Neurobiology UMN - Lecture 7
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the two types of transporters?
ATPase Pumps: Energy source ATP
Ion Exchangers: Energy source is chemical gradients, “secondary active transport.”
Moving ions against their concentration gradient takes energy.
What Ions do ATPase pumps move?
Actively (using ATP as an energy source) moves 2 K+ ions in and 3 Na+ ions out.
Helps to increase internal potassium and reduce sodium intake.
What happens to the internal environment of a neuron because of the ATPase pumps that are bringing 2 potassium in and 3 sodiums out?
The internal environment becomes electrogenic, making it relatively more negative on the inside.
Ion Exchangers: What are antiporters?
They exchange intracellular and extracellular ions.
Example: A common example is the sodium-calcium exchanger (Na+/Ca2+ exchanger), where the influx of sodium ions provides the energy to pump calcium ions out of the cell.
What are co-transporters?
These are membrane proteins that move several ions or molecules at once across the cell membrane. They are also called symporters when all the ions go in the same direction.
What is the NKCC1 Co-Transporter?
Example: Na⁺/K⁺/Cl⁻ co-transporter
Also called NKCC1.
It carries sodium (Na⁺), potassium (K⁺), and chloride (Cl⁻) together into the cell.
especially active in young, immature neurons
For every transport cycle, the protein moves:
1 sodium ion (Na⁺)
1 potassium ion (K⁺)
2 chloride ions (Cl⁻)
All go into the cell. (
1 +1 + (-2) = 0 -- Making thiselectroneutral
What is the KCC2 Co-Transporter?
Expressed in mature neurons
1K:1Cl (OUT) making the electrical charge balanced
Keeps chloride OUT, lowering intracelluar Cl-
What are leak channels?
Generally open at rest.
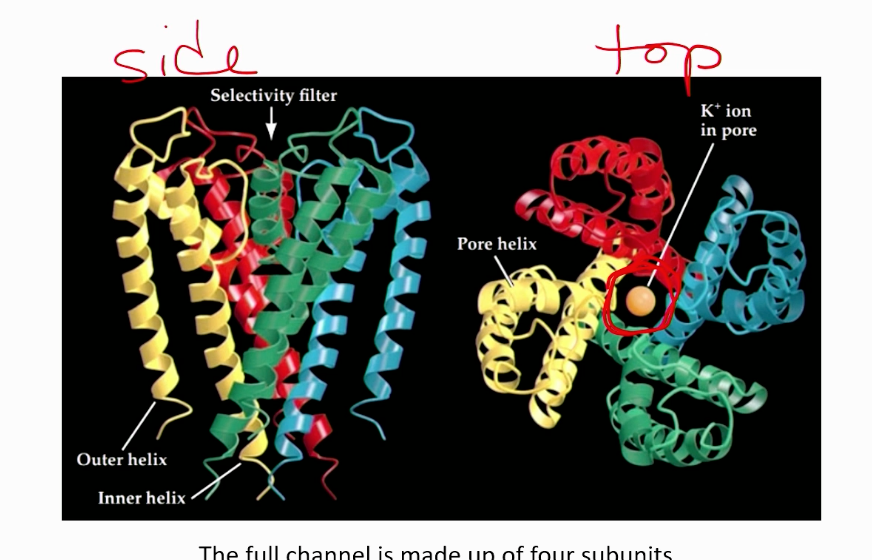
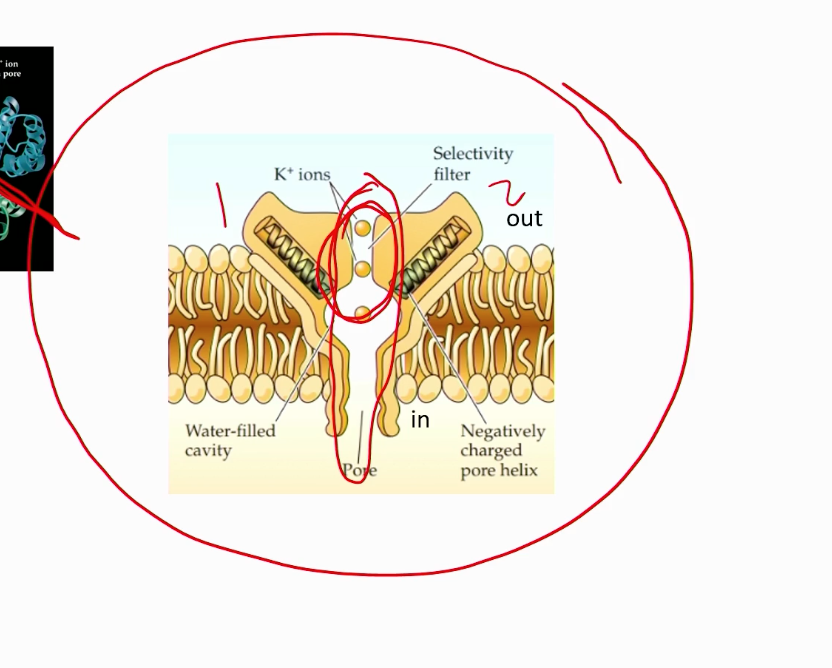
What is the “pore” loop in leak channels?
Works as a “selectivity filter” providing specificity. Makes it only selective for potassium ions coming through.
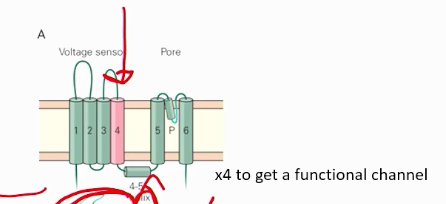
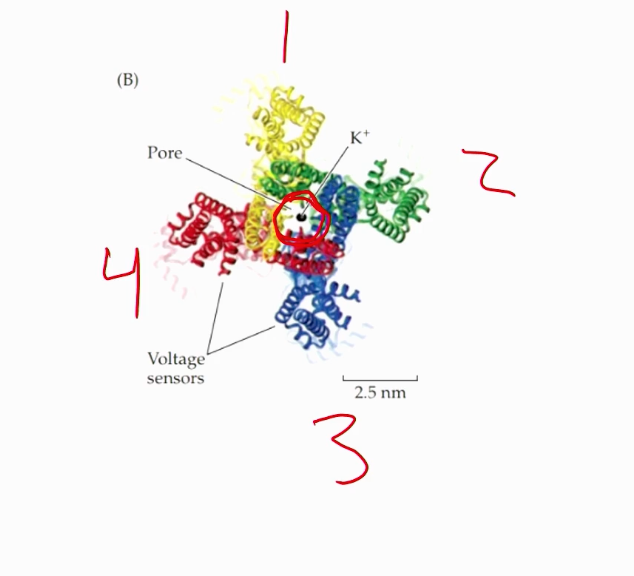
What makes up voltage gated potassium channels? How do voltage-gated potassium channels function?
The voltage gated section (labelled 1-4 in the image), with the 4th bar being the most important for sensing voltage, the LINKER between bar 4 and bar 5, and the pore loop for potassium connected.
When the potassium channel is hyper polarized, is the pore open or closed for the channel?
Closed
When the potassium channel is depolarized, is the pore open or closed for the channel?
Open
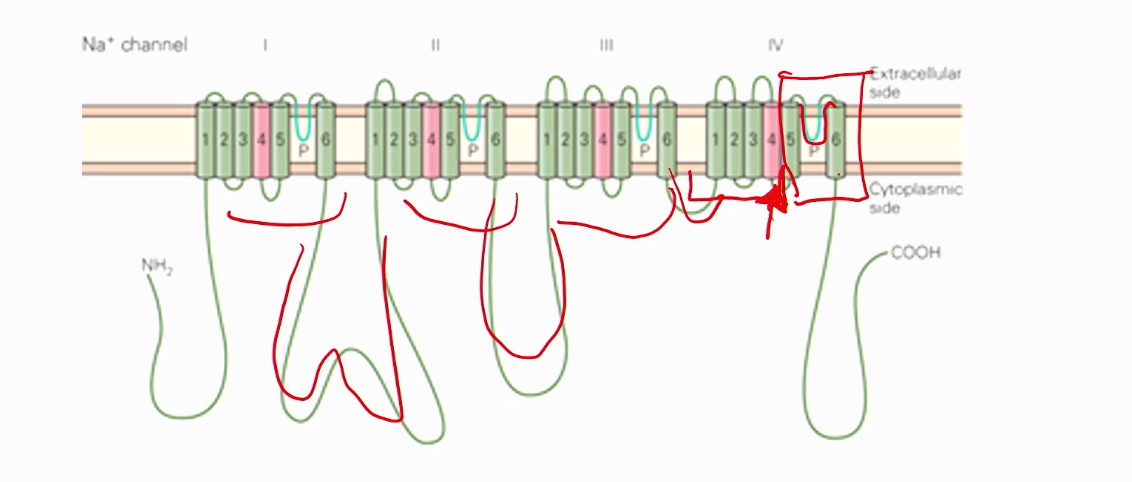
Voltage gated sodium channels are similar to potassium channels in that they..? However, two key differences they have include ..?
also have a pore
selectively pass Na+
voltage also induces a conformational change in voltage-gated sodium channels
Differ..
Besides opening/closing, voltage-gated sodium channels can also INACTIVATE.
Instead of 4 different subunits like in K+, we repeat the voltage channels in the same gene as they are all connected.
What are channelopathies?
Broad term for any disorder arising from an issue with a channel.
Do voltage gated calcium channels open FASTER or SLOWER in comparison to voltage gated sodium channels?
Slower
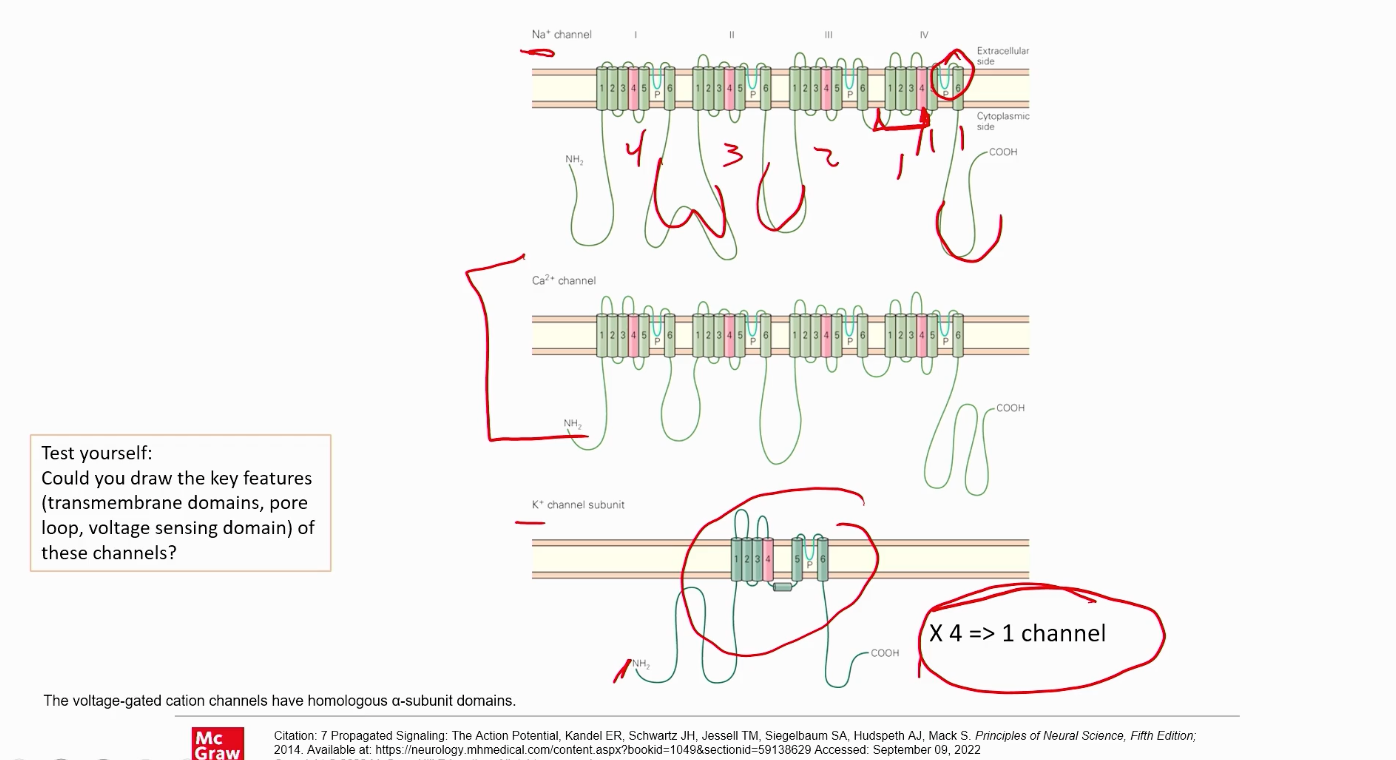
Compare sodium, potassium, and calcium channels, and draw each one out!
Does your answer match the image?
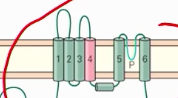
how many of the given image would we need to make a channel?
4
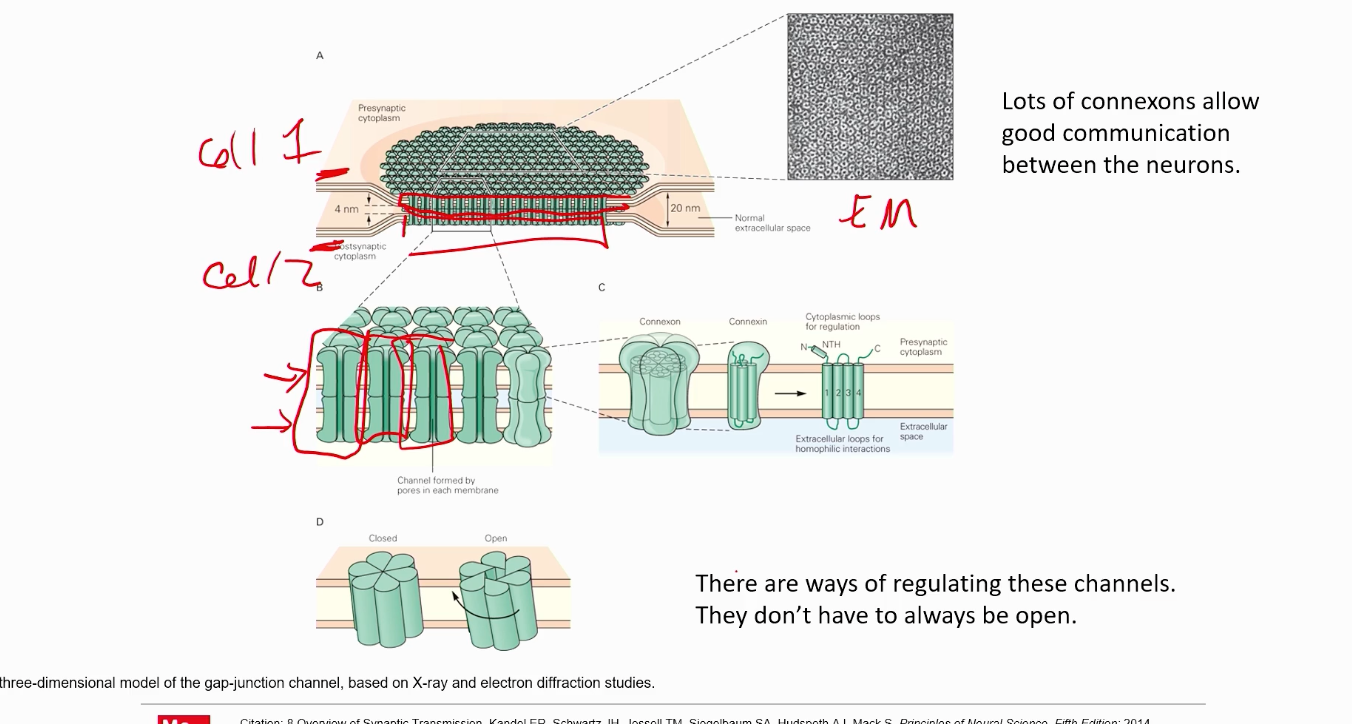
What are gap junctions?
Allow for direct electrical communication between two neurons.
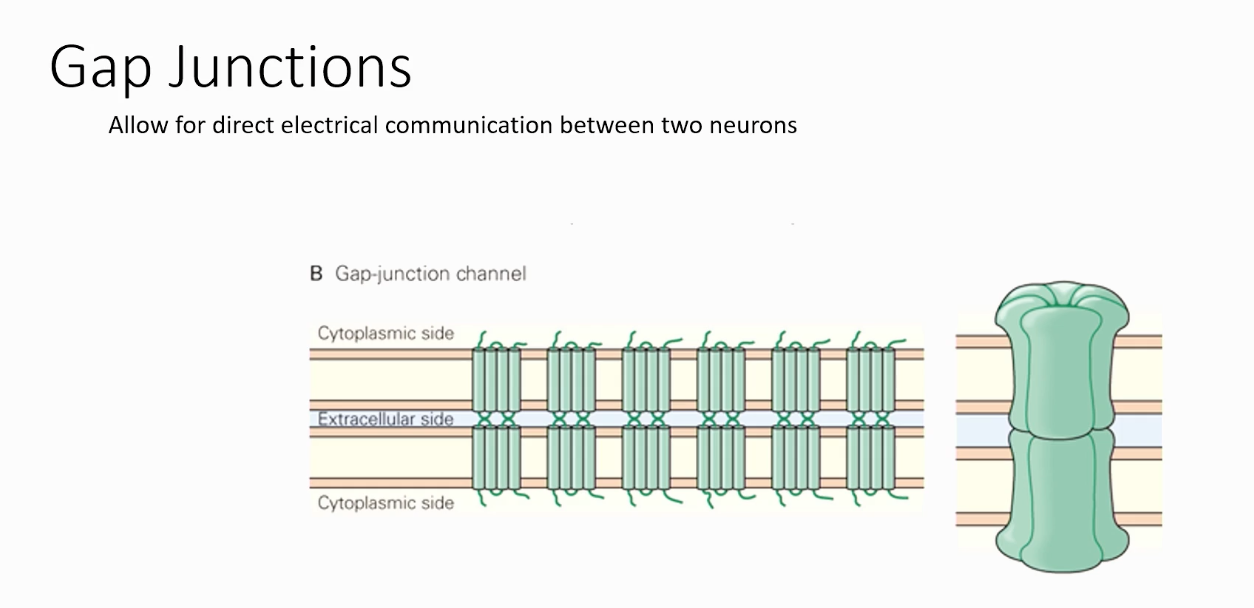
Gap junctions are mediated by pairs of..
Hemichannels
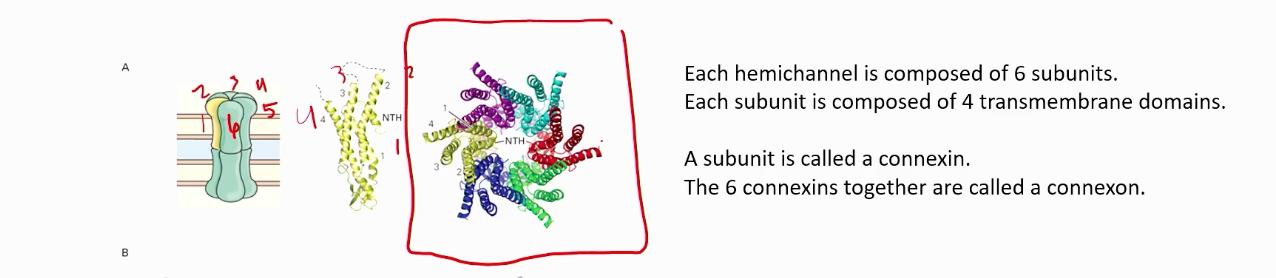
Each hemichannel is composed of __ subunits. Each subunit is composed of __ transmembrane domains.
blank 1: 6
Blank 2: 4
A subunit is called a..?
Connexin
What do 6 connexins form?
A connexon, better known as a hemichannel.
LOTS of connexons allow for what?
Good communication between the neurons
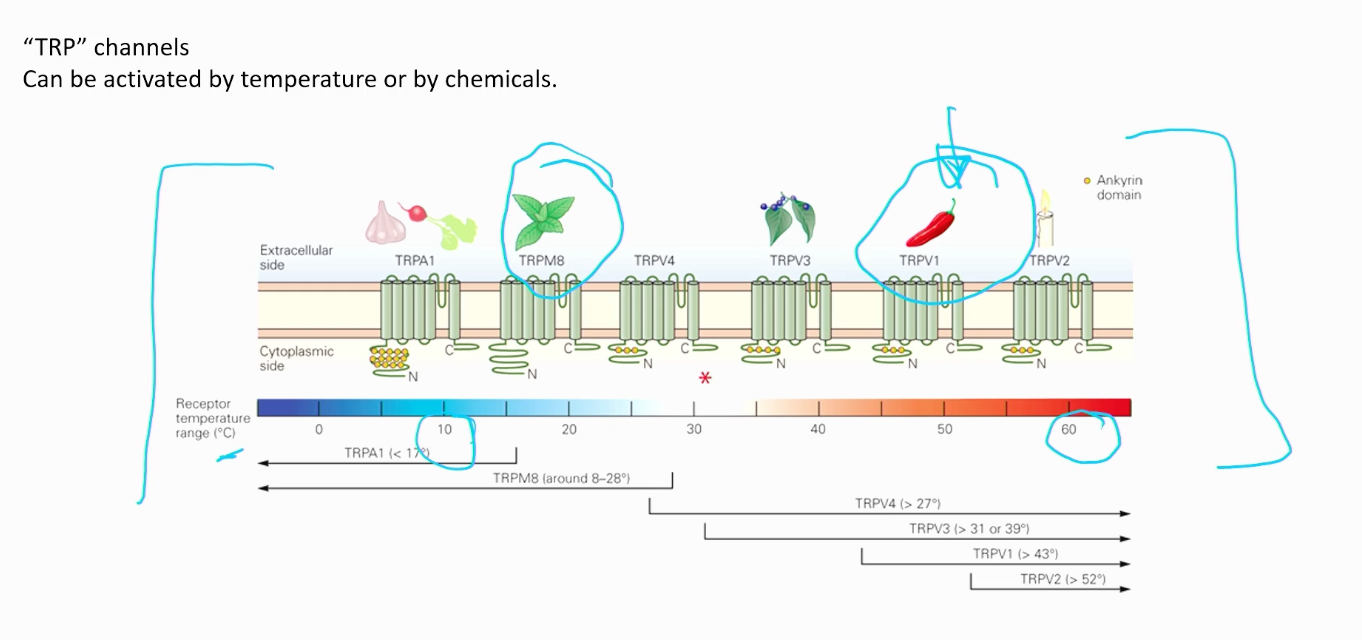
what are “TRP” channels?
Can be activated by temperature or by chemicals. Like when you cut garlic or chillies, it feels like you marinated your fingers when they start burning. These channels basically activate!
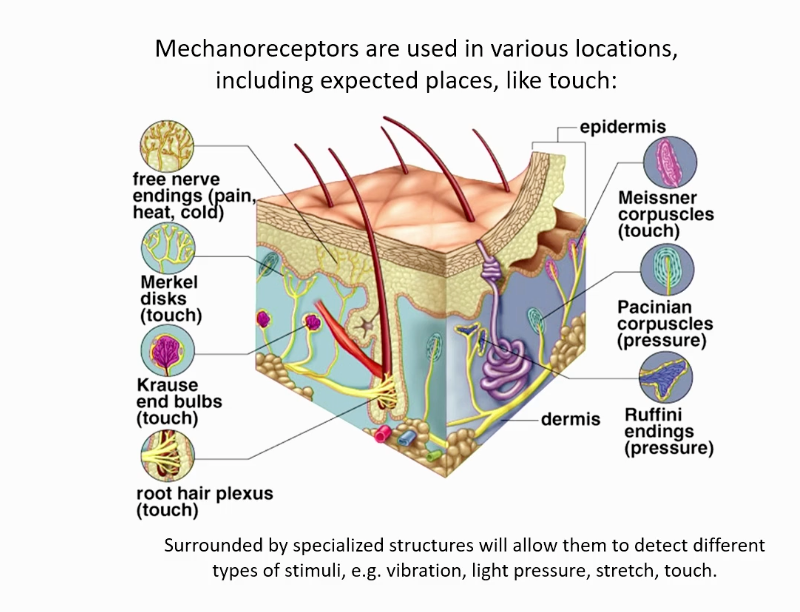
What are mechanoreceptors?
A sense organ or cell that responds to mechanical stimuli such as touch or sound.
The hair cells in our inner ear are important for our overall sense of equilibrium and hearing; these mechanoreceptors are important for the detection of sound waves.
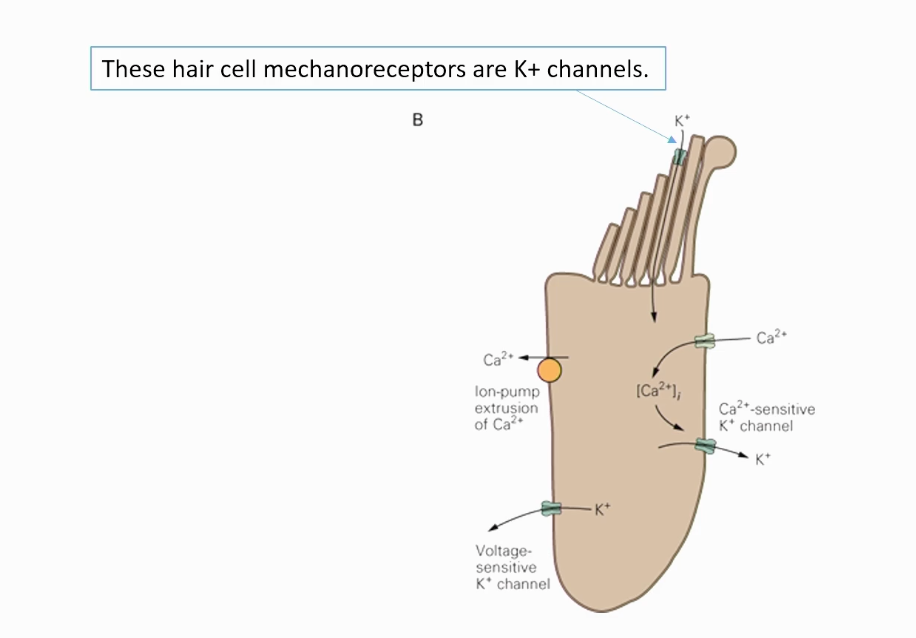
Describe the FULL action potential process for this channel!
we pull on “linkers,” potassium channels open
potassium comes into the cell and depolarizes it
Activates voltage gated calcium channels
potassium channels also open
certain voltage gated potassium channels also help to repolarize the cell