Heart and Blood Vessels
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Open Circulatory System
The blood is pumped into open ended vessels. The blood leaves the vessels and surrounds the tissue cells. Blood re-enters the heart before being pumped through the vessels again.
Systole + Diastole (Difference)
Systole is when the heart contracts to pump blood out.
Diastole is when the heart relaxes to fill with blood.
Closed Circulatory System
Blood flows through a continuous network of blood vessels. Substances are exchanged between the blood and cells across the thin walls of the smallest blood vessels. More efficient.
The human circulatory system consists of…
Blood Vessels
Blood
Heart
Blood Vessels (3 Types)
Arteries - Carry blood away from the heart. Divide into smaller vessels called arterioles.
Veins - Carry blood to the heart. Divide into smaller vessels called venules.
Capillaries - Tiny vessels that link arterioles and venules.
Arteries
Have a thick, elastic wall which can withstand high pressure blood flowing through it.
Inner Layer - Endothelium
Centre - Lumen
Veins
Carry blood towards the heart, contains valves, have a large lumen.
Thinner walls than arteries.
Capillaries
Deliver nutrients and oxygen to all cells and remove waste products.
Substances are transferred between the blood and cells by diffusion.
Differences between arteries and veins
Carry blood from the heart/Carry blood to the heart
Thick wall/Thin wall
Small lumen/Large lumen
The Heart (Location)
In the thoracic cavity, above the diaphragm and between the 2 lungs.
Double Circulation
the heart is a double pump. It has a right and a left side separated by a wall called the septum. This ensures that oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are kept separate.
The right side pumps blood to the lungs to get oxygen and it returns to the left side of the heart (Pulmonary Circuit).
The left side pumps oxygenated blood to cell parts of the body (Systemic Circuit).
Heart Structure (Diagram)
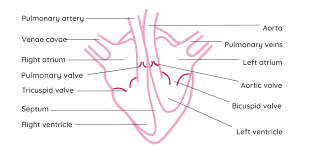
Heart Structure
2 Chambers:
Atrium + Ventricle
Left ventricle has thicker walls than the right as it pumps blood all around the body, right ventricle only pumps blood to the lungs.
Valves ensure that blood flows only in one direction.
Oxygenated blood comes in on (our) right side.
Portal System
Begins and ends in capillaries.
Does not connect directly to the heart.
Example - Hepatic portal system.
Control of Heartbeat
Controlled by a bundle of specialized cells called the pacemaker.
The SA node sends out an electrical signal which causes the atria to contract. The impulse from the SA node stimulates the AV node, located between the right atrium and right ventricle.
The Cardiac Cycle (Stages of Heartbeat)
1.Blood enters the heart into the left and right atria, the valves are closed and the atria and ventricles are relaxed (diastole).
2.Impulses from the pacemaker causes the atria to contract (systole), the bicuspid and tricuspid valves open, blood is pumped into the ventricles.
3.The atria relax. Impulses from the AV node cause the ventricles to contract. The semilunar valves are forced open, the tricuspid and bicuspid valves close (“Lub” sound). Blood flows out of the heart through the pulmonary artery and aorta. The ventricles relax and the semilunar valves close (”dub” Sound).
Pulse
The expansion of arteries felt after the contraction of the ventricles. Caused by the pressure of blood being forced into the aorta.
Blood Pressure
The force exerted by the blood against the wall blood vessels.
Factors Affecting the Circulatory System (Smoking)
Chemicals in cigarettes include nicotine and carbon monoxide. Nicotine increases heart rate and blood pressure. Carbon monoxide decreases the amount of oxygen carried by the blood.
Factors Affecting the Circulatory System (Diet)
Fats - diets high in saturated fats and cholesterol increases the risk of atherosclerosis leading to heart attacks and strokes.
Salt - increases blood pressure, more likely to have a stroke.
Obesity - increases the risk of high blood pressure + heart disease.
Factors Affecting the Circulatory System (Exercise)
Regular exercise makes the heart muscle stronger and more efficient at pumping blood around the body.
Exercise reduces blood pressure and helps maintain body weight.
Effect of exercise on pulse rate (Experiment Conclusion)
The experiment showed that exercise increases pulse rate. Before exercise, the pulse rate was lower. After exercising, the pulse rate went up and then slowly returned to normal after resting. This happens because the heart beats faster during exercise to deliver more oxygen and remove waste products from the muscles. The results support the idea that exercise has a clear effect on pulse rate.
Heart Dissection Experiment
Put on gloves and place the heart on the dissection board with the front (ventral side) facing up.
Identify the left and right atria and ventricles, coronary artery, and major blood vessels (aorta, pulmonary artery, vena cava, pulmonary vein).
Use a scalpel or scissors to cut open the left side of the heart. Observe the thick muscular wall of the left ventricle.
Cut open the right side of the heart. Note that the wall is thinner than the left ventricle.
Locate and examine the tricuspid and bicuspid (mitral) valves, the chordae tendineae, and the semi-lunar valves at the base of the aorta and pulmonary artery.
Use the probe to trace the path of blood through the chambers and valves.