ECON 248 5.4 Real Vs. Nominal GDP
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
One of the outcomes of total spending rising is that the economy is () a larger () of goods.
Producing, Amount
One of the outcomes of total spending rising is that goods and services are being sold at ().
Higher Prices
The value of all produced goods and services at their current prices.
Nominal GDP
A form of calculating GDP where the prices of the base year are used, while the quantities of a different year are used. Due to this, the prices we use to calculate it are always fixed, but the quantities change based on the year.
Real GDP
Since real GDP mainly relies on the amounts of goods being produced, and not differing price levels, it gives us better () into the economy’s ability to satisfy needs and desires than Nominal GDP.
Insight
An equation of GDP which reflects the prices of goods and services but not the quantities produced.
GDP Deflator
GDP Deflator is calculated as following.
(Nominal GDP/Real GDP) * 100
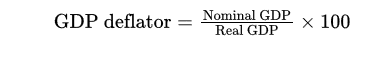
GDP deflator measures the () of prices relative to the level of prices in the ().
Current Level, Base Year
A situation in which the overall price level is rising.
Inflation
The percentage change in some measure of the price level from one period to the next.
Inflation Rate
Inflation rate is calculated as the following:
((Year 2 GDP Deflator - Year 1 GDP Deflator)/(Year 1 GDP Deflator)) * 100

Fluctuations in real GDP are referred to as the (), which is a cycle or regular and irregular increases and decreases of the production of goods and services.
Business Cycle
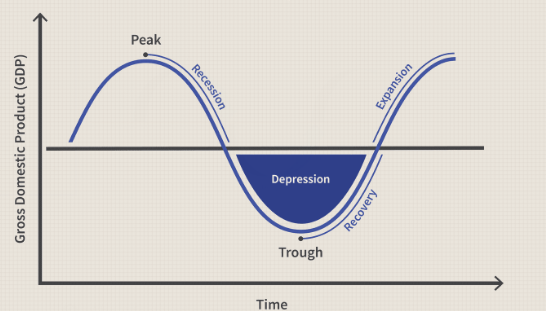
The business cycle comprises 2 phases, which represent upward and downward shifts called () and () as well as 2 turning points which represent the highest and lowest points called () and ().
Expansion, Recession, Peak Trough