Skeletal System KIN 202-M1
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Structure and Function
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
The 3 mechanical functions of bone
Weight bearing
protection of internal organs
linkages and sites for muscle attachment
The 3 physiological functions of bone
storage of essential minerals
productions of blood cells
immune function
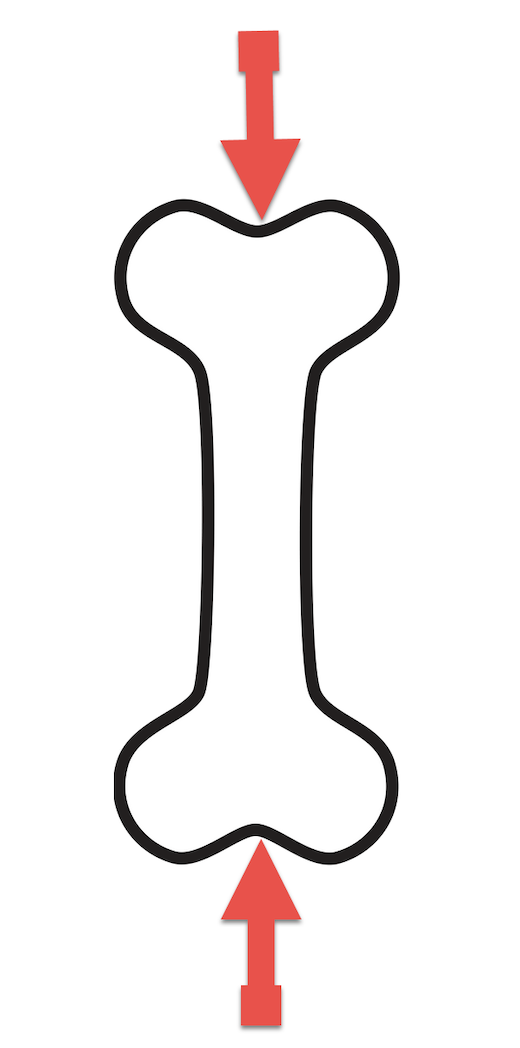
What force is acting on the bone?
Compression
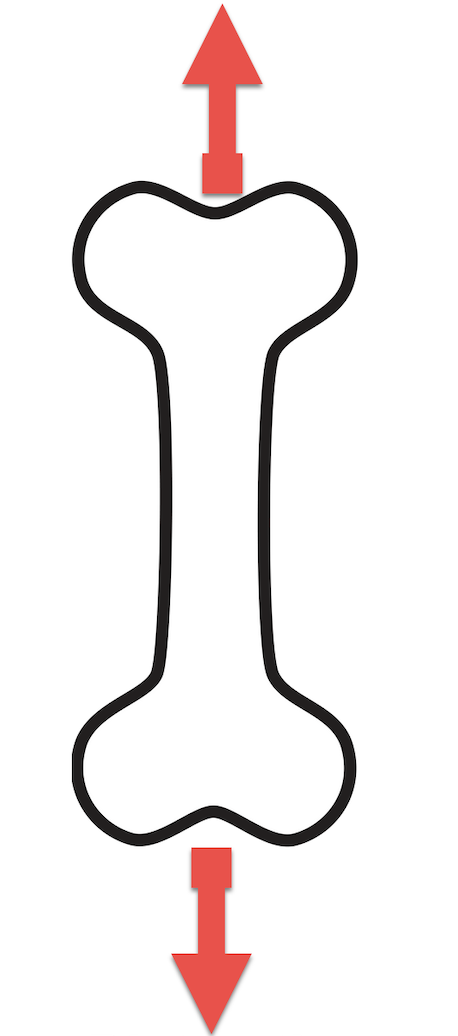
What force is acting on the bone?
Tension
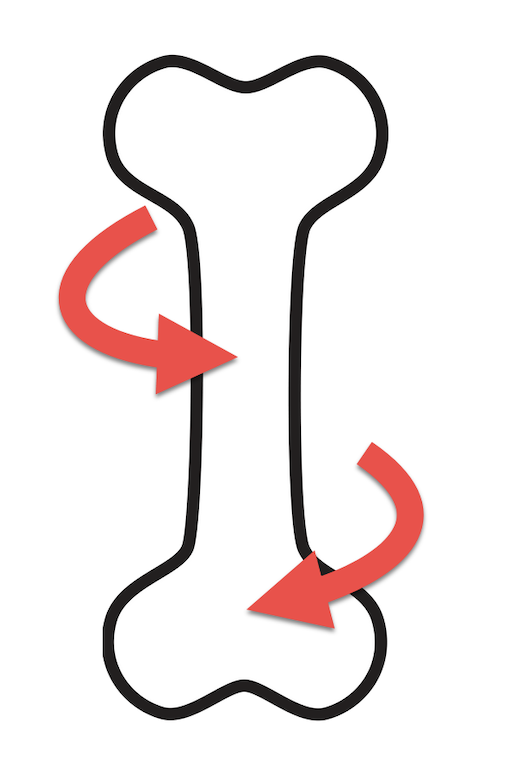
What force is acting on the bone?
Torsion
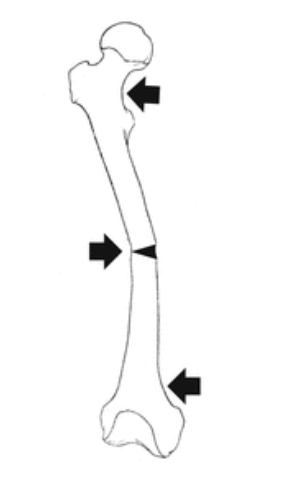
What force is acting on the bone?
Bending
What force is acting on the bone?
Shear
Living bone is made up of how much water?
~25%
2/3 of the remaining weight in bones
inorganic crystals
The 2 inorganic crystals that make up 2/3 of weight in bones
calcium and phosphorus
The remaining 1/3 of weight in bones
organic collagen fibers
The 3 types of bone cells
osteocytes
osteoblasts
osteoclasts
Bone is what type of material
composite material
What is a composite material
material made up of 2 or more materials
Bone is a lot like what?
Fiberglass
What is fiberglass?
Glass fibers cured in an epoxy resin
Collagen
Tough and flexible
Calcium
Rigidity and stiff
The optimal make-up of bone
2/3 calcium
1/3 collagen
Osteoblast function
Osteogenic (bone building)
Osteoclast function
bone degrader, breaks down bone mineral
Osteoclasts are derived from what?
monocytes (WBC)
Osteocytes function
mature bone cells that are trapped in bone matrix
Osteocytes were once what and can become them again?
Osteoblasts
The 2 types of bone
spongy and compact
2 other names for spongy bone
cancellous and trabecular
How much more deformable than compact bone is spongy bone?
10-15x
Another name for compact bone
cortical
T or F: compact bone is much stronger than spongy bone
T
The significance of bone architecture
efficient strength-to-weight ratio
withstands large forces and are relatively light
Compact bone protects what?
cartilage
Where does compact bone transfer forces?
to spongy bone
T or F: spongy bone absorbs forces
T
The 3 types of bone shape
flat
short
long
Flat bone function and make-up
Protection
lots of compact bone
Short bone function and make-up
weight bearing, absorbs ground reaction forces
less compact, lots of spongy
long bone function and make-up
weight bearing, muscle attachment
rigid links between joints
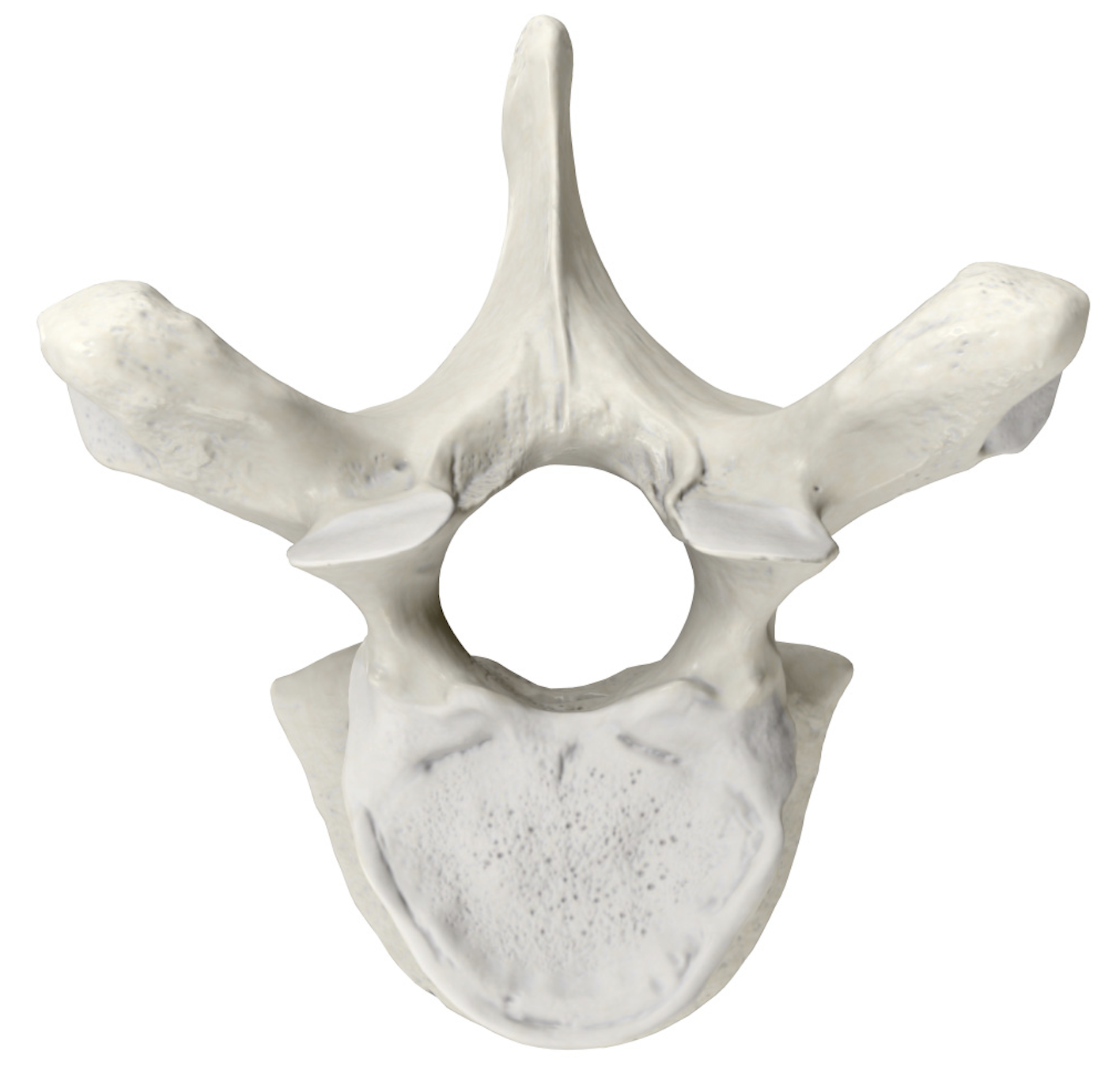
The 3 basic parts of a vertebrae
body
arch
spinous processes
Vertebral body function
weight bearing; cushions compressive forces
vertebral arch function
protects spinal cord
spinous processes function
provides leverages to attached ligaments and muscles; resists bending and twisting
hollow shafts functions (architecture of long bones)
resists bending, resists twisting
architecture of long bones
expanded ends with spongy bone: absorption of energy with compact, large contact area between bones
bone changes with “____”
training
training definition
mechanical loading of bone
training
ground reaction forces, forces from muscular contraction
detraining definition
absence of mechanical forces
detraining
bed rest, casting, spaceflight, hindlimb suspension of animals
bone mass in dominant limb of tennis players and carpenters are around _____ than non-dominant
30% greater
muscle mass accounts for what?
more than half of difference in bone mass between race or gender
weight bearing activity
4 hours of walking or standing restores bone loss from 20 hours of bed rest
Wolff’s Law
1892, the infrastructure of tissues adapted to the internal demands placed upon it
Wolff’s law example
bone forms in areas of stress and is reabsorbed in areas of non-stress
Basset and Becker
1982, bone acts as piezoelectric crystal
____ occur slowly in contrast to ____ with detraining, therefor exercise must be ____ and ____ to maximize benefits on bone
initial positive changes, rapid negative changes, regular, maintained
remodeling cycle of bone
3-5 months, 3-4 cycle required to maintain new steady state
stress fractures
particularly prevalent in young amenorrhoeic female athletes, 3-5%
what age do you reach peak bone mass?
30