Infection associated lymphoma
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Are MALT - mucosal associated lymphoid tissue palpable nodes?
No
Example of agent that cause infection associated lymphomas
Directly oncogenic - infect a subset of lymphocytes in which they express viral products that act as oncogenes
Epstein Barr virus EBV
Human herpes virus 8 HHV8
Human T-lymphotropic virus 1HTLV1
EBV
Burkitt lymphoma
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease
Hodgkin disease (early age)
Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma
HHV8
Primary effusion lymphoma
HTLV1
Adult T-cell leukaemia/ lymphoma
Agents that cause infection associated lymphomas
Indirectly oncogenic - directly infect lymphocytes but persist in tissues and trigger a lymphocytic proliferation that is primary reactive but might escape regulation
Helicobacter pylori
Campylobacter pylori
Hepatitis C virus
Helicobacter pylori - Gastric lymphoma
Campylobacter pylori - Bowel lymphoma
Hepatitis C virus
- Marginal zone lymphoma; nodal and splenic
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
(liver cancer)
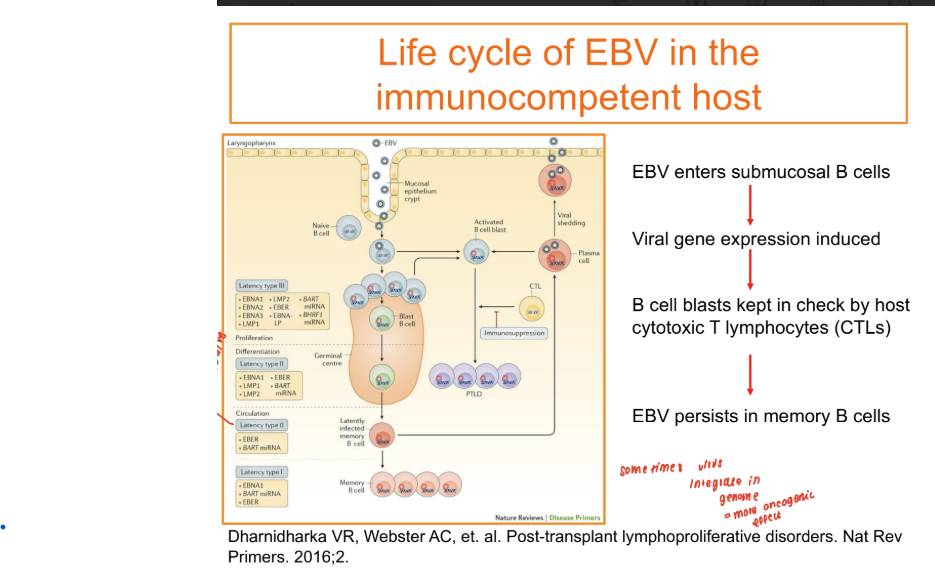
EBV infection in the immunocompetent host
85-90% population are EBV positive
Typically transmitted through contact via saliva of a carrier
Enters the nasopharyngeal tract and infects epithelial cell
Establish a lytic infection which infects the tonsillar B cells.
Infected B cells are kept from prolierating by CTL
LYTIC → LATENT
EBV estabilishes a latent infection which it remains as an episome in a subset of resting memory B cells
What is infectious mononucleosis?
Initiation of EBV infection - EBV establishes a lytic infection which is associated with the production of new viral particles that can infect naive tonsillar B cells and transmit the virus to other individuals
Oncogenicity of EBV - driving role of LMP1 and LMP2
Increase in Bcl-2
Decrease in checkpoint p16
p27
Increase in cell proliferation and survival - increase in JNK, ERK/MEK, NF-kb, PI3K/ Akt
Increase in Ras, PI3K/ Akt
Decrease in BcR
EBV latency
PTLD - post transplant lymphoproliferative disorder
drug induced immunosuppression
Increases the risk of new infections
Reactivates latent infections - EBV
Causes immune dysregulation
Increase the risk of lymphoma
25-60% patients may die of PTLD
PTLD incidence
Incidence highest in heart-lung, lung or intestinal transplant up to 20%
Liver or heart 1-5%
Less likely in renal, HPSC transplant 1-2%
60% occurs within the first 6 months after transplant
but 10-15% also occur >10years after transplant
Cardinal features of PTLD
Variation of disruption of the lymphoid architecture - exacerbation of a reactive pattern, may not be clonal
Pleomorphic
to DESTRUCTION of the lymph node structure: Monomorphic clonal
Reactive pattern
Follicular hyperplasia
Plasma cell hyperplasia
Destructive
Large B-cell lymphoma
clonal k or l
Starry pattern