Dysphagia Rem
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
One of your patients complains about coughing while not eating. What is the possible associated sign?
Aspiration of saliva
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following conditions is considered a red flag during the evaluation of the gag reflex?
-The asymmetry of velum elevation
- Having hyper or hypoactive gag response
- The course of gag reflex function before and after the disease
- Both a and c
Both a and c
All of the following statements are correct regarding the Mann Assessment of Swallowing Ability (MASA) test, EXCEPT
It was developed to clinically assess patients' functional eating skills in a natural environment
A patient eats a regular diet but cuts all solid foods into small pieces and uses water to wash them through the throat. What is the FOIS score for this patient?
5_Total oral intake of multiple consistencies requiring special preparation
A patient receives most of his daily foods through the PEG tube but sometimes eats a few spoons of thickened materials.
What is the FOIS score for this patient?
2_Tube dependent with minimal/inconsistent oral intake
All the following are among standardized swallowing tests EXCEPT
Cervical Auscultation
The 2nd low-frequency burst in cervical auscultation during swallowing indicates
the bolus entering the esophagus
Which of these choices are among the rationales for conducting a clinical evaluation?
Defining potential cause
Establishing a working hypothesis for the swallowing disorder
Establishing a tentative treatment plan
Establishing readiness of patient to cooperate with further testing (and treatment)
All of the above
All of the above
A clinical swallow evaluation includes all of the following EXCEPT
Obtaining medical history
Inspecting the physical swallowing musculature
Conducting Imaging studies
Observing swallowing competence with test swallows
Conducting Imaging studies
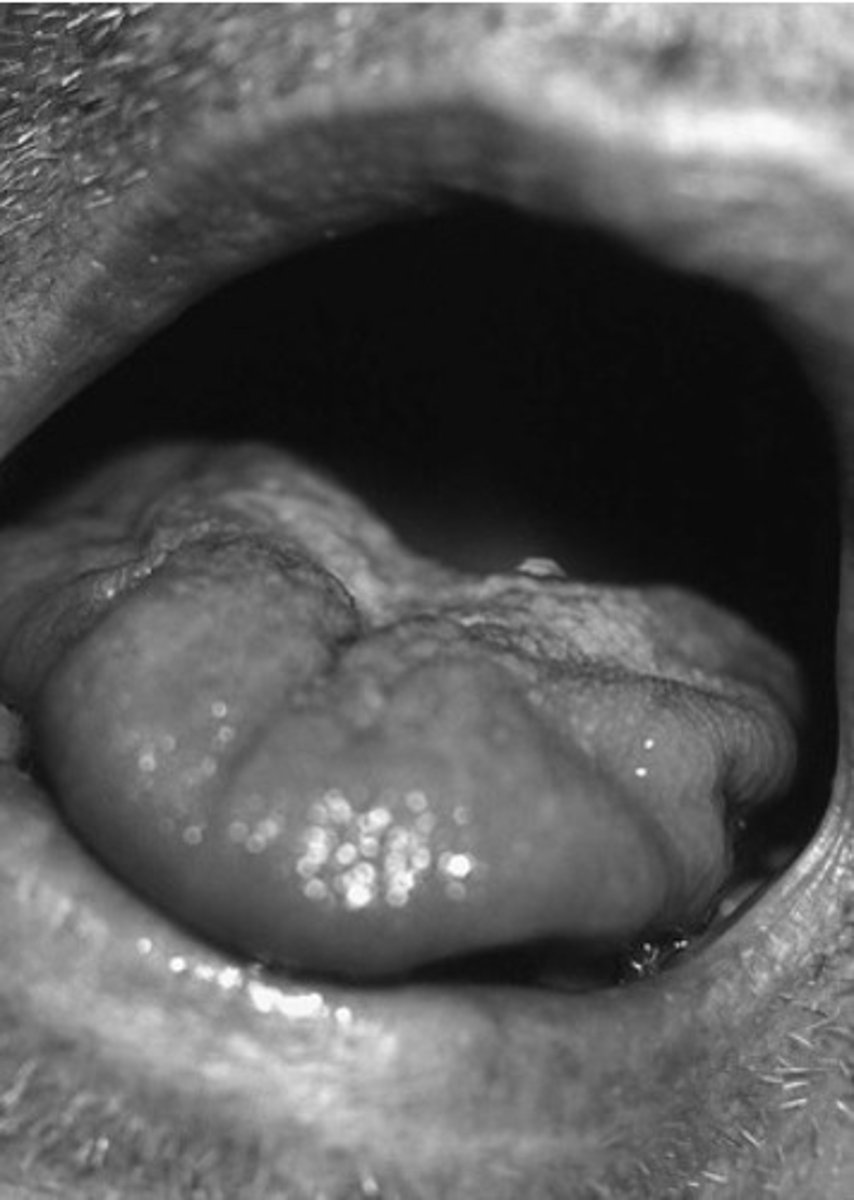
James has neurogenic dysphagia. During your cranial nerve exam, you ask him to open his mouth. What does this picture tell you about his tongue condition?
Tongue atrophy
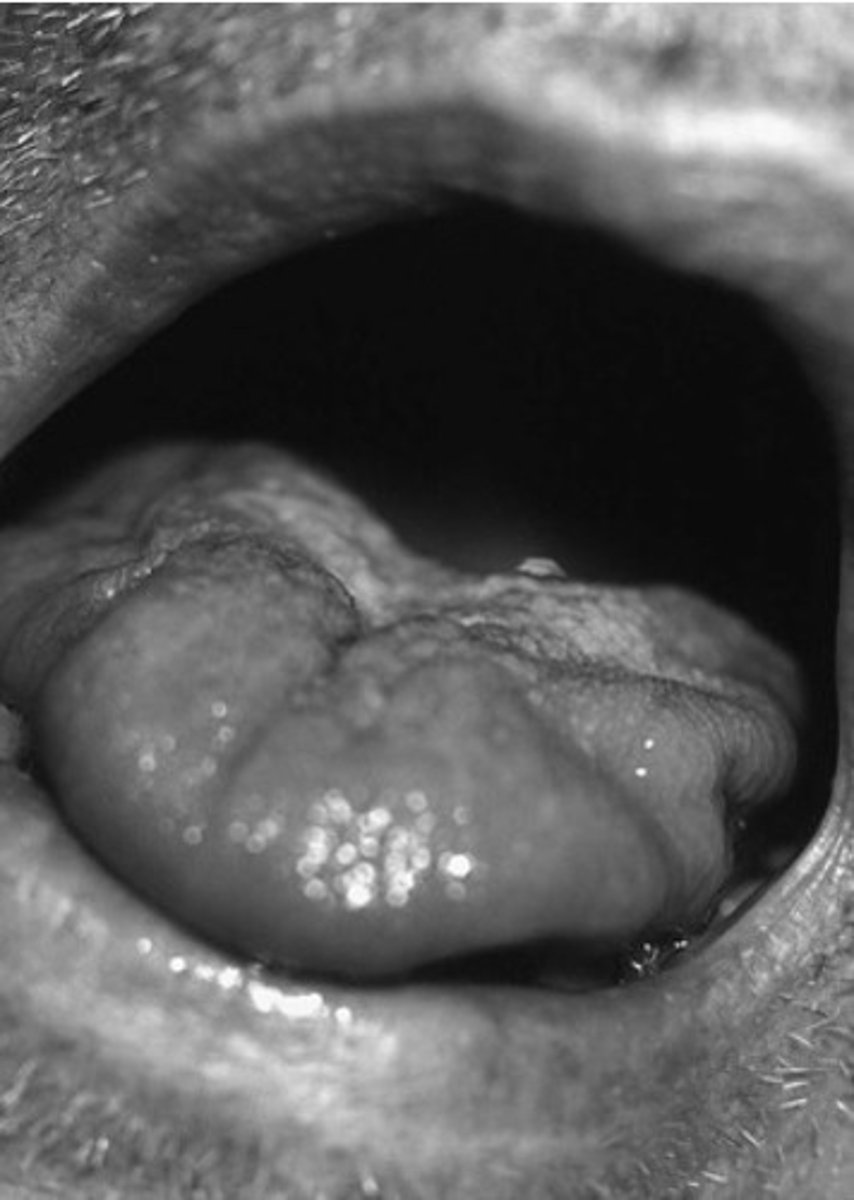
Based on the tongue picture from the previous question, which level of the nervous system is more likely involved?
Lower motor neuron
Laryngeal palpation during a clinical evaluation can help an examiner to
assess the presence and extent of laryngeal elevation
A patient coughs following a clinician's instruction, yet shows no response to aspirated materials during the VFSS. What does this observation imply?
The voluntary cough is intact, but the reflexive cough is impaired
Wet or gurgly voice quality after swallowing can indicate that
The residue remains on the surface of the vocal folds
Which test is best to detect aspiration in patients with tracheostomies and limited mobility?
Modified Evans Blue Dye Test
Which of the following instruments can measure submental muscle activity during swallow?
Surface Electromyography
A dysphagia screening test with high specificity means
The test is very good at identifying people who do not have dysphagia.
All the following conditions can cause difficultly chewing EXCEPT
Infrequent swallows
Videofluoroscopy is indicated in all of the following situations EXCEPT
The patient is too medically compromised
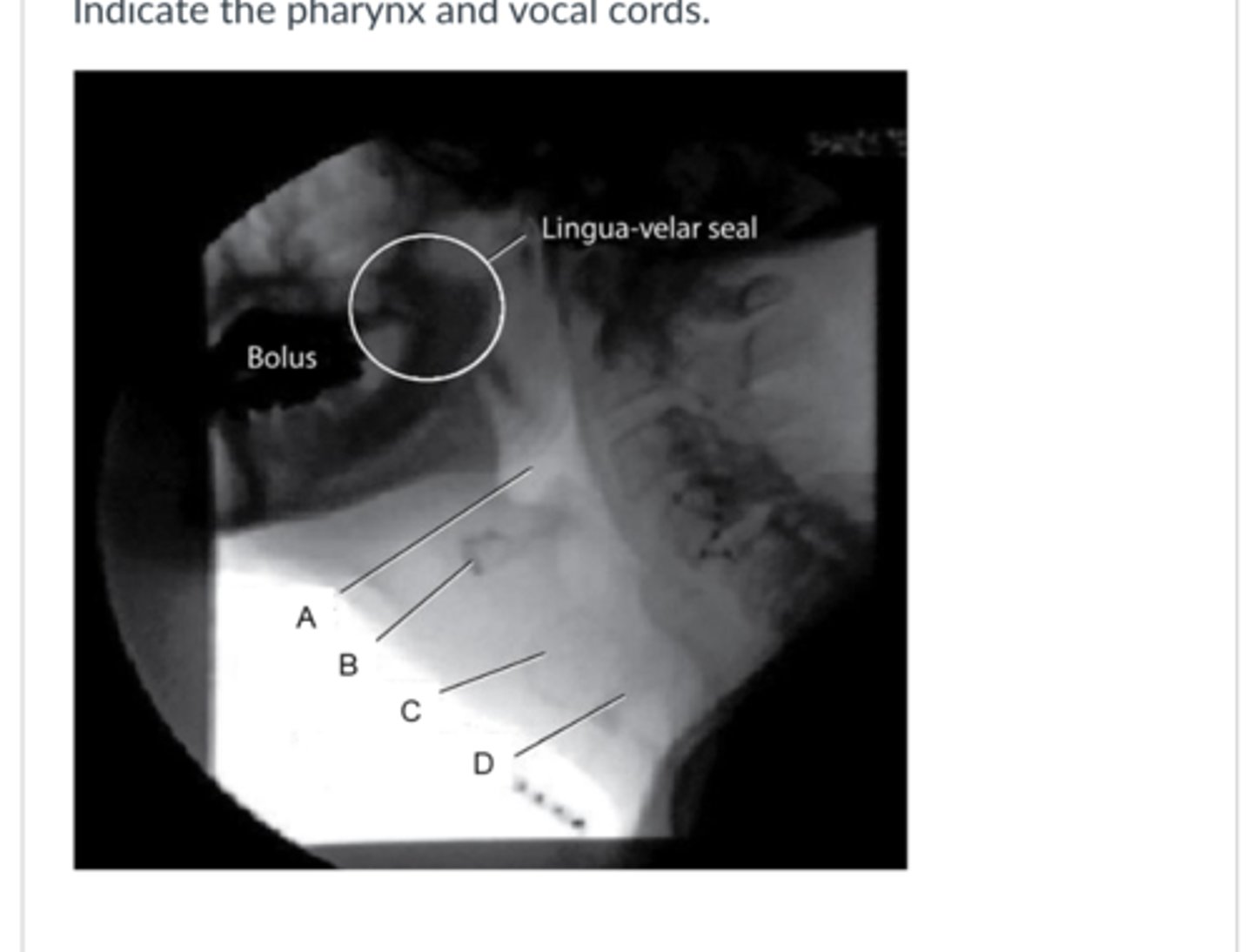
Indicate the pharynx and the hyoid bone.
A,B
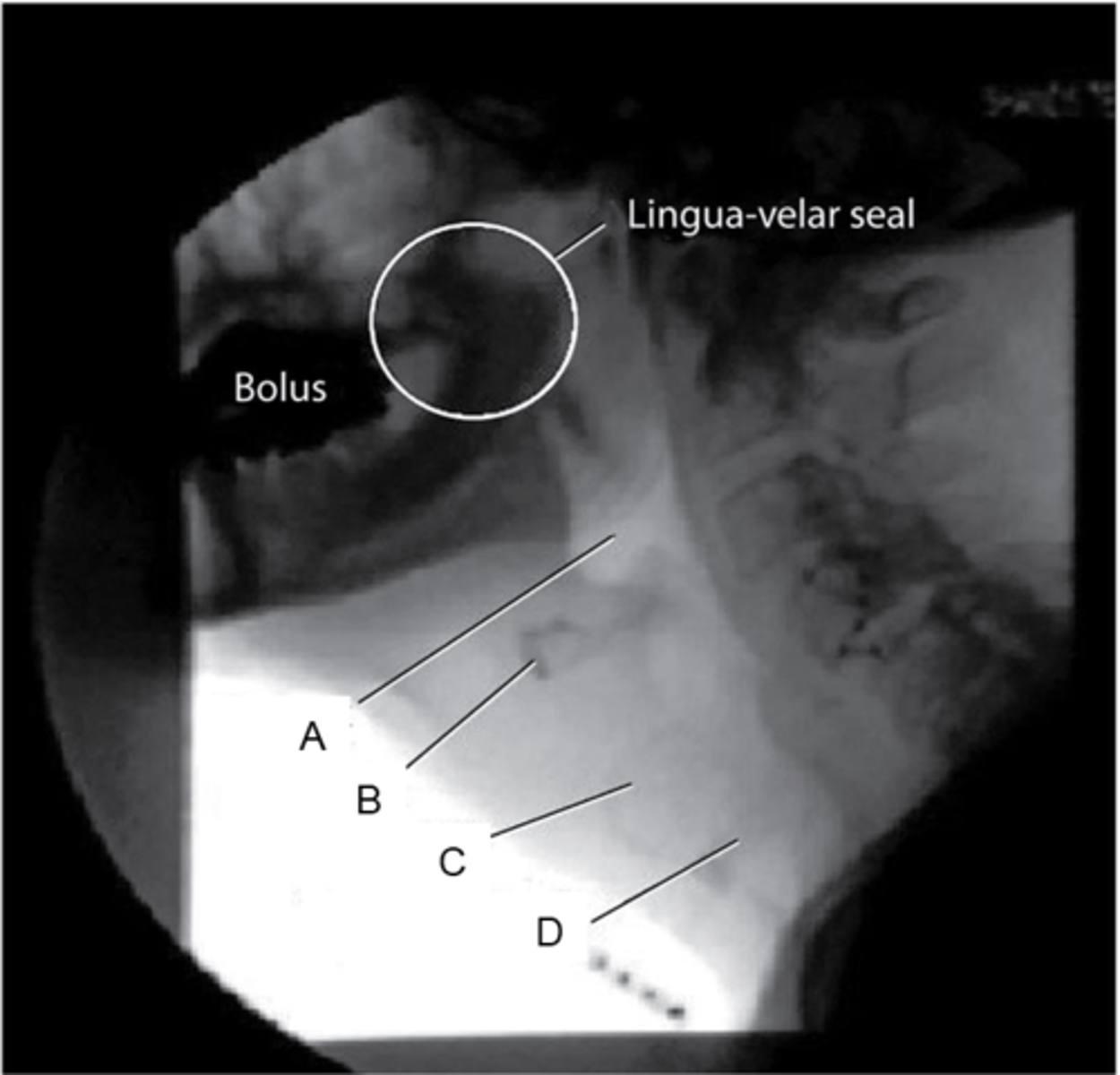
Aspiration happens when a bolus passes through
D
Based on the individualized material sequence approach in videofluoroscopy, specify the next step in each of these scenarios for the following two questions
5ml nectar thick liquid → No aspiration but an excessive residue
5 ml thin liquid
5 ml nectar thick liquid → aspiration
5 ml pudding
All the following events can usually be observed during FEES EXCEPT
Aspiration during swallowing
Please match each swallowing event with the optimal imaging tool to evaluate each event.
The pooling of saliva in the pyriform sinuses.
The esophageal structure and function during swallowing
1. FEES
2. VFSS
Not seeing whiteout during FEES in a patient with dysphagia may indicate
Weak pharyngeal contraction
A 76-year-old man reports swallowing difficulty after a hemispheric stroke. His primary complaint is that food sticks; he localizes the problem to the base of the neck just above the sternum. He coughs while swallowing thin liquids. However, his cough is weak, and his voice is dysphonic and breathy.
What is the primary instrumental evaluation for the "food sticking" complaint?
Videofluoroscopy
What is the best instrumental evaluation for identifying the associated sign of dysphonic and breathy voice?
FEES
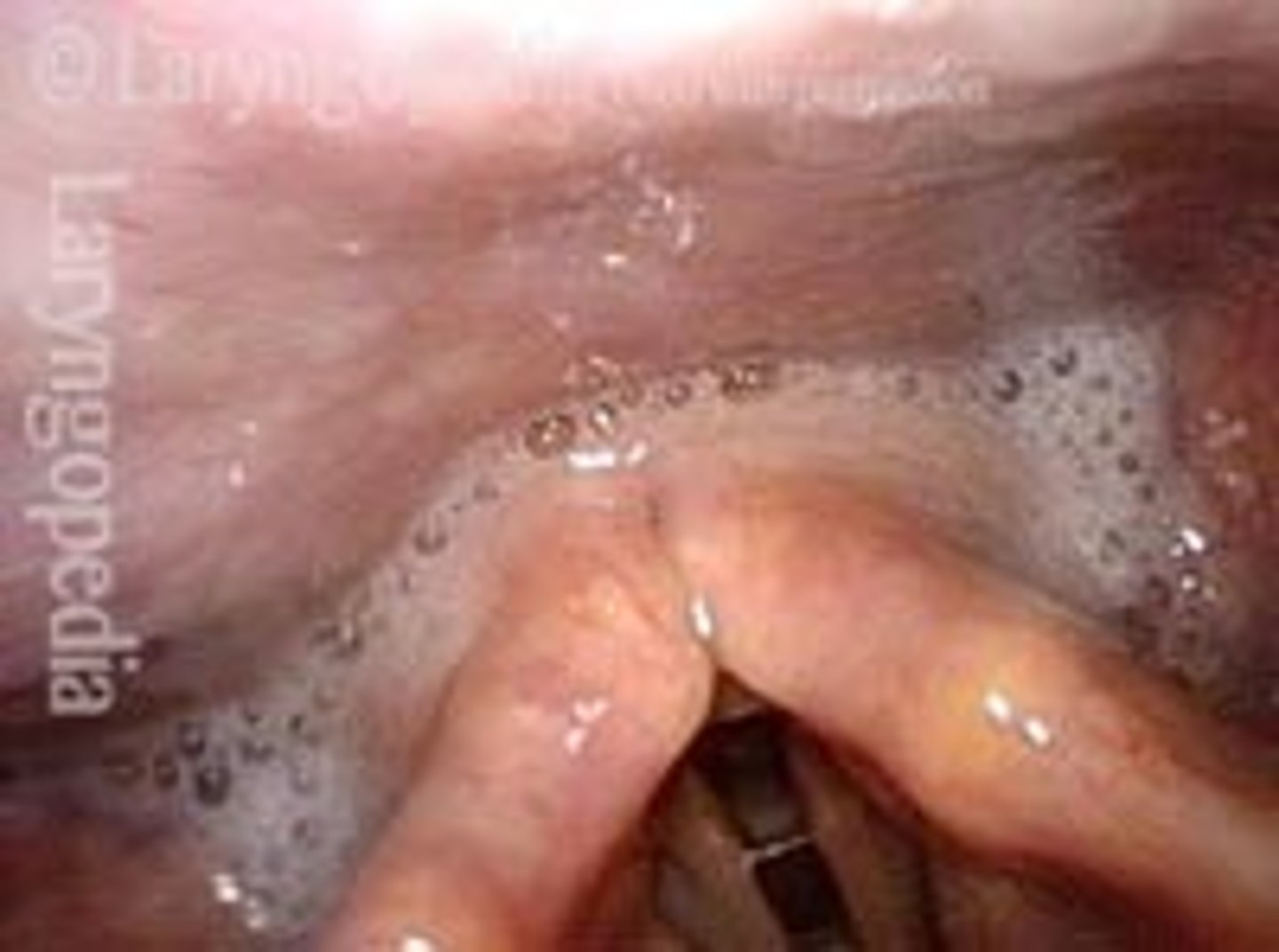
What do you see in the following picture?
Secretions pooling in the pyriform sinus
Which description best fits with the following video?
Material enters the airway, passes below the vocal folds, and no effort is made to eject.
Dysphagia Outcome Severity Scale addresses all the following domains EXCEPT
Depth of entrance of material into the airway
Which benefit is unique to FEES and not offered by Videofluoroscopy?
Ease of transport to patients
A patient reports a feeling of solid food being stuck after swallowing. FEES exam shows no sign of anatomic deviation or pharyngeal dysfunction during swallowing. What is the next step?
Doing a VFSS and tracking the bolus through the esophageal stage
What is the PAS score for this patient?
Level 3. Penetration above TVF/ not ejected
Which of the following events can not be detected under FEES?
Drooling
The following video shows a FEES exam of a person chewing a bolus. What happened during oral preparation?
Premature spillage to the valleculae
When implementing evidence-based practice in dysphagia management, which element is essential for effective treatment planning?
Integrating the best available research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values
You are looking for supporting evidence regarding the effect of transcutaneous electrical stimulation therapy on dysphagia. Which of these studies may provide the highest level of evidence for you?
Systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Please read the following case scenario and answer the question.
An 81-year-old patient with a history of Parkinson’s disease was admitted to the hospital with aspiration pneumonia, believed to be attributable to increased oropharyngeal dysphagia. A progression of Parkinson’s disease was suspected, and a nasogastric tube was inserted. A thorough medical history review revealed that the patient had recently seen his primary care physician because of increased pain in his right arm that had become progressively rigid. At that time, he was given dantrolene sodium (Dantrium) to relax his arm and relieve the pain.
Based on the medical history, what is the primary factor for the patient’s new problem with swallowing?
Addition of the muscle relaxant has weakened the swallowing muscles further
In reference to dysphagia treatment considerations, adequate oral intake refers to ___________________.
Nutrition and hydration
John, a 65-year-old male with dysphagia post-stroke, experiencing difficulty in safely swallowing thin liquids. Match each statement with the corresponding treatment plan. Match the components of John's dysphagia management treatment plan with their corresponding descriptions.
Objective
Action plan
Goal
Please read the following case scenario and answer the next two questions.
A new clinician was told by her supervisor that patients who demonstrate swallow delay might benefit from the therapeutic intervention of a sour bolus. The clinician was told that the hospital kept a large supply of lemon ice on each floor for this purpose. The clinician was working with a patient who showed a swallow delay due to a partial tongue resection secondary to cancer. After 6 days of therapy with the lemon ice, the clinician did not believe that the swallow delay had improved.
What level of evidence did the clinician use to implement this therapy technique?
Expert opinion
The sour bolus did not help triggering a faster swallow in this patient because _______________________________.
this technique should not be applied for patients with this etiology
Based on the IDDSI framework, what food consistency level does the following testing method refer to?
"Food should fall off the spoon and hold together. It should not fall apart, drip, or spatter, and it should not adhere to the spoon."
Level 4- Pureed
Based on the IDDSI Flow Test, 4-8 mL of the liquid remains in the
Level 2- Mildly thick
All of the following are correct regarding the physiologic impact of thickened liquids EXCEPT ______________________________.
Decreased pharyngeal pressure
Which of these pictures shows the supraglottic swallow maneuver?
Image 1

The purpose of the Shaker exercise (aka Head-lift exercise) is to
Increase PES opening
Considering the demonstrated electrode placement, what are the likely immediate and long-term effects of Transcutaneous Electrical Stimulation on hyolaryngeal excursion during swallowing?
Short-term decrease, followed by a long-term increase in hyolaryngeal excursion.
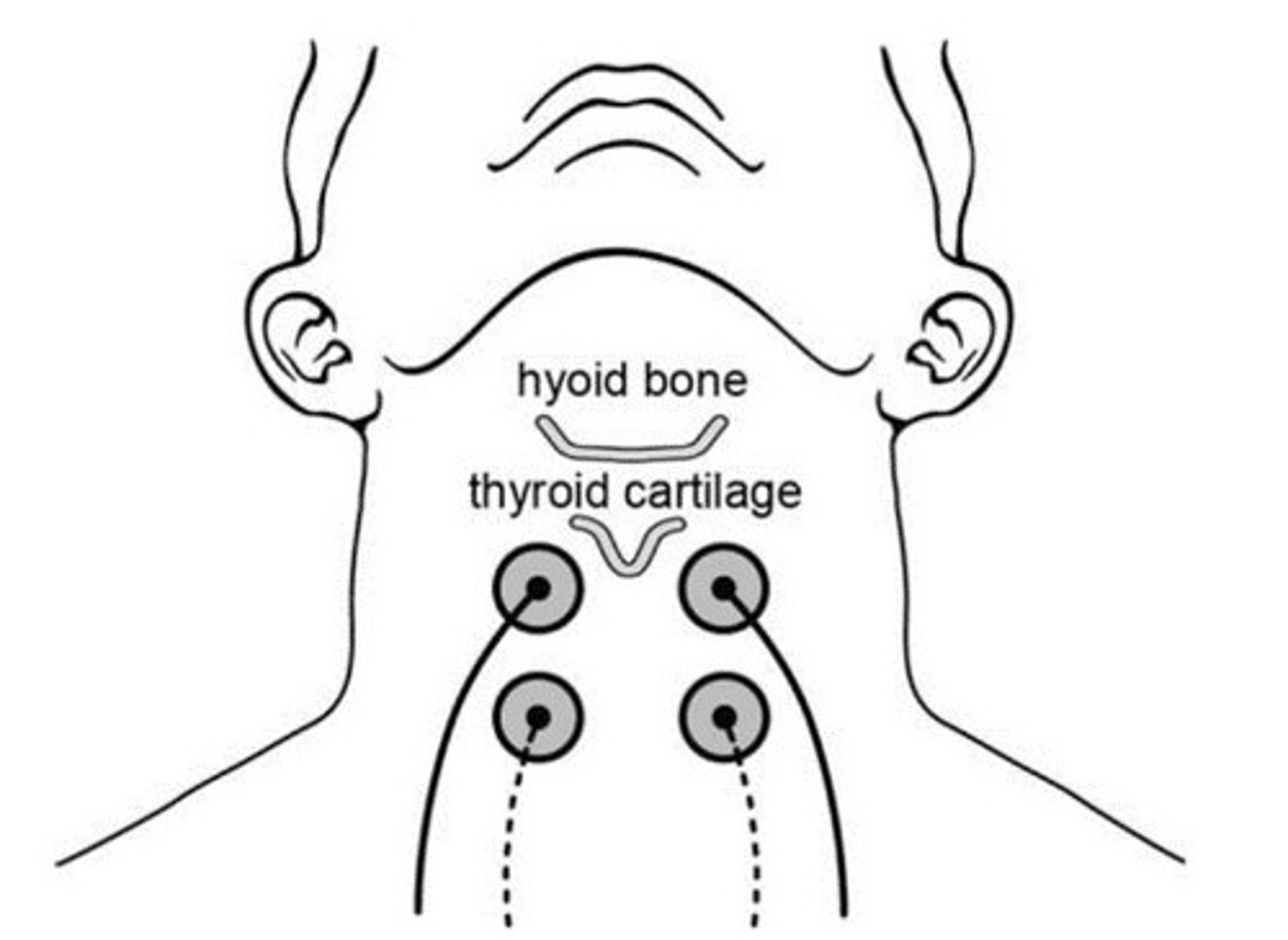
Lingual resistance training for improving dysphagia utilizes all the following exercise principles EXCEPT
Specificity
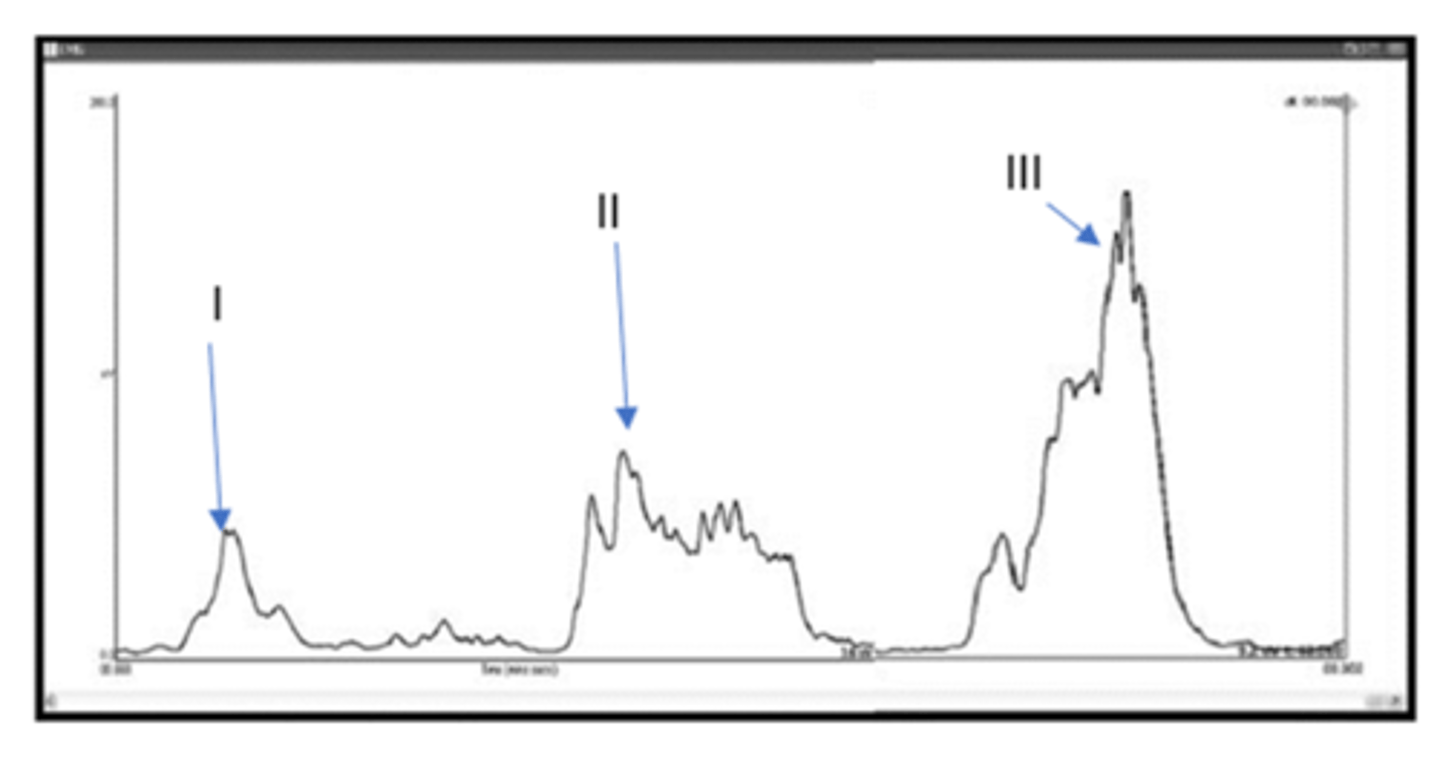
Which of the following three submental sEMG traces possibly shows the Mendelson Maneuver?
II
What is the effect of the tongue-hold (Masako) maneuver on swallowing physiology?
Increasing the bulge of the posterior pharyngeal wall
Which of the following is more effective as a compensatory strategy in a patient with unilateral vocal cord paresis for a safe swallow?
Supraglottic swallow
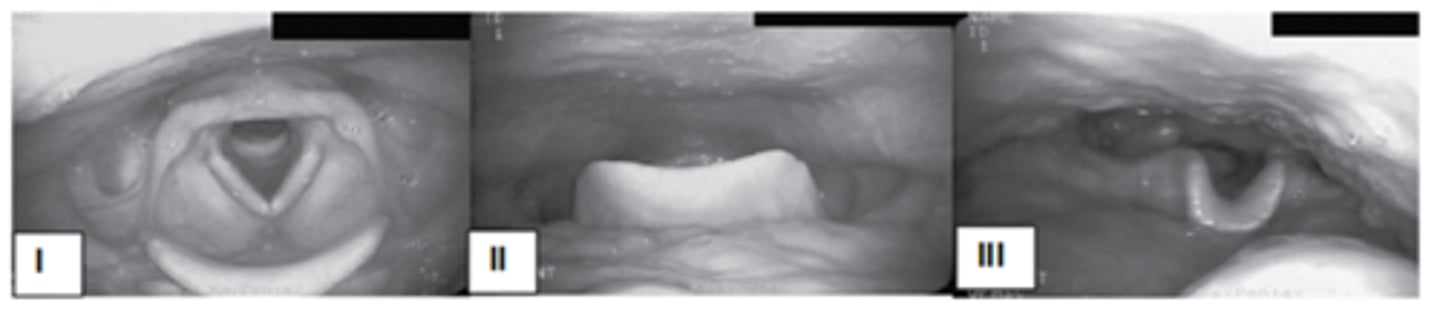
The pictures show the endoscopic view of three different head postures on the oropharyngeal structure. Use these pictures to answer the following two questions.
A dysphagia patient with unilateral pharyngeal deficit may benefit from ___________________________.
III
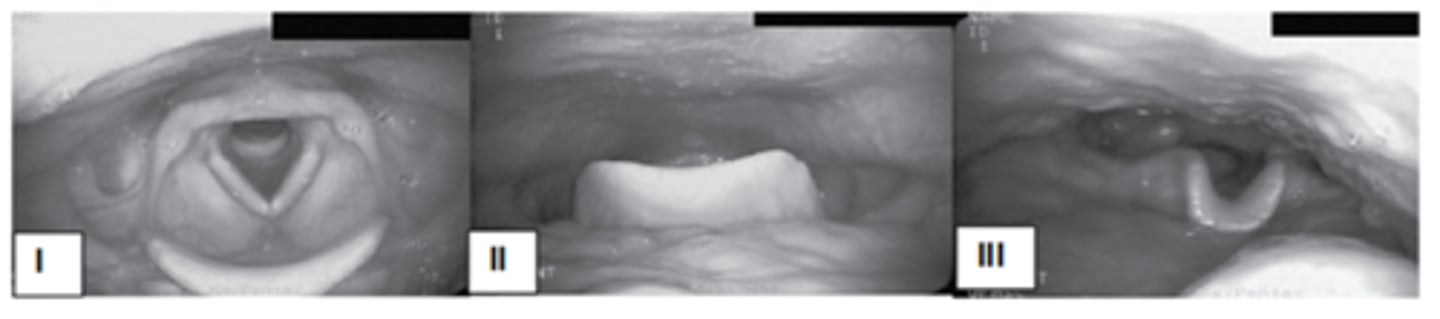
Which posture widens the oropharynx?
I
All statements are correct regarding factors affecting the thickness of thickened fluids EXCEPT _____________.
Fluids generally get thinner with time.
This maneuver should not be used for patients with respiratory disease.
Mendelson
Which maneuver(s) may increase the tongue pressure during swallowing?
Both a and d
All the following are correct regarding the effect of carbonated drinks on swallowing EXCEPT
Decreased lingual-palatal pressure
All the following techniques have rehabilitative indications EXCEPT
Supraglottic Swallow
This exercise program designed to prevent dysphagia and related morbidities in head/neck cancer patients
Pharyngocise
Which statement is correct regarding TES?
Controversial evidence exists regarding the clinical effect of TES on swallowing function
All the following tools can facilitate instructing Mendelson maneuver EXCEPT
Cervical auscultation
Which of the following is an example of passive dysphagia intervention as apposed to active and environmental interventions?
Diet changes
"Repeatedly practice a movement, skill or task to alter muscle condition." Which exercise principle does this statement describe?
Adaptation