Equilibrium
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
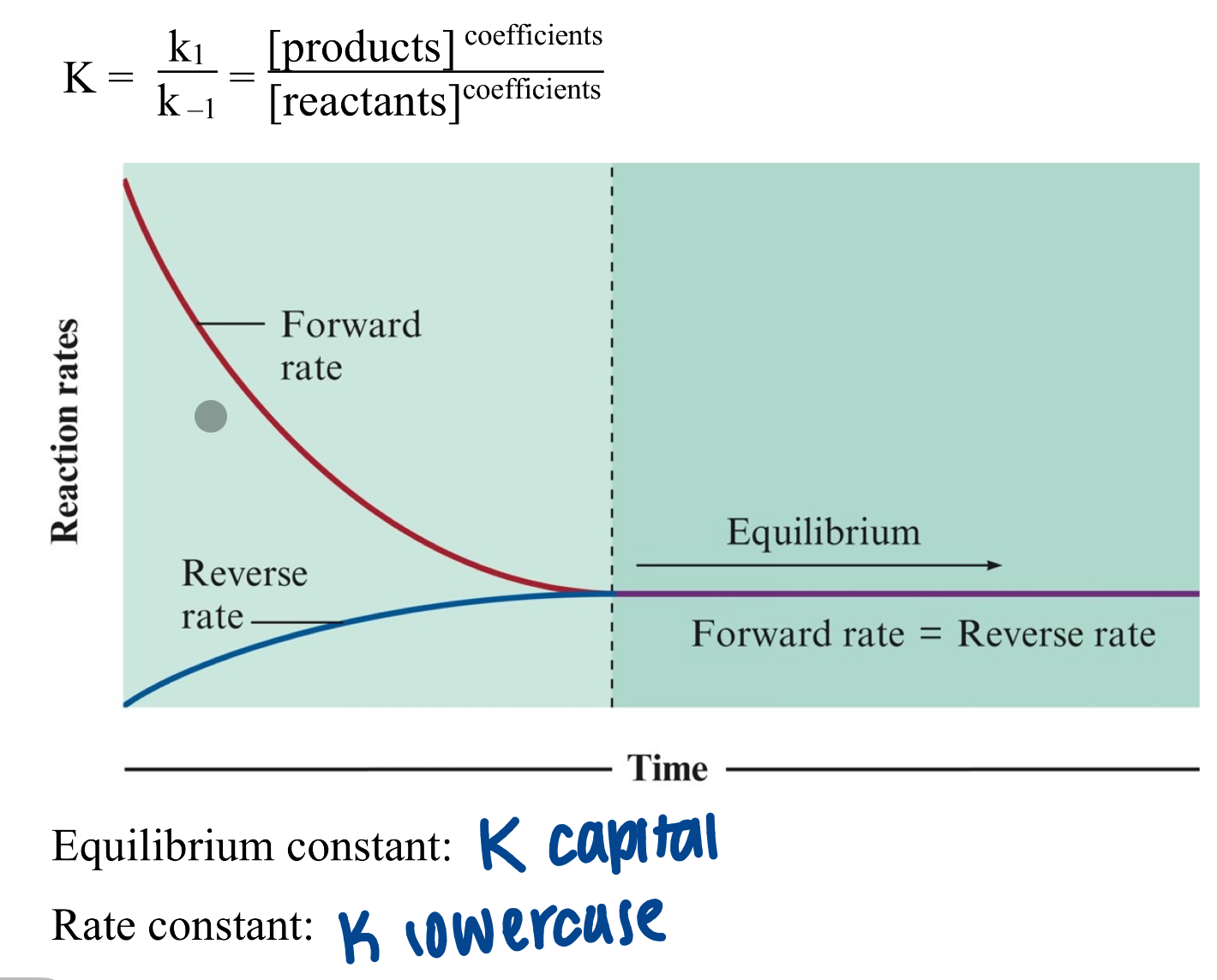
chemical equilibrium
state when concentration of reactants and products remain constant with time
dynamic state
rate fwd = rate rvs
characteristics of chemical equilibria systems
mixture of reactants and products is present
composition of reaction mixture no longer changes = constant
chemical equilibrium is dynamic (still continue on a molecular level)
dynamic equilibrium can be controlled; Le Chatelier’s
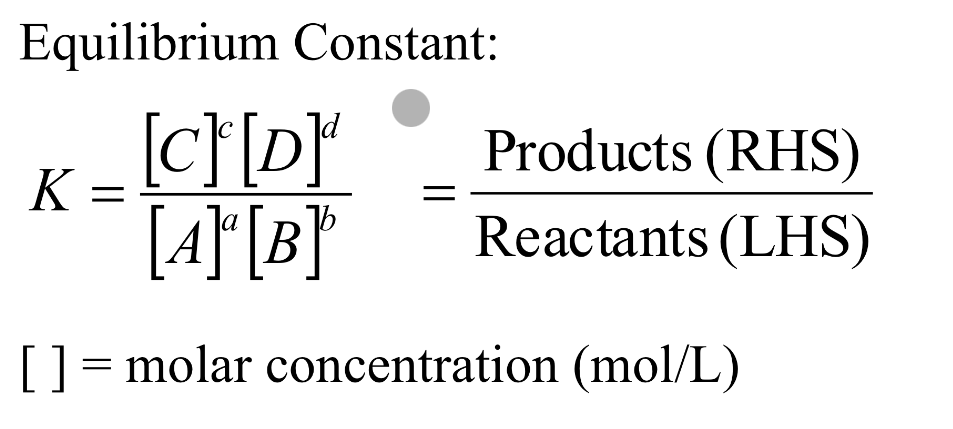
equilibrium constants
only temperature can change
heterogeneous equilibria
more than 1 phase (different phases)
pure solids or liquids no concentrations or pressures
magnitude of equilibrium constant
indicates the extent to which the forward and reverse reactions take place
large K: >=10³
intermediate K: ~10-3 to 102
small K: <=10-4
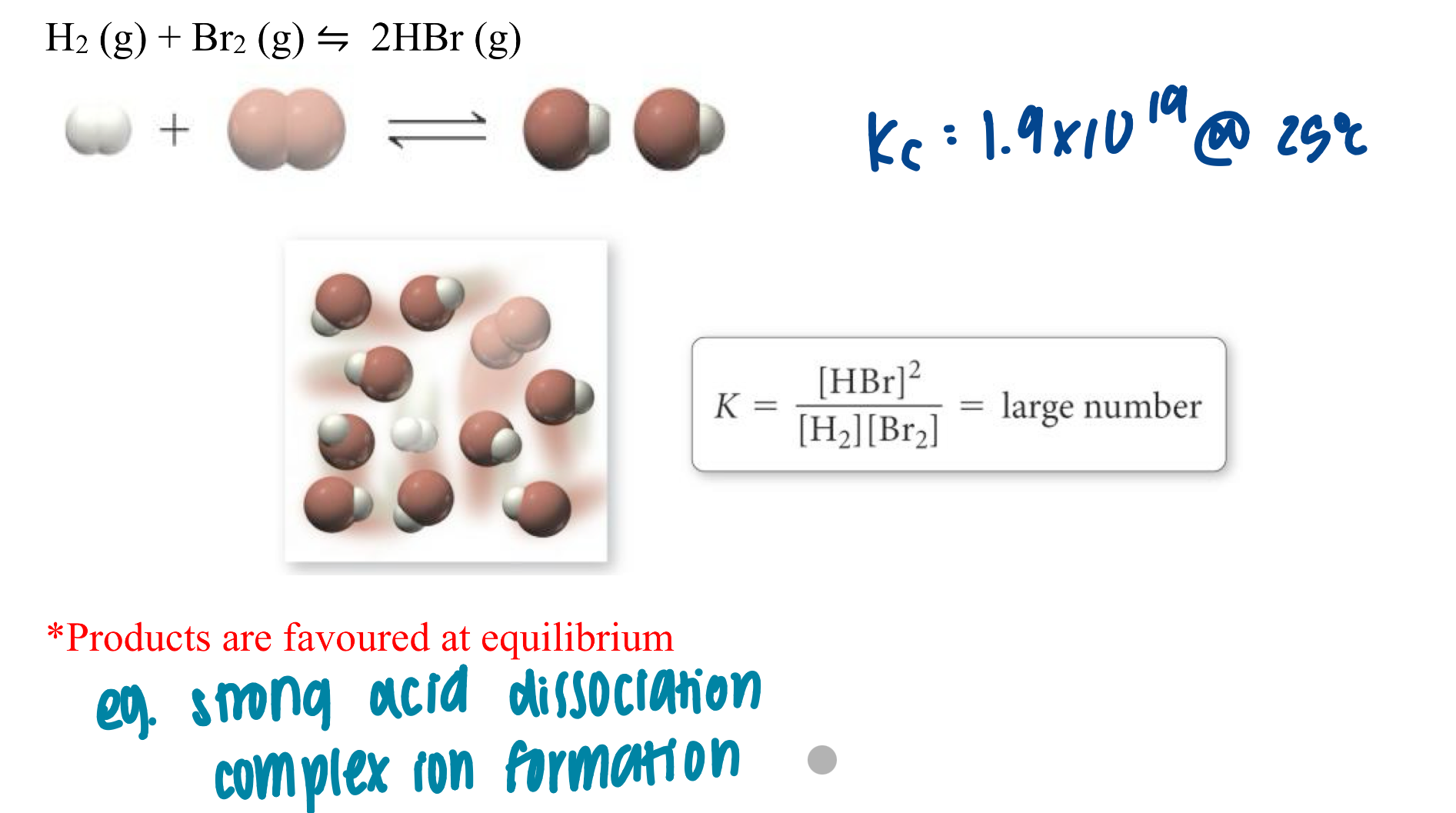
large K
at equilibrium, large [product] small [reactant]
reaction proceeds essentially to completion
intermediate K
at equilibrium, significant amounts of reactants and product
small K
at equilibrium, small [product] large [reactant]
reaction doesnt proceed much
![<ul><li><p>at equilibrium, small [product] large [reactant]</p></li><li><p>reaction doesnt proceed much</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8bfd5639-e75e-4579-931a-6712cd408bea.png)
reaction quotient
same form as K
ratio of concentrations/pressures at a given time in reaction

Q<K
reaction proceeds forwards towards products
products > reactants
Q gets LARGER
Q>K
reaction proceeds reverse
products < reactants
Q gets SMALLER
le chatelier’s principle
change in
concentration, pressure, volume, catalyst, temperature
imposed on a system at equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to reduce change
system moves out of equilibrium state (Q=K) temporarily
shifts til equilibrium re-established
how to reach equilibrium
addition of substance (concentration increases) equilibrium shifts to consume it
removal of substance (concentration decreases) equilibrium shifts to produce it
addition of solids/liquids → no change; dont appear in Q or K expressions
effect of changes in presssure
change pressure by adding/removing reactants/products
adding inert gas
as long as volume stays constant, it wont make an effect
pressure total increases, partial pressures dont change
change pressure by changing volume
reaction at equilibrium: add/remove product/reactions cause shifts
effect of changes in volume
concentrations or pressures of reactants and products change
increase volume = shift to increase number of gas molecules
decrease volume = shift to decrease number of gas molecules
effect of changes in temperature
equilibrium constant K changes
exothermic/endothermic reactions (released/absorbed heat)
increase temperature = shift to consume heat
decrease temperature = shift to produce heat