Overview of Minerals & Calcium
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
MINERAL OVERVIEW
what are the major elements (5)
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur
what are the main categories for minerals? (5)
major/macro, trace, possibly essential, probable contaminants, toxic
2 MAIN categories?
major and trace minerals
what are the essential major/macro minerals?
calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, chloride, magnesium.
Essential Minerals require intake of at least
> 100 mg/day
what are the Essential Trace Minerals (9)
Fe, Zn, selenium, manganese, Cu, iodine, molybdenum, cobalt (as B12), chromium
essential trace minerals are needed in how much?
required intake < 100 mg/day
Possibly Essential Trace Minerals (7)
boron, fluoride, nickel, silicon, tin, vanadium, arsenic
Probable Contaminants (6)
aluminum, antimony, bismuth, bromine, lithium, silver
Toxic Elements (3)
cadmium, lead, mercury
minerals can come from (3- not food)
from soils, water, and air
minerals are incorporated into __________, then _____________, and are widely distributed in ________________________________________________
incorporated into plants, then animals, and are widely distributed in whole grains, fruits and vegetables, meat and seafood
individuals on low-calorie diets may rely more on what to meet requirements?
on processing and fortification to meet requirements
Absorption of minerals occurs through what organ
intestine
absorption of minerals is mediated by
mediated by carrier proteins
absorption of minerals is enhanced or inhibited by
composition of diet
absorption of minerals is also affected by
individual and dietary factors
individual factors are _____________ (ex/intrinsic)
intrinsic
dietary factors are _____________ (ex/intrinsic)
extrinsic
Individual Factors are (extrinsic/intrinsic?)
Intrinsic factors which influence mineral bioavailability
Individual Factors examples: (10)
-Nutritional status
-General Health
-Growth
-Pregnancy
-Lactation
-Age
-Physical activity
-Diseases
-Genetic factors
-Inborn errors of metabolism
Dietary Factors are (extrinsic/intrinsic?)
Extrinsic factors that affect bioavailability
extrinsic factors refer to those
we do not control (the chemical process, interactions, comp)
Dietary Factors examples (6)
-presence in foods
-chemical composition
-other minerals
-other nutrients
-other non-nutrients
-processing
CALCIUM
Calcium is the....
5th most abundant element in the human body
What percentage of calcium is found in hard tissue such as bone and teeth?
99%
What percentage of calcium is distributed intra- and extracellularly?
1%
What is the reserve site for calcium in the body?
Bone
What percentage of body weight does calcium represent in the body?
1-2%
primary sources of Ca (food)
Dairy products
calcium also found in
fish with bones (sardines), fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, and legumes
Fortified sources of calcium include
grain products and juices
Some vegetables are good or bad sources?
poor sources
what do some vegetables have that makes them a bad source of Ca?
oxalic acid (inhibit)
Meat and non-fortified grains are good or bad sources?
poor sources
Supplements forms include (6)
carbonate, citrate, lactate, gluconate, acetate, monophosphate
what forms of calcium are predominant in supplements (2)
citrate and gluconate are predominant
Ca ingested as
insoluble salts
If solubilized, calcium can
can bind to other compounds
Average absorption in adults
~25-30%
Paracellular diffusion occurs at what %
~5-20%
Paracellular diffusion of calcium occurs where?
throughout the intestine, but mostly in jejunum and illeum
what does paracellular mean?
between the cells; so does not go from the lumen—> intestinal cell—> blood, but goes between them to get to the blood
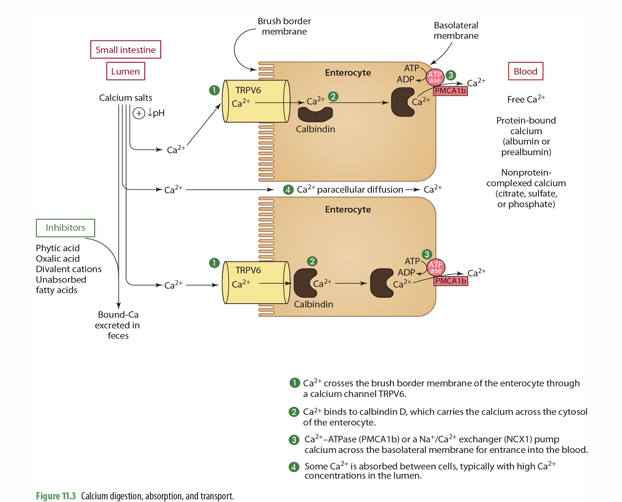
what influences rate of paracellular diffusion of calcium
dietary factor influence rate
How much of calcium is absorbed through active transport? and where?
~80-95% (duodenum and jejunum)
for active transport, Ca binding relies on
a calcium binding protein
Calcium active transport is regulated by ___________, stimulated by _________ & ___________
regulated by calcitriol
stimulated by calcitriol & low-calcium diets
for active transport of calcium, what receptor/transporters does it use to enter enterocyte?
transient receptor potential vallinoid (TRPV6) or calcium transporter 1
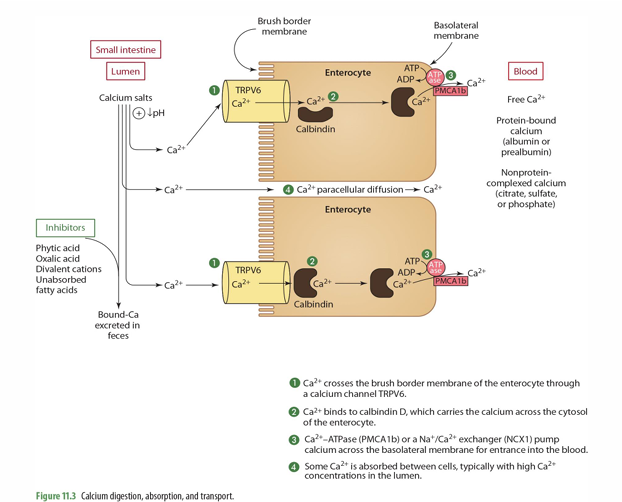
transient receptor potential vallinoid (TRPV6) is what type fo receptor?
cellular receptor
in the enterocyte cytosol, what protein is needed to carry calcium?
vit D dependent calbindin
how is calcium released from the intestinal cell (lumen) into the plasma?
utilizing the vitamin D dependent calcium ATPase pump
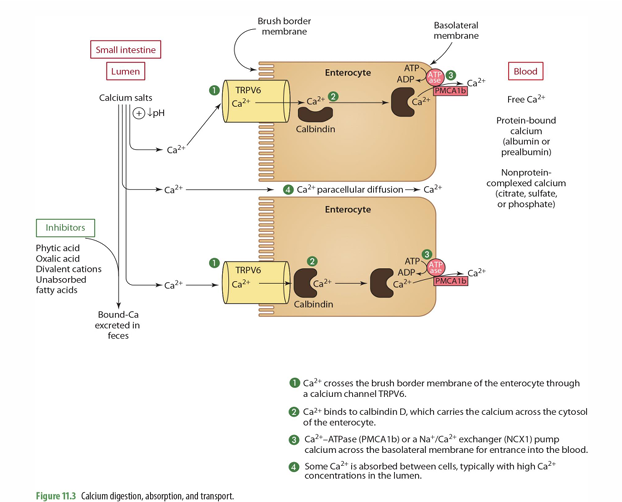
where in the cell is Vit D dependent calcium ATPase pump found?
basolateral membrane
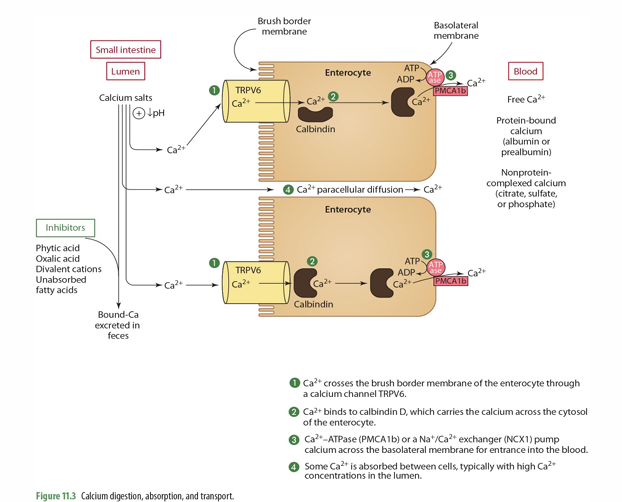
___ and ___ decline during aging resulting in ______ need and recommendation
TRPV6 & calbindin
higher calcium
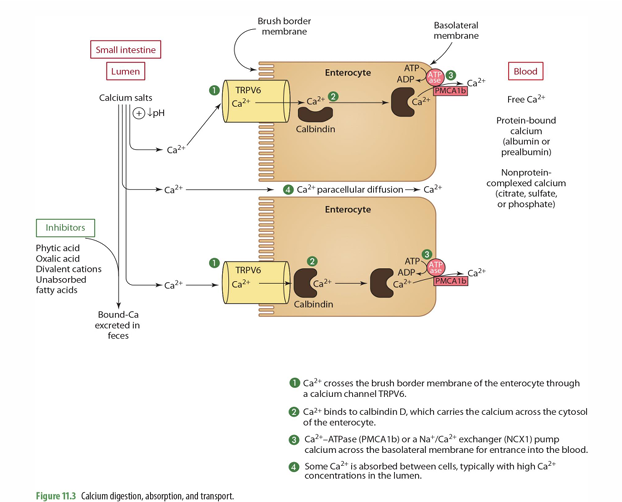
step 1 of Ca absorption: Ca2+ crosses the ____ of the enterocyte through ___________
Brush border membrane
Ca channel TRPV6
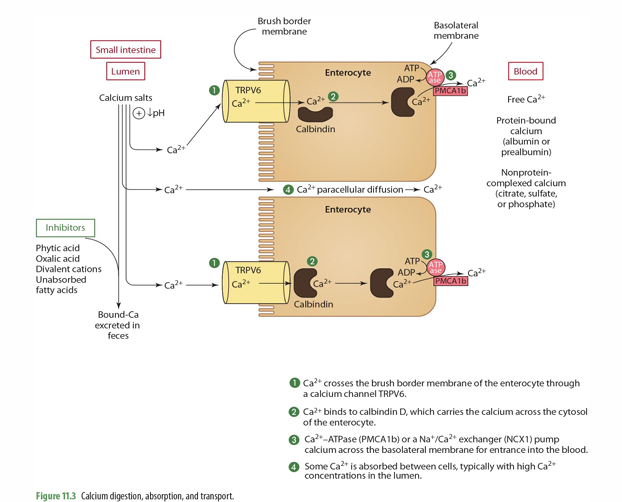
step 2 of Ca absorption: Ca2+ binds to _____, which carries the Ca across the ______
Calbindin D; cytosol
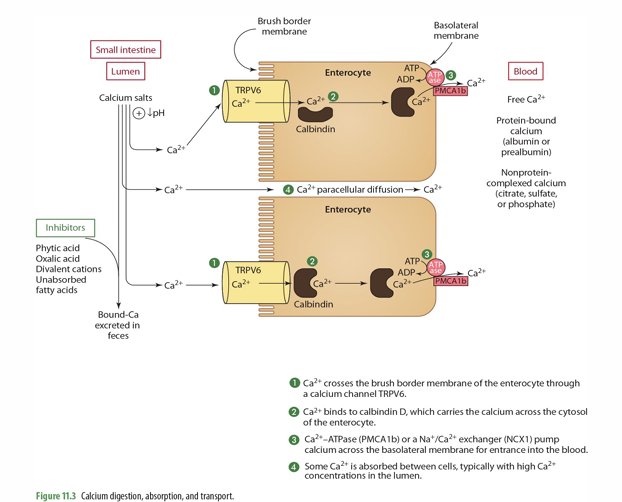
step 3 of Ca absorption: _____ or a ______ pump Ca across the basolateral membrane for entrance into the ____
Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA1b) or a Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1)
blood
step 4 of Ca absorption: Some Ca2+ is _______, typically w/ ___ Ca2+ concentrations in the _____
absorbed between cells (paracellular diffusion)
high
lumen
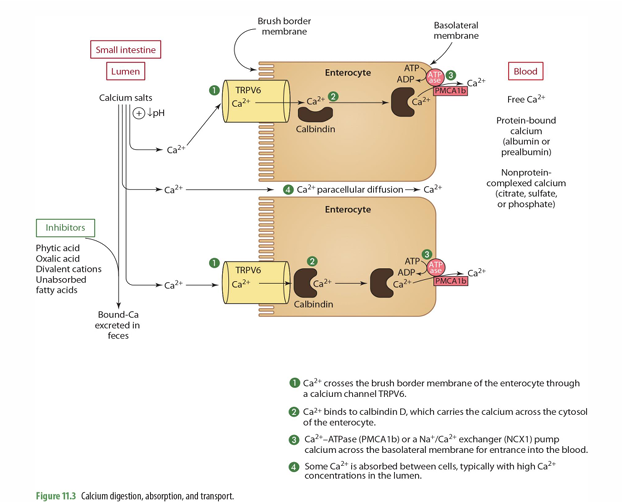
in the blood, what are the 3 forms of calcium that can be found?
Free calcium
Protein bound
Nonprotein complexed calcium
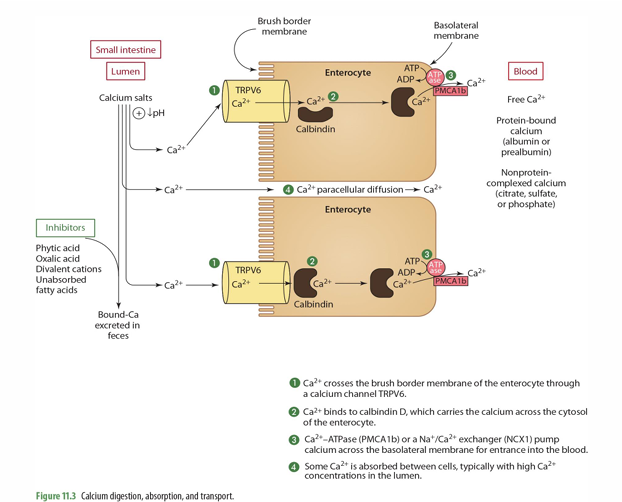
what can inhibit calcium absorption?
Phytic acid
Oxalic acid
Divalent cations
Unabsorbed FA
what is another mechanism of transport calcium can have?
vesicular transport
what do we mean by vesicular Transport
Endocytosis of Ca & vesicles formation.
what is used for vesicular transport of Ca?
vit D dependent rapid response steroid binding protein (MARRS)
what do rapid response steroid binding protein (MARRS) do?
facilitates calcium transport from the basolateral membrane
In the large intestine what can occur
bacteria may release bound calcium from fermentable fibers for colonic absorption
so absorption can also occur in the
colon (but amount is unknown)
what nutrients/substances enhance Ca absorption (3)
vit D (through Calbindin and MARRS)
Sugar & sugar alcohols
Protein
nutrients/substances inhibiting Ca absorption (5)
oxalic acid
Phytic acid
fiber
Excessive divalent cations (Zn & Mg)
unabsorbed FA
Nutrients enhancing urinary Ca excretion (3)
Na
Protein (mainly animal protein)
Caffeine
Nutrients in which absorption may be inhibited by excessive Ca (3)
Phosphorus
Fe
FAs
from intake of 600-800mg of dietary Ca, about __% is absorbed into plasma
30%
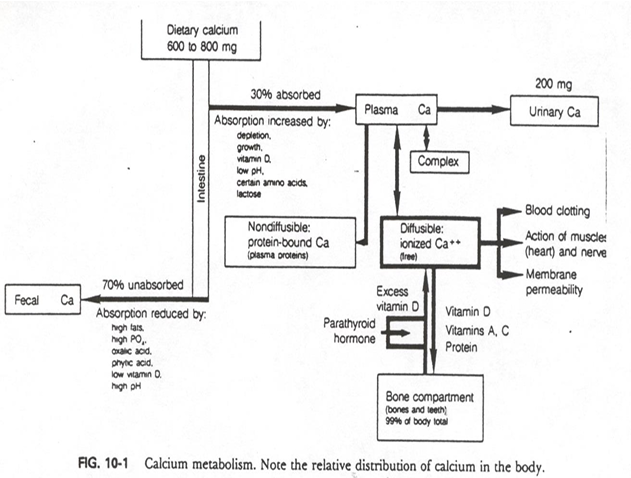
from intake of 600-800mg of dietary Ca, about __% is absorbed into fecal (unabsorbed)
70%
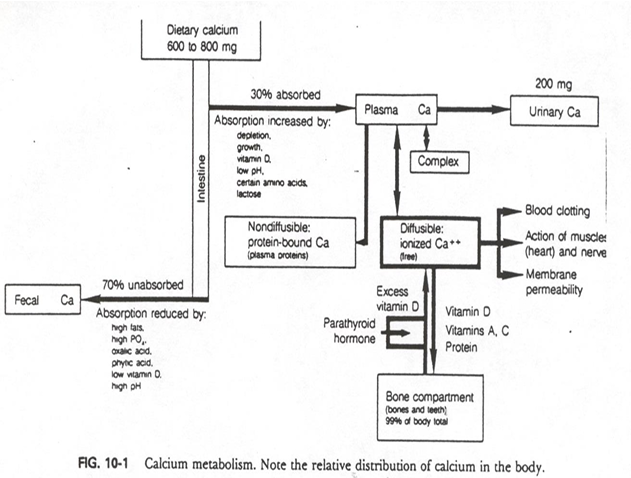
biggest route of excretion of calcium is
fecal
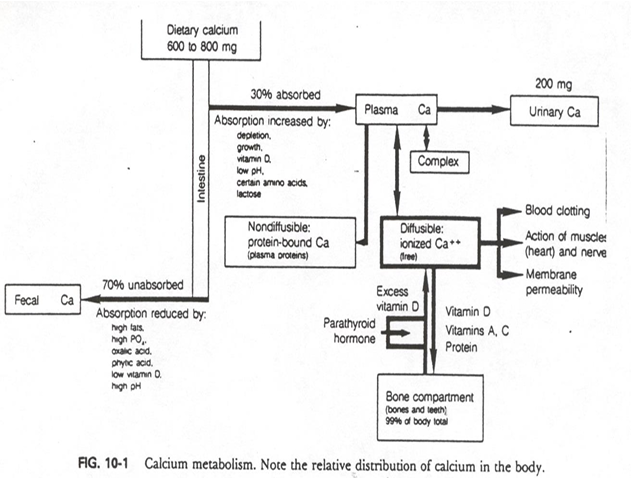
how much of calcium is excreted through urine
about 200mg (small amount)
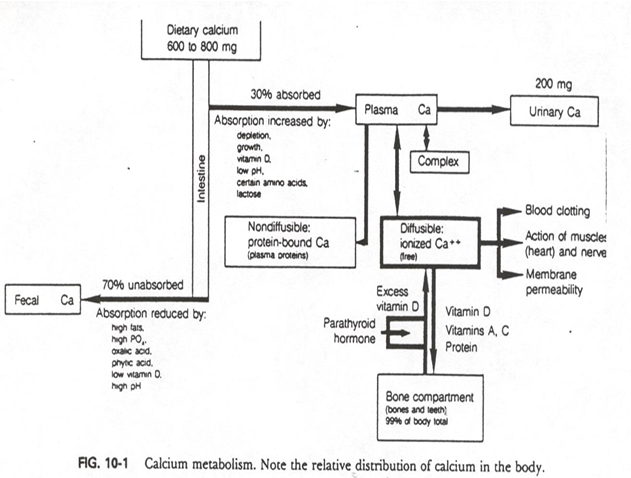
so calcium absorption and retention is
LOW
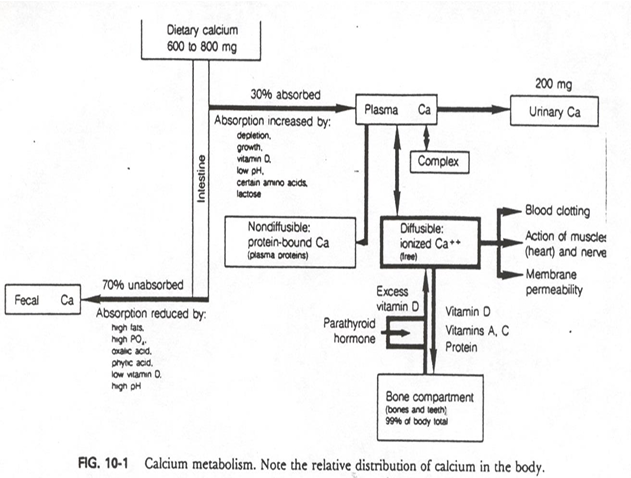
From plasma Ca (calcium absorbed), what can occur to it? (4 options)
- non-diffusible: protein bound
- Diffusible: ionized (free)
- Complex
- Urinary Ca
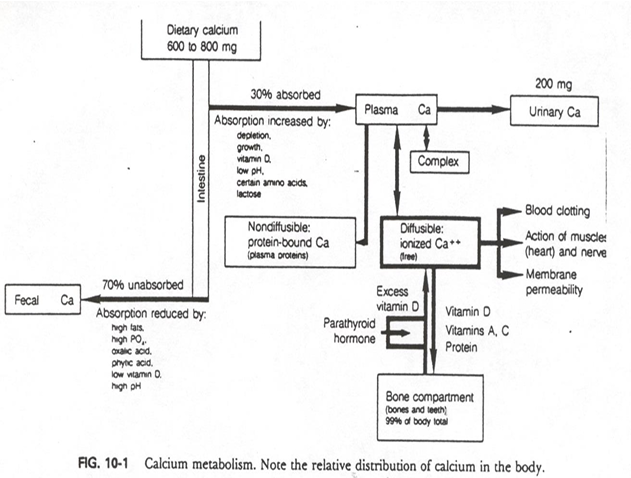
Ca Transport occurs through which 3 methods? (how can calcium be found in the plasma)
binding to proteins (albumin, prealbumin)
complexed w/ sulfate
free form
Regulation of calcium concentrations is based on ______________
extracellular calcium concentration regulation
extracellular calcium concentration regulation uses what? (3)
PTH, Calcitriol, Calcitonin
intracellular calcium concentration regulation refers to
calmodulin
Serum Total Calcium (what is the ideal amount)
8.5-10.5 mg/dL, 10 mg/dL (ideal)
what are the primary regulatory hormones for calcium?
PTH and calcitonin
ionized calcium is critical for
the control of neuromuscular excitability
also in blood clotting factor activation
Decreased Calcium levels may cause .... (3)
irritability, seizures, and cardiac problems
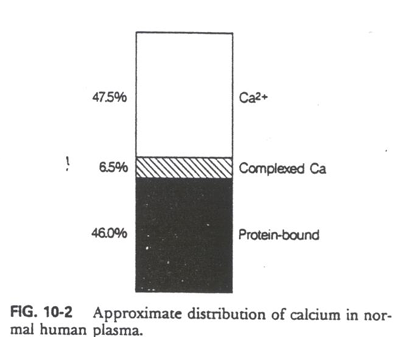
calcium in blood
% as Ca2+ (pre-calcium)
% as complexed Ca
% as protein bound
47.5% as Ca2+
6.5% as complexed Ca
46% as protein bound
Low blood Ca levels signals what to do what?
Parathyroid Gland to release PTH into blood
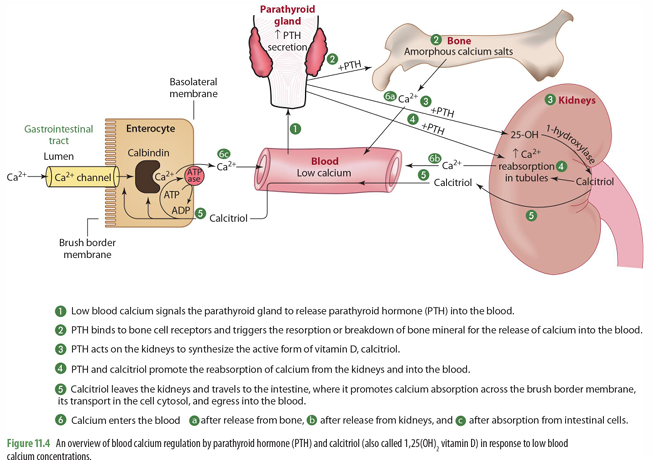
once PTH is released into the blood, what does it do (2)
it binds to bone cell receptors & triggers resorption of bone to release Ca into blood
it goes to kidney to trigger synthesis of 1-hydroxylase for calcitriol synthesis
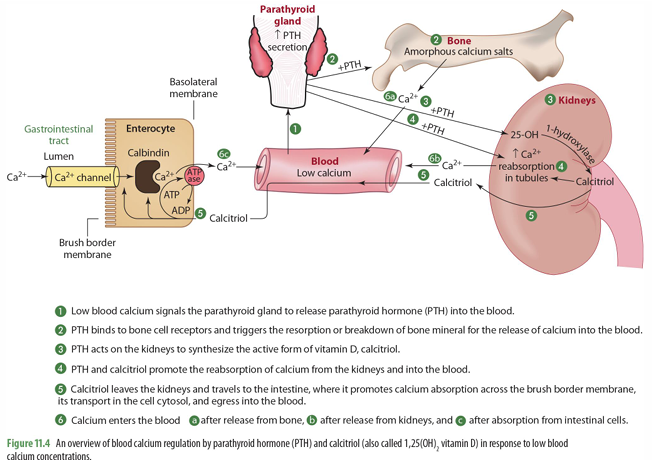
mobilization of calcium in bone means what?
bone moving out of the bone and into the blood (when calcium levels are low)
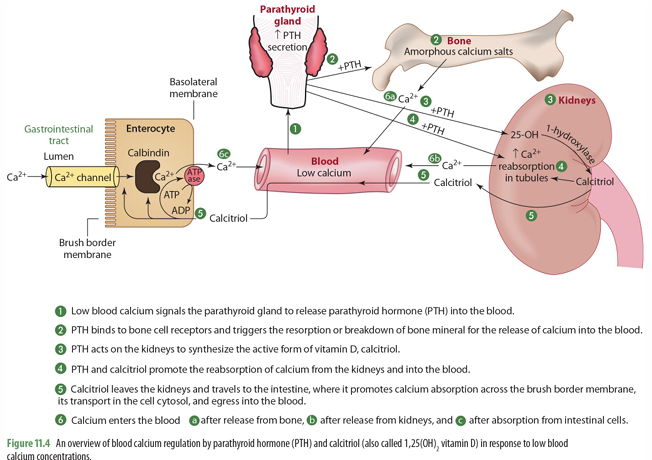
PTH and calcitriol promote
the reabsorption of calcium from the kidneys into the blood
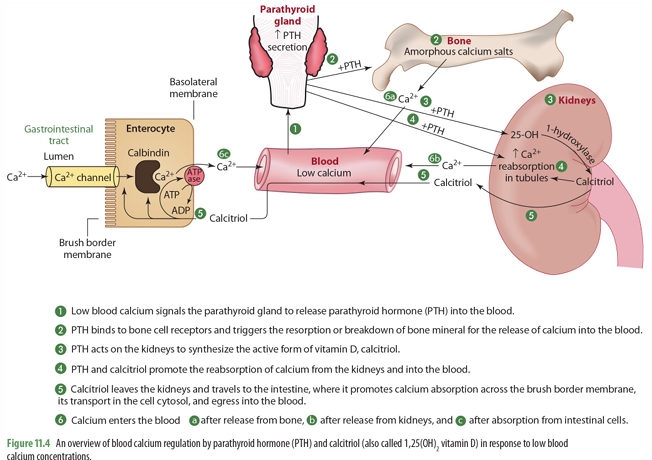
calcitriol made in the kidneys then can do what?
goes to intestines to trigger absorption of calcium across brush border in the SI through calbindin
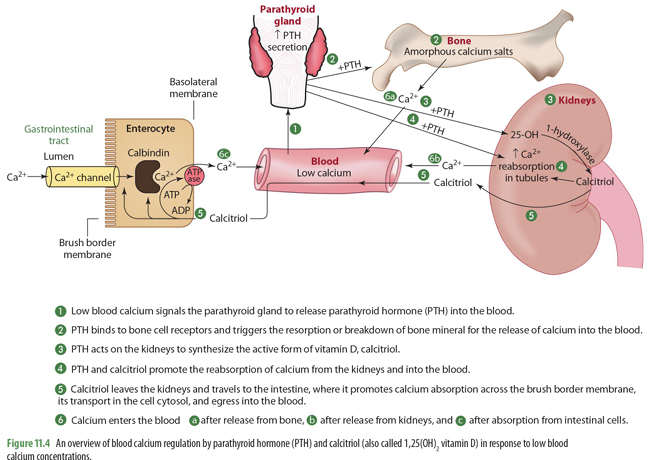
Ca enters blood from what 3 things
release from bone
release from kidneys
absorption from intestinal cells
Hypercalcemia causes what (to regulate levels)-4
•Decreased Ca mobilization from bone
•Increased Calcitonin release to shuttle Ca to skeletal tissue for storage
•Increased renal excretion & decreased reabsorption
•Slows intestinal Ca absorption
when we have hypercalcemia, what is decreases? (bone)
calcium mobilization from bone
when we have hypercalcemia, what occurs in skeletal tissue
Increased calcitonin release to shuttle calcium to skeletal tissue for storage
when we have hypercalcemia, what occurs in the kidneys?
Increased renal excretion and decreased reabsorption
when we have hypercalcemia, what occurs in the intestines?
slowed intestinal absorption of calcium
Intracellular Calcium is ______% compared to extracellular
0.01%
intracellular calcium regulation involves
Cell activation via depolarization, neurotransmitter, and hormones that results in Ca movement into the cell
Channels used in intracellular Ca regulation
voltage gates, ligand gates, and stretch activated