GCSE CHEMISTRY - PERIODIC TABLE
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is the atomic number
the number of protons in an atom
what is the atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
how to work out the amount of electrons in an atom
look at the atomic number
how was the first table of elements ordered
by atomic mass
what was the problem with the first table of elements
they were grouped inappropriately
How was Mendeleev's periodic table arranged
by increasing atomic mass
How was Mendeleev's periodic table grouped
by chemical properties
How is the modern periodic table arranged?
by increasing atomic mass
how is the modern periodic table grouped
by number of electrons
What are the group one metals
alkali metals
What is a property of group 1 metals regarding their hardness?
They are soft and can be cut with a scalpel.
How do group 1 metals react with water?
They are highly reactive, even with cold water.
What is the melting point characteristic of group 1 metals?
They have low melting points compared to most other metals.
How does reactivity change in group 1 metals?
Reactivity increases as you go down the group.
What is the physical state of group 1 metals at room temperature?
They are solid at room temperature.
How many electrons do group 1 metals have in their outer shell?
They have 1 electron in the outer shell.
What is the density characteristic of group 1 metals?
They have low density.
What color are the compounds formed by group 1 metals?
The compounds are white.
What type of ions do group 1 metals form?
They form 1+ ions.
Are group 1 metals useful as catalysts?
Yes, they are useful as catalysts.
when group one metals react what happens
they lose an electron from the outer shell
An ionic compound is formed
definition of malleable
able to be hammered or pressed permanently out of shape without breaking or cracking.
definition of ductile
a material that can be pulled out into a long wire
transition metals properties
-Dense
-Form coloured compounds
-High melting pts
-Act as catalysts to speed up reactions
-Not very reactive
-Form ionic compounds
-Form different ions
flame tests
lithium - crimson
sodium - orange
potassium - lilac
calcium - orange
copper - green
ion tests
zinc - white
cobalt - blue
magnesium - white
copper - blue
iron (ii) - green
iron (iii) - red, brown
how to store group 1 metals
in oil to stop it reacting
what is the reactivity series
A list of elements ordered by their reactivity
the reactivity series
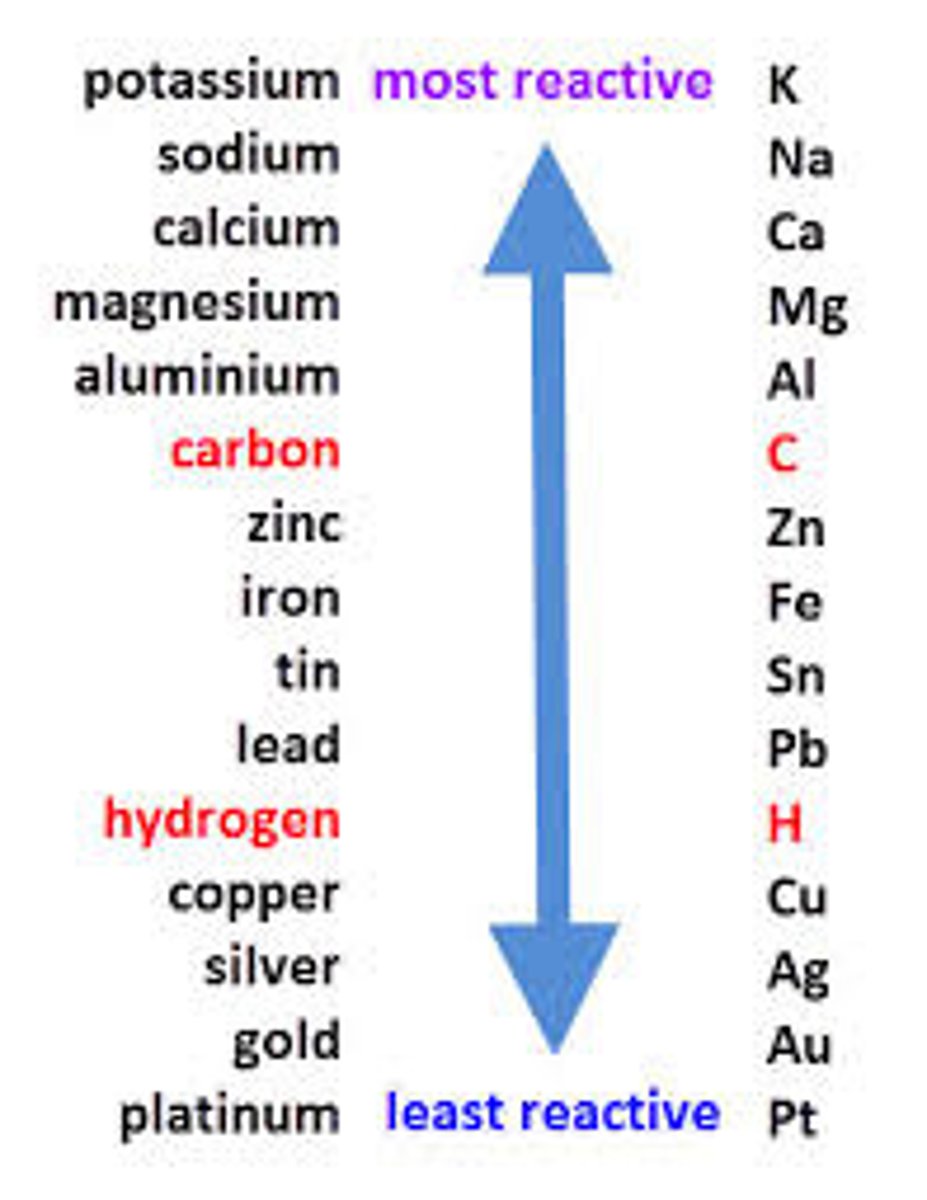
what is displacement reaction
A reaction in which a more reactive element takes the place of a less reactive element in a compound
what does OILRIG stand for
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
what is reduction
gain of electrons, loss of oxygen
what is oxidation
Loss of electrons, gain of oxygen
what are group 7 elements called
Halogens (non-metals)
what are the halogens' properties
they naturally occur in pairs
boiling points become higher down the group (diatomic)
what compound is formed when halogens react
halide ions
what are the group 0 elements
noble gases
group 0 propeties
gas at room temperature
unreactive
outer shell is completely full
not flammable
The boiling point goes higher down the group
what is an ionic compound
A compound that consists of positive and negative ions
What a covalent compounds
substances formed when atoms, typically non-metals, share electrons to create strong chemical bonds