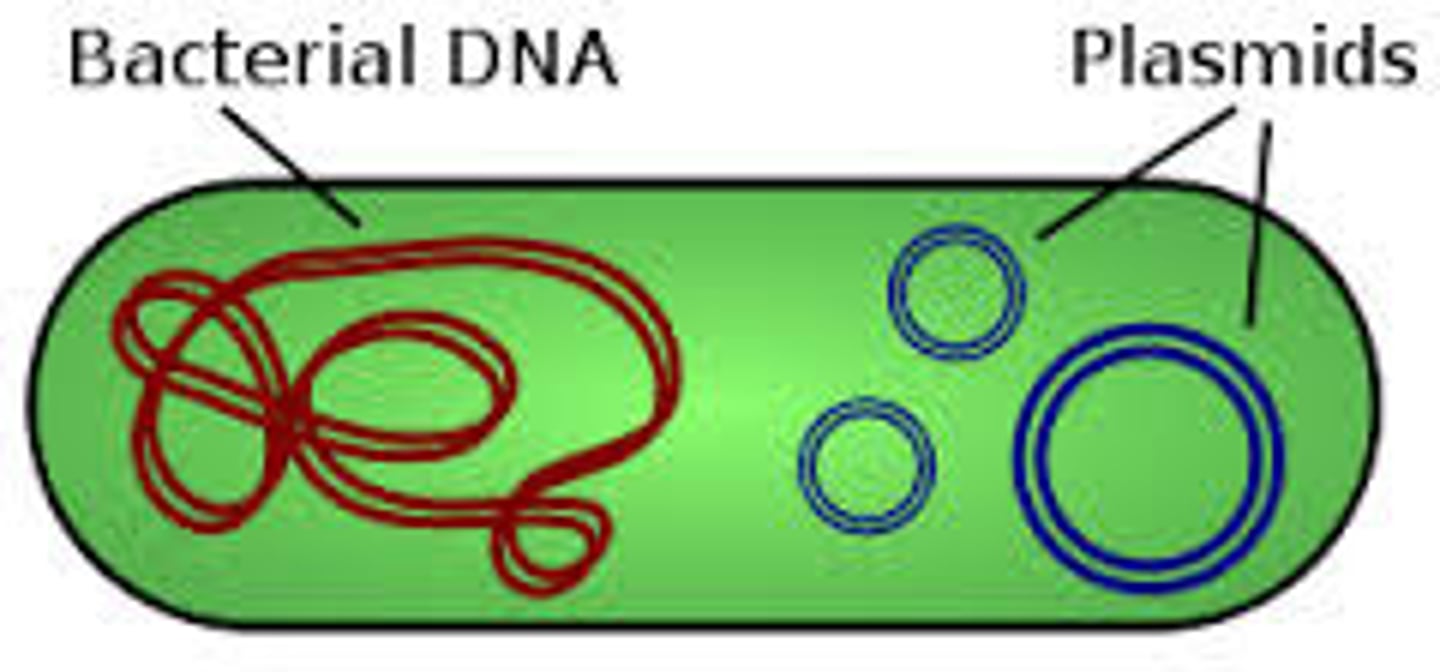
Plasmid
An autonomous, self replication, extra-chromosomal DNA molecule
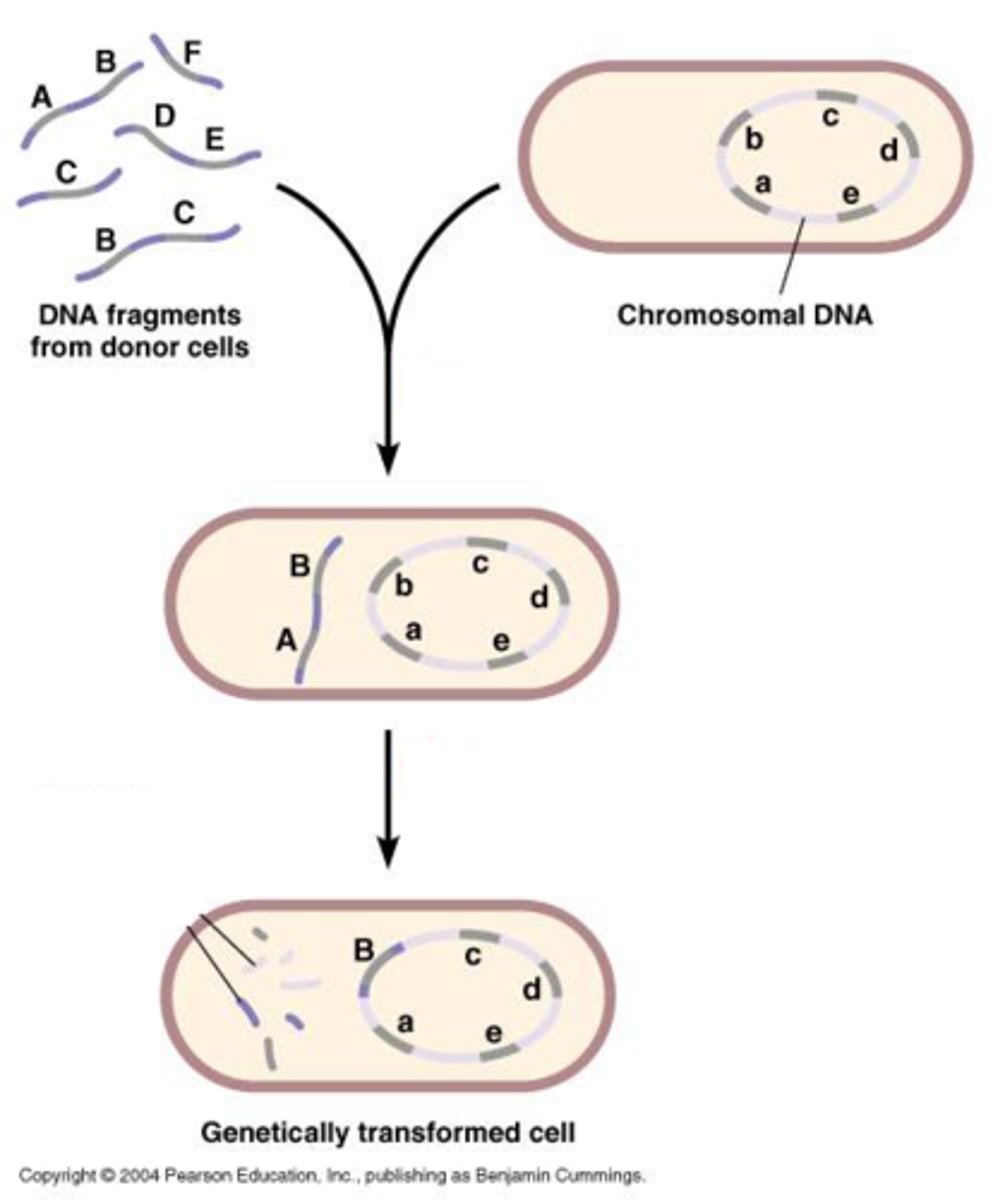
Cloning
Incorporating a DNA molecule into a chromosomal site or a cloning vector
Clone
A population of cells that carry a cloning vehicle with the same DNA insert
Transformation
The uptake of extra chromosomal DNA in a bacterium or yeast in which the DNA often changes the phenotype of the recipient organism
Competent cells
Cells which have been treated by chemical or physical means in order to be sensitive to foreign DNA
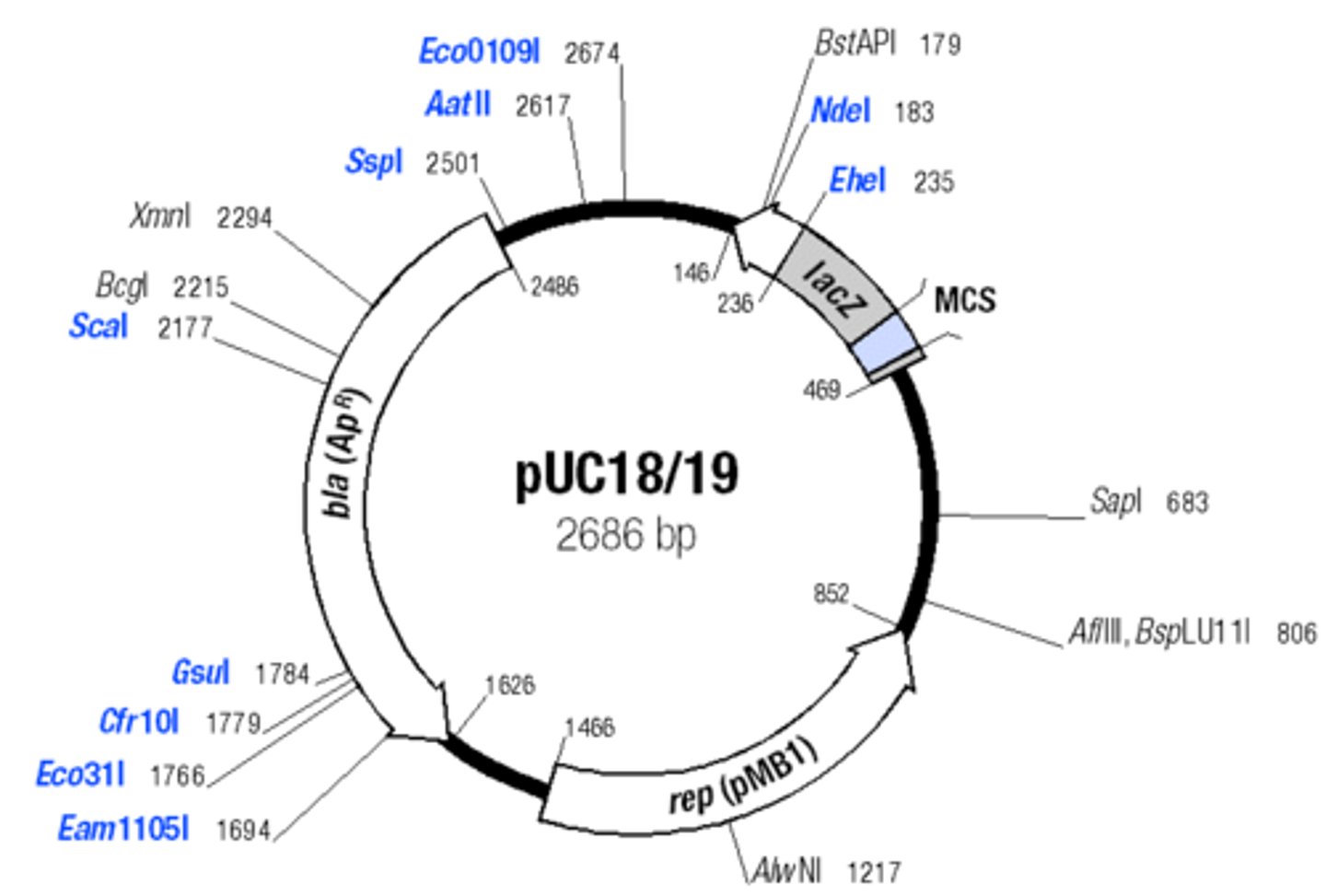
pUC18 plasmid
Contains ampicillin resistance gene, origin of DNA replication, portion of the lacZ gene ligated to the gene, and MCS
pKAN plasmid
Contains kanamycin resistance gene
Blue selection technique
Cells are able to make beta-galactosidase and produce blue colonies on plates containing the substrate, X-gal
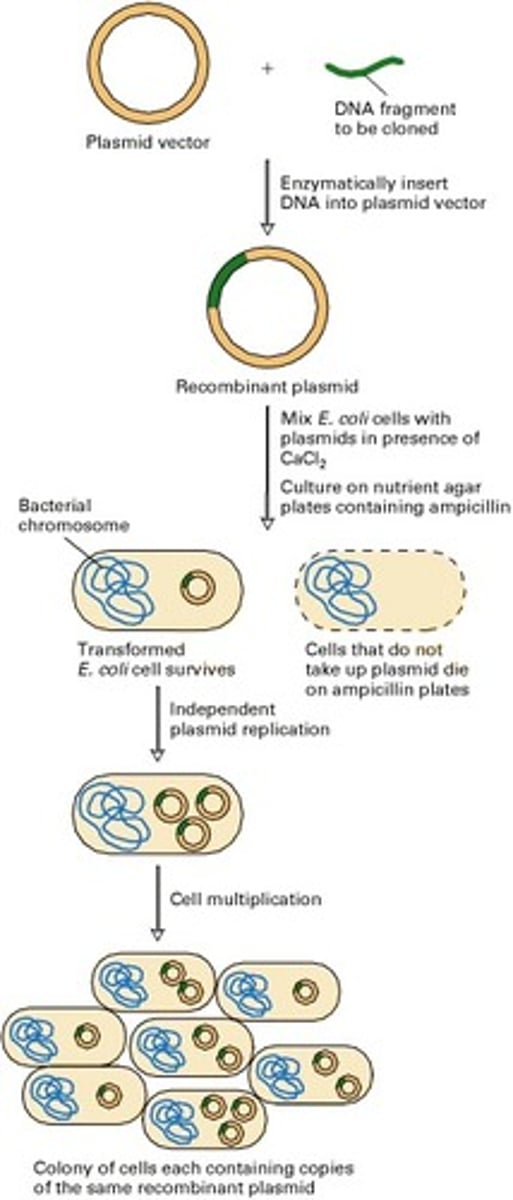
White selection technique
Appearance of white colonies on the X-gal plates indicative of the presence of the kanamycin gene inserted into the pUC18 vector
What is the molecular weight of pKan plasmid
4194 bp
What is the molecular weight of the pUC18 plasmid and how many plasmid will appear on the gel image?
2,686 bp, and 2 bands will appear on the gel image
Supercoiled
Occurs when extra twists are introduced into double helix strand. Migrates faster than predicted
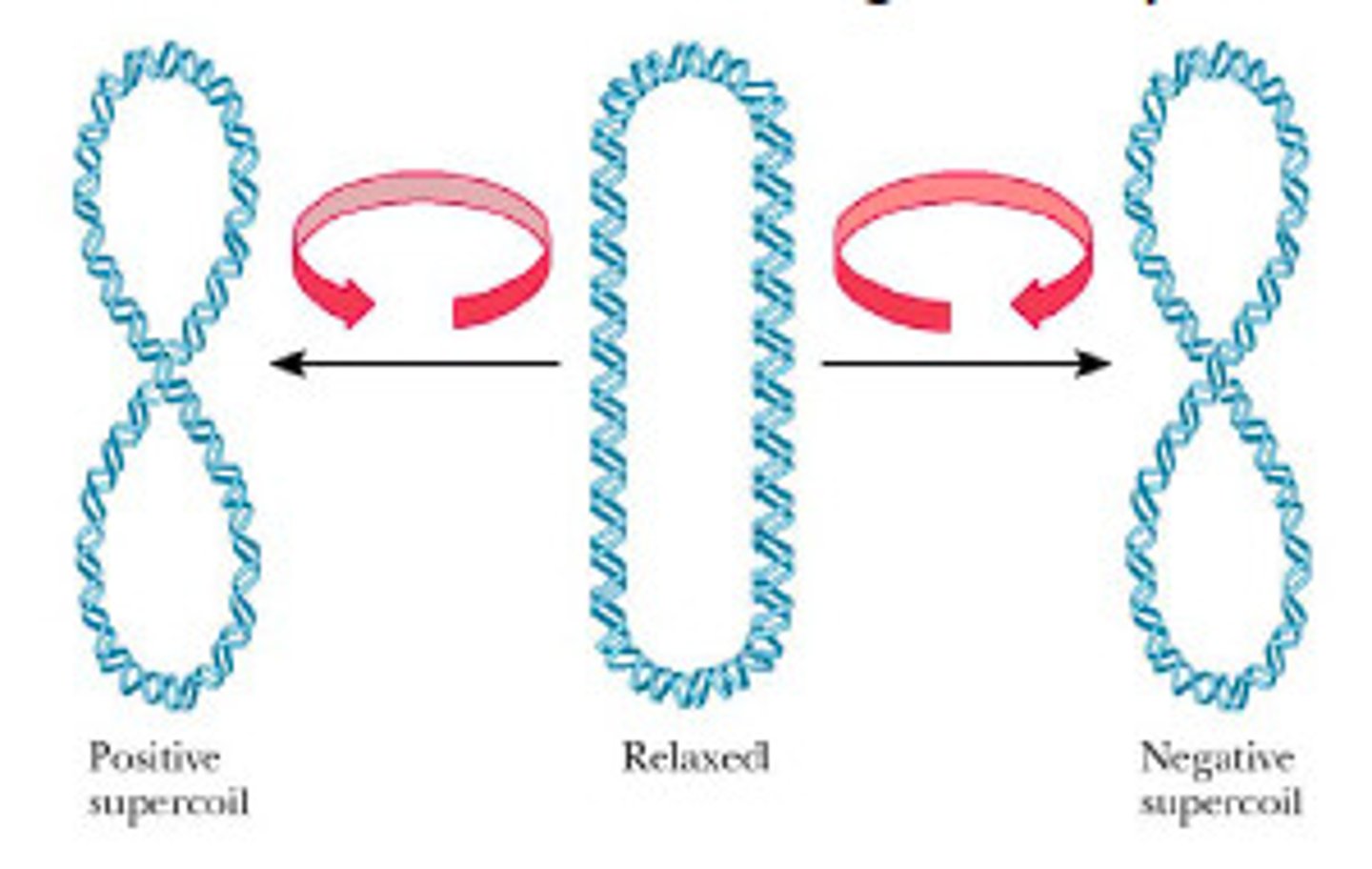
Nicked, Relaxed Circular Plasmid
Cellular topisomerases nick one strand of the DNA helix and relaxes the superhelical tension. Migrated the slowest in the gel
Linear Plasmid
DNA helix is cut in both strands at the same place
Circular, single stranded plasmid
DNA is permanently denatured resulting in single stranded closed circles
Restriction endonuclease digestion of pUC18 and pKAN
Open up the MCS in pUC18 using restriction enzymes that a fragment from pKAN (containing the kanamycin resistance gene) is inserted into the MCS
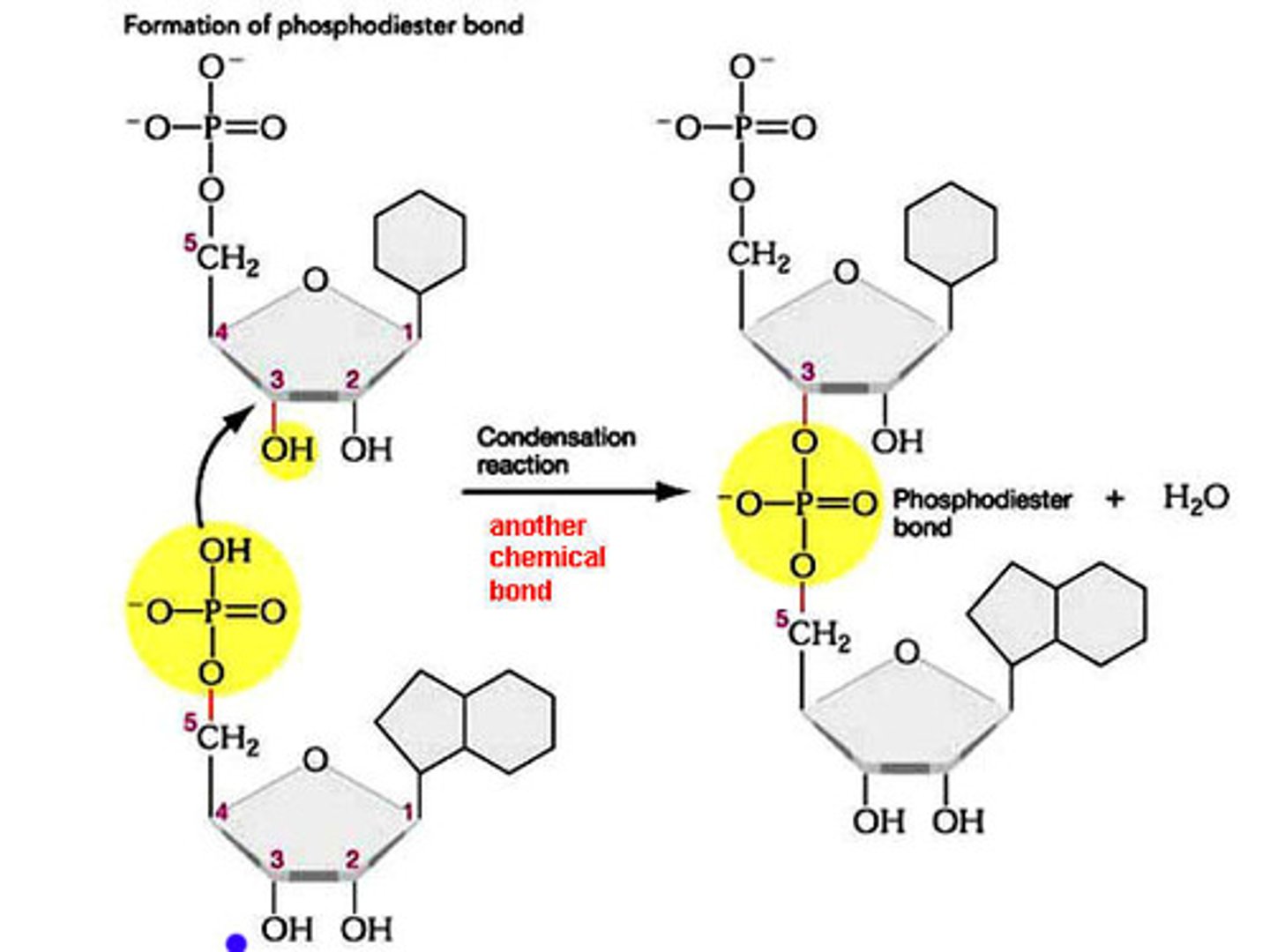
Ligation reaction
Ligases use ATP to link the 5' end of one DNA strand to the OH group on the 3' strand---> phosphodiester bond
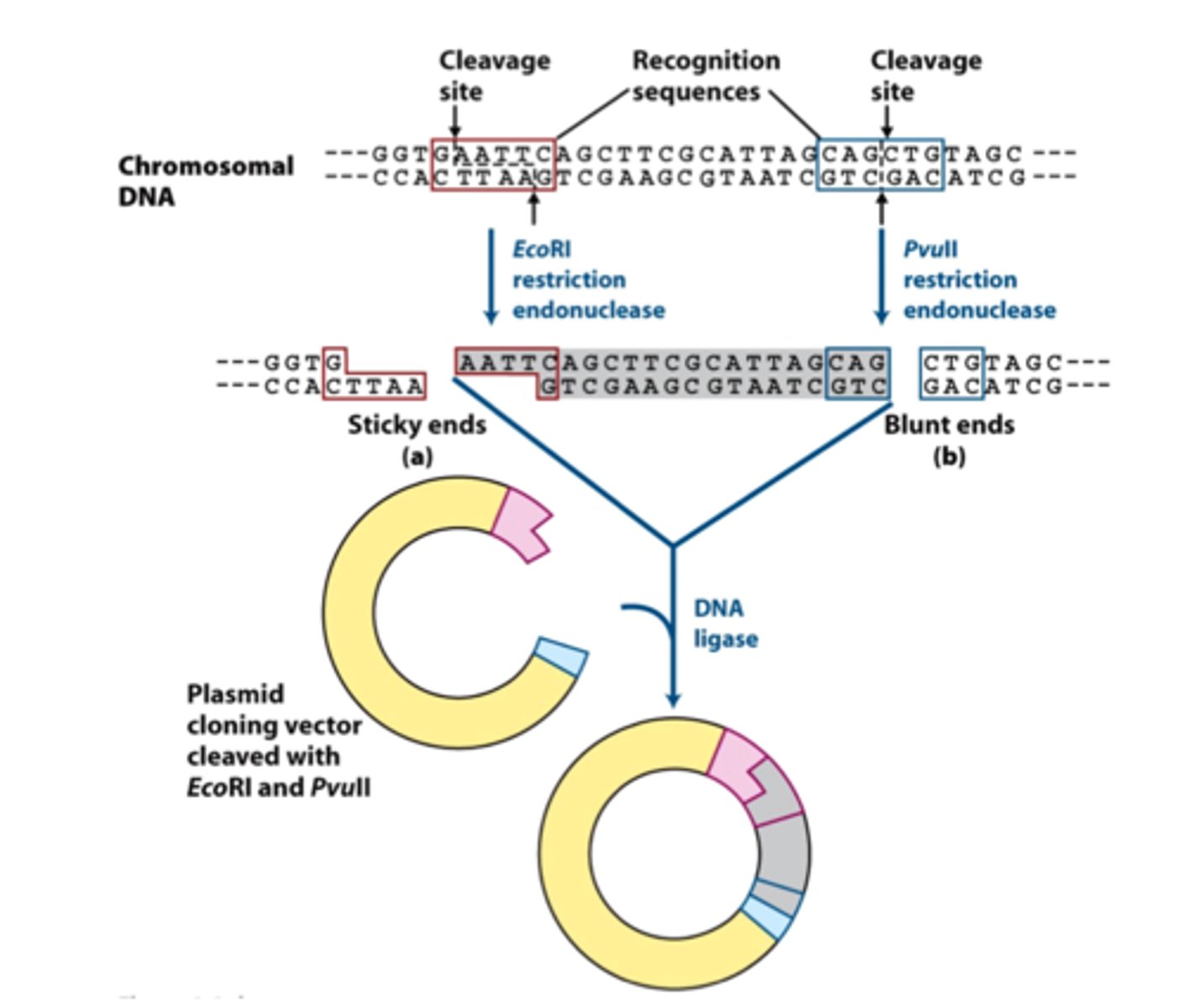
Restriction endonucleases
- Palindrome sequence
- Creates sticky ends or blunt ends
- 3-letter designation nomenclature system (E.g., EcoRI, HindIII)
puC18 plasmid characteristics
1) the pMB1 replicon rep
2 ) bla gene
3) lac operon
Direct screening method
Plating on Lb/amp/kan plates and selecting for the presence of kanamycin gene
Indirect screen method
Plating on the amp/X-gal plates to detect the presence of kanamycin gene inserts and then plated onto plates containing the kanamycin gene.
LB broth
Nutriontially rich medium used to grow a variety of bacteria in the laboratory

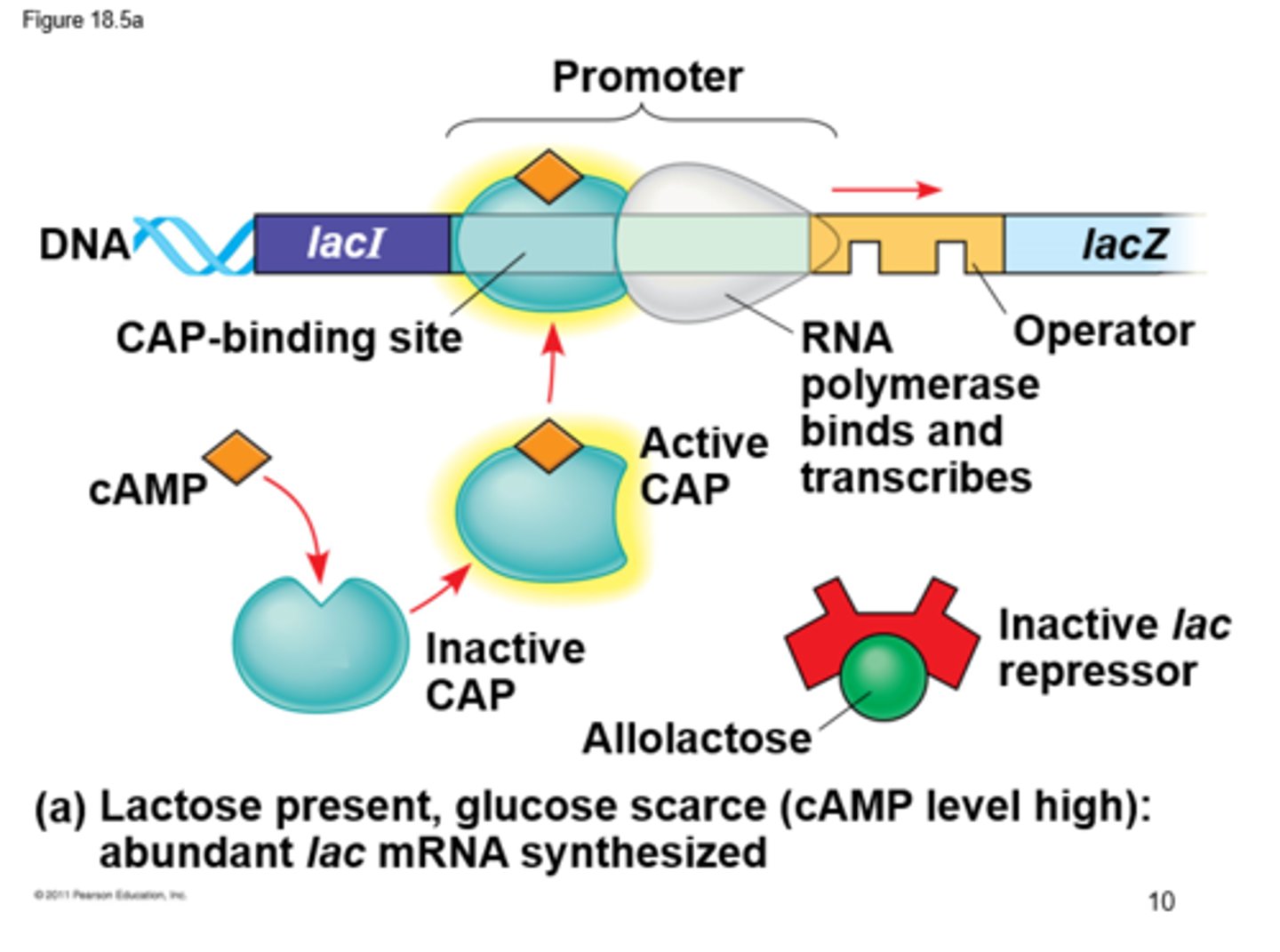
operon
structural genes,together with promoter and operator or activator-binding sires
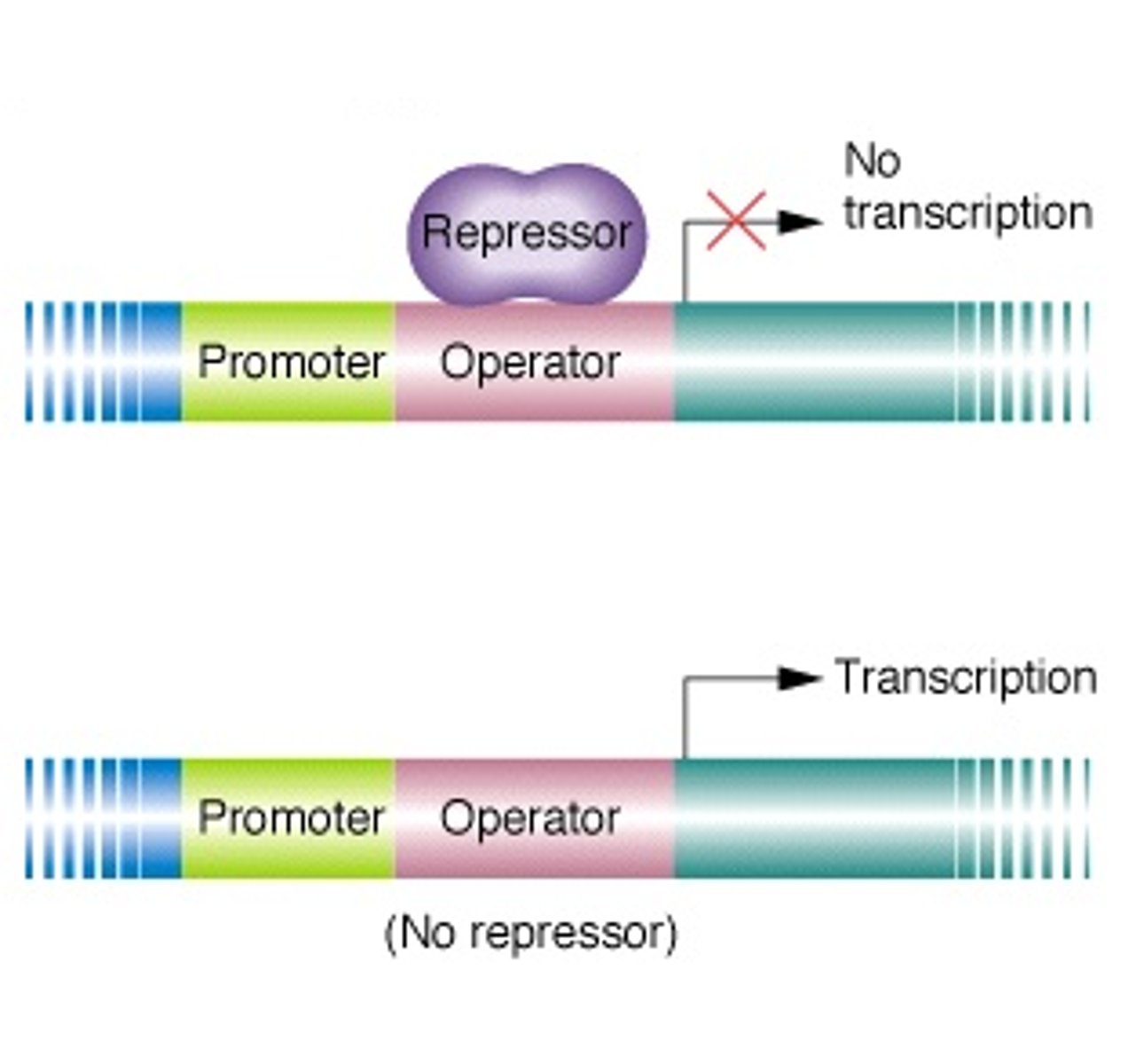
Promoter
A region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene
Repressor
That inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator
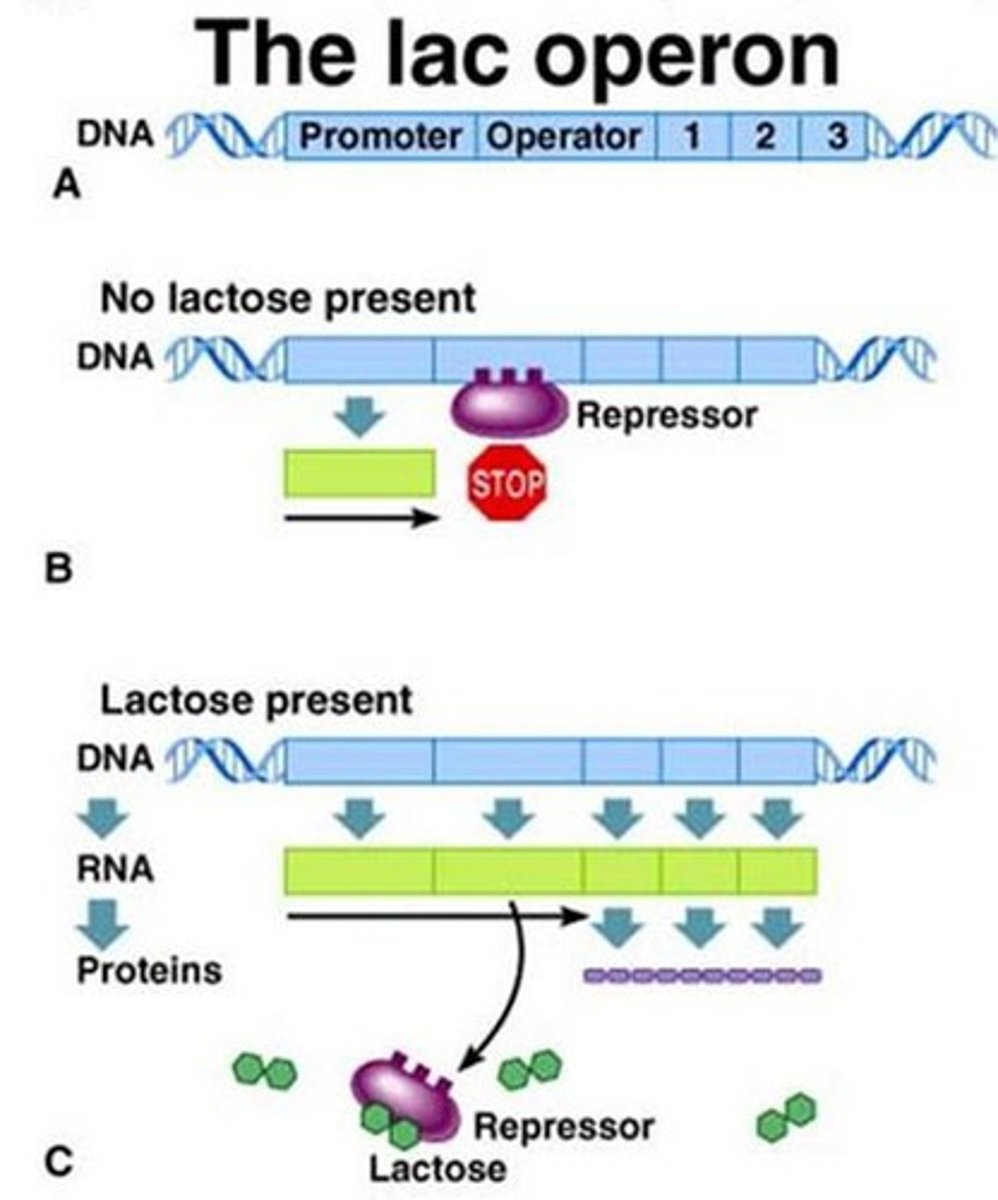
lac Z
Encodes beta-galactosidase, which converts lactose to allolactose (inducer of the the operon)
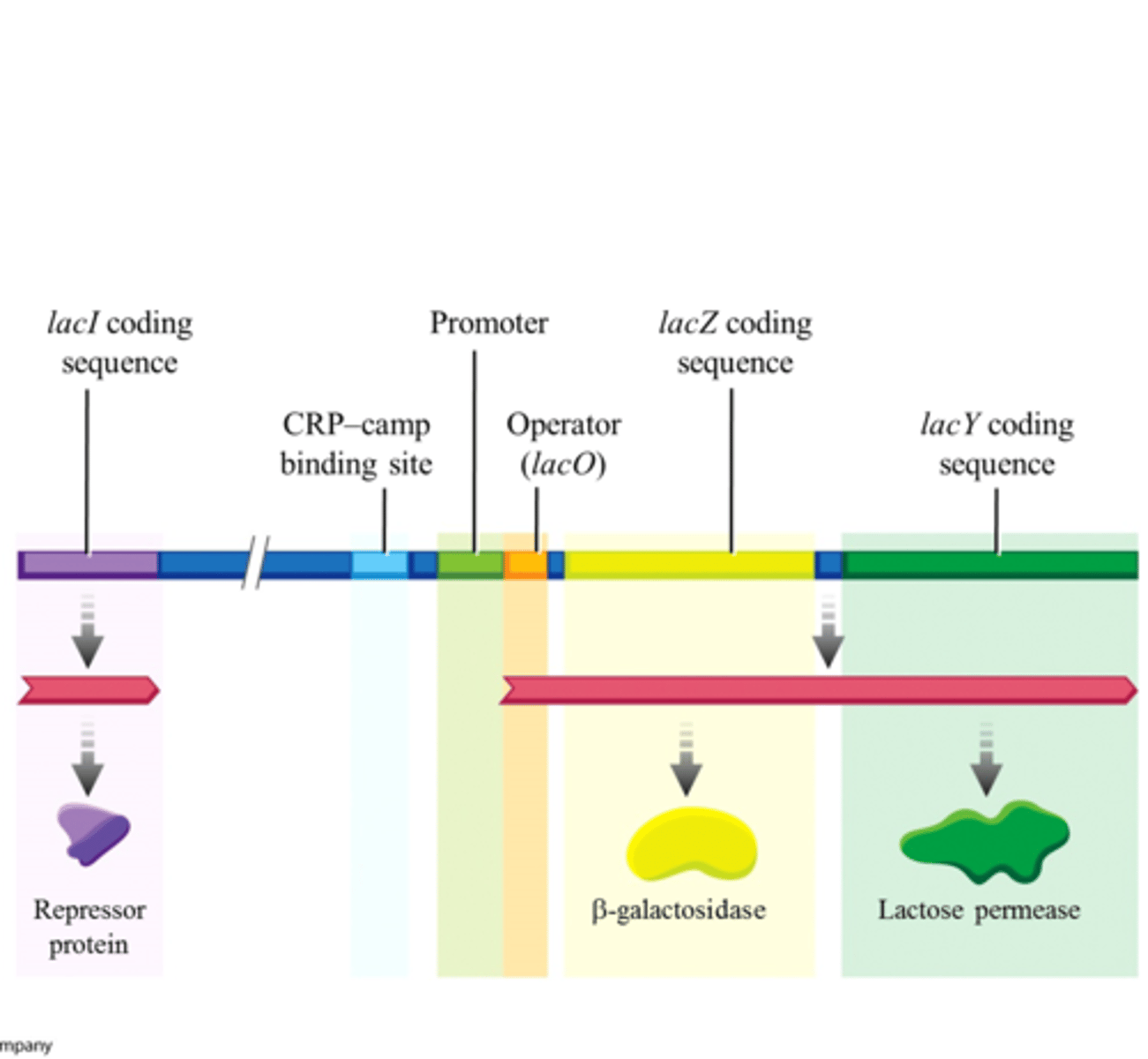
CAP (catabolite activator protein)
transcription activator