Bio 210 lecutre exam 3
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Transmit signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to muscles or glands, enabling movement and other bodily functions
What is the function of motor neurons?
Muscle tendons that cross the joint help to stabilize joints by keeping tension on tendons. the slight tension or resistance in muscles when they are at rest
What are muscle tones?
Troponin I inhibits the binding of myosin
Troponin T binds to tropomyosin
Troponin C binds to calcium (Ca2+)
What is the function of troponin?
It regulates muscle contraction by physically blocking active sites on actin
What is the function of tropomyosin?
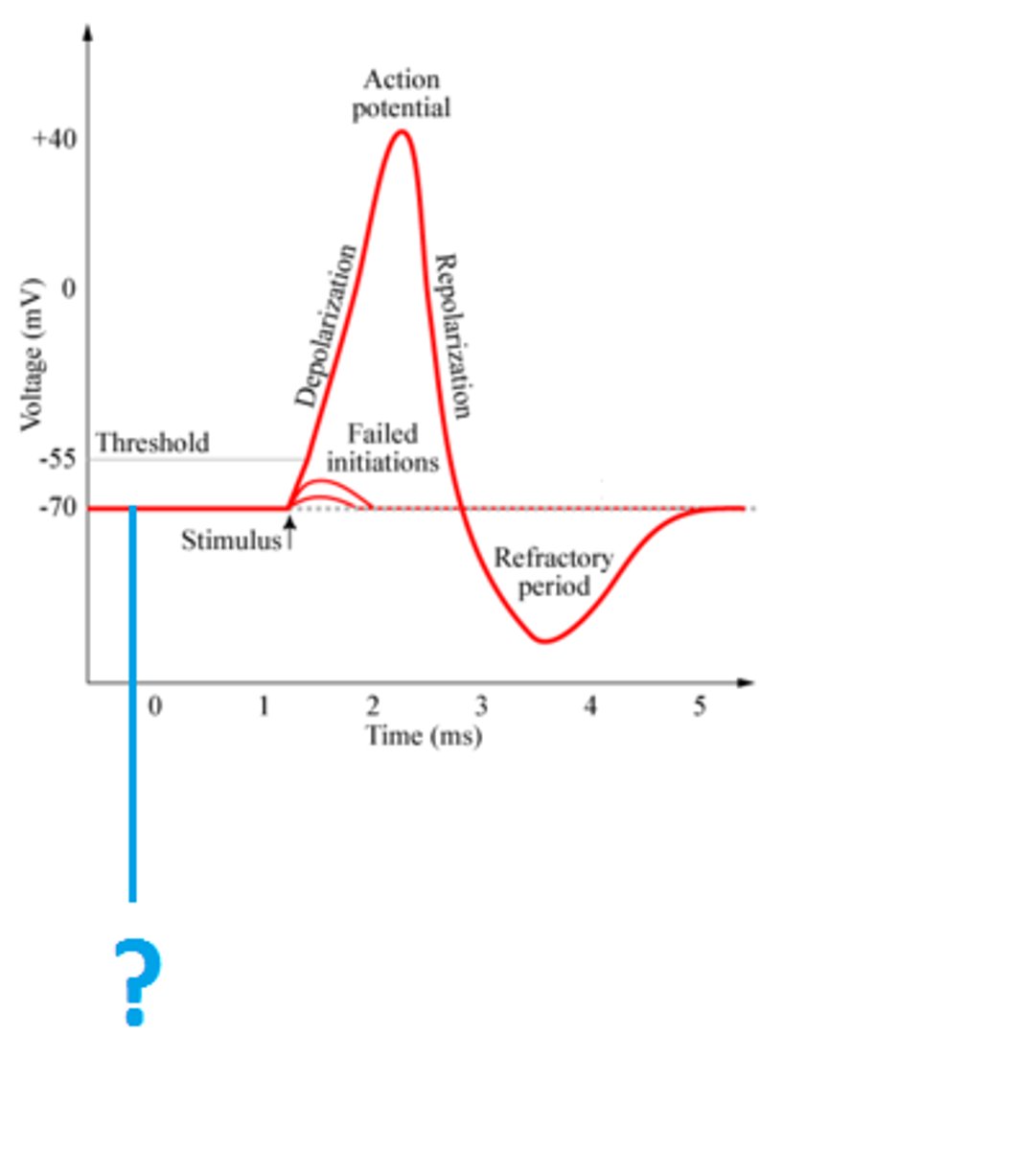
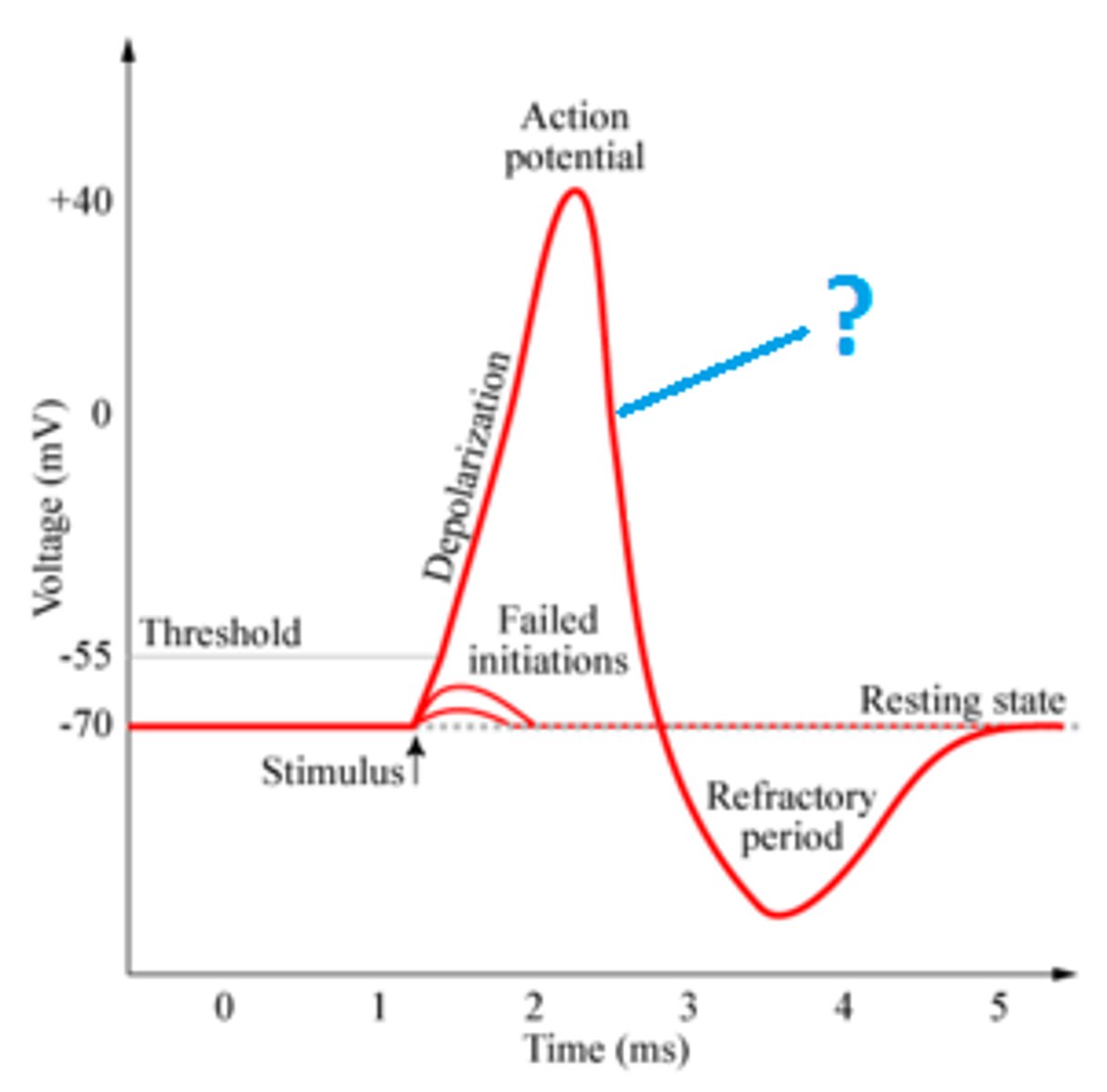
Resting membrane potential (-70 mV)
Identify
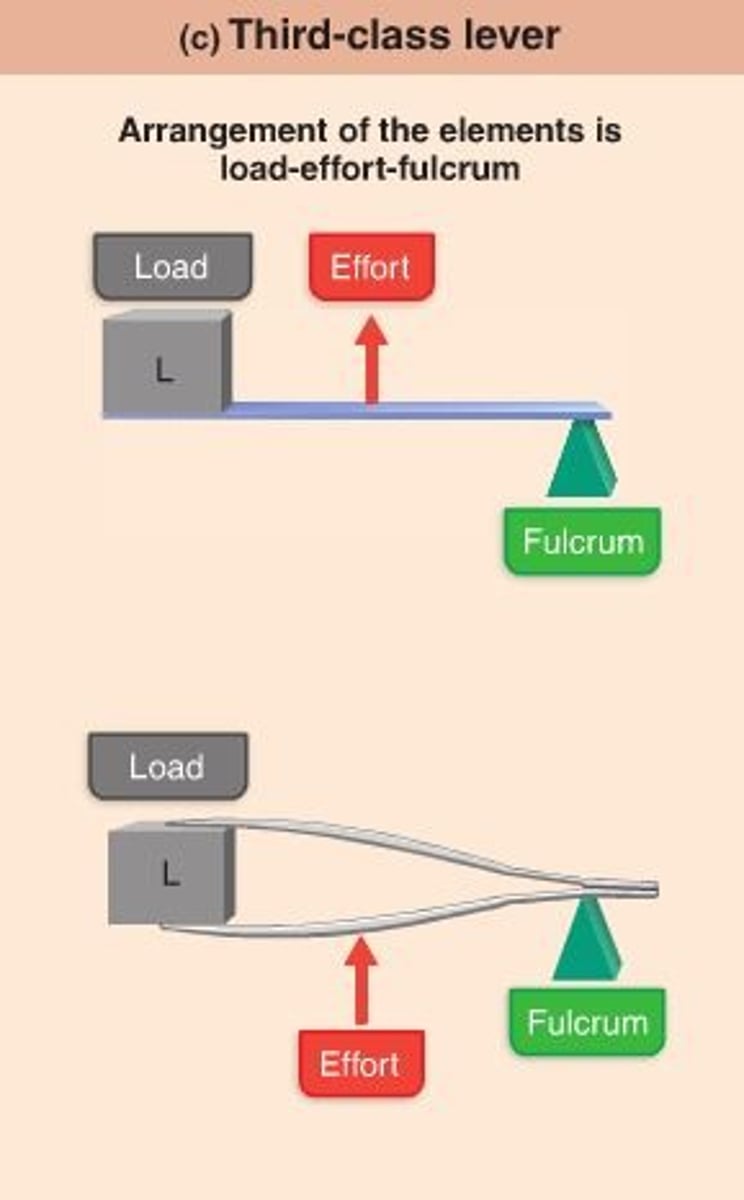
Third class lever (Effort applied between fulcrum and load)
Identify
inflammatory disease often resulting in joint pain
What is lyme disease?
Hip joint
What is the name of the joint that uses the acetabulum?
Filament arrangement gives skeletal muscle striations (thin and thick) (actin and myosin)
What produces striations in skeletal muscle cells?
Calmodulin
Calcium activates what protein in smooth muscle contraction?
Myoblasts
What type of embryological cell gives rise to muscle fibers?
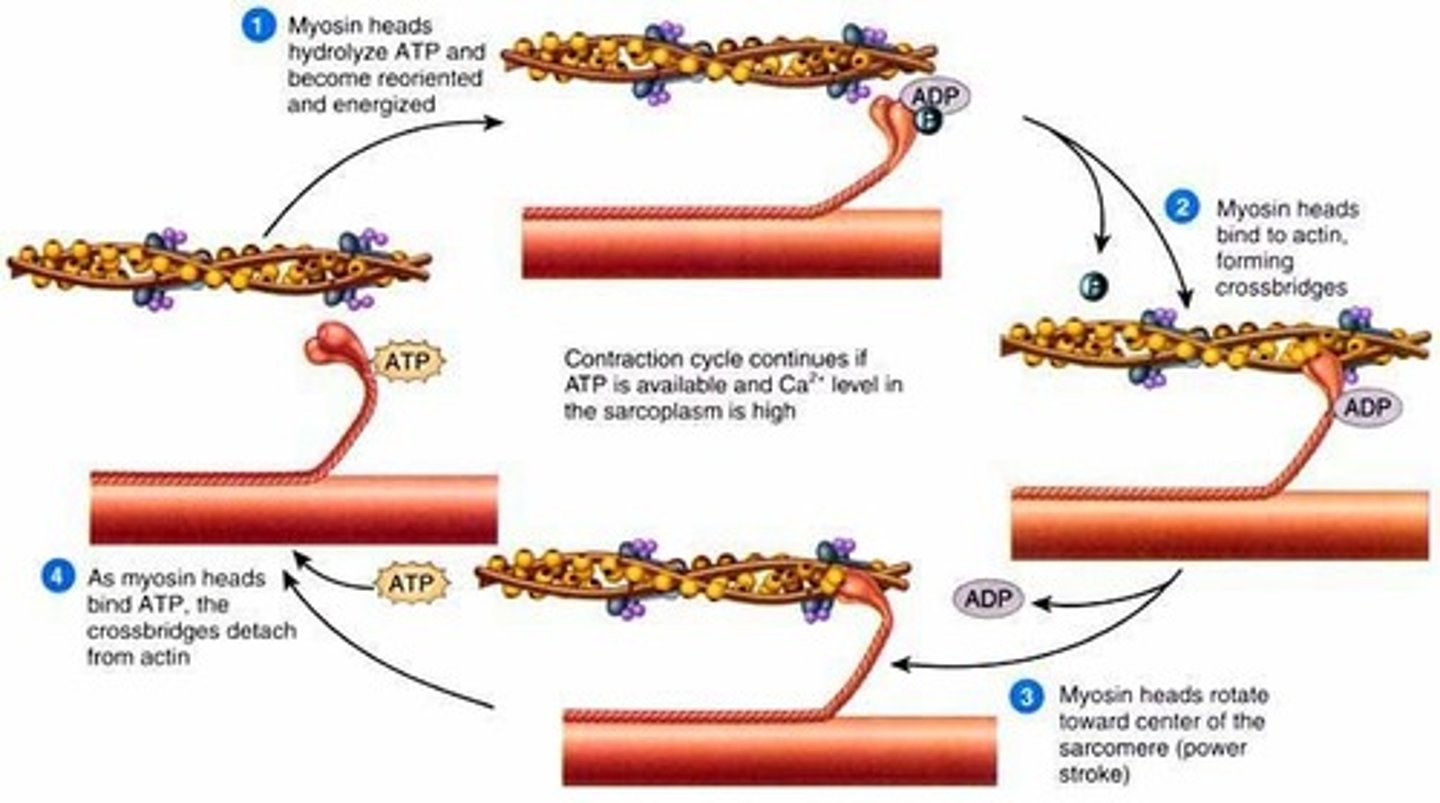
view image
What are the steps in muscle contraction?
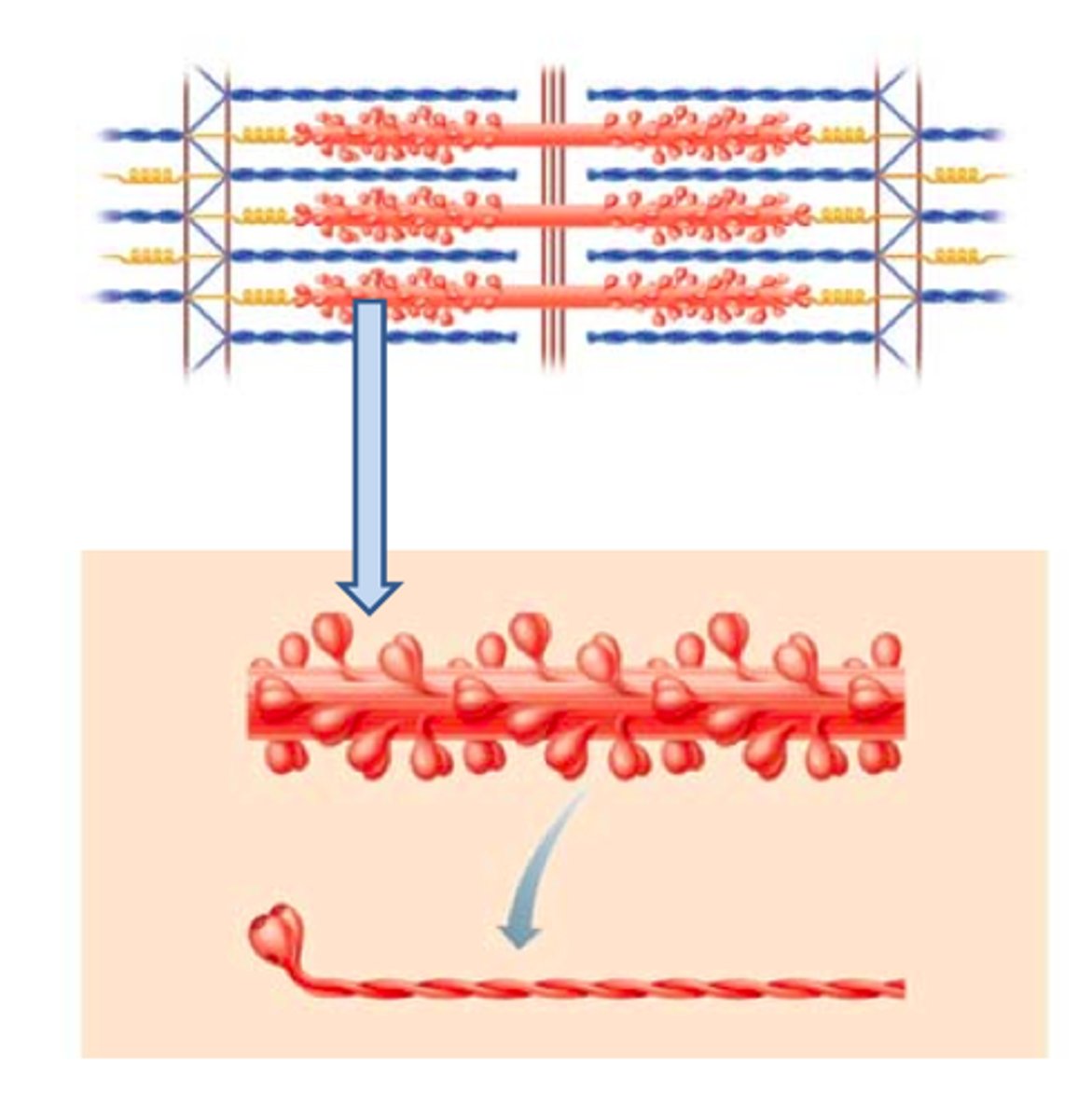
Thick filament
Identify
ACh
What is an example of neurotransmitters?
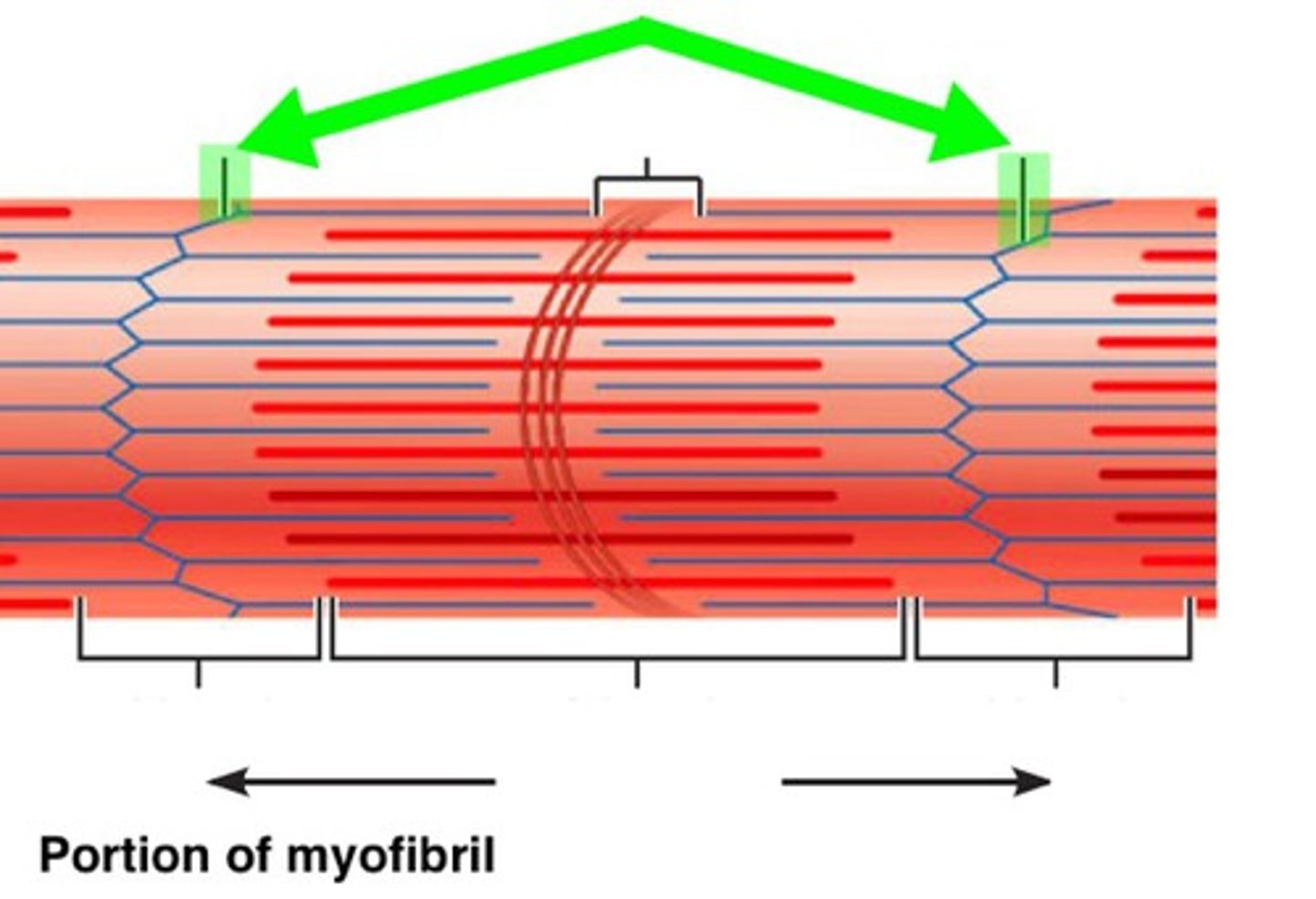
Z line (disc)
Identify
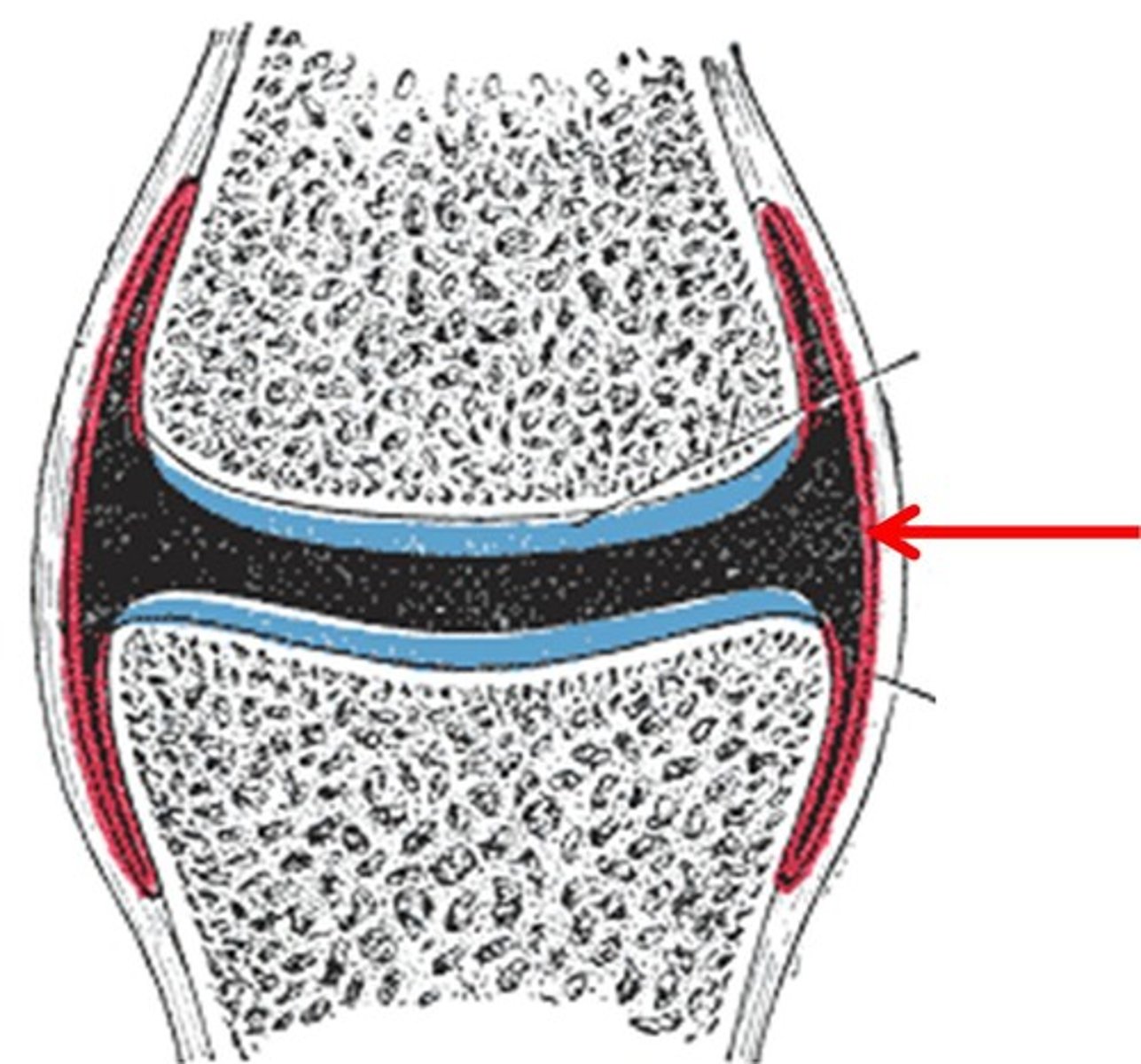
Synovial membrane
Identify
Internal dome-shaped muscle that physically separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
What is a diaphragm?
Physiological inability to contract despite continued stimulation
What is muscle fatigue?
elongated bursa wrapped around a tendon
What is a tendon sheath?
It is when the myosin head pivots and pulls thin filament toward M line
What is a power stroke?
Repolarization
Identify
Axon terminal of neurons
Where are synaptic vesicles located?
The stiffening of muscles with weak rigidity that occurs after death
What is rigor mortis?
ATP and Ca2+ (calcium ions)
Contraction and excitation requires what substances?
act as tracks for myosin thick filaments to slide along, shortening the muscle.
What is the function of actin filaments during muscle contraction?
Responsible for the rhythmic contractions of the heart, which pump blood throughout the body
What is the function of cardiac muscles?
Stabilize the knee joint by preventing excessive forward and backward movement of the tibia (shinbone) relative to the femur (thighbone)
What is the function of the cruciate ligament of the knee?
Glenohumeral joint
What joint is stabilized by the glenohumeral ligament?
Junctional folds
What part of the sarcolemma contains acetylcholine receptors?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is the name of the structure in skeletal muscle cells that functions in calcium storage?
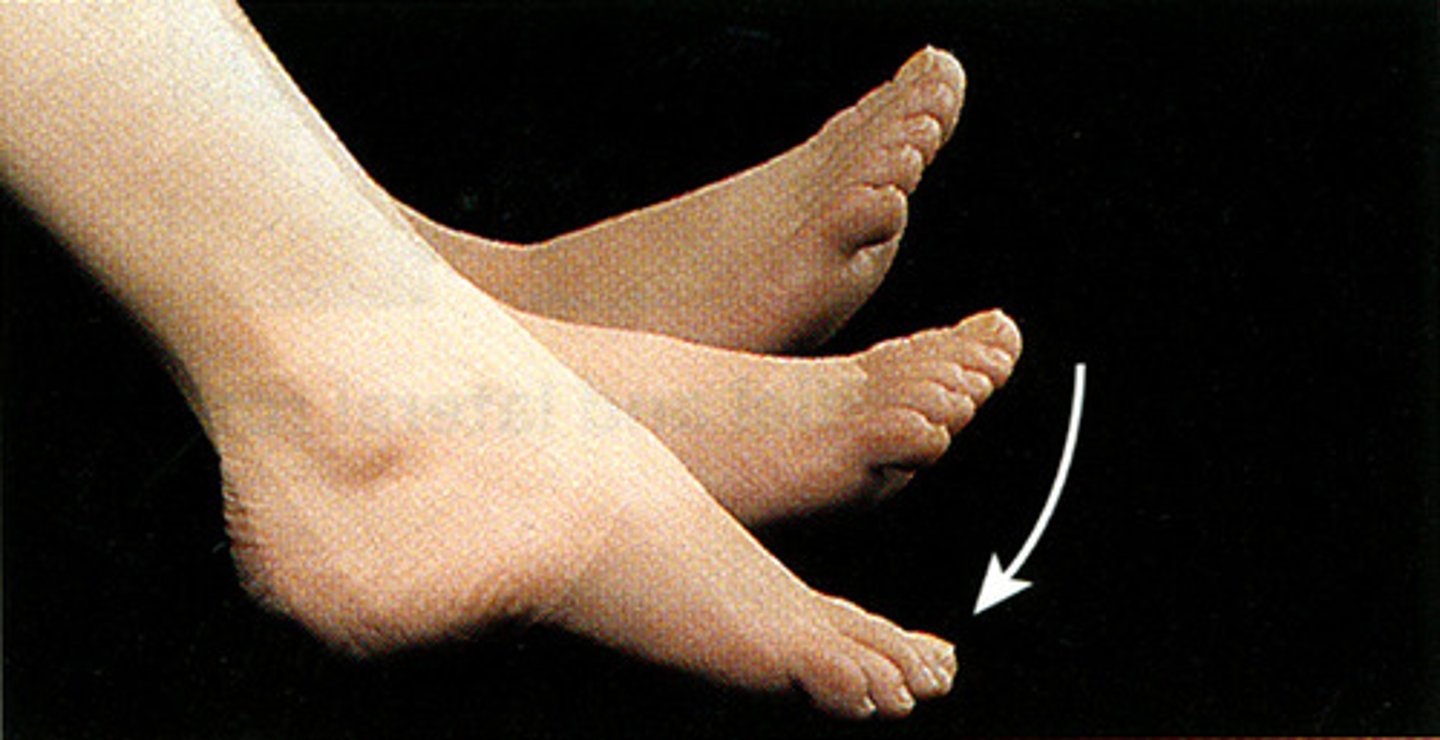
the movement of pointing your foot and toes downward, away from your leg
What is plantar flexion?
Enables the interaction between the proteins actin and myosin
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
Contract fast using anaerobic metabolism. Have large stores of glycogen, few capillaries & mitochondria, little myoglobin. designed for short, powerful, and quick bursts of movement.
What is the function of fast glycolytic fibers?
Movement away from the midline
What is abduciton movement?
regulate muscle contraction by blocking the binding sites on actin filaments when the muscle is at rest, preventing myosin from interacting with actin and causing contraction.
What is the role of tropomyosin in skeletal muscle contraction?
Elongated spindle shaped cells arranged in sheets
- Cell diameter size = 5-10 um
- Cell length = 30-200 um
• Has no sarcomeres; no striations
• Has gap junctions
• Contains 16X more actin than myosin
- Allows greater stretching and contracting
What are the characteristics of smooth muscles?
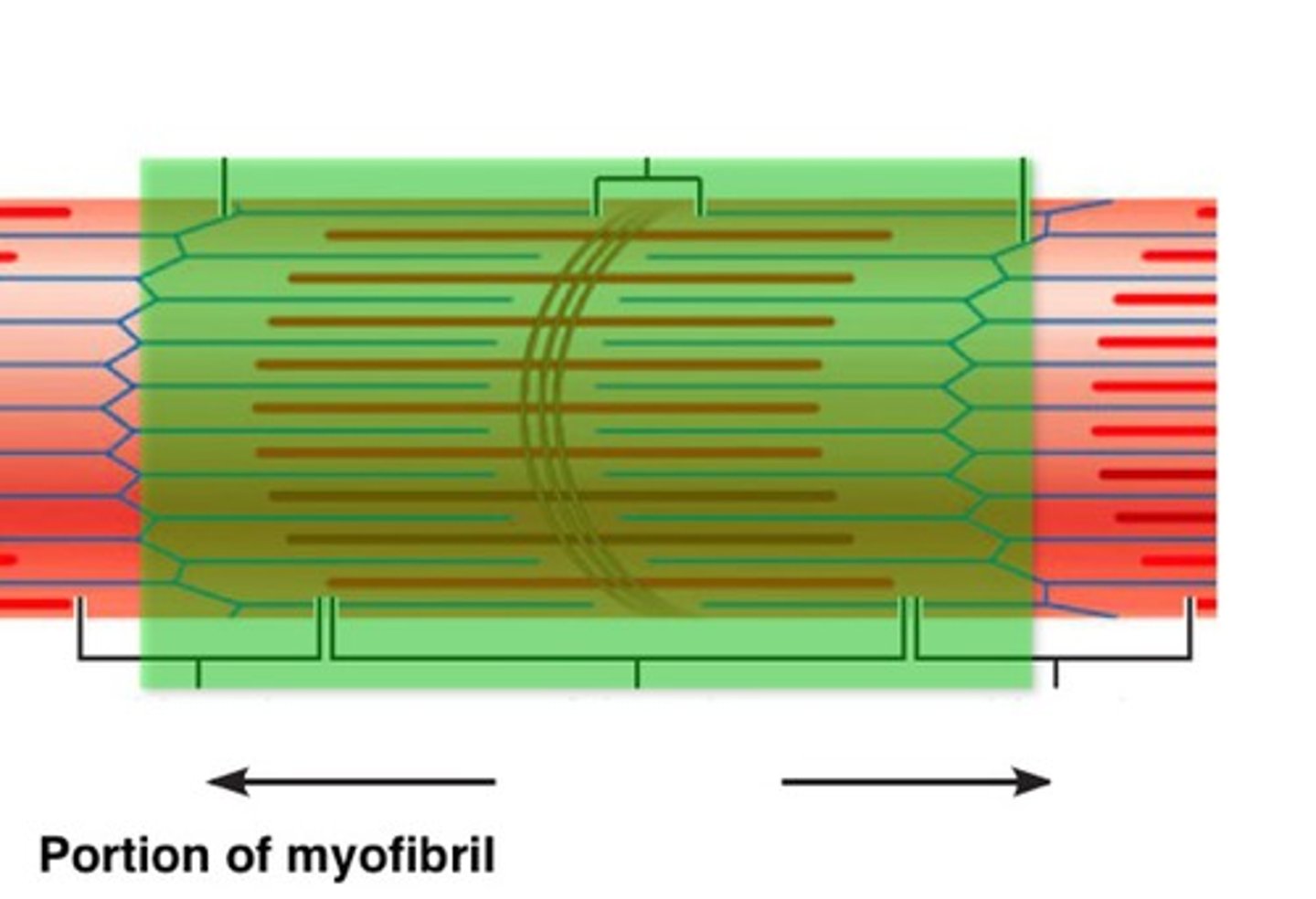
A region between two successive Z discs
What is a sarcomere?
Used for mastication (chewing); elevates & protracts the mandible
What is the function of the masseter?
Holds food between teeth; compresses cheek for whistling and sucking
What is the function of the buccinator?
Smooth muscle cells
What is the name of the muscle cell that has greatest ability to regenerate
Lines the appositional surfaces of the articulating bones and avoids direct bone-to-bone contact during compression of joints
What is the function of articular cartilages?
movement toward the midline
What is adduction movement
The innermost layer that surrounds and electrically insulates each muscle fiber
What is the function of the endomysium?
The mechanism for contraction is explained by the sliding filament theory (model). Muscle fibers contract by the interaction between thin and thick filaments within each sarcomere
What is the sliding filament model of contraction?
Flexes hip joint/thigh. Flexes & laterally rotates the thigh. Flexes & medially rotates the leg. Helps us sit cross-legged
What is the function of the sartorius muscle?
Lubricates and nourishes articular cartilage and acts as a shock absorber during compression of the joint
What is the function of the synovial fluid?
A type of joint in the human body that allows for very little or no movement
What are synarthrotic joints?
articulation between bodies of adjacent vertebrae and diarthrotic articulation between articular processes. Slightly movable joints
What are amphiarthrotic articulations?
Hyaluronic acid
What acid is found in the synovial fluid?
movement beyond the anatomical position
What is hyperextension movement?
Plane joint
Gliding motion in your wrist uses what joint?
share the fundamental ability to contract and use the proteins actin and myosin to generate force.
Compare the functions of skeletal and smooth muscles
The axon terminal of a motor neuron
In muscle contraction acetylcholine is stimulated from where?
O2 storage molecule and gives fibers their red color
What is the function of myoglobin?
a type of skeletal muscle where the muscle fibers (fascicles) run parallel to the long axis of the muscle
What are parallel muscles?
Fibrocartilage separates articular surfaces to improve "fit" of bone ends, stabilize joint, and reduce wear and tear
What are menisci?
It is the fine, delicate, extensible membrane surrounding each muscle fiber
What is sarcolemma?
Common, irreversible,degenerative (''wear-and-tear'') arthritis
What is osteoarthritis?
Peg-in-socket joints of the teeth in alveolar sockets of mandible and maxilla
What is gomphosis?
Bursitis
Inflammation of a bursa due to injury or friction
Diplopia
Double vision
Ptosis
Dropping or falling of upper or lower eyelid
Subluxation
Partial dislocation of a joint
Rheumatoid arthritis
A chronic inflammatory disorder
Temporomandibular junction
Diarthrotic, hinge joint between head (condyle) of mandible and temporal bone of skull.
Isometric contraction
no shortening; muscle tension increases but does not exceed load
Isotonic contraction
muscle shortens because muscle tension exceeds load
Gouty arthritis
Uric acid build-up that causes pain in joints
Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS)
A chronic pain disorder that affects the muscles and fascia (the connective tissue surrounding muscles). Bands of muscle fibers tighten and contract after the skin is stimulated; may produce goose bumps,sweating, flushing of the skin; affects 50% of people in 30-60 yr age range.
Treatment - massage,muscle stretching,NSAIDs
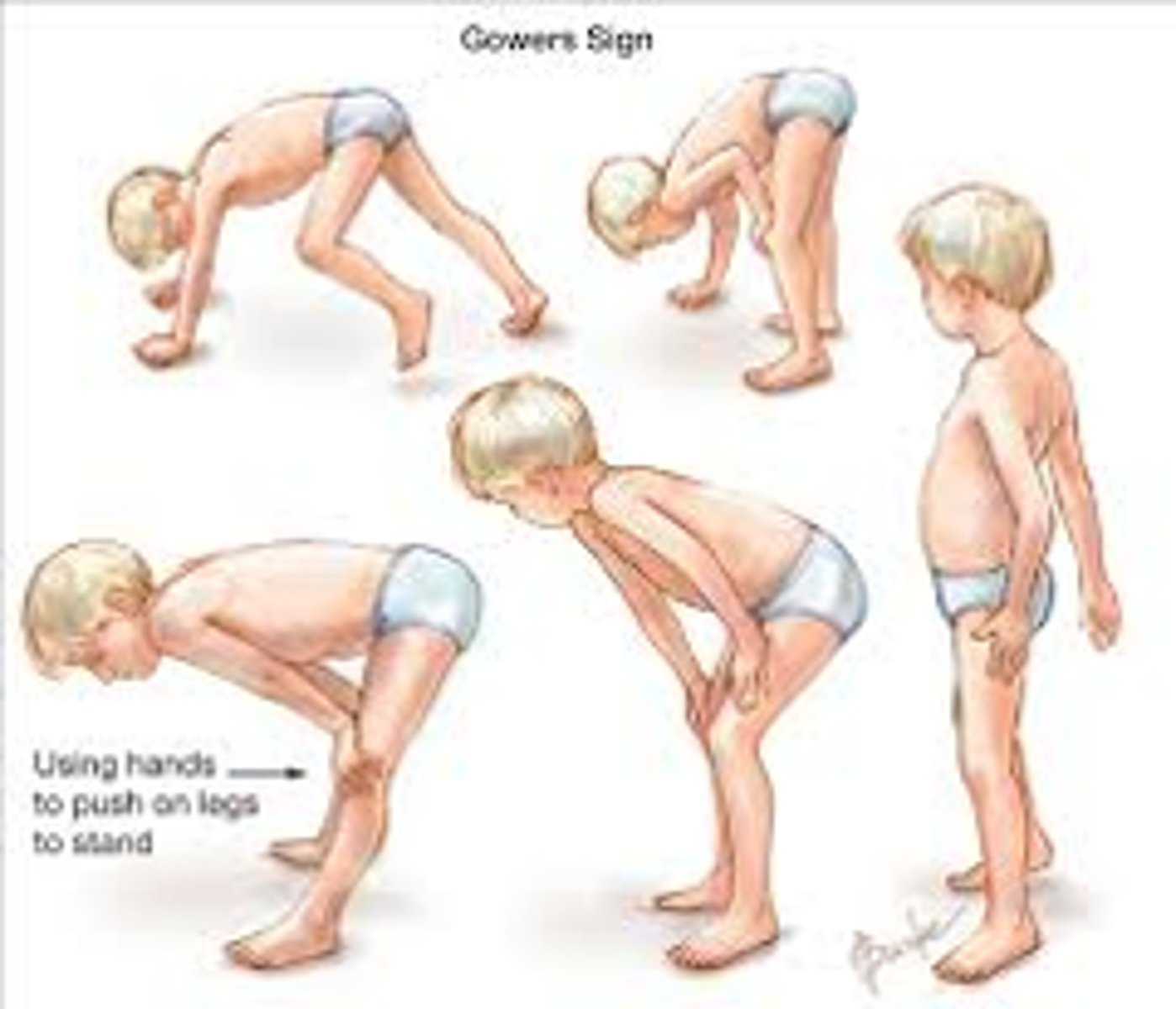
Gower's maneuver
a physical examination finding where a person uses their hands to "walk" up their own body to stand from a prone or squatting position
Dysarthria
a motor speech disorder that results from impaired muscle movement in the face, mouth, and respiratory system, affecting speech clarity and intelligibility
Sarcopenia
age-related loss of skeletal muscle mass, strength, and function
Glycolysis
a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to produce 2 pyruvic acid molecules. Produces ATP. Anaerobic.
Myasthenia gravis
a chronic neuromuscular disease that causes weakness in the voluntary muscles. Antibodies attack the neuromuscular junctions and bind up ACh receptors so muscles cannot be stimulated.
Fibromyalgia
Syndrome of chronic severe pain in muscles & skeleton
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)
One of the most severe forms of inherited muscular dystrophies. Genetic disorder and causes progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
Origin of muscle
point of attachment to bone that does not move
Convergent fascicles
A muscle fiber arrangement where fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers) originate over a broad area and converge towards a single tendon or aponeurosis (a sheet-like tendon)
Parallel fascicles
Where fascicles run parallel to the long axis of the muscle. Ex) biceps brachii and sternocleidomastoid
Creatine phosphate
a high-energy molecule stored in muscles that plays a crucial role in rapid energy production for muscle contraction. Plays a role in the direct phosphorylation of ADP.