Zool 110 Lecture: Understanding Human and Avian Respiration (Week 6)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
problem of respiration
O2 is used for cellular metabolism, which produces CO2 (how do we remove CO2 and get O2 in?)
air, water
diffusion is fast in ____ it is slow in _____
very small animals
what kind of animals can rely on body surface for O2 intake
larger animals
what kind of animals need specialized respiratory organs
respiration by diffusion
direct diffusion of gases between organism and environment (seen in single celled eukaryotes, sponges, cnidiarians, flatworms)
surface area, mass
increase of _____ relative to _____ enables multicellular animals to use diffusion
gills, tracheae, and lungs
what are the three types of respiratory organs
gills
evagination of the body
lung
invagination of the body
the digestion tract
what tract are lungs an outgrowth of
circulatory system
gills and lungs need to be coupled with a _____ to work
tracheae
in insects air reaches internal parts through tubes called the _____
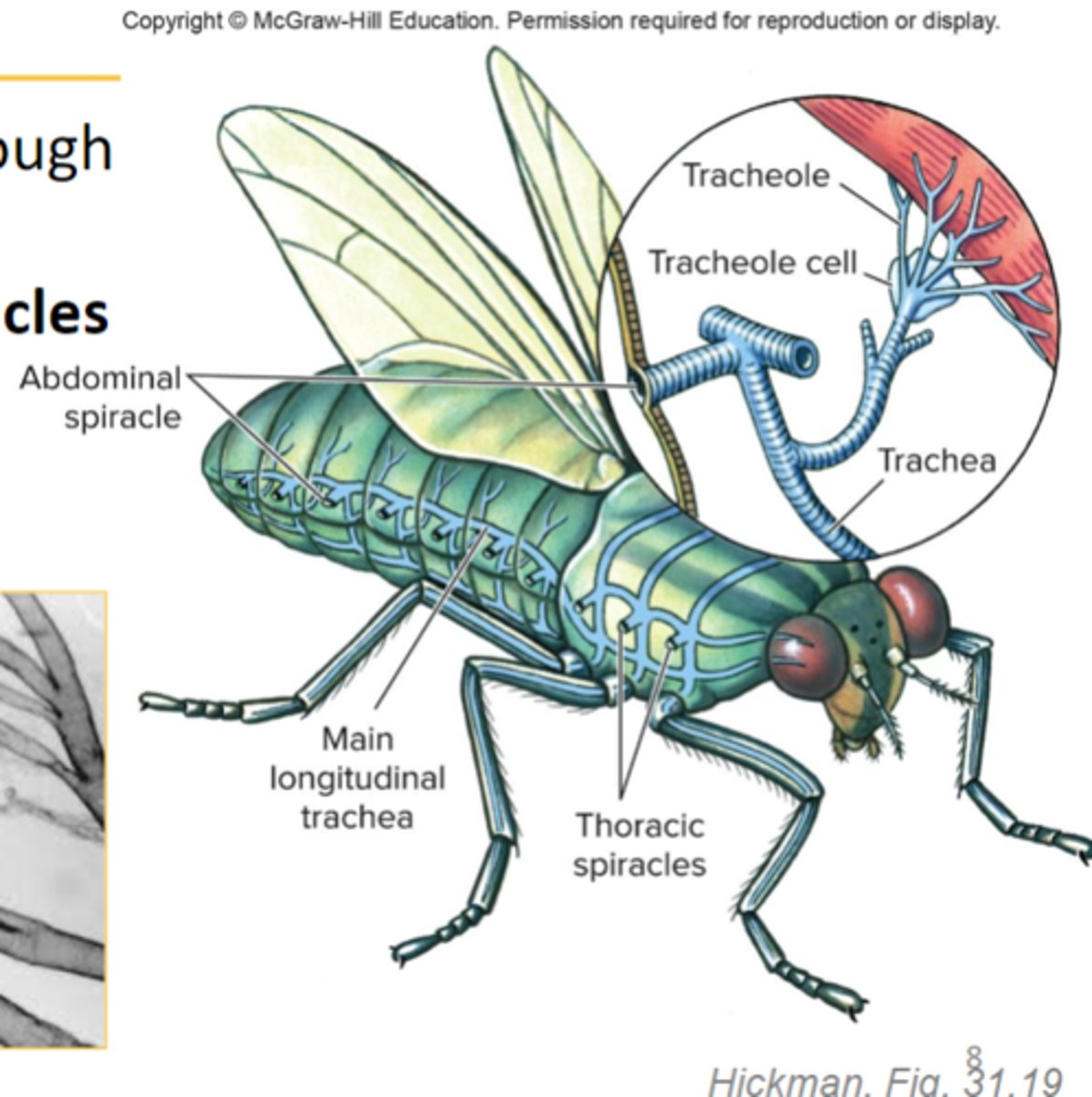
spiracles
openings in the abdomen of an insect that are used for breathing
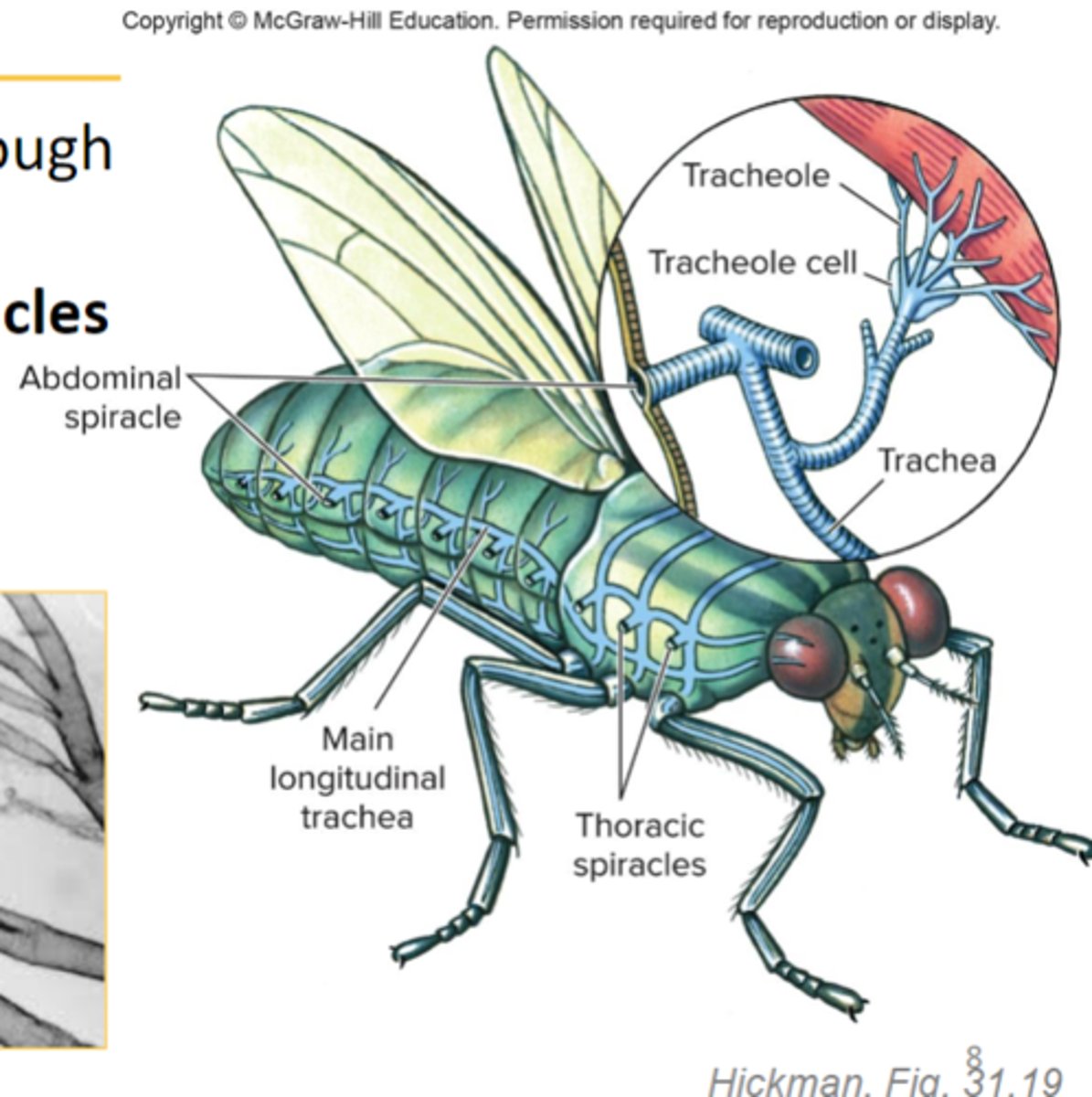
hemocoel
capillaries in humans are similar to what in insects
open
do insects have an open or closed circulatory system
flow of blood in insects
heart, arteries, hemocoel, veins, heart
external gills
evaginated from the body and project directly into the environmental medium

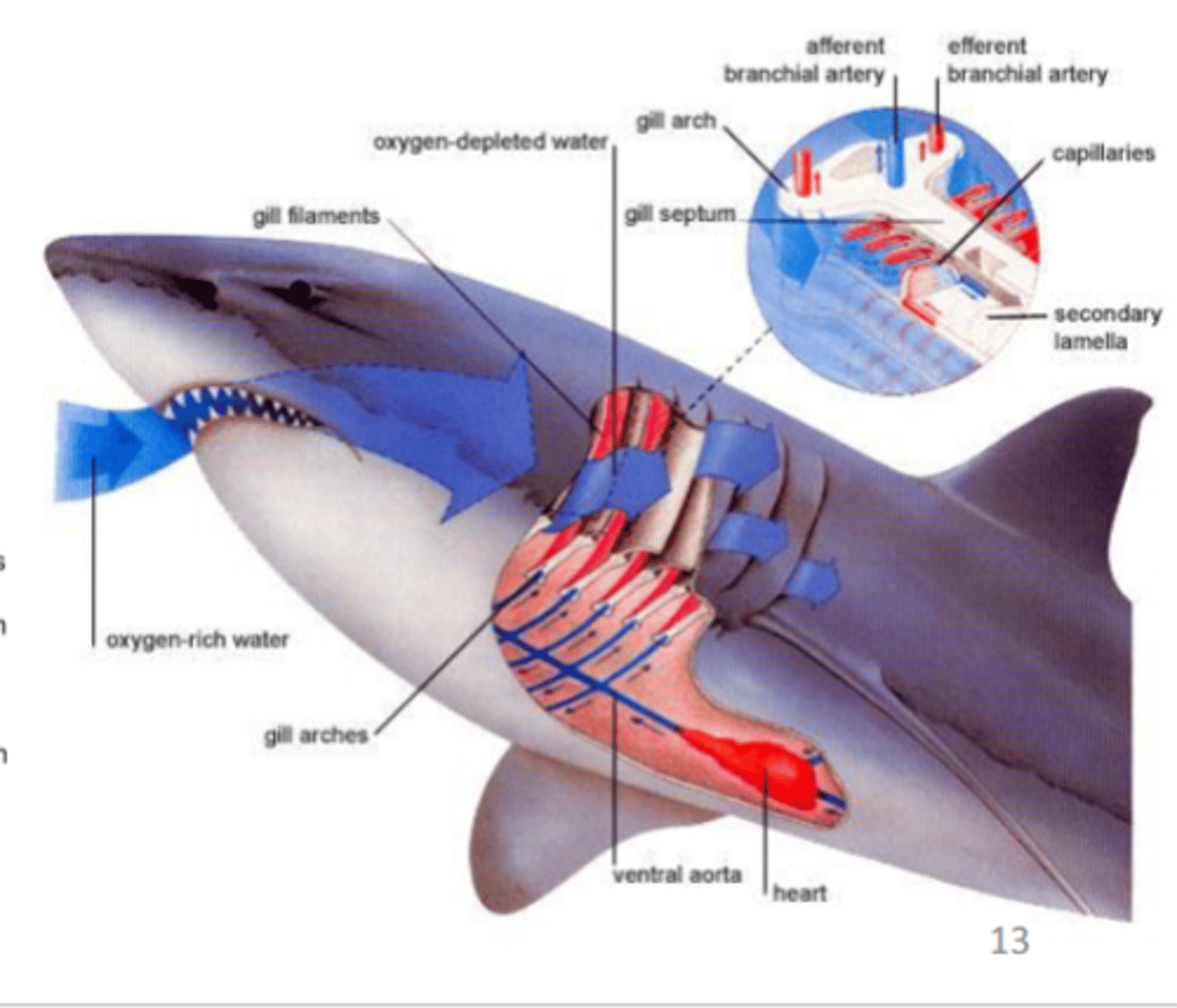
internal gills
Gills enclosed in protective body cavities; typical of mollusks, arthropods, and fishes

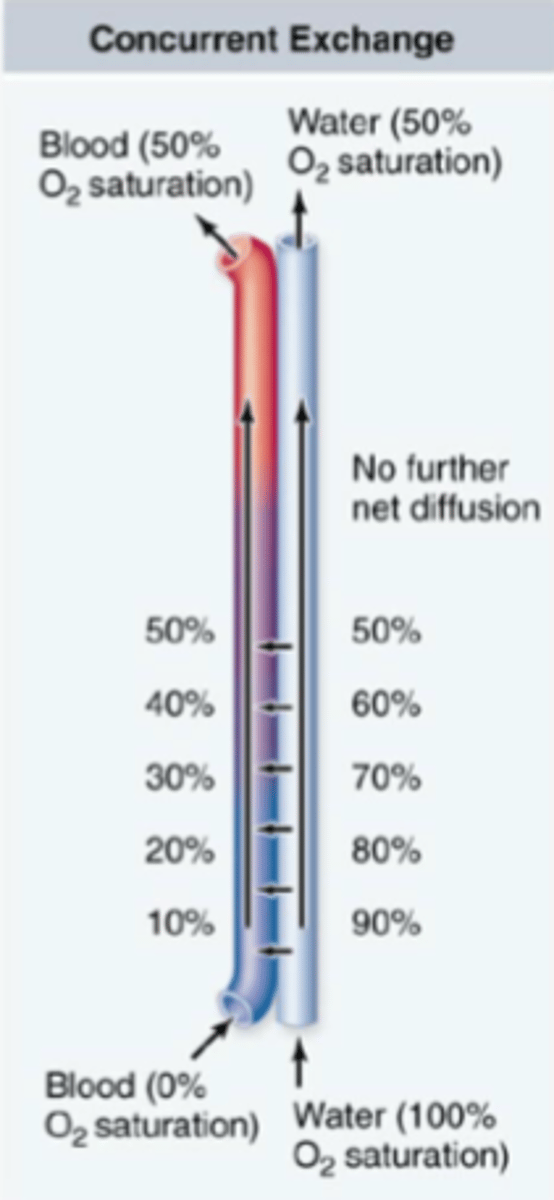
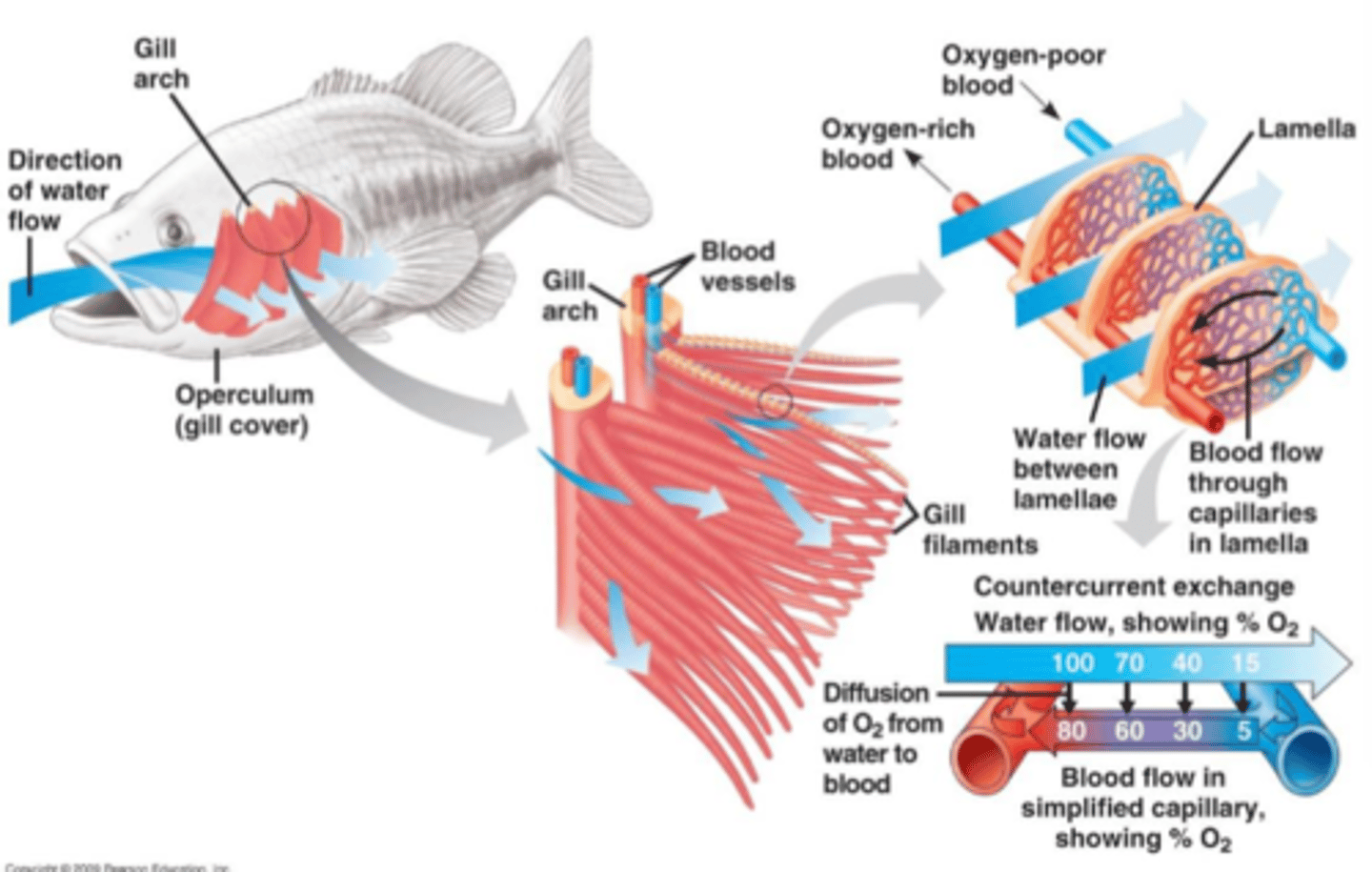
concurrent exchange
When blood flows along the respiratory surface in the same direction as the respiratory medium
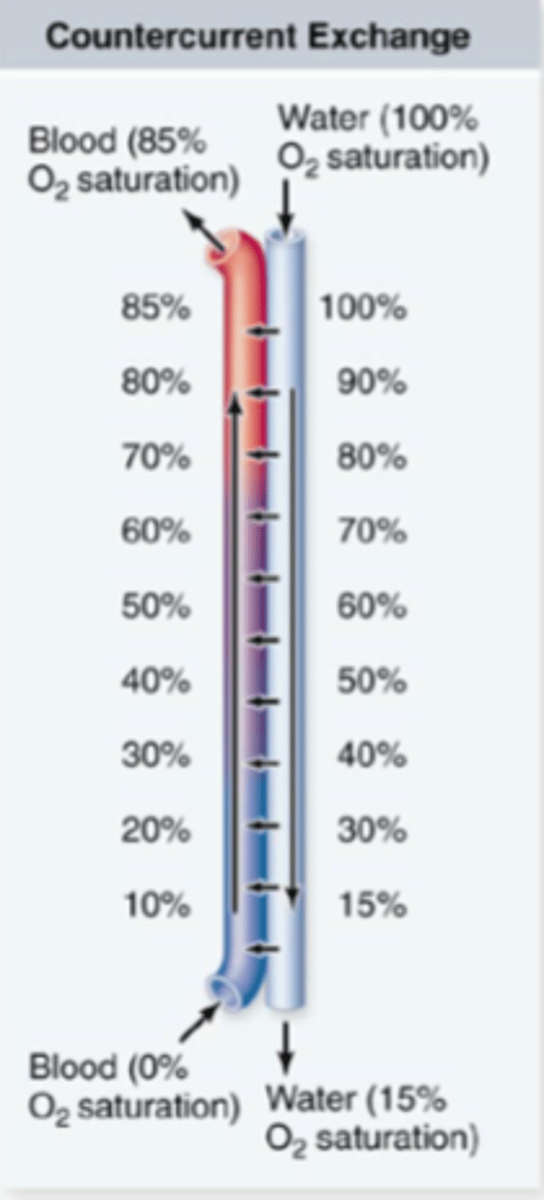
countercurrent exchange
the transfer of heat between fluids that are flowing in opposite directions
ventilation of fish gills
continuous one way flow of water, countercurrent exchange
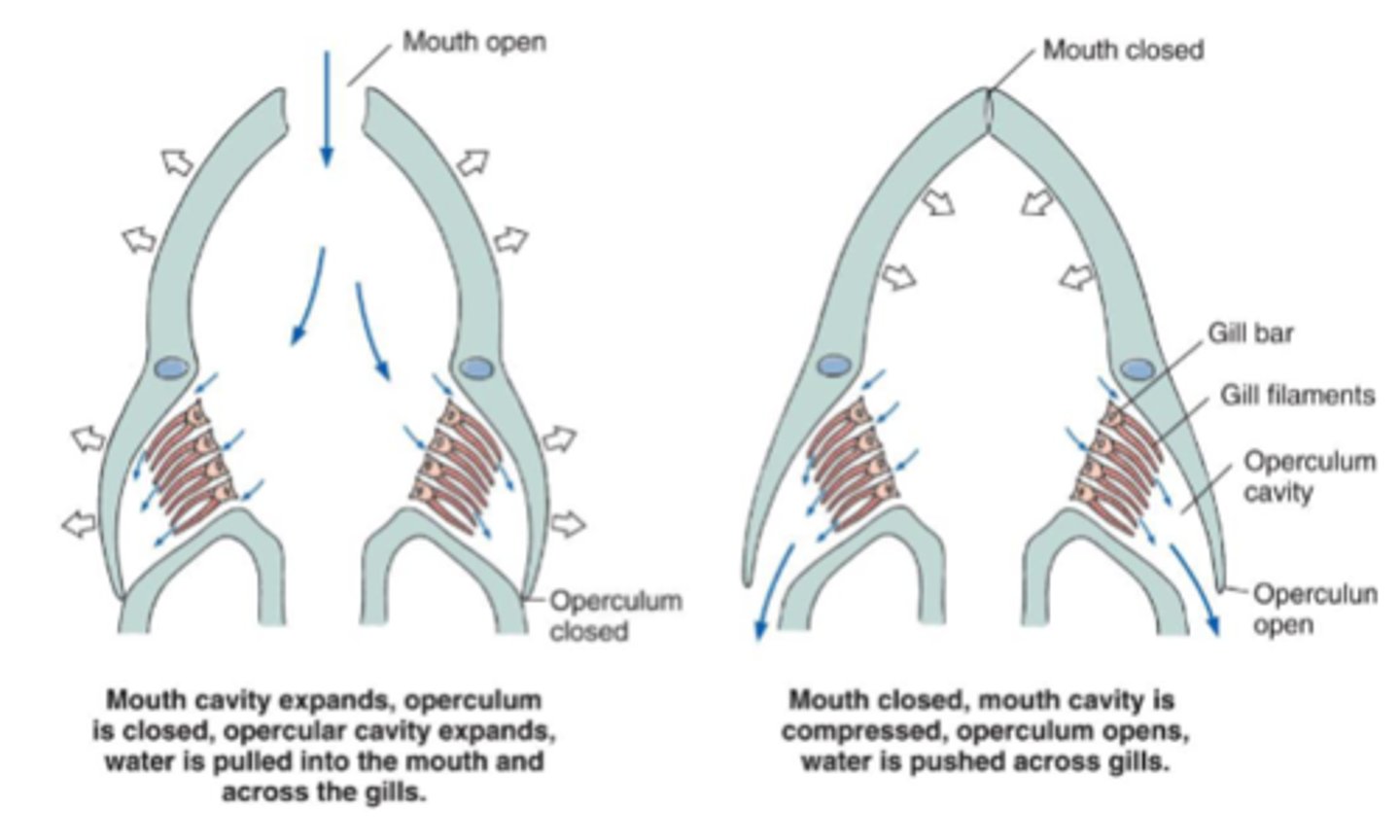
buccal pumping
1. open mouth to let water in, gills closed 2. close mouth and open gills to flush water out
ram ventilation
method of opening the mouth and swimming forward
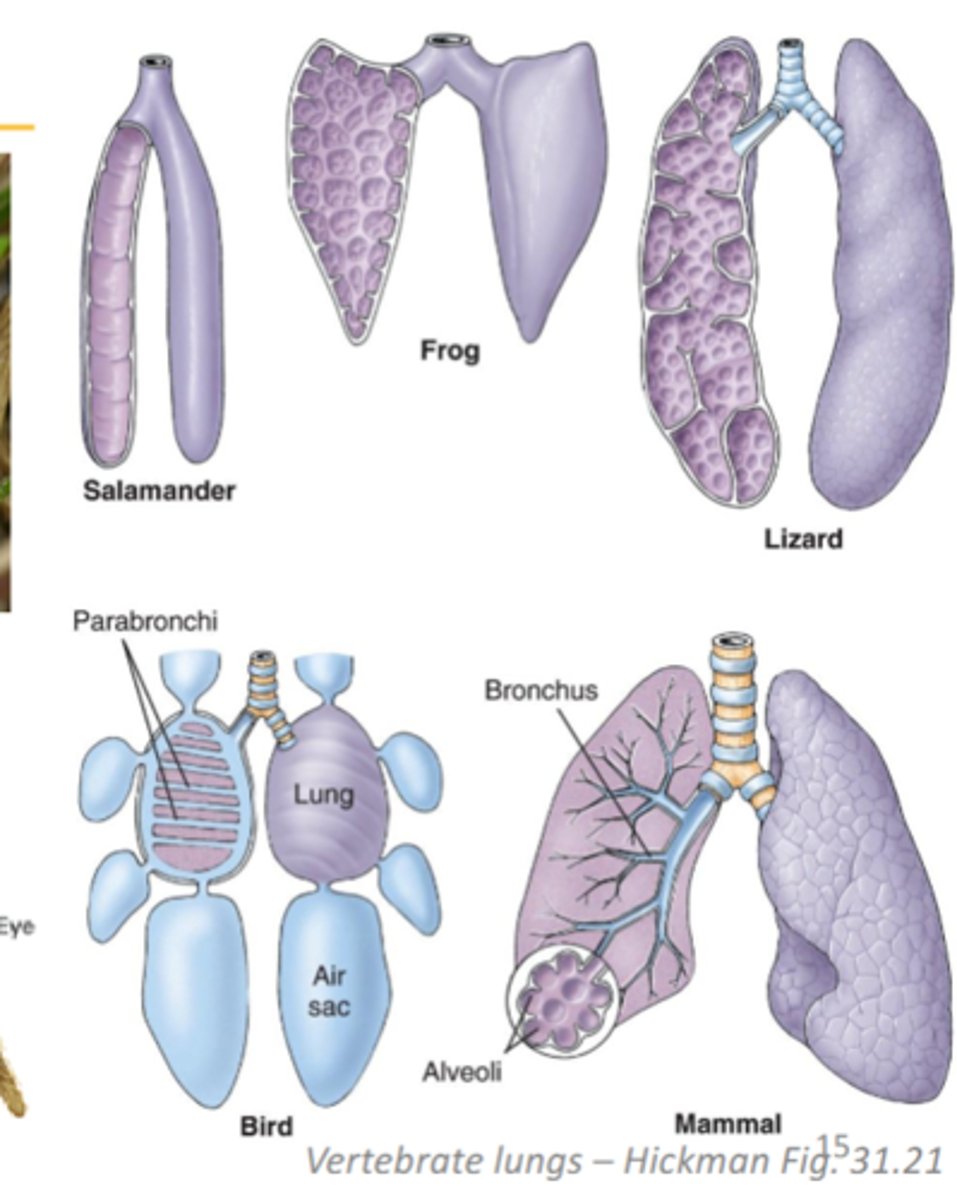
lungs
internal vascularized cavity (snails, slugs spiders, vertebrates)
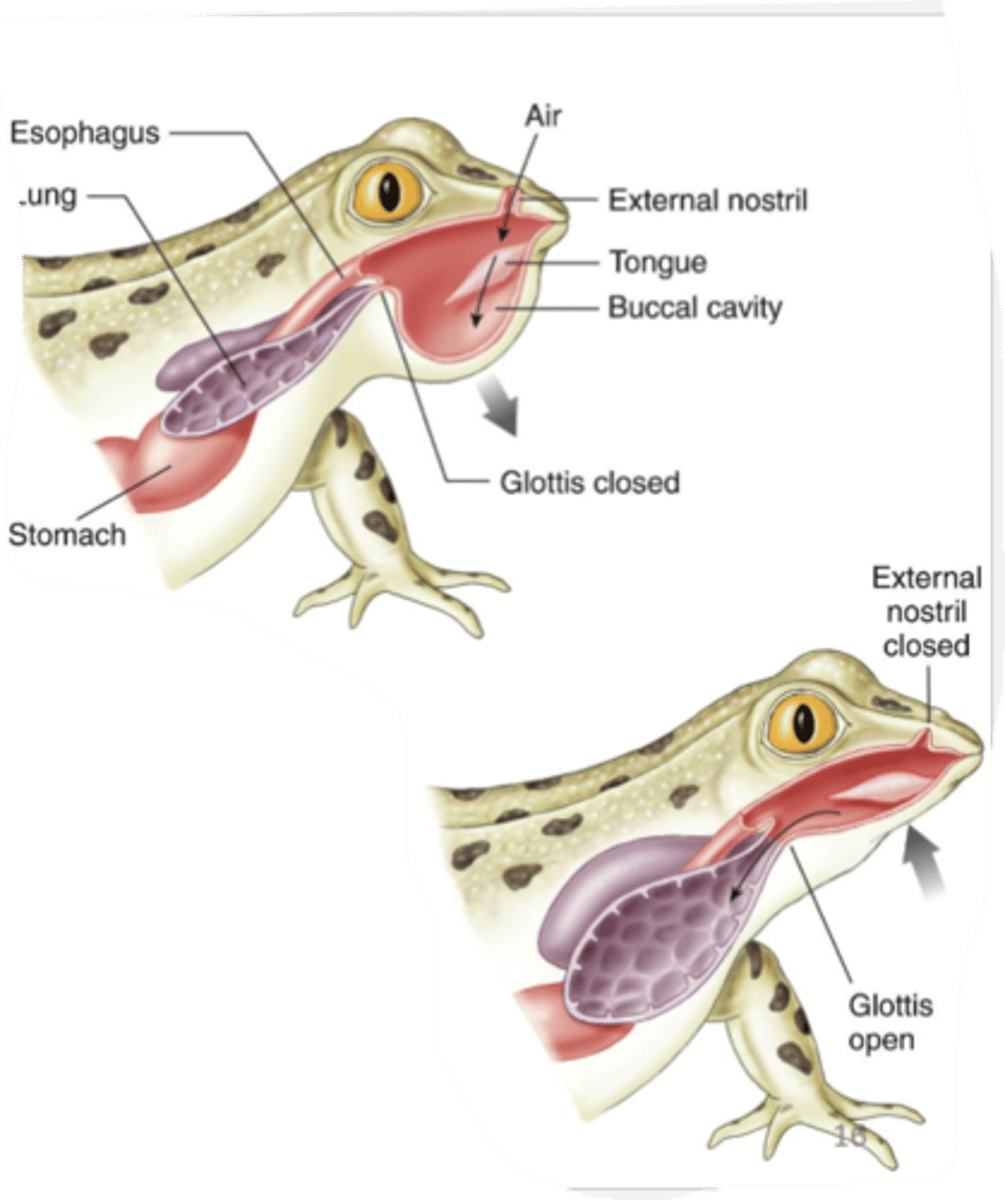
ventilation of amphibian lungs
buccal force pump, brief period of apnea
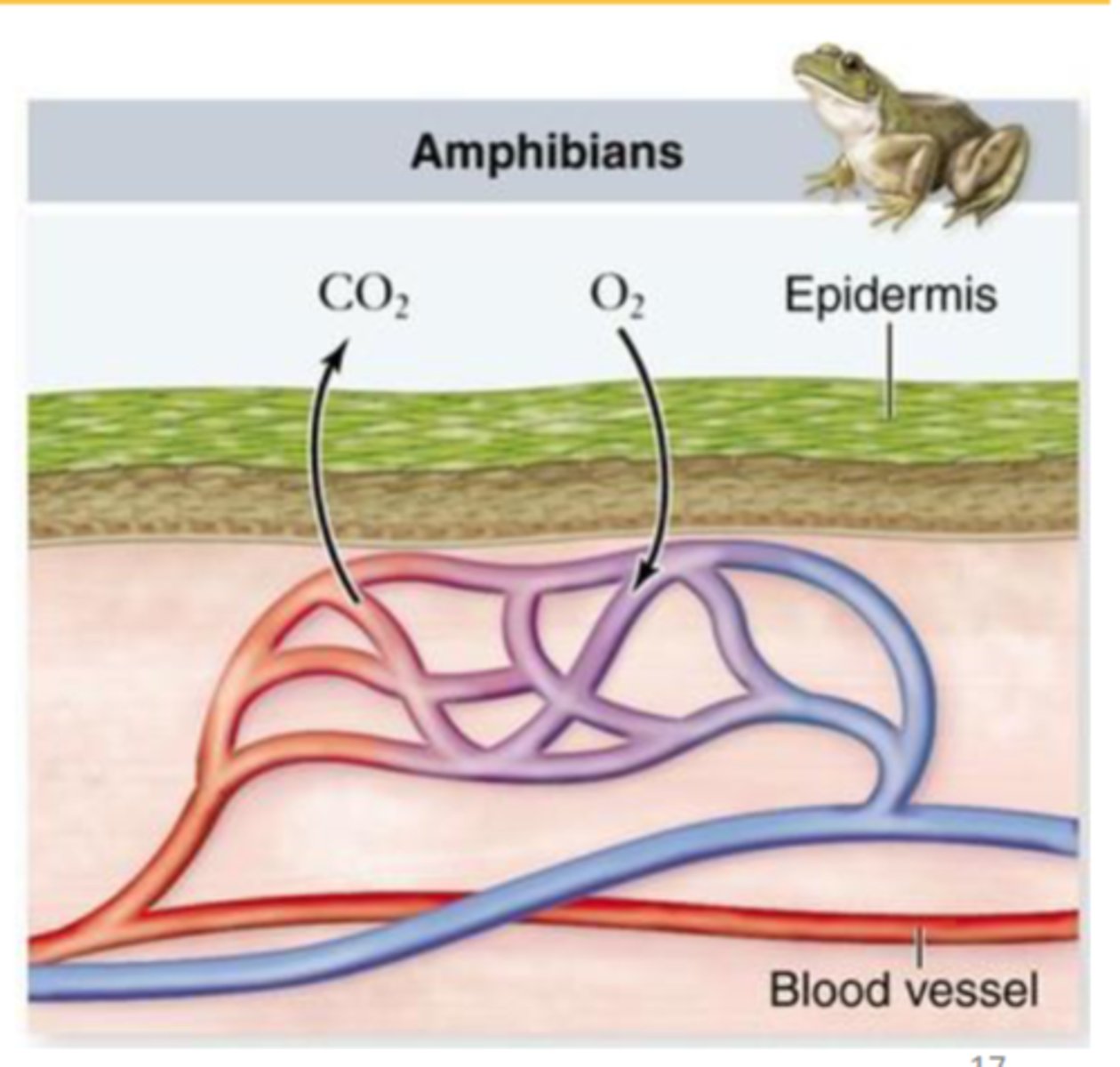
cutaneous respiration (diffusion)
supplements gills or lungs in large animals such as amphibians and fishes
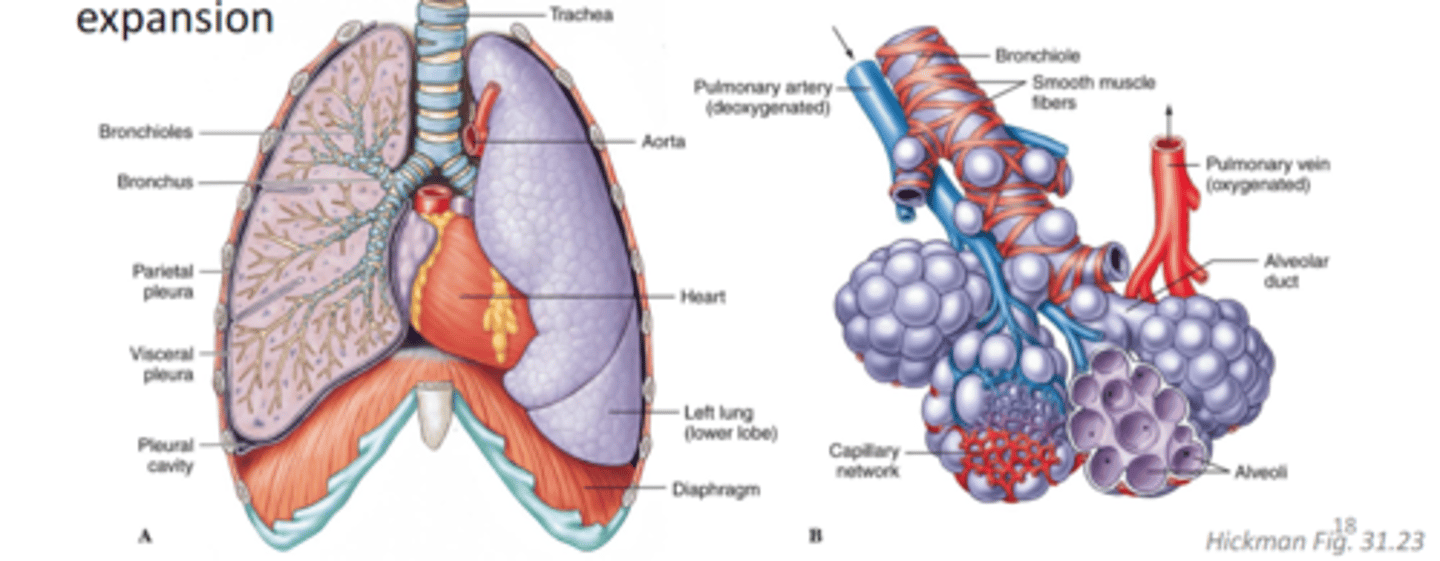
ventilation of lungs using negative pressure
diaphragm is pulled down, opening thoracic cavity and driving lung expansion
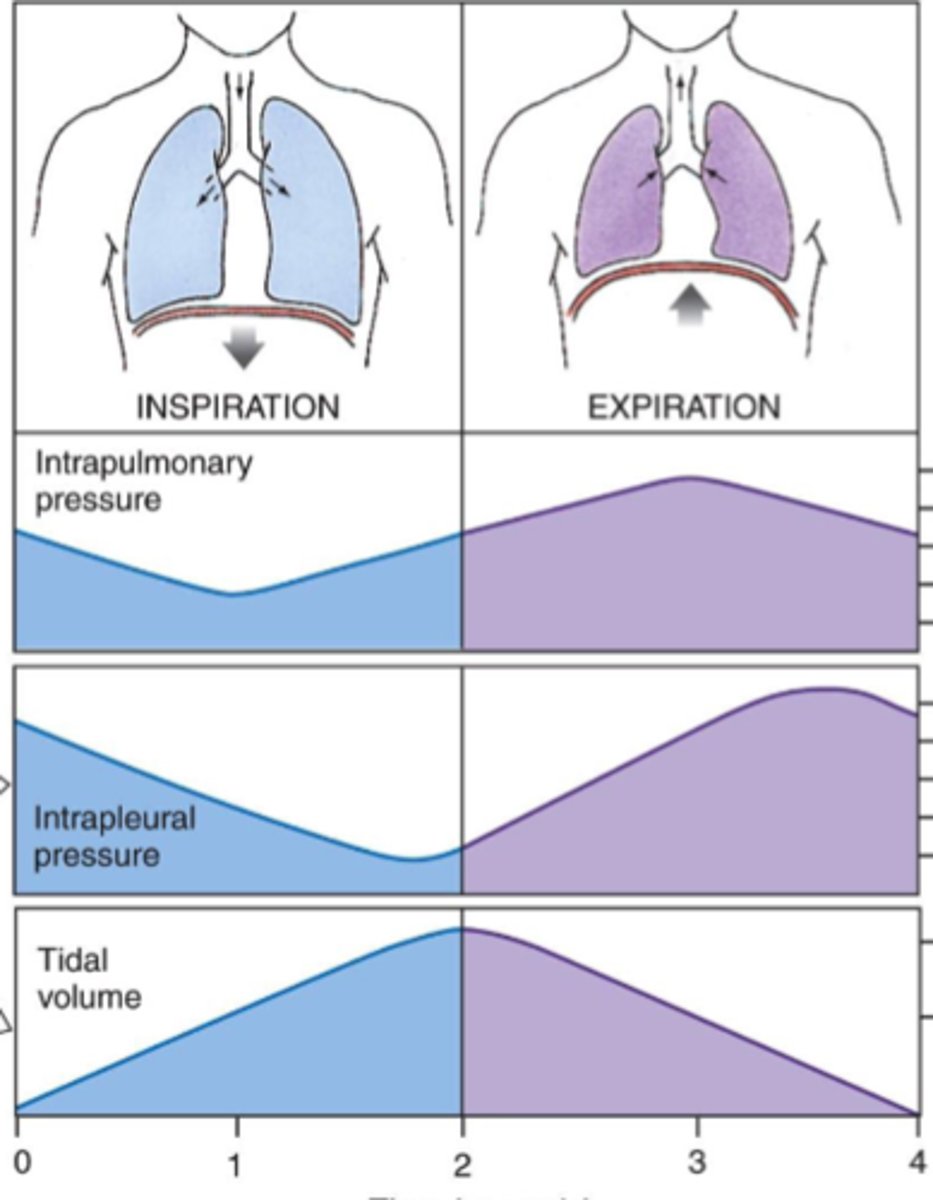
aspiration
negative pressure (amniotes)
increase of CO2 in the body
what tells the brain to take a breath in
inspiration vs aspiration diagram
pathway of air into human lungs
external nares, nasal cavities, pharynx, glottis, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveolar sacs, alveoli
specialized one way respiratory system of birds
adapted for high metabolic demands of flight, parabronchi instead of alveoli, and nine interconnecting air sacs, enable continuous air flow
respiratory pigments
proteins in blood cells that carry O2 and CO2
hemoglobin
most common respiratory pigment, RED, iron containing protein, in all vertebrates and many invertebrates
hemocyanin
type of respiratory pigment, BLUE, copper containing protein, found in crustaceans and most molluscs