Block 4 - The Cranium
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
8
How many bones are in the neurocranium?
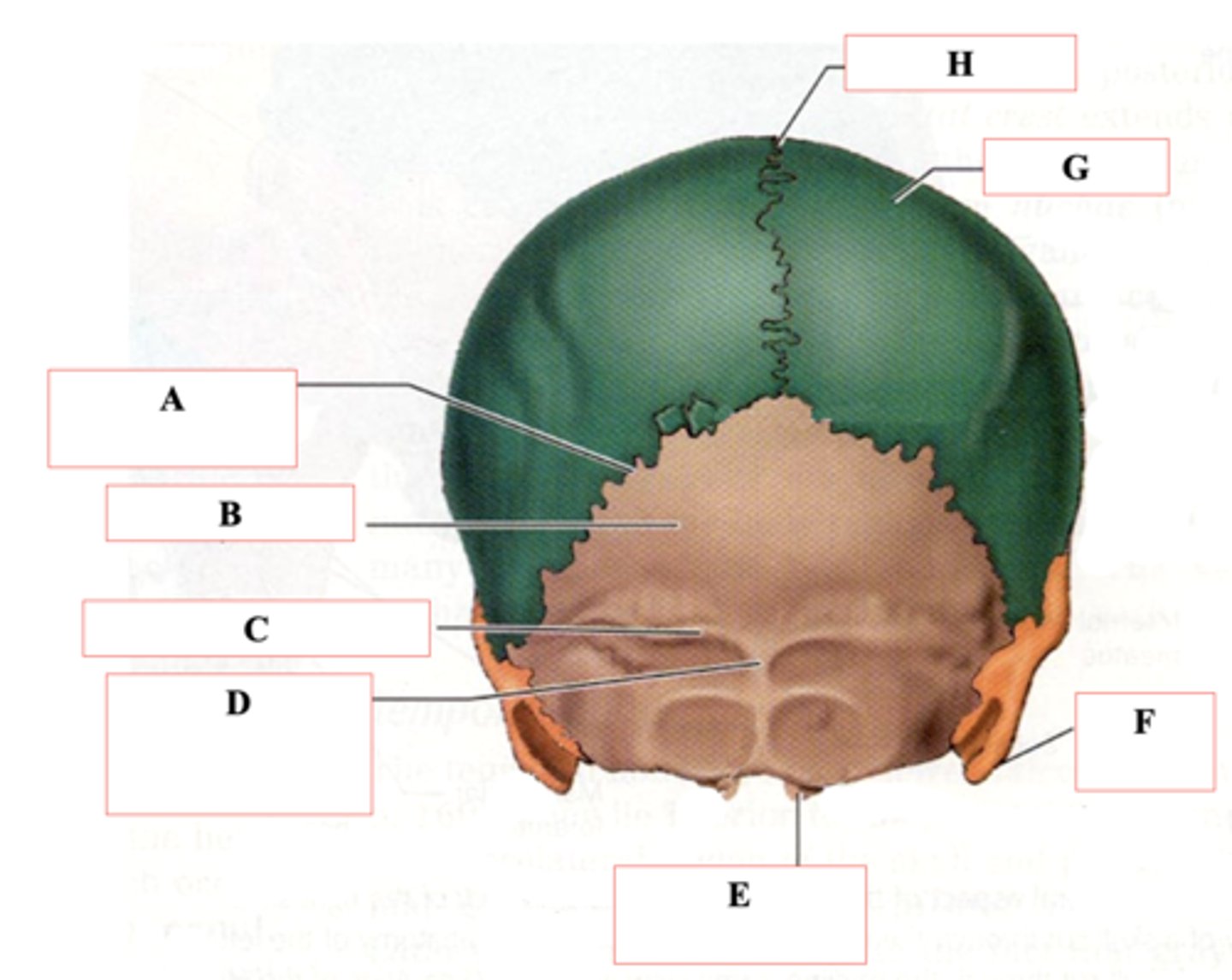
Parietal Bone
Identify A.
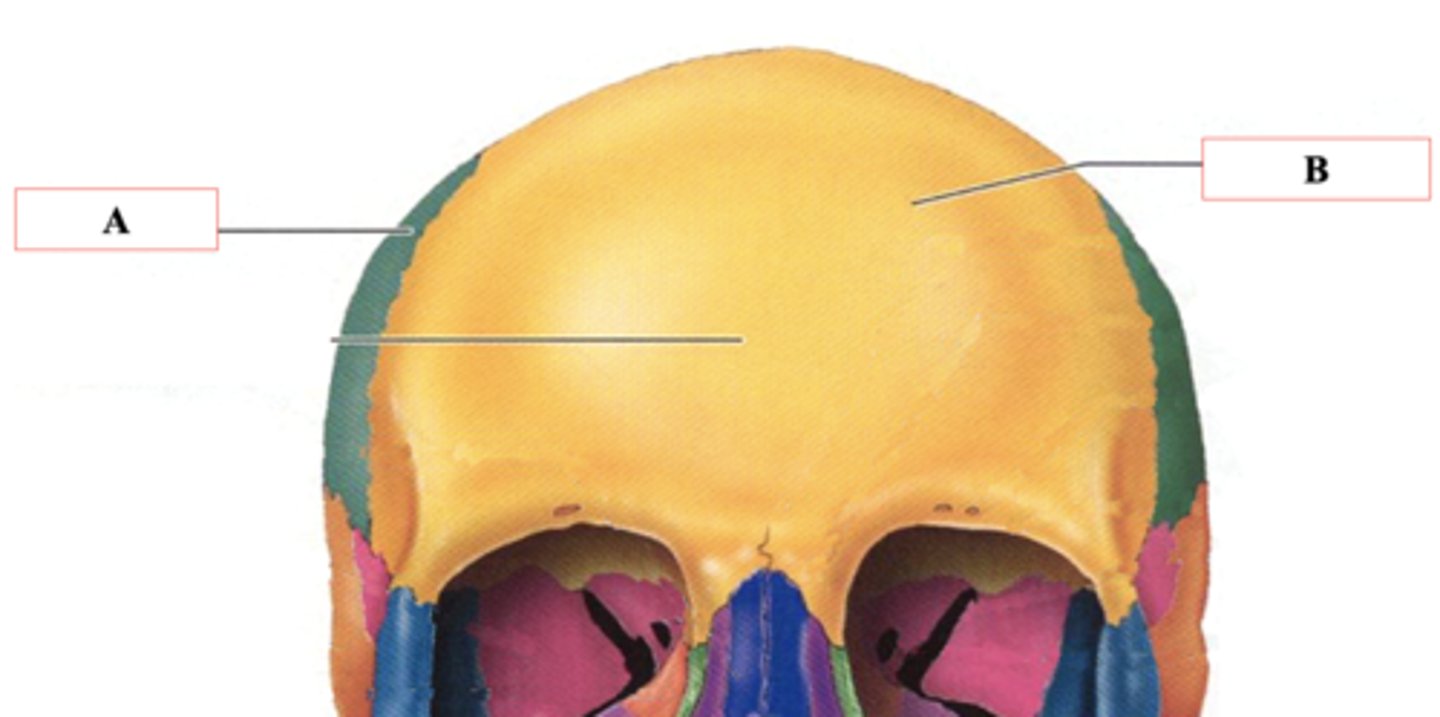
Frontal Bone
Identify B.
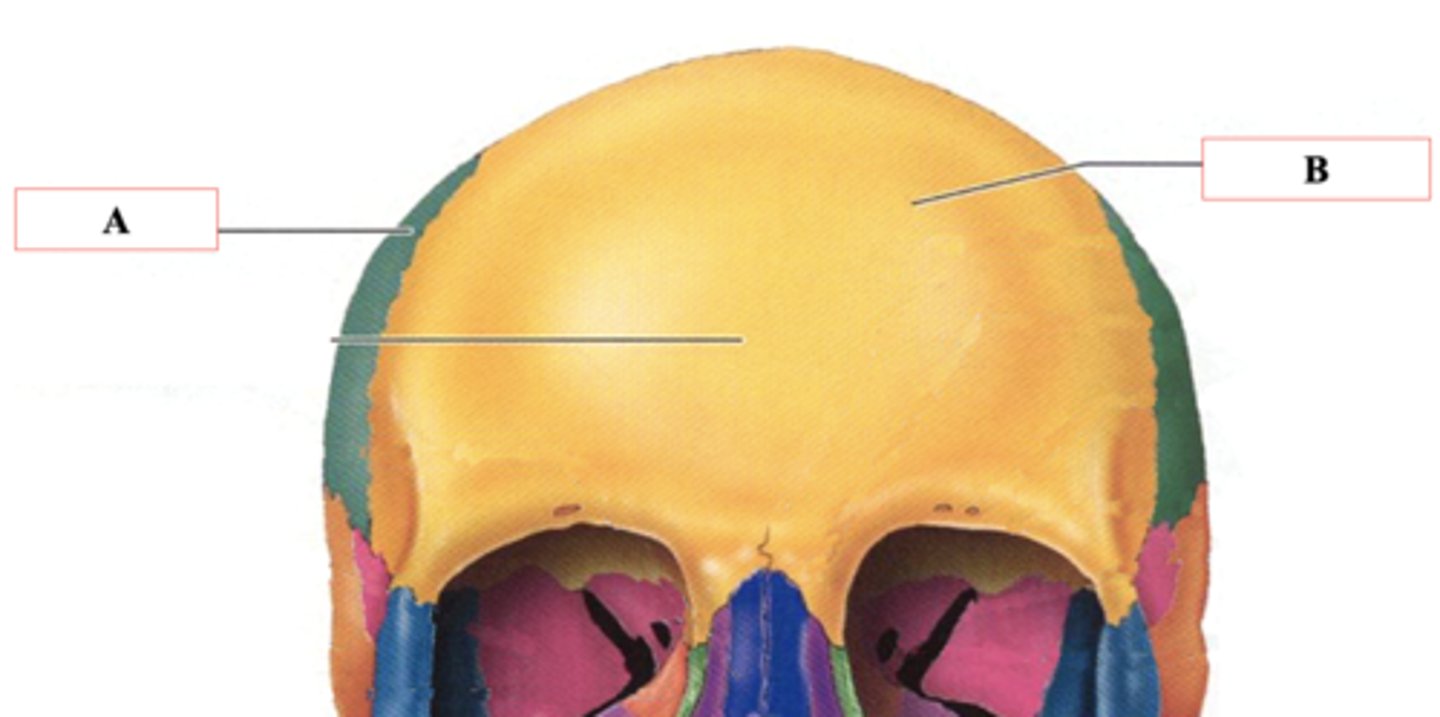
Lambdoid Suture
Identify A.
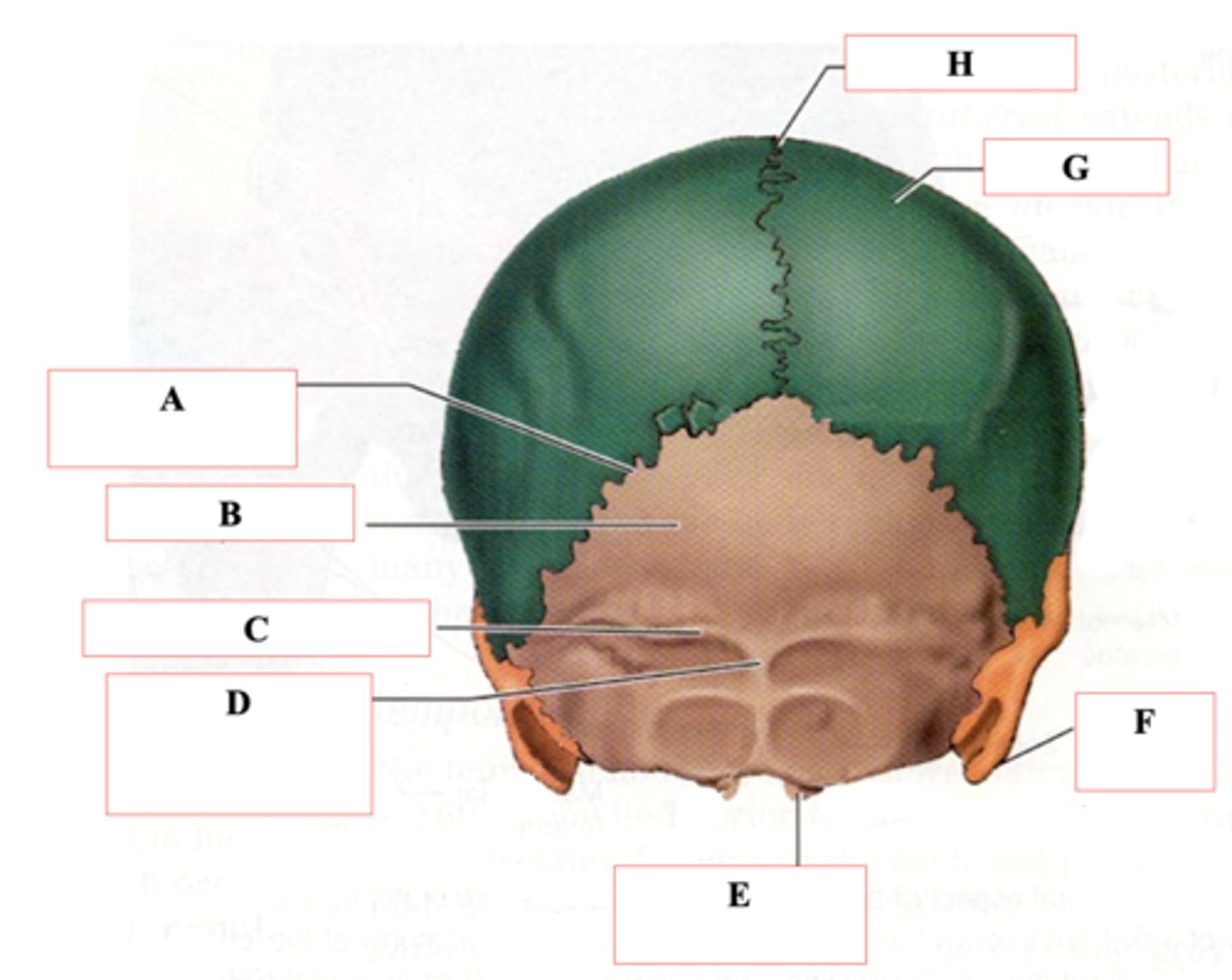
Occipital Bone
Identify B.
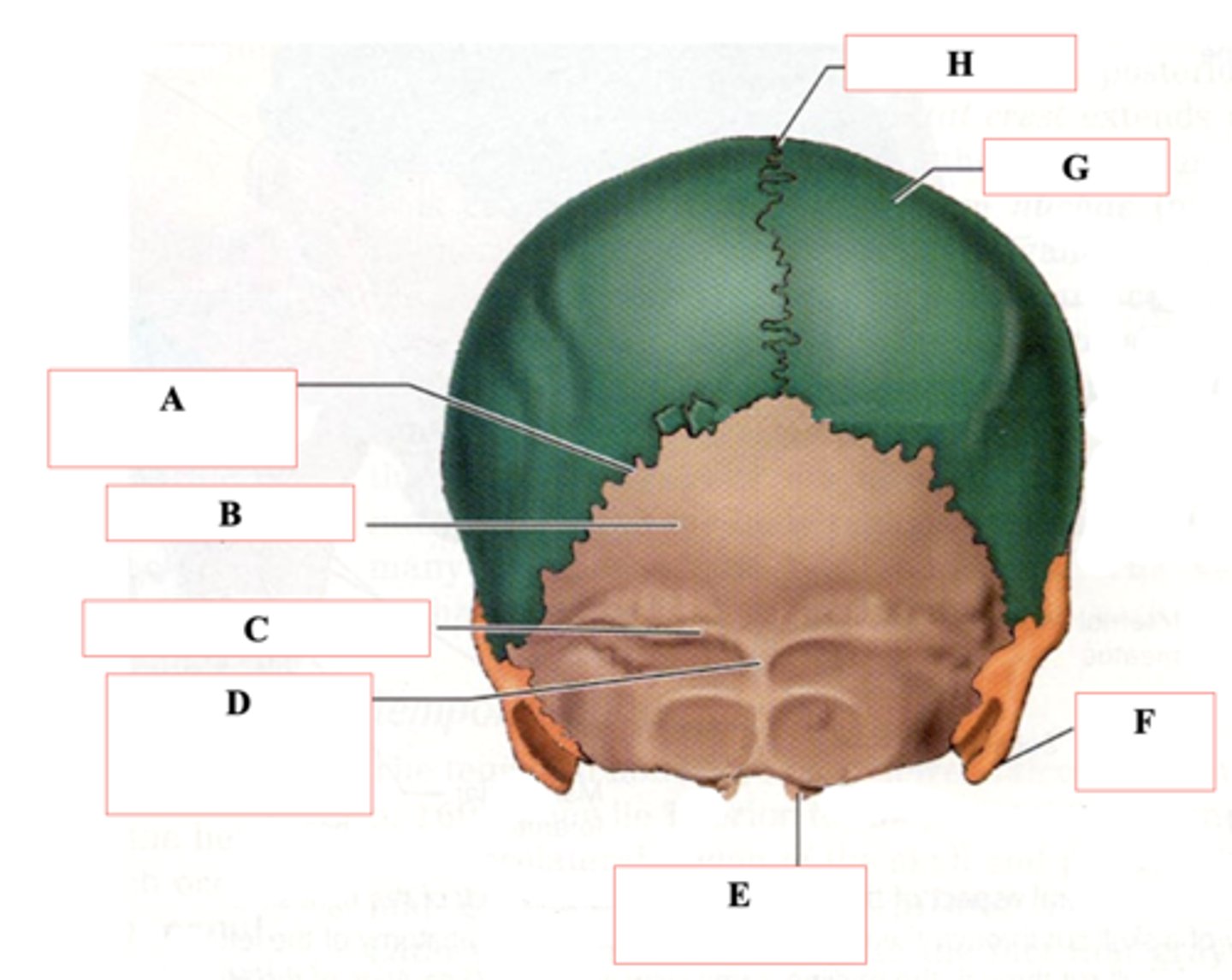
Superior Nuchal Line
Identify C.
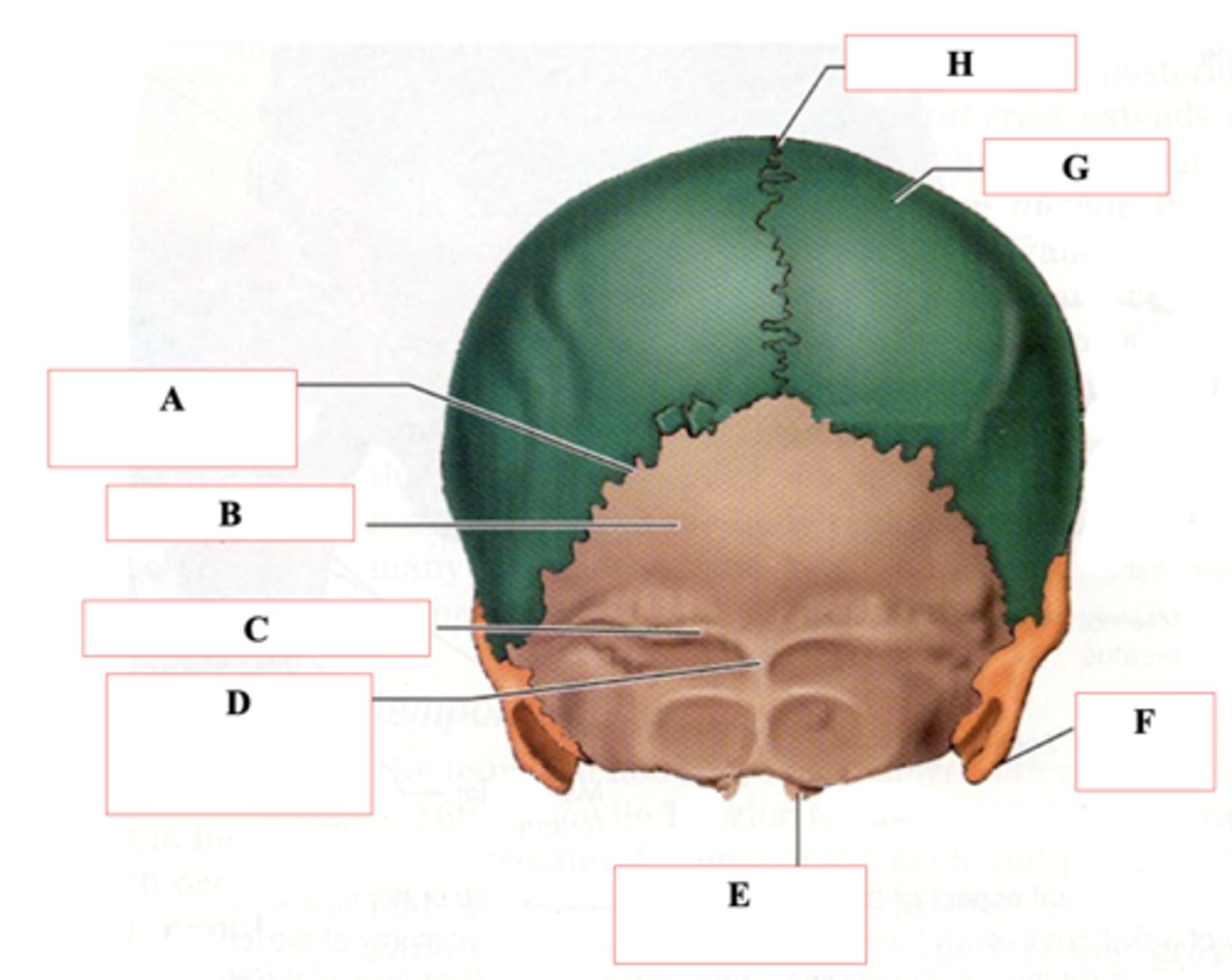
External Occipital Protuberance
Identify D.
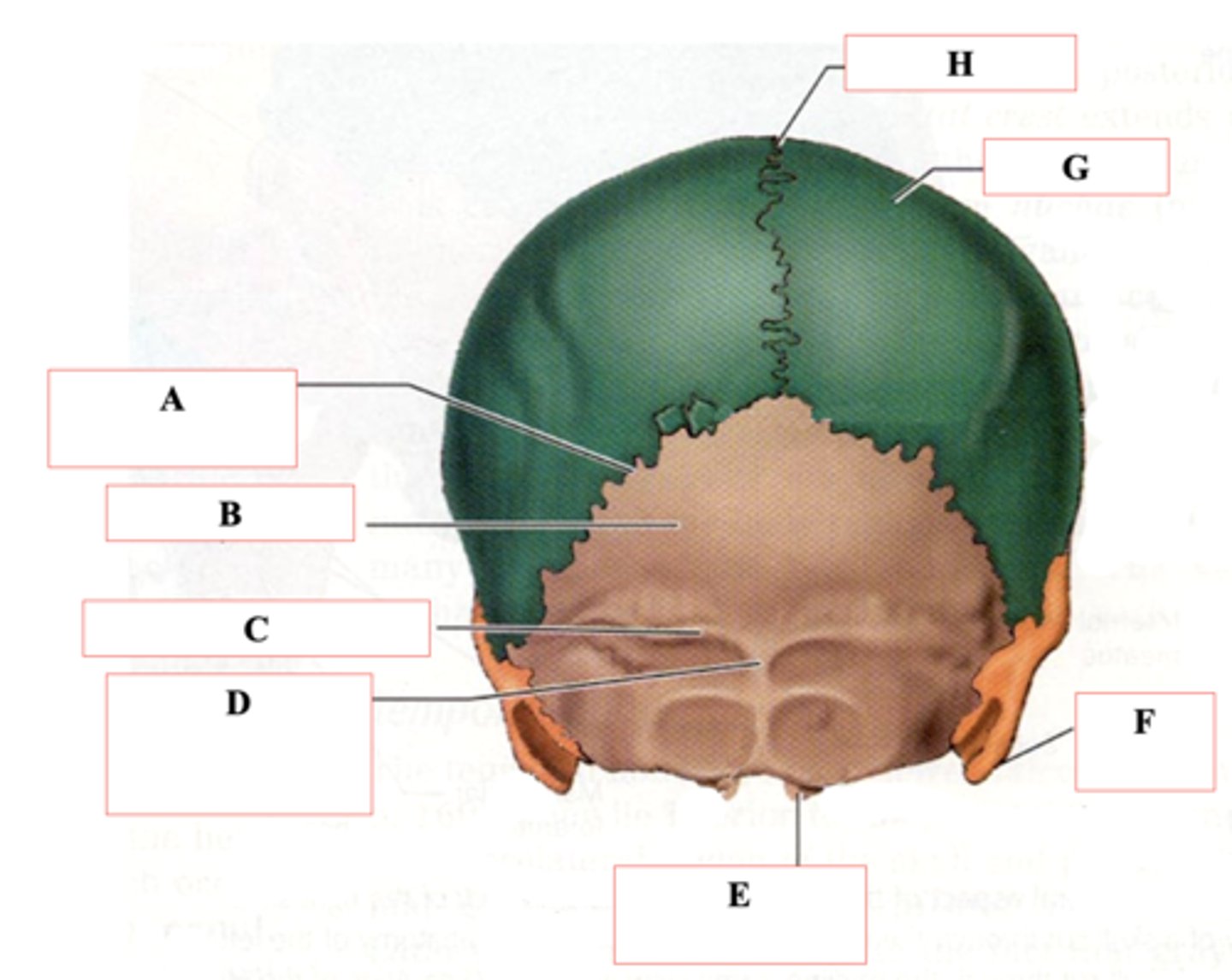
Occipital Condyle
Identify E.
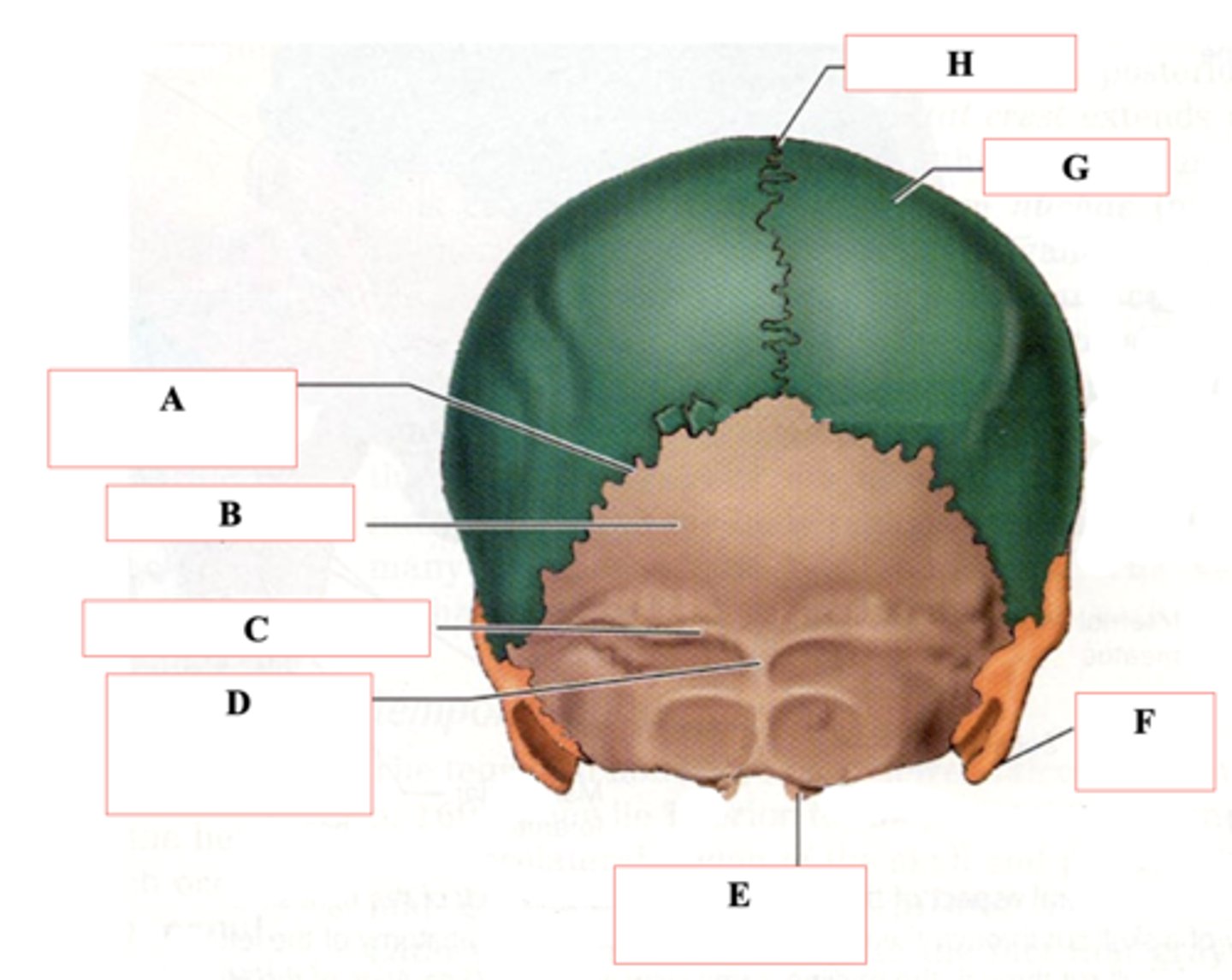
Mastoid Process
Identify F.
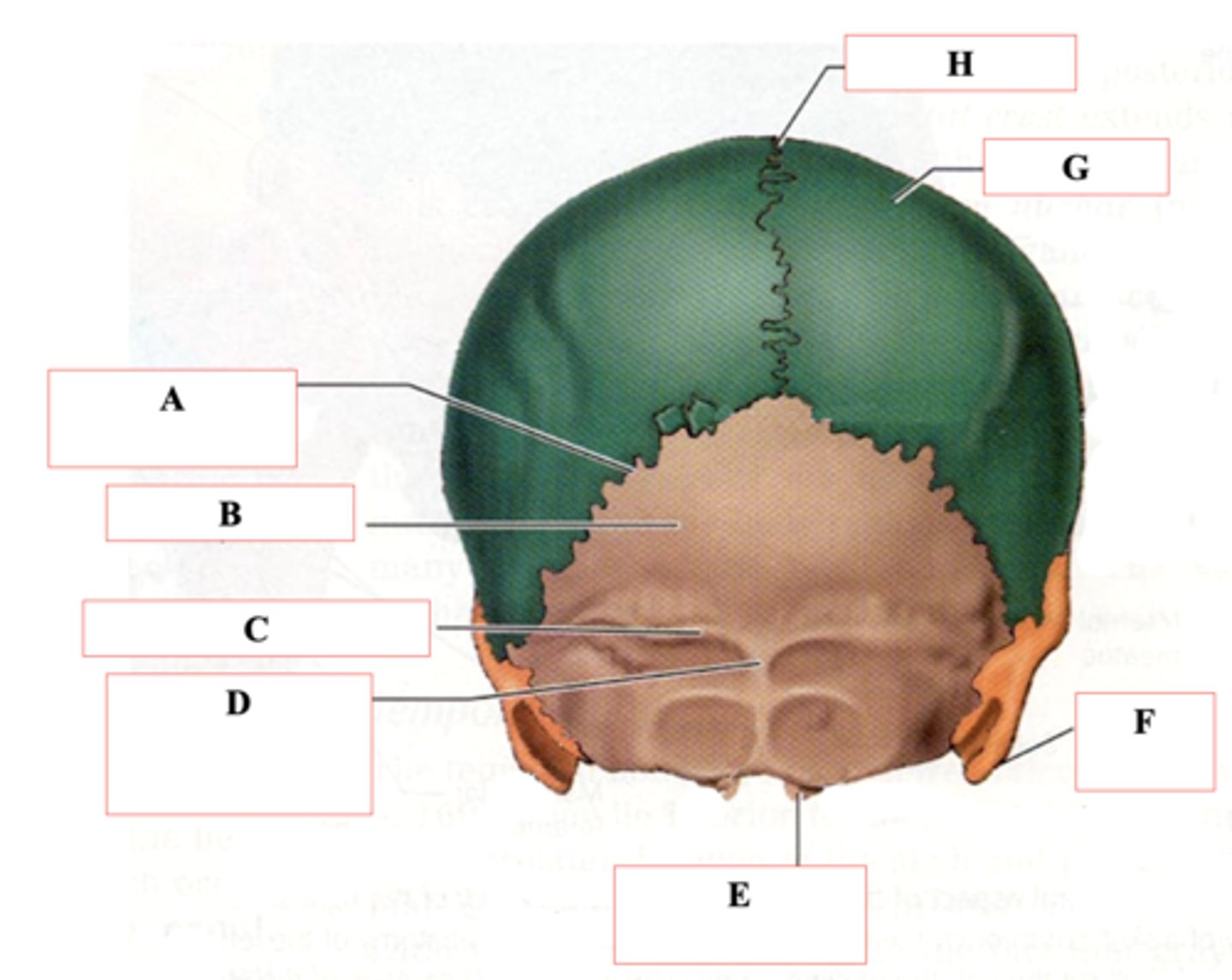
Parietal Bone
Identify G.
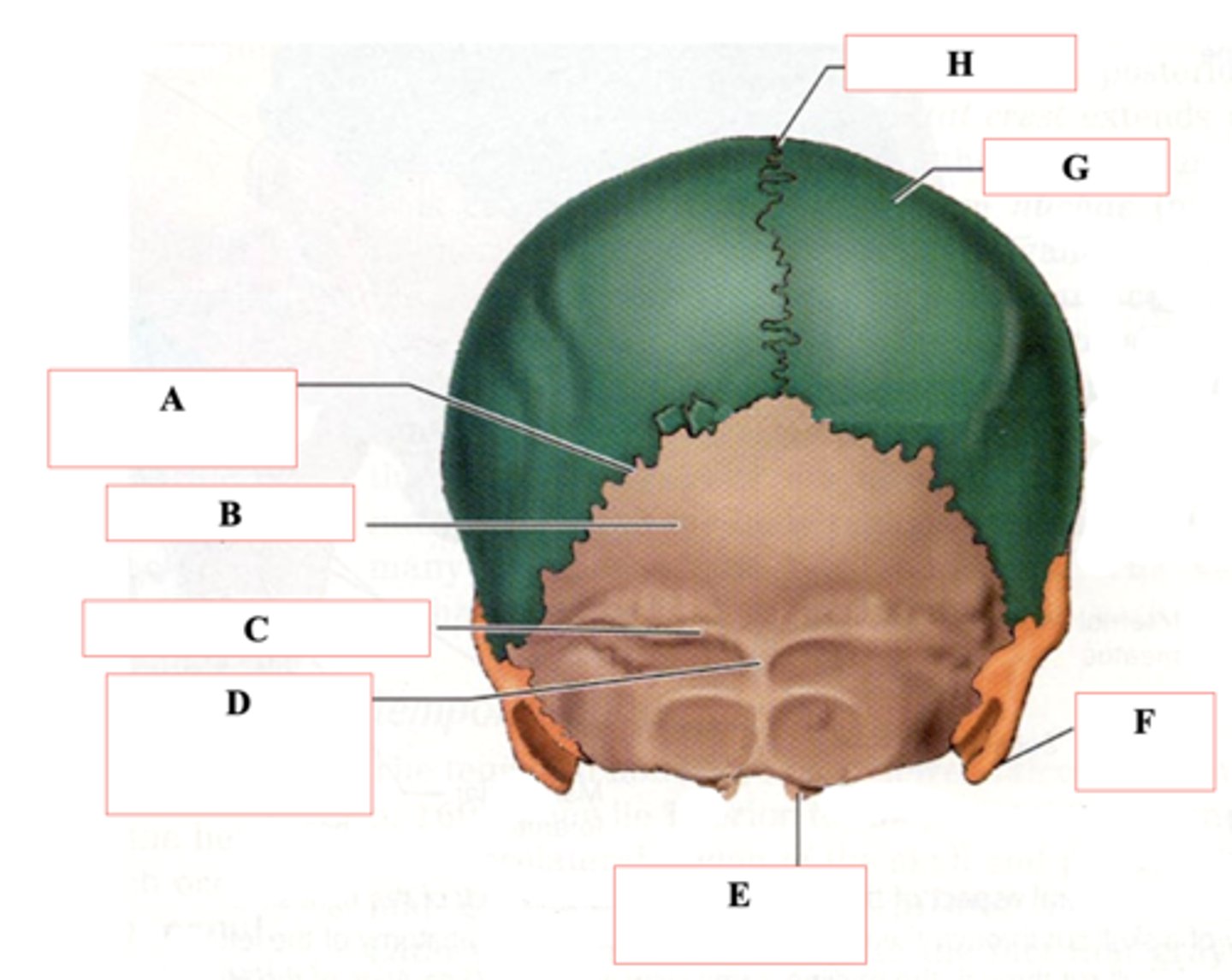
Sagittal Suture
Identify H.
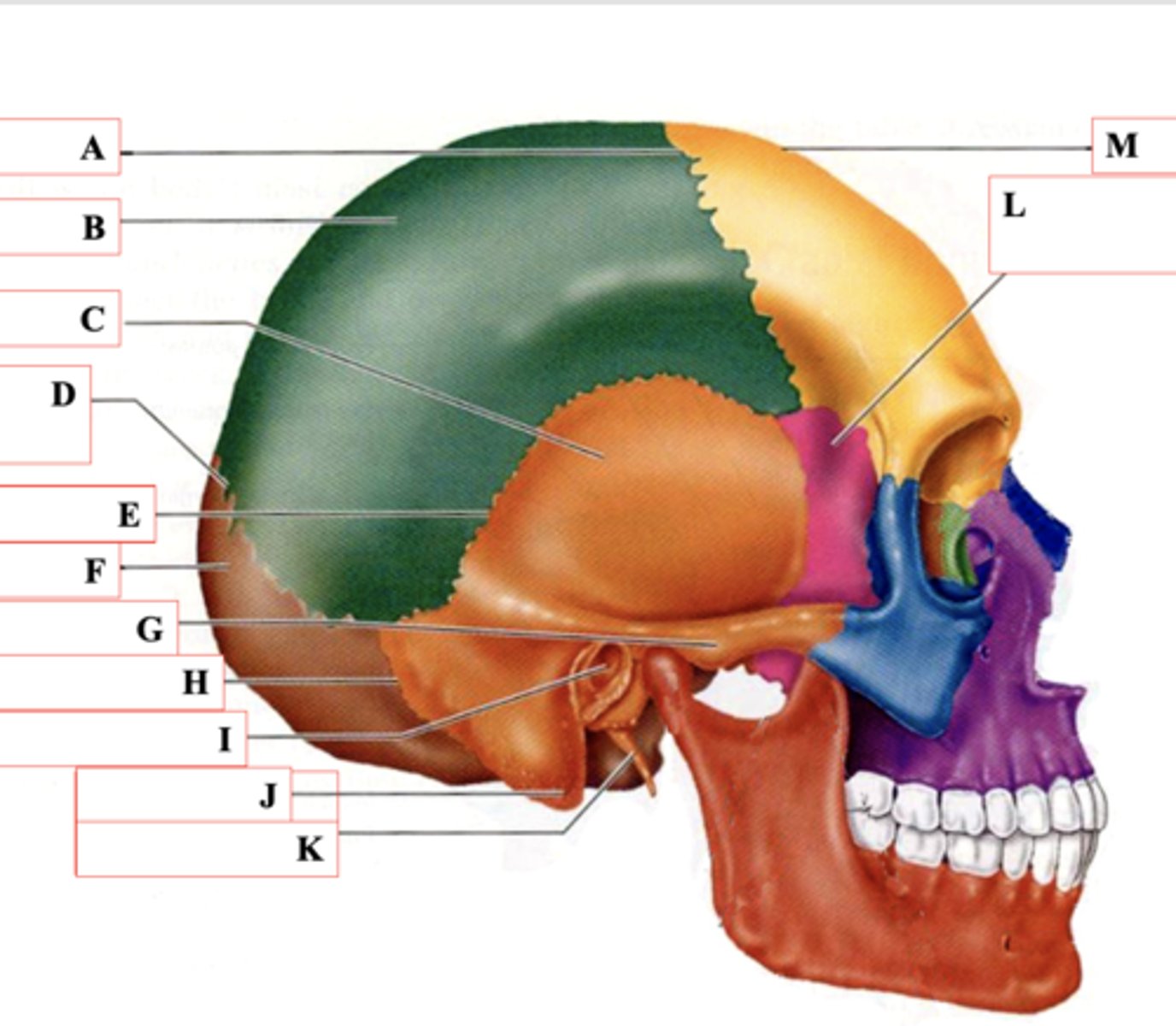
Coronal Suture
Identify A.
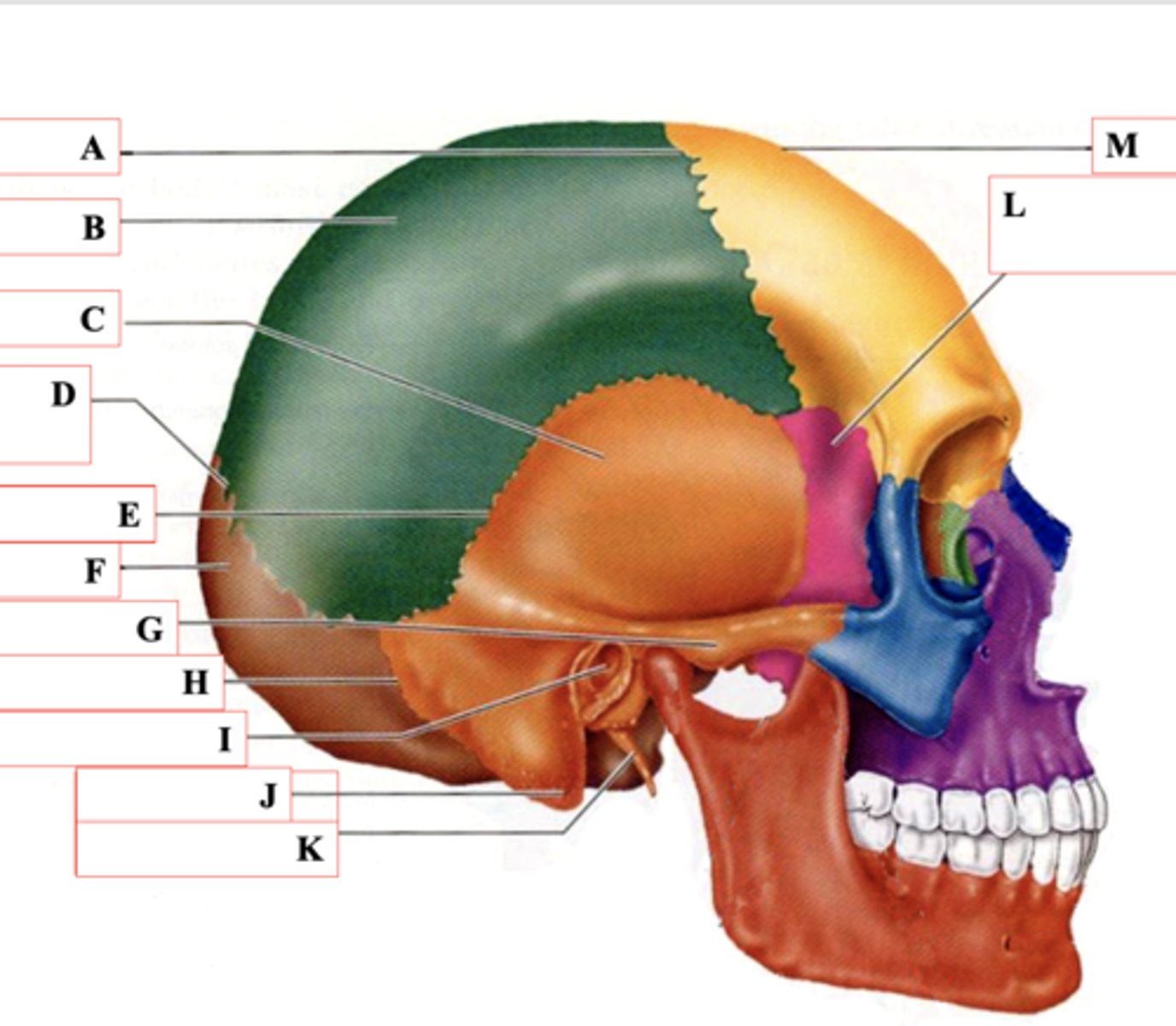
Parietal Bone
Identify B.
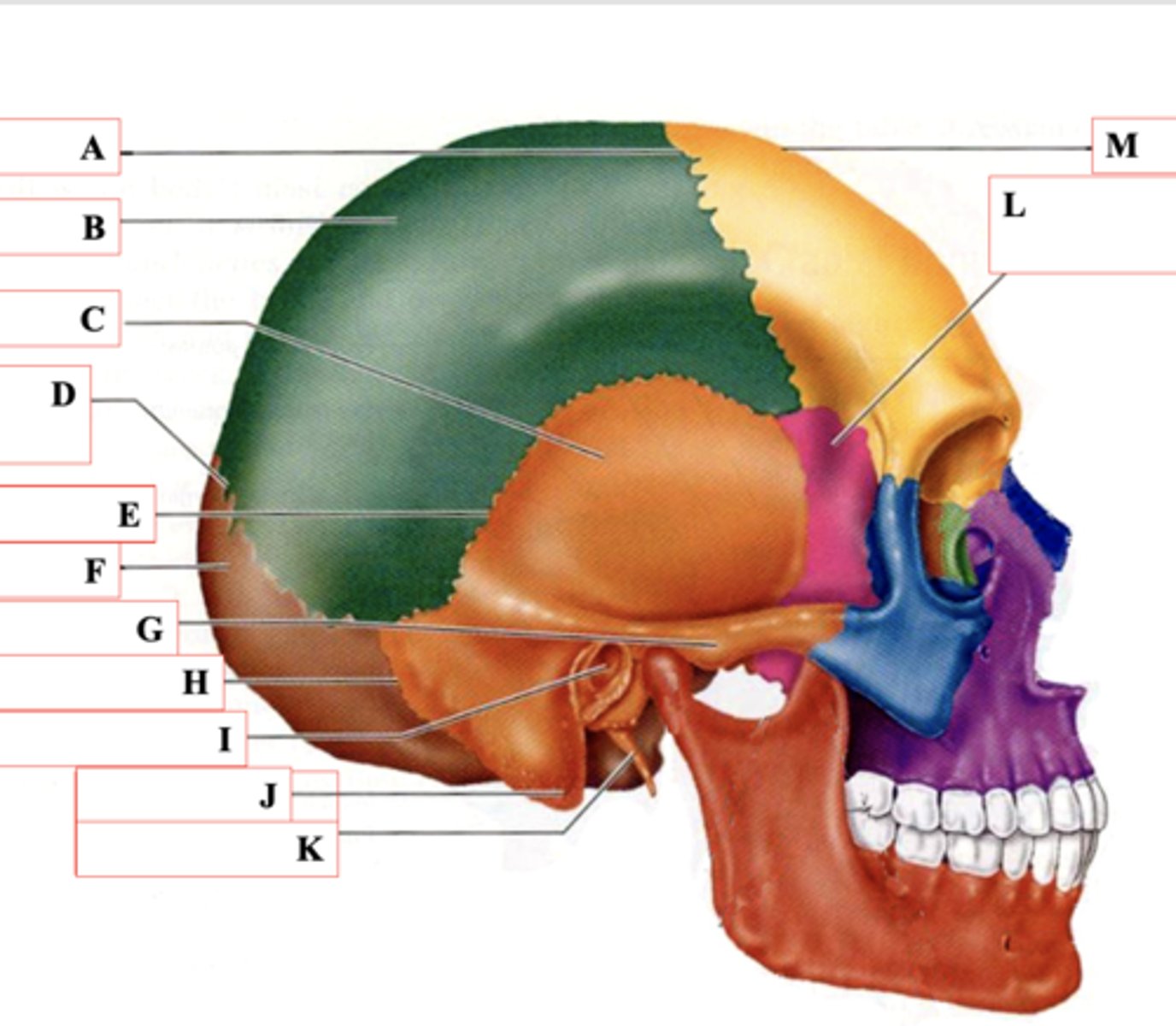
Temporal Bone
Identify C.
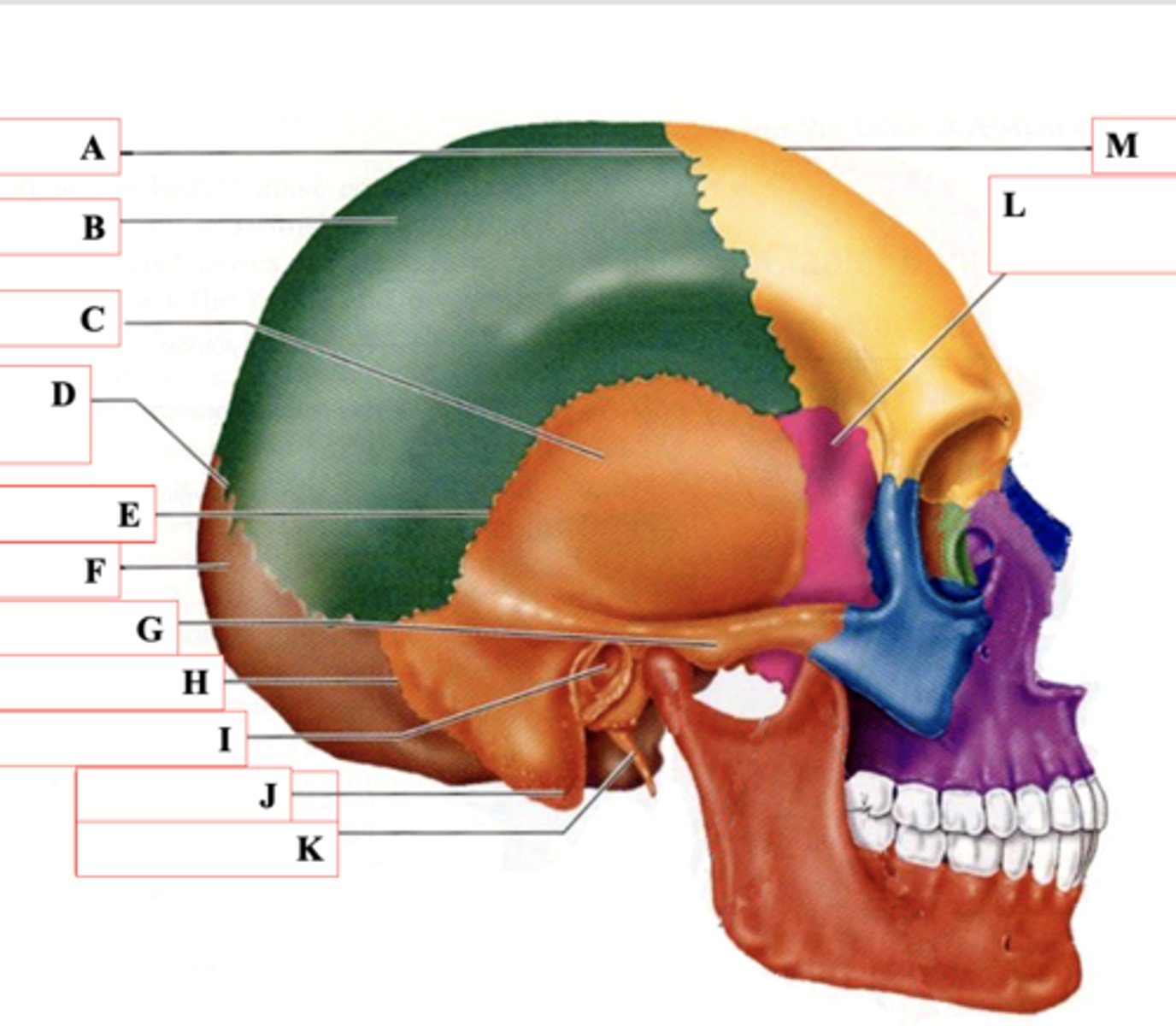
Lamboid Suture
Identify D.
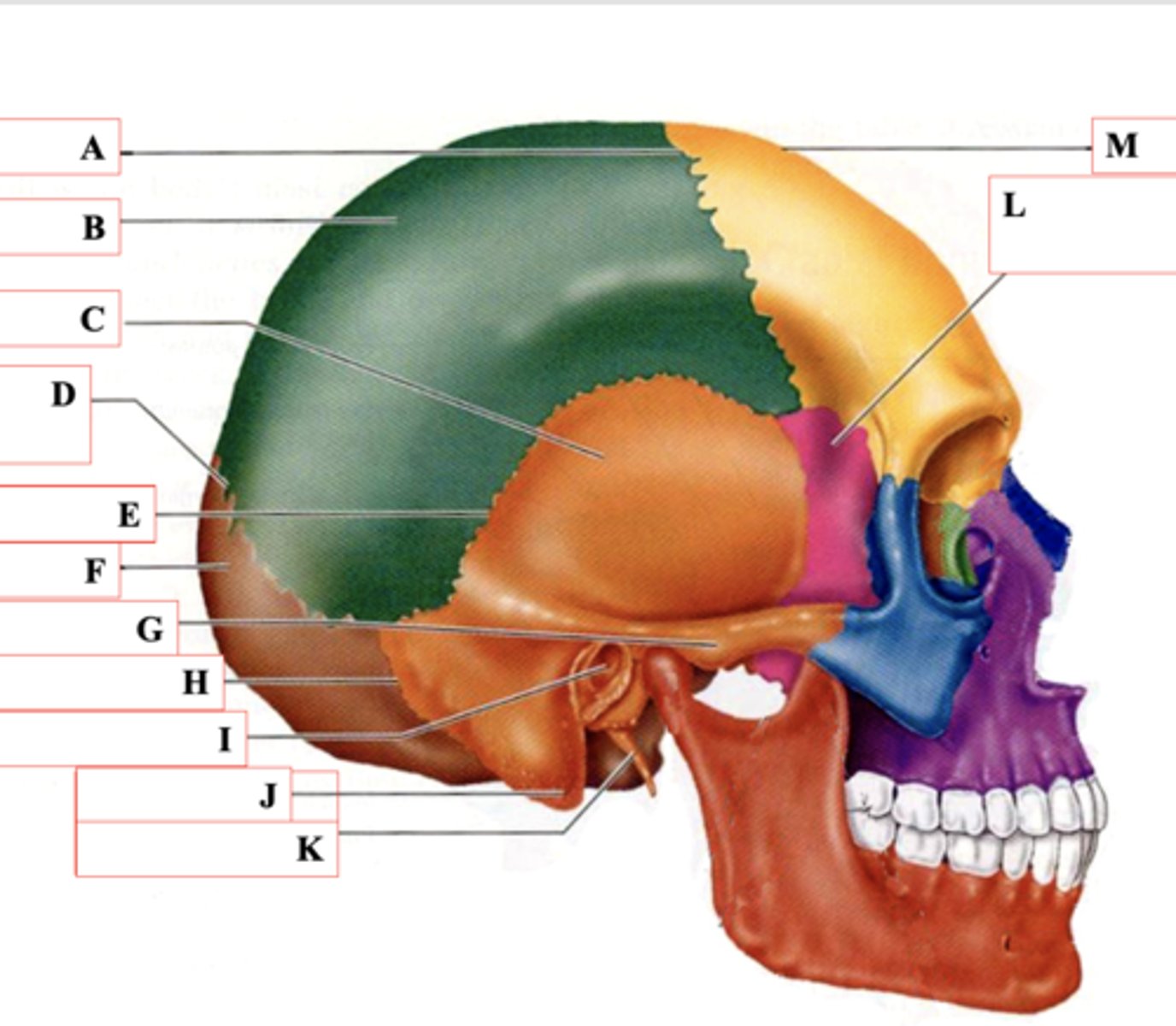
Squamous Suture
Identify E.
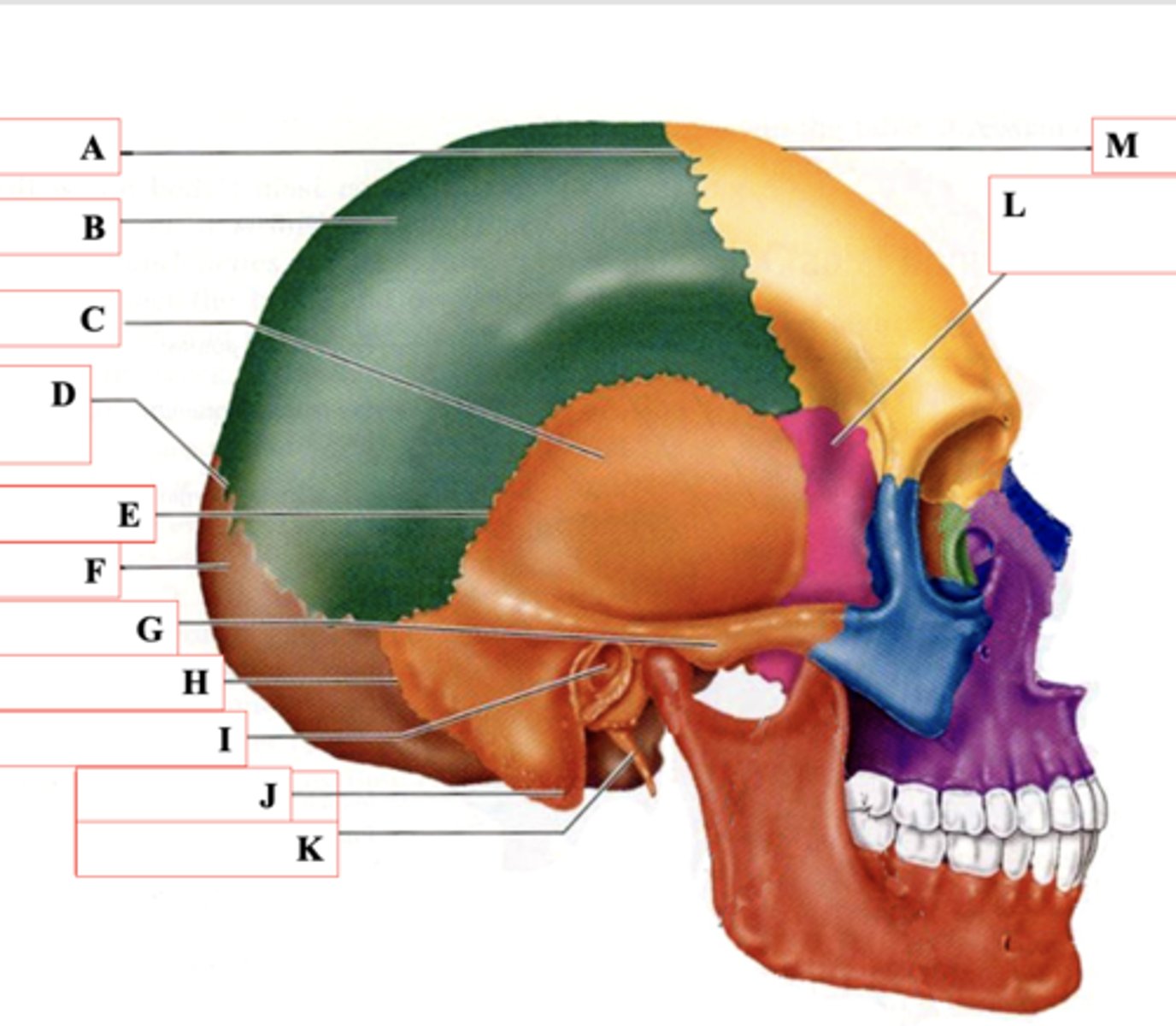
Occipital Bone
Identify F.
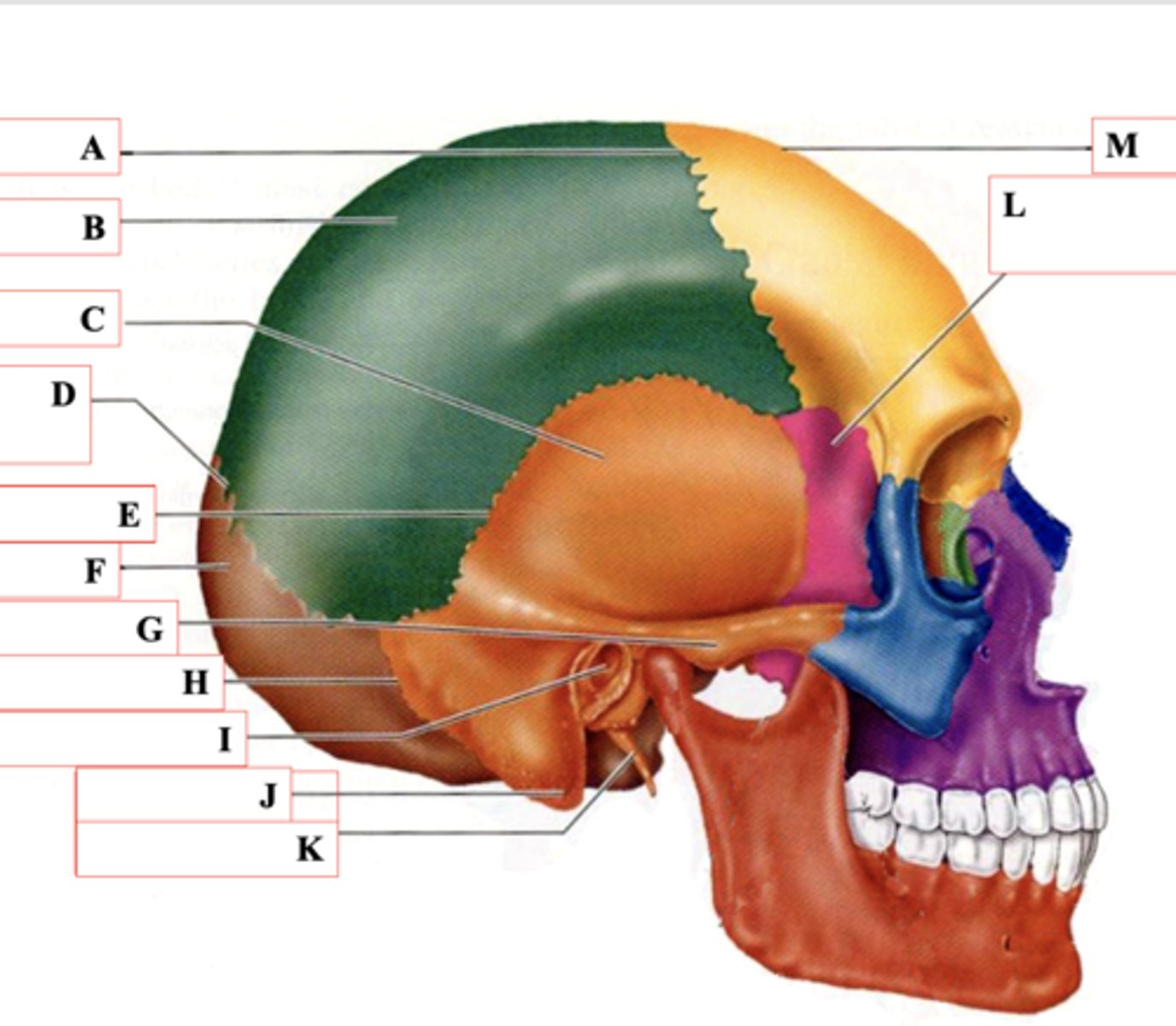
Zygomatic Process
Identify G.
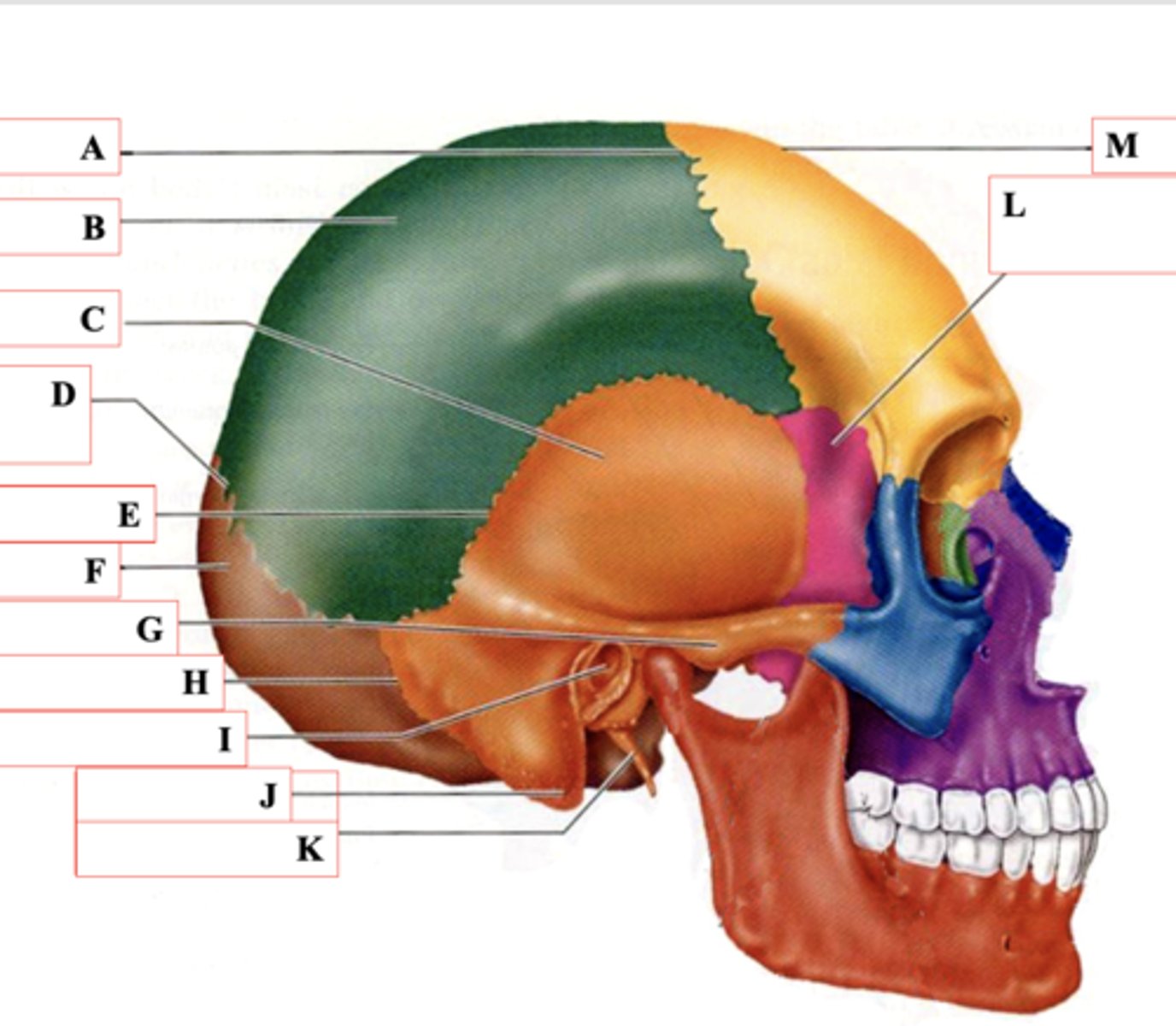
Occipitomastoid Suture
Identify H.
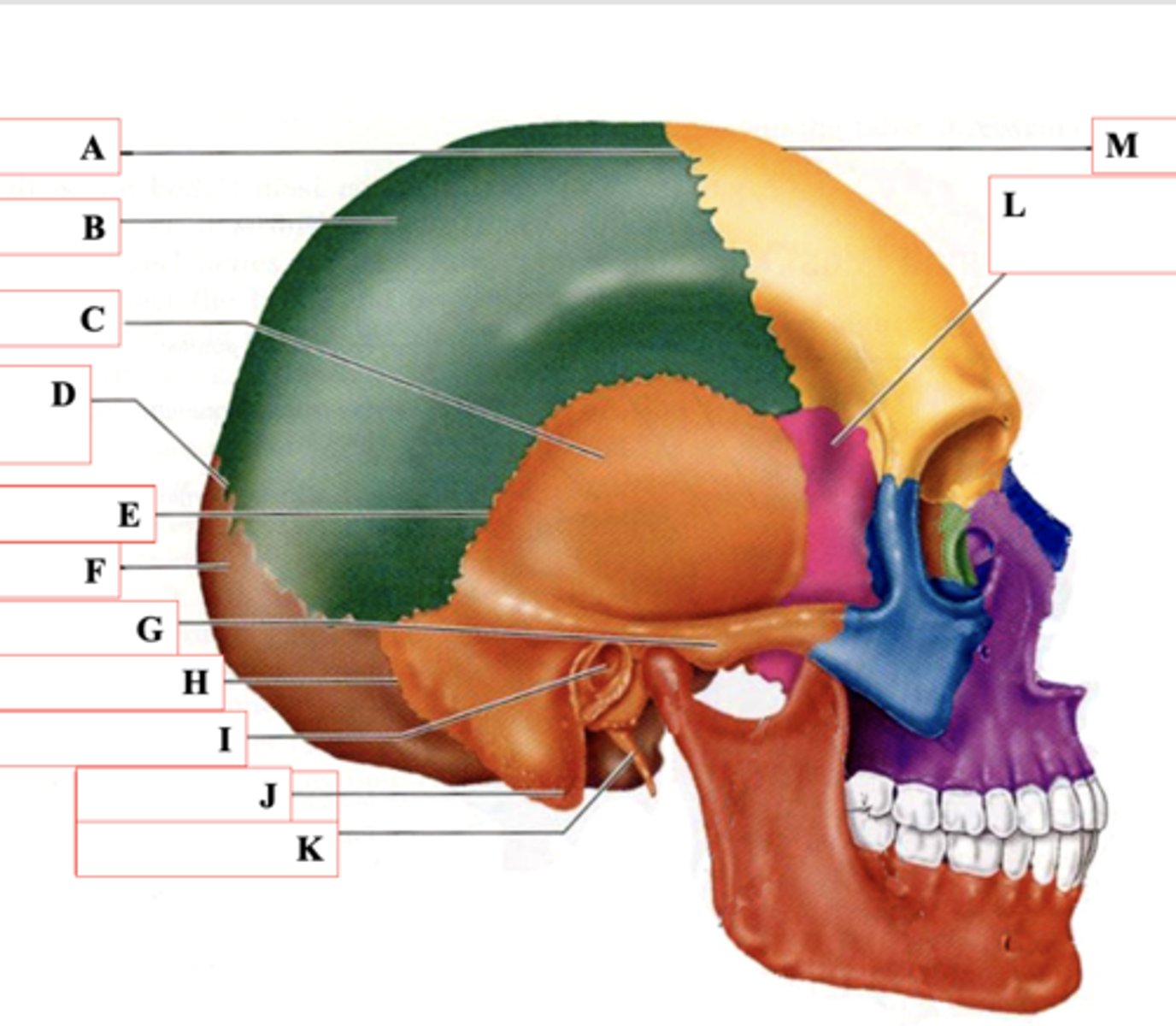
External Auditory Meatus
Identify I.
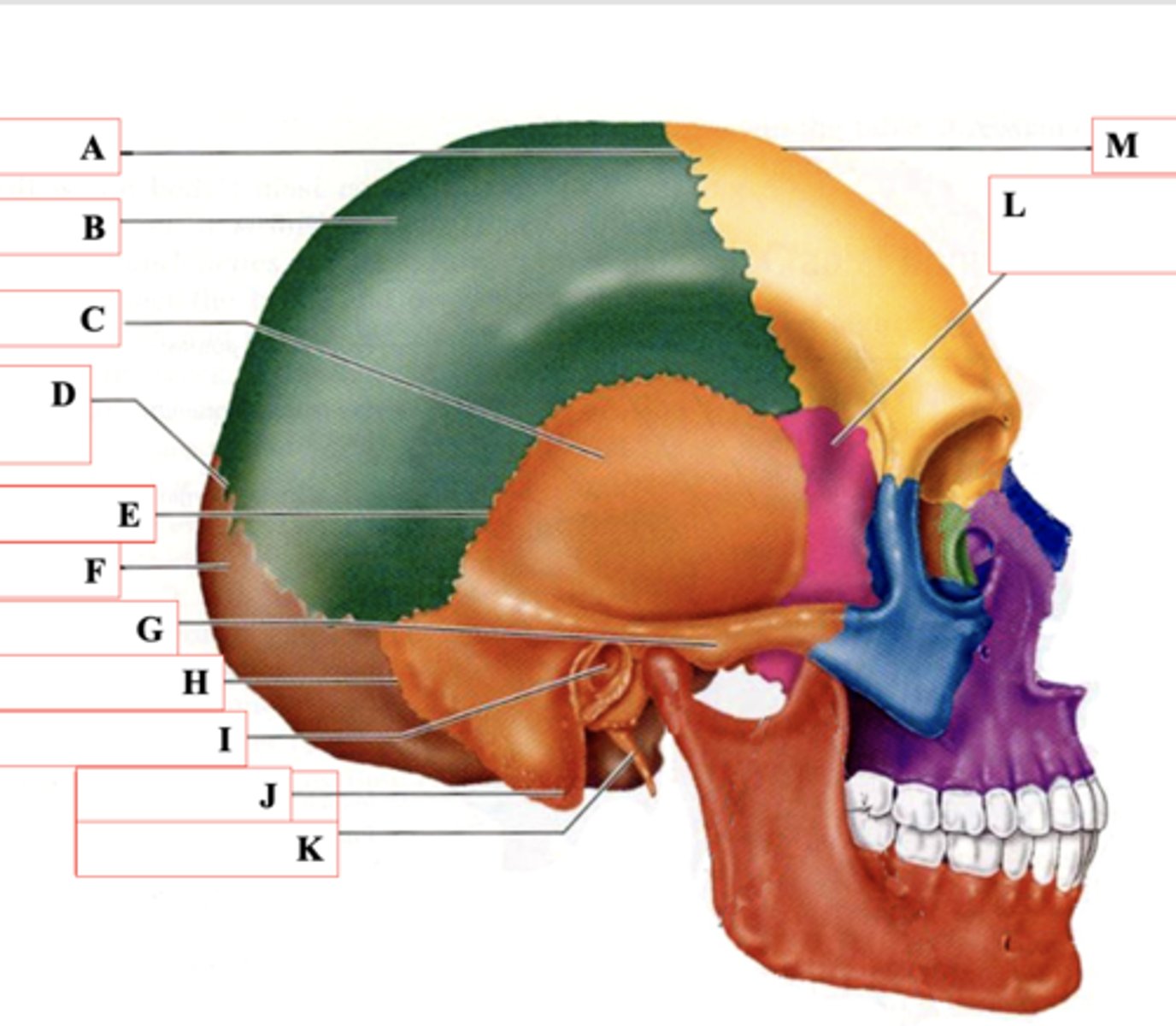
Mastoid Process
Identify J.
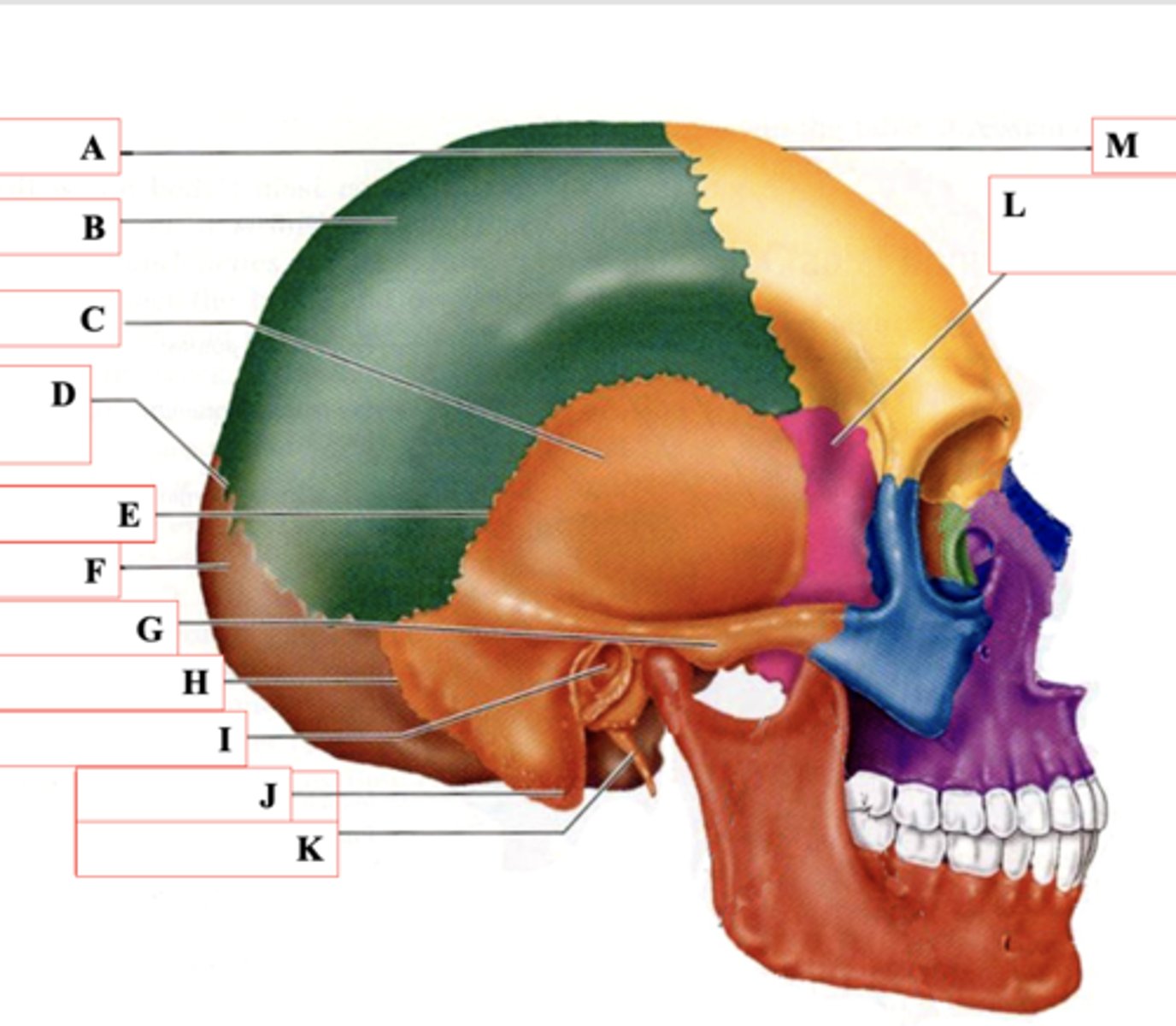
Styloid Process
Identify K.
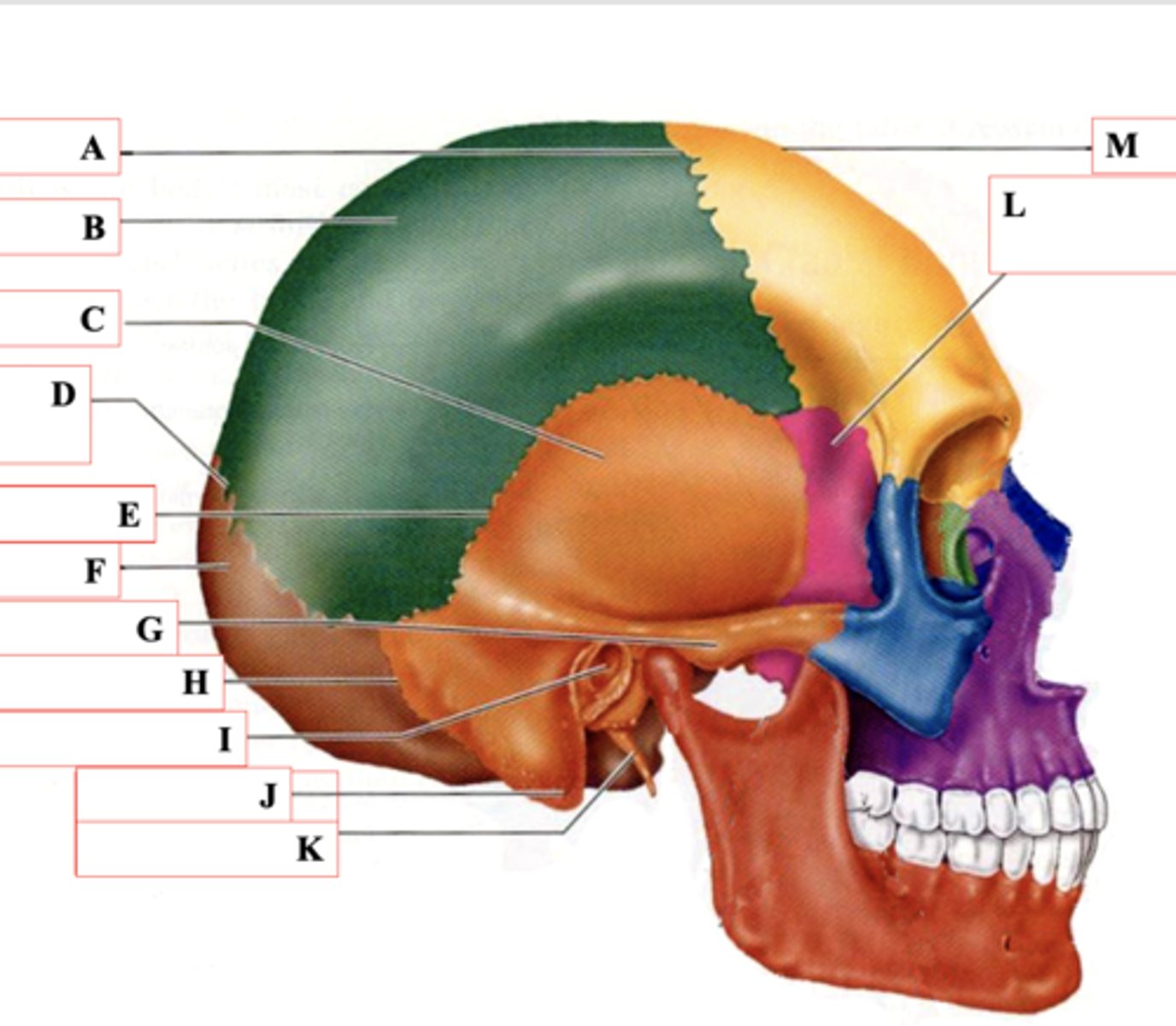
Sphenoid Bone
Identify L.
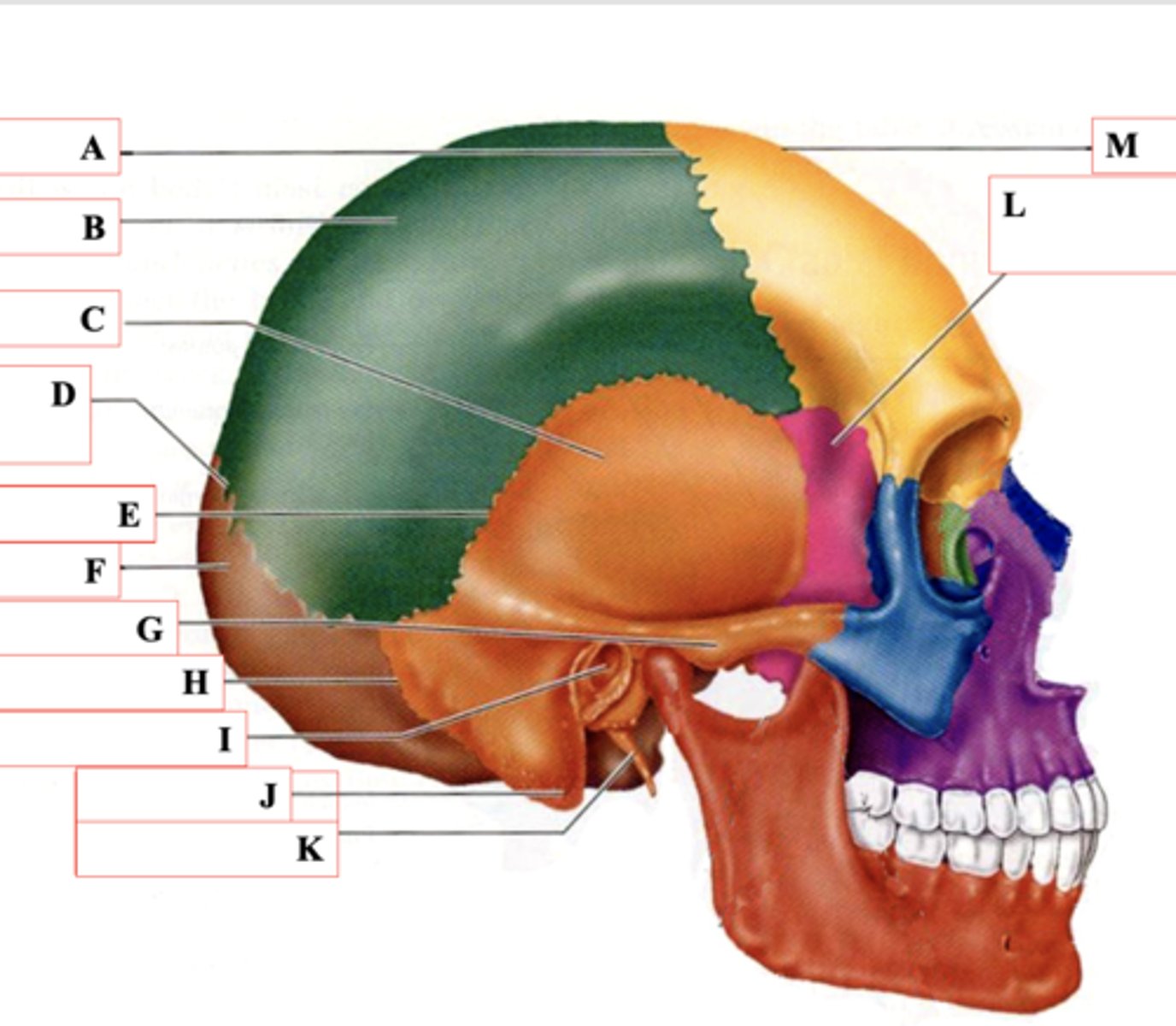
Frontal Bone
Identify M.
Coronal Suture
Identify A.
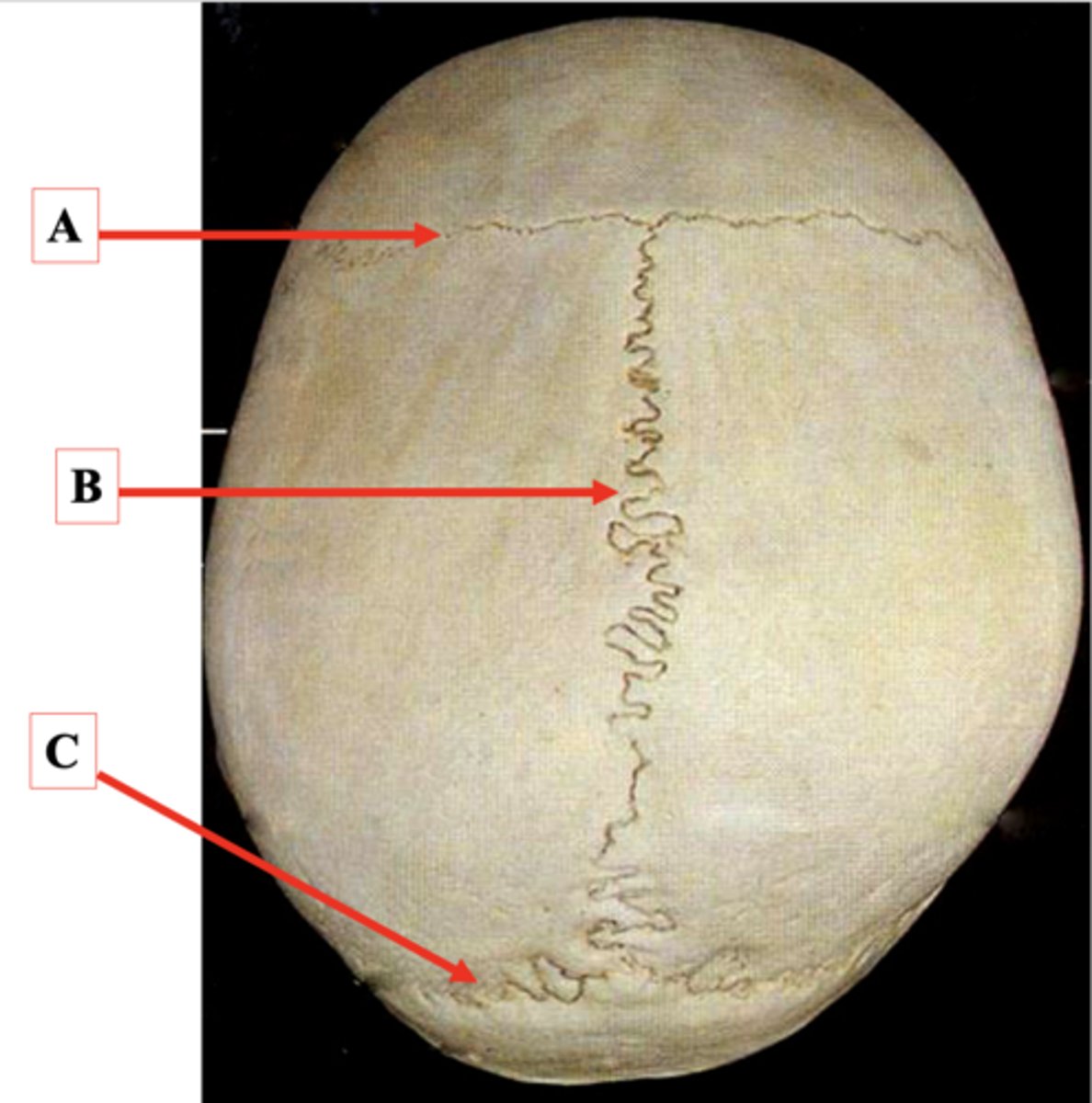
Sagittal Suture
Identify B.
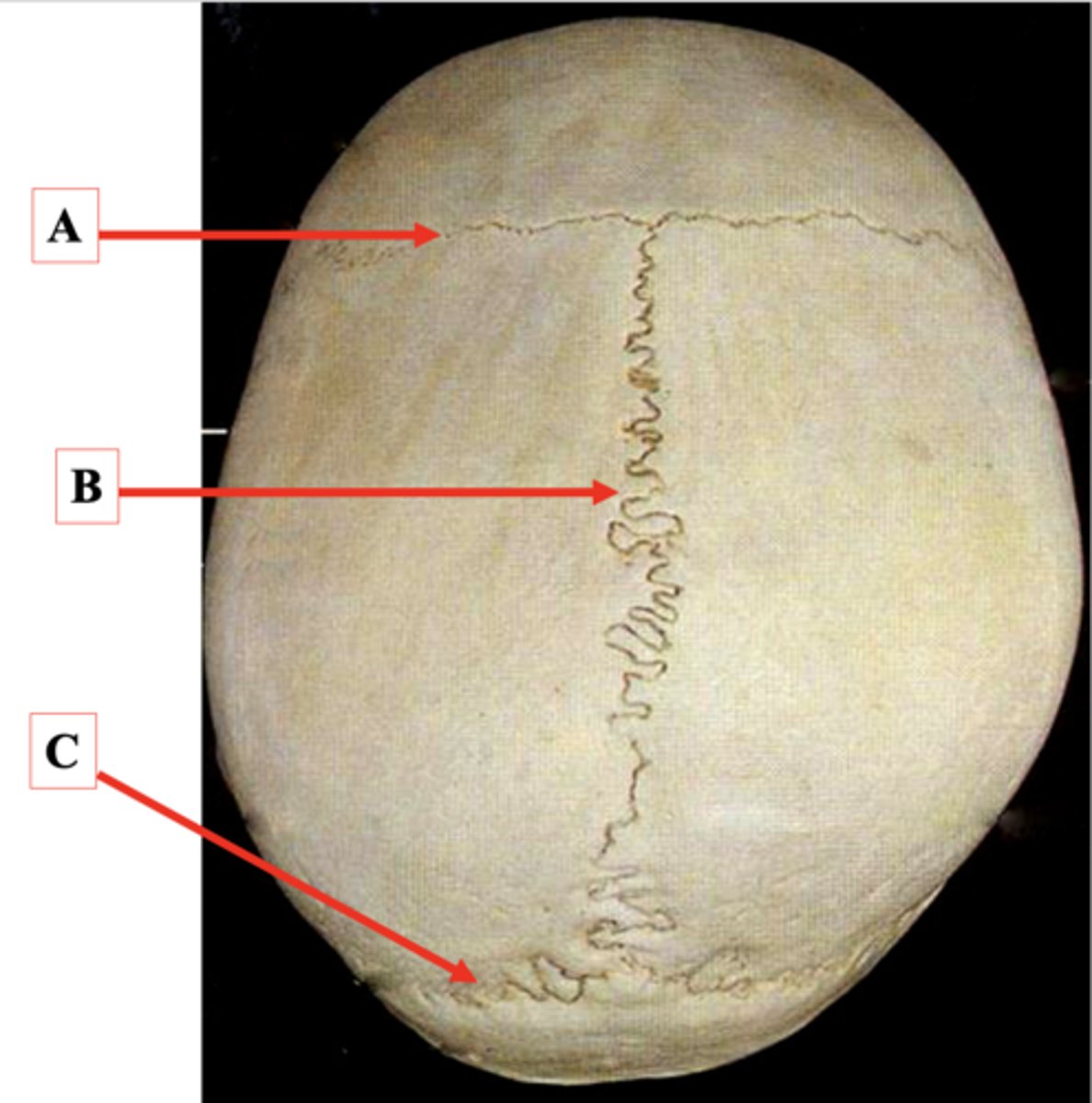
Lambdoid Suture
Identify C.
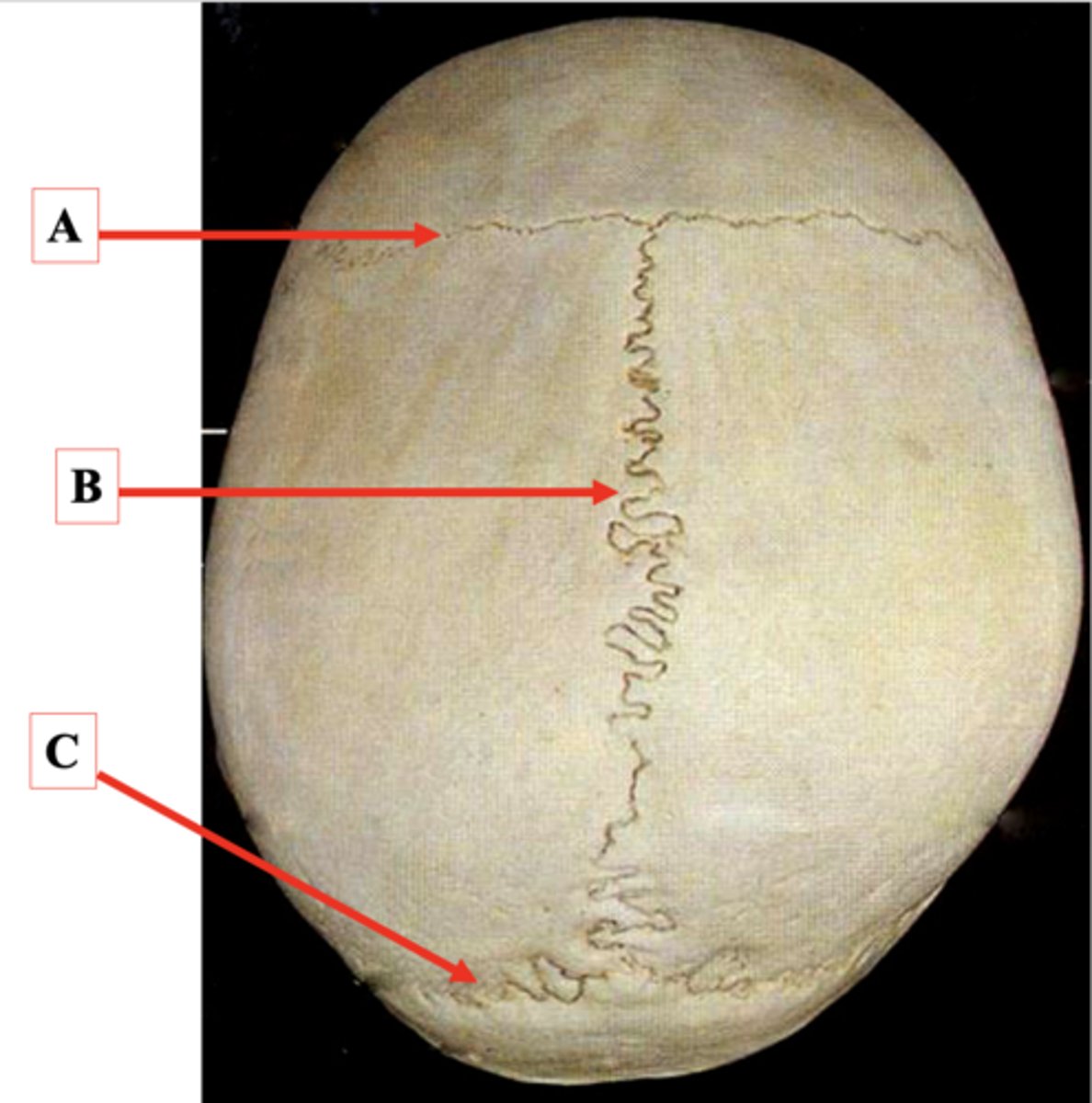
Sagittal Suture
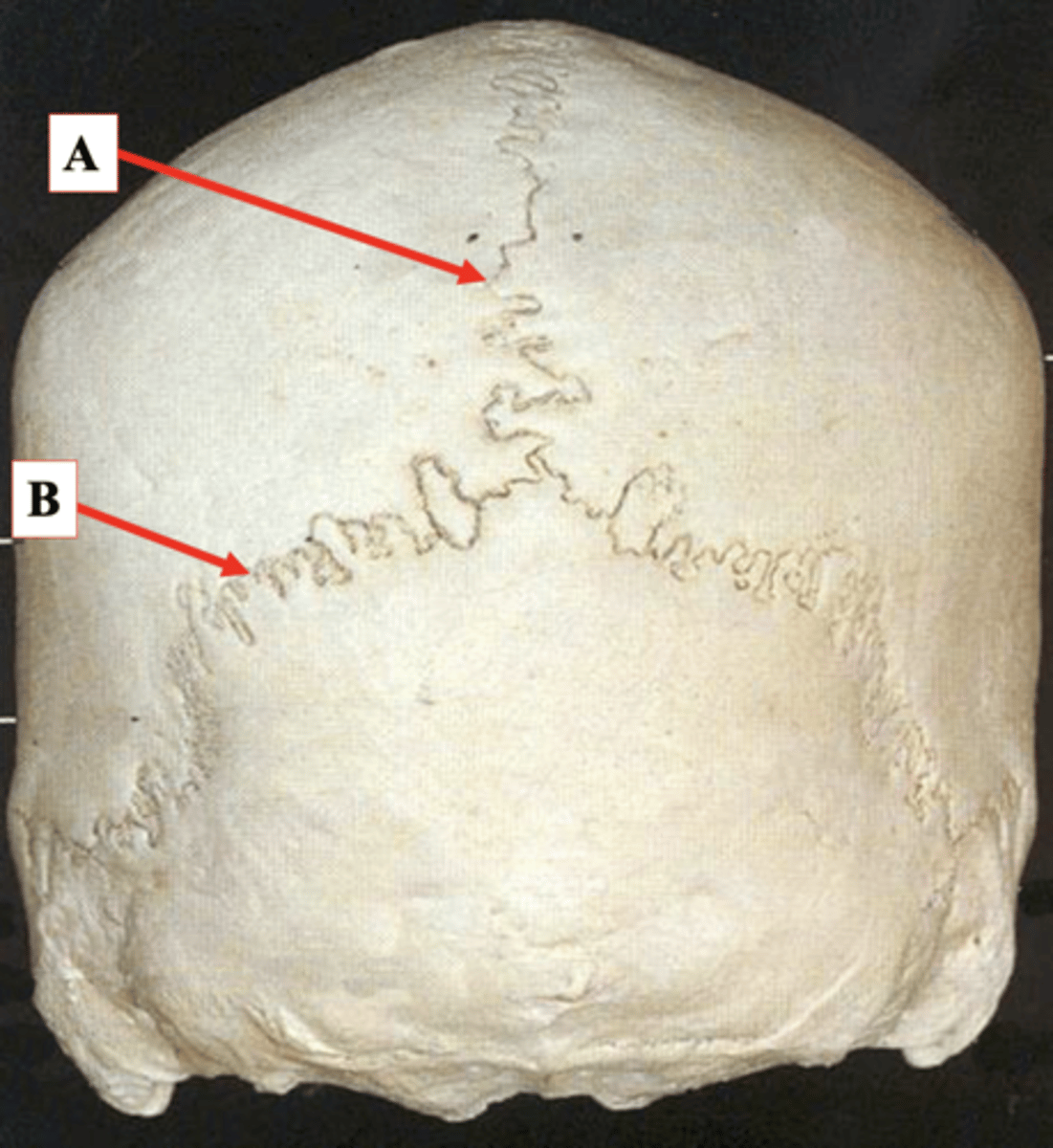
Identify A.
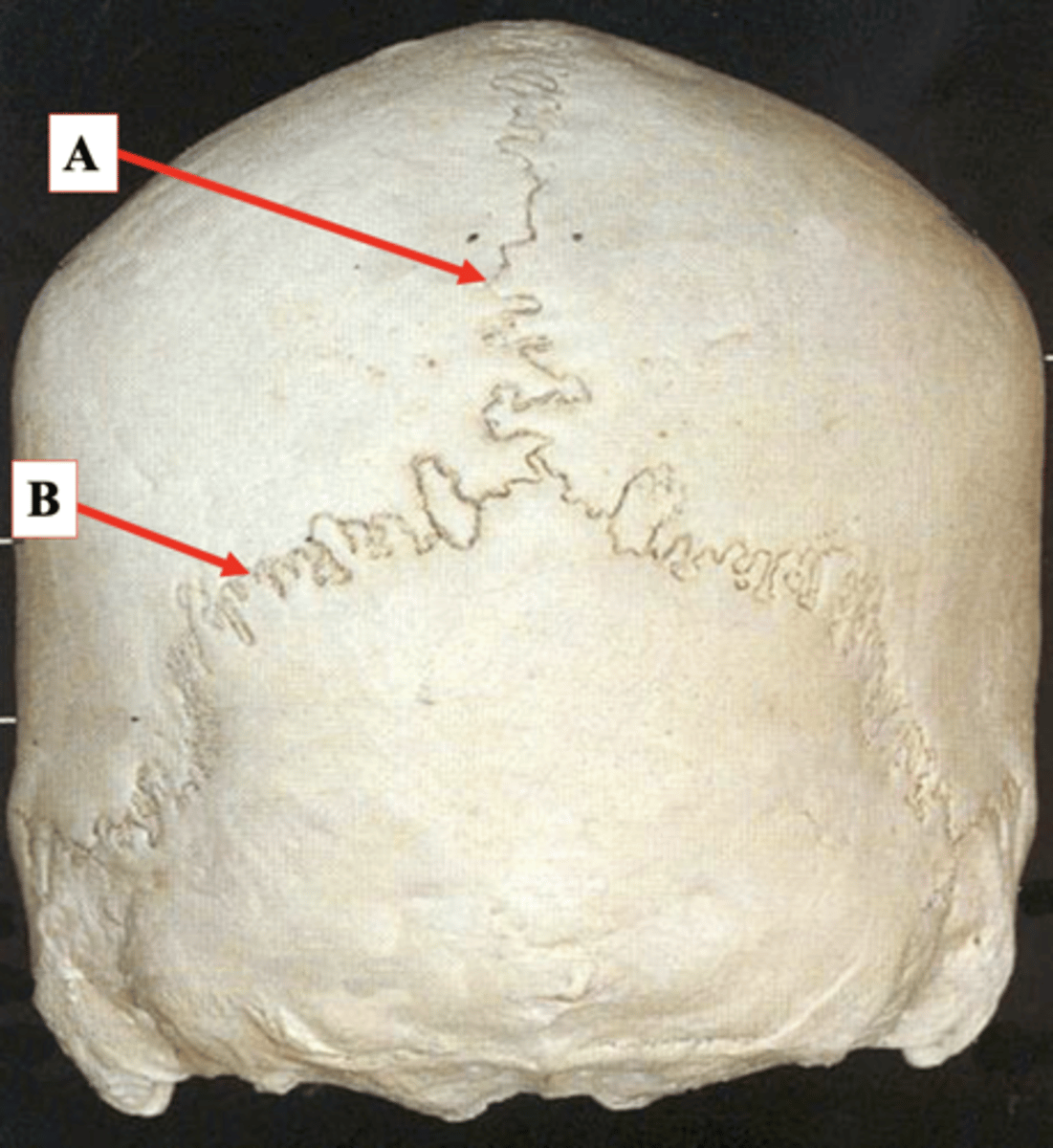
Lambdoid Suture
Identify B.
Flexible Fibrous Joints
What are sutures in a newborn infant?
Anterior Fontanelle
Should close by the age of 2
Anterior Fontanelle
Identify A.
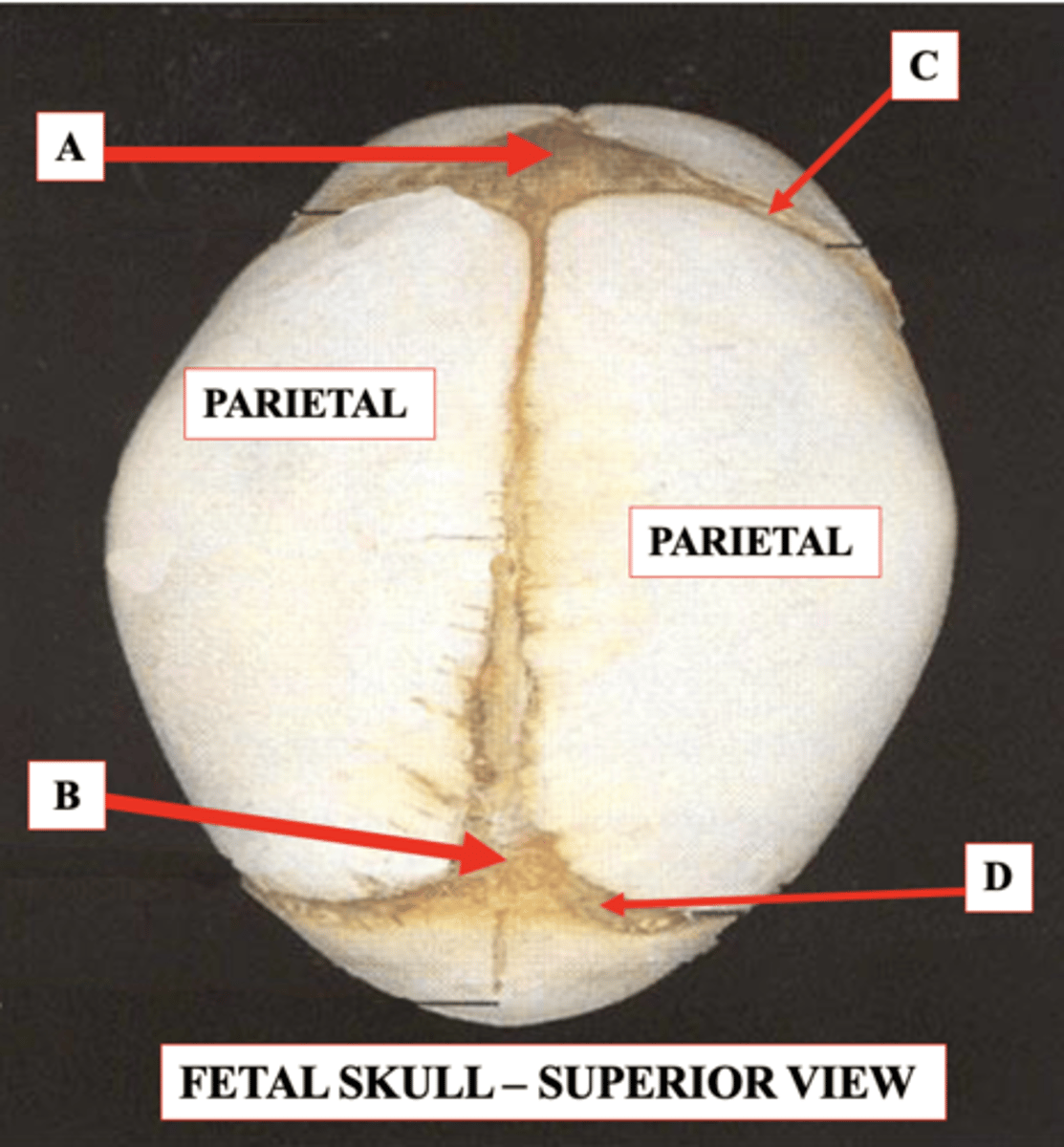
Posterior Fontanelle
Should close by about 3-4 months of age
Posterior Fontanelle
Identify B.
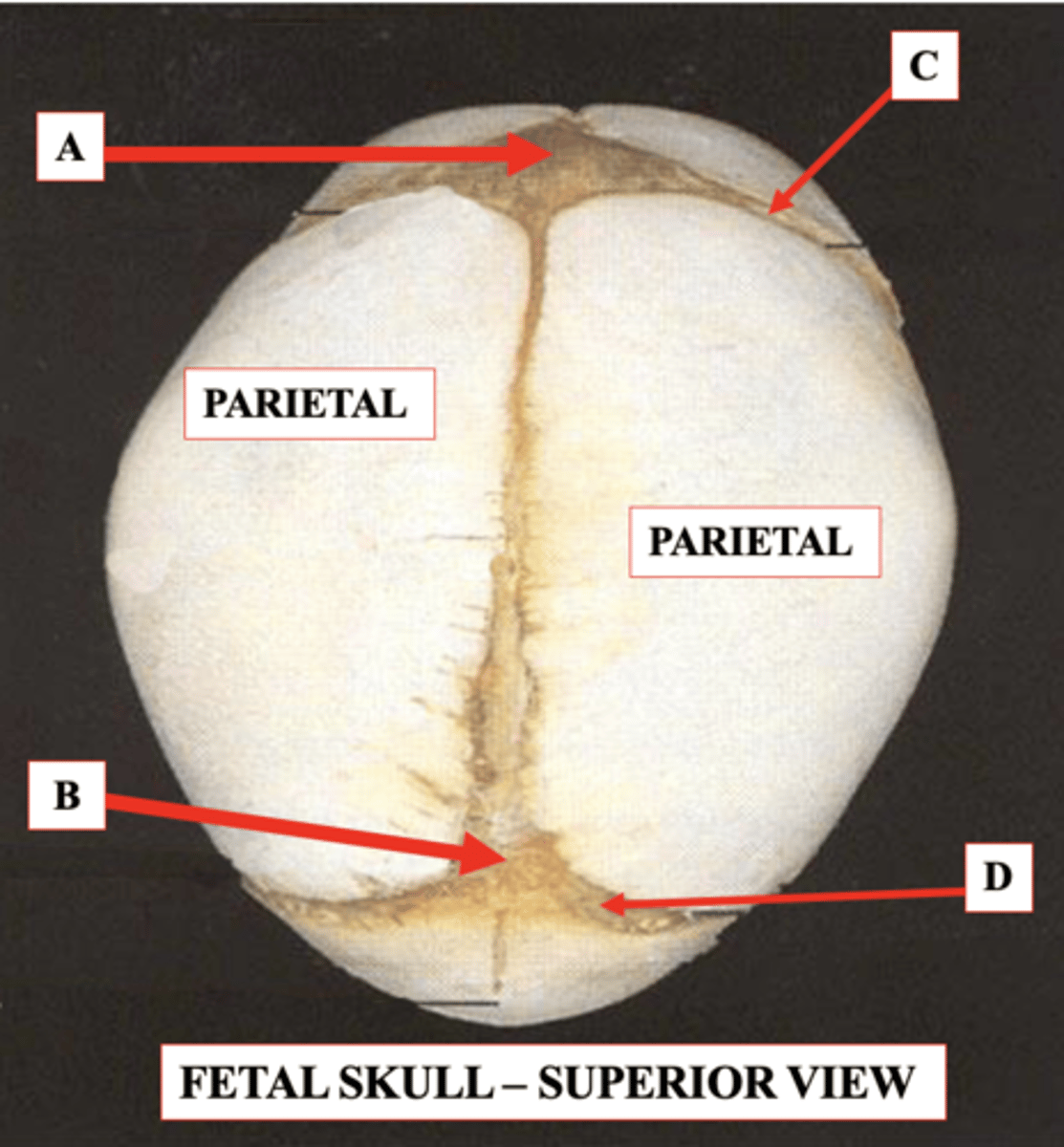
Coronal Suture
Identify C.
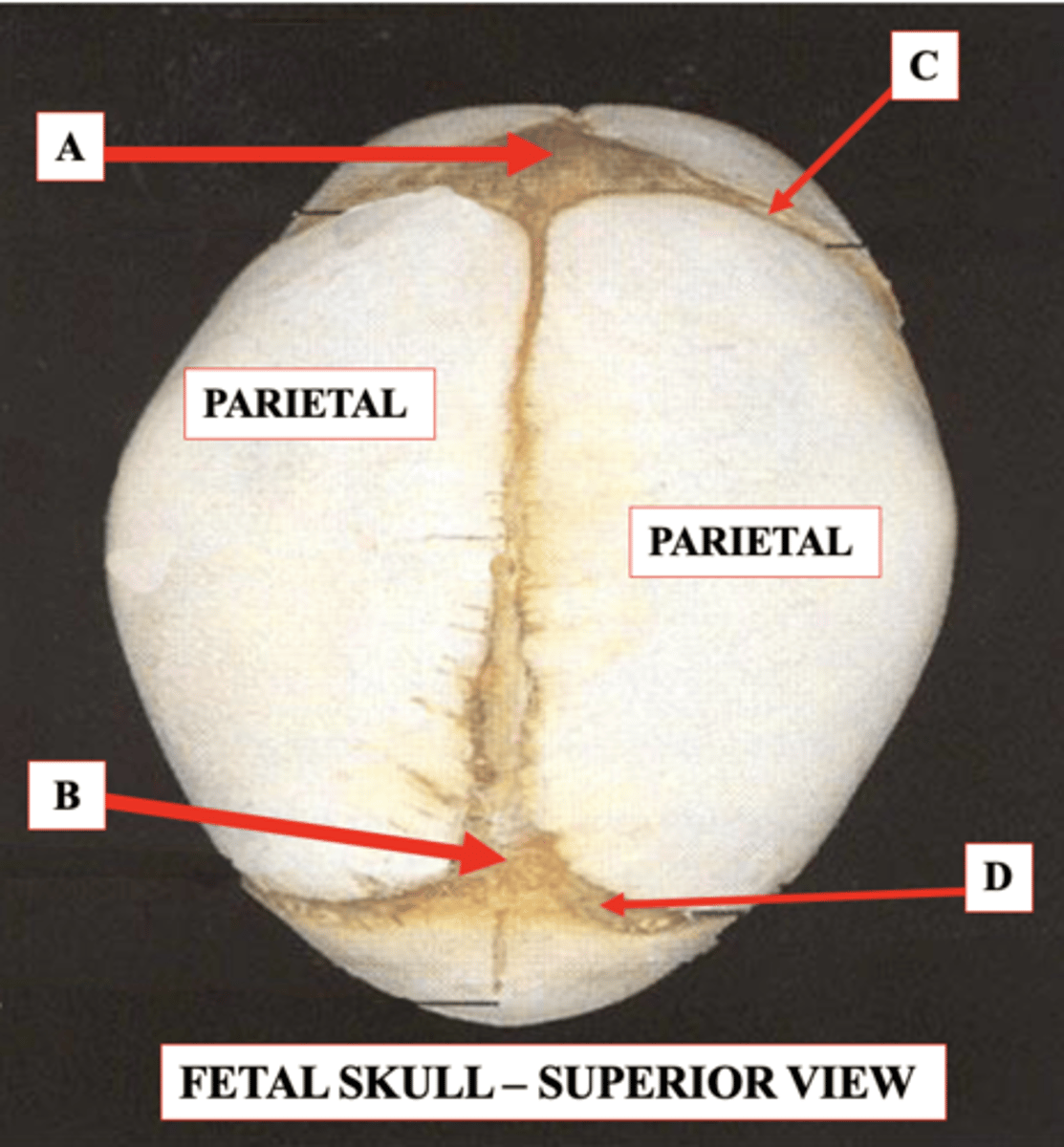
Lambdoid Suture
Identify D.
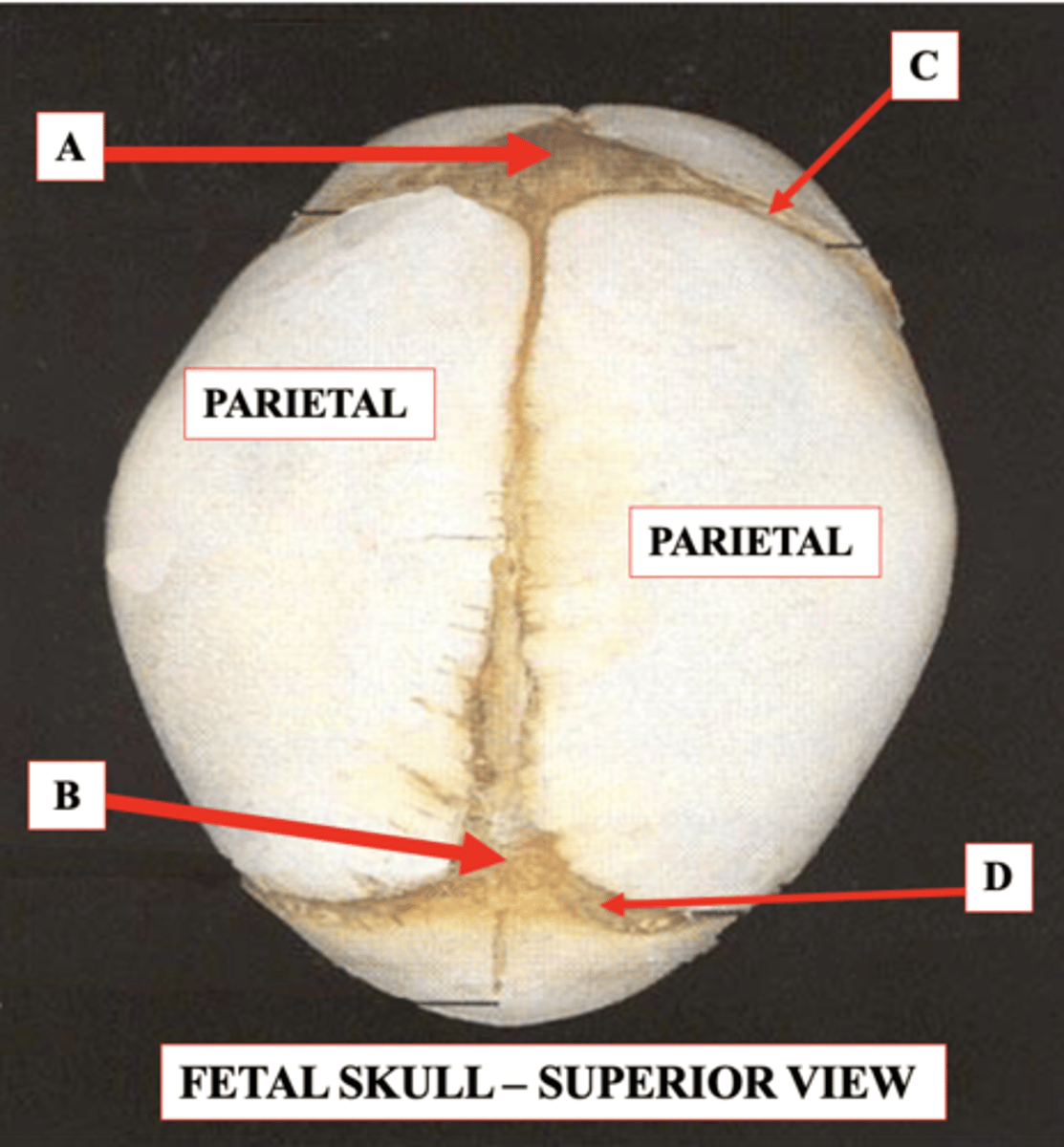
Anterior Fontanelle
Identify A.
Metopic Suture
Identify B.
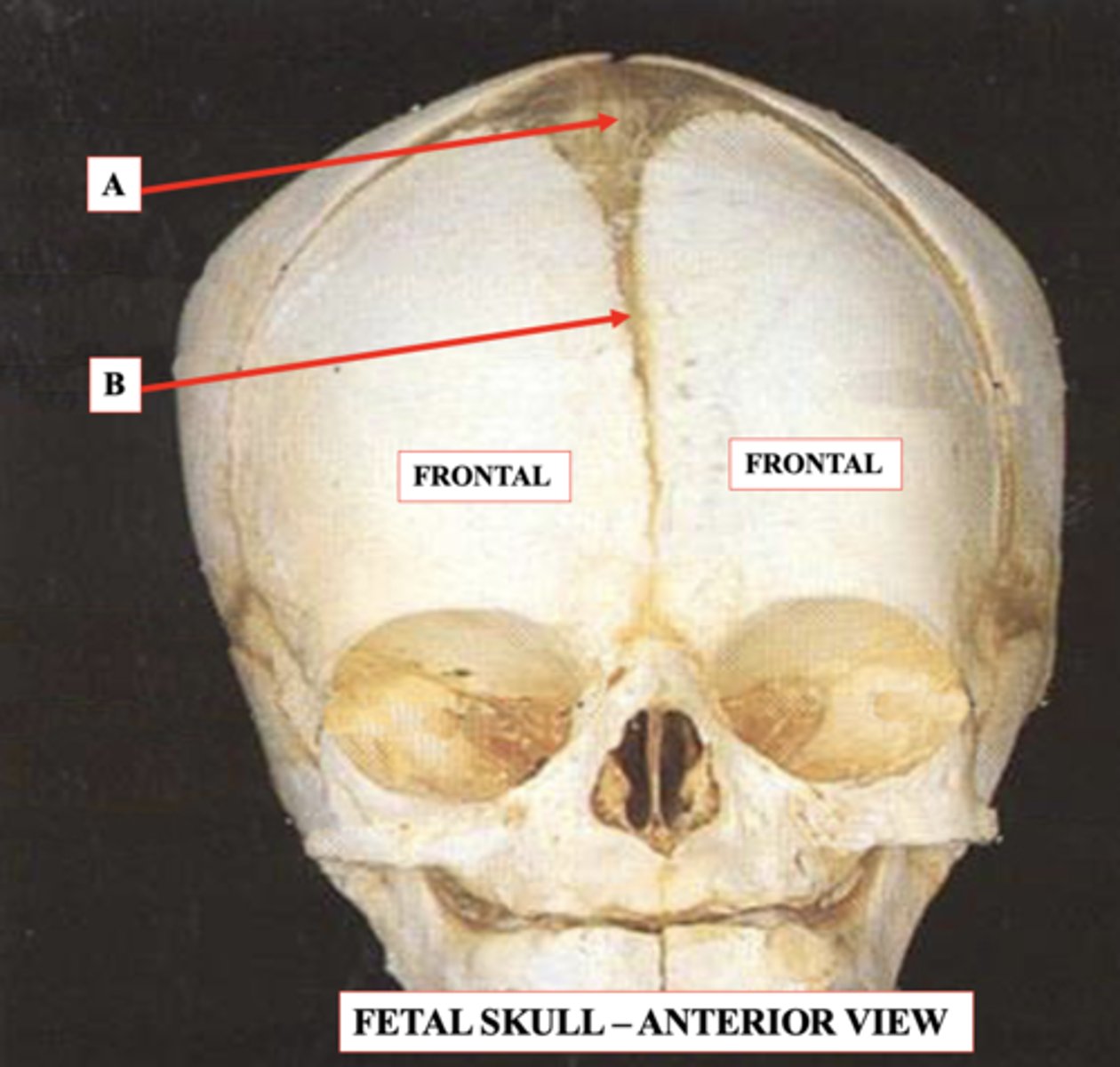
Craniosynostosis
- Premature closure of cranial suture(s) causes abnormal head shape as the brain grows unevenly
- Can be part of various genetic syndromes (~20%)

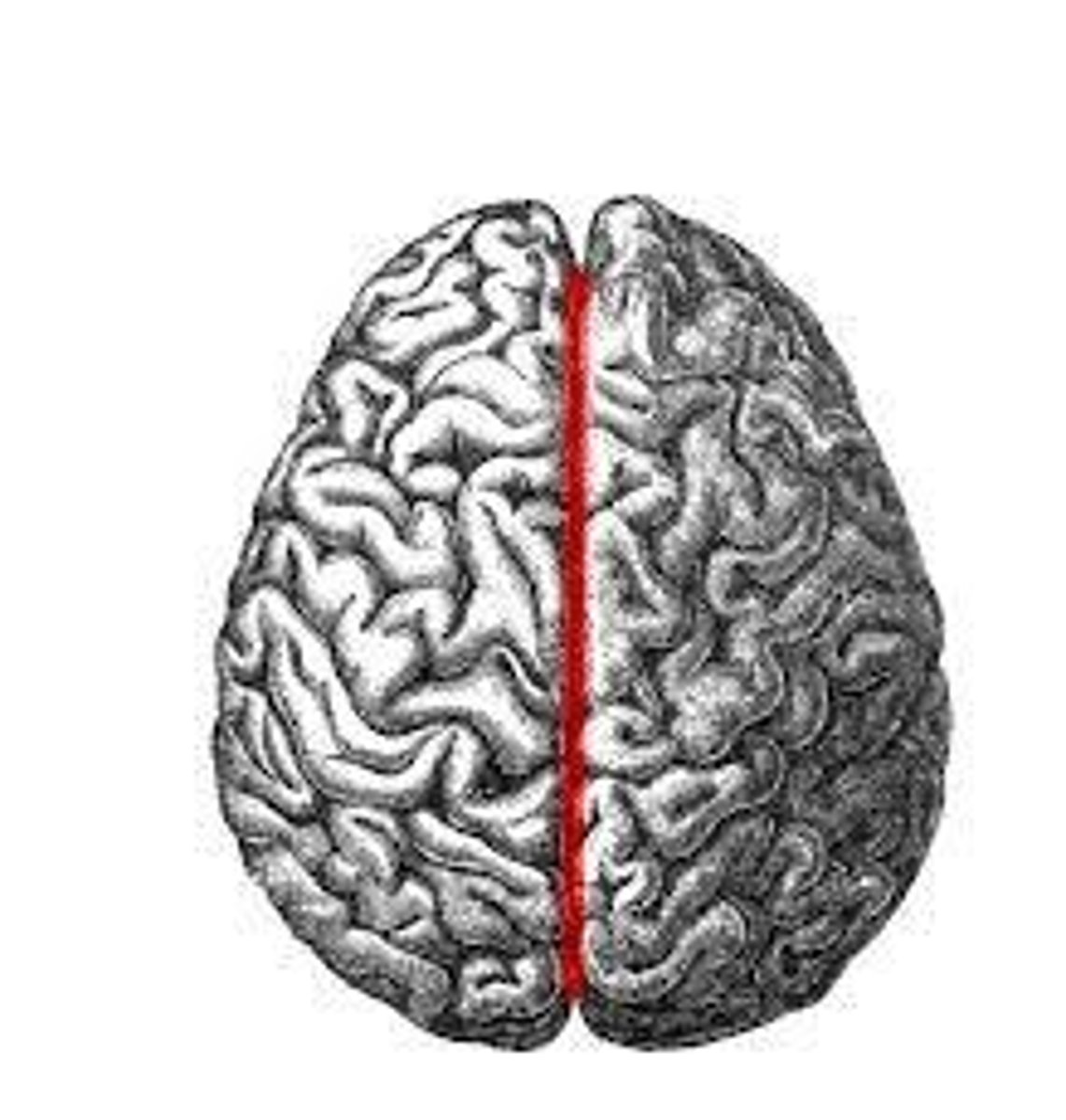
Median Longitudinal Fissure
What are the 2 cerebral hemispheres separated by?
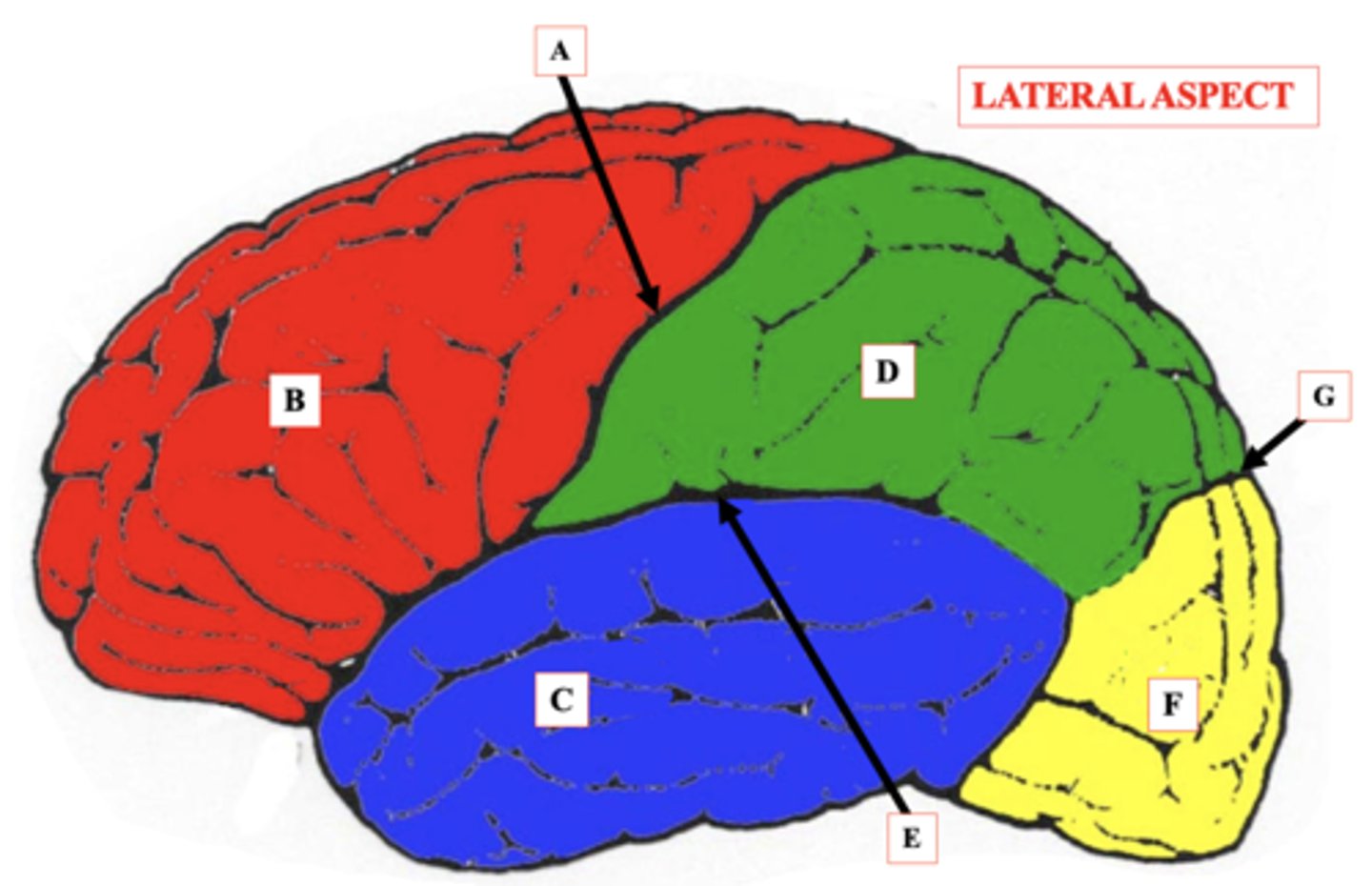
Central Sulcus
Identify A.
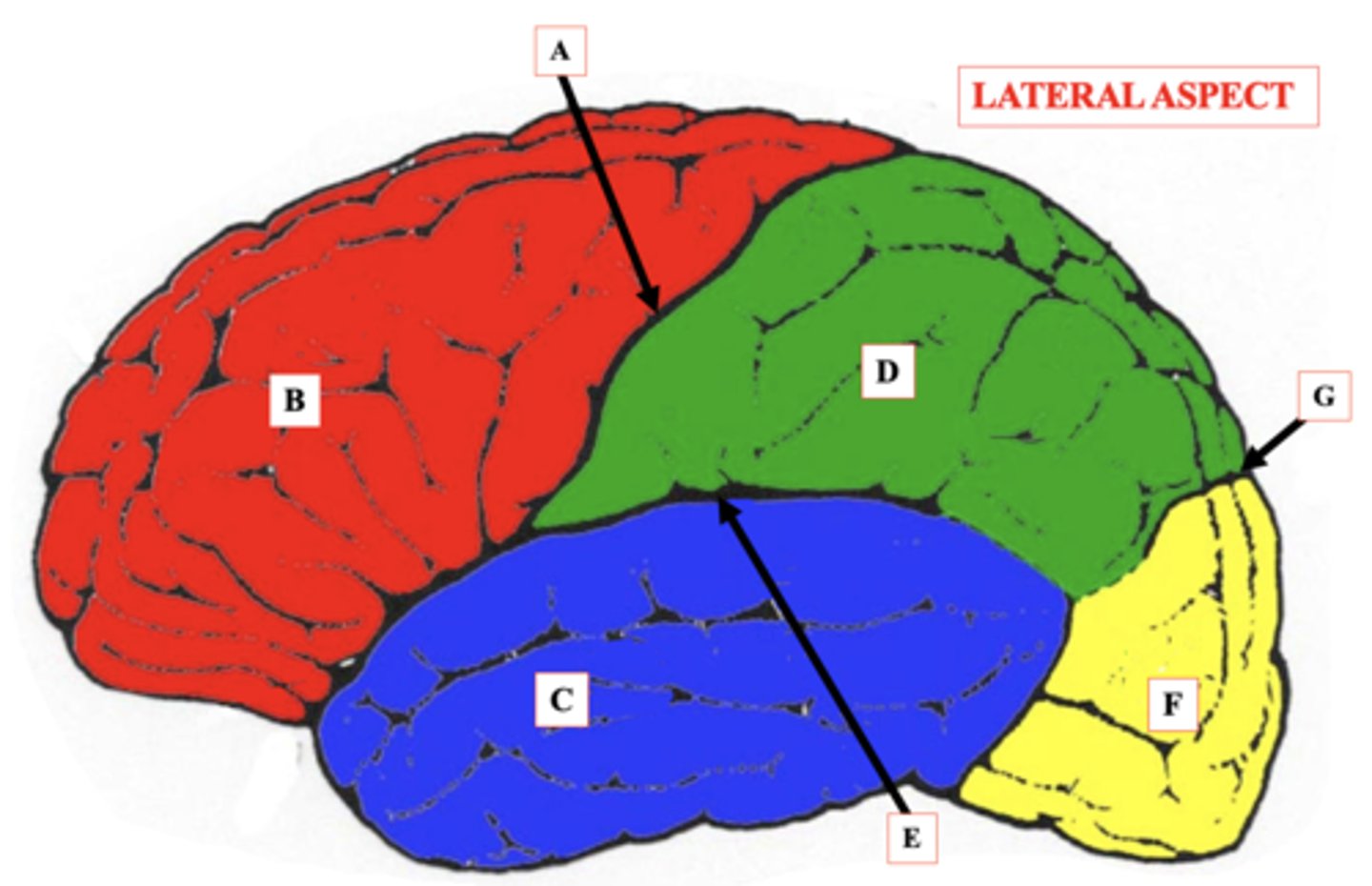
Frontal Lobe
Identify B.
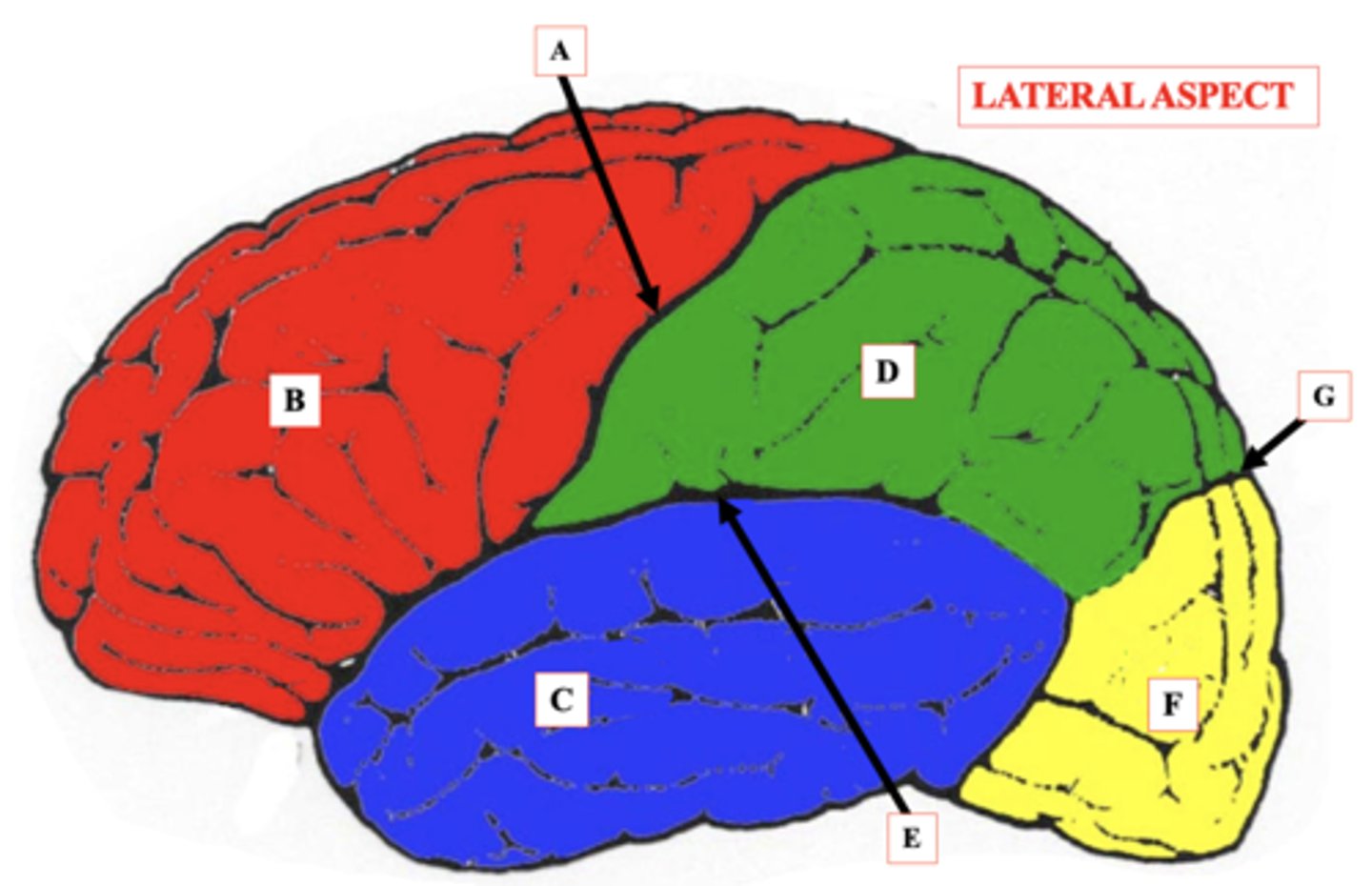
Temporal Lobe
Identify C.
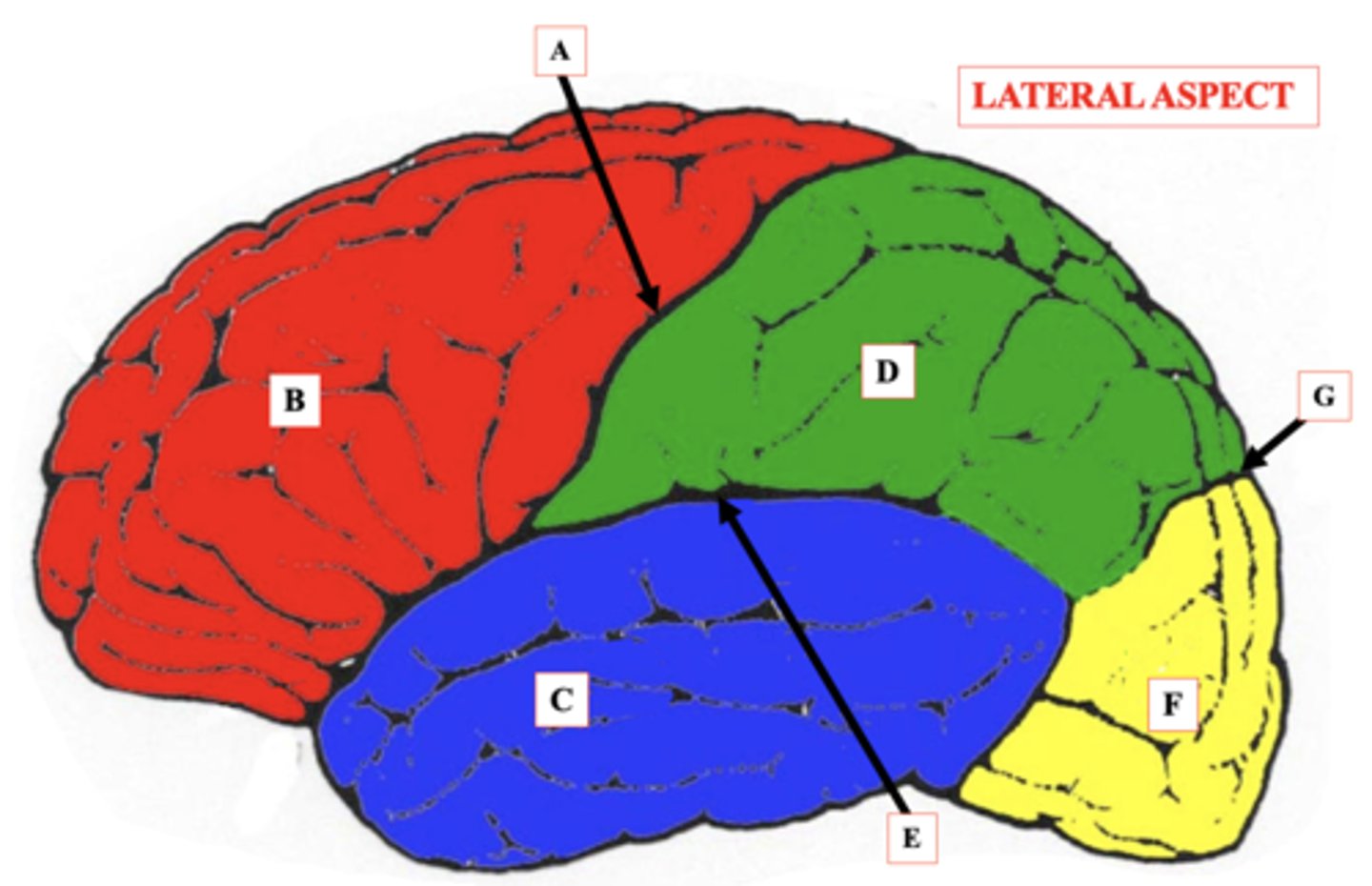
Parietal Lobe
Identify D.
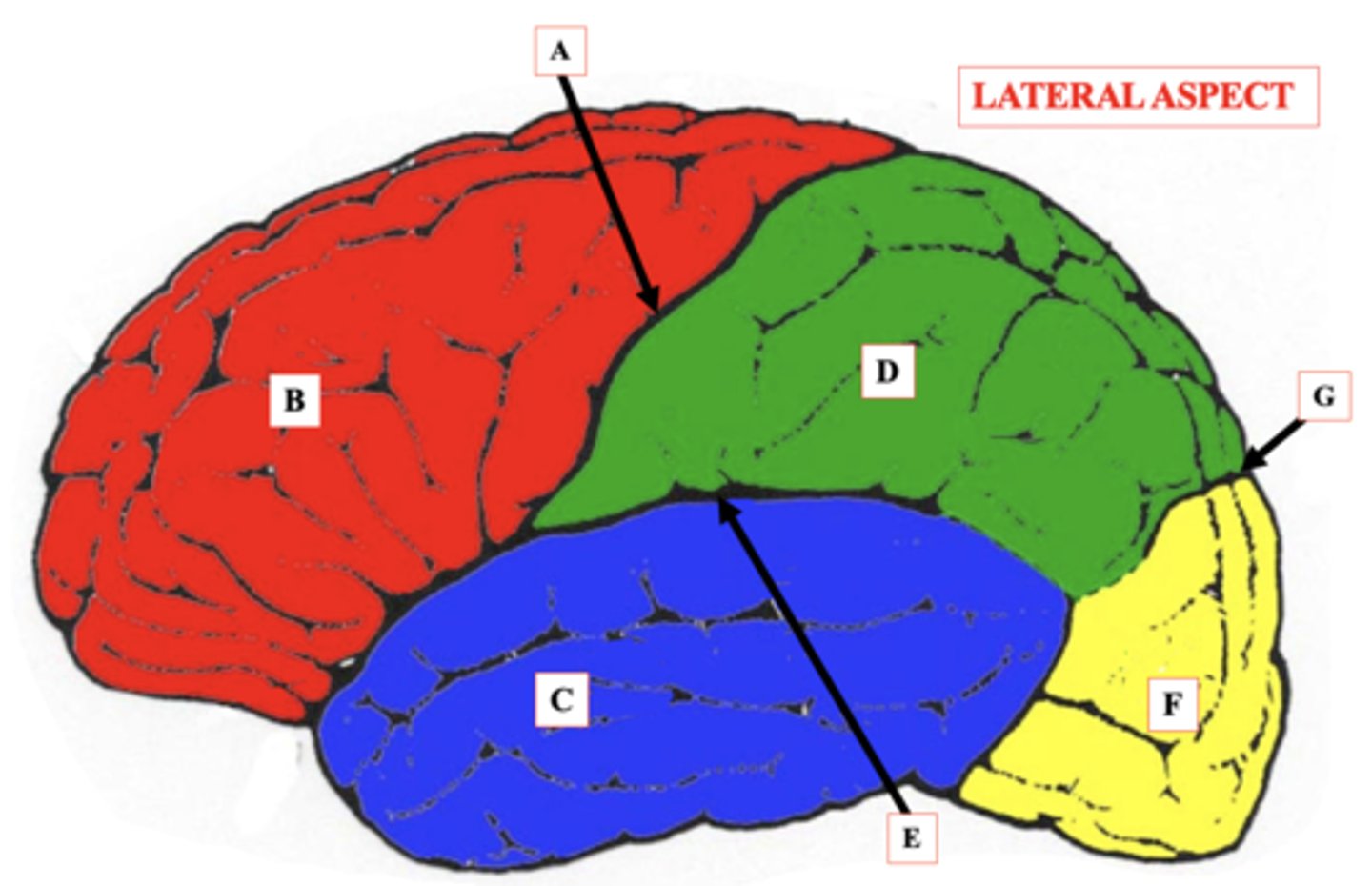
lateral Sulcus
Identify E.
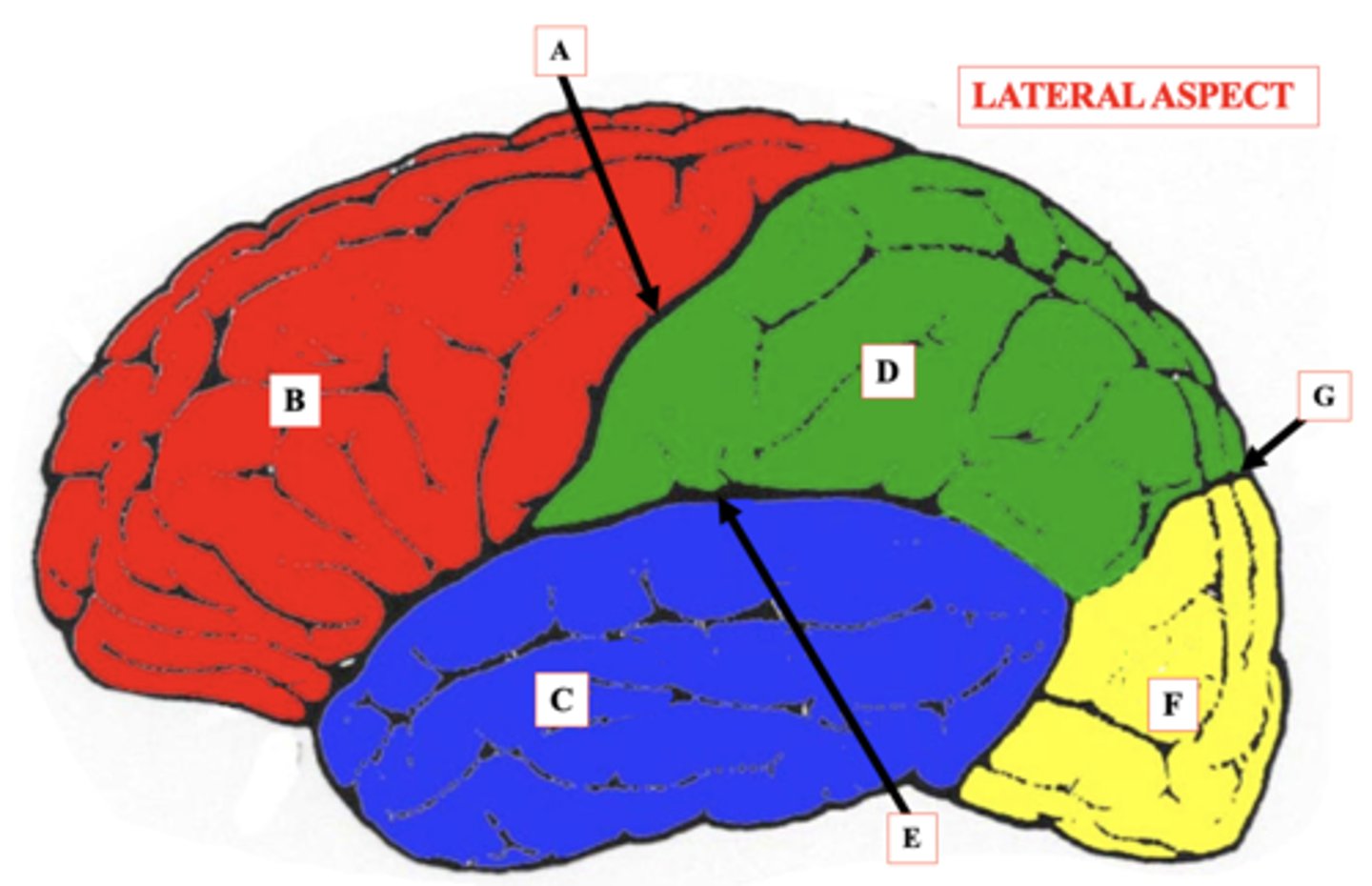
Occipital Lobe
Identify F.
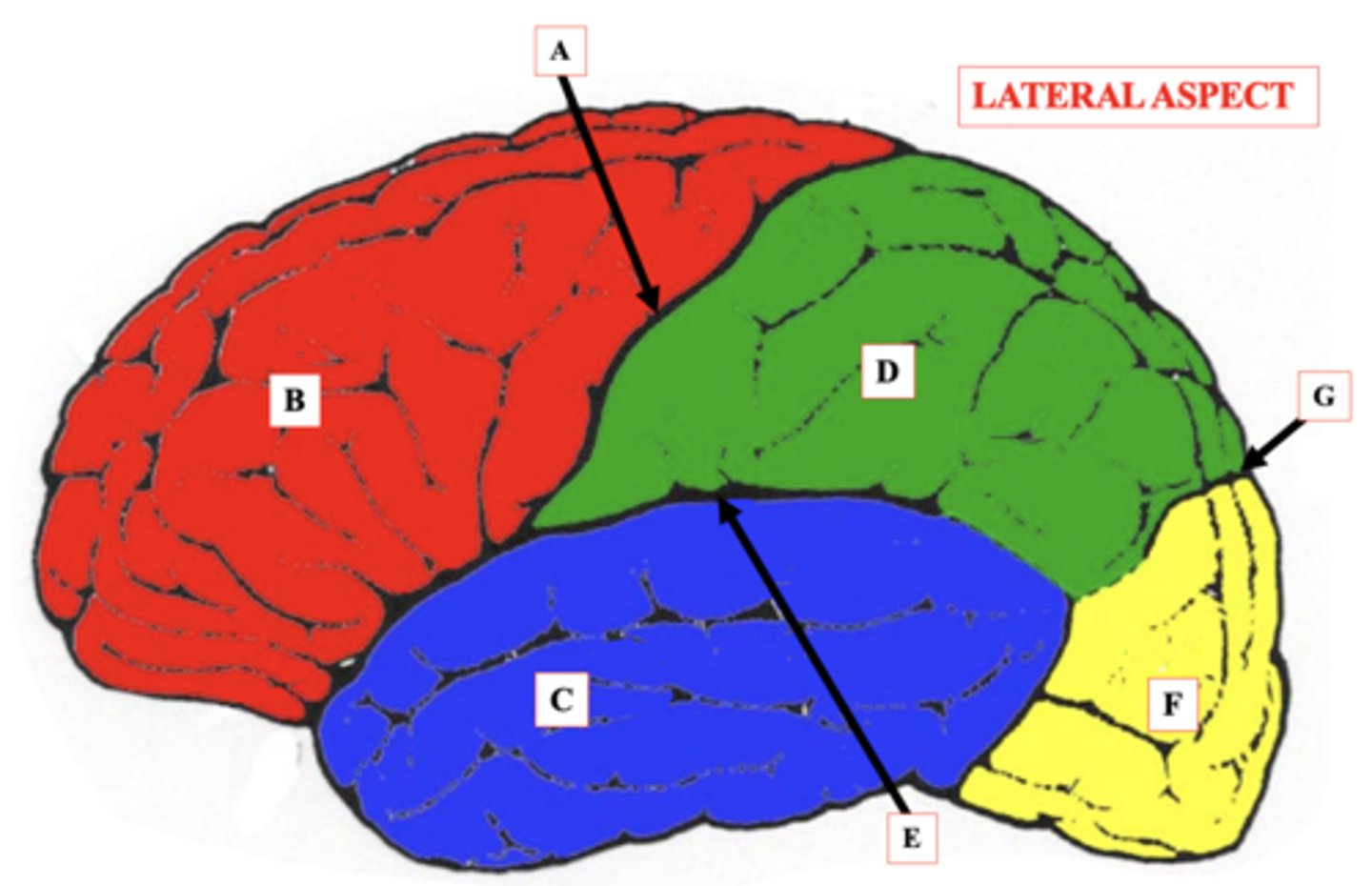
Parieto-Occipital Notch
Identify G.
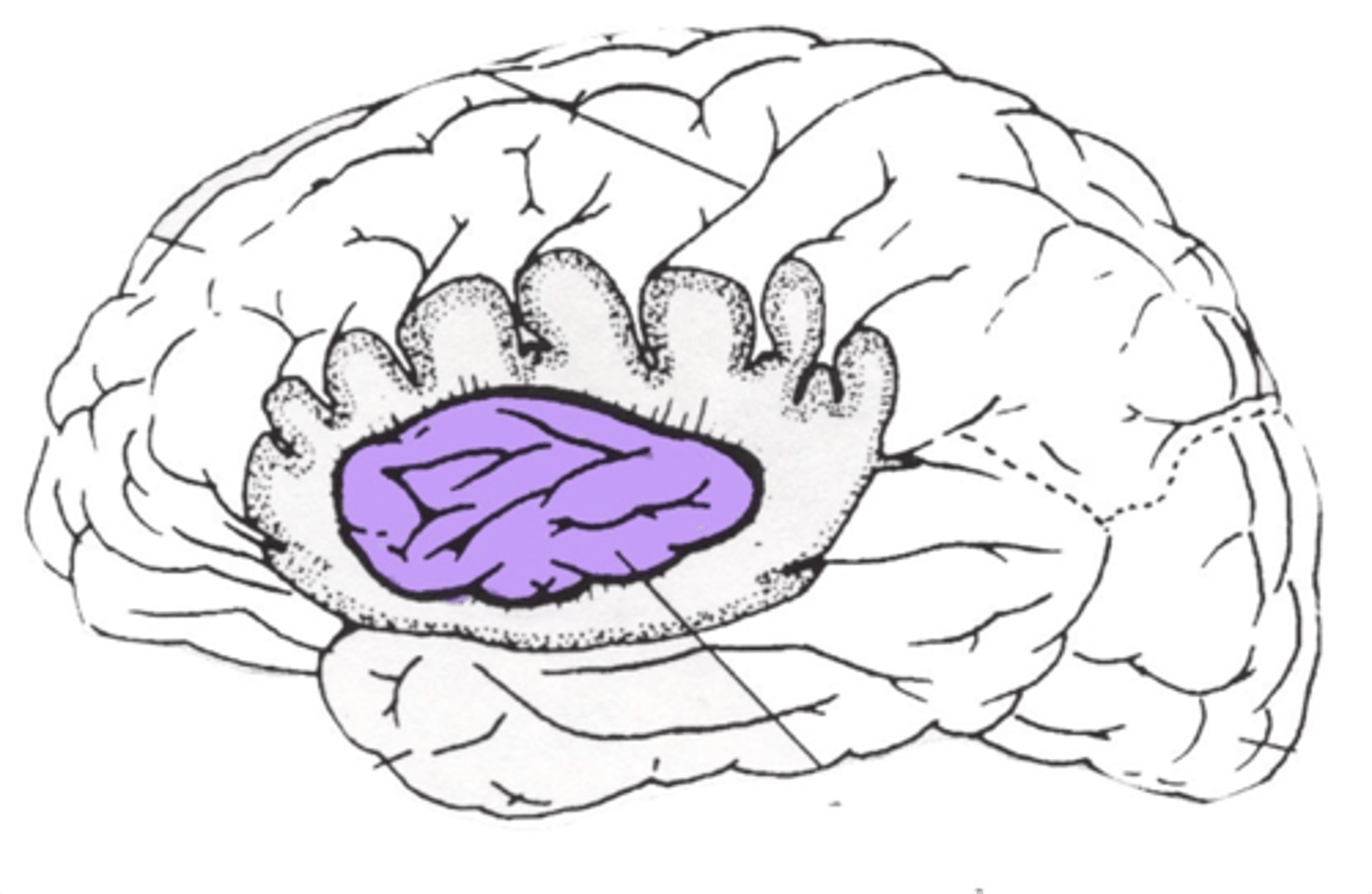
The Insula - Lobe #5
Identify.
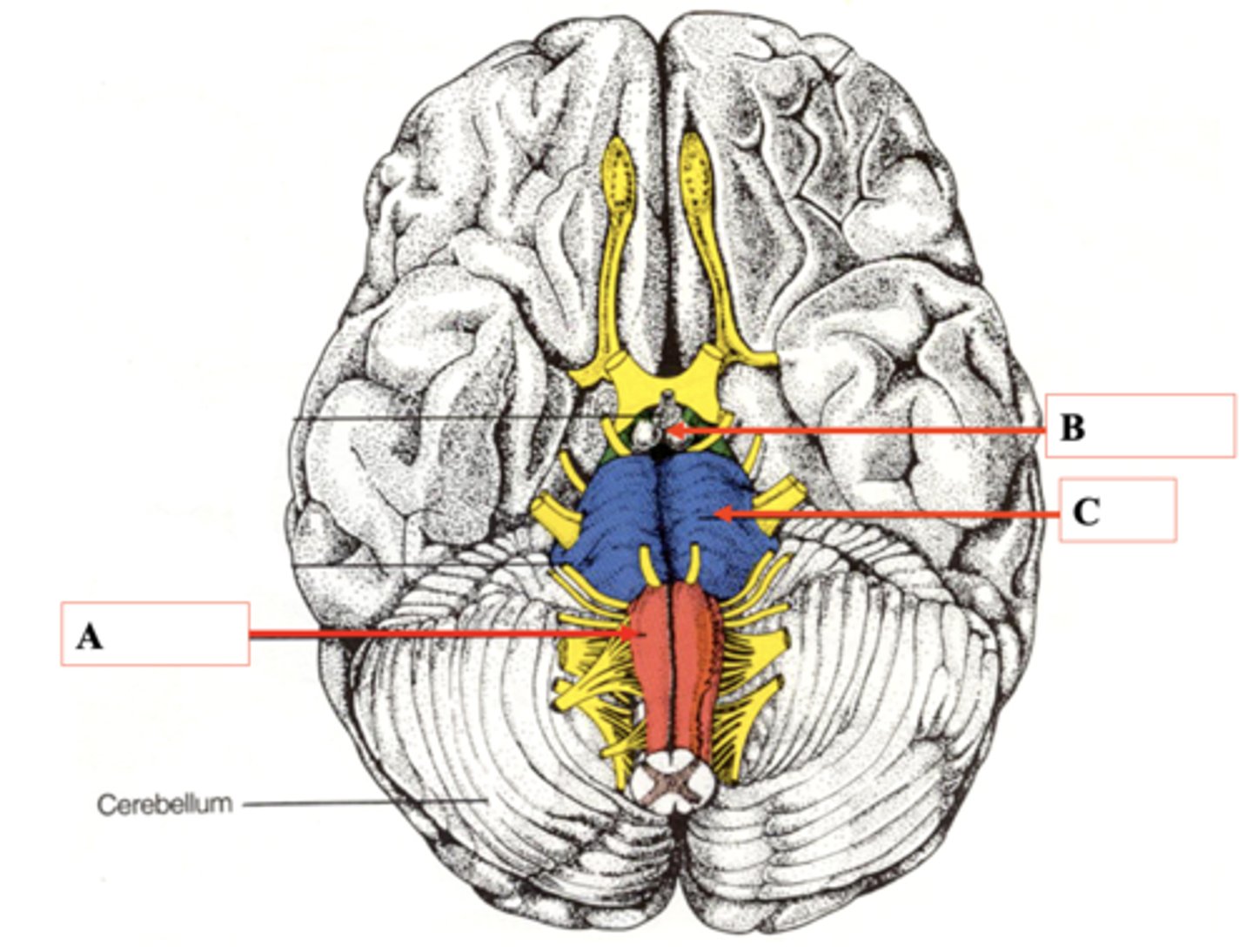
Medulla
Identify A.
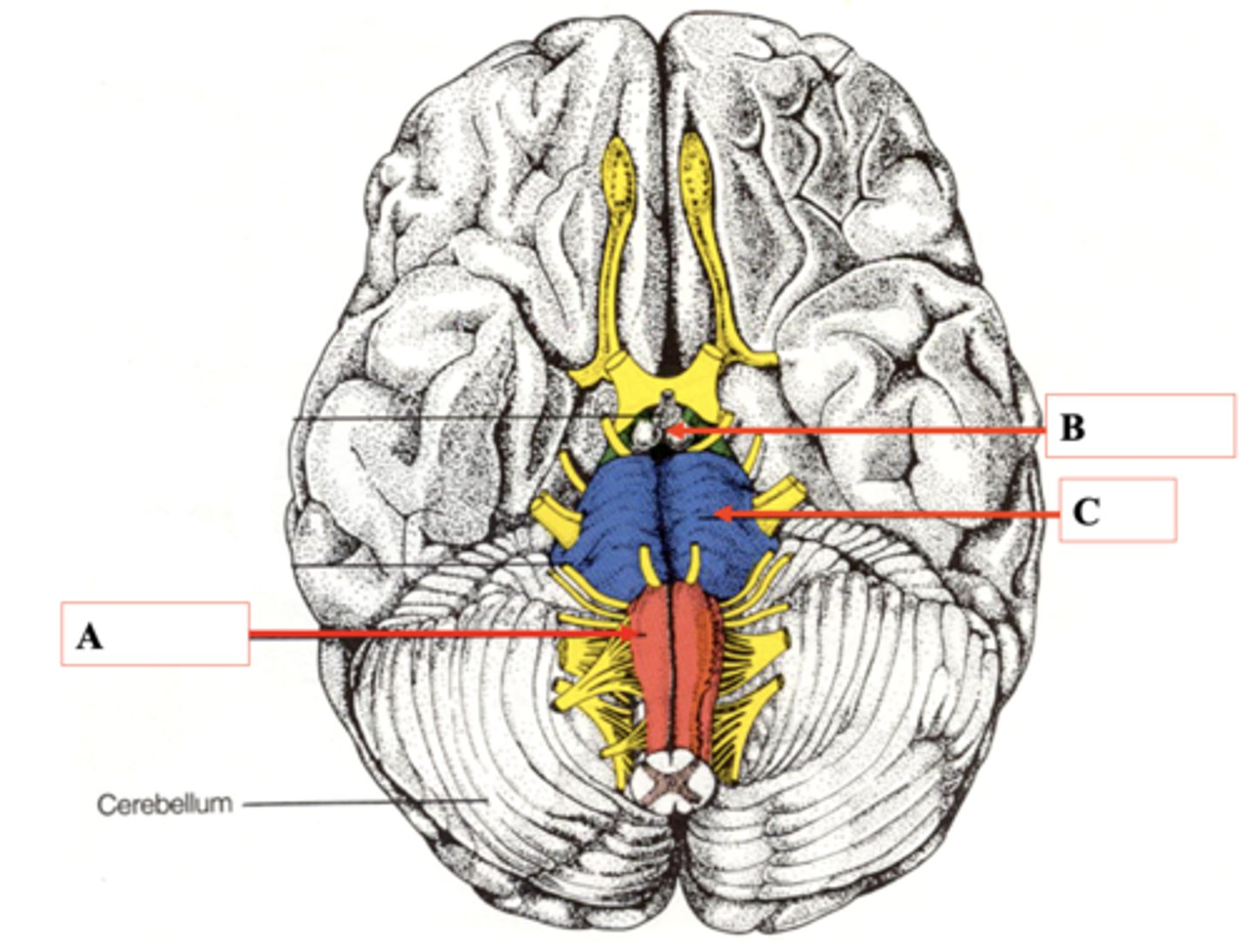
Midbrain
Identify B.
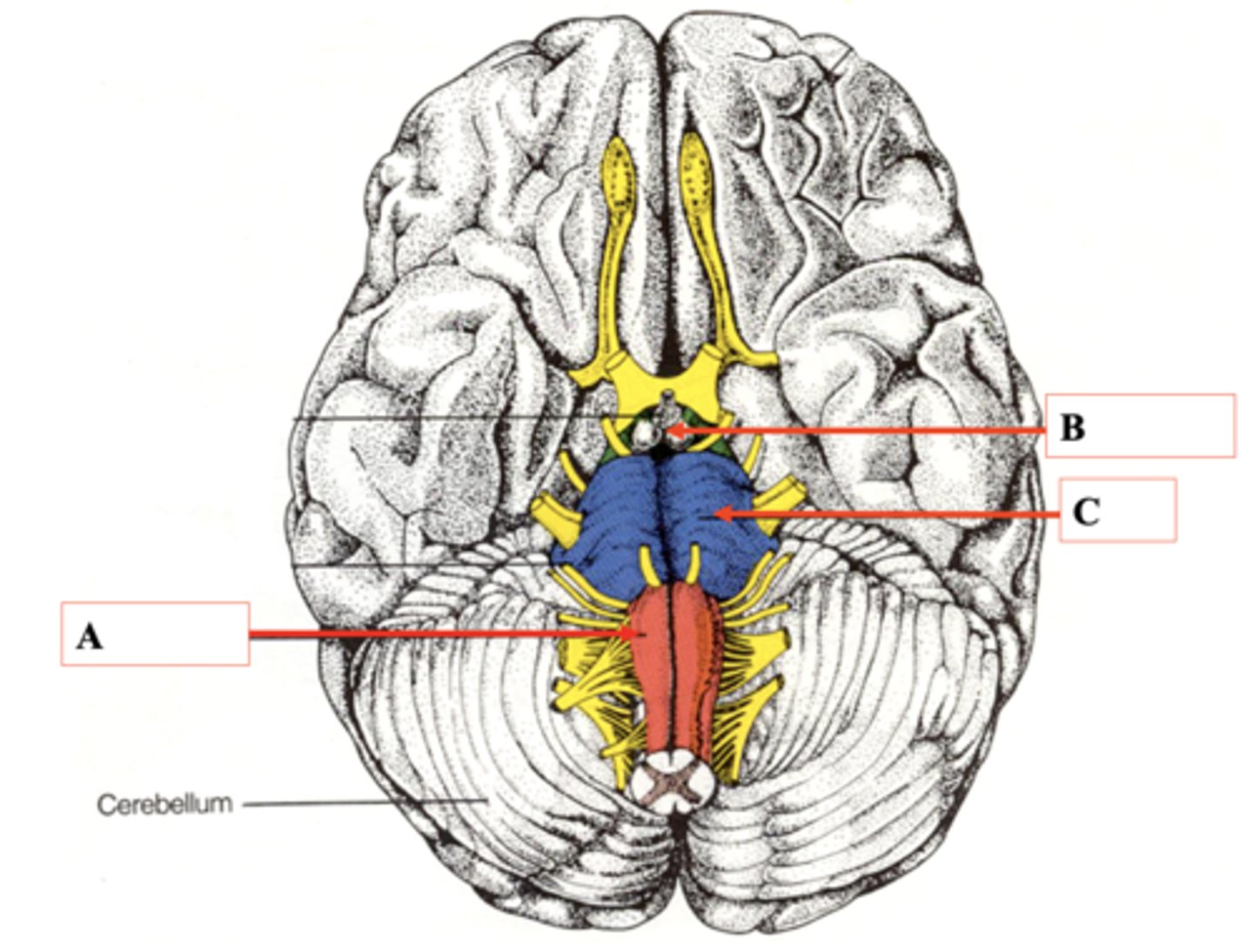
Pons
Identify C.
Dura Mater
Identify A.
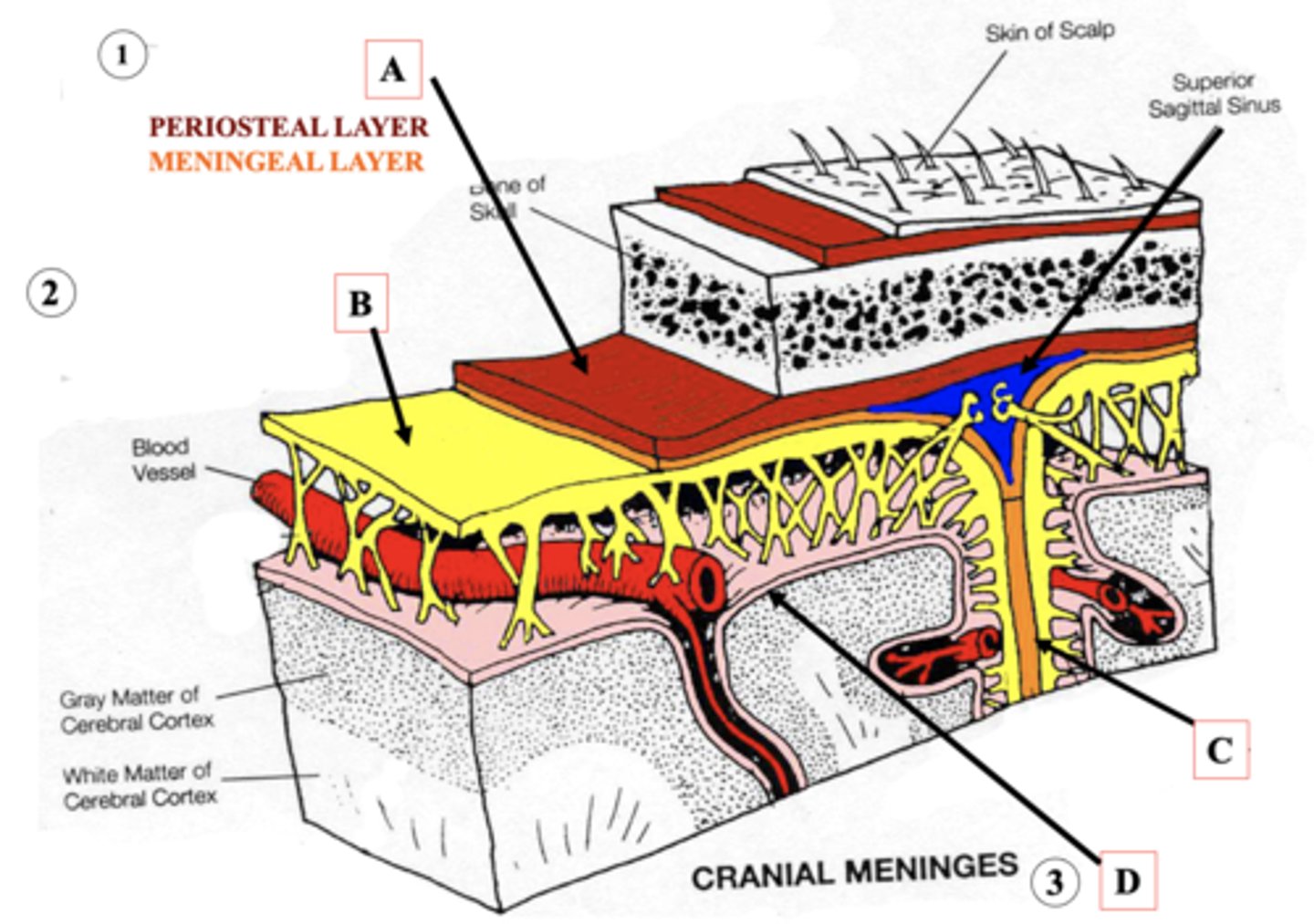
Arachnoid Mater
Identify B.
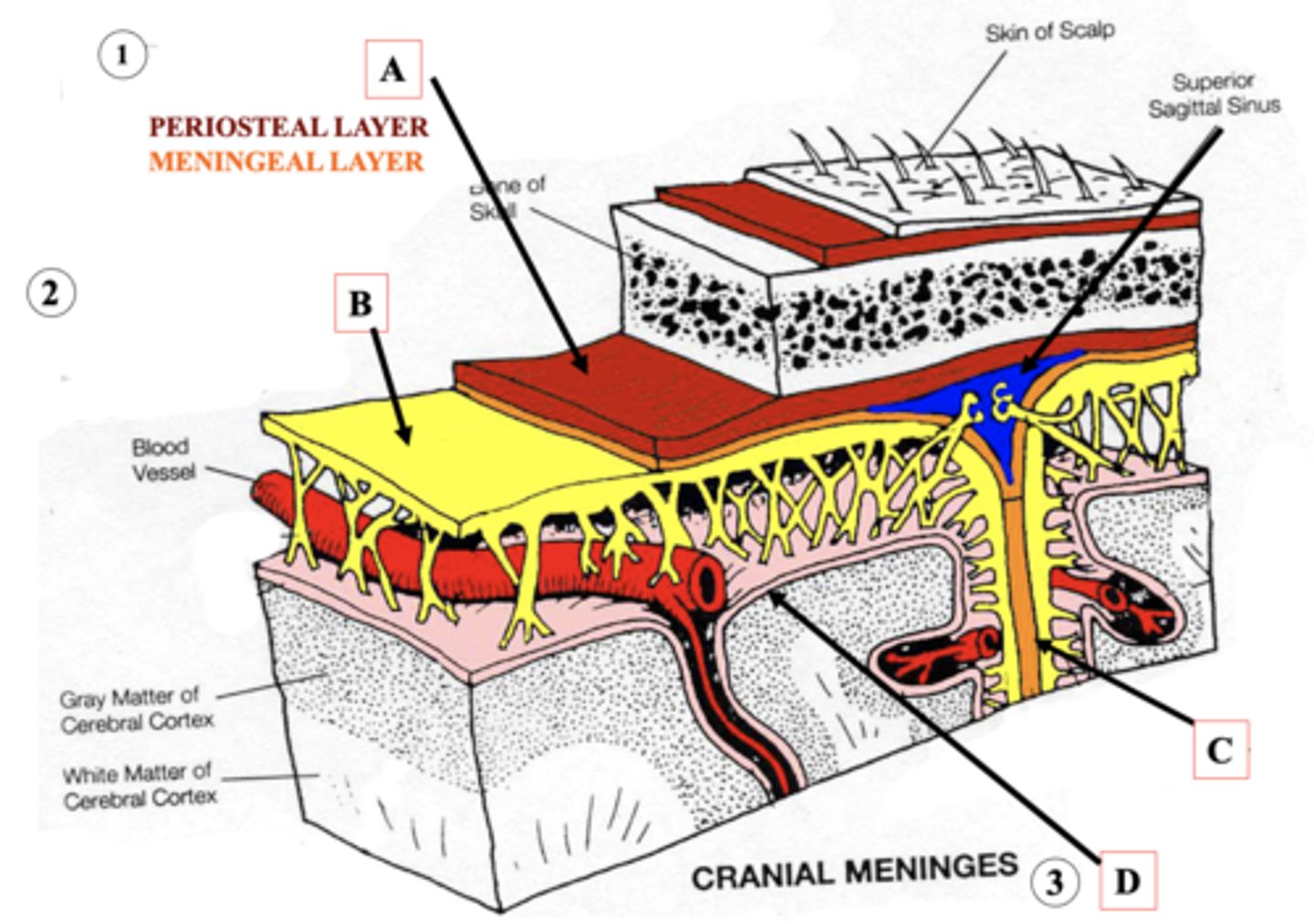
Dural Fold
Identify C.
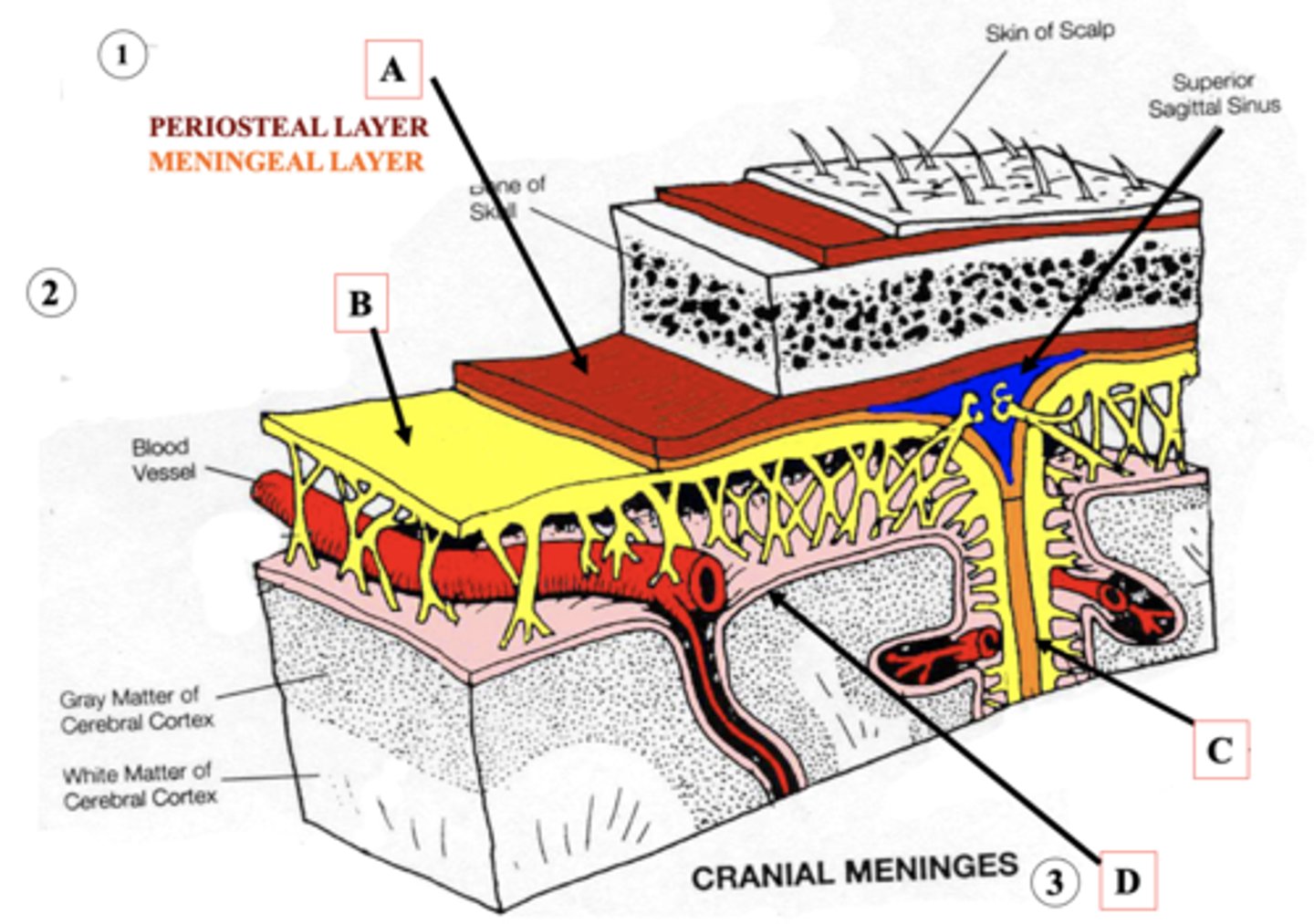
Pia Mater
Identify D.
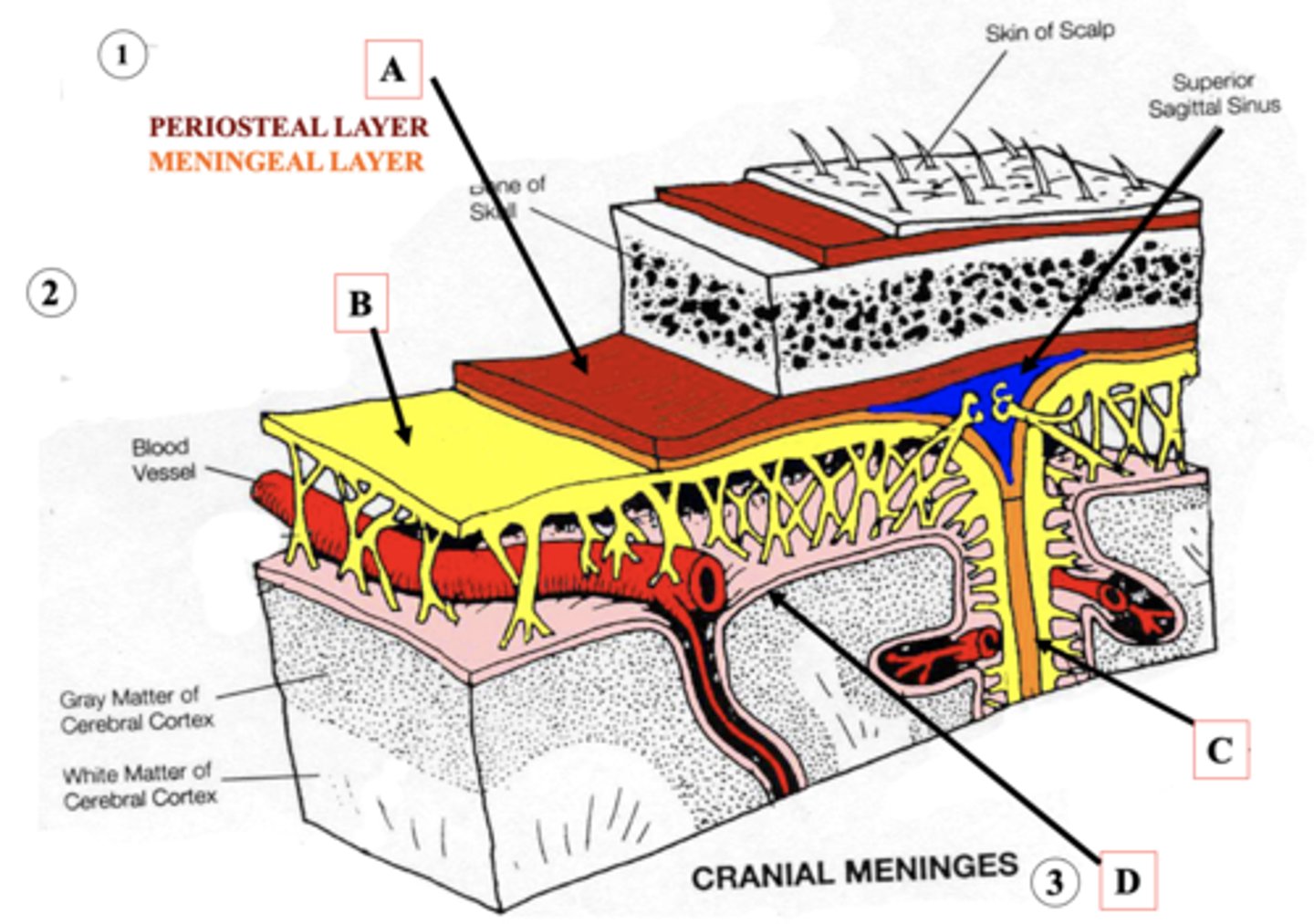
Bacterial Meningitis
- Bacterial infection of meninges
- Symptoms: rigid neck/back, nausea/vomiting, photophobia, irritability, bulging fontanelle, abducens nerve palsy, fever, coma
Falx Cerebri
Between the 2 cerebral hemispheres
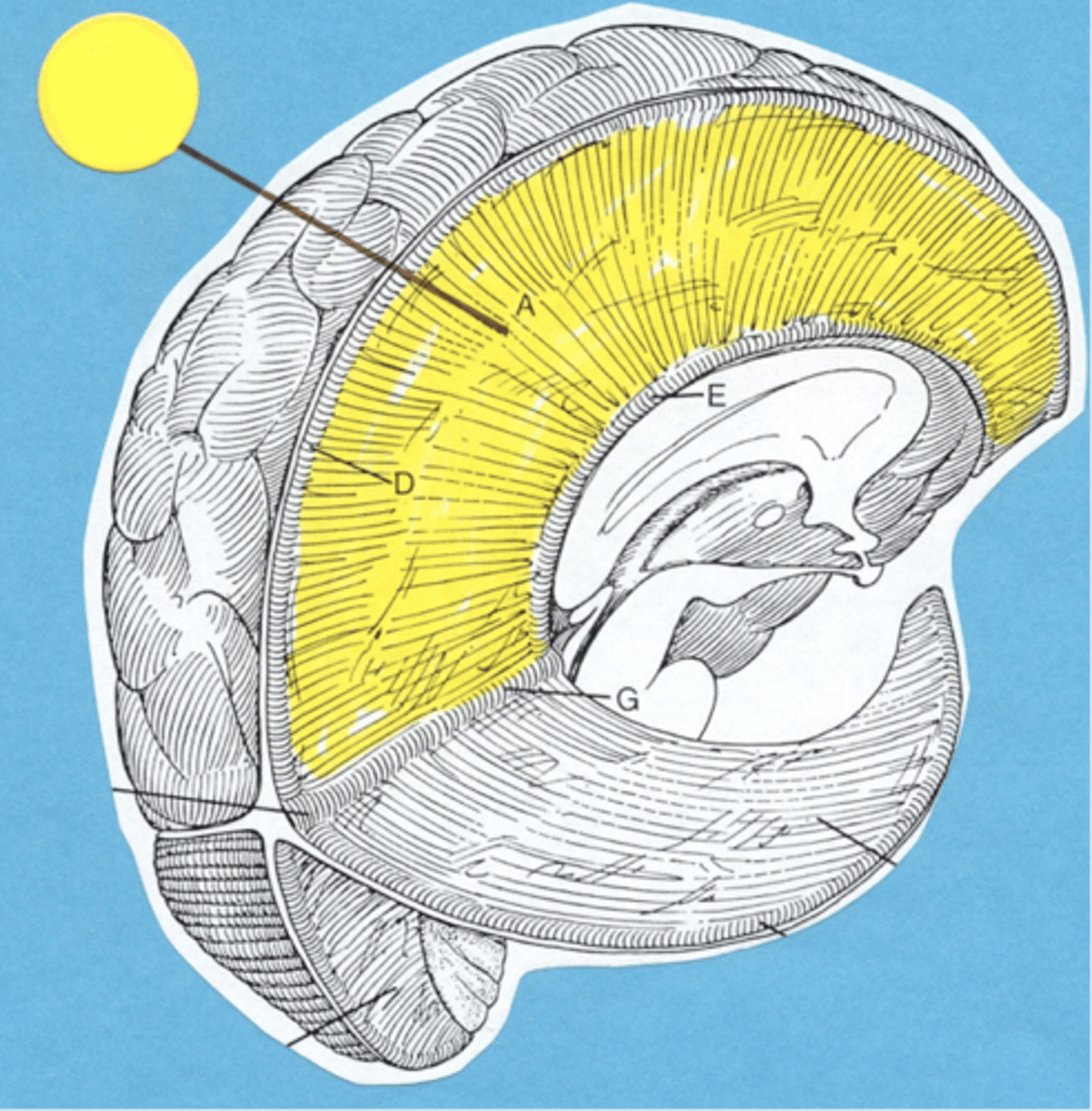
Tentorium Cerebelli
Between the cerebrum and cerebellum
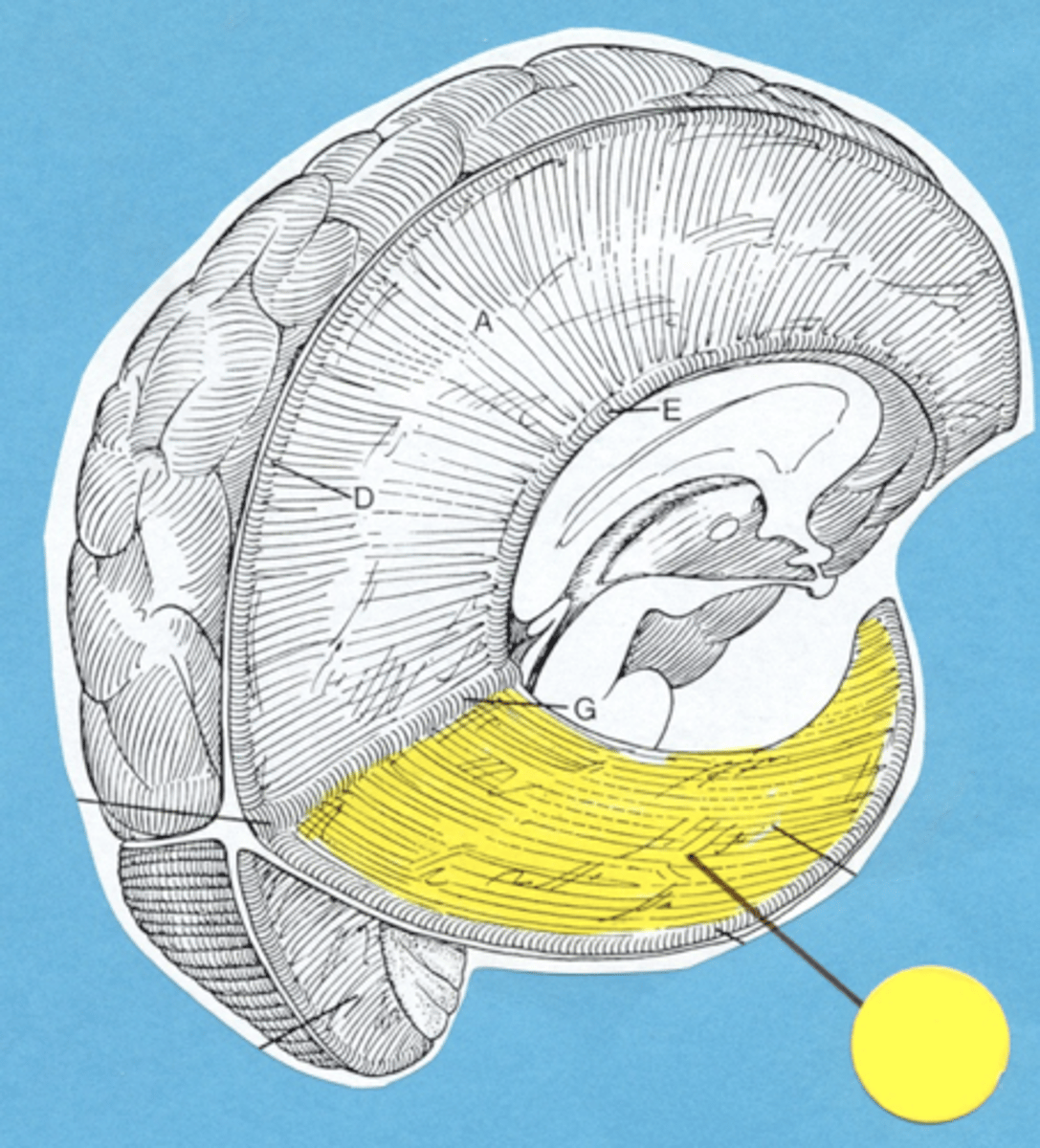
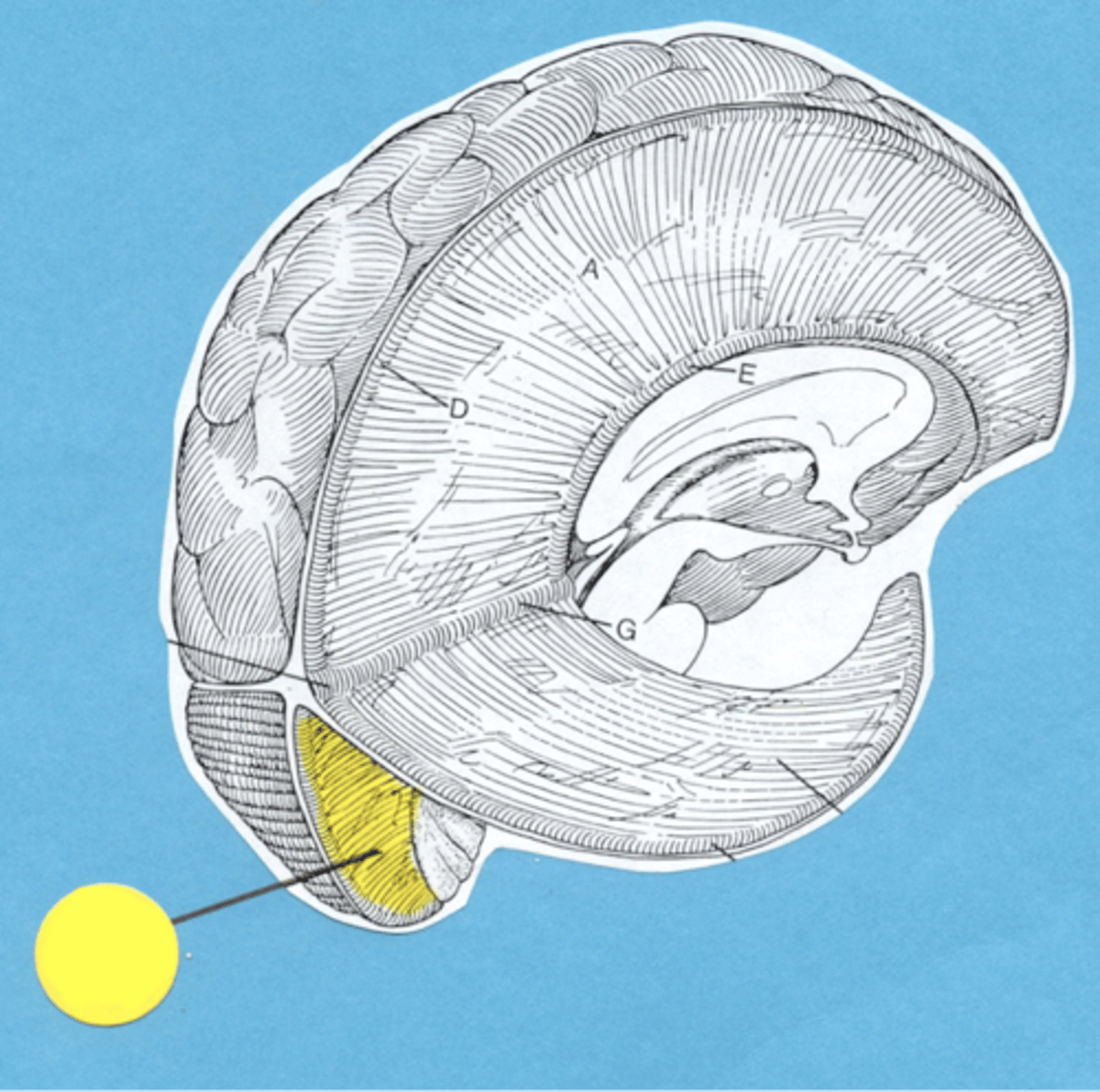
Falx Cerebelli
Between the cerebellar hemispheres
Epidural Hematoma
- Accumulation of blood in the epidural space (between the dura mater and the skull)
- Decreased consciousness, contusion, dilated/fixed pupil(s), coma, death (~25%)
Arterial laceration - middle meningeal artery from skull fracture
What are causes of an epidural hematoma?
Osmotic diuretic, surgical evacuation through burr hole/craniotomy
What are treatments for an epidural hematoma?
Subdural Hematoma
- Accumulation of blood in subdural space- frequently leads to brain damage
- Altered consciousness, dilated/nonreactive pupil, coma, death (~60% of cases)
Rupture of vein running from brain to dura, often along sagittal sinus/anterior temporal lobe
What are the causes of a subdural hematoma?
- Mannitol-osmotic diuretic
- Surgical evacuation through burr hols/craniotomy
What are the treatments of a subdural hematoma?
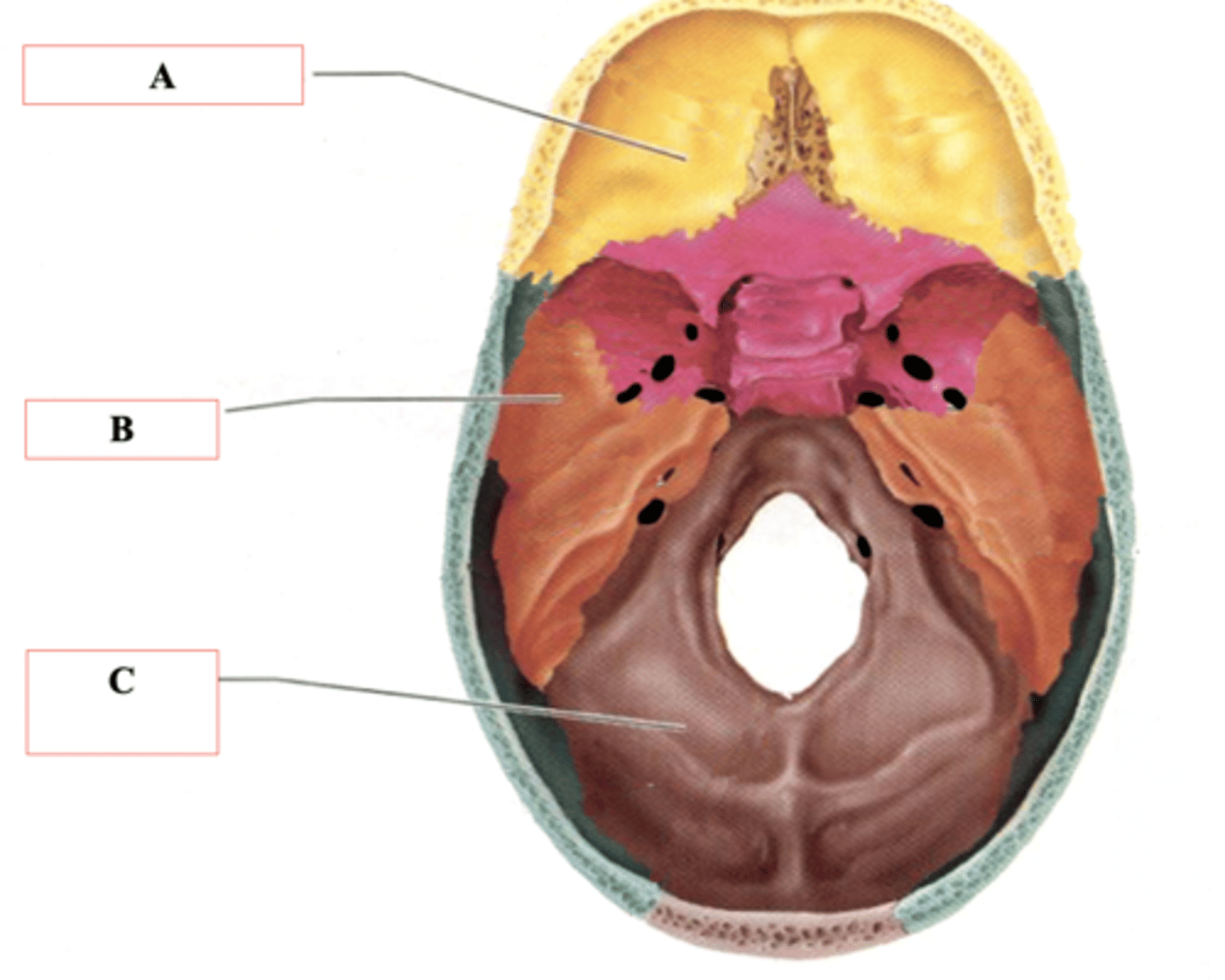
Anterior Cranial Fossa
Identify A.
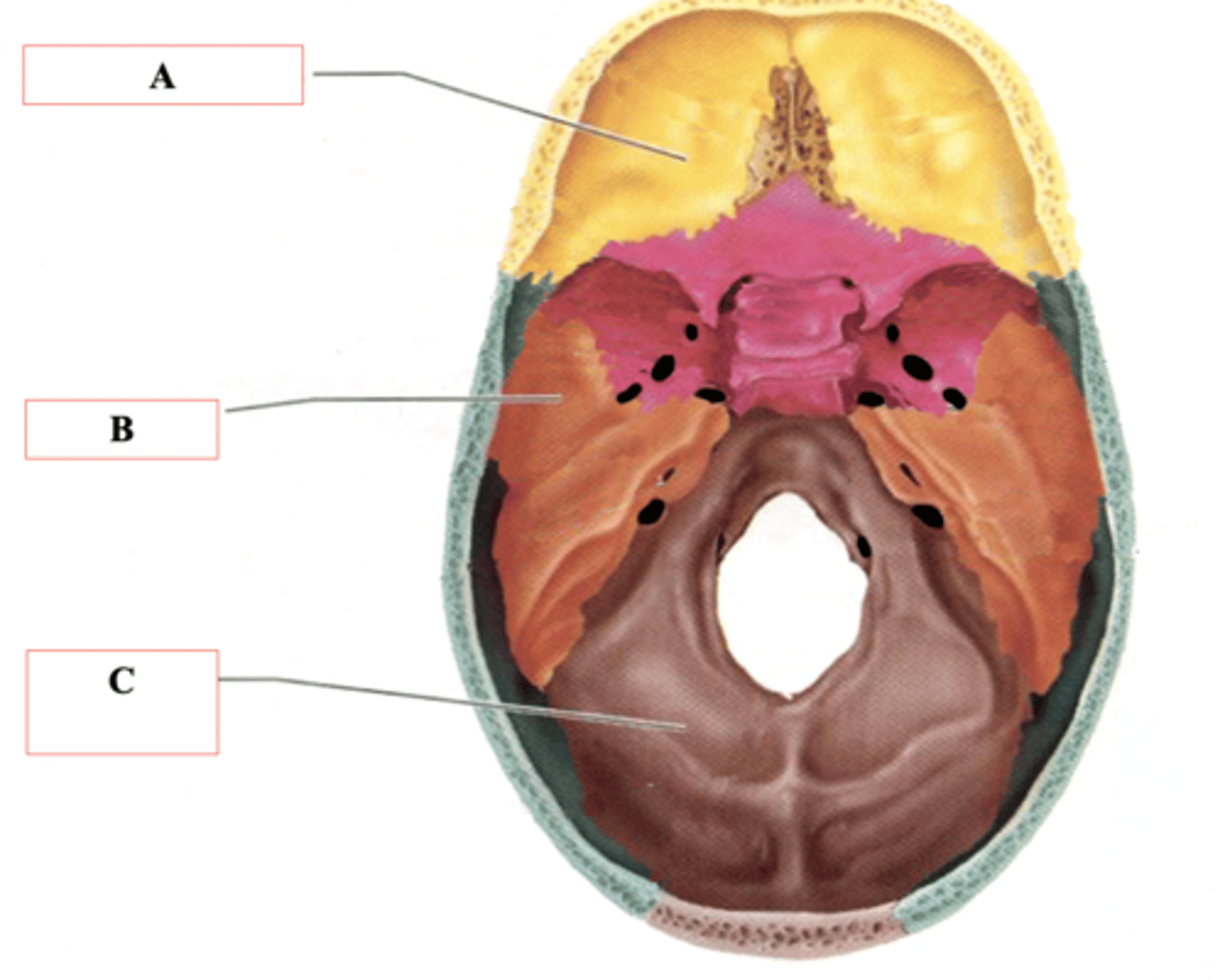
Middle Cranial Fossa
Identify B.
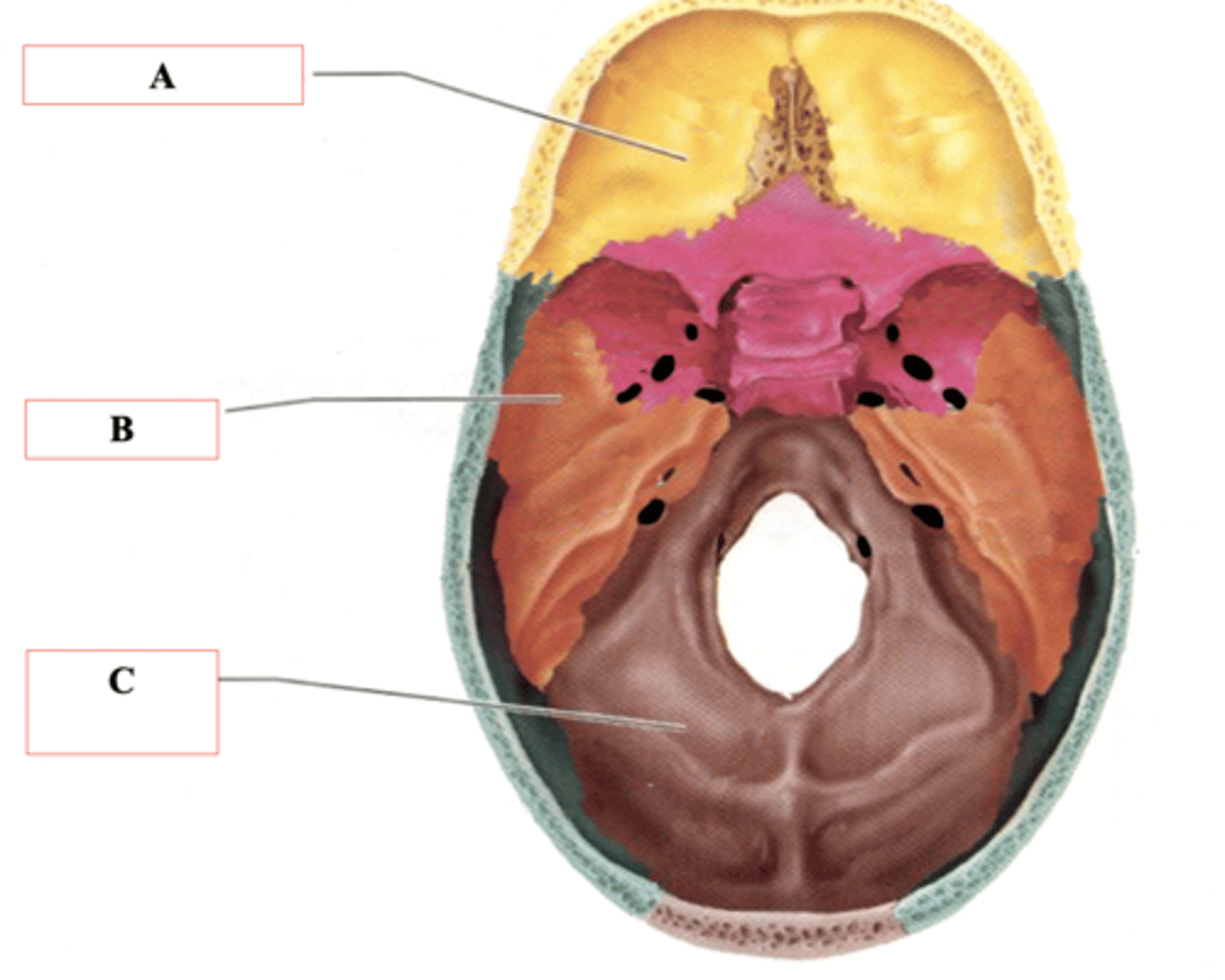
Posterior Cranial Fossa
Identify C.
Crista Galli
Attachment of falx cerebri
Lesser Wing of Sphenoid
Attachment of tentorium cerebelli
Crista Galli
Identify A.
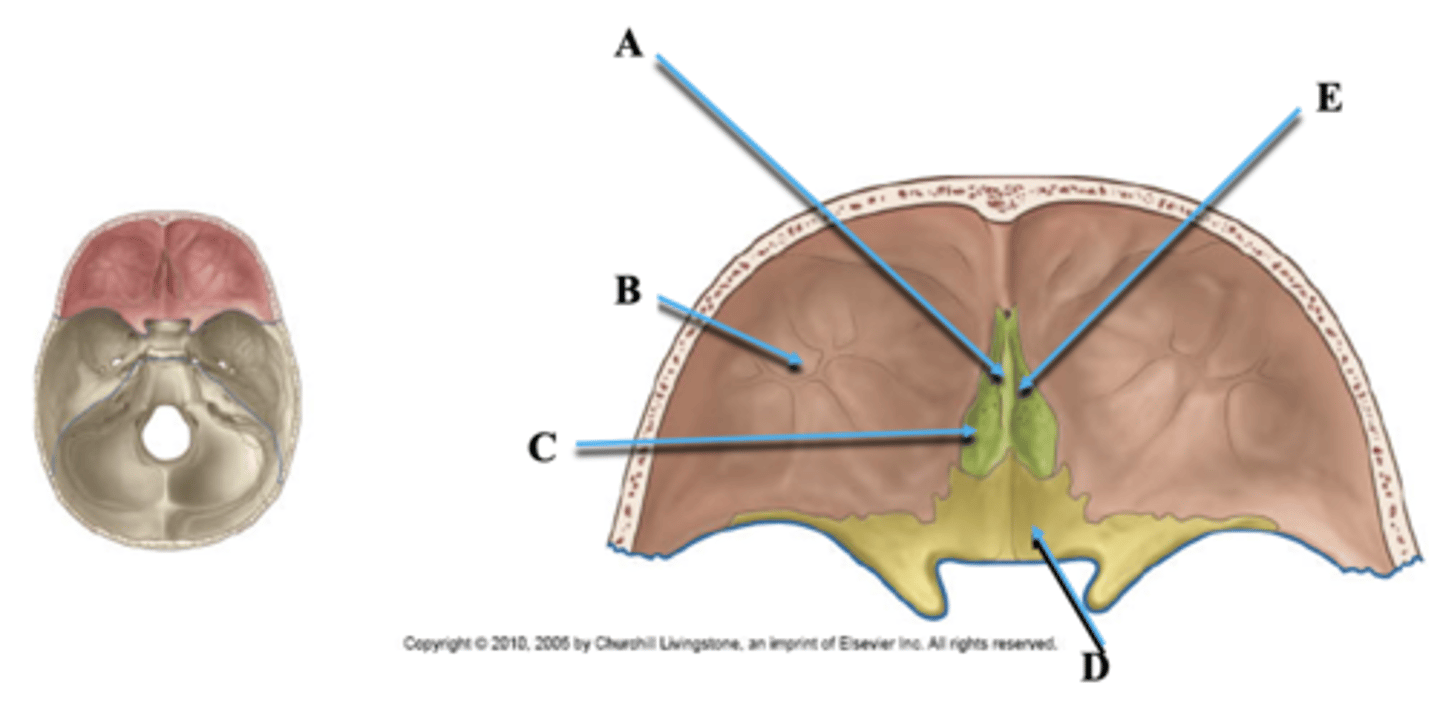
Orbital Plate of Frontal Bone
Identify B.
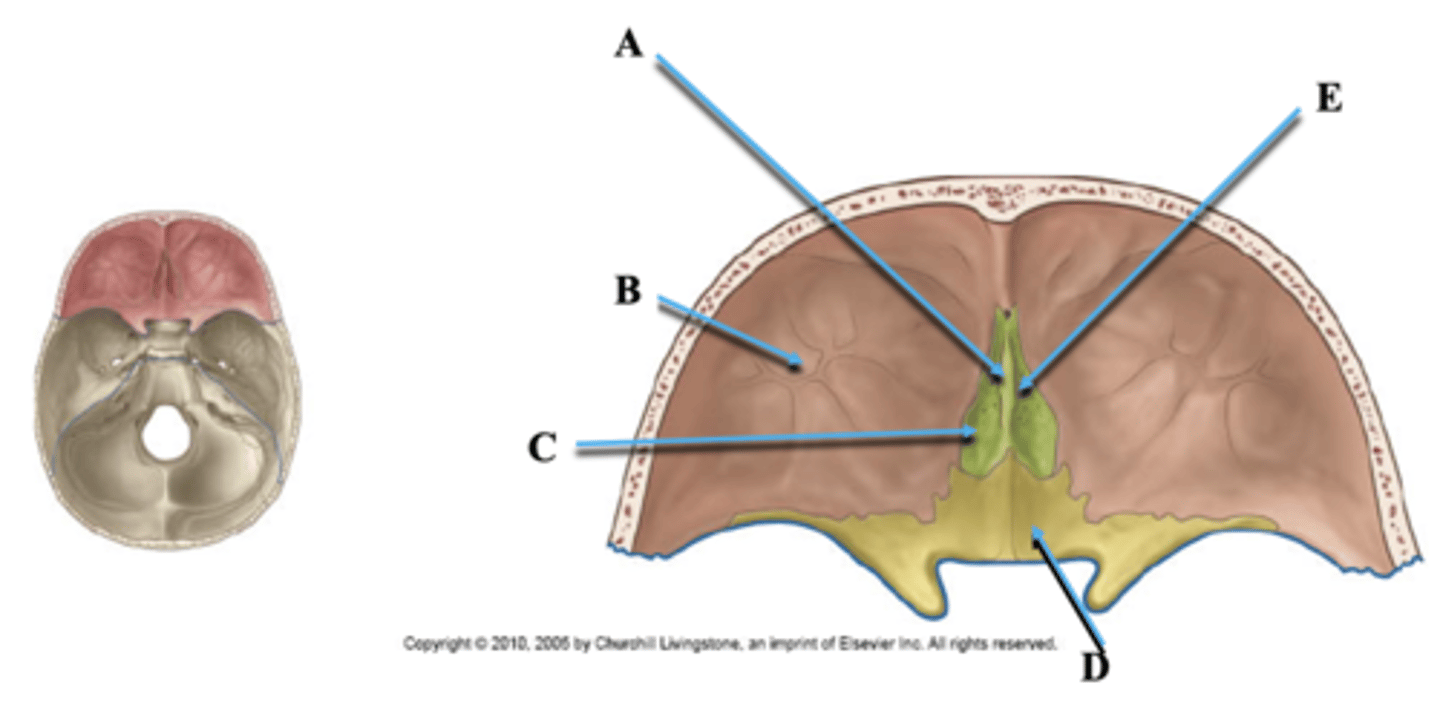
Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid
Identify C.
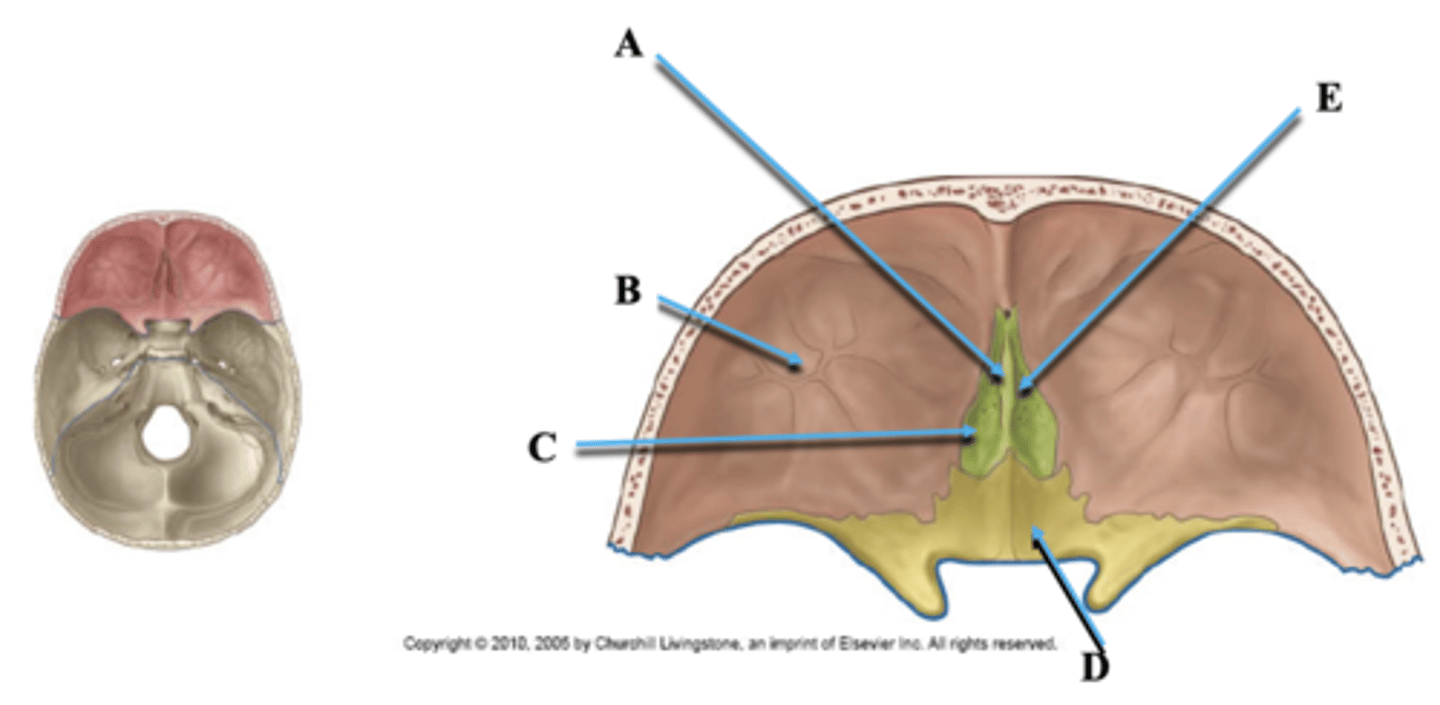
Lesser Wing of Sphenoid
Identify D.
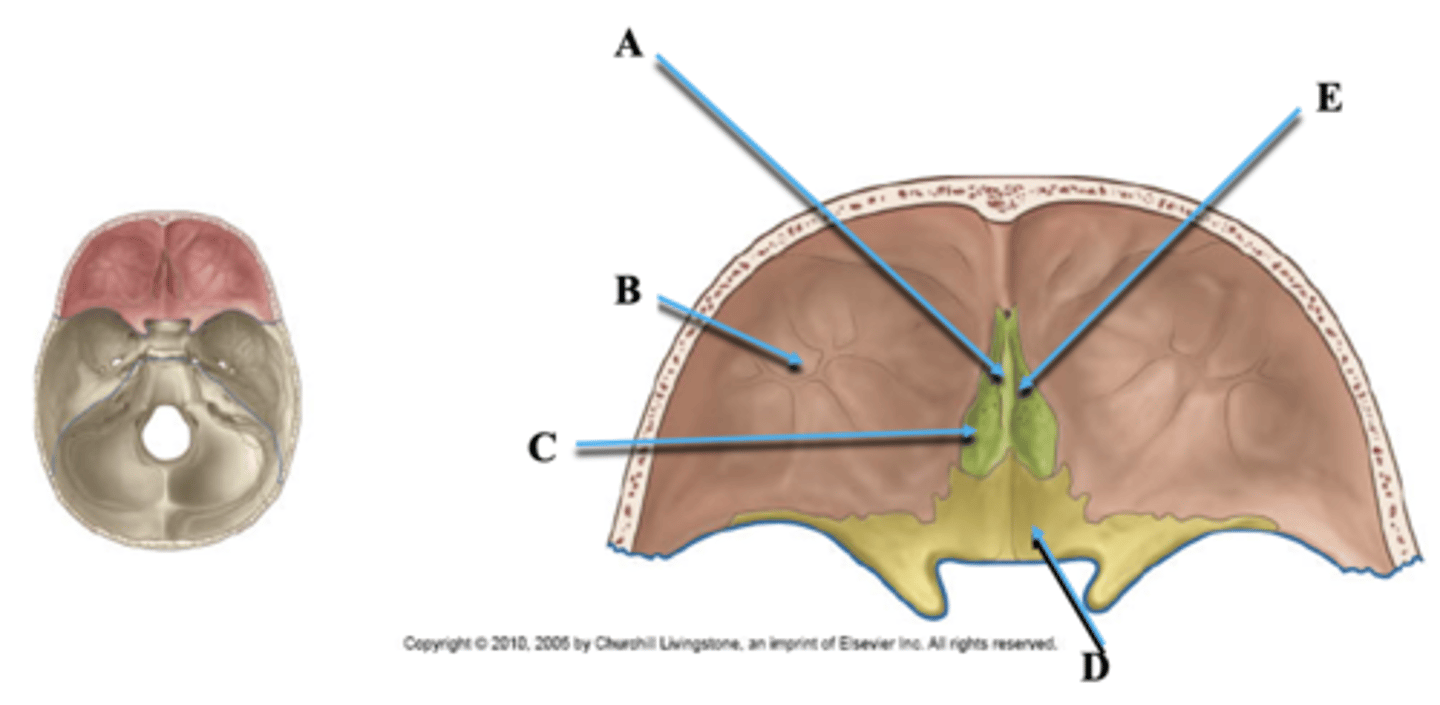
Olfactory Nerve Foramina
Identify E.
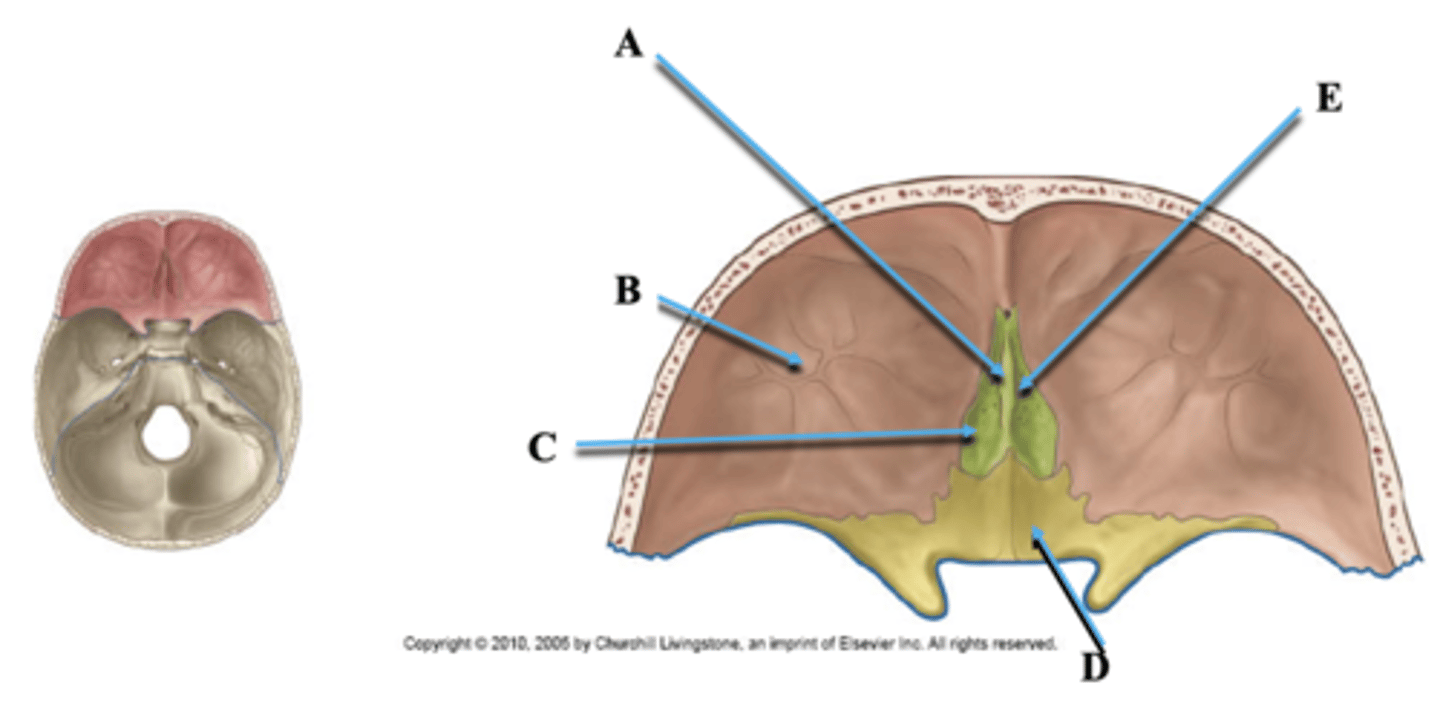
Cranial Nerve II
Goes through optic canal in lesser wing of sphenoid
Cranial Nerve 1 Tract and Bulb
Identify A.
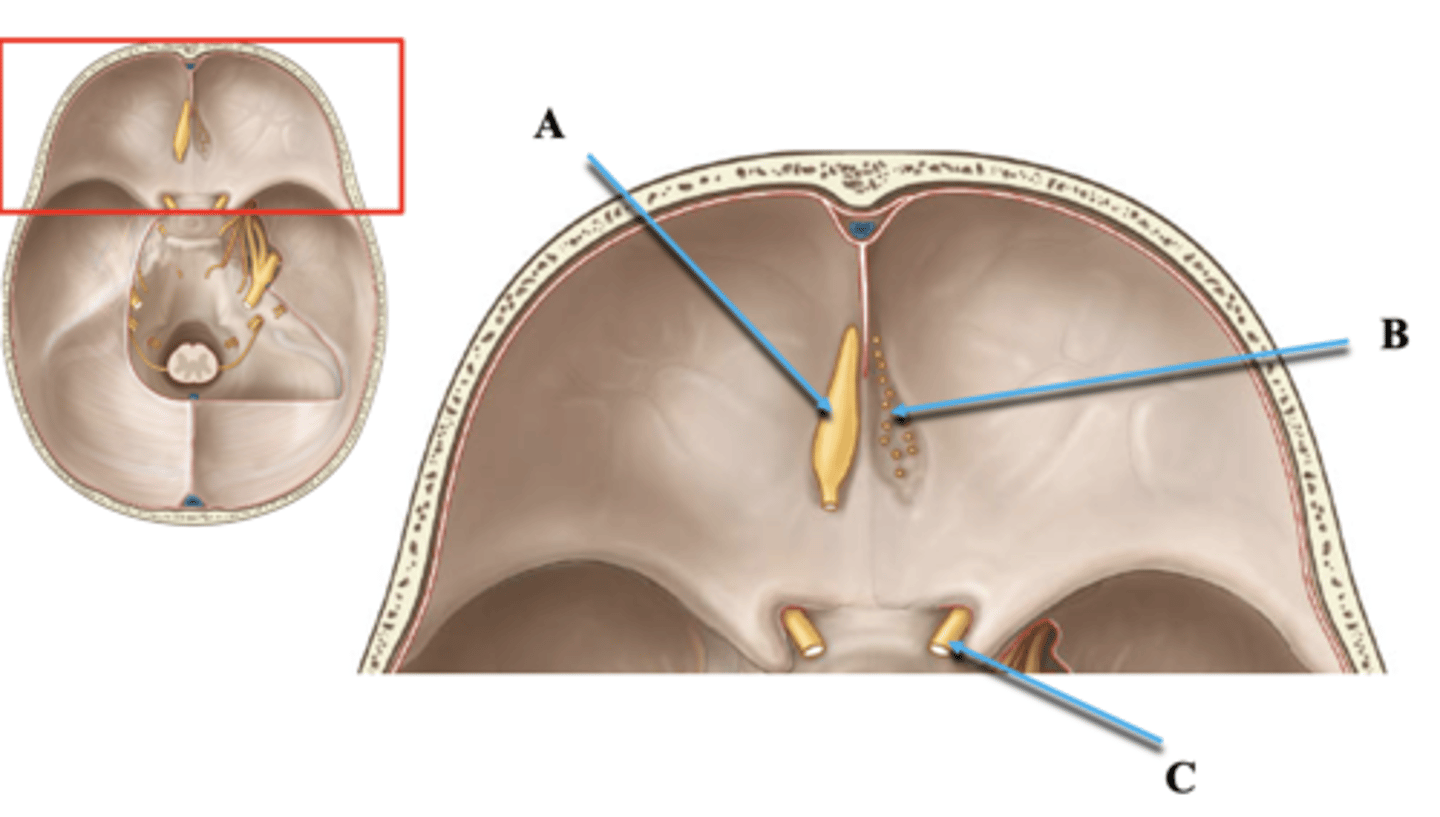
Cranial Nerve 1 Branches
Identify B.
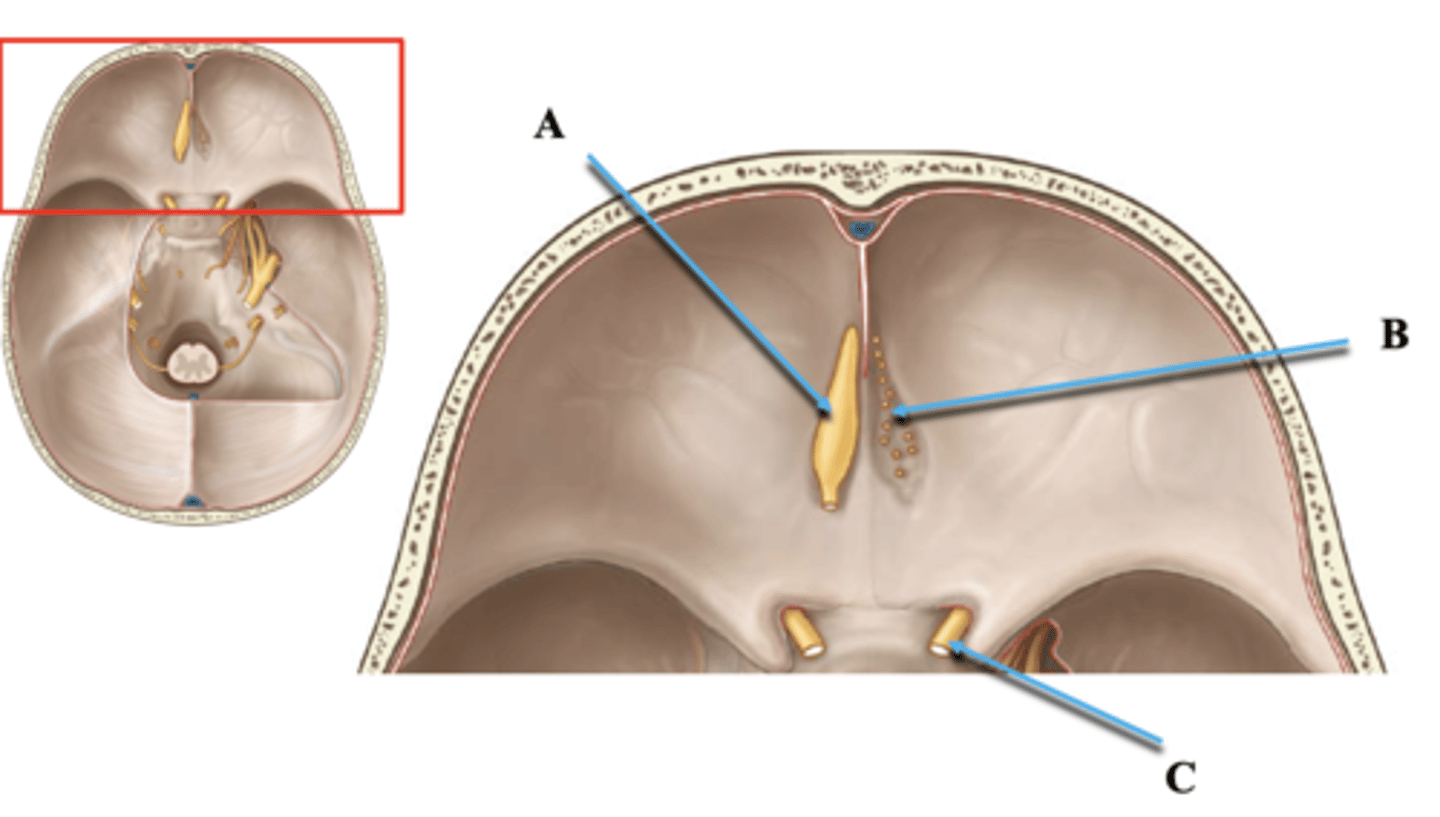
Cranial Nerve 2
Identify C.
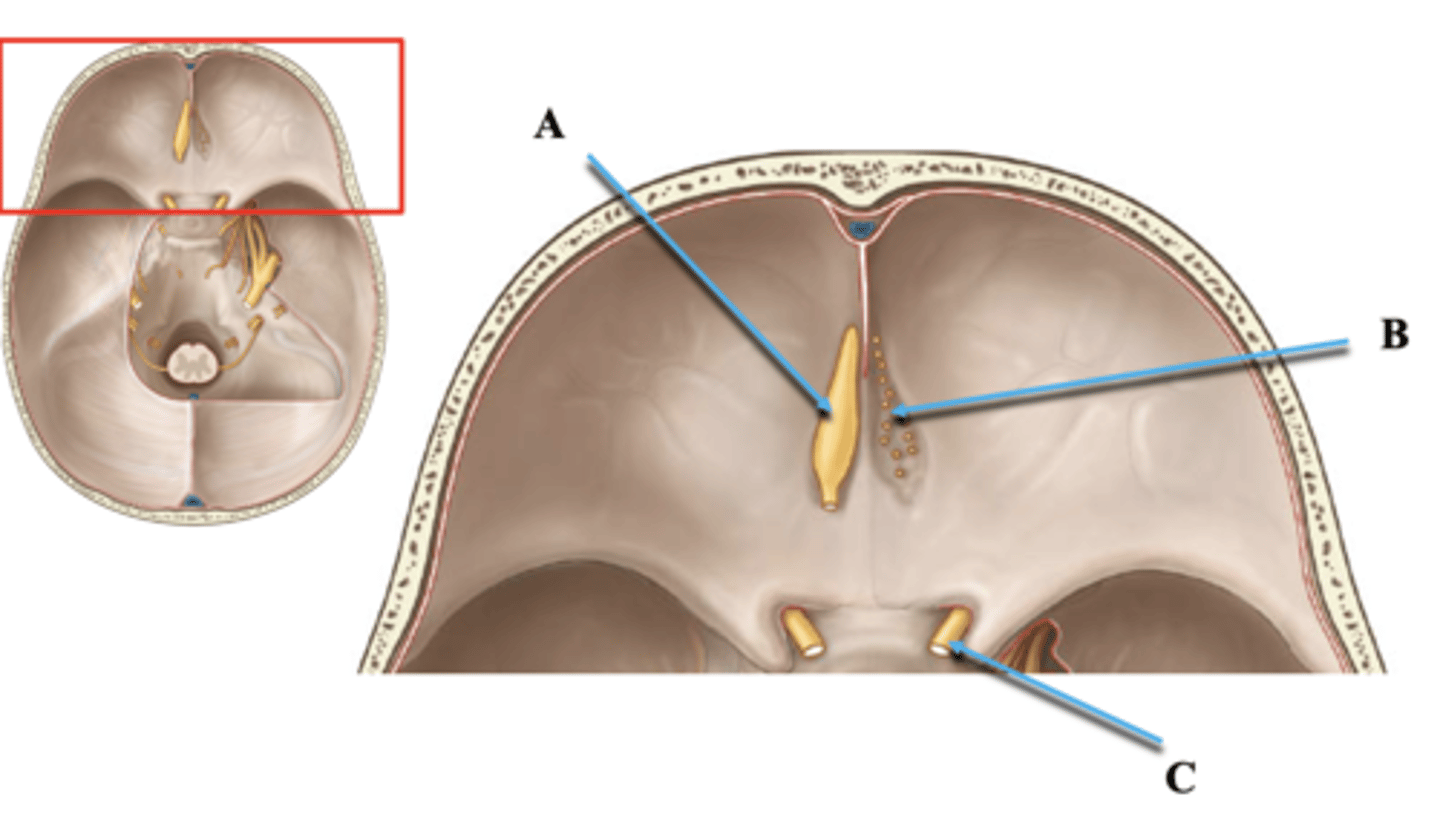
Foramen Rotundum
Maxillary branch (V2) of trigeminal nerve exits
Sella Turcica
Holds pituitary gland
Foramen Ovale
Mandibular branch (V3) of trigeminal nerve exits
Foramen Spinosum
Middle meningeal artery enters
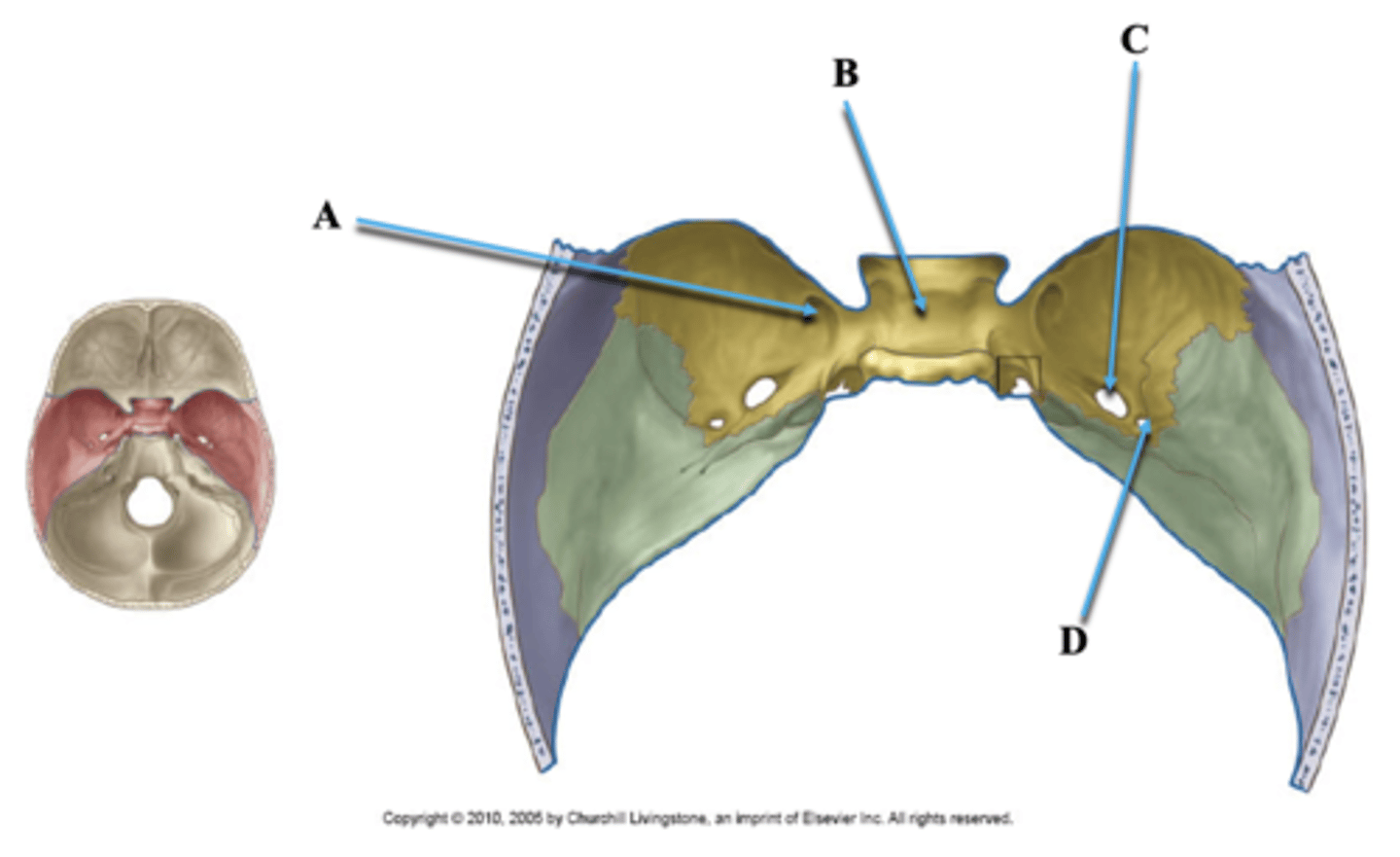
Foramen Rotundum
Identify A.
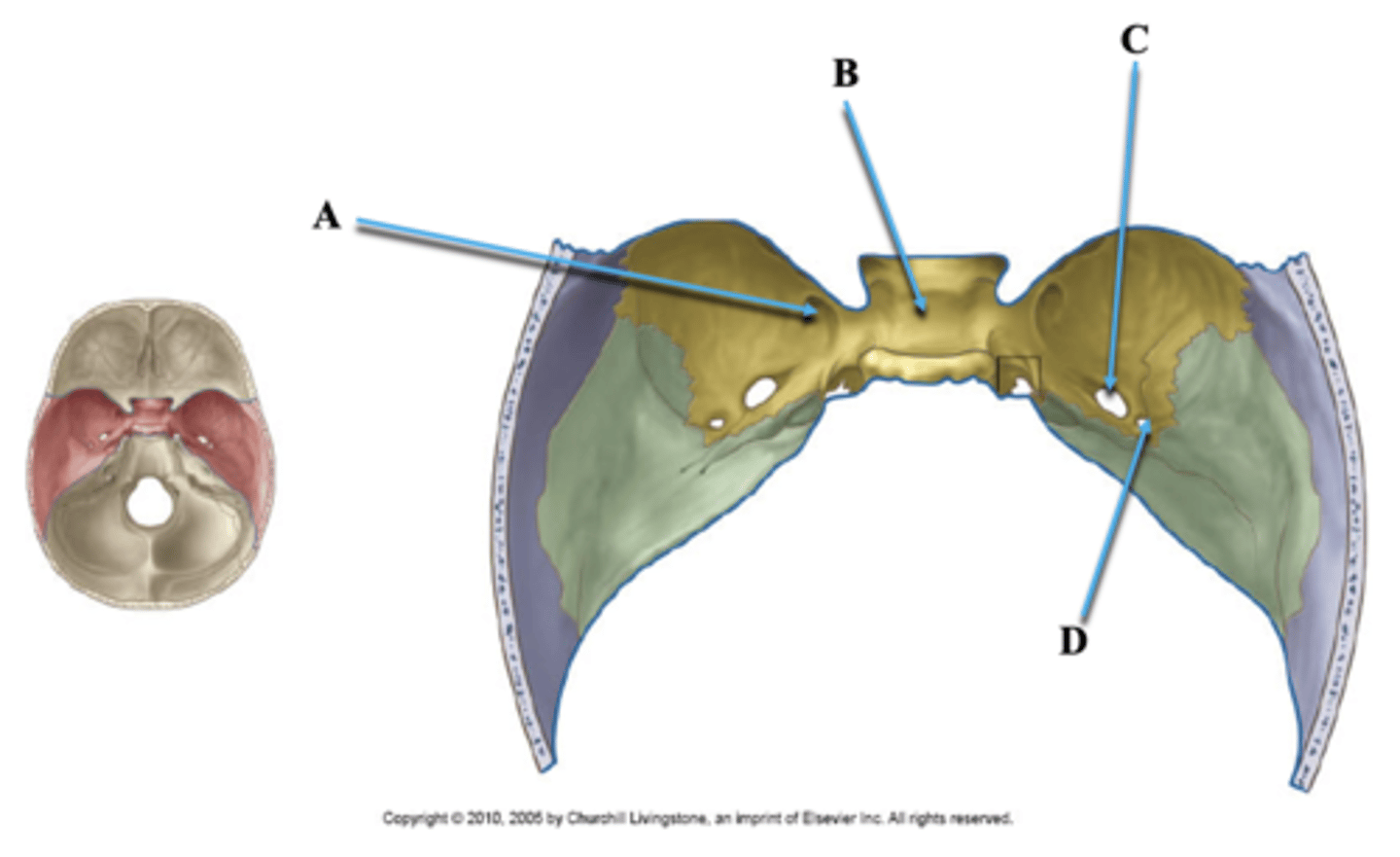
Sella Turcica
Identify B.
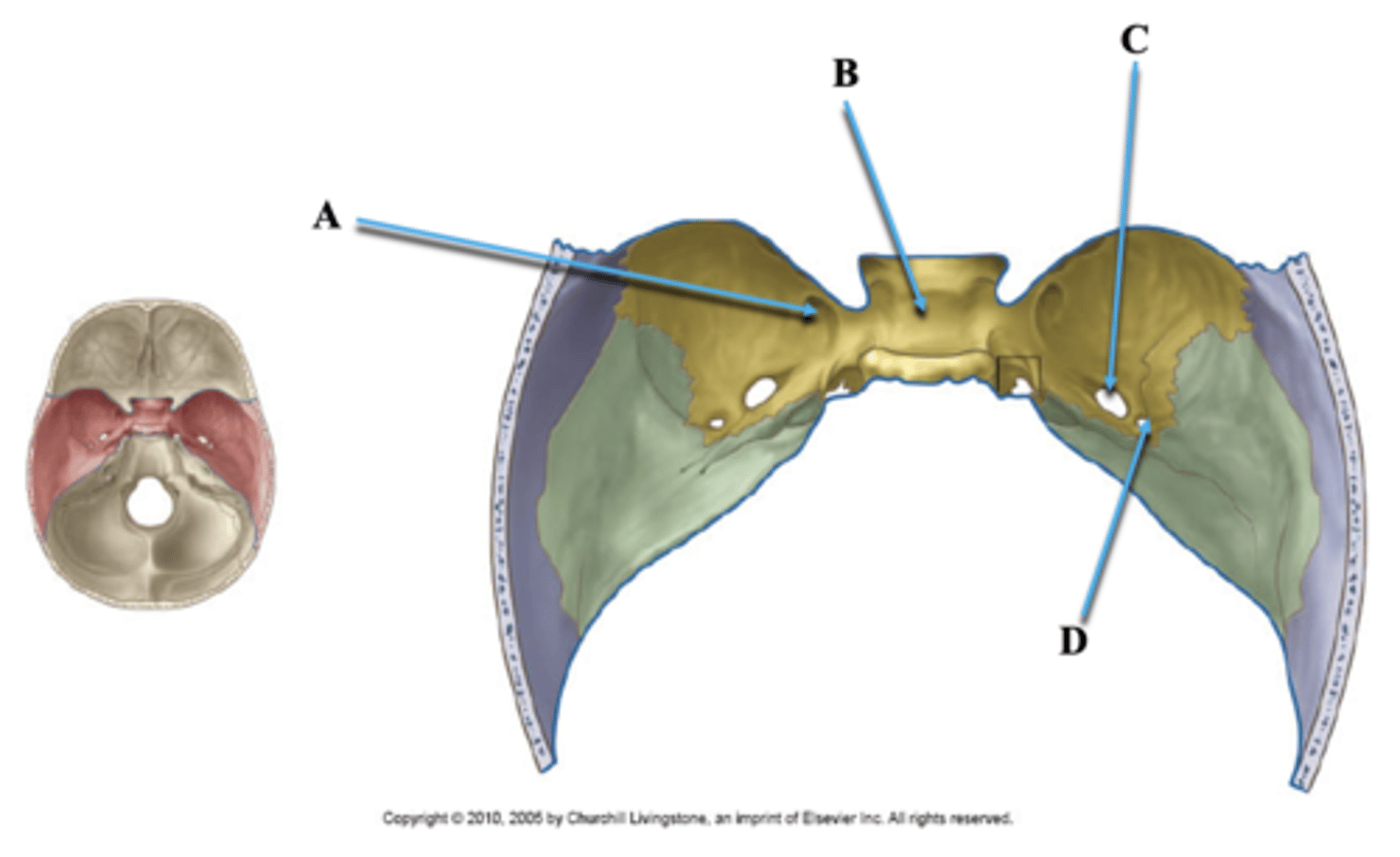
Foramen Ovale
Identify C.

Foramen Spinosum
Identify D.
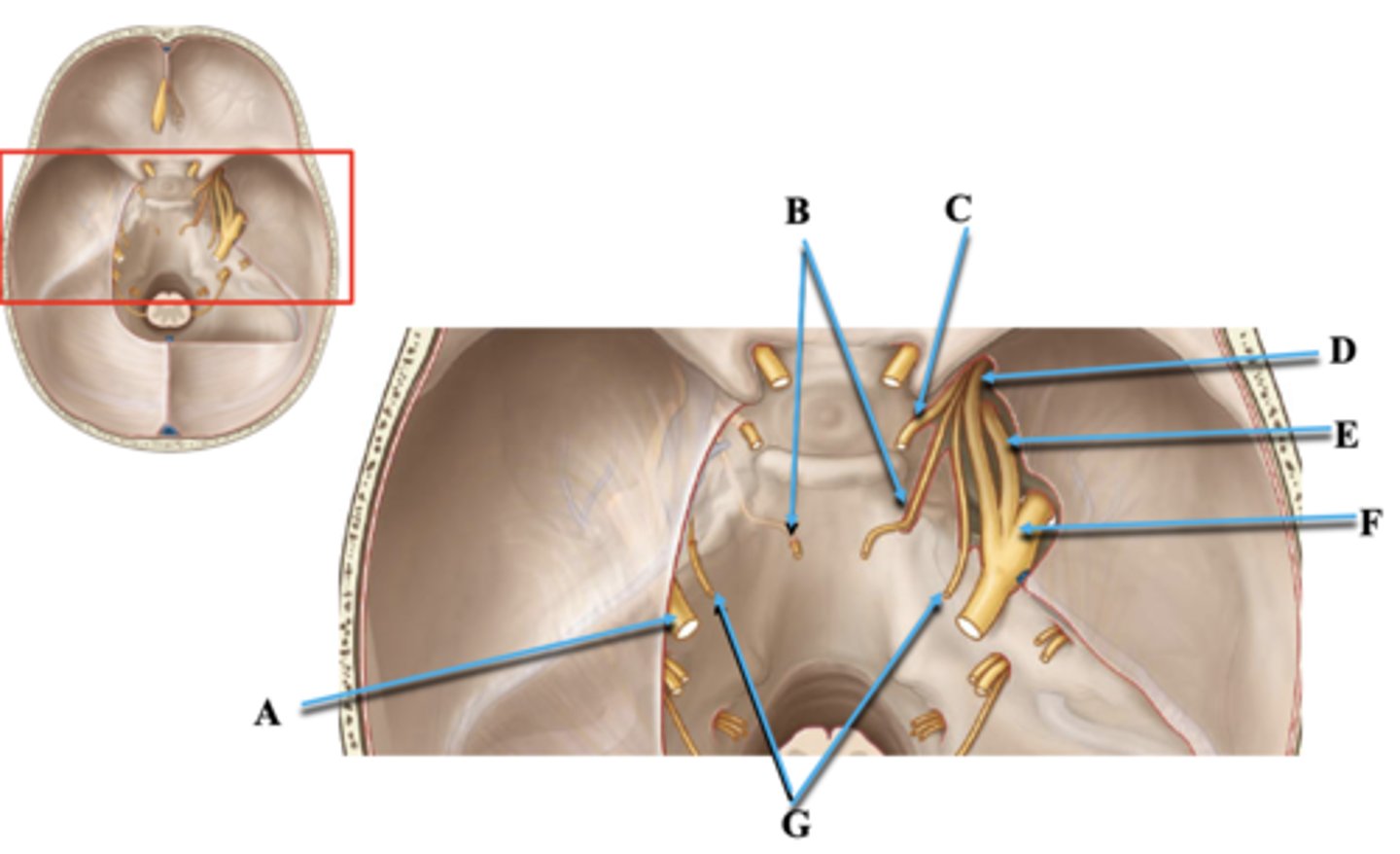
Cranial Nerve V
Identify A.
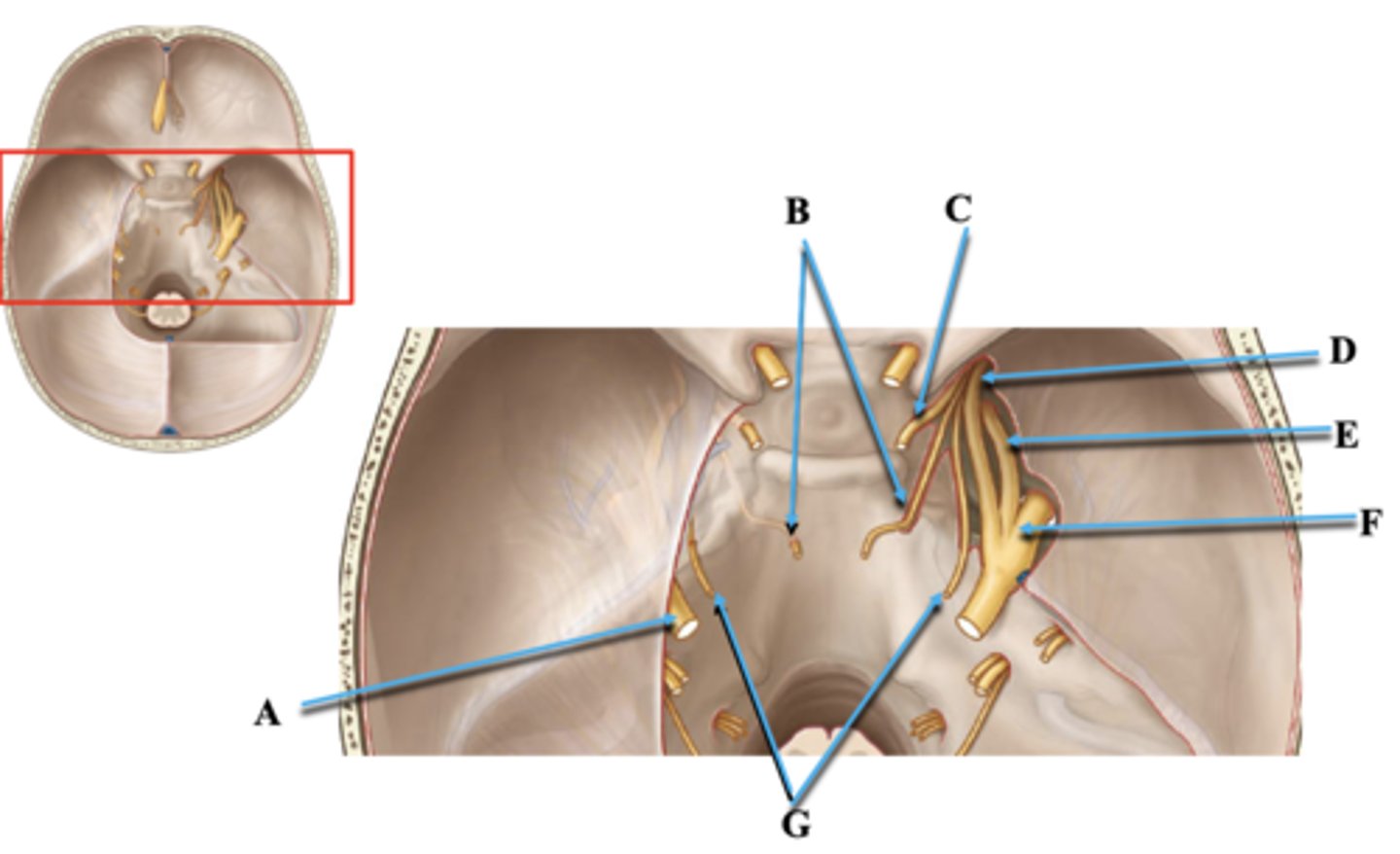
Cranial Nerve VI
Identify B.
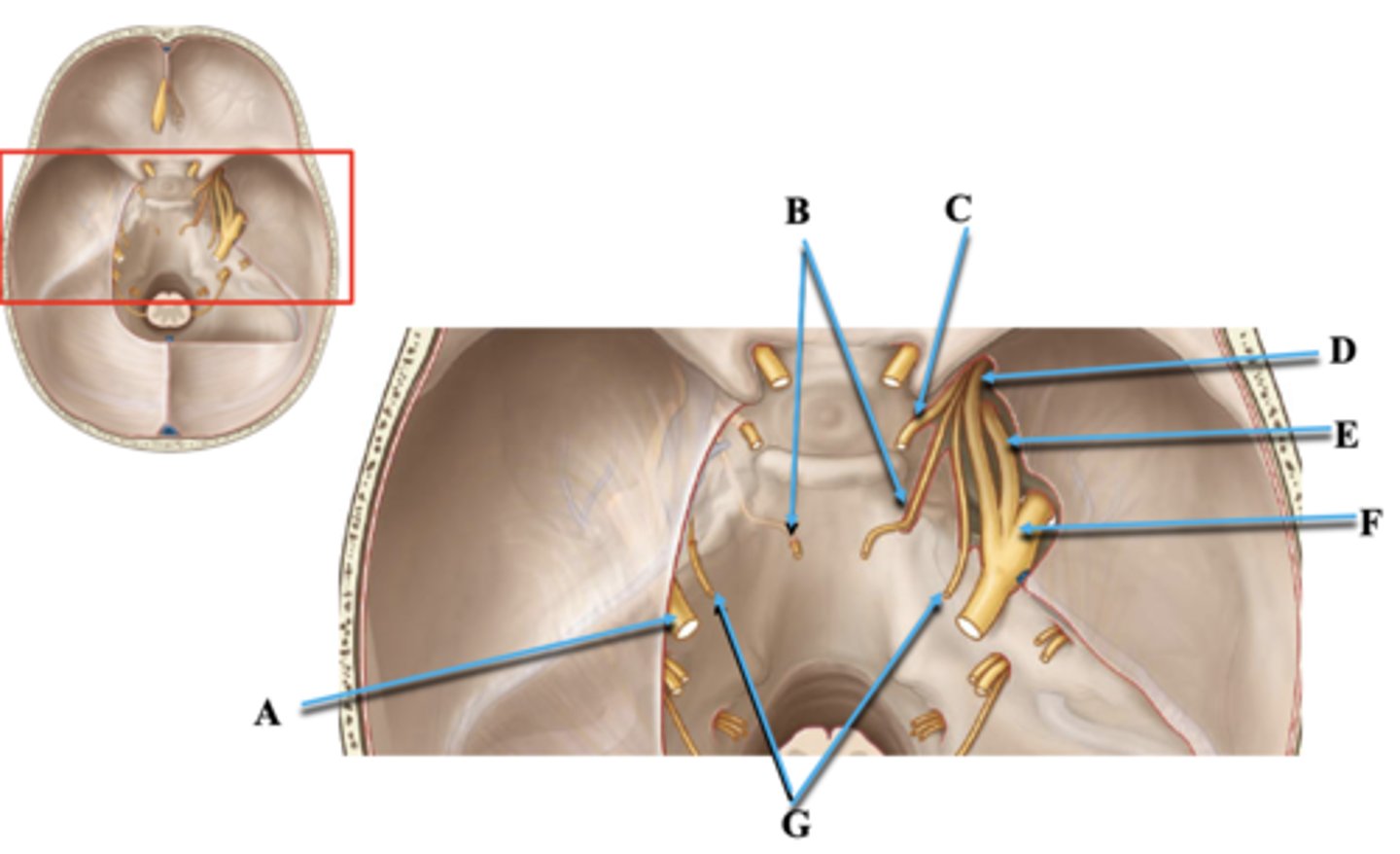
Cranial Nerve III
Identify C.
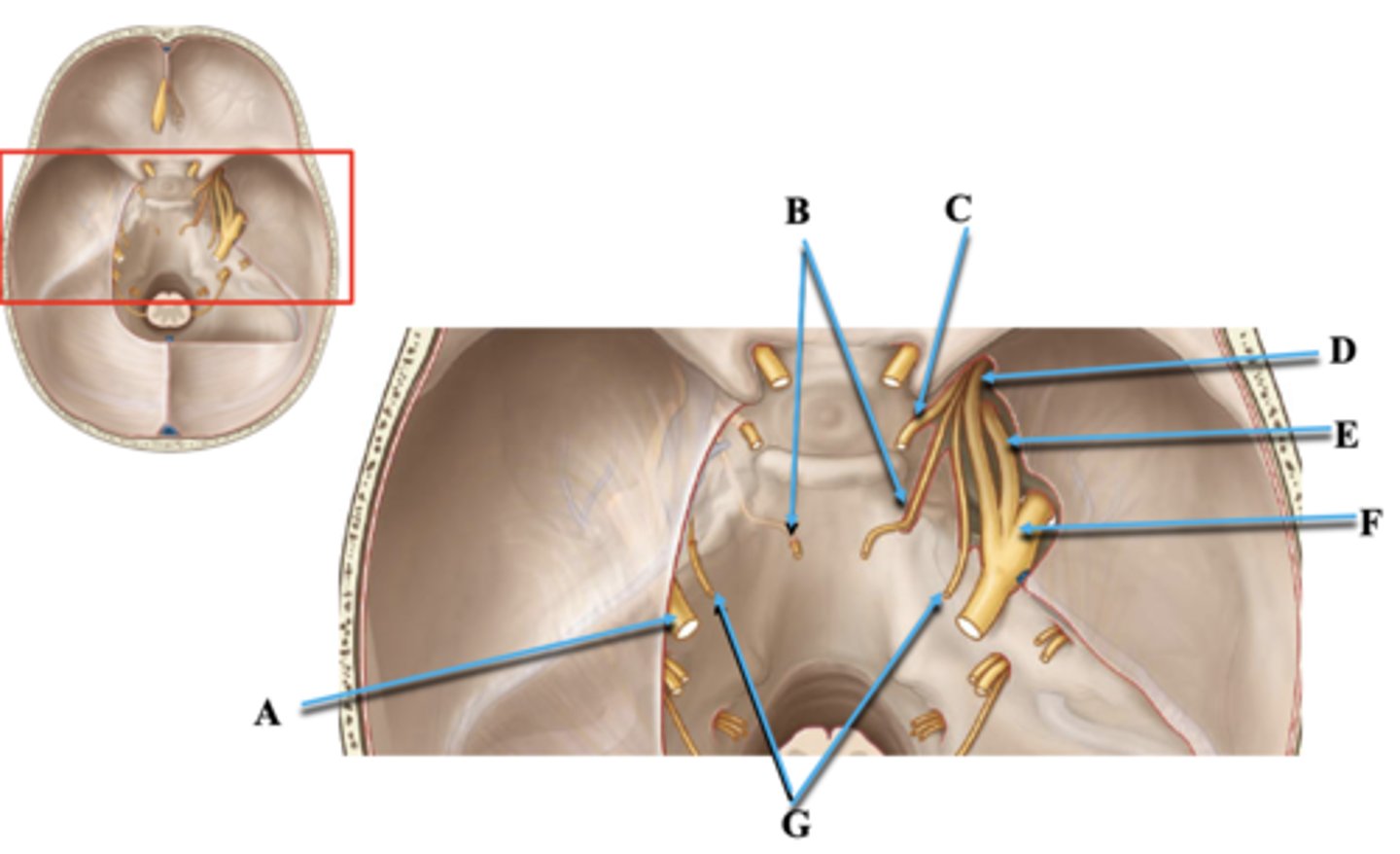
Cranial Nerve V1
Identify D.
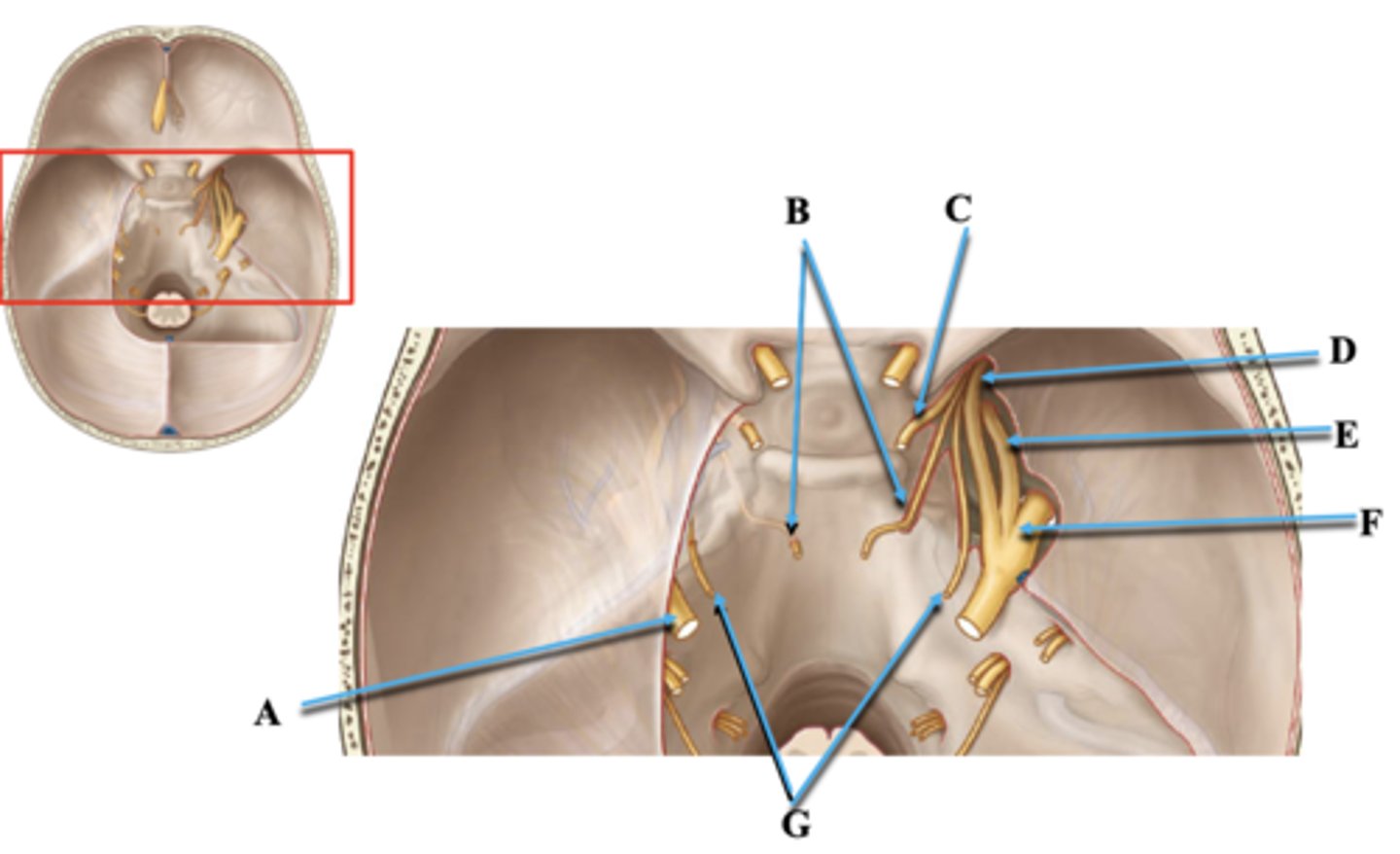
Cranial Nerve V2
Identify E.
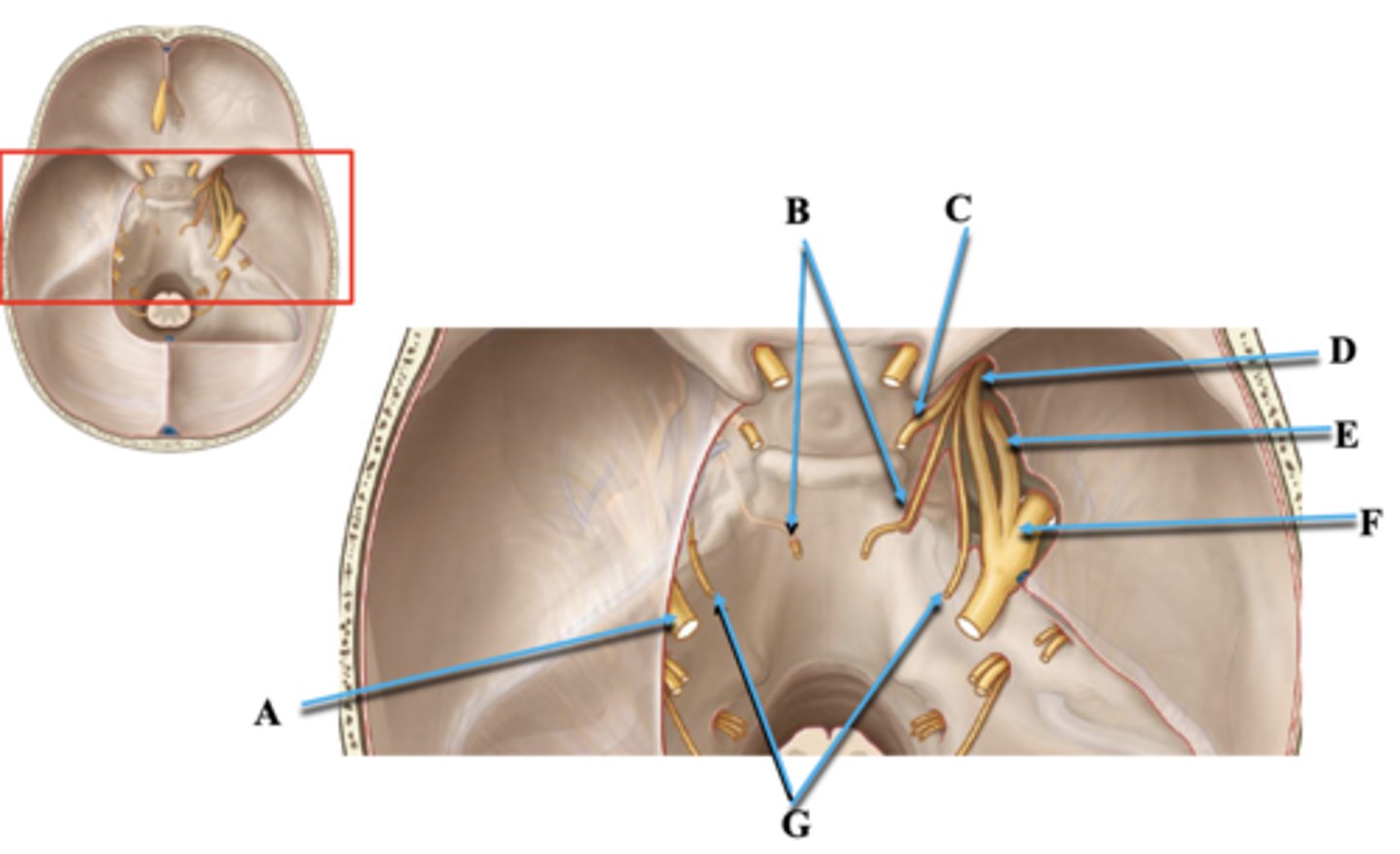
Cranial Nerve V3
Identify F.
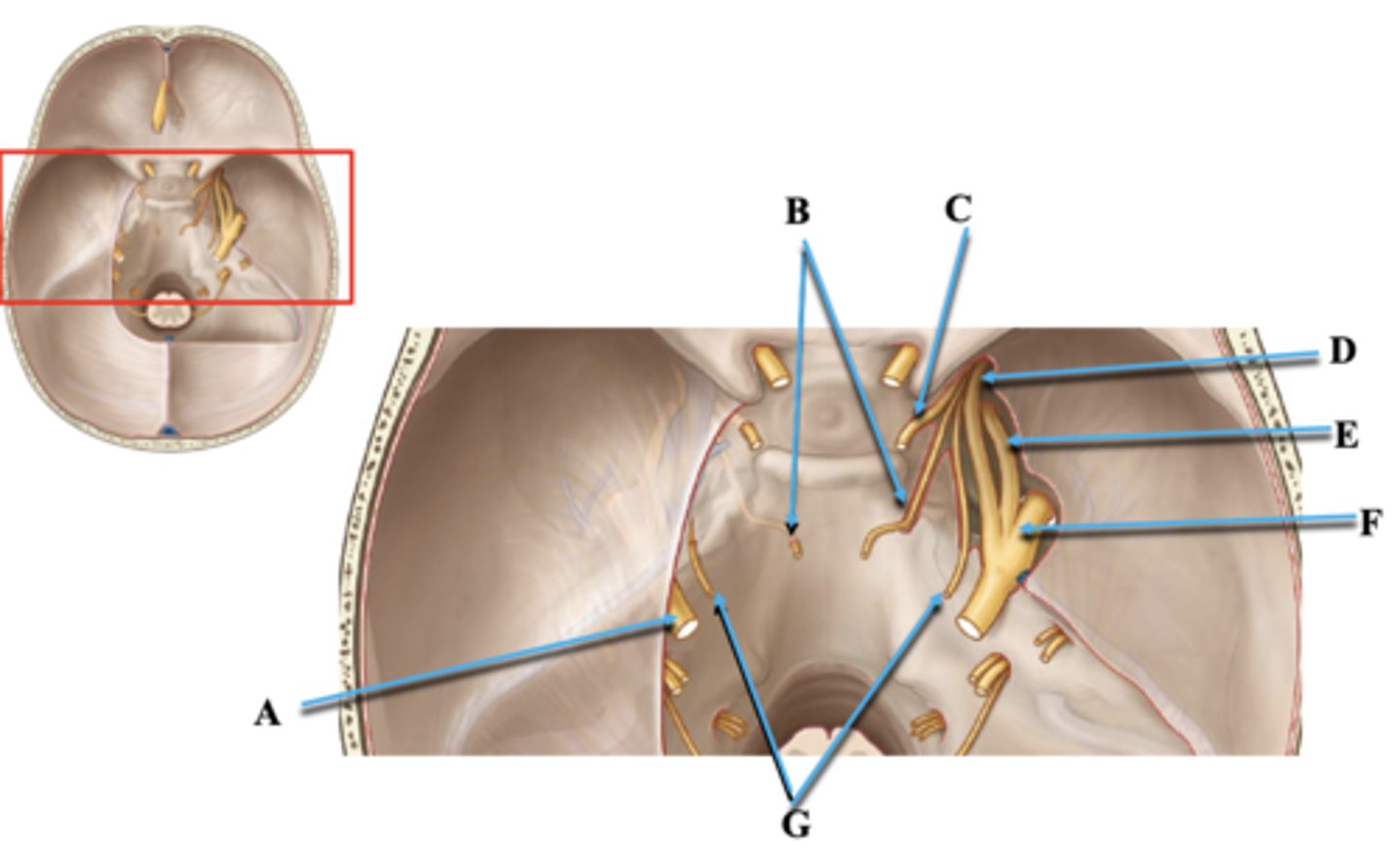
Cranial Nerve IV
Identify G.
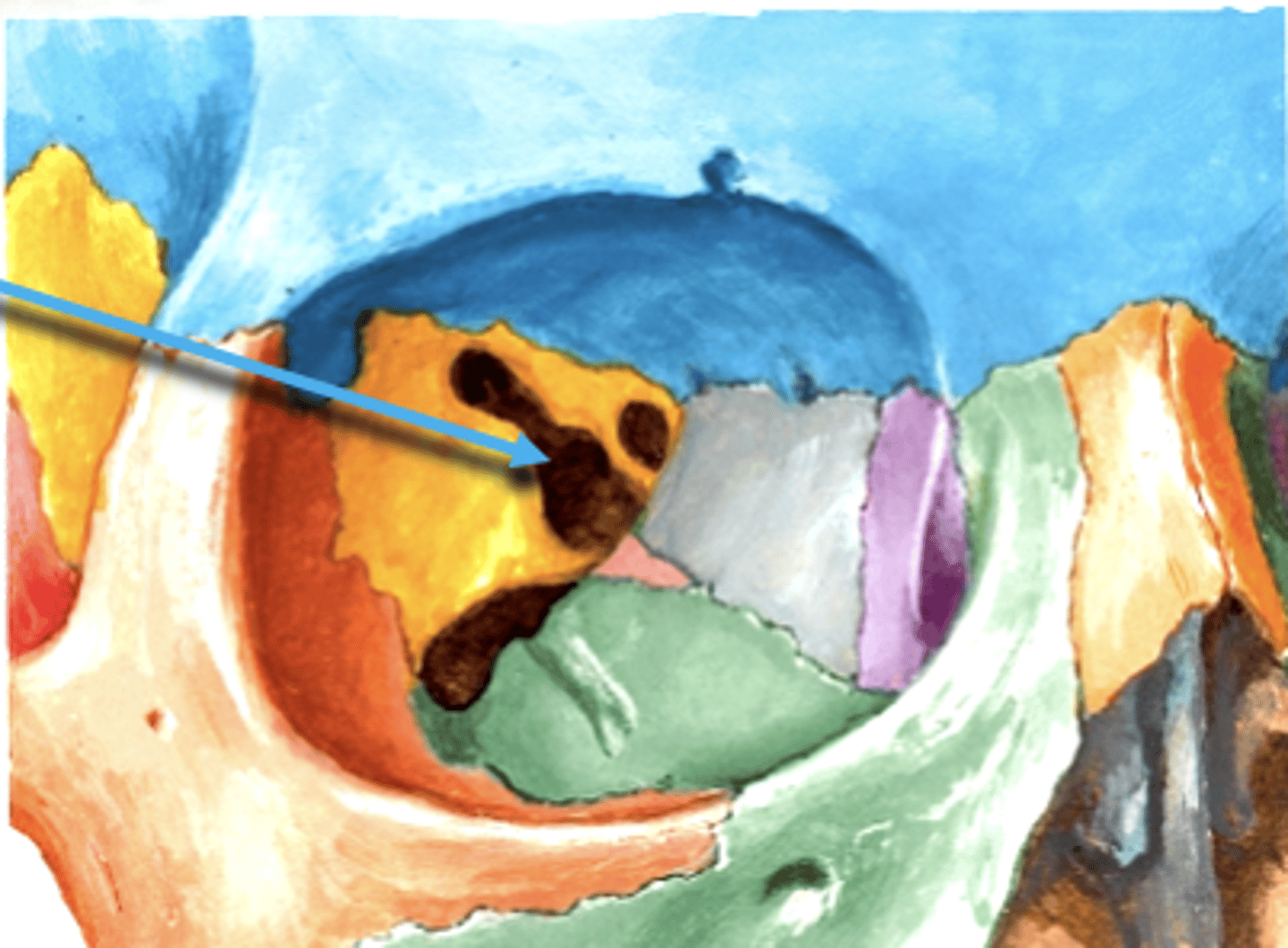
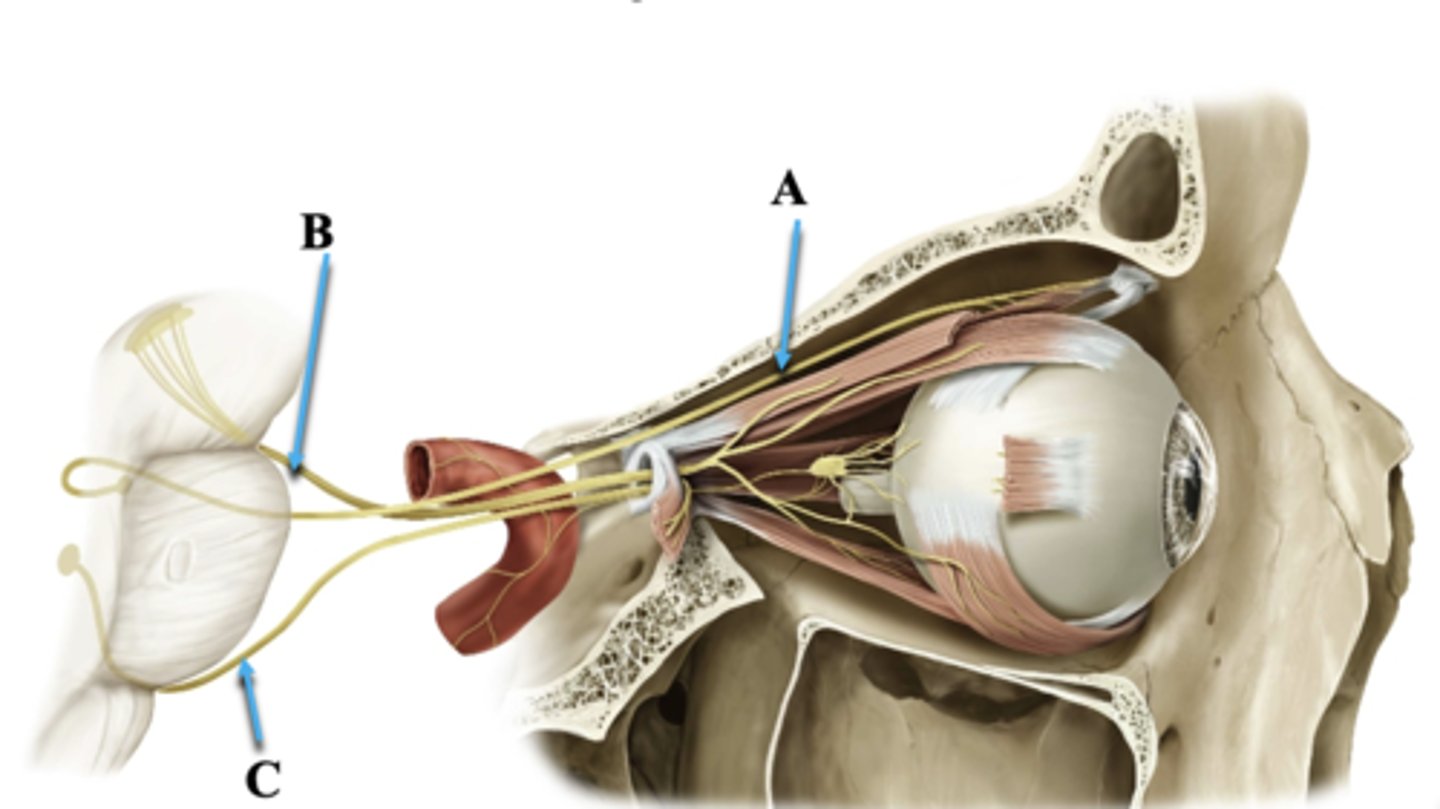
Superior Orbital Fissue
Space through which cranial nerves III, IV, V1, VI travel from middle cranial fossa into orbit
Cranial Nerve IV
Identify A.
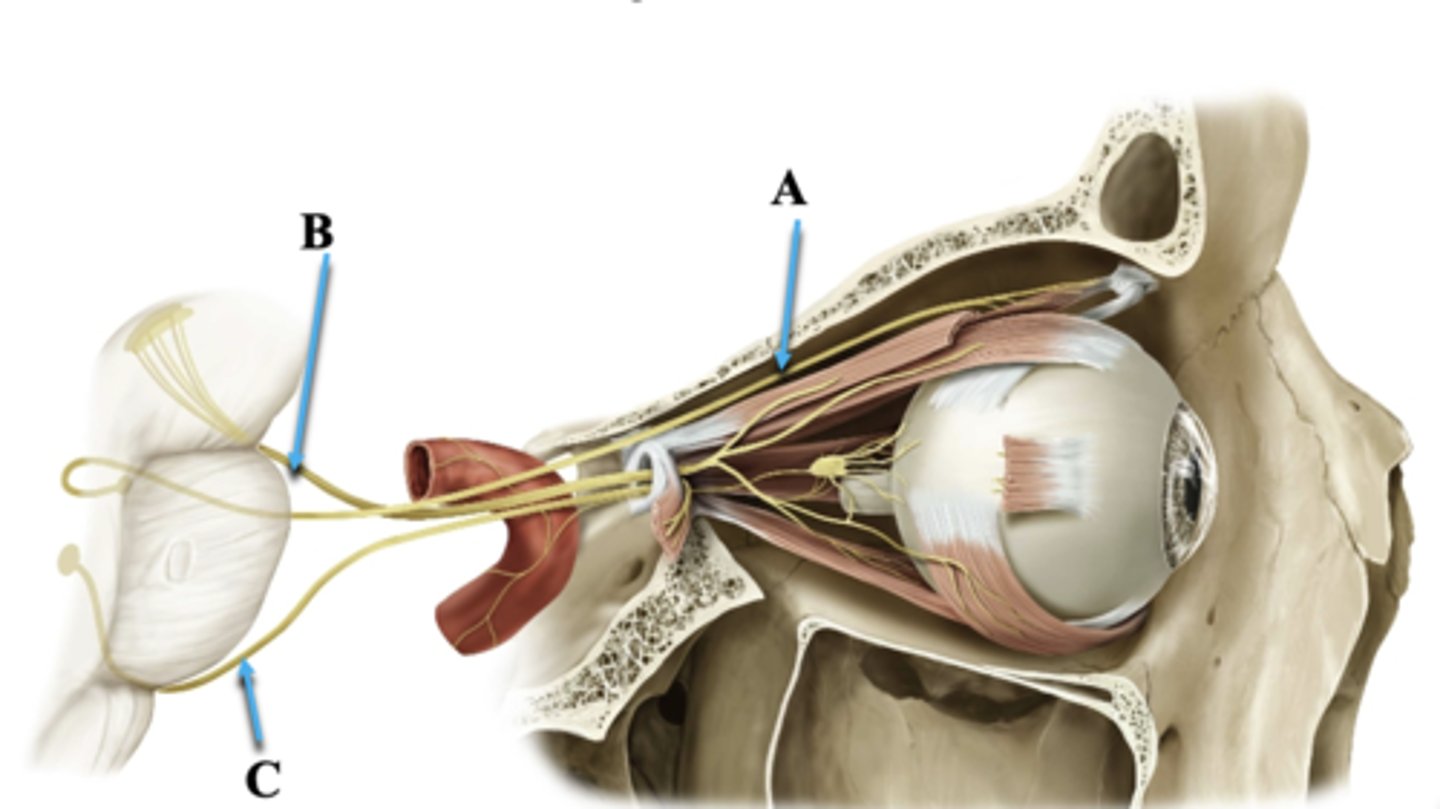
Cranial Nerve III
Identify B.
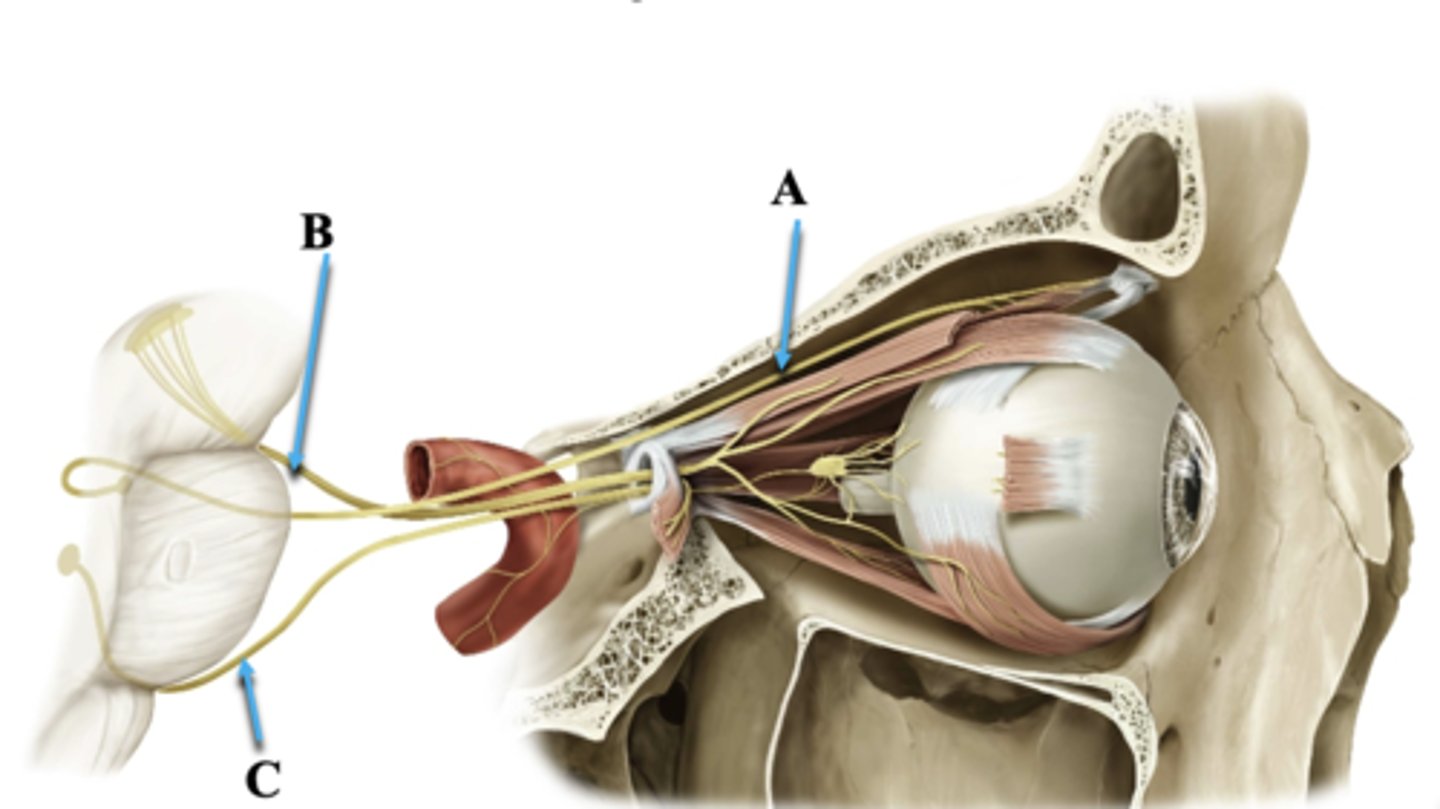
Cranial Nerve VI
Identify C.
SLIDE 31